Submitted:
16 January 2023
Posted:
31 January 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Hyperthermia in Cancer Therapy – The Clinical Picture
2.1. Ovarian Cancer
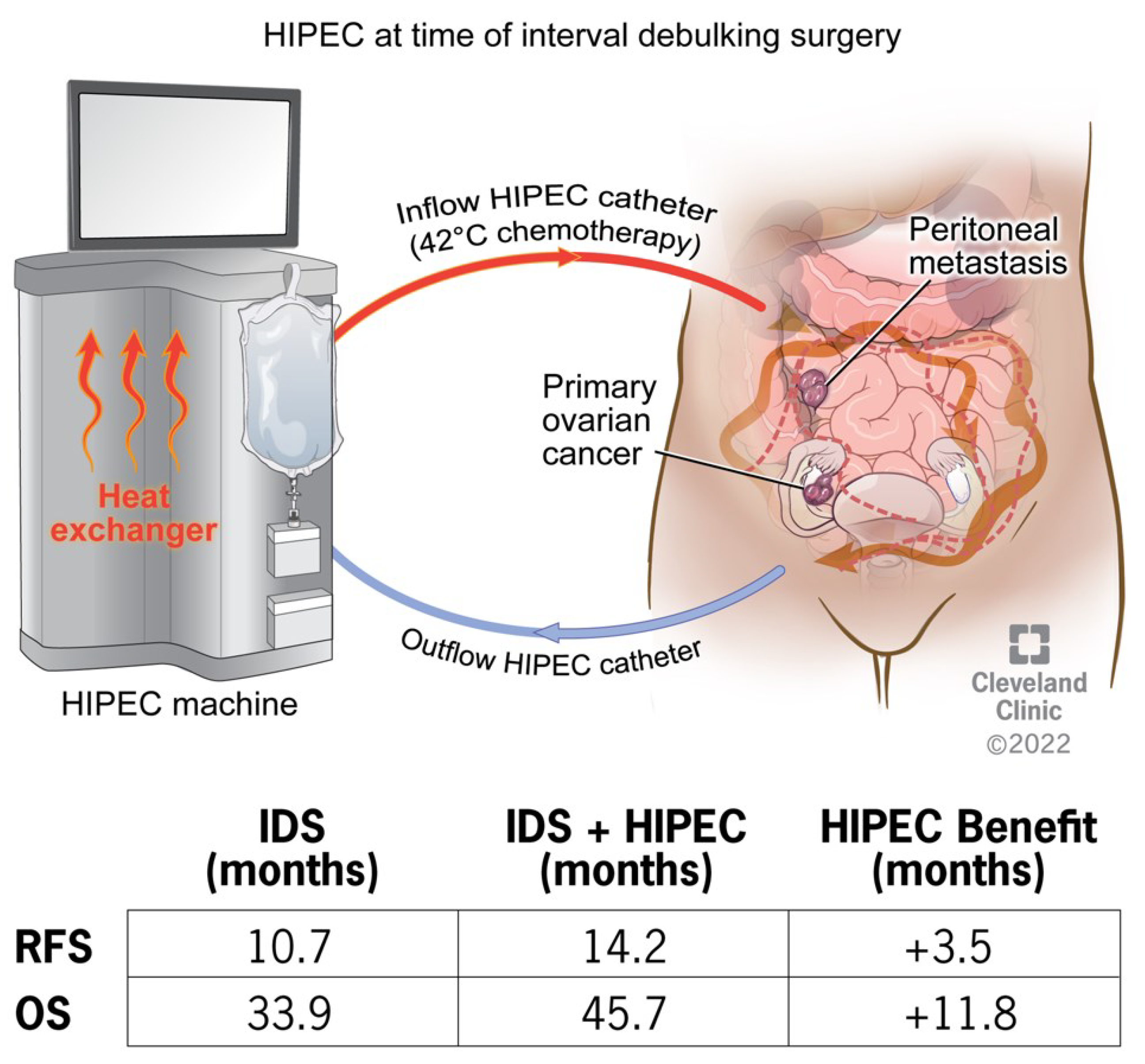
2.1. HIPEC in Peritoneal Cancers
| Author | Year | Study Type | N | Study Details | OS Benefit | PFS Benefit | RFS Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lim et al | 2022 | Single-Blind Randomized | 184 | HIPEC + interval CRS after NACT in ovarian cancer | 13.6 months | 2 months | N/A |
| Ghirardi et al | 2022 | Retrospective | 70 | HIPEC + BRCA mutational status in EOC | No difference between BRCA status | No difference between BRCA status | N/A |
