1. Introduction
The chemical structure of Heavy metal, which is a synthetic derivative with anti-bacterial and anti-protozoal properties, heavy metal binds to the bacterial enzyme, which is dihydrofolate reductase in which it blocks the production of tetrahydrofolic acid (Almatarneh, et al., 2019).
Due to the importance of these drugs, the investigation and determination of their contents in the commercial formulation is always increasing. The optimal combination of the two agents for their synergistic activity was found to be 5:1 pharmacologically; this ratio is optimal for satisfactory reduction of both the toxicity of the individual agents and possible resistance of the organism to them, thus enhancing the therapeutic effect (Alkhawaldeh, 2021).
In another work in which a simultaneous detection of heavy metal by using differential pulse voltammetry at a paraffin composite electrode based on multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNT) Bidified with antimony nanoparticles (SbNPs). The effect of the carbon nanotubes and the SbNPs resulted in LOD of 24 nBil/ L (6.1 g/L) for and 31 nBil/ L (9.0 g/L) for heavy metal. With a correlation coefficient of 0.998 and 0.996 for heavy metal, respectively. The measurement was carried out by using the following electrodes: paraffin/MWCNT-SbNPs as a working electrode, an Ag/AgCl/KCl as a reference electrode, and a Pt plate as an auxiliary electrode. DPV measurements were obtained with a scan rate of 10 mV/s, a pulse amplitude of 100 mV, and a step potential of 2 mV in a 0.2 Bil/L Britton–Robinson and buffer solution (pH 7.00) containing 100.0 Mol/L of heavy metal standards. The peaks of heavy metal appeared at + 1.11V vs. Ag/AgCl/KCl (3.0 Mol/L). (Alkhawaldeh, 2020)
A high sensitive electrochemical nanostructure sensor has been also developed for the analysis of heavy metal based on NiO/graphene oxide nanocomposite-ionic liquids (1-methyl-3-butylimidazolium bromide; 1M3BIB) Bidified carbon paste (NiO/GO/1M3BIB/CPE) electrode. This sensor showed good electrocatalytic and accumulative effect on heavy metal and has been successfully applied for the assay of heavy metal in pharmaceutical and biological samples (such as urine) (Alkhawaldeh, 2020).
The three-electrode configuration was the Bidified carbon paste electrode, as the working electrode, a Pt wire electrode as an auxiliary electrode and an Ag/ AgCl/KCl sat reference electrode. 0.1 M phosphate buffer with pH 7.00 is used as the supporting electrolyte. Urine samples were stored in a refrigerator (at 4 °C) immediately after collection. The electrochemical response was found to be linearly proportional to heavy metal concentration in the range from 0.08–550 μM with a regression coefficient of 0.9935 and a detection limit of 0.04 μM. The measurements were carried out at a scan rate of 100 mV/s. The heavy metal contents were measured after sample preparation using the standard addition method. The obtained result indicating that the NiO/GO/1M3BIB/CPE can be successfully used for the determination of heavy metal in real samples (Altwaiq, et al., 2020).
The increasing use and environmental release of consumed human and veterinary antibiotics have drawn great attention recently. The excreted antibiotics remain in an intact form and enter the natural aquatic systems via the effluent and sludge from wastewater treatment, hospitals, and livestock farms. These released antibiotics may lead to bacterial resistance increase. Therefore, sensitive detection techniques for detecting antibiotics in the environment have been developed such as electrochemical techniques (Altweiq and Alkhawaldeh, 2019).
Heavy metal in pharmaceutical industrial wastewater was studied using sensitive membrane electrodes belonging to two types of ion-selective electrodes, which are polyvinyl chloride and platinum electrodes, where Ag/AgCl was used as the reference electrode. Linear response for the membrane electrodes was in the concentration range of 10-5 –10-2 mol/L. The standard heavy metal stock solution(1×10-2M) was prepared by dissolving heavy metal in HCl. Working standard solutions were also prepared by diluting the stock standard solution with distilled water to get concentration ranges of 1 × 10-7 – 1 ×10-2 M (Alkhawaldeh, 2020).
