Introduction
Marketing is an important aspect of every business, whether big or small. Successful marketing can help a business increase sales, develop a brand and increase customer awareness. In the digital era, it is important for companies to leverage technology and data to strengthen their marketing strategy. Utilization of customer data is becoming increasingly important for companies to achieve their marketing goals, especially for Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) who wish to compete with larger businesses (Kementerian Keuangan, 2022).
Customer data is information collected by companies about the preferences and behavior of their customers. Customer data can be in the form of demographic information, purchasing information, online behavior and product preferences. Utilization of customer data can help companies better understand the needs and preferences of their customers, enabling companies to provide more personalized and relevant services. This can increase customer satisfaction, strengthen customer loyalty, and ultimately improve the company's business performance. However, despite the importance of customer data, there are still many SMEs that have not made full use of it. Constraints such as lack of resources, lack of technical expertise, and lack of understanding of how best to use customer data can prevent MSMEs from leveraging it. Therefore, this research will discuss how MSMEs can leverage customer data to develop personalized experiences for their customers.
MSMEs can collect customer data through various means, such as surveys, recording transaction data, and tracking online behavior. This customer data can be analyzed to understand customer behavior and preferences, so that companies can provide more personalized and relevant services. Personalized customer experiences can also include features such as special offers, product recommendations and friendly customer service. This can help companies build stronger relationships with their customers. However, there are still many challenges in leveraging customer data. Such as the lack of resources and technical expertise which is an obstacle for companies to utilize customer data effectively. In addition, companies may also face challenges in maintaining the security and privacy of customer data. The use of customer data in marketing and personalized customer experiences has the potential to improve a company's business performance. However, there are still challenges in making effective use of customer data, especially for SMEs who may have limited resources and technical expertise. Therefore, this research will discuss how SMEs can utilize customer data in an effective way to develop personalized customer experiences.
Literature Review
The use of customer data to develop personalized customer experiences is becoming increasingly important in today's digital age. Several previous studies have identified the benefits of using customer data in marketing, and how this can improve a company's business performance. The following is a review of the literature on this topic.
Customer and Marketing Data
Customer data is information collected about customer behavior, preferences and needs. The use of customer data in marketing can help companies to develop more effective marketing strategies and achieve their business goals (Mekari, 2022). The use of customer data can increase the effectiveness of advertising and promotions, improve market segmentation, and increase customer loyalty. One example of implementing customer data is the personalization of content and offers, where customer data is used to produce offers that are more relevant and attractive to certain customers (Subagio et al., 2020). This can increase the likelihood of conversion and customer loyalty. However, the use of customer data also has challenges that companies need to overcome. These challenges include issues of privacy, data security, and technical and resource limitations (Subagio et al., 2020). Therefore, it is important for companies to have a clear and transparent privacy policy to ensure that customers feel comfortable about providing their personal information.
In addition, research also shows that the use of customer data by SMEs can improve marketing efficiency, increase customer engagement, and improve overall business performance.han (Taghizadeh et al., 2021). SMBs can take advantage of available technologies, such as analytics software and business intelligence applications, to collect and analyze customer data in an effective way. In the context of using customer data for marketing, it is important to understand customer goals and needs. On the other hand, the use of customer data can increase customer retention, increase customer lifetime value, and increase customer loyalty. Therefore, companies must develop marketing strategies that adapt their products and services to customer preferences and needs. Similar studies also show that the use of customer data can help companies improve market segmentation.
By using customer data, companies can identify groups of customers who share similar preferences and needs, and develop more focused marketing strategies for each of these groups. This can increase the effectiveness of marketing campaigns and increase customer conversions. In conclusion, the use of customer data in marketing has significant benefits for companies, including increasing the effectiveness of advertising and promotions, improving market segmentation, and increasing customer loyalty. However, the use of customer data also has challenges that need to be overcome, such as privacy issues, data security, and technical and resource limitations.
