Submitted:
07 February 2023
Posted:
08 February 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
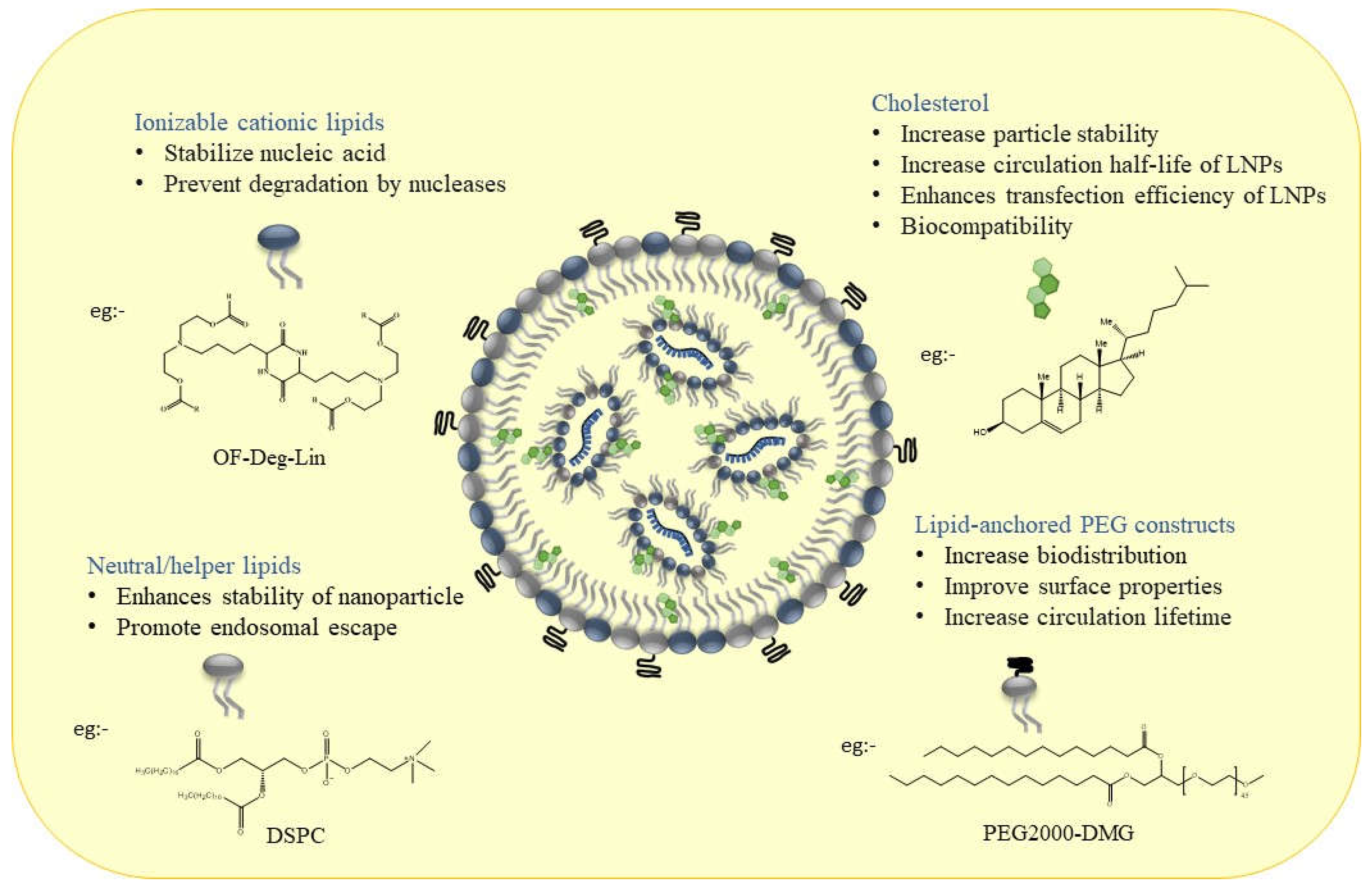
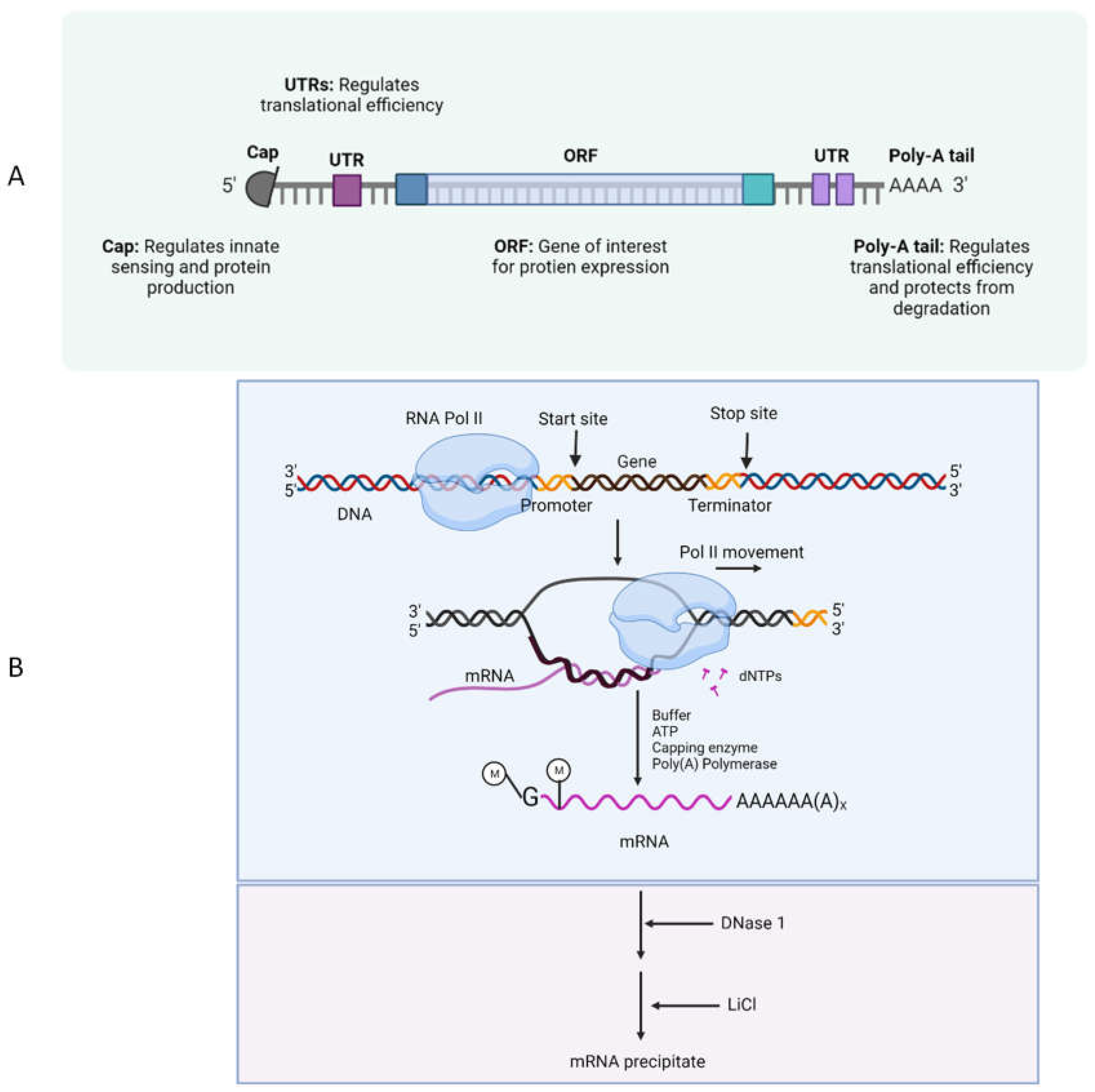
2. Role and Importance of LNPs Structural Composition in Designing mRNA Therapeutics
2.1. Material Aspects and Structural design of LNPs for mRNA Therapeutics
