Introduction
The definition of health is often redefined to be more encompassing of the many components that contribute to one’s wellbeing. Health is described as an overall state of physical, mental, emotional, economic and social wellbeing (Wiens et al., 2020). Mental health is regarded as an essential resource that improves an individual’s self-perception, increases their likelihood of achieving success and allows them to positively contribute to society (Wiens et al., 2020). When people experience poor mental health, this can significantly impact morbidity and mortality (Statistics Canada, 2020a). Social support is a crucial factor in reducing the impact of stress and helping to improve perceived mental health (Perreault et al., 2017). Less social support is correlated with the incidence of negative coping mechanisms during stressful situations and can exacerbate poor mental health (Perreault et al., 2017).
On March 11, 2020, the World Health Organization (WHO) declared the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) a global pandemic (The Lancet Infectious Diseases (LID), 2020). To reduce the spread of the virus, governments implemented non-pharmaceutical interventions (NPIs) in March 2020 such as quarantine, school closures and personal protective behaviours which included avoiding gatherings, reducing personal contacts and meetings, and increased hand hygiene (LID, 2020). These interventions increased physical isolation, school closures and, inadvertently, widespread job loss (LID, 2020).
While these measures were put in place to protect people from an unknown virus, this had unintended individual, social, and economic repercussions worldwide (LID, 2020). The WHO released a report that disclosed an increase in substance misuse and direct neurological consequences such as stress, burnout, depression and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) since the pandemic began (LID, 2020). In addition to the cognitive impacts of social distancing, the frequency of news reports regarding the high number of cases and fatalities has likely had an impact on the stress levels of many Canadians (LID, 2020).
Resilience research states that when people have more control and stability during a stressful event, they are more capable of coping with stress (Vinkers et al., 2020). As mental health and substance use are often correlated with employment and financial stability, the policies that governments have put in place regarding the Canadian economy are likely to have a significant impact on the mental health and well-being of Canadians. While the COVID-19 vaccine rollout in Canada began in January 2021, a possible return to normal life was envisioned; however, the long-term stress that people have experienced during this pandemic has likely had negative consequences that may have long-lasting effects on their mental health.
The effects of past epidemics and pandemics on mental health have been studied extensively and highlight the lasting negative impact they can have. During the 2009 H1N1 pandemic, researchers found an increased incidence and prevalence of depression and distress among the general population, family members of patients and health care workers (Jalloh et al., 2018; Tucci et al., 2017). In the United States, people reported higher levels of anxiety, uncertainty and engaged in more risky behaviours, such as smoking, drinking, recklessness and unsafe work practices during the H1N1 pandemic (Tucci et al., 2017).
During the 2003 SARS epidemic, it was found that individuals in China and Taiwan who were quarantined and experienced the perceived threat of SARS had a high incidence of depressive symptoms and were at an increased risk of developing mental health disorders. There was also a statistically significant increase in suicide rates in the years following the epidemic (Tzeng et al., 2020). In one cohort, the cumulative post-SARS incidence of mental health disorders was 58.9%, while during the post illness stage, the point period prevalence of PTSD was 32.2%, depression was 14.9% and anxiety was 14.8% (Tzeng et al., 2020).
Kübler-Ross Model
The Kübler-Ross model was designed by physician Dr. Elisabeth Kübler-Ross based on the observation that terminally ill patients and their relatives experienced similar emotions during bereavement (Kübler-Ross, 1969). These include denial, anger, bargaining, depression and acceptance (Kübler-Ross, 1969). This model has been adapted to reflect stages of personal and organizational change as the Kübler-Ross Change Curve (KRCC) (Rosenbaum et al., 2018). It can have up to seven stages: shock, denial, frustration, depression, experimentation, decision and integration (Tempski et al., 2020). This model may help in analyzing how loss and change during the pandemic may affect the self-rated stress and mental health of Canadians.
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to analyze the statements that Canadians made on Twitter regarding their experiences with the perceived threat of COVID-19 and the non-pharmaceutical interventions implemented during the pandemic. The tweets were analyzed to determine the presence of prominent themes and sentiments and examined using the stages of the Kübler-Ross Change Curve to assess the stress resilience and adjustment of Canadians during the pandemic, as these are essential components of developing healthy coping mechanisms and positive long-term mental health (Perreault et al., 2017).
Significance
It is predicted that the content of the tweets may be helpful in assessing whether people reach the critical stage of acceptance or integration in the Kübler-Ross model over several months. The responses may shed light on public perception regarding the appropriateness of government interventions and supports. The sentiment regarding government interventions could highlight if the interventions helped Canadians during the pandemic, how their mental well-being may have been affected and possible recommendations to COVID-19 policies to promote resilience.