Personalized Customer Experience
The personalized customer experience is an important concept in modern marketing that can help companies increase customer satisfaction and loyalty and improve their overall business performance. This concept emerged because the company realized that each customer has unique needs and preferences and wants to feel cared for and valued.
Personalized customer experience can be achieved by collecting customer data and analyzing it to identify customer preferences and needs (Agustina et al., 2016). This data can then be used to develop more focused marketing strategies, such as tailoring products and services to customer preferences and needs. This research shows that a personalized customer experience can increase customer satisfaction and loyalty, as well as improve a company's business performance. This is because a personalized customer experience can provide added value to customers, making them feel valued and cared for by the company. As a result, customers are more likely to choose products and services from these companies and recommend them to others. Personalized customer experiences can also improve marketing efficiency by reducing unnecessary marketing costs and increasing advertising and promotion effectiveness.
By tailoring marketing messages to customer preferences and needs, companies can reach more relevant customers and have the potential to become loyal customers. However, there are several challenges to be overcome in implementing a personalized customer experience. One of them is the difficulty in collecting and analyzing customer data in an effective way. Companies must also ensure that customer data collected is safe and protected from cybersecurity threats.
In addition, companies must also consider the privacy policy and customer consent in collecting and using customer data. Companies must ensure that customers are comfortable providing their personal information and ensure that the data is only used for lawful purposes.
Overall, the personalized customer experience is an important concept in modern marketing that can help companies increase customer satisfaction and loyalty and improve their overall business performance. By leveraging customer data, companies can develop more focused marketing strategies and adapt products and services to customer needs and preferences. However, companies must also pay attention to the challenges and ethical considerations in collecting and using customer data.
Utilization of Customer Data by MSMEs
The use of customer data by MSMEs is becoming increasingly important in today's digital era. MSMEs may face greater challenges in utilizing customer data compared to large companies (Subagio et al., 2020). Several previous studies have identified the benefits of using customer data in marketing, and how this can improve MSME business performance. SMEs can take advantage of available technology to collect and analyze customer data in an effective way. One of the technologies that can be used by MSMEs is analytic software and business intelligence applications (Sudarwati & Izzaty, 2022). The use of this technology can help MSMEs collect and analyze customer data more easily and quickly, as well as provide better insight into customer preferences and needs (Taghizadeh et al., 2021).
In addition, relevant research also shows that the use of customer data by SMEs can improve marketing efficiency. Personalized customer data can make the relationship between customers and business actors significantly influence customer engagement (Suryawijaya et al., 2023). This is especially the case because customers feel more understood and valued as individuals, so they tend to respond positively to brands or products that offer a more personalized experience. In the context of SMEs, this can help increase customer loyalty and differentiate themselves from competitors. MSMEs that are able to collect and analyze customer data effectively can offer a more personalized and tailored experience to their customers, which can help increase customer engagement with their brand or product. Thus, the utilization of customer data by MSMEs can help improve marketing efficiency and overall business performance.
Research Methods
This study uses the Structural Equation Modeling-Partial Least Squares (SEM-PLS) method with a quantitative approach. This method is used to evaluate the causal relationship between variables (Abdillah & Jogiyanto, 2015). The population in this study are SMEs that operate in the city of Semarang and have loyal customers for the past year. Meanwhile, the sample in this study was selected using the Quota Sampling technique with the criteria of MSMEs that have implemented personalized marketing and have loyal customers, namely 100 samples (Sugiyono, 2019). The questionnaire design in this study was a question that was developed based on indicators of predetermined variables (Table 1).
Table 1.
Research Questionnaire Design.
Table 1.
