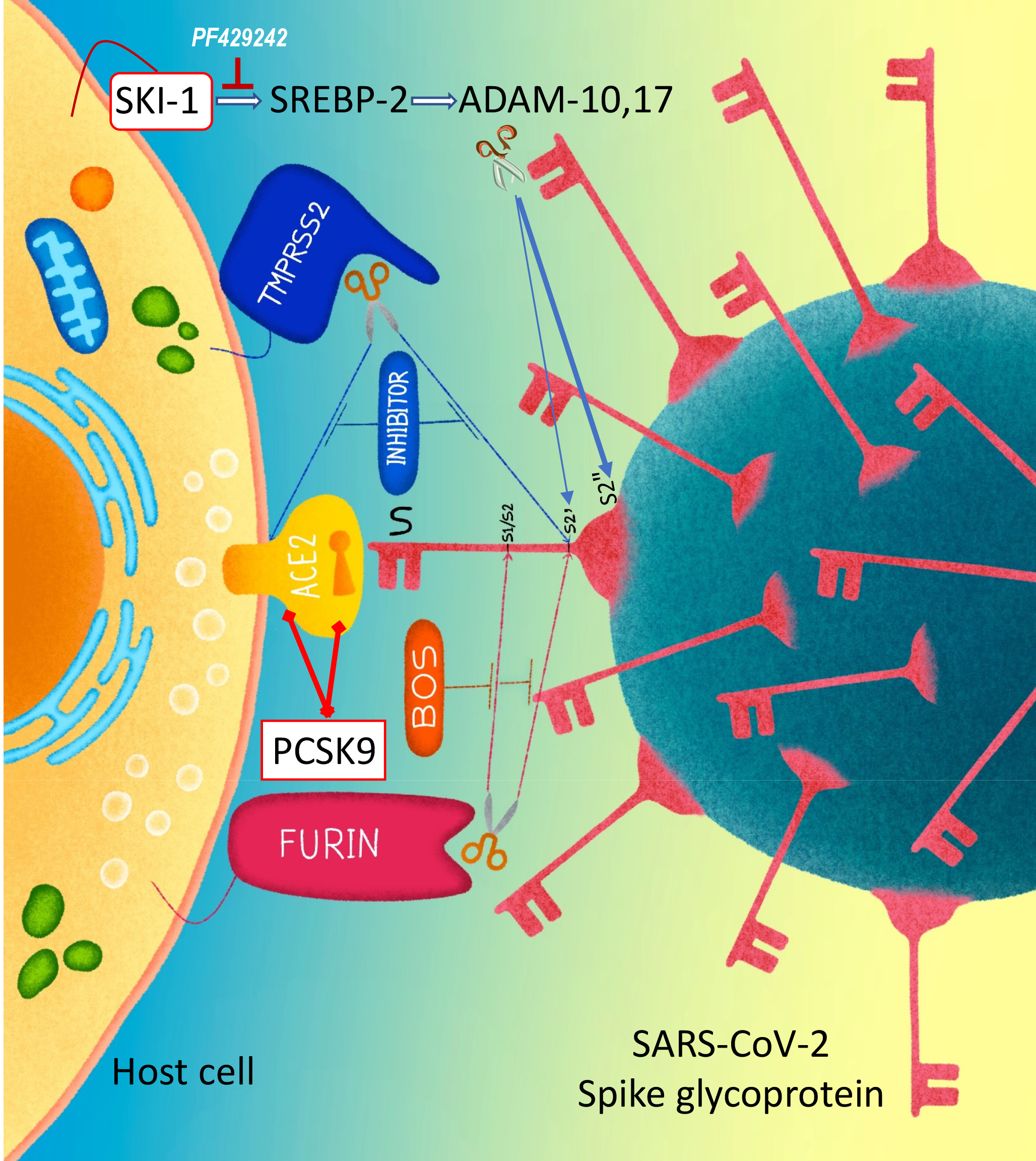
Proprotein convertases activate various envelope glycoproteins and participate in cellular entry of many viruses. We recently showed that the convertase furin is critical for the infectivity of SARS-CoV-2. This study investigated the implication of the two cholesterol-regulating convertases SKI-1 and PCSK9 in SARS-CoV-2 entry. We used cell-to-cell fusion assays in HeLa cells and pseudoparticle entry into Calu-3 cells. SKI-1 increases cell-to-cell fusion by enhancing the activation of SREBP-2, whereas PCSK9 reduces cell-to-cell fusion by promoting the cellular degradation of ACE2. Metalloprotease activation is sensitive to enhanced cholesterol levels resulting from SKI-1-activated SREBP-2 that leads to enhanced S2’ formation. However, high metalloprotease activity results in S2’ shedding into a new C-terminal fragment (S2”), leading to reduced cell-to-cell fusion. Indeed, S-mutants that increase S2’’ formation, abolish S2’ and cell-to-cell fusion, as well as pseudoparticles entry, indicating that the formation of S2’’ prevents SARS-CoV-2 cell-to-cell fusion and entry. We next demonstrated that PCSK9 enhanced the cellular degradation of ACE2, thereby reducing cell-to-cell fusion. However, different from the LDLR, a canonical target of PCSK9, the C-terminal CHRD domain of PCSK9 is dispensable for the PCSK9-induced degradation of ACE2. Molecular modeling suggested binding of ACE2 to the Pro/Catalytic domains of mature PCSK9. Thus, both cholesterol-regulating convertases SKI-1 and PCSK9 can modulate SARS-CoV-2 entry via two independent mechanisms.