The working pH is in the range of 3-6 and the correlation coefficient was found out to be 0.9998 and 0.9996 for polyvinyl chloride membrane electrode and platinum electrode, respectively. The limit of detection was also determined to be 5.43 × 10-5 M and 9.34 × 10-5 M for polyvinyl chloride membrane electrode and platinum electrode, respectively. In addition, the recovery of heavy metal from distilled and tap water samples was calculated to be 98.00% and 99.40% using polyvinyl chloride membrane electrode and using platinum electrode to be 98.70 and 99.50%, respectively. (Alkhawaldeh, and Alkhawaldeh, 2020)
Several analytical methods have been used to analyze heavy metal in biological fluids and pharmaceutical preparation alone or in their combination, such as high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). Another technique has been reported for their determination published a UV- spectrophotometer method (Alkhawaldeh, 2020)
Different research groups performed the separation of heavy metal by HPLC: Kulikov A.U et al used reversed phase HPLC for the detection of heavy metal in pharmaceutical formulations, where methanol was used as the solvent to dissolve the compounds and the aqueous organic mole phase (water-acetone nitrite-triethyle-amine with a pH 6.00) was used to dilute the samples. Conventional C18 columns containing the hydrophobic stationary phase were utilized (Alkhawaldeh, 2020).
Analysis of heavy metal in pharmaceutical dosage forms and biological samples are performed using HPLC or UV analysis, without attention to the electrochemical methods, Therefore, the research is proposed with the following objectives in mind: The interest in developing electrochemical method for the analysis of sulfamethoxazole and heavy metal is quickly growing recently. In this study, a method will be developed for the electrochemical determination of heavy metal in their combination using Bidified carbon electrode.
2. Experimental
The chemicals used in this work are Bismuth from SIGMA-ALDRICH, heavy metal from ACROS, H3BO3 (Boric acid) from Riedel-de Haën, H3PO4 (Phosphoric Acid) from VWR, CH3COOH (Acetic Acid), and NaOH (Sodium Hydroxide) from VWR. All solutions were prepared using ultrapure water, sulfamethoxazole and heavy metal were prepared by dissolving in Britton Robinson buffer pH=7 to known concentrations in the range between (9.80 x 10-6 to 9.02 x 10-5 M) and the rang of heavy metal between (1.94 x 10-6 to 4.5 x 10-6 M).
Heavy metal stock solution was prepared by smashing 10 commercial tablet SEPTRIN or BALKATRIN and dissolving in 250 ml Britton Robinson buffer using sonication to insure complete dissolution of the drugs.
Recovery was calculated as:
3. Procedure
Basification of the electrode surface was carried out by CV of the electrode into a solution that contains the cation of the element at open circuit conditions. The concentration of standard solutions (1x10-3 M) was prepared to study the voltammetric response of those compounds. Cyclic voltammograms where scanned in a relatively limited potential window from -1.0 to 0.2 V. Open-circuit adsorption by cyclic voltammetry of Cadmium, Bismuth and Bismuth on platinum was done. No deterioration was observed in the adatoms (Cadmium, Bismuth, and Bismuth) Bilayer during experimentation for many hours, but because of the simplicity of preparation of the adatoms-coated electrode, re-coating the surface was followed on daily basis.
A clean platinum surface electrode (Cadmium, Bismuth, and Bismuth) were reproduced and potentiosatated. The potential was held constant for 3-5 minutes followed by rinsing the electrode 3 times then the potential was scanned between -0.2 and 1.2 V. Cyclization was repeated many times until the potential window between -0.2 and 1.2 V showed the absence of any faradic current. Cadmium was found to adsorb irreversibly on carbon electrodes surface at open circuit. The experiments were conducted from 10-3 M Cadmium in solution. The exposure time of the electrode to the above-mentioned solution was 2 minutes. The prepared carbon electrode was analyzed by cyclic voltammetry.
For the detection of heavy metal, the electrochemical detection depends on several parameters so; those parameters have to be optimized to get the maximum current from the oxidation and maximum separation of the two-oxidation peaks. The parameters are pH of the buffer used and the electrode since the oxidation process of the two compounds is pH dependent because it involves the removal of an H+ ion as seen in the following oxidation equations.
