1. Introduction
Afforestation is a major forest activity in many parts of the world, especially in areas where forests replace degraded lands in order to promote soil protection, habitat conservation and connectivity [
1] Nevertheless, afforestation activities in tropical areas frequently occur on natural ecosystems such as grassland and secondary forests that are considered poorly productive but might not be the most suitable to maximize conservation goals and increase biodiversity levels [
2] Also, large-scale afforestation for C sequestration has received a lot of attention [
3,
4] bringing into question the possibility of influencing conservation goals [
5] Thus, it is of paramount importance to understand the link between afforestation activities and biodiversity levels in order to evaluate the environmental costs and benefits of afforestation policies and to design afforestation programs that contribute rather than reduce biodiversity levels.
On this direction, one of the most significant effects of afforestation is changes in landscape characteristics. Fragmentation of large, continuous habitats into smaller, isolated patches surrounded by a matrix that may be hostile to resident fauna is one major consequence of forest plantations [
6]. On the other hand, forest plantations may result in a positive effect when the targets are the expansion of forests [
7]. However, according to several authors planted forests appear to be insufficient for promoting conservation forest wild animal communities [
8], even though this is influenced by forest management and composition [
9]. Plantations may also have negative effects because they remove species with high conservation value from the habitats they replace, particularly birds strictly associated with open habitat and grasslands [
8].
Although theoretical and empirical evidence suggests that effects of forest plantations may extend beyond forest boundaries [
10], little is known about the effects of afforestation on fragmentation. These effects are brought about by habitat fragmentation, in which complex land uses matrixes (agriculture, secondary forests, grasslands, etc.) are broken up into smaller patches. The capacity of animal and vegetal species to use the matrix surrounding forest plantations partly determines the degree to which those contribute to connect to one another and other isolated forest areas [
11]. The idea that fragmented systems are comprised of "island-like" remnants of suitable habitat surrounded by matrices with no ecological value can oversimplify the complexity of fragmented landscapes and underestimate ecological values of anthropic landscapes [
12]. Those “human matrix” can still provide sufficient connectivity to sustain populations even if it lacks the characteristics required for more complex habitat functionality [
13]. This matrix can significantly increase the amount of suitable habitat in a forest planted landscape mediating changes in species richness, composition, and abundances [
14]. For instance, some species may experience an increase in habitat availability due to an increase of forest edges. These species tend to rise in more fragmented landscapes [