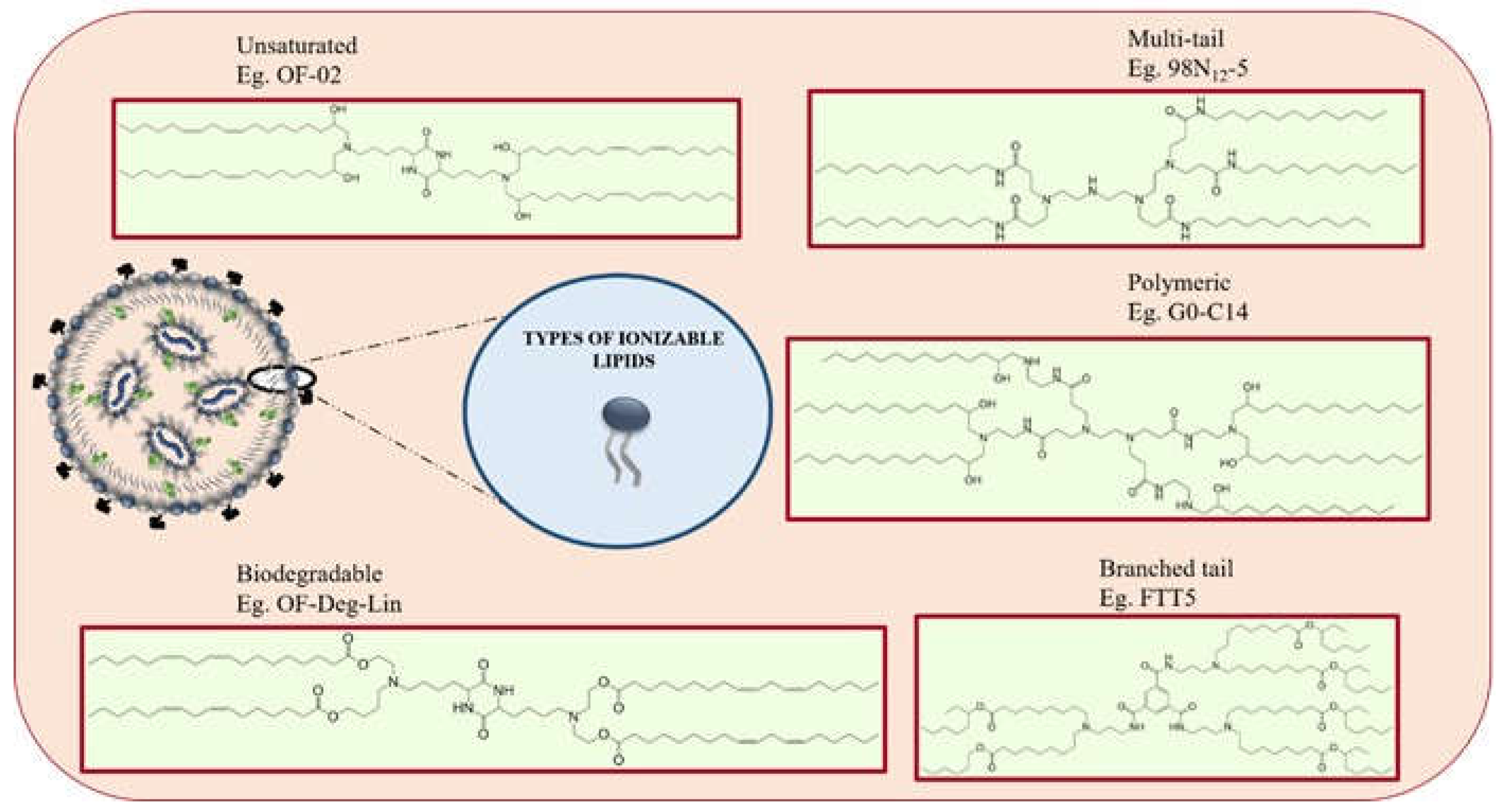
2.2. Role of Ionizable Lipids in mRNA Delivery
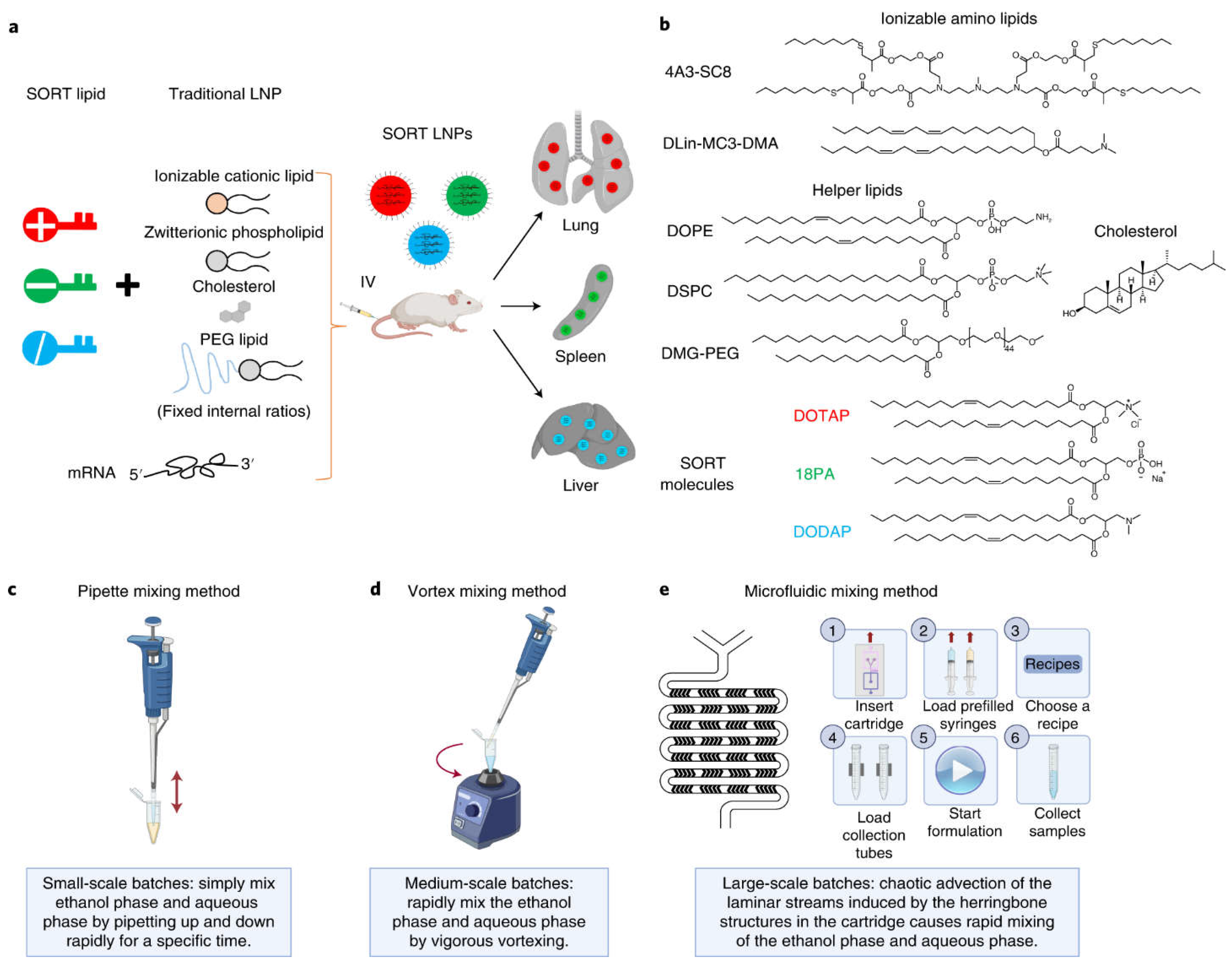
3. Moving beyond Classical Lipid Carriers to Specialized LNPs Design
3.1. Microfluidics over Other Conventional Methods
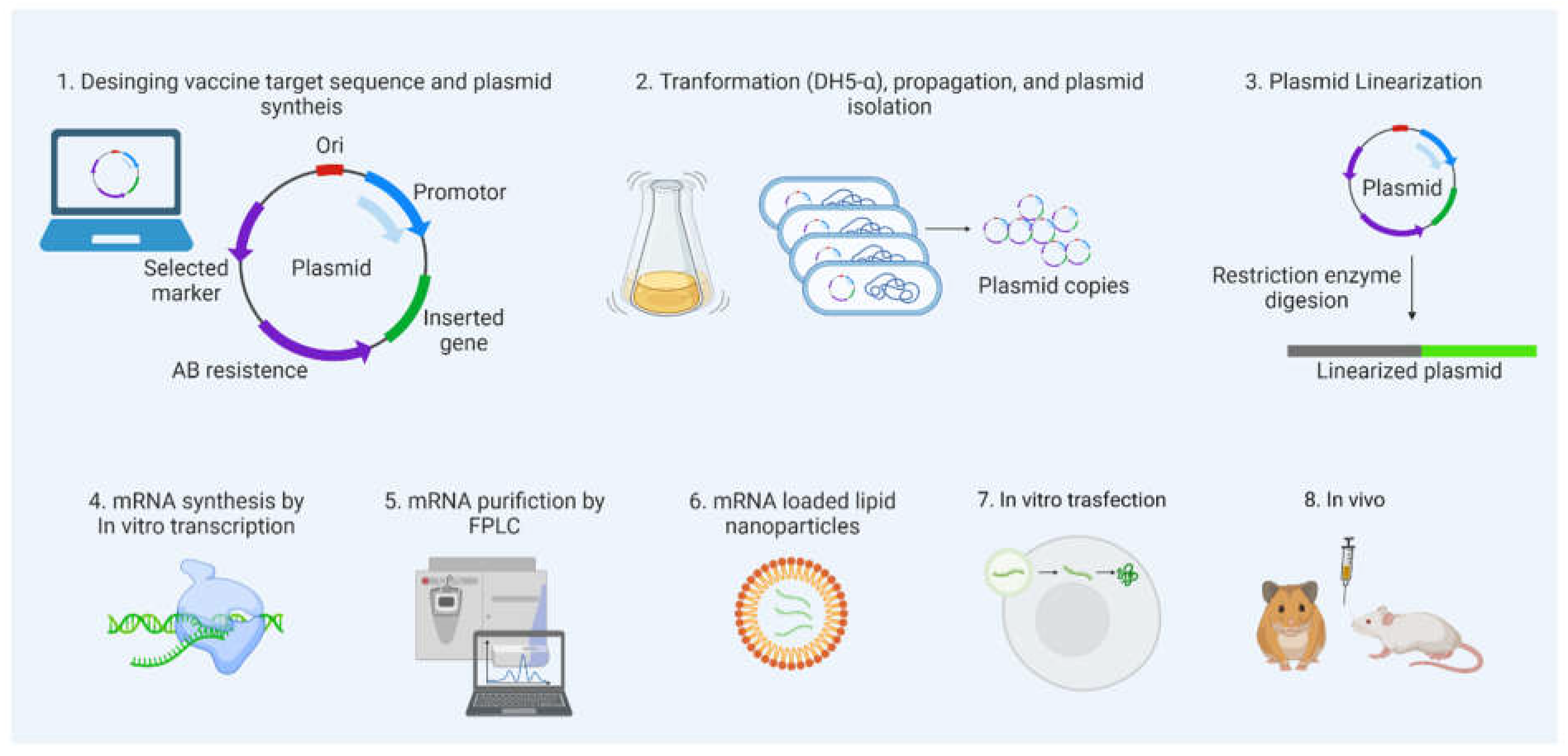
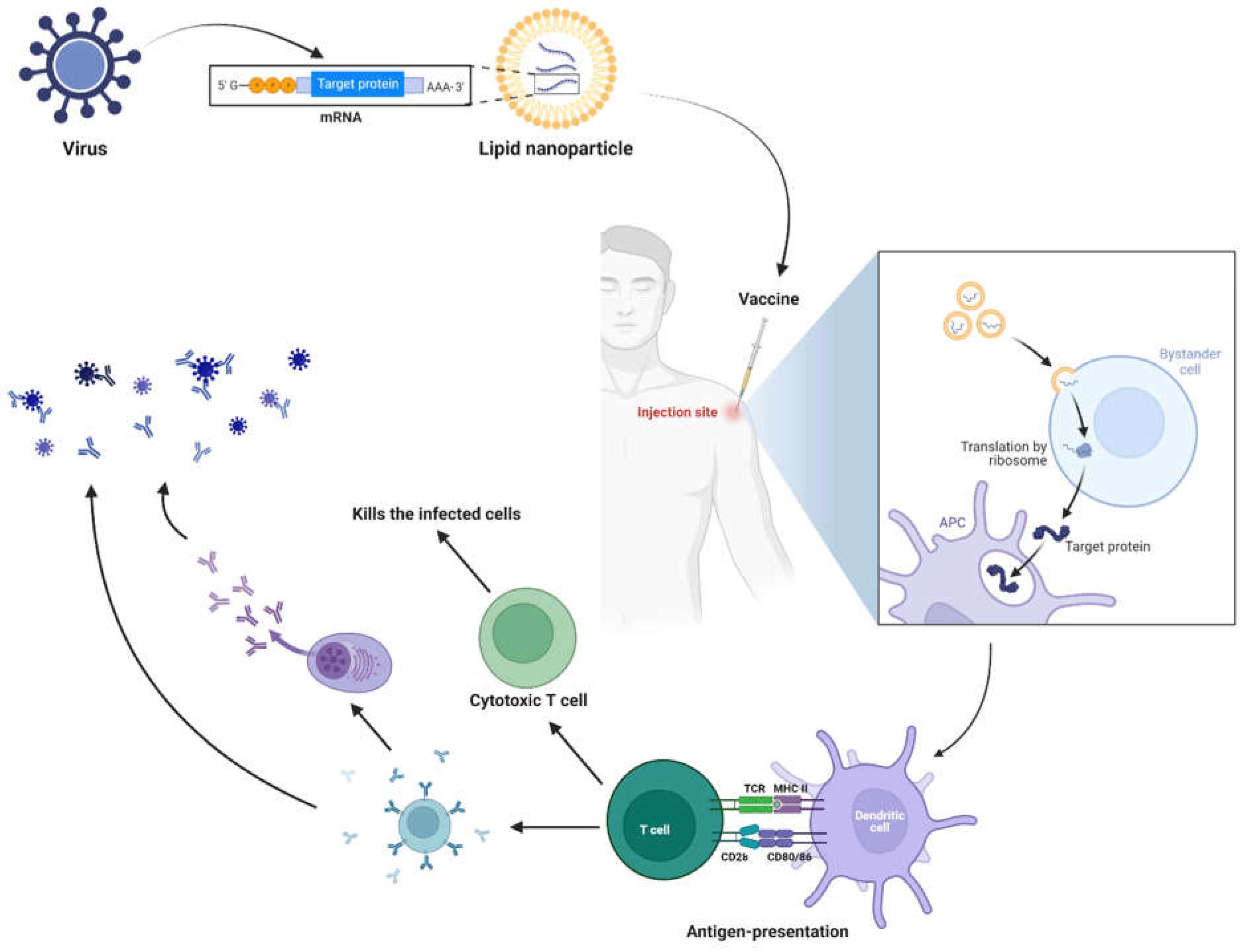
4. Applications of LNPs in mRNA Delivery
Use of mRNA as Prophylactics and Therapeutics
LNP Role in mRNA Delivery
Salient Features of LNP-Based Therapeutics[2], [4], [62]
- Naked mRNA is not suitable for the therapeutic purpose, as it rapidly degraded by extracellular RNases. Several nanotechnology platforms have been set and optimized for mRNA targeted delivery.