| Herold et al | 2022 | Retrospective | 218 | CRS + HIPEC in mucinous CRC | Could not be determined | Could not be determined | Could not be determined |
| Costales et al | 2021 | Retrospective | 48 | PS vs PR EOC patients given HIPEC after CRS | median 26.9 months in PR patients | N/A | 11.2 months in PS patients |
| Van Driel et al | 2018 | Open-Label Randomized | 245 | Interval CRS ± HIPEC for EOC | 11.8 months | N/A | 3.5 months |
| Tentes et al | 2018 | Retrospective | 6 | CRS + HIPEC for PC | N/A | N/A | >12 months |
| Boerner et al | 2016 | Retrospective | 38 | CRS + HIPEC for gastric cancer + PC | 6.2 months | N/A | N/A |
| Safra et al | 2014 | Case-Control Study | 27 | CRS ± HIPEC ± BRCA mutation in EOC | Not reached at time of analysis (70% patients alive) | 9 months, no difference in BRCA status | N/A |
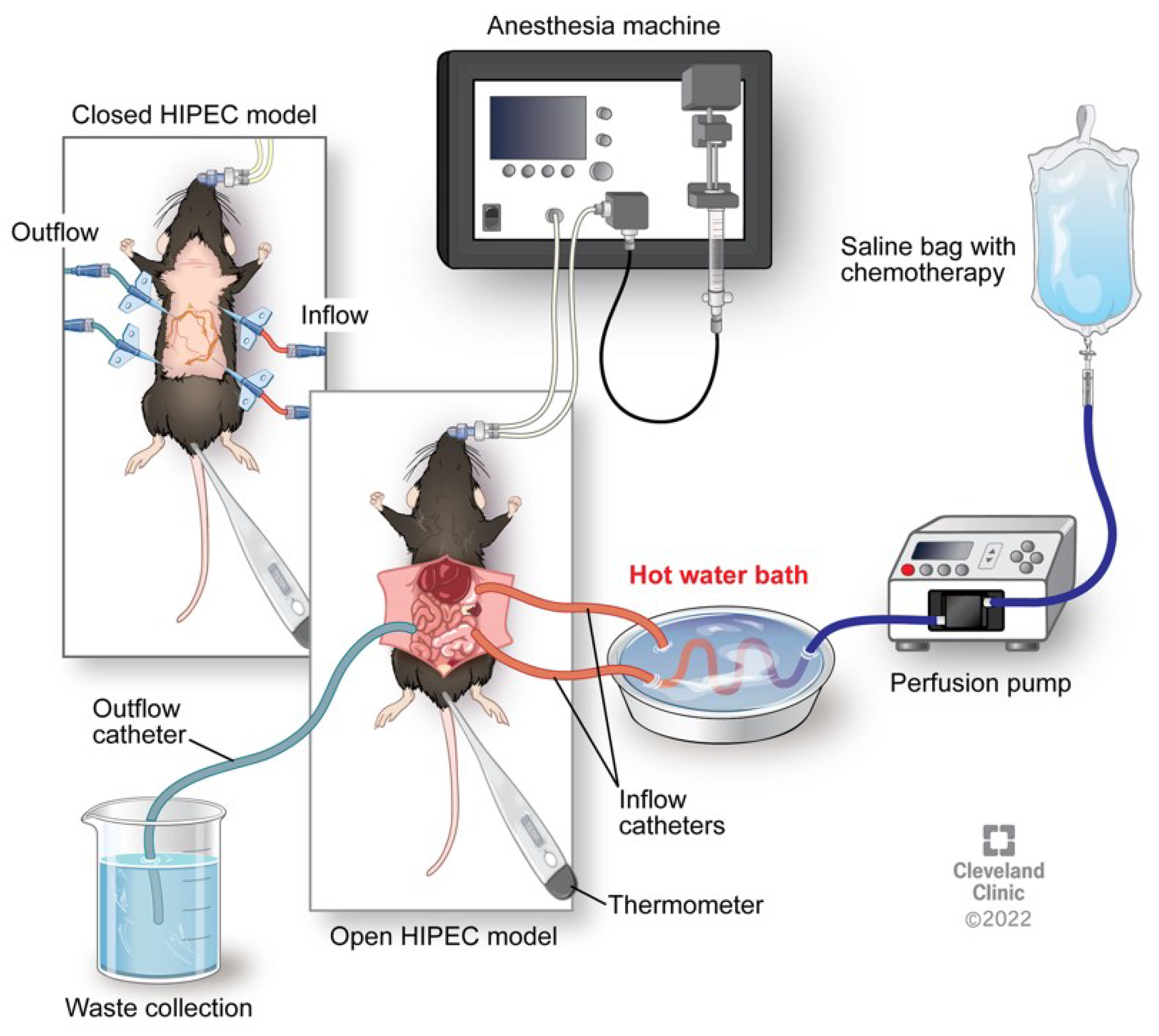
3. Animal Models of HIPEC
3.1. Summary of Pre-Clinical Findings and Challenges
4. Mechanisms of Hyperthermia with or without Chemotherapy
4.1. Heat Shock Response
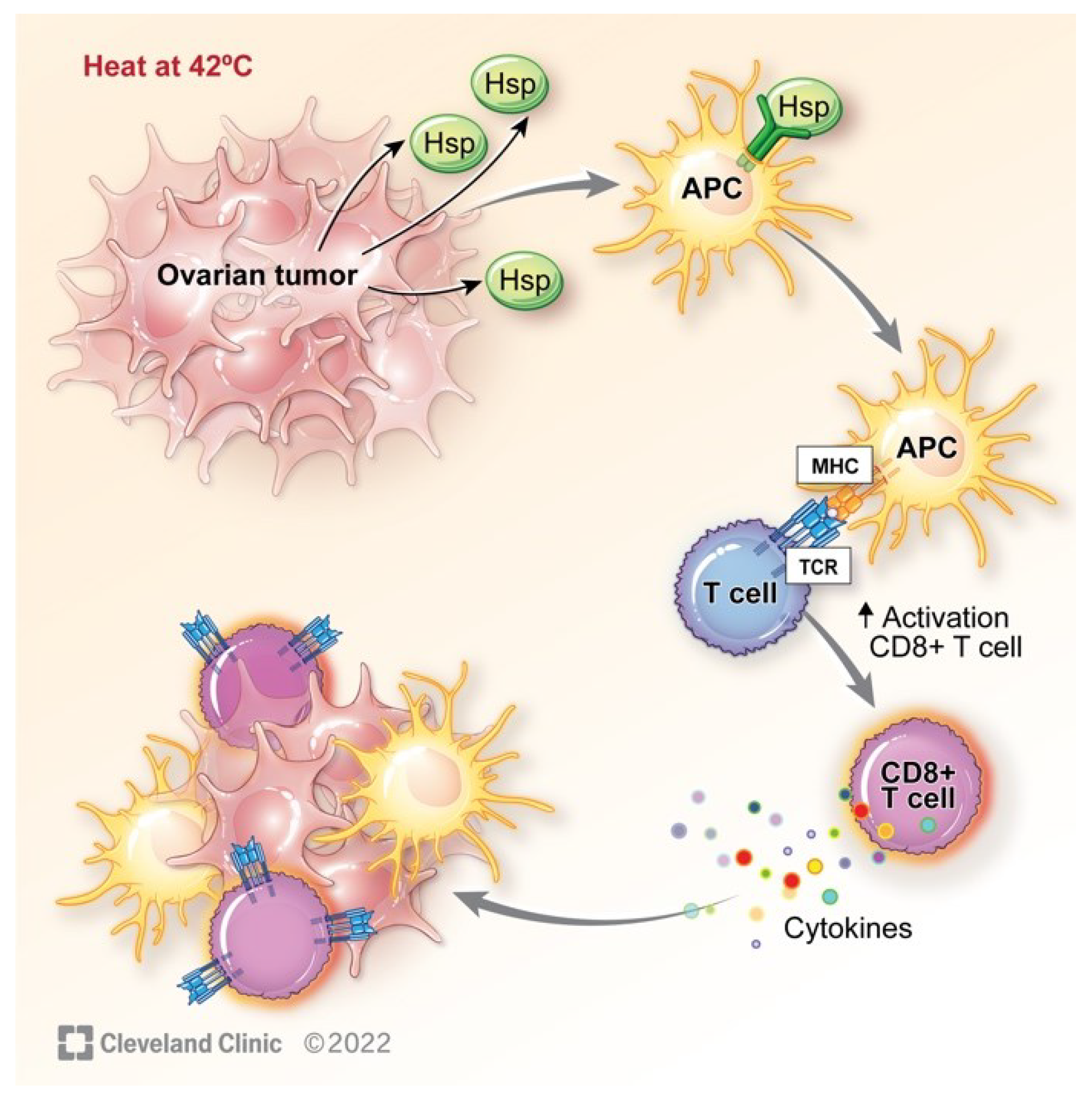
5. Hyperthermia Impact on the Immune System
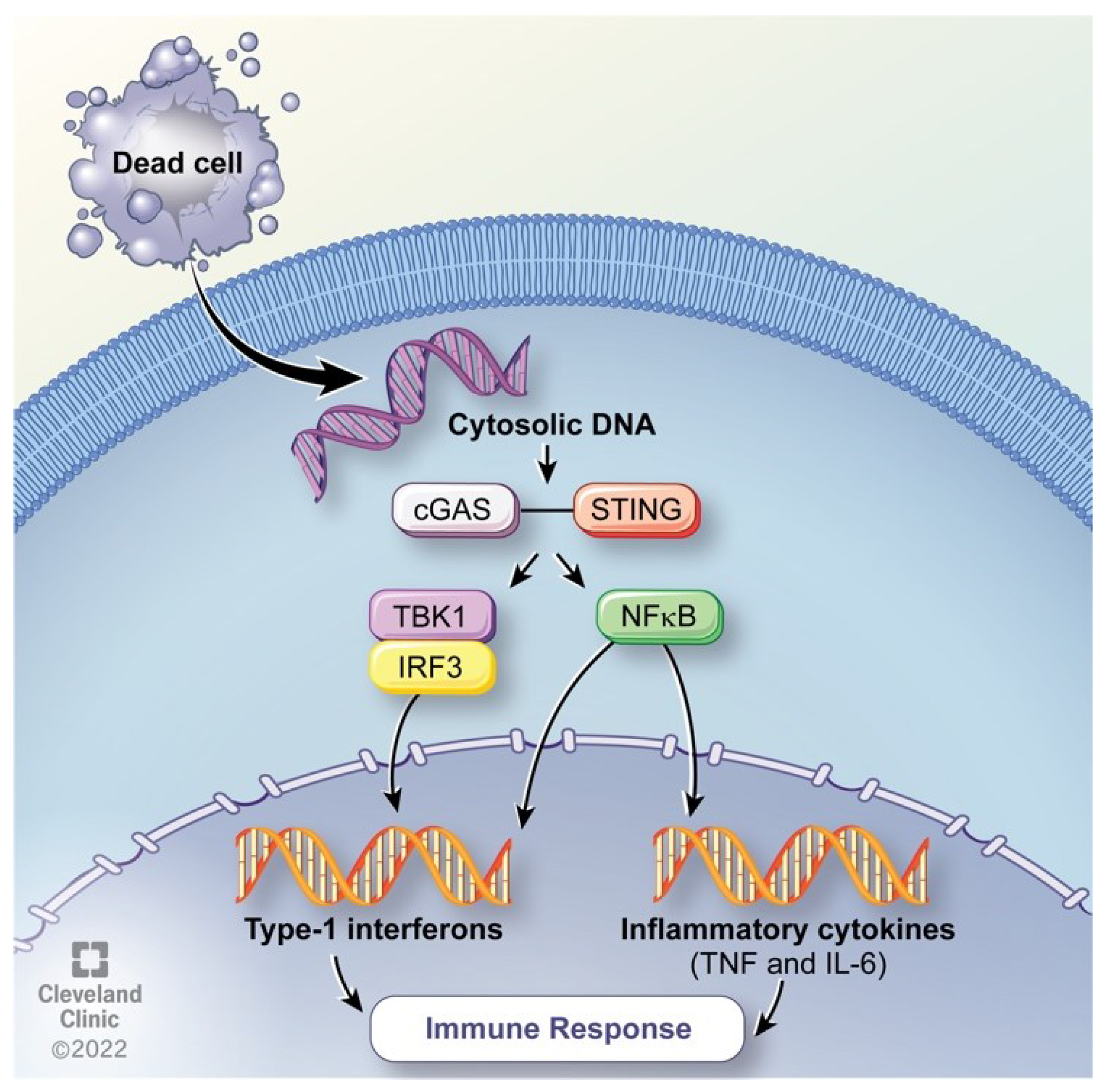
6. Hyperthermia Impact on Genome Instability
7. Clinical Correlates on Immune and DNA Repair Activity in HIPEC
8. Conclusions and Prospects of Future Therapeutic Strategy
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J Clin 2021, 71, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, M.; Singh, N.; Ghatage, P. Past, Present, and Future of Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy (HIPEC) in Ovarian Cancer. Cureus 2021, 13, e15563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Driel, W.J.; Koole, S.; Schagen van Leeuwen, J.H.; Schreuder, H.W.R.; Hermans, R.H.M.; de Hingh, I.H.J.T.; van der Veldern, Jacobus, Arts; Massuger, L.F.A.G.; et al. Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy in Ovarian Cancer. N Engl J Med 2018, 378, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clinic, C. Epithelial Ovarian Cancer, 2022.
- Torre, L.A.; Trabert, B.; DeSantis, C.E.; Miller, K.D.; Samimi, G.; Runowicz, C.D.; Gaudet, M.M.; Jemal, A.; Siegel, R.L. Ovarian cancer statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin 2018, 68, 284–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Society, A.C. Cancer Statistics Center, http://cancerstatisticscenter.cancer.org (2022).
- Kurnit, K.C.; Fleming, G.F.; Lengyel, E. Updates and New Options in Advanced Epithelial Ovarian Cancer Treatment. Obstet Gynecol 2021, 137, 108–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, D.K.; Alvarez, R.D.; Bakkum-Gamez, J.N.; Barroilhet, L.; Behbakht, K.; Berchuck, A.; Berek, J.S.; Chen, L.M.; Cristea, M.; DeRosa, M.; et al. NCCN Guidelines Insights: Ovarian Cancer, Version 1.2019. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 2019, 17, 896–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, M.C.; Chang, S.J.; Park, B.; Yoo, H.J.; Yoo, C.W.; Nam, B.H.; Park, S.Y. Survival After Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy and Primary or Interval Cytoreductive Surgery in Ovarian Cancer: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Surg 2022, 157, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, C.; Horowitz, M.; Costales, A.; Yao, M.; Chichura, A.; Morton, M.; Gruner, M.; Rose, P.; Michener, C.; Debernardo, R. Cisplatin and paclitaxel are associated with improved progression-free survival compared to cisplatin alone during interval debulking surgery with hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy in women with advanced epithelial ovarian cancer. Science Direct 2021. [CrossRef]
- Dasari, S.; Tchounwou, P.B. Cisplatin in cancer therapy: molecular mechanisms of action. Eur J Pharmacol 2014, 740, 364–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zivanovic, O. et al. Secondary Cytoreduction and Carboplatin Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy for Platinum-Sensitive Recurrent Ovarian Cancer: An MSK Team Ovary Phase II Study. J Clin Oncol 2021, 39, 2594–2604. [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.; Tinker, A.V.; Friedlander, M. "Platinum resistant" ovarian cancer: what is it, who to treat and how to measure benefit? Gynecol Oncol 2014, 133, 624–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spiliotis, J.; Halkia, E.; Lianos, E.; Kalantzi, N.; Grivas, A.; Efstathiou, E.; Giassas, S. Cytoreductive surgery and HIPEC in recurrent epithelial ovarian cancer: a prospective randomized phase III study. Ann Surg Oncol 2015, 22, 1570–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakrin, N.; Bereder, J.M.; Decullier, E.; Classe, J.M.; Msika, S.; Lorimier, G.; Abboud, K.; Meeus, P.; Ferron, G.; Quenet, F.; et al. Peritoneal carcinomatosis treated with cytoreductive surgery and Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy (HIPEC) for advanced ovarian carcinoma: a French multicentre retrospective cohort study of 566 patients. Eur J Surg Oncol 2013, 39, 1435–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costales, A.B.; Chambers, L.; Chichura, A.; Rose, P.G.; Mahdi, H.; Michener, C.M.; Yao, M.; Debernardo, R. Effect of platinum sensitivity on the efficacy of hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC) in recurrent epithelial ovarian cancer. J Gynecol Obstet Hum Reprod 2021, 50, 101844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norquist, B.M.; Brady, M.F.; Harrell, M.I.; Walsh, T.; Lee, M.K.; Gulsuner, S.; Bernards, S.S.; Casadei, S.; Burger, R.A.; Tewari, K.S.; et al. Mutations in Homologous Recombination Genes and Outcomes in Ovarian Carcinoma Patients in GOG 218: An NRG Oncology/Gynecologic Oncology Group Study. Clin Cancer Res 2018, 24, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Yao, S.; Dai, M.; Cai, H. Cytoreductive Surgery (CRS) Combined With Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy (HIPEC) for Platinum-Sensitive Recurrence Epithelial Ovarian Cancer With HRR Mutation: A Phase III Randomized Clinical Trial. Technol Cancer Res Treat 2022, 21, 15330338221104565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toh, M.; Ngeow, J. Homologous Recombination Deficiency: Cancer Predispositions and Treatment Implications. The Oncologist 2021, 26, e1526–e1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foulkes, W.D. BRCA1 and BRCA2: chemosensitivity, treatment outcomes and prognosis. Fam Cancer 2006, 5, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghirardi, V.; De Felice, F.; D’Indinosante, M.; Bernardini, F.; Giudice, M.T.; Fagotti, A.; Scambia, G. Hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC) after primary debulking surgery in advanced epithelial ovarian cancer: Is BRCA mutational status making the difference? Cancer Treat Res Commun 2022, 31, 100518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koole, S.N.; Schouten, P.C.; Hauke, J.; Kluin, R.J.C.; Nederlof, P.; Richters, L.K.; Krebsbach, G.; Sikorska, K.; Alkemade, M.; Opdam, M.; et al. Effect of HIPEC according to HRD/BRCAwt genomic profile in stage III ovarian cancer: Results from the phase III OVHIPEC trial. Int J Cancer 2022, 151, 1394–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safra, T.; Grisaru, D.; Inbar, M.; Abu-Abeid, S.; Dayan, D.; Matceyevsky, D.; Weizman, A.; Klausner, J.M. Cytoreduction surgery with hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy in recurrent ovarian cancer improves progression-free survival, especially in BRCA-positive patients- a case-control study. J Surg Oncol 2014, 110, 661–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colombo, N.; Lorusso, D.; Scollo, P. Impact of Recurrence of Ovarian Cancer on Quality of Life and Outlook for the Future. Int J Gynecol Cancer 2017, 27, 1134–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chambers, L.M.; Yao, M.; Morton, M.; Gruner, M.; Chichura, A.B.; Horowitz, M.; Costales, A.; Rose, P.G.; Michener, C.M.; Debernardo, R. Patterns of recurrence in women with advanced and recurrent epithelial ovarian cancer treated with cytoreductive surgery and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy. Gynecol Oncol 2021, 161, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, S.S.; Gelli, M.; Agarwal, D.; Goéré, D. Complications of Cytoreductive Surgery and HIPEC in the Treatment of Peritoneal Metastases. Indian J Surg Oncol 2016, 7, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Lee, D.E.; Lee, Y.; Ha, H.I.; Chang, Y.J.; Chang, S.J.; Park, S.Y.; Lim, M.C. Quality of life outcomes from the randomized trial of hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy following cytoreductive surgery for primary ovarian cancer (KOV-HIPEC-01). J Gynecol Oncol 2022, 33, e54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boerner, T.; Graichen, A.; Jeiter, T.; Zemann, F.; Renner, P.; Marz, L.; Soeder, Y.; Schlitt, H.J.; Piso, P.; Dahlke, M.H. ; CRS-HIPEC Prolongs Survival but is Not Curative for Patients with Peritoneal Carcinomatosis of Gastric Cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 2016, 23, 3972–3977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tentes, A.A.; Pallas, N.; Karamveri, C.; Kyziridis, D.; Hristakis, C. Cytoreduction and HIPEC for peritoneal carcinomatosis of pancreatic cancer. J buon 2018, 23, 482–487. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, C.; Cen, S.; Ding, G.; Wu, W. Mucinous colorectal adenocarcinoma: clinical pathology and treatment options. Cancer Commun (Lond) 2019, 39, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herold, Z.; Acs, M.; Szasz, A.M.; Olasz, K.; Hussong, J.; Mayr, M.; Dank, M.; Piso, P. Patients with Metachronous Peritoneal Metastatic Mucinous Colorectal Adenocarcinoma Benefit More from Cytoreductive Surgery (CRS) and Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy (HIPEC) than Their Synchronous Counterparts. Cancers 2022, 14, 3978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lurvink, R.J.; Bakkers, C.; Rijken, A.; van Erning, F.N.; Nienhuijs, S.W.; Burger, J.W.; Creemers, G.J.; Verhoef, C.; Lemmens, V.E.; De Hingh, I.H. Increase in the incidence of synchronous and metachronous peritoneal metastases in patients with colorectal cancer: A nationwide study. Eur J Surg Oncol 2021, 47, 1026–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helderman, R.; Loke, D.R.; Tanis, P.J.; Tuynman, J.B.; Ceelen, W.; de Hingh, I.H.; van der Speeten, K.; Franken, N.A.P.; Oei, A.L.; Kok, H.P.; Crezee, J. Preclinical In Vivo-Models to Investigate HIPEC; Current Methodologies and Challenges. Cancers (Basel) 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- M. Peterson, E.M.-L.; B. McCarthy, B. Levi-Polyachenko. Survival Mouse Model of Intraperitoneal Perfusion Mimicking Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy (HIPEC). Academic Surgical Congress (2018).