15], suggesting that forest plantations on agricultural dominated lands may contain more species than either of the adjacent simple agricultural habitats. Also, the penetration of edge effects into adjacent habitats, which may be greatly influenced by changes in edge and landscape features, determines the magnitude of these impacts [
16] Due to the synergistic interactions between edge and patch area effects [
13], their strength may shift with forest plantations. Therefore, understanding the changes in landscape configuration and composition due to forest plantations is extremely relevant to characterize their potential effects on fragmentation and connectivity.
Tropical forests in Ecuador have been extensively deforested, primarily for agricultural purposes, and about 24% (2020-2022) of these forests have vanish [
16] To reverse this process, Ecuador has promoted an ambitious National Forest Plantation Program [
17] A long-term trend of social rural changes and abandonment of poorly productive soils has led to an increase in marginal agricultural land afforestation in Ecuadorian tropical dry forests over the past decade. Implementation of public regulations provided financial support for afforestation and was partly justified by the goal of restoring ancient forest habitats and their associated biodiversity [
18,
19]. Our main goal was to characterize how new forest plantations from 2008 a 2018, ave changed habitat fragmentation and connectivity in dry areas of Ecuador. Specifically, we aimed to i) assess land cover changes and their effect on fragmentation and connectivity across planted landscapes in comparison to native forests remains, ii) identify consequences of these changes for certain vertebrate species that are quality indicators of Ecuadorian tropical dry forests, and iii) determine whether particular areas of the landscape are important in future plantations in this fragmented system. Based on that, we analyzed the implications of afforestation for conservation in dry tropical areas of Ecuador.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study sites
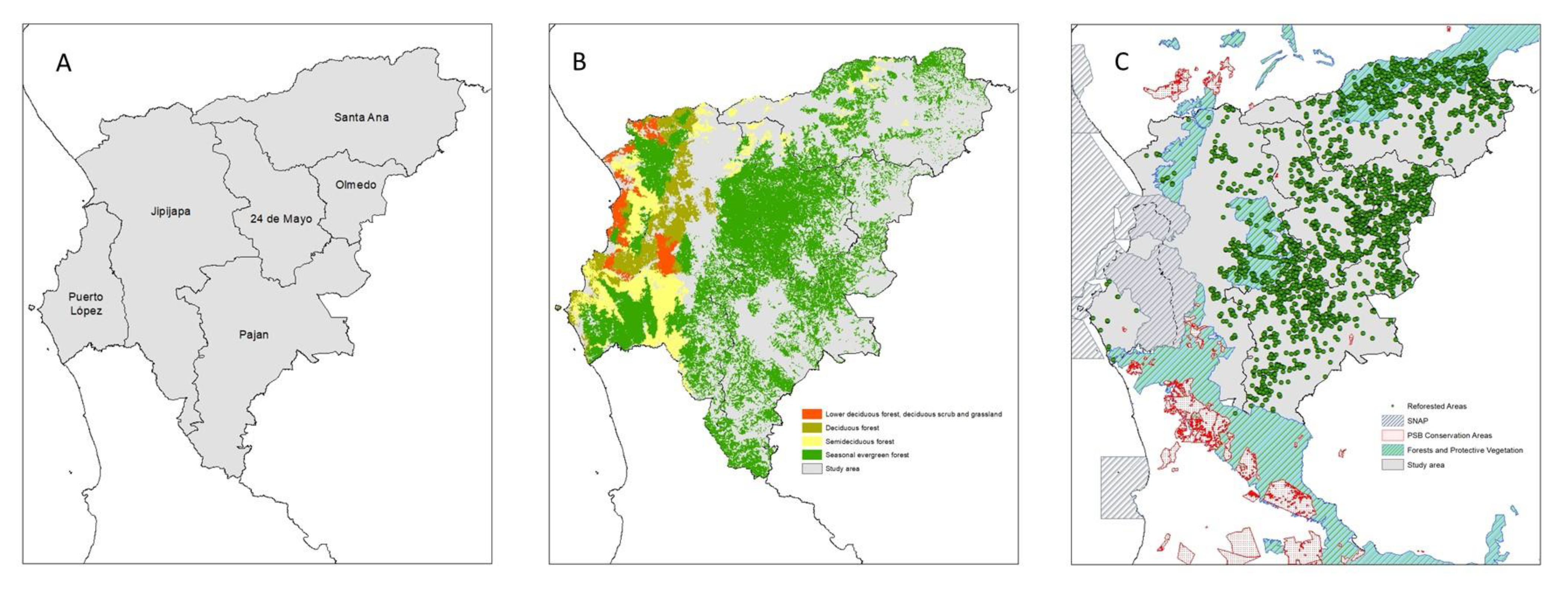
Manabí is located in the center of the coastal region of Ecuador and in the most western part of the South American continent, on the margins of the Pacific Ocean. It maintains an extension of 19,516.6 km
2, 7.36% of the national surface, positioning it as the fourth province with the largest continental area and the first in agricultural production. Manabí is distributed in three zones [
20] (north, center and south), in this last zone our study area covered six cantons (Jipijapa, Pajan, Santa Ana, 24 de Mayo, Olmedo and Puerto López), all of them located in the southern zone of the province of Manabí (0°45′00″S-80°05′00″W,
Figure 1), in the biogeographical region of Ecuador Coast. Five types of ecosystems are found in this area: low deciduous forest, deciduous scrub and grassland, deciduous forest, semi-deciduous forest, and seasonal evergreen forest [
21,
22,
23]. The types of forests can be divided into two: deciduous (low deciduous forest, deciduous forest and semi-deciduous forest). Deciduous forests presenting a higher degree of threat, greater fragility and less connectivity, in addition to less protection and research than green forests [
24].