Methodology
Ethics Approval
This study did not require ethics approval as it collected publicly available information from Twitter. To protect the privacy of Twitter users, no identifiable or personal information is present in this study.
Data Collection
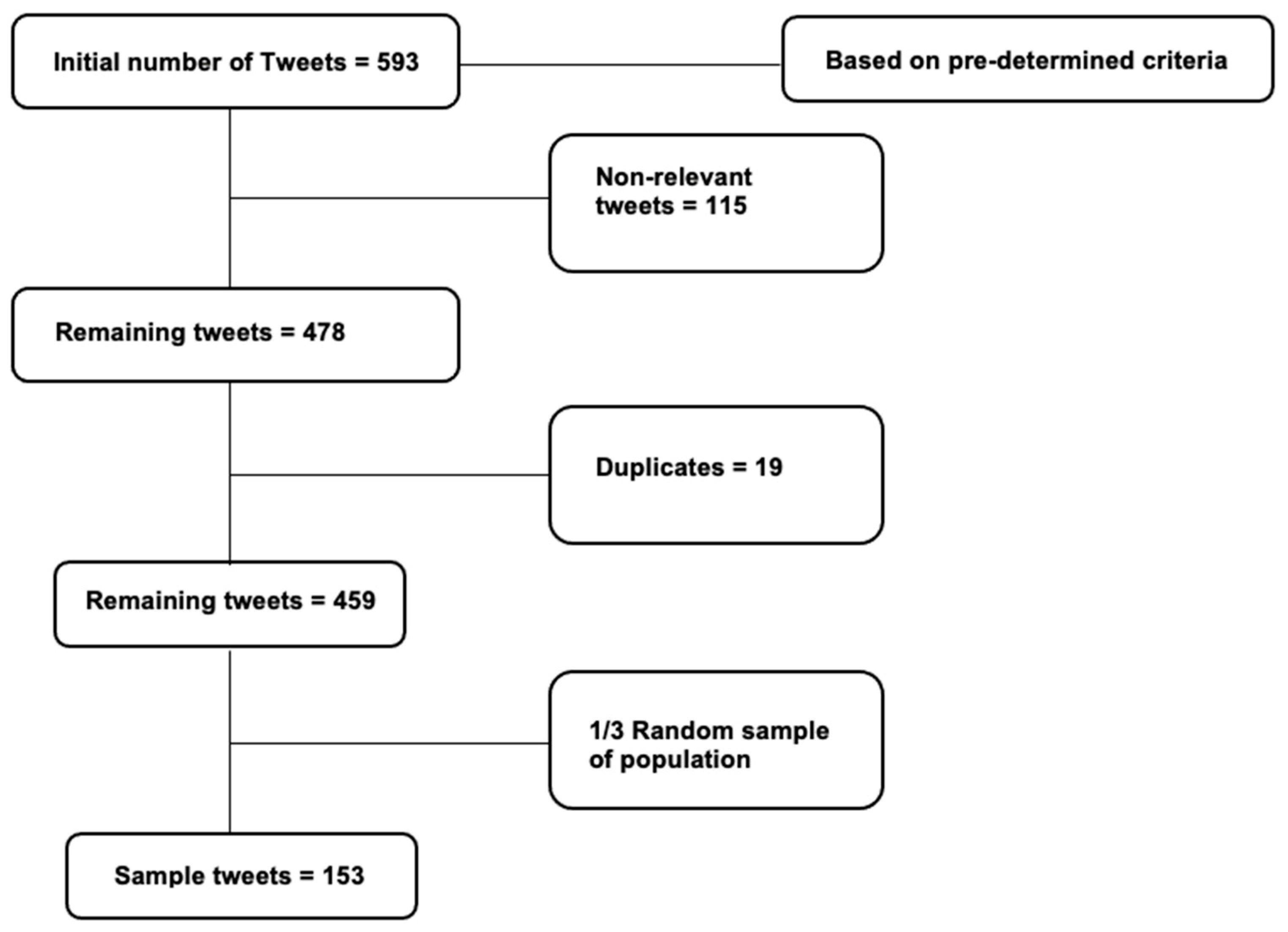
Using Twitter, a search was conducted using keywords from five categories: COVID-19, Canadian policies, finances, non-pharmaceutical interventions and mental health pertaining to COVID-19 (
Table 1). The inclusion criteria for the tweets were those that were tweeted from Canada, included at least one hashtag from the COVID-19 category and one other category, tweets in English, and tweets dated from March 2020 to August 2020.
