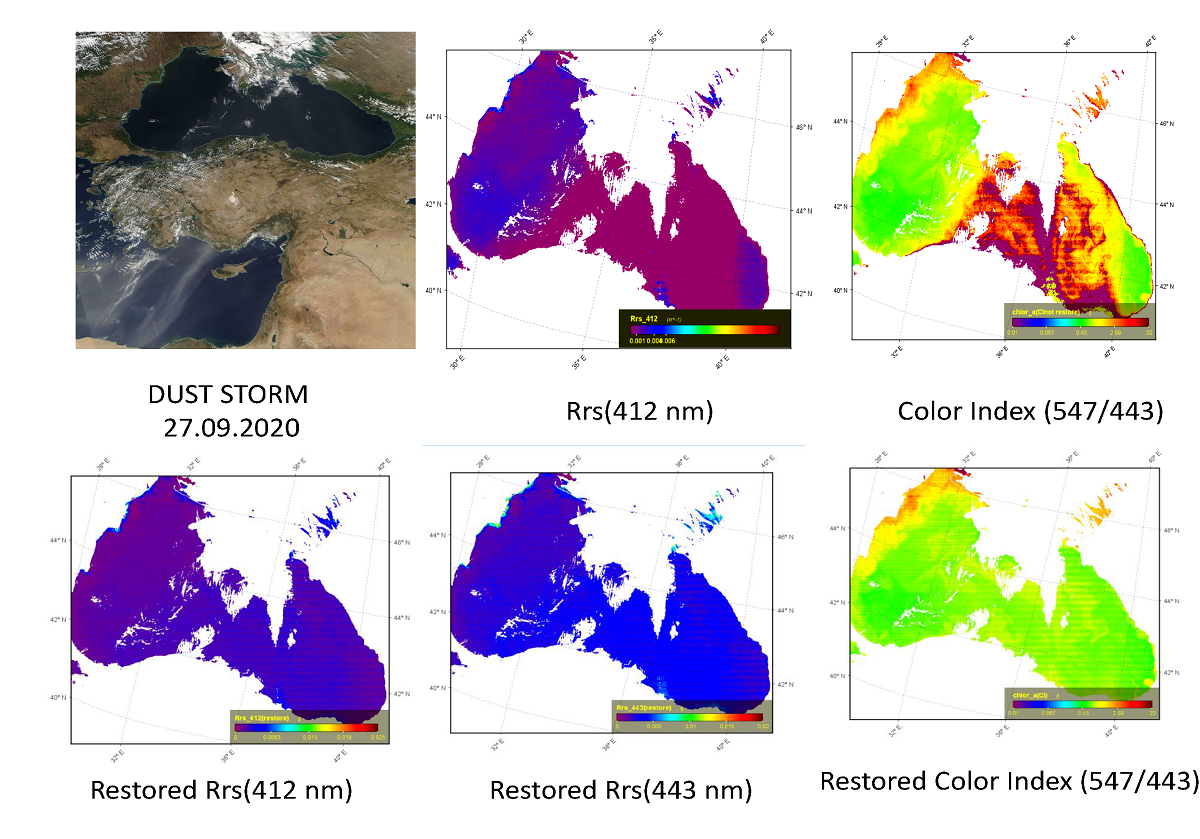
In the presence of absorbing aerosol in the atmosphere a number of systematic errors of standard Ocean Color algorithms were noted, for example, negative values of remote sensing reflectance in the short-wavelength region at 412 nm and 443 nm. The main goal of this work is to develop an algorithm for additional correction of remote sensing reflectance level 2 satellite data, taking into account the presence of absorbing aerosol over the Black Sea, where a large number of dust transfers from the Sahara are observed annually. To implement the algorithm, an analytical and experimental evaluation of the interpolation function is carried out, taking into account the optical effects caused by the stratification of the absorbing aerosol. This algorithm is based on the constancy of the color index value, characteristic of the selected region. For the Black Sea the average value of CI(412/443) = 0.80±0.08, a small standard deviation indicates that the sample is slightly variable. Therefore, CI(412/443) = 0.80 will be further considered as the reference value of the color index for calculating new restored Rrs(λ).