- As mRNA is thermolabile, LNPs would enhance its stability and half-life at room-temperature, and also useful for avoiding vaccine cold-chain.
- Modifications of the type of delivery system (carrier molecules) rule out the organ specific mRNA delivery (for lung, spleen, liver, etc.) and its in vivo half-life.
- Composition of LNP could decide the type of immune response induces.
- LNPs acts as adjuvants system for mRNA vaccines.
- The stable LNPs make the less dose of mRNA to work.
- Composition of LNPs also decides the number of booster doses required, if it admixed with suitable adjuvant.
- Moreover, for chronic treatments, multiple administration via different routes of administration is possible.
Mechanism of mRNA Vaccines
Salient Features of mRNA Based Therapeutics.[2], [4], [62]
Expert Opinion
Unanswered questions
- Is the ionizable lipids deciding the fate of immune response against mRNA encoded protein. Changing the ionizable lipid composition will vary the type of immune response, B or T cell response. Perhaps some mRNA vaccines show T cell-mediated protection without having notable neutralizing antibody inducing capacity.
- As documentation of evidence showing the mRNA vaccine induced local and system adverse events,[77] are these events are related to the vaccine or presence of minute amounts of dsRNA.
- Several new strategies have been developed in codon optimization by keeping the mRNA template intact, are these lead to transient immunogenicity (if not immunosilent) rather than durability as they lack naïve uridine or modified uridines.
- Do we have enough data to support the best route of mRNA vaccine administration for durable immune responses with less boosters?
References
- Sahin, U.; Karikó, K.; Türeci, Ö. , mRNA-based therapeutics — developing a new class of drugs. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery 2014, 13, 759–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardi, N.; Hogan, M. J.; Porter, F. W.; Weissman, D. , mRNA vaccines — a new era in vaccinology. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery 2018, 17, 261–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalski, P. S.; Rudra, A.; Miao, L.; Anderson, D. G. , Delivering the Messenger: Advances in Technologies for Therapeutic mRNA Delivery. Molecular therapy : the journal of the American Society of Gene Therapy 2019, 27, 710–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, X.; Zaks, T.; Langer, R.; Dong, Y. , Lipid nanoparticles for mRNA delivery. Nature Reviews Materials 2021, 6, 1078–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kauffman, K. J.; Webber, M. J.; Anderson, D. G. , Materials for non-viral intracellular delivery of messenger RNA therapeutics. J Control Release 2016, 240, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenchov, R.; Bird, R.; Curtze, A. E.; Zhou, Q. , Lipid Nanoparticles─From Liposomes to mRNA Vaccine Delivery, a Landscape of Research Diversity and Advancement. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 16982–17015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Fan, N.; Huang, H.; Jiang, X.; Qin, S.; Xiao, W.; Zheng, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Duan, X.; Qin, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, J.; Wei, Y.; Song, X. , mRNA Vaccines Against SARS-CoV-2 Variants Delivered by Lipid Nanoparticles Based on Novel Ionizable Lipids. Adv Funct Mater 2022, 32, 2204692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akinc, A.; Maier, M. A.; Manoharan, M.; Fitzgerald, K.; Jayaraman, M.; Barros, S.; Ansell, S.; Du, X.; Hope, M. J.; Madden, T. D.; Mui, B. L.; Semple, S. C.; Tam, Y. K.; Ciufolini, M.; Witzigmann, D.; Kulkarni, J. A.; van der Meel, R.; Cullis, P. R. , The Onpattro story and the clinical translation of nanomedicines containing nucleic acid-based drugs. Nature Nanotechnology 2019, 14, 1084–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swingle, K. L.; Hamilton, A. G.; Mitchell, M. J. , Lipid Nanoparticle-Mediated Delivery of mRNA Therapeutics and Vaccines. Trends Mol Med 2021, 27, 616–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baden, L. R.; El Sahly, H. M.; Essink, B.; Kotloff, K.; Frey, S.; Novak, R.; Diemert, D.; Spector, S. A.; Rouphael, N.; Creech, C. B.; McGettigan, J.; Khetan, S.; Segall, N.; Solis, J.; Brosz, A.; Fierro, C.; Schwartz, H.; Neuzil, K.; Corey, L.; Gilbert, P.; Janes, H.; Follmann, D.; Marovich, M.; Mascola, J.; Polakowski, L.; Ledgerwood, J.; Graham, B. S.; Bennett, H.; Pajon, R.; Knightly, C.; Leav, B.; Deng, W.; Zhou, H.; Han, S.; Ivarsson, M.; Miller, J.; Zaks, T. , Efficacy and Safety of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine. The New England journal of medicine 2021, 384, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polack, F. P.; Thomas, S. J.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Perez, J. L.; Pérez Marc, G.; Moreira, E. D.; Zerbini, C.; Bailey, R.; Swanson, K. A.; Roychoudhury, S.; Koury, K.; Li, P.; Kalina, W. V.; Cooper, D.; Frenck, R. W., Jr.; Hammitt, L. L.; Türeci, Ö.; Nell, H.; Schaefer, A.; Ünal, S.; Tresnan, D. B.; Mather, S.; Dormitzer, P. R.; Şahin, U.; Jansen, K. U.; Gruber, W. C. , Safety and Efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 Vaccine. The New England journal of medicine 2020, 383, 2603–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sercombe, L.; Veerati, T.; Moheimani, F.; Wu, S. Y.; Sood, A. K.; Hua, S. , Advances and Challenges of Liposome Assisted Drug Delivery. 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, M. J.; Billingsley, M. M.; Haley, R. M.; Wechsler, M. E.; Peppas, N. A.; Langer, R. , Engineering precision nanoparticles for drug delivery. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery 2021, 20, 101–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eygeris, Y.; Gupta, M.; Kim, J.; Sahay, G. , Chemistry of Lipid Nanoparticles for RNA Delivery. Accounts of Chemical Research 2022, 55, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, W.; Hu, C. M.; Fang, R. H.; Zhang, L. , Liposome-like Nanostructures for Drug Delivery. Journal of materials chemistry. B 2013, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoenmaker, L.; Witzigmann, D.; Kulkarni, J. A.; Verbeke, R.; Kersten, G.; Jiskoot, W.; Crommelin, D. J. A. , mRNA-lipid nanoparticle COVID-19 vaccines: Structure and stability. International Journal of Pharmaceutics 2021, 601, 120586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swingle, K. L.; Hamilton, A. G.; Mitchell, M. J. , Lipid Nanoparticle-Mediated Delivery of mRNA Therapeutics and Vaccines. Trends in Molecular Medicine 2021, 27, 616–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashiba, K.; Sato, Y.; Taguchi, M.; Sakamoto, S.; Otsu, A.; Maeda, Y.; Shishido, T.; Murakawa, M.; Okazaki, A.; Harashima, H. , Branching Ionizable Lipids Can Enhance the Stability, Fusogenicity, and Functional Delivery of mRNA. Small Science 2023, 3, 2200071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilstra, G.; Couture-Senécal, J.; Lau, Y. M. A.; Manning, A. M.; Wong, D. S. M.; Janaeska, W. W.; Wuraola, T. A.; Pang, J.; Khan, O. F. , Iterative Design of Ionizable Lipids for Intramuscular mRNA Delivery. Journal of the American Chemical Society 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajj, K. A.; Whitehead, K. A. , Tools for translation: non-viral materials for therapeutic mRNA delivery. Nature Reviews Materials 2017, 2, 17056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanasty, R.; Dorkin, J. R.; Vegas, A.; Anderson, D. , Delivery materials for siRNA therapeutics. Nature Materials 2013, 12, 967–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, P. E.; Mannock, D. A.; Lewis, R. N. A. H.; McElhaney, R. N.; Gruner, S. M. , X-Ray Diffraction Structures of Some Phosphatidylethanolamine Lamellar and Inverted Hexagonal Phases*. Biophysical Journal 2001, 81, 2693–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Lee, R. J. , The role of helper lipids in lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) designed for oligonucleotide delivery. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews 2016, 99, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pozzi, D.; Marchini, C.; Cardarelli, F.; Amenitsch, H.; Garulli, C.; Bifone, A.; Caracciolo, G. , Transfection efficiency boost of cholesterol-containing lipoplexes. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes 2012, 1818, 2335–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.; Ashwanikumar, N.; Robinson, E.; Xia, Y.; Mihai, C.; Griffith, J. P.; Hou, S.; Esposito, A. A.; Ketova, T.; Welsher, K.; Joyal, J. L.; Almarsson, Ö.; Sahay, G. , Naturally-occurring cholesterol analogues in lipid nanoparticles induce polymorphic shape and enhance intracellular delivery of mRNA. Nature Communications 2020, 11, 983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evers, M. J. W.; Kulkarni, J. A.; Van Der Meel, R.; Cullis, P. R.; Vader, P.; Schiffelers, R. M. , State-of-the-Art Design and Rapid-Mixing Production Techniques of Lipid Nanoparticles for Nucleic Acid Delivery. Small Methods 2018, 2, 1700375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jokerst, J. V.; Lobovkina, T.; Zare, R. N.; Gambhir, S. S. , Nanoparticle PEGylation for imaging and therapy. Nanomedicine 2011, 6, 715–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knop, K.; Hoogenboom, R.; Fischer, D.; Schubert, U. S. , Poly(ethylene glycol) in Drug Delivery: Pros and Cons as Well as Potential Alternatives. Angewandte Chemie International Edition 2010, 49, 6288–6308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Eygeris, Y.; Gupta, M.; Sahay, G. , Self-assembled mRNA vaccines. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews 2021, 170, 83–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinc, A.; Goldberg, M.; Qin, J.; Dorkin, J. R.; Gamba-Vitalo, C.; Maier, M.; Jayaprakash, K. N.; Jayaraman, M.; Rajeev, K. G.; Manoharan, M.; Koteliansky, V.; Röhl, I.; Leshchiner, E. S.; Langer, R.; Anderson, D. G. , Development of Lipidoid–siRNA Formulations for Systemic Delivery to the Liver. Molecular Therapy 2009, 17, 872–879. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Tao, W.; Liu, D.; Wu, J.; Guo, Z.; Ji, X.; Bharwani, Z.; Zhao, L.; Zhao, X.; Farokhzad, O. C.; Shi, J. , Surface De-PEGylation Controls Nanoparticle-Mediated siRNA Delivery In Vitro and In Vivo. Theranostics 2017, 7, 1990–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenton, O. S.; Kauffman, K. J.; Kaczmarek, J. C.; McClellan, R. L.; Jhunjhunwala, S.; Tibbitt, M. W.; Zeng, M. D.; Appel, E. A.; Dorkin, J. R.; Mir, F. F.; Yang, J. H.; Oberli, M. A.; Heartlein, M. W.; DeRosa, F.; Langer, R.; Anderson, D. G. , Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Ionizable Lipid Materials for the In Vivo Delivery of Messenger RNA to B Lymphocytes. Advanced materials (Deerfield Beach, Fla.) 2017, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenton, O. S.; Kauffman, K. J.; McClellan, R. L.; Kaczmarek, J. C.; Zeng, M. D.; Andresen, J. L.; Rhym, L. H.; Heartlein, M. W.; DeRosa, F.; Anderson, D. G. , Customizable Lipid Nanoparticle Materials for the Delivery of siRNAs and mRNAs. Angewandte Chemie (International ed. in English) 2018, 57, 13582–13586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhao, W.; Nguyen, G. N.; Zhang, C.; Zeng, C.; Yan, J.; Du, S.; Hou, X.; Li, W.; Jiang, J.; Deng, B.; McComb, D. W.; Dorkin, R.; Shah, A.; Barrera, L.; Gregoire, F.; Singh, M.; Chen, D.; Sabatino, D. E.; Dong, Y. , Functionalized lipid-like nanoparticles for in vivo mRNA delivery and base editing. Science advances 2020, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, L.; Lin, J.; Huang, Y.; Li, L.; Delcassian, D.; Ge, Y.; Shi, Y.; Anderson, D. G. , Synergistic lipid compositions for albumin receptor mediated delivery of mRNA to the liver. Nature Communications 2020, 11, 2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenton, O. S.; Kauffman, K. J.; McClellan, R. L.; Appel, E. A.; Dorkin, J. R.; Tibbitt, M. W.; Heartlein, M. W.; DeRosa, F.; Langer, R.; Anderson, D. G. , Bioinspired Alkenyl Amino Alcohol Ionizable Lipid Materials for Highly Potent In Vivo mRNA Delivery. Advanced materials (Deerfield Beach, Fla.) 2016, 28, 2939–2943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Zhang, H.; Butowska, K.; Swingle, K. L.; Alameh, M.