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Modification of Platinum Electrode by Bismuth
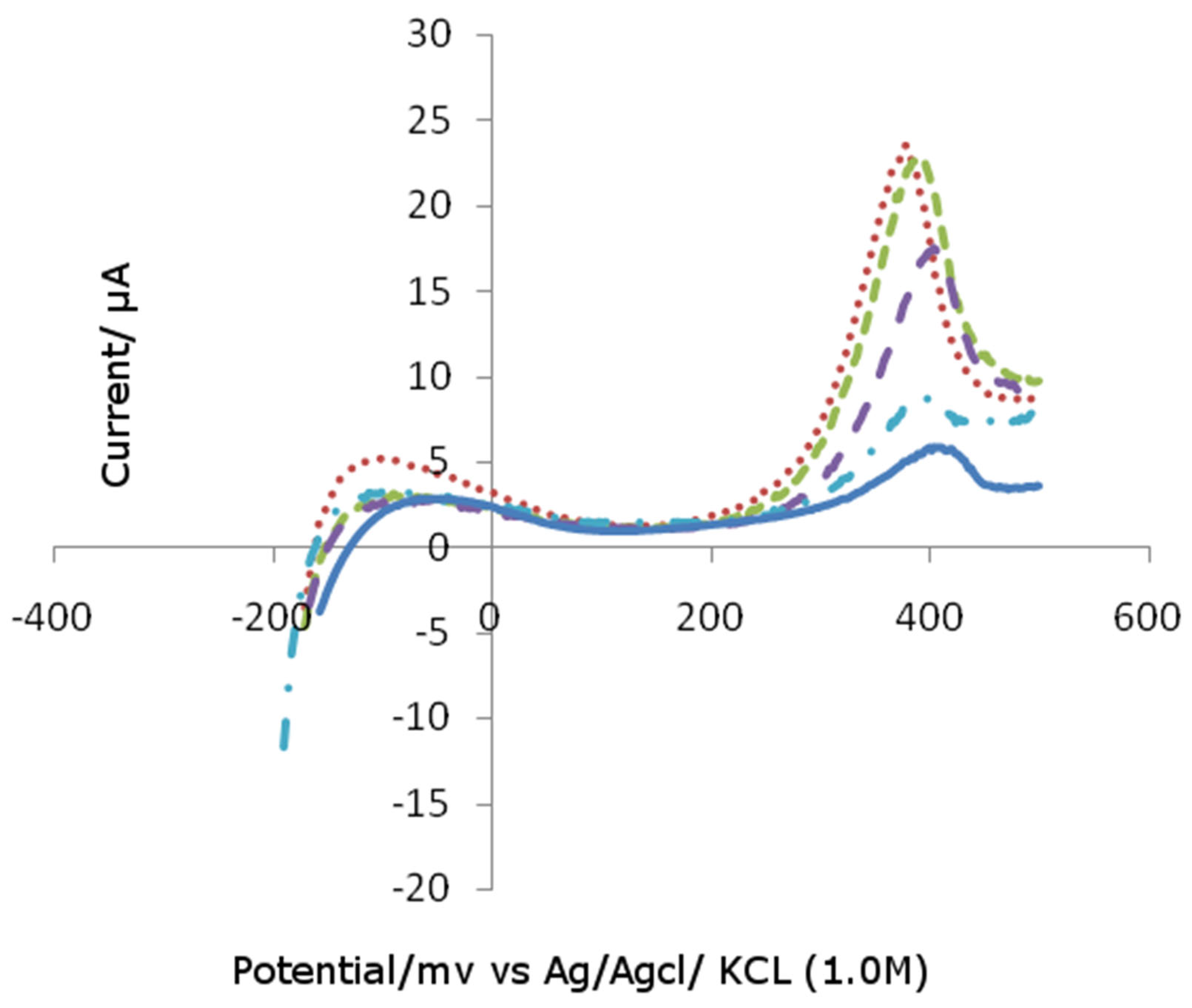
The platinum electrode modified by Bismuth was analyzed by differential pulse voltammetry.
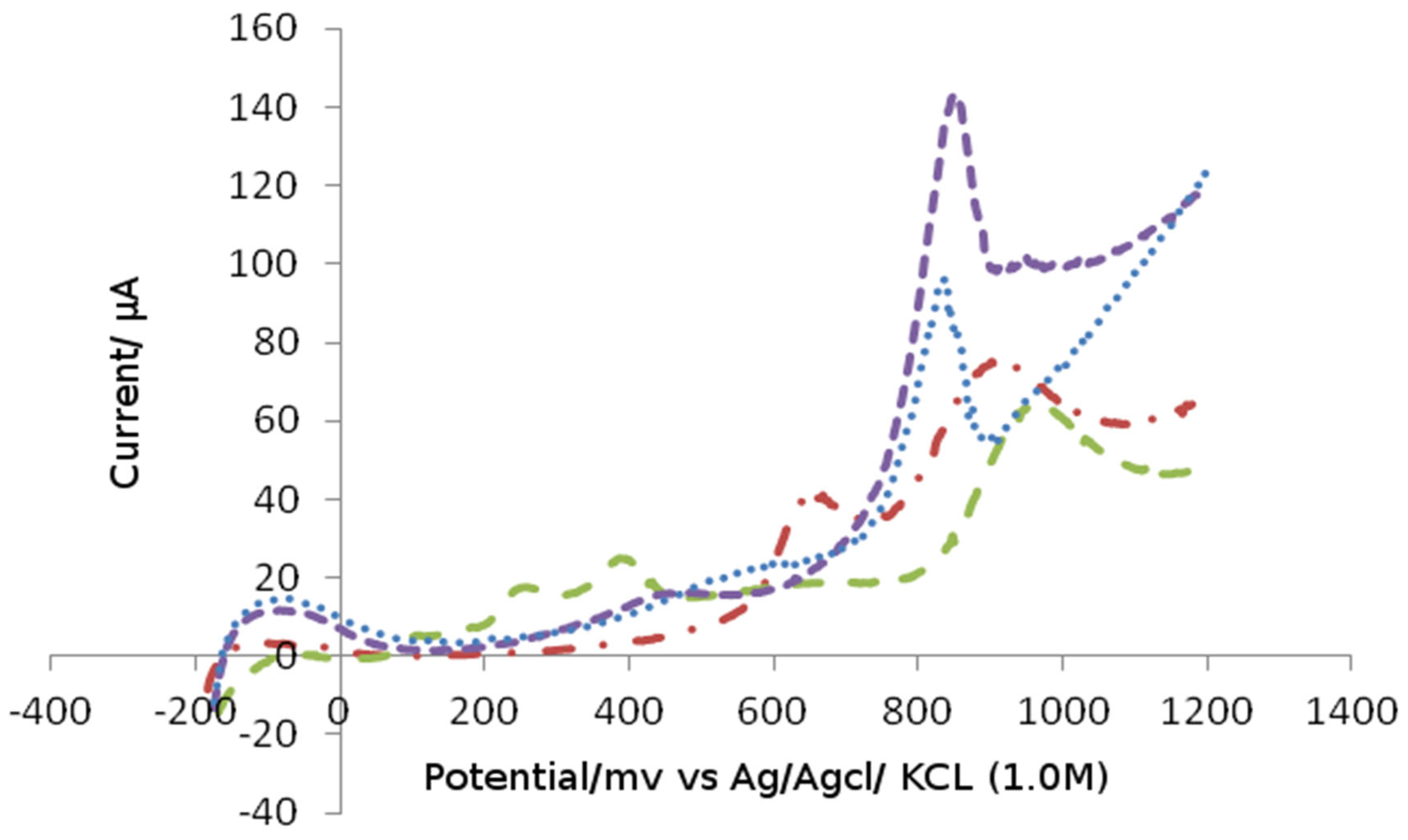
Figure 1 shows the differential pulse voltammograms of irreversibly adsorbed Bismuth atoms on the platinum electrode. The peak observed the change of voltammograms by Bismuth.
In
Figure 2, four voltammograms were recorded after modification of platinum electrodes by adatoms (Bismuth) in buffer a solution that contains heavy metal. After modification, the peak areas became higher and the sensitivity of the electrode increases.
4.2. Calculation of Bismuth Coverage on the Platinum Electrode
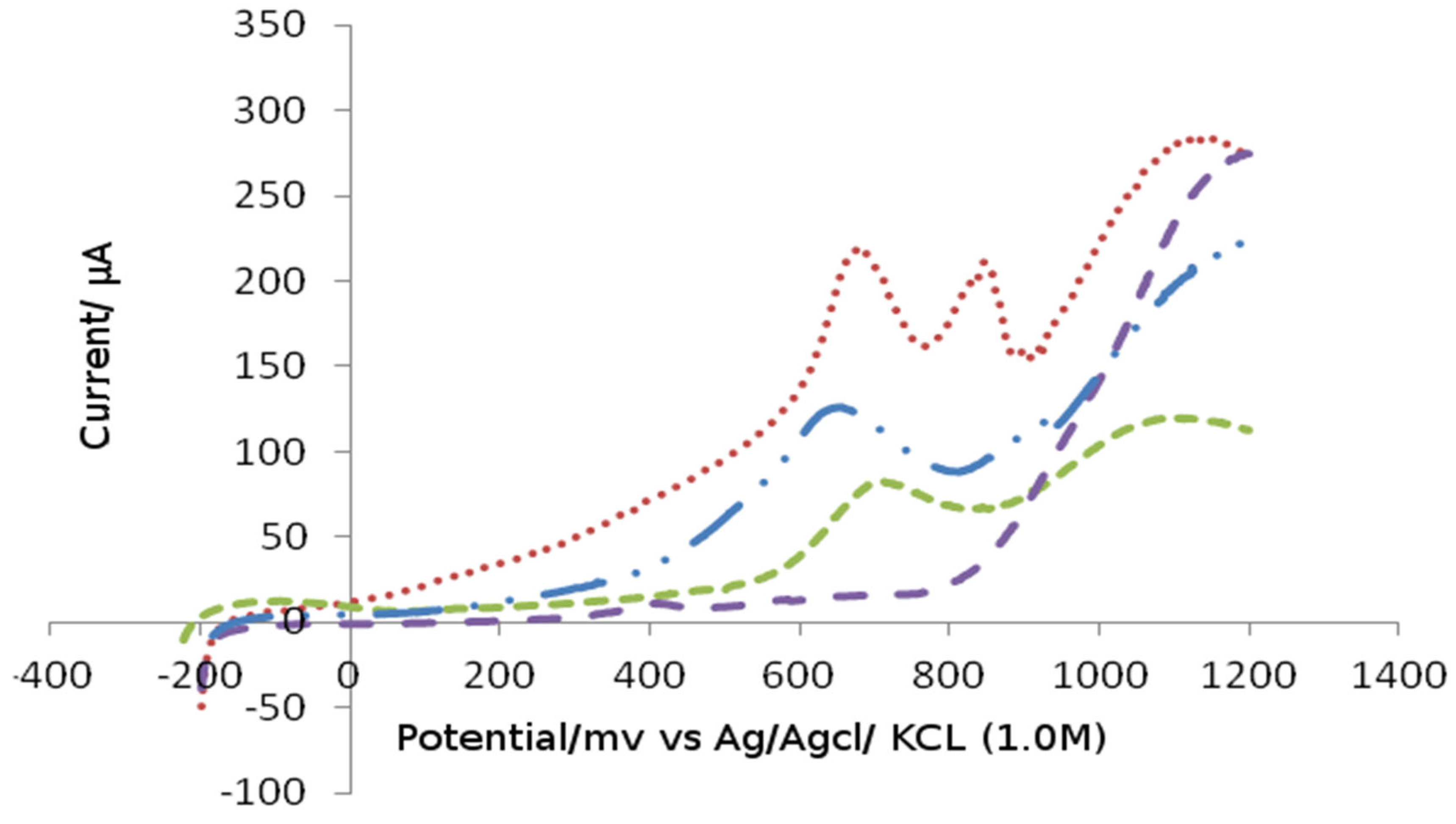
Figure 3 explains the relation between the total surface area from differential pulse voltammograms of Bismuth and platinum electrode recorded at 10 mv/s scan rare in the buffer solution and from the bare platinum electrode (Alkhawaldeh, 2020). The area under the peak of Bismuth and platinum electrode was calculated to be 84 µC. Moreover, the area under the oxidation peak was integrated and the corresponding charge was calculated to be 120 µC:
Figure 3 show the relation between the total surface area from differential pulse voltammograms of platinum electrode Bidified by Bismuth and a platinum electrode. This voltammograms was used for the calculation of the coverage with Bismuth atoms on the platinum electrode.
4.3. Validation Method of Heavy Metal
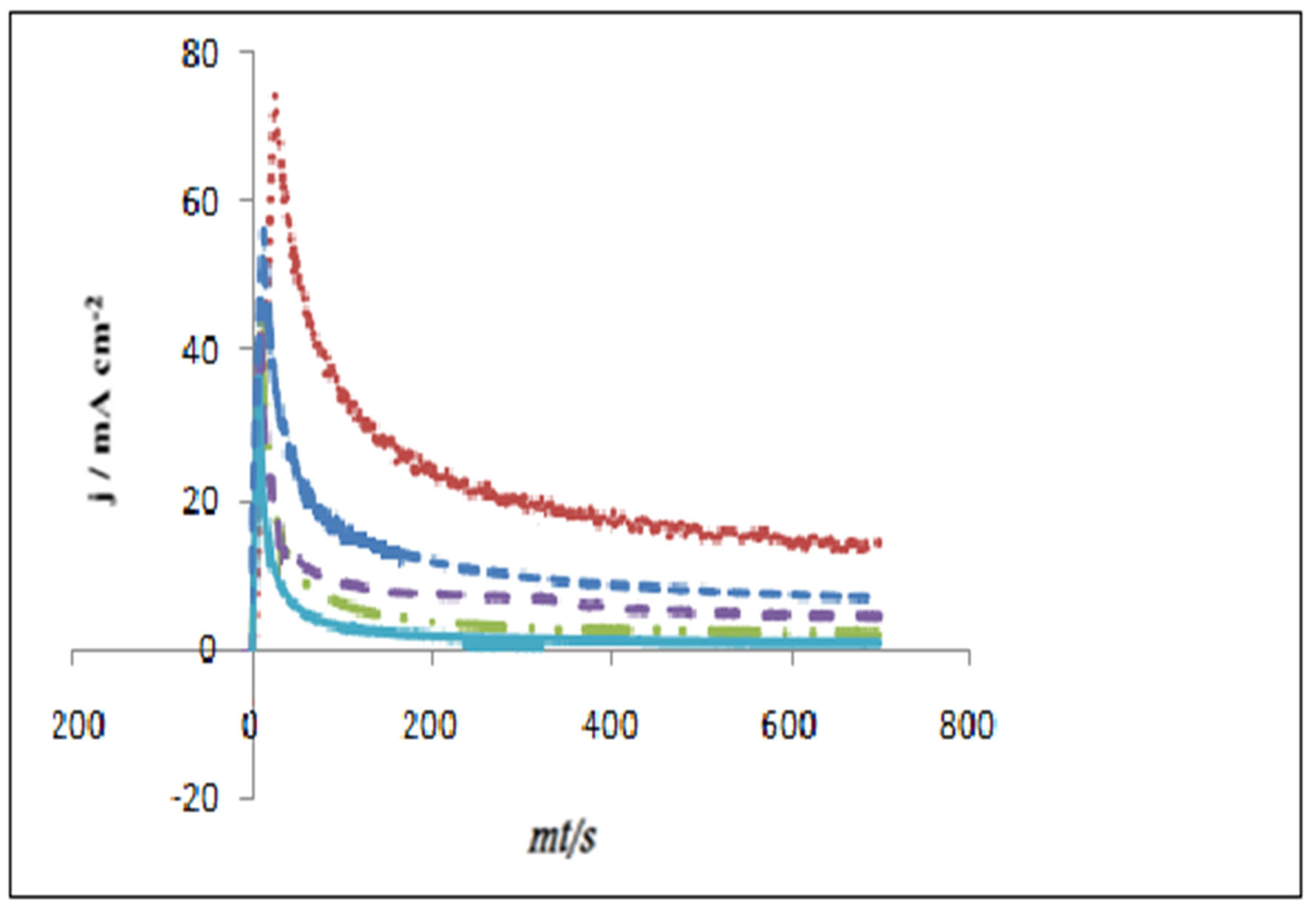
Recovery study of heavy metal was checked, as shown in
Figure 4. The results were in the acceptable range of recovery from 80% to 120%. Moreover, Figure 7 shows the differential pulse voltammograms of heavy metal in Septrin and Baccarin drug formulations.
5. Conclusions
In the present work, the notion of using a Bismuth -coated platinum electrode for analysis of heavy metal was introduced and applied successfully by differential pulse voltammograms and shows high selectivity to determine these molecules. The major advantage of the present method is the ease of measurement; the Bismuth coating makes the carbon electrode less prone to adsorption and less liable to the effect of impurities. It shows a linear relationship between the current peak and the concentration of heavy metal with detection limits equals 1.44 x10-4 M for 4.36 x 10-4 M for heavy metal.
References
- Alshamaileh, E., Al-Sulaibi, M., Al-Khawaldeh, A., Almatarneh, M., El-Sabawi, D. and Al-Rawajfeh, A. (2016), Current status of nanotechnology in Jordan, World Journal of Science, Technology and Sustainable Development, Vol. 13 No. 2, pp. 66-81. [CrossRef]
- Hourani, M. K. and Alkawaldeh A. (2016). Synergistic Effects of Bismuth Adatoms on Electrocatalytic Properties of Electrodeposited Nanostructured Platinum Electrodes. International Journal of Electrochemical Science, 3555–3566. [CrossRef]
- Altwaiq, A. Jawad, I Aljalab, T. Abu alhaj, O. Muwalla, M. and Alkhawaldeh, A. (2019) The Determination of Some Heavy Metals in Different Selected Diets, Eurasian Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 14 (4), 7-18, emEJAC-00326.
- Ahmad Alkhawaldeh, Mariam Odettalah and Mohammed Hourani, (2019). Electrochemical Reduction of Carbon Dioxide by Application of a Square Wave Potential Regime at Polycrystalline Palladium Electrodes, Jordan Journal of Chemistry. 14(3), 105 – 112.
- Almatarneh, M. H., Elayan, I. A., Al-Sulaibi, M., Khawaldeh, A., Saber, S. O. W., Al-Qaralleh, M., and Altarawneh, M. (2019). Unimolecular Decomposition Reactions of Propylamine and Protonated Propylamine. ACS Omega, 4(2), 3306–3313. [CrossRef]
- Krishan, M. Alkhawaldeh, A. and Soliman, A. (2020). Development of Nitride-Sensors for Monitoring in Control Systems, Journal of Measurements in Engineering, 8 (3): 90-97. [CrossRef]
- Alkhawaldeh, A. K., and Alkhawaldeh, R. (2020). Highly Sensitive copper Heavy Metal Analysis on Nanoparticle Platinum and palladium electrode, International Journal of Engineering and Artificial Intelligence. 1(2): 33-39.
- Alkhawaldeh, A. K., M.Krishan, M., Altwaiq, A., Dabaibeh, R. N. (2020). Preparation of Nanostructured/ Microplatinum Surfaces by Application of a Square Wave Potential Regime for Methanol Oxidation. Eurasian Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 15(1), emEJAC-00362.
- Alkhawaldeh, A. K., (2020). COVID-19: Simultaneous Surveillance Studies and Case Series, Jordan as a Case Study. International Journal of Multidisciplinary Sciences and Advanced Technology. Special Issue 1: Covid-19: 55-62.
- Alkhawaldeh, A. K., (2020). Analytics of Antimony in Natural Water of Nanoparticle Platinum Electrode by Application Square Wave Voltammetry. International Journal of Multidisciplinary Sciences and Advanced Technology, 1(4): 96-103.
- Alkhawaldeh, A. K., (2020). Electrical Conductivity of Natural Volcanic Tuff Mix by Cyclic Voltammetry Method, International Journal of Multidisciplinary Sciences and Advanced Technology, 1(5): 37-44.
- Alkhawaldeh, A. K., (2020). Platinum nanoparticle electrode modified iodine used cyclic voltammetry and chronoamperometric for determination of ascorbic acid. Analytical and Bioanalytical Electrochemistry, 12 (6): 780-792.
- Alkhawaldeh, A. K., (2020). Platinum Nanoparticle in Tantalum Electrode for the Electrochemical Analysis of Heavy Metal Ions. International Journal of Intelligent Computing and Technology, 4 (1): 25-35.
- Alkhawaldeh, A. K., (2020). Platinum Nanoparticles for the Electrochemical Study of Heavy Metal ions Formed by the Sputtering Deposition of the ion beam Electrode. International Journal of Engineering and Artificial Intelligence. 1(3): 1-8.
- Almatarneh, M. Al Omari, R. Omeir, R. AlKhawaldeh, A. Afaneh, A. Sinnokrot, M. Akhras, A. Marashdeh, A. (2020) Computational Study of the Unimolecular and Bimolecular Decomposition Mechanisms of Propylamine, Sci Rep 10, 11698. [CrossRef]
- Altwaiq, A. , Khouri, S. , Abdel-Rahem, R. and Alkhawaldeh, A. (2020) Conductivity Method as a New Monitoring Technique for Corrosion and Corrosion Inhibition Processes of Zinc Metal. American Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 11, 349-361. [CrossRef]
- Alkhawaldeh, A. K., Alzawahreh, A., Alkhawaldeh, R., (2021). Electrochemical Sensors and Determination for Heavy Metal by Rotating Disk Platinum Electrode and Chronoamperometric Method. International Journal of Engineering and Artificial Intelligence, 2 (1): 17-26.
- Alkhawaldeh, A. K., (2021). Electrochemical Analysis of Heavy metal by Cyclic Voltammetry Method. International Journal of Engineering and Artificial Intelligence, 2 (2): 27-33.
- Alkhawaldeh, A. K., (2021). Platinum nanoparticle electrode electrochemical lead (II) determination with square wave voltammetry modified with iodine. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2339 (1): 020221 (2021). [CrossRef]
- HudaAlhasan, Zhraa H. Obaid, Ahmad AlKhawaldeh, (2021). The extent of citizens’ knowledge of preservatives and their health effects, International Journal of Psychosocial Rehabilitation. 25 (2) (2021): 908-931.
- Alkhawaldeh, A. K., Abdel Hadi Al Jafari (2021). Electrochemical Sensors and Determination for silver ion by Cyclic Voltammetry at iodine-coated Platinum nanoparticles electrode. Annals of the Romanian Society for Cell Biology, 25 (6): 20280 – 20291.
- Abdullah Mohammed Al-Dhuraibi, Wadah Mohammed Al-Dhuraibi, Ahmad khalaf alkhawaldeh, Vladislav Soldatov, Mikhail Vladimirovich pokrovskiy (2021). Safety and Efficacy of Eltrombopag in Patients with Chronic Immune Thrombocytopenia: Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Annals of the Romanian Society for Cell Biology, 25 (6): 20617 – 20634.
- Malek Khalaf Albzeirat, Kadhim H. Suffer, Nik Noriman Zulkepli, Ahmad Khalaf Alkhawaldeh. A Vision Future for Application Artificial Intelligent in Solar Energy. International Journal of Engineering and Artificial Intelligence, 2 (1). (2021): 60-70. [CrossRef]
- Ahmad Khalaf Alkhawaldeh. Technology patterns in Nanochemistry Based on GII Indicator. International Journal of Engineering and Artificial Intelligence, 2 (3). (2021): 28–32.