Research Questionnaire Design.
| Variable |
Indicator |
Information |
| Personalized Marketing (X) |
X1
|
Product or Service Personalization |
| X2
|
Use of customer data to customize experience |
| X3
|
Personal interaction with customers |
| X4
|
Special offers based on customer preferences |
| Customer Convenience (Y) |
Y1
|
Easy access when interacting with MSMEs |
| Y2
|
The level of satisfaction with the product or service received |
| Y3
|
Convenience when interacting with MSME employees |
| Y4
|
Trust in MSMEs |
| Customer Loyalty (Z) |
Z1
|
Desire to continue buying products or services |
| Z2
|
MSME products or services are the main reference |
| Z3
|
Desire to recommend UMKM to others |
| Z4
|
Interest in trying new products from UMKM |
Research data was obtained by means of field studies to MSMEs in Semarang City by providing questionnaires to be filled out. The questionnaire used an online study (Google Form) and we distributed it via the Whatsapp group which contains MSME actors in the city of Semarang. The time to fill out the questionnaire was open for one month. Furthermore, the data obtained was analyzed using SmartPLS 3.0 software which was then tested for validity using AVE and reliability using Composite Reliability.
Variable Identification
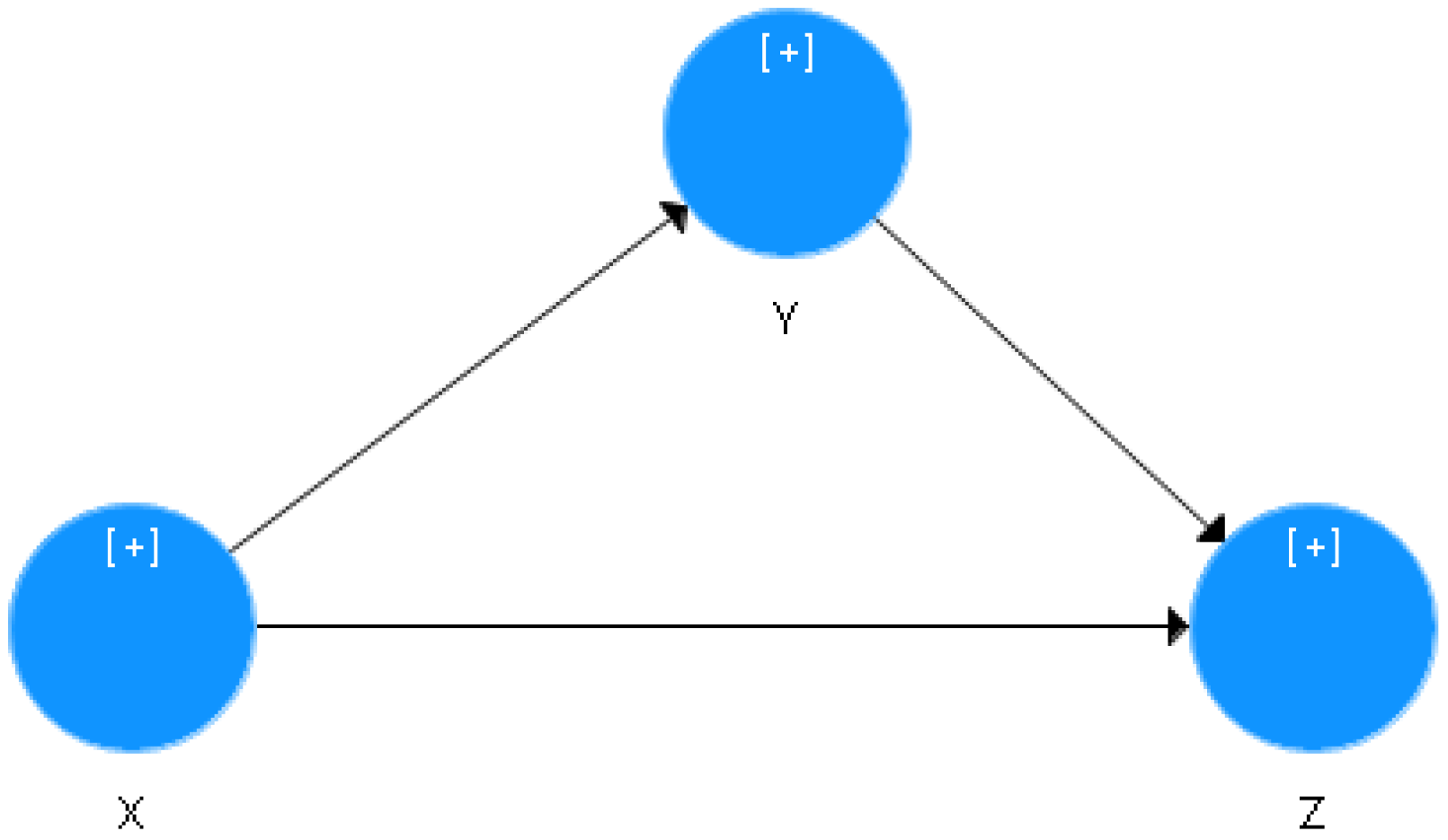
The variables in this study consist of Personalized Marketing (X), Customer Convenience (Y) and Customer Loyalty (Z). Furthermore, the influence between variables in this study was tested according to the path diagram in
Figure 1 as follows:
The Effect of Personalized Marketing (X) on Customer Convenience (Y)
The Effect of Personalized Marketing (X) on Customer Loyalty (Z)
The Effect of Customer Convenience (Y) on Customer Loyalty (Z)
Figure 1.
Path Diagrams For SEM. Source: Author Data Elaboration, 2022.
Figure 1.
Path Diagrams For SEM. Source: Author Data Elaboration, 2022.
Discussion & Result
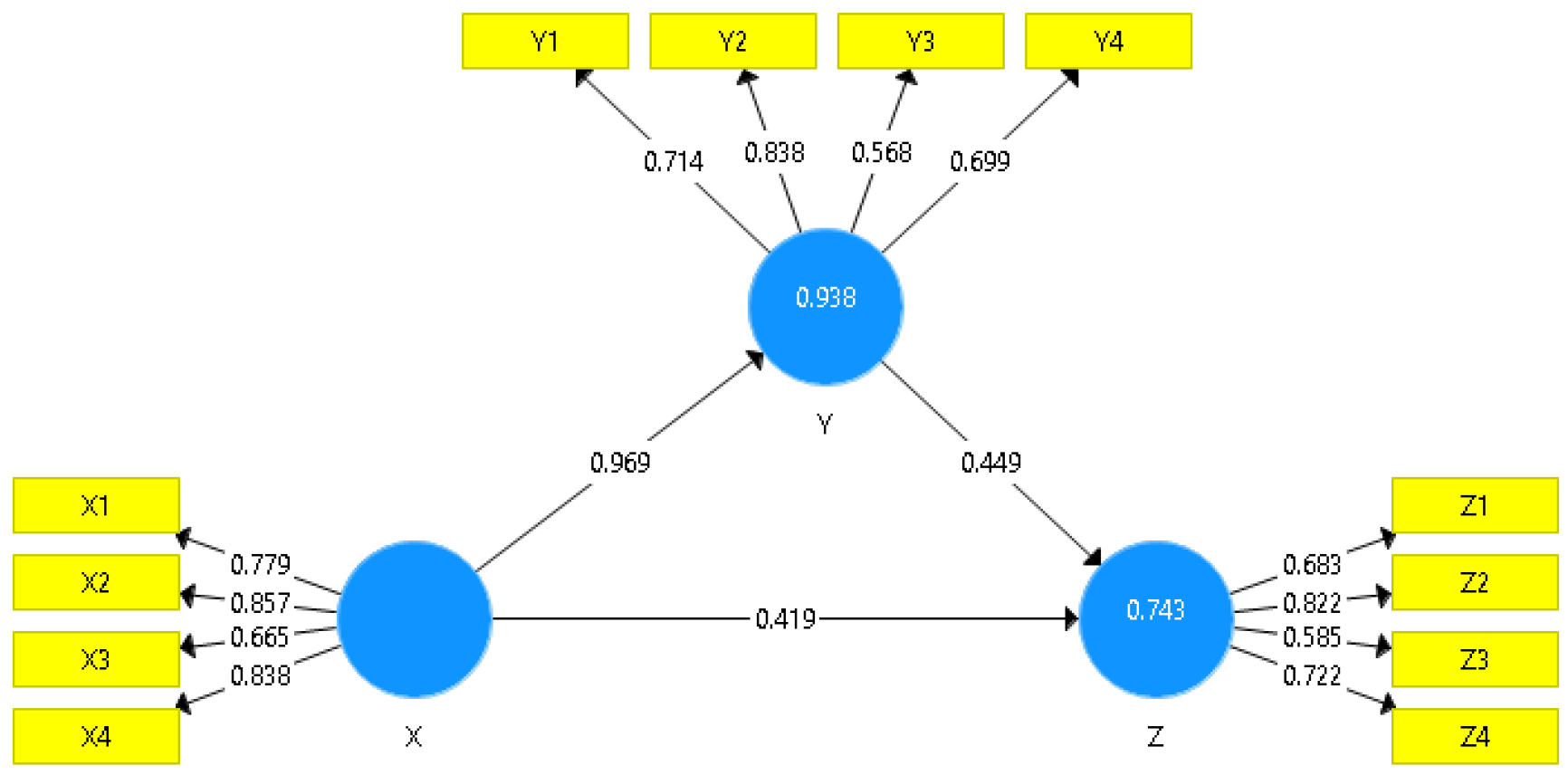
Figure 2 shows the results of path diagram analysis using the SmartPLS 3.0 application. Next, to test the validity and reliability.
Table 2 describes the test results using AVE (average variance extracted) and Composite Reliability.
Figure 2.
Model SEM-PLS. Source: Author Data Elaboration, 2022.
Figure 2.
Model SEM-PLS. Source: Author Data Elaboration, 2022.
Table 2.
Data Validity and Reliability Test Results with SEM-PLS.
Table 2.
Data Validity and Reliability Test Results with SEM-PLS.
| Variable |
AVE |
Composite Reliability |
| Personalized Marketing (X) |
0.621 |
0.867 |
| Customer Convenience (Y) |
0.506 |
0.801 |
| Customer Loyalty (Z) |
0.502 |
0.799 |
The results of the validity and reliability tests indicated that the data used in this study were valid with an AVE result of >0.5 for each variable. Meanwhile, each variable in the Composite Reliability test results has a value of > 0.7, which means that the data in this study are reliable and can be used in data analysis.
Interpretation of SmartPLS Test Results
The results of data processing with smartPLS are as follows:
Outer loading aims to assess whether the construct has adequate discriminant validity by comparing the relationship between variable indicators with the correlation of these indicators with other variables. If the construct indicator has a higher value compared to the relationship of the indicator to other variables, then the construct has a high value of discriminant validity as well (Hair et al., 2016). In other words, it can be said that variable indicators are better than other variable indicators. The results of the outer loading test show that the personalized marketing variable (X) has a good indicator prediction compared to other block indicators. Supported with X indicator2 has the highest value, which is equal to 0.857. That is, the use of customer data to customize the customer experience is effective for MSMEs in determining customer loyalty.
To assess discriminant validity can be done by comparing the square of average variance extracted (AVE) for each variable with a correlation value between variables (> 0.5). The model will have good discriminant validity if the AVE value for each variable is greater than the correlation between the constructs (Abdillah & Hartono, 2015). Table 2 shows the AVE value on each variable> 0.5 and the AVE value on the customer loyalty variable with a value of 0.502> 0.5. So it can be concluded that the model made is correct. The latent variable and its indicators significantly influence each other.