-G.; Weissman, D.; Mitchell, M. J. , An ionizable lipid toolbox for RNA delivery. Nature Communications 2021, 12, 7233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyes, J.; Palmer, L.; Bremner, K.; MacLachlan, I. , Cationic lipid saturation influences intracellular delivery of encapsulated nucleic acids. Journal of Controlled Release 2005, 107, 276–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauffman, K. J.; Dorkin, J. R.; Yang, J. H.; Heartlein, M. W.; DeRosa, F.; Mir, F. F.; Fenton, O. S.; Anderson, D. G. , Optimization of Lipid Nanoparticle Formulations for mRNA Delivery in Vivo with Fractional Factorial and Definitive Screening Designs. Nano Letters 2015, 15, 7300–7306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Xu, Y.; Solis, L. M.; Tao, W.; Wang, L.; Behrens, C.; Xu, X.; Zhao, L.; Liu, D.; Wu, J.; Zhang, N. ; Wistuba, II; Farokhzad, O. C.; Zetter, B. R.; Shi, J., Long-circulating siRNA nanoparticles for validating Prohibitin1-targeted non-small cell lung cancer treatment. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2015, 112, 7779–7784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, M. A.; Jayaraman, M.; Matsuda, S.; Liu, J.; Barros, S.; Querbes, W.; Tam, Y. K.; Ansell, S. M.; Kumar, V.; Qin, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Q.; Panesar, S.; Hutabarat, R.; Carioto, M.; Hettinger, J.; Kandasamy, P.; Butler, D.; Rajeev, K. G.; Pang, B.; Charisse, K.; Fitzgerald, K.; Mui, B. L.; Du, X.; Cullis, P.; Madden, T. D.; Hope, M. J.; Manoharan, M.; Akinc, A. , Biodegradable Lipids Enabling Rapidly Eliminated Lipid Nanoparticles for Systemic Delivery of RNAi Therapeutics. Molecular Therapy 2013, 21, 1570–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitehead, K. A.; Dorkin, J. R.; Vegas, A. J.; Chang, P. H.; Veiseh, O.; Matthews, J.; Fenton, O. S.; Zhang, Y.; Olejnik, K. T.; Yesilyurt, V.; Chen, D.; Barros, S.; Klebanov, B.; Novobrantseva, T.; Langer, R.; Anderson, D. G. , Degradable lipid nanoparticles with predictable in vivo siRNA delivery activity. Nature Communications 2014, 5, 4277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paunovska, K.; Loughrey, D.; Dahlman, J. E. , Drug delivery systems for RNA therapeutics. Nature Reviews Genetics 2022, 23, 265–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabnis, S.; Kumarasinghe, E. S.; Salerno, T.; Mihai, C.; Ketova, T.; Senn, J. J.; Lynn, A.; Bulychev, A.; McFadyen, I.; Chan, J.; Almarsson, Ö.; Stanton, M. G.; Benenato, K. E. , A Novel Amino Lipid Series for mRNA Delivery: Improved Endosomal Escape and Sustained Pharmacology and Safety in Non-human Primates. Molecular Therapy 2018, 26, 1509–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapp, C. M.; Guo, P.; Whitehead, K. A. , Lipidoid Tail Structure Strongly Influences siRNA Delivery Activity. Cellular and Molecular Bioengineering 2016, 9, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajj, K. A.; Ball, R. L.; Deluty, S. B.; Singh, S. R.; Strelkova, D.; Knapp, C. M.; Whitehead, K. A. , Branched-Tail Lipid Nanoparticles Potently Deliver mRNA In Vivo due to Enhanced Ionization at Endosomal pH. Small 2019, 15, 1805097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabnis, S.; Kumarasinghe, E. S.; Salerno, T.; Mihai, C.; Ketova, T.; Senn, J. J.; Lynn, A.; Bulychev, A.; McFadyen, I.; Chan, J.; Almarsson, Ö.; Stanton, M. G.; Benenato, K. E. , A Novel Amino Lipid Series for mRNA Delivery: Improved Endosomal Escape and Sustained Pharmacology and Safety in Non-human Primates. Molecular therapy : the journal of the American Society of Gene Therapy 2018, 26, 1509–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Fan, N.; Huang, H.; Jiang, X.; Qin, S.; Xiao, W.; Zheng, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Duan, X.; Qin, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, J.; Wei, Y.; Song, X. , mRNA Vaccines Against SARS-CoV-2 Variants Delivered by Lipid Nanoparticles Based on Novel Ionizable Lipids. Advanced Functional Materials 2022, 32, 2204692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, R. S.; Kashyap, M. V.; Billingsley, M. M.; White, B.; Alameh, M.-G.; Bose, S. K.; Zoltick, P. W.; Li, H.; Zhang, R.; Cheng, A. Y.; Weissman, D.; Peranteau, W. H.; Mitchell, M. J. , Ionizable lipid nanoparticles for in utero mRNA delivery. Science Advances 7 eaba1028. [CrossRef]
- Samaridou, E.; Heyes, J.; Lutwyche, P. , Lipid nanoparticles for nucleic acid delivery: Current perspectives. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews 2020, 154-155, 37–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, Y.; Miyazaki, T.; Muto, H.; Kubara, K.; Mukai, Y.; Watari, R.; Sato, S.; Kondo, K.; Tsukumo, S. I.; Yasutomo, K.; Ito, M.; Tsukahara, K. , Design and lyophilization of lipid nanoparticles for mRNA vaccine and its robust immune response in mice and nonhuman primates. Molecular therapy. Nucleic acids 2022, 30, 226–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, S.; Dhawan, V.; Holm, R.; Nagarsenker, M. S.; Perrie, Y. , Liposomes: Advancements and innovation in the manufacturing process. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews 2020, 154-155, 102–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuura-Sawada, Y.; Maeki, M.; Nishioka, T.; Niwa, A.; Yamauchi, J.; Mizoguchi, M.; Wada, K.; Tokeshi, M. , Microfluidic Device-Enabled Mass Production of Lipid-Based Nanoparticles for Applications in Nanomedicine and Cosmetics. ACS Applied Nano Materials 2022, 5, 7867–7876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Zhang, H.; Cito, S.; Fan, J.; Mäkilä, E.; Salonen, J.; Hirvonen, J.; Sikanen, T. M.; Weitz, D. A.; Santos, H. A. , Core/Shell Nanocomposites Produced by Superfast Sequential Microfluidic Nanoprecipitation. Nano Letters 2017, 17, 606–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utharala, R.; Tseng, Q.; Furlong, E. E. M.; Merten, C. A. , A Versatile, Low-Cost, Multiway Microfluidic Sorter for Droplets, Cells, and Embryos. Analytical Chemistry 2018, 90, 5982–5988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeki, M.; Uno, S.; Niwa, A.; Okada, Y.; Tokeshi, M. , Microfluidic technologies and devices for lipid nanoparticle-based RNA delivery. Journal of Controlled Release 2022, 344, 80–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, B. G.; Ceccato, B. T.; Michelon, M.; Han, S. W.; de la Torre, L. G. , Advanced Microfluidic Technologies for Lipid Nano-Microsystems from Synthesis to Biological Application. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, S.; Sun, Y.; Yu, X.; Lee, S. M.; Cheng, Q.; Wei, T.; Gong, J.; Robinson, J.; Zhang, D.; Lian, X.; Basak, P.; Siegwart, D. J. , Preparation of selective organ-targeting (SORT) lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) using multiple technical methods for tissue-specific mRNA delivery. Nature Protocols 2023, 18, 265–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Q.; Wei, T.; Farbiak, L.; Johnson, L. T.; Dilliard, S. A.; Siegwart, D. J. , Selective organ targeting (SORT) nanoparticles for tissue-specific mRNA delivery and CRISPR–Cas gene editing. Nature Nanotechnology 2020, 15, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gros, F.; Hiatt, H.; Gilbert, W.; Kurland, C. G.; Risebrough, R. W.; Watson, J. D. , Unstable Ribonucleic Acid Revealed by Pulse Labelling of Escherichia Coli. Nature 1961, 190, 581–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oude Munnink, B. B.; Nieuwenhuijse, D. F.; Stein, M.; O’Toole, Á.; Haverkate, M.; Mollers, M.; Kamga, S. K.; Schapendonk, C.; Pronk, M.; Lexmond, P.; van der Linden, A.; Bestebroer, T.; Chestakova, I.; Overmars, R. J.; van Nieuwkoop, S.; Molenkamp, R.; van der Eijk, A. A.; GeurtsvanKessel, C.; Vennema, H.; Meijer, A.; Rambaut, A.; van Dissel, J.; Sikkema, R. S.; Timen, A.; Koopmans, M.; Oudehuis, G. J. A. P. M.; Schinkel, J.; Kluytmans, J.; Kluytmans-van den Bergh, M.; van den Bijllaardt, W.; Berntvelsen, R. G.; van Rijen, M. M. L.; Schneeberger, P.; Pas, S.; Diederen, B. M.; Bergmans, A. M. C.; van der Eijk, P. A. V.; Verweij, J. J.; Buiting, A. G. N.; Streefkerk, R.; Aldenkamp, A. P.; de Man, P.; Koelemal, J. G. M.; Ong, D.; Paltansing, S.; Veassen, N.; Sleven, J.; Bakker, L.; Brockhoff, H.; Rietveld, A.; Slijkerman Megelink, F.; Cohen Stuart, J.; de Vries, A.; van der Reijden, W.; Ros, A.; Lodder, E.; Verspui-van der Eijk, E.; Huijskens, I.; Kraan, E. M.; van der Linden, M. P. M.; Debast, S. B.; Naiemi, N. A.; Kroes, A. C. M.; Damen, M.; Dinant, S.; Lekkerkerk, S.; Pontesilli, O.; Smit, P.; van Tienen, C.; Godschalk, P. C. R.; van Pelt, J.; Ott, A.; van der Weijden, C.; Wertheim, H.; Rahamat-Langendoen, J.; Reimerink, J.; Bodewes, R.; Duizer, E.; van der Veer, B.; Reusken, C.; Lutgens, S.; Schneeberger, P.; Hermans, M.; Wever, P.; Leenders, A.; ter Waarbeek, H.; Hoebe, C.; The Dutch-Covid-19 response, t. , Rapid SARS-CoV-2 whole-genome sequencing and analysis for informed public health decision-making in the Netherlands. Nature Medicine 2020, 26, 1405–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verbeke, R.; Hogan, M. J.; Loré, K.; Pardi, N. , Innate immune mechanisms of mRNA vaccines. Immunity 2022, 55, 1993–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arevalo, C. P.; Bolton, M. J.; Le Sage, V.; Ye, N.; Furey, C.; Muramatsu, H.; Alameh, M.-G.; Pardi, N.; Drapeau, E. M.; Parkhouse, K.; Garretson, T.; Morris, J. S.; Moncla, L. H.; Tam, Y. K.; Fan, S. H. Y.; Lakdawala, S. S.; Weissman, D.; Hensley, S. E. , A multivalent nucleoside-modified mRNA vaccine against all known influenza virus subtypes. Science 2022, 378, 899–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonam, S. R.; Partidos, C. D.; Halmuthur, S. K. M.; Muller, S. , An Overview of Novel Adjuvants Designed for Improving Vaccine Efficacy. Trends in Pharmacological Sciences 2017, 38, 771–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaca, G. B.; Meyer, M.; Cadete, A.; Hsiao, C. J.; Golding, A.; Jeon, A.; Jacquinet, E.; Azcue, E.; Guan, C. M.; Sanchez-Felix, X.; Pietzsch, C. A.; Mire, C. E.; Hyde, M. A.; Comeaux, M. E.; Williams, J. M.; Sung, J. C.; Carfi, A.; Edwards, D. K.; Bukreyev, A.; Bahl, K. , Intranasal mRNA-LNP vaccination protects hamsters from SARS-CoV-2 infection. bioRxiv 2023. 2023.01.11.523616. [Google Scholar]
- Jansen, E. M.; Frijlink, H. W.; Hinrichs, W. L. J.; Ruigrok, M. J. R. , Are inhaled mRNA vaccines safe and effective? A review of preclinical studies. Expert Opinion on Drug Delivery 2022, 19, 1471–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phua, K. K. L.; Leong, K. W.; Nair, S. K. , Transfection efficiency and transgene expression kinetics of mRNA delivered in naked and nanoparticle format. Journal of Controlled Release 2013, 166, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassett, K. J.; Benenato, K. E.; Jacquinet, E.; Lee, A.; Woods, A.; Yuzhakov, O.; Himansu, S.; Deterling, J.; Geilich, B. M.; Ketova, T.; Mihai, C.; Lynn, A.; McFadyen, I.; Moore, M. J.; Senn, J. J.; Stanton, M. G.; Almarsson, Ö.; Ciaramella, G.; Brito, L. A. , Optimization of Lipid Nanoparticles for Intramuscular Administration of mRNA Vaccines. Molecular Therapy - Nucleic Acids 2019, 15, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ols, S.; Yang, L.; Thompson, E. A.; Pushparaj, P.; Tran, K.; Liang, F.; Lin, A.; Eriksson, B.; Karlsson Hedestam, G. B.; Wyatt, R. T.; Loré, K. , Route of Vaccine Administration Alters Antigen Trafficking but Not Innate or Adaptive Immunity. Cell Reports 2020, 30, 3964–3971.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, N.; Hovdal, D.; Edmunds, N.; Nordberg, P.; Dahlén, A.; Dabkowska, A.; Arteta, M. Y.; Radulescu, A.; Kjellman, T.; Höijer, A.; Seeliger, F.; Holmedal, E.; Andihn, E.; Bergenhem, N.; Sandinge, A.