Manabí Region is characterized by high levels of biodiversity [
25], although large forest areas are modified from extensive and unsustainable agricultural practices leading to fragmented landscapes with forest patches in the range of 5 and 100 ha. Due to their proximity to primary lowland dry forests, these fragmentary remnants represent primary forests. However, large areas of forests suffer from uncontrolled deforestation and land use change [
26].
Manabi presents three types of nature protection areas: National Systems of Protected Areas (SNAP), Forests and Protective Vegetation and PSB Conservation Areas. SNAP covers 51 nature reserves that extend in approximately 20% of the surface of Ecuador oriented to guaranty connectivity of the most important ecosystems. PSB Conservation Areas are zones that maintain native forest, paramo, and other native vegetable formations, of natural or legal persons that meet the objectives indicated in the agreement established by the socio bosque program and Protective forests and vegetation are those plant formations, natural or cultivated, arboreal, shrubby or herbaceous in the public or private domain, which are located in areas of rugged topography, in the headwaters of hydrographic basins or in areas that due to their climatic, edaphic and hydric conditions. In Ecuador it has been shown that SNAP prevent deforestation, but not all protection figures are effective [
27].
2.2. GIS sources
We downloaded GIS layers to delimit the provinces, land uses, and deforested-forested areas between 2008 and 2018. Administrative division was obtained from of the Military Geographic Institute of Ecuador (available at
https://www.geoportaligm.gob.ec/portal/index.php/cartografia-de-libre-acceso-escala-50k/). Land uses and deforestation were obtained by the Ecuadorian Ministry of the Environment (available at
http://ide.ambiente.gob.ec/mapainteractivo) based on Landsat and ASTER satellite images at a pixel size of 30 m to quantify land uses changes for the years 2008 and 2018 [
22,
28,
29];
Table 1). Kappa index of this maps was approximately 0.7 [
22]. To obtain the geographical location of the reforested areas, we obtained the coordinates and area of all reforested activities from the Department of Environmental Management of the Provincial Government of Manabí, for the period 2008 - 2018. For each set of coordinates, we created individual forest plantations polygons with square shape and the size of the area reforested. The geographic coordinates of the centroid of each forest plantation were calculated for fragmentation and connectivity analyses.
2.3. Land cover change and fragmentation
A land-use changes matrix was made taking 2008 (LUSES2008) as the initial year. This land-uses layer was intercepted with land uses of 2018 (LUSES2018), and with deforested and reforested areas. This allows to measure land use changes between 2008-2018, between LUSES2008 and forested and deforested areas, and between forested and deforested areas and LUSES2018. With these layers (see section 2.2), four study scenarios were created: i) LUSES2008, ii) LUSES2018, iii) LUSES2018 + avoiding deforestation (the areas deforested between 2008-2018 are added as native forest in LUSES2018) and iv) LUSES2018+ reforested (the areas reforested between 2008-2018 are added as plantations in LUSES2018). Once the four scenarios were formed, several fragmentation metrics were calculated: number of patches, average patch size and edge density [
30].
2.4. Connectivity analysis
We used graph theory to look at structural connectivity. Graph theory is a good way to find conservation targets because it does not need demographic data like most other conservation priority methods do [
26]. According to Calabrese and Fagan (2004), this approach provides a comprehensive, robust analysis of connectivity with minimal data requirements. Graphad 2.6 software [
31] was used to evaluate structural connectivity.
Functional connectivity was calculated for a set of generic species, for the four scenarios, and these scenarios were converted to raster layers (30 x 30 m) and each land cover was assigned a displacement cost (
Table 1). Native forest areas were considered "habitat". Subsequently, the links between the patches were created with a maximum cost of 166 (this equates to approximately 5 km of distance if the terrain has a cost of 1). This value represents a gradient of vagility for some of the characteristic fauna of Ecuadorian forests, such as the jaguarondi (
Puma yagouaroundi) [
32]. It allowed to assess the significance of individual planted patches within each regional network (via node-level metrics that can identify which patches facilitate landscape connectivity [
33]. Subsequently, global connectivity metrics (Flux, Equivalent Connectivity, Probability of Connectivity and Number of Components) and metric per patch (Current Flow) were calculated (
Table 2). Number, distance in cost and distance of the links for the four scenarios were also calculated. Finally, with these links, the corridors were calculated for a distance equal to that of the links (166). Corridors were used to establish the potential areas representing a set of possible “new forested paths” for connecting natural forest areas.