- McCabe-Lankford, E.; Peterson, M.; McCarthy, B.; Brown, A.J.; Terry, B.; Galarza-Paez, L.; Levi-Polyachenko, N. Murine Models of Intraperitoneal Perfusion for Disseminated Colorectal Cancer. J Surg Res 2019, 233, 310–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liesenfeld, L.F.; Wagner, B.; Hillebrecht, H.C.; Brune, M.; Eckert, C.; Klose, J.; Schmidt, T.; Buchler, M.W.; Schneider, M. HIPEC-Induced Acute Kidney Injury: A Retrospective Clinical Study and Preclinical Model. Ann Surg Oncol 2022, 29, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miailhe, G.; Arfi, A.; Mirshahi, M.; Eveno, C.; Pocard, M.; Touboul, C. A new animal model for hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC) in tumor-bearing mice in the treatment of peritoneal carcinomatosis of ovarian origin. J Visc Surg 2018, 155, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelz, J.O.; Doerfer, J.; Hohenberger, W.; Meyer, T. A new survival model for hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC) in tumor-bearing rats in the treatment of peritoneal carcinomatosis. BMC Cancer 2005, 5, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.C.; Hsu, Y.T.; Chang, C.L. Hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy enhances antitumor effects on ovarian cancer through immune-mediated cancer stem cell targeting. Int J Hyperthermia 2021, 38, 1013–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Lv, L.; Yang, K. Chemotherapy targeting cancer stem cells. Am J Cancer Res 2015, 5, 880–893. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wagner, B.R.; Adamus, A.L.; Sonnecken, D.; Vahdad, R.; Jank, P.; Denkert, C.; Mahnken, A.H.; Seitz, G. Establishment of a new valid animal model for the evaluation of hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC) in pediatric rhabdomyosarcoma. Pediatr Blood Cancer 2021, 68, e29202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graziosi, L.; Mencarelli, A.; Renga, B.; Santorelli, C.; Cantarella, F.; Bugiantella, W.; Cavazzoni, E.; Donini, A.; Fiorucci, S. Gene expression changes induced by HIPEC in a murine model of gastric cancer. In Vivo 2012, 26, 39–45. [Google Scholar]
- Wallin, R.P.; Lundqvist, A.; More, S.H.; von Bonin, A.; Kiessling, R.; Ljunggren, H.G. Heat-shock proteins as activators of the innate immune system. Trends Immunol 2002, 23, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, A.; Prajapati, K.S.; Swamy, M.; Pachauri, V. Heat shock proteins: a therapeutic target worth to consider. Vet World 2015, 8, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubrez, L.; Causse, S.; Borges Bonan, N.; Dumétier, B.; Garrido, C. Heat-shock proteins: chaperoning DNA repair. Oncogene 2020, 39, 516–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calderwood, S.K.; Gong, J.; Murshid, A. Extracellular HSPs: The Complicated Roles of Extracellular HSPs in Immunity. Front Immunol 2016, 7, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenu, E.W.; Staines, D.R.; Tajouri, L.; Huth, T.; Ashton, K.J.; Marshall-Gradisnik, S.M. Heat shock proteins and regulatory T cells. Autoimmune Dis 2013, 2013, 813256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsan, M.F.; Gao, B. Heat shock protein and innate immunity. Cell Mol Immunol 2004, 1, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Park, H.K.; Yoon, N.G.; Lee, J.E.; Hu, S.; Yoon, S.; Kim, S.Y.; Hong, J.H.; Nam, D.; Chae, Y.C.; Park, J.B.; Kang, B.H. Unleashing the full potential of Hsp90 inhibitors as cancer therapeutics through simultaneous inactivation of Hsp90, Grp94, and TRAP1. Exp Mol Med 2020, 52, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, S.S.; Repasky, E.A.; Fisher, D.T. Fever and the thermal regulation of immunity: the immune system feels the heat. Nat Rev Immunol 2015, 15, 335–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skitzki, J.J.; Repasky, E.A.; Evans, S.S. Hyperthermia as an immunotherapy strategy for cancer. Curr Opin Investig Drugs 2009, 10, 550–558. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Decout, A.; Katz, J.D.; Venkatraman, S.; Ablasser, A. The cGAS-STING pathway as a therapeutic target in inflammatory diseases. Nat Rev Immunol 2021, 21, 548–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.U.; Brooks, G.; Guo, N.N.; Chen, J.; Guo, F. Fever-range hyperthermia promotes cGAS-STING pathway and synergizes DMXAA-induced antiviral immunity. Int J Hyperthermia 2021, 38, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopfner, K.P.; Hornung, V. Molecular mechanisms and cellular functions of cGAS-STING signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2020, 21, 501–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, K.N.; Victorelli, S.G.; Salmonowicz, H.; Dasgupta, N.; Liu, T.; Passos, J.F.; Adams, P.D. Cytoplasmic DNA: sources, sensing, and role in aging and disease. Cell 2021, 184, 5506–5526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.; Lester, G.M. S.; Petishnok, L.C.; Dean, D.A. Cytoplasmic transport and nuclear import of plasmid DNA. Biosci Rep 2017, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Wu, J.; Du, F.; Chen, X.; Chen, Z.J. Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase is a cytosolic DNA sensor that activates the type I interferon pathway. Science 2013, 339, 786–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motwani, M.; Pesiridis, S.; Fitzgerald, K.A. DNA sensing by the cGAS-STING pathway in health and disease. Nat Rev Genet 2019, 20, 657–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, J.; Bakhoum, S.F. The Cytosolic DNA-Sensing cGAS-STING Pathway in Cancer. Cancer Discov 2020, 10, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oei, A.L.; Vriend, L.E.; Crezee, J.; Franken, N.A.; Krawczyk, P.M. Effects of hyperthermia on DNA repair pathways: one treatment to inhibit them all. Radiat Oncol 2015, 10, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, M.; Hou, Z.; Wang, M.; Li, C.; Lin, J. Recent Advances in Hyperthermia Therapy-Based Synergistic Immunotherapy. Advanced Materials 2021, 33, 2004788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krawczyk, P.M.; Eppink, B.; Essers, J.; Stap, J.; Rodermond, H.; Odijk, H.; Zelensky, A.; van Bree, C.; Stalpers, L.J.; Buist, M.R.; et al. Mild hyperthermia inhibits homologous recombination, induces BRCA2 degradation, and sensitizes cancer cells to poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 inhibition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2011, 108, 9851–9856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A. PARP inhibitors: its role in treatment of cancer. Chin J Cancer 2011, 30, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaaf, L.; Schwab, M.; Ulmer, C.; Heine, S.; Murdter, T.E.; Schmid, J.O.; Sauer, G.; Aulitzky, W.E.; van der Kuip, H. Hyperthermia Synergizes with Chemotherapy by Inhibiting PARP1-Dependent DNA Replication Arrest. Cancer Res 2016, 76, 2868–2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moukarzel, L.A.; Ferrando, L.; Dopeso, H.; Stylianou, A.; Basili, T.; Pareja, F.; Da Cruz Paula, A.; Zoppoli, G.; Abu-Rustum, N.R.; Reis-Filho, J.S.; et al. Hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC) with carboplatin induces distinct transcriptomic changes in ovarian tumor and normal tissues. Gynecol Oncol 2022, 165, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dellinger, T.H.; Han, E.S.; Raoof, M.; Lee, B.; Wu, X.; Cho, H.; He, T.F.; Lee, P.; Razavi, M.; Liang, W.S.; et al. Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy-Induced Molecular Changes in Humans Validate Preclinical Data in Ovarian Cancer. JCO Precis Oncol 2022, 6, e2100239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiorentini, G.; Sarti, D.; Patriti, A.; Eugeni, E.; Guerra, F.; Masedu, F.; Mackay, A.R.; Guadagni, S. Immune response activation following hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy for peritoneal metastases: A pilot study. World J Clin Oncol 2020, 11, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