-S.; Johansson, C.; Hultin, L.; Johansson, M.; Lindqvist, J.; Björsson, L.; Jing, Y.; Bartesaghi, S.; Lindfors, L.; Andersson, S. , Functionalized lipid nanoparticles for subcutaneous administration of mRNA to achieve systemic exposures of a therapeutic protein. Molecular Therapy - Nucleic Acids 2021, 24, 369–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alameh, M.-G.; Tombácz, I.; Bettini, E.; Lederer, K.; Ndeupen, S.; Sittplangkoon, C.; Wilmore, J. R.; Gaudette, B. T.; Soliman, O. Y.; Pine, M.; Hicks, P.; Manzoni, T. B.; Knox, J. J.; Johnson, J. L.; Laczkó, D.; Muramatsu, H.; Davis, B.; Meng, W.; Rosenfeld, A. M.; Strohmeier, S.; Lin, P. J. C.; Mui, B. L.; Tam, Y. K.; Karikó, K.; Jacquet, A.; Krammer, F.; Bates, P.; Cancro, M. P.; Weissman, D.; Luning Prak, E. T.; Allman, D.; Igyártó, B. Z.; Locci, M.; Pardi, N. , Lipid nanoparticles enhance the efficacy of mRNA and protein subunit vaccines by inducing robust T follicular helper cell and humoral responses. Immunity 2021, 54, 2877–2892.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Chen, J.; Xu, Q. , Current Developments and Challenges of mRNA Vaccines. Annual Review of Biomedical Engineering 2022, 24, 85–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbier, A. J.; Jiang, A. Y.; Zhang, P.; Wooster, R.; Anderson, D. G. , The clinical progress of mRNA vaccines and immunotherapies. Nature Biotechnology 2022, 40, 840–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naveed, Z.; Li, J.; Wilton, J.; Spencer, M.; Naus, M.; Velásquez García, H. A.; Kwong, J. C.; Rose, C.; Otterstatter, M.; Janjua, N. Z. , Comparative Risk of Myocarditis/Pericarditis Following Second Doses of BNT162b2 and mRNA-1273 Coronavirus Vaccines. Journal of the American College of Cardiology 2022, 80, 1900–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagenhäuser, I.; Reusch, J.; Gabel, A.; Krone, L. B.; Kurzai, O.; Petri, N.; Krone, M. , Bivalent BNT162b2mRNA original/Omicron BA.4-5 booster vaccination: adverse reactions and inability to work compared to the monovalent COVID-19 booster. medRxiv 2022. 2022.11.07.22281982. [Google Scholar]
- Bolhassani, A.; Javanzad, S.; Saleh, T.; Hashemi, M.; Aghasadeghi, M. R.; Sadat, S. M. , Polymeric nanoparticles: potent vectors for vaccine delivery targeting cancer and infectious diseases. Human vaccines & immunotherapeutics 2014, 10, 321–332. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenblum, H. G.; Gee, J.; Liu, R.; Marquez, P. L.; Zhang, B.; Strid, P.; Abara, W. E.; McNeil, M. M.; Myers, T. R.; Hause, A. M.; Su, J. R.; Markowitz, L. E.; Shimabukuro, T. T.; Shay, D. K. , Safety of mRNA vaccines administered during the initial 6 months of the US COVID-19 vaccination programme: an observational study of reports to the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System and v-safe. The Lancet Infectious Diseases 2022, 22, 802–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, Y.; Lee, W. S.; Pilkington, E. H.; Kelly, H. G.; Li, S.; Selva, K. J.; Wragg, K. M.; Subbarao, K.; Nguyen, T. H. O.; Rowntree, L. C.; Allen, L. F.; Bond, K.; Williamson, D. A.; Truong, N. P.; Plebanski, M.; Kedzierska, K.; Mahanty, S.; Chung, A. W.; Caruso, F.; Wheatley, A. K.; Juno, J. A.; Kent, S. J. , Anti-PEG Antibodies Boosted in Humans by SARS-CoV-2 Lipid Nanoparticle mRNA Vaccine. ACS Nano 2022, 16, 11769–11780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szebeni, J.; Storm, G.; Ljubimova, J. Y.; Castells, M.; Phillips, E. J.; Turjeman, K.; Barenholz, Y.; Crommelin, D. J. A.; Dobrovolskaia, M. A. , Applying lessons learned from nanomedicines to understand rare hypersensitivity reactions to mRNA-based SARS-CoV-2 vaccines. Nature Nanotechnology 2022, 17, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Lipid | Function | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Cationic ionizable lipids | ||
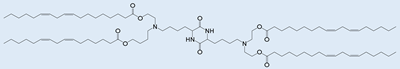 OF-Deg-Lin OF-Deg-Lin |
Selective delivery of mRNA into B lymphocytes | [32] |
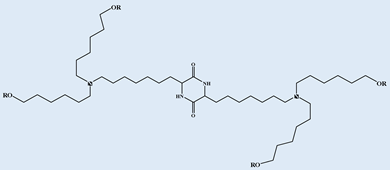 OF-C4-Deg-Lin OF-C4-Deg-Lin |
Selective delivery of siRNAs and mRNAs | [33] |
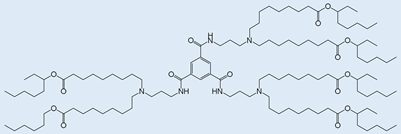 FTT5 FTT5 |
In vivo delivery of mRNA encoding human factor VIII and base editing components | [34] |
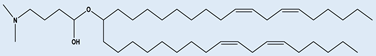 Dlin-MC3-DMA Dlin-MC3-DMA |
Used in albumin receptor mediated delivery of mRNA to the liver | [35] |
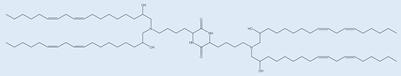 OF-02 OF-02 |
Enhanced hepatic mRNA delivery | [36] |
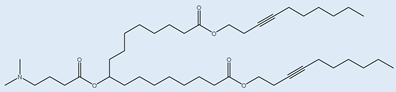 A6 A6 |
Albumin receptor mediated mRNA delivery | [35] |
| Neutral/helper lipids | ||
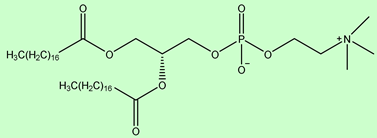 DSPC DSPC |
Used in mRNA vaccines and vaccine candidates, including COVID19. | [6] |
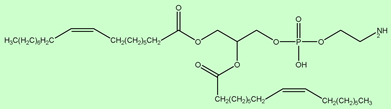 DOPE DOPE |
Delivery of variety of nucleic acids. | [26] |
| PEG lipids | ||
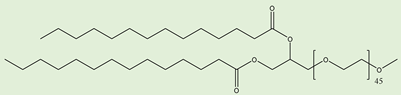 PEG2000-DMG PEG2000-DMG |
Used in mRNA vaccines and vaccine candidates, including COVID19. | [6] |
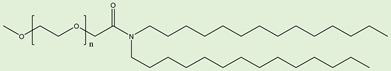 ALC-0159 ALC-0159 |
Delivery of mRNA vaccines. | [6] |
| Name | mRNA specific to | LNP Composition | Adverse effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| BNT162b2 | Spike glycoprotein of SARS-CoV-2 | NT162b2 LNPs composition: lipids ((4- hydroxybutyl)azanediyl) bis(hexane-6,1- diyl)bis(2- hexyldecanoate), 2 [(polyethylene glycol)- 2000]-N,Nditetradecylacetamide, 1,2-distearoyl-snglycero- 3-phosphocholine, and cholesterol), potassium chloride, monobasic potassium phosphate, sodium chloride, dibasic sodium phosphate dihydrate, and sucrose |
Myocarditis Pericarditis |
| mRNA- 1273 |
Spike glycoprotein of SARS-CoV-2 | LNP: Proprietary Ionic lipid SM-102, polyethylene glycol (PEG) 2000, dimyristoylglycerol (DMG), cholesterol, 1,2- distearoyl-sn-glycero-3- phosphocholine [DSPC]), tromethamine hydrochloride, acetic acid, sodium acetate, and sucrose |
Myocarditis Pericarditis |
| LUNARCOv- 19 (ARCT- 021) |
Self-replicating mRNA specific to Spike glycoprotein of SARS-CoV-2 |
Arcturus Therapeutics proprietary ionizable lipid, DSPC, cholesterol, and PEG2000-DMG dissolved in ethanol |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