3. Results
3.1. Land cover change and fragmentation
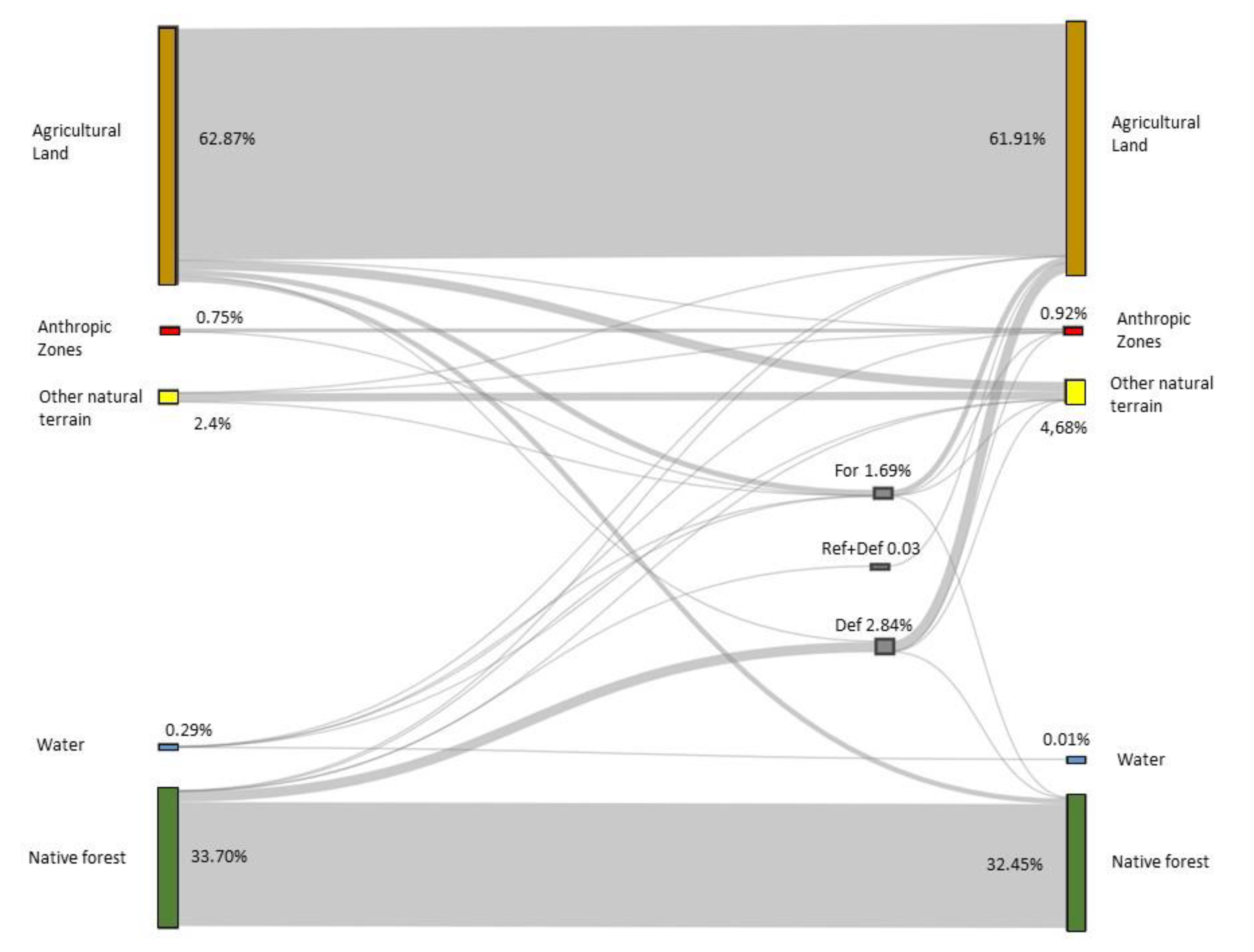
In 2008, the dominant land use in the study area (4791.43 km
2) was agriculture (61.91%). