Preprint
Communication
The Flavonoid Rich Black Currant (Ribes nigrum) Gemmotherapy Extract Prevents Microglial Body Swelling in Hippocampus and Reduces Serum TNF-α Level: Pilot Study
Altmetrics
Downloads
243
Views
165
Comments
0
This version is not peer-reviewed
Submitted:
24 October 2022
Posted:
27 October 2022
You are already at the latest version
Alerts
Abstract
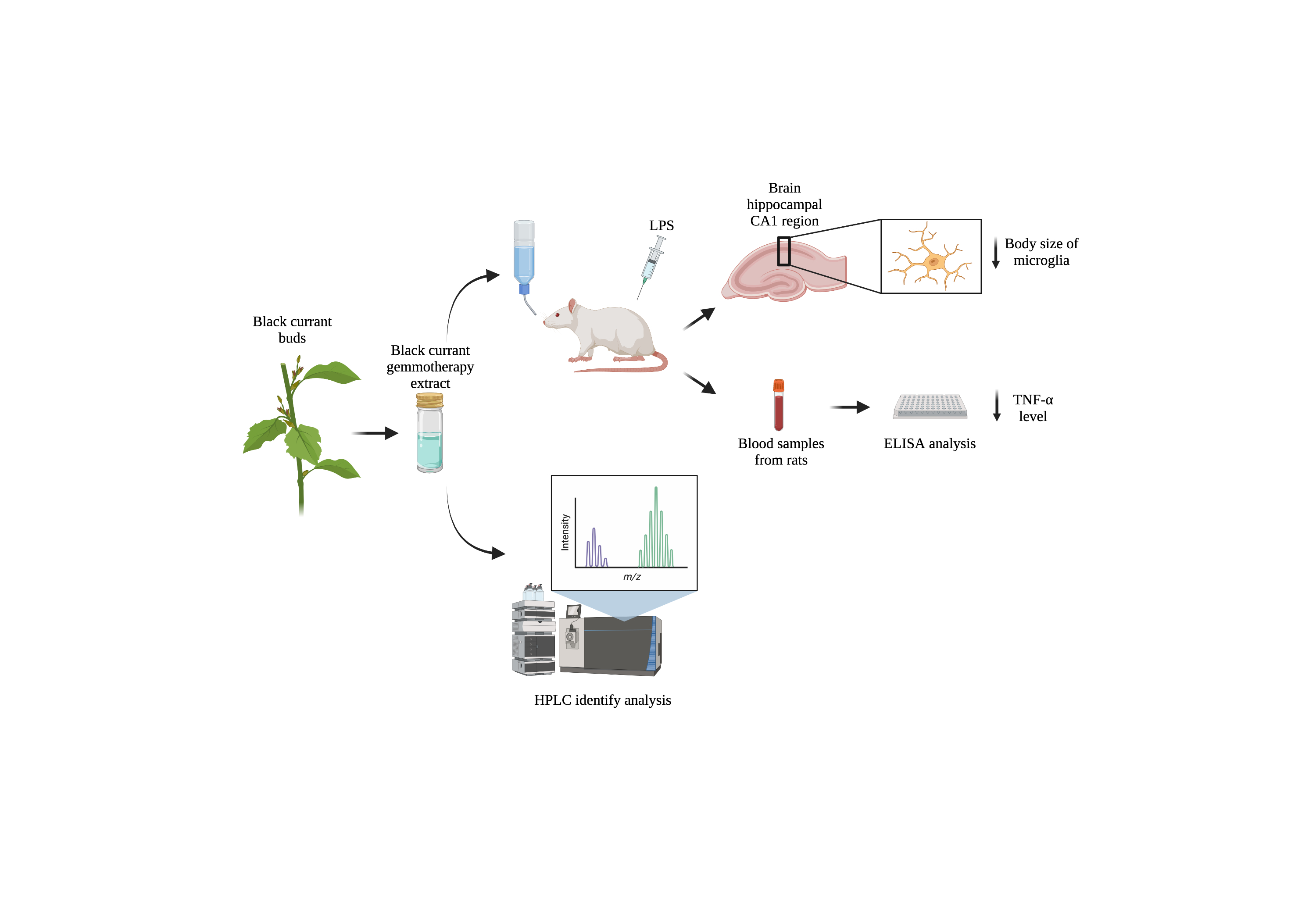
The fruits and leaves of the black currant (BC, Ribes nigrum) contain phytochemicals with thera-peutic benefits. The current paper reports on a standardized BC gemmotherapy extract (BC-GTE) prepared from fresh buds, and details the extract specific flavonoid content, antioxidant, and an-ti-inflammatory properties, respectively. The main HPLC identified aglyka flavonoids were lute-olin, quercetin, apigenin and kaempferol, while all together, at about 133 phytonutrients could be detected in the reported BC-GTE, so that the BC specific presence of many compounds was re-ported for the first time. We also demonstrated that in adult male Wistar rats pretreated with BC-GTE, and assessed after the LPS injection, the body size modifications of the activated microglial cells in the hippocampal CA1 region were not apparent, and no elevated serum specific TNF-α levels were seen under such LPS induced inflammatory conditions. The specific flavonoid content, and the LPS induced in-flammatory model based experimental data are all suggesting that the assessed BC-GTE seems to feature anti-neuroinflammatory property, holding the promise of a novel GTE based comple-mentary therapeutic approach.
Keywords:
Subject: Biology and Life Sciences - Cell and Developmental Biology
Copyright: This open access article is published under a Creative Commons CC BY 4.0 license, which permit the free download, distribution, and reuse, provided that the author and preprint are cited in any reuse.
MDPI Initiatives
Important Links
© 2024 MDPI (Basel, Switzerland) unless otherwise stated