Tweets were manually geolocated to ensure that users were living in Canada and impacted by Canadian policies regarding COVID-19.
Figure 1 shows the breakdown of the tweet selection and sampling process.
Data Analysis
From the initial tweets collected from Twitter, a sample number of tweets were randomly drawn. From this sample, a sentiment analysis was conducted using the Microsoft Excel Azure Machine Learning add-in. These tweets received a sentiment ranging from positive, negative, neutral or mixed. These sentiments were then manually verified to ensure the accuracy.
A thematic content analysis was conducted using NVivo 11. The sample population was coded by month and a query was performed to determine common words in the tweets. These words were grouped together by similarity to determine prominent themes in the tweets. Once the themes were extracted, they were compared with the sentiments that were expressed in each month to determine the strongest sentiments associated with each theme.
In addition, the Kübler-Ross Change Curve was used to assess which stage of the KRCC the user was experiencing at the time of the tweet. Each tweet was manually evaluated and assigned to the appropriate stage of the curve. In addition, the accounts were assessed to determine whether the user was an individual, organization, researcher or news reporter. The sentiments, themes and KRCC stage were compared by month to determine whether there were trends between March and August 2020. The content of the tweets was analyzed to identify possible impacts of COVID-19 response on mental health and to identify opinions regarding the efficacy and repercussions of COVID-19 response policies and how this impacted resilience and stress levels for Canadians.
Results and Discussion
This study explored the issues that were most prevalent among Canadian Twitter users and how they navigated them during the first six months of the pandemic. The sentiment analysis and thematic content analysis identified the theme(s) within the tweets and the sentiment that was associated with them. The Kübler-Ross Change Curve identified what stage of the curve the users were likely experiencing when they wrote the tweet.
The sentiment analysis found that 71/153 (46.4%) of tweets expressed a negative sentiment. Among the negative sentiment tweets, 51/71 (71.8%) belonged to individuals, 12/71 (16.9%) belonged to organizations (for-profit and non-profit), 5/71 (7.0%) belonged to news reports and 3/71 (4.2 %) belonged to researchers. This shows that most of the tweets are coming from individual accounts and are a good representation of the general Canadian public.
Themes
The themes that were present in the tweets were based on six categories: Canadian policies, Financial Concerns, Impacts of NPIs, Direct health impacts of COVID-19, Research, and Support and Encouragement. Tweets categorized as Canadian policies were ones that referenced policies surrounding COVID-19 response, mentioned the actions of politicians or compared policies in Canada to those of other countries. Financial concerns were tweets that mentioned the effects of economic policies, such as the Canadian Emergency Relief Benefit (CERB) and Employment Insurance (EI) and stress due to financial difficulties experienced directly and indirectly from the pandemic. Impacts of non-pharmaceutical interventions (NPIs) referred to the effects of physical distancing measures in place such as school closures, isolation/quarantine, and the importance of personal protective behaviours. Direct health impacts were related to concerns regarding the health and safety of citizens, the disclosure of those who experienced COVID-19 related symptoms and impacts of physical or mental health issues that may have resulted indirectly from the pandemic. Research referred to tweets that shared new information on research advancements in understanding COVID-19 and its impacts, vaccine development, and treatment. Support and Encouragement referred to tweets that shared words of encouragement for others and provided support for people.
The four categories that were referenced the most from March to August were
Canadian policies, Financial concerns, Impacts of NPIs, and Direct health impacts.
Table 2 shows the percentage of tweets with a negative sentiment that had these categories.
Opinions on Canadian policies
This theme received the most negative remarks on Twitter from March to August 2020. Most users expressed that government policies were not implemented early enough to protect people from COVID-19. Some referenced that while Canada was not prepared for the 2003 SARS epidemic, the government should have been better prepared for the COVID-19 pandemic 17 years later.
Canada made sweeping reforms to infectious disease control after SARS, such as the creation of the Public Health Agency of Canada, a stronger federal presence in public health, enhanced surveillance, and increased preparation and equipment for infection control (Webster, 2020; Silverman et al., 2020). While Canada introduced a lockdown soon after the pandemic announcement by the WHO, the policies in place did not protect vulnerable groups, particularly those in long-term care homes (Webster, 2020; Silverman et al., 2020). One Twitter user described frustration that more thorough inspection of long-term care facilities should have been conducted to identify issues with infection prevention and control. Those brought in to inspect these facilities highlighted that basic health care and infection prevention were not being conducted in many facilities (Silverman et al., 2020). In addition, it was found that the mortality rate in long-term care facilities in Canada was higher than 16 countries belonging to the Organisation for Economic and Co-operation and Development (OECD) (Silverman et al., 2020).
Financial concerns
The major subthemes in this category were opinions on the efficacy of the Canadian Emergency Response Benefit, experiences with unemployment and changing work landscape, and stress from financial difficulties. To reduce the spread of the virus, many retail stores and small businesses were required to close during lockdowns. This led to many lay-offs and small business owners being forced to close, while big businesses such as Walmart, Costco and Amazon were allowed to continue operating and saw more profit (Statistics Canada, 2020b). While CERB and the Canadian Emergency Business Account (CEBA) were available to business owners, they expressed that it was not enough money for them to support themselves and their families. One tweet stated, “#CEBA is still leaving #soleproprietors in the cold.”
Some Twitter users expressed that CERB would discourage people from seeking permanent employment and allow them to take advantage of taxpayer dollars. Some tweets stated that lower income groups would use this as an opportunity to not seek employment. One person tweeted, “Why work? When #refugees arrive in #Canada, they hit the jackpot. No need to work.” Contrary to this belief, the economic impacts of the pandemic disproportionately affected refugees and immigrants (Statistics Canada, 2020b). Statistics Canada found that members of these groups were much more likely to lose their jobs than Canadian-born workers because they often work low paying jobs with less opportunity to work from home and at increased risk of being replaced by automation (Statistics Canada, 2020b).
While CERB and other governmental financial aid has temporarily helped people who experienced job loss, this brought up the debate of universal basic income (UBI) in Canada. UBI is an income paid to individuals regardless of employment status or education (Ståhl and MacEachen, 2020). As the financial concerns brought on by the pandemic were difficult for many people of lower income groups, many Twitter users felt that CERB could be expanded upon to become UBI to improve the social safety net in Canada and protect vulnerable groups from poverty.
Impacts of NPIs
Within this theme, the major subthemes that were present were disclosure regarding isolation, the efficacy of NPIs and coping with NPIs. In March, while many tweets were encouraging people to follow public health protocols, by May when the number of COVID-19 positive people continued to increase, people felt that Canada had not learned from SARS and could have kept the number of community cases lower if swift action had been taken to reduce transmission. In August, all tweets about NPIs were negative. Some of these tweets expressed a belief that the government did not do enough to curb the spread of COVID-19, that NPIs were unfair and ineffective, and that social isolation was having negative effects on the mental health and well-being of Canadians.
A cross-sectional study on the mental health of people that experienced isolation and quarantine during the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic in China found that those who were isolated experienced high rates of depression, anxiety, and stress, especially during the first week of isolation (Gong et al., 2021). Further research found that longer isolation was associated with worse mental health outcomes due to prolonged stress as the mental health of people that experienced isolation and fear of the virus was more negatively impacted than the control group even several years after the epidemic or pandemic had ended (Jalloh et al., 2018; Bah et al., 2020; Gong et al., 2021).
Twitter users also highlight that due to the confinement required with lockdowns, many cases of domestic abuse increased during the pandemic. This left many victims of abuse unable to leave their abuser and seek help (Kato et al., 2020). For example, one tweet stated, “Many victims have lost access to telephones or computers, including children who may be in danger.” In addition, due to NPIs, there was a greater demand for telework and online learning, which placed a high strain on broadband internet. Many people that live in rural communities often faced issues with high-speed internet and this made it especially difficult for people to work from home. This further highlights the inequities that exist with access to technology in Canada (Lai and Widmar, 2020).
Direct health impacts
This theme was present in tweets that described the number of active cases of COVID-19, the death toll, people’s personal experiences with COVID-19, and possible long-term health effects. In March, the majority of tweets were concerned with flattening the curve and reminding people to follow public health protocols to reduce the number of active cases. One tweet listed the number of people that died from COVID-19 in March from various countries around the world. The tweets from March to August show a shift in the countries that had the highest active cases and death rates. In the very beginning of the pandemic China and Italy were leading the world in deaths from COVID-19, but this quickly changed with the United Kingdom, the United States and Canada seeing a rapid surge in COVID-19 transmission.
By May 2020, when lockdown restrictions started to ease, some tweets expressed concern about a second wave because at the time it was not known where the source of the transmission was coming from, whether it was community or travel, and because COVID-19 testing was not mandatory. One tweet stated, “B.C. could see 2nd wave of COVID-19 in September bigger than the first. Do not forget to wear your masks and sanitize regularly.”