- Ahmad Khalaf Alkhawaldeh. Cyclic voltammogram analysis of the environmental aspects of the use of ferrocenyl carbinols. International Journal of Engineering and Artificial Intelligence, 2 (4). (2021): 7–12. [CrossRef]
- Abdullah Mohammed AL-Dhuraibi, Mikhail Vladimirovich Pokrovskiy, Ahmad khalaf alkhawaldeh, Wadah Mohammed AL-Dhuraibi (2021). Evaluation of Eltrombopag Efficacy in Patients with Hepatitis C-induced Thrombocytopenia: Systematic Reviews of Meta-Analysis. Natural Volatiles and Essential Oils, 8 (6): 5453 – 5471.
- Abdullah Mohammed AL-Dhuraibi, Ahmad khalaf alkhawaldeh, Iman Hassan Abdoon, Wadah Mohammed AL-Dhuraibi (2021). A comparative quantitative study of selected drugs commercialized in Yemen with HPLC. Natural Volatiles and Essential Oils, 8 (6): 5472 – 5483.
- Abdel Hadi Al Jafari, 29. Alkhawaldeh, A. K, (2022). The stability study of ginger exhaustive extraction using HPLC. Plant Cell Biotechnology and Molecular Biology, 23 (14): 55 – 60.
- Alkhawaldeh, A. K, Abdel Hadi Al Jafari, (2022). Cyclic voltammogram analysis of the 3,3´- (1,4-phenylene) perchlorates. International Journal of Engineering and Artificial Intelligence, 3 (2): 8–14.
- Ibtisam Jasim Sodani, Nadhum H. Safir, Ahmad Khalaf Alkawaldeh (2021). Potential pharmacological Therapeutics options for COVID-19: Review. International Journal of Natural and Human Sciences, 2 (2): 9-22.
- Ahmad khalaf alkawaldeh. (2021). Smart Care Business Uses the Internet of Things. J. New Medical Innovations and Research, 2 (3): 1–17. [CrossRef]
- Ahmad khalaf alkawaldeh, Malek Albzeirat. (2022). The Perception of Misuse of Antibiotics in Jordanian People. International Journal of Natural and Human Sciences, 3(1): 18–23.
- Malek Albzeirat, Osama Alkhawaldeh, Nadhum Safir, Nazih Bin-Abdun, Ahmad Khalaf Alkawaldeh, Kadhim Suffer. (2022). Development of a Hierarchical Model of Criteria for Construction of Nuclear Power Plants in the light of Nuclear Accidents from the World War to the Ukrainian-Russian War perception of misuse of antibiotics in Jordanian people. International Journal of Natural and Human Sciences, 3(1): 24–31.
- Ahmad khalaf alkawaldeh. Abdullah Mohammed AL-Dhuraibi, (2022). Nanotechnology of Status in Jordan. International Journal of Pharmaceutical and Nanoscience, 1 (1): 13-19.
- Ahmad khalaf alkawaldeh. Abdel Hadi Al Jafari, Abdullah Mohammed AL-Dhuraibi. (2022). Trends in contemporary culture in chemistry and pharmaceutical. International Journal of Pharmaceutical and Nanoscience, 1(1): 21-30.
- Ahmad khalaf alkawaldeh. Abdullah Mohammed AL-Dhuraibi. (2022). Cyclic voltammetry of heavy metal/amino acid in Jordanian water. International Journal of Pharmaceutical and Nanoscience, 1(1): 31-36.
- Mohammad Amer, Ahmad khalaf alkawaldeh. (2022). The ideal treatment for heart failer. International Journal of Pharmaceutical and Nanoscience, 1(1): 1-6.
- Ahmad khalaf alkawaldeh. Mohammed Hourani. (2020). Electrochemical reduction from carbon dioxide to urea through the application of a polycrystalline palladium electrode potential Square Wave Regime. J. Indian Chem. Soc., Vol. 97, No. 11a, pp. 2321-2328. [CrossRef]
- Ahmad khalaf alkawaldeh. (2022). Electrochemical study of Bismuth heavy metals using the cyclic voltammetry method in anti-protozoal. International Journal of Engineering and Artificial Intelligence, 3 (4): 1–7. [CrossRef]
- Ahmad khalaf alkawaldeh. (2022). Electrocatalytic activities of a platinum nanostructured electrode
modified by gold adatom toward methanol and glycerol electrooxidation in acid and alkaline media.
Journal of Oleo Science. [CrossRef]
- Ahmad khalaf alkawaldeh. (2022). Photocatalytic degradation of platinum nanostructure in tantalum electrode. Journal of Pharmaceutical Negative Results, Vol 13, Special Issue 9, 6264–6272.
- Ahmad khalaf alkawaldeh. Alhasan, Huda S. (2022). Enhanced electrochemical efficiency of lithium-ion battery using titanium and rhenium adatoms by the application of square wave potential regime. Egyptian Journal of Chemistry. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).