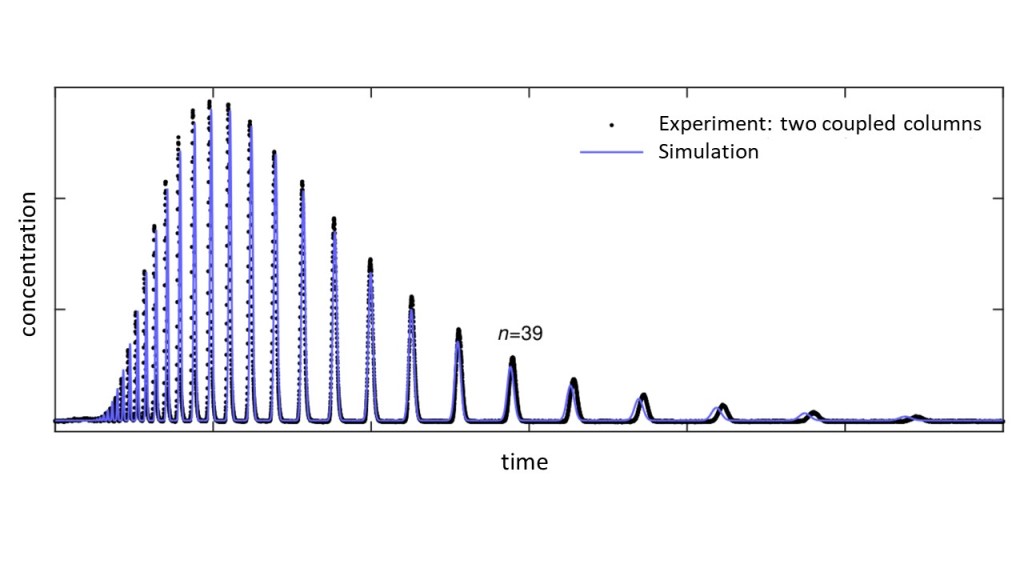
Separation of polyethylene glycols (PEGs) into single homologs by reversed-phase chromatography is investigated experimentally and theoretically. The used core-shell column is shown to achieve baseline separation of PEG homologs up to molar weights of at least 5000 g/mol. A detailed study is performed elucidating the role of the operating conditions temperature, eluent composition, and degree of polymerization of the polymer. Applying Martin's rule yields a simple model for retention times that holds for a wide range of conditions. In combination with relations for column efficiency, the role of the operating conditions is discussed and separations are predicted for analytical-scale chromatography. Finally, the approach is included in an efficient process model based on discrete convolution, which is demonstrated to predict with high accuracy also advanced operating modes with arbitrary injection profiles.