Composite Reliability is done by measuring the value between variables whether they have good reliability or not. If the research variable has a value above 0.70, the variable reliability is in the good category, and vice versa. In this study, all variables have a composite reliability value of >0.7 (Table 2). The variable value obtained using composite reliability for customer convenience is (Y) 0.801 and customer loyalty variable (Z) is 0.799. It can be concluded that the reliability value is in the good category as a construct as measured by its indicators.
Inner Model Test
The Inner Model test is carried out by looking at the direct and indirect effects (total effect) which are measured between constructs to see the significance and strength of the relationship through bootstrapping to determine the extent of influence between variables. The values obtained range from -1 to +1. The closer the value obtained is to +1, the stronger the influence between the two constructs. Conversely, if the value gets closer to -1, it means that the two constructs have no effect (Hair et al., 2016).
Table 3 displays the results of the bootstrapping test for the inner model (original sample). From the test results, it can be seen that there are variables that have a significant influence on other variables. Personalized Marketing Variable (X) has a significant influence on the variables Customer Convenience (Y) and Customer Loyalty (Z). This can be seen from the original sample value which is close to +1.
Table 3.
Inner Model Test Results.
Table 3.
Inner Model Test Results.
| Indicator |
Original Sample |
Sample Mean |
Standard Deviation |
T-Statistic |
P Values |
| X =>AND |
0.969 |
0.969 |
0.006 |
164.130 |
0.001 |
| X =>Z |
0.419 |
0.404 |
0.299 |
1.402 |
0.162 |
| AND =>Z |
0.449 |
0.467 |
0.296 |
1.519 |
0.129 |
Discussion
The Effectiveness of Personalized Marketing on Customer Loyalty
The marketing industry has recently become obsessed with personalization. In today's marketing industry, personalization is an important focus because it brings significant benefits to businesses. Personalization is a marketing strategy that focuses on adapting the product or service that customers receive to the customer's individual needs and preferences (MIA, 2023). This is done by leveraging technology and data to study customer habits and preferences. By understanding customers better, businesses can adapt their offers more effectively and strengthen customer relationships (Qiscus, 2020).
The effectiveness of the personalization strategy can be seen in increasing customer loyalty. This concept is very important for MSME businesses, because they have a more limited target market and need to ensure that their customers are loyal (Subagio et al., 2020). Personalized marketing helps MSMEs understand their customers better and adapt their offers according to customer needs (Mekari, 2022). Thus, MSMEs can maintain and increase their customer loyalty.
Basically, personalization helps build stronger and more effective customer relationships. By understanding customer needs and preferences, businesses can provide more relevant offers and meet customer expectations (Qiscus, 2020). This helps strengthen long-term relationships with customers and ensures that they feel valued and recognized as individuals (Taghizadeh et al., 2021). Personalized marketing has the potential to help businesses increase results, strengthen customer relationships and help maintain customer loyalty. Therefore, MSMEs must consider implementing personalized marketing strategies in their business practices (Subagio et al., 2020).
Conclusions & Suggestions
Conclusion
Research shows that personalized marketing has an important role in increasing customer loyalty to MSMEs. MSMEs should focus on personalized marketing to maintain and increase their customer loyalty (Zalova & Karaduman, 2018). This can be done by effectively collecting and analyzing customer data and interacting and communicating with customers through various channels (Taghizadeh et al., 2021). Personalization helps build stronger customer relationships and meet customer needs and preferences.
Suggestion
MSMEs must leverage technology and data to learn customer habits and preferences. They must be open to interacting and communicating with customers through various channels and ensure that their offers match customer needs. MSMEs should also understand that personalized marketing helps strengthen long-term relationships with customers and ensures that they feel valued and recognized as individuals.
References
- Abdillah, W., & Jogiyanto. (2015). Partial Least Square (PLS) Alternatif. Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) dalam Penelitian Bisnis. ANDI.