Another concern with COVID-19 as expressed by 4/33 of Direct health impact tweets, was the concern about how COVID-19 may affect other underlying conditions such as gestational diabetes and stroke. By August 2020, 3/6 tweets had a negative sentiment and expressed concern about people not following COVID-19 protocols, not getting tested and whether people would be vaccinated once the vaccine was made publicly available.
As SARS-CoV-2 is a relatively new virus, there is still much being researched about its long-term effects. Since COVID-19 manifests differently in different people and is still not well understood, it is still feared by many Canadians. The fear of the virus coupled with the isolation that many experienced during the pandemic has likely had a significant impact on the mental health and well-being of many Canadians.
Analysis using Kübler-Ross Change Curve
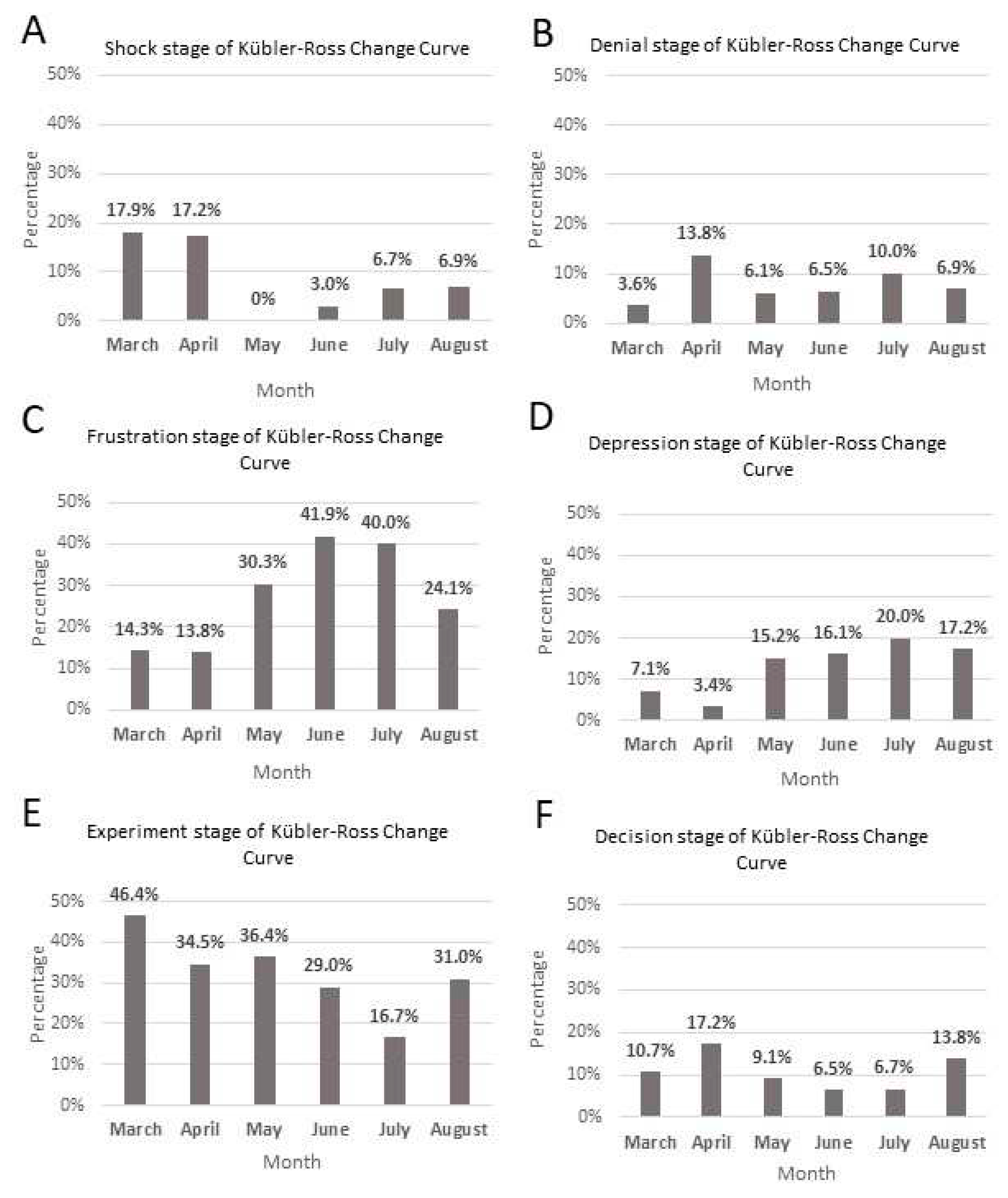
The Kübler-Ross Change Curve was a critical tool in understanding the stages of adaptation that Canadians were experiencing throughout the many changes of the pandemic. There are seven categories: shock, denial, frustration, depression, experimentation, decision and integration. The tweets analyzed did not display integration as data collection occurred early during the pandemic and integration may take longer than the six-month timeline of this project. The stages that were present in the sample are shown in
Figure 2A–F.
Shock
Shock is the initial stage of the KRCC when a person is faced with an unexpected change (Rosenbaum et al., 2018). From the sample tweets in March, 5/28 (17.6%) of the tweets expressed shock (
Figure 2A). These tweets expressed shock in the NPIs implemented and Canada’s Economic Response Plan. In March, there was considerable shock concerning the NPIs as people were unaccustomed to the sudden isolation. There was also shock at the reactions of others after the announcement of the pandemic and NPIs. This included stocking up on essential items for fear that they would run out in stores. After March, the number of tweets that expressed shock continued to decrease in the following months and by August only 2/29 (6.9%) expressed shock (
Figure 2A).
Denial
Denial is the second stage of the Kübler-Ross model when a sudden change can become difficult to believe or accept and this is expressed through disbelief by the individual (Rosenbaum et al., 2018; Tempski et al., 2020). In March 1/28 tweets expressed denial (
Figure 2B). While in the following months, the number of tweets that expressed denial increased. In April there were 4/29 (13.8%), with most of the tweets that expressed denial continuing to believe that the virus was not dangerous and mistrust in the government for implementing NPIs (
Figure 2B. In the following months, the percentage of tweets with denial decreased to become 6.9% in August (
Figure 2B). The content of those tweets continued to express distrust in government policies with the belief that NPIs were unfair and ineffective.
Frustration
Frustration is the third stage of the Kübler-Ross model when an individual recognizes the change and can become upset or angry because of it (Rosenbaum et al., 2018; Tempski et al., 2020). In March 4/28 (14.3%) expressed frustration (
Figure 2C). These tweets expressed frustration with the new challenges that resulted because of COVID-19. For example, because of the work from home policies put in place due to COVID-19, many people experienced slow broadband internet service, especially those living in rural areas. By May, the number of tweets expressing frustration grew to 10/33 (30.3%) (
Figure 2C). These tweets mentioned issues that have worsened since the pandemic and the implementation of NPIs such as the increase of domestic abuse, business bankruptcies and unemployment, and high COVID-19 mortality rate in long-term care homes. By August 6/29 (24.1%) tweets expressed frustration, specifically surrounding issues with finances (
Figure 2C).
Frustration demonstrates that people are attempting to interact with the new system and trying to reduce the stress response (Kübler-Ross, 1969; Malone, 2018). While it is understood that frustration is a normal part of the learning and adjustment period, studies show the importance of a strong support system during this time, especially with the unprecedented length of time that restrictive measures have been in place (Tempski et al., 2020; Malone, 2018). To manage the frustration period, it is critical for people that are experiencing this stage to feel they are supported by government, employers, educational institutions and other organizations. While many efforts are being made to help people during the pandemic, it is important that there be equal access to a wide variety of resources to help people that may be feeling frustrated, as this can have a significant impact on preserving mental health and resilience.
Depression
Depression is the fourth stage of the Kübler-Ross model when an individual feels overwhelmed with the new change and lacks the energy to interact with the change (Rosenbaum et al., 2018; Tempski et al., 2020). In March, there were few tweets that expressed depression (6.9%). These were mainly concerned with the deaths that resulted as a result of COVID-19 (
Figure 2D). While the number of tweets that expressed depression decreased in April, this number increased in the months that followed. In May 5/33 (15.2%) tweets expressed feelings of depression (
Figure 2D). Some individuals also expressed sadness surrounding the number of people who died due to COVID-19 and depression over financial concerns and unemployment. One person wrote, “People are losing their jobs, freedom, and ability to socialize and see loved ones.” Tweets that expressed depression continued to increase in June and July (
Figure 2D). In August, there were 7/29 (17.9%) that expressed depression (
Figure 2D). These tweets expressed more concern about the impending second wave and feeling overwhelmed due to financial difficulties.
The classroom study using KRCC found that to manage depression, it was important for individuals to provide their feedback about the new system and to incorporate their suggestions where possible (Tempski et al., 2020; Malone, 2018). Providing a space for Canadians to provide their feedback during this pandemic may prove to be helpful as some policies may not have been as effective as desired. Therefore, if government officials and policymakers conducted more comprehensive policy impact assessments by incorporating the opinions of the Canadian public, this would allow for more specific and targeted support being offered and may help people better adjust to the changes.
Experiment
Experiment is the fifth stage of the Kübler-Ross model when an individual begins engaging with the new situation (Rosenbaum et al., 2018; Tempski et al., 2020). In March, experimentation was the most common KRCC stage in tweets with 13/28 (46.4%) expressing it and 5/13 that had a positive sentiment (
Figure 2E). These tweets demonstrated that early in the pandemic, many people were attempting to interact with the changes brought on by the pandemic. This included encouraging people to comply with the public health protocols, informing people about the new services and supports that the government was providing, and writing encouraging messages to people while they were at home.
The number of tweets with experimentation decreased in the following months with the tweets in July containing the fewest reference to experiment (
Figure 2E). In August, there were 9/29 (31.0%) tweets that expressed experiment (
Figure 2E). These focused on encouraging the Canadian government to expand COVID-19 response policies to support more Canadians and propose mandatory COVID-19 testing.
Studies show that this experiment is an important stage that should be rewarded to encourage people to continue working towards integration (Tempski et al., 2020; Malone, 2018). While this study was conducted in the beginning of the pandemic and was not able to see people’s progression towards integration, if continued support is provided to people throughout the adjustment period, it can be expected that people will be able to reach integration and have a positive outlook on the experience. It is important to note that reaching integration is contingent upon the level of support and resilience that people receive during the adjustment period and may mean increasing the supports available (Tempski et al., 2020; Malone, 2018).
Decision
Decision is the sixth stage of the Kübler-Ross model when an individual is learning to interact in the new situation and is feeling more positive about the future (Rosenbaum et al., 2018; Tempski et al., 2020). In March 3/28 (10.7%) demonstrated decision (
Figure 2F). These tweets highlighted how people adjusted to the changes, the scientific accomplishments in treating and preventing COVID-19 and optimism about the future. These tweets decreased after March, with the fewest in June (6.5%) (
Figure 2F). In August 4/29 (13.8%) tweets demonstrated decision (
Figure 2F). These expressed gratitude to public servants and frontline workers that helped people throughout the pandemic and appreciation towards businesses that have adjusted to the pandemic such as becoming online retailers. One tweet stated, “Shoutout to the thousands of #publicservants across #Canada that continue to work to #help #Canadians in a variety of ways.”
Integration
Integration is the final stage of the Kübler-Ross model when an individual has fully accepted and integrated with the change and becomes a renewed person (Rosenbaum et al., 2018; Tempski et al., 2020). Throughout this study, no tweets expressed integration from March to August 2020 as this was still early in the pandemic to potentially see this stage of the KRCC.
Limitations
This study looked at the tweets from the first six months of the pandemic. Therefore, one limitation of the dataset is that it does not capture any issues that have emerged since August 2020; especially related to vaccination which we thought would confound the current results. As the pandemic has been rapidly changing, follow-up studies are needed for tweets that may be related to various changes in policies from lock-downs to vaccination mandates after August 2020. Another limitation is that the data were gathered exclusively from Twitter and may not be representative of the entire population of Canada.
Conclusion
This study analyzed Twitter data to understand the perspectives of Canadians to COVID-19 response in Canada. While the government attempted to implement swift action to reduce the spread of COVID-19 early during the pandemic, many Twitter users expressed that it was not effective in containing the virus. Based on the KRCC, the level of impact that the pandemic had on Canadians determined how well they were able to adjust to the change. These findings demonstrate that for more Canadians to be able to adjust to changes and maintain good or excellent mental health, there may need to be more supports made available to help people adapt, achieve their highest potential, and positively contribute to society, especially the most vulnerable in communities. These data also speak to the communication available to Canadians by different governmental bodies and how well messages may or may not have been related to the lay person’s real life.
References
- Bah, A. J., James, P. B., Bah, N., Sesay, A. B., Sevalie, S., & Kanu, J. S. (2020) Prevalence of anxiety, depression and post-traumatic stress disorder among Ebola survivors in northern Sierra Leone: a cross-sectional study. BMC public health 20(1): 1391. [CrossRef]
- Gong, J., Cui, X., Xue, Z., Lu, J., & Liu, J. (2021) Mental health status And Isolation/quarantine during the COVID -19 Outbreak: A large sample size study of the Chinese population. Psychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences. [CrossRef]
- Jalloh, M. F., Li, W., Bunnell, R. E., Ethier, K. A., O'Leary, A., Hageman, K. M., Sengeh, P., Jalloh, M. B., Morgan, O., Hersey, S., Marston, B. J., Dafae, F., & Redd, J. T. (2018) Impact of Ebola experiences and risk perceptions on mental health in Sierra Leone, July 2015. BMJ global health 3(2). [CrossRef]
- Kato, T. A., Sartorius, N., & Shinfuku, N. (2020) Forced social isolation due to covid-19 and consequent mental health problems: Lessons from hikikomori. Psychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences 74(9): 506-507. [CrossRef]
- Kübler-Ross E (1969) On Death and Dying. New York: Macmillan Publishing Company.
- Lai, J., & Widmar, N. O. (2020) Revisiting the digital divide in the COVID -19 Era. Applied Economic Perspectives and Policy 43(1): 458-464. [CrossRef]
- Malone, E. (2018) The Kubler-Ross change curve and the Flipped classroom: Moving students past the pit of despair. Education in the Health Professions 1(2): 36. [CrossRef]
- Perreault, M., Touré, E. H., Perreault, N., & Caron, J. (2017) Employment status and mental health: Mediating roles of social support and coping strategies. Psychiatric Quarterly 88(3): 501-514. [CrossRef]
- Rosenbaum, D., More, E., & Steane, P. (2018) Planned organisational change management. Journal of Organizational Change Management 31(2): 286-303. [CrossRef]
- Silverman, M., Clarke, M., & Stranges, S. (2020) Did Lessons From SARS help Canada’s Response to COVID-19? American Journal of Public Health 110(12): 1797-1799. [CrossRef]
- Sinnenberg, L., Buttenheim, A. M., Padrez, K., Mancheno, C., Ungar, L., & Merchant, R. M. (2017) Twitter as a Tool for Health Research: A Systematic Review. American journal of public health 107(1): e1–e8. [CrossRef]
- Ståhl, C., & MacEachen, E. (2020) Universal basic income as a policy response to COVID-19 and precarious employment: Potential impacts on rehabilitation AND Return-to-Work. Journal of Occupational Rehabilitation 31(1): 3-6. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Statistics Canada (2020a) Canadian Community Health Survey, 2019: Annual component. Available online: https://www150.statcan.gc.ca/n1/daily-quotidien/200806/dq200806a-eng.htm (accessed on 15 January 2021).
- Statistics Canada (2020b) COVID-19 in Canada: A Six-month Update on Social and Economic Impacts. Available online: https://www150.statcan.gc.ca/n1/pub/11-631-x/11-631-x2020003-eng.htm#b (accessed on 10 March 2021).
- Talbot, J., Charron, V., Konkle, A.T.M. (2021) Feeling the void : lack of support for isolation and sleep difficulties in pregnant women during the COVID-19 pandemic revealed by Twitter data analysis. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 18(2): 393. [CrossRef]
- Tempski, P., Danila, A. H., Arantes-Costa, F. M., Siqueira, M., Torsani, M. B., & Martins, M. A. (2020) The COVID-19 pandemic: time for medical teachers and students to overcome grief. Clinics (Sao Paulo, Brazil) 75: e2206. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Lancet Infectious Diseases (LID) (2020) The intersection of COVID-19 and mental health. The Lancet Infectious Diseases. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tucci, V., Moukaddam, N., Meadows, J., Shah, S., Galwankar, S., & Kapur, G. (2017) The forgotten plague: Psychiatric manifestations of Ebola, Zika, and emerging infectious diseases. Journal of Global Infectious Diseases 9(4): 151. [CrossRef]
- Tzeng, N. S., Chung, C. H., Chang, C. C., Chang, H. A., Kao, Y. C., Chang, S. Y., & Chien, W. C. (2020) What could we learn from SARS when facing the mental health issues related to the COVID-19 outbreak? A nationwide cohort study in Taiwan. Translational psychiatry 10(1): 1-9. [CrossRef]
- Vinkers, C. H., van Amelsvoort, T., Bisson, J. I., Branchi, I., Cryan, J. F., Domschke, K., Howes, O. D., Manchia, M., Pinto, L., de Quervain, D., Schmidt, M. V., & van der Wee, N. (2020) Stress resilience during the coronavirus pandemic. European neuropsychopharmacology: the journal of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology 35: 12-16. [CrossRef]
- Webster, P. (2020) Canada and COVID-19: Learning from SARS. The Lancet 395(10228): 936-937. [CrossRef]
- Wiens, K., Bhattarai, A., Pedram, P., Dores, A., Williams, J., Bulloch, A., & Patten, S. (2020) A growing need for youth mental health services in Canada: Examining trends in youth mental health from 2011 to 2018. Epidemiology and Psychiatric Sciences 29. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).