- Agustina, D., Najib, M., & Suharjo, B. (2016). PENGARUH PERSONALISASI IKLAN ONLINE TERHADAP SIKAP DAN MINAT BELI KONSUMEN. MIX: Jurnal Ilmiah Manajemen, 6(3). [CrossRef]
- Brodie, R. J., Saren, M., & Pels, J. (2011). Theorizing about the service dominant logic: The bridging role of middle range theory. SAGE Journal, 11(1). [CrossRef]
- Forbes. (2022, August 10). The Power Of Personalization. forbes.com. Available online: https://www.forbes.com/sites/stevedenning/2019/06/10/the-power-of-personalization/?sh=6003672c1c3e (accessed on 12 December 2022).
- Hair, J. F., Hult, G. T. M., Ringle, C. M., & Sarstedt, M. (2016). A Primer on Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM). SAGE Publications. Available online: https://us.sagepub.com/en-us/nam/a-primer-on-partial-least-squares-structural-equation-modeling-pls-sem/book244583.
- Haloho, F. J., & Parahyanti, E. (2020). Personalized Online Advertisements as A Means of Enhancing Purchase Intention:The Mediating Effect of Advertising Value. PSIKODIMENSIA: Kajian Ilmiah Psikologi, 19(2), 156-164. [CrossRef]
- Kementerian Keuangan. (2022, August 24). Ini Upaya Pemerintah Jaga Peran UMKM sebagai Tulang Punggung Perekonomian. Kementerian Keuangan. Available online: https://www.kemenkeu.go.id/informasi-publik/publikasi/berita-utama/Ini-Upaya-Pemerintah-Jaga-Peran-UMKM (accessed on 08 January 2023).
- Mekari. (2022, June 9). Mengenal Apa Itu Personalized Marketing dan Strateginya. Qontak. Available online: https://qontak.com/blog/personalized-marketing/ (accessed on 29 December 2022).
- MIA. (2023, January 25). Dampak Personalisasi Terhadap Keterlibatan Dan Loyalitas Pelanggan. Marketing In Asia. Available online: https://marketinginasia.com/id/how-the-giants-do-it-the-impact-of-personalisation-on-customer-engagement-and-loyalty/ (accessed on 09 December 2022).
- Qiscus. (2020, December 16). Loyalitas Konsumen: Efektivitas, Efesiensi dan Empati Layanan. Qiscus. Available online: https://www.qiscus.com/id/blog/loyalitas-konsumen-efektivitas-efesiensi-dan-empati-layanan/ (accessed on 09 January 2023).
- Subagio, G. I., Jawhar, R., Wibowo, A. J. I., & Yudianto, B. R. (2020). Hubungan Personalisasi Iklan, Keterlibatan Konsumen, dan Manfaat Strategis Terhadap Nilai dalam Konteks: Studi Empiris dari Perspektif Ekosistem Layanan. Kajian Branding Indonesia, 2(1), 35-68.
- Sudarwati, Y., & Izzaty, I. (2022). MANAJEMEN HUBUNGAN PELANGGAN BAGI USAHA MIKRO, KECIL, DAN MENENGAH. Jurnal Ekonomi & Kebijakan Publik, 13(1), 13-28. [CrossRef]
- Sugiyono. (2019). Metode Penelitian Kuantitatif dan Kualitatif Dan R&D. ALFABETA.
- Suryawijaya, T. W. E., Utomo, M. T. R. S., & Rahayuningtyas, T. E. (2023, International E-Conference Management & Small Medium Enterprises (ICMSME)). Self-Service Optimizatiom: Comprehending Customer Satisfaction. Jurnal Manajemen (Edisi Elektronik), 14(Special Issue 1), 203-216.
- Taghizadeh, H., Panahi, K., & Iranzadeh, S. (2021). The Impact of Personalization on Customers’ Loyalty and the Intention to Use E-banking Services. International Economics Studies, 51(2), 37-52. [CrossRef]
- Zalova, Z., & Karaduman, İ. (2018). The Effects Of Personalized Online Promotions On Consumer Loyalty: A Study İn Turkey. Journal of Business Management and Economic Research, 2(5), 49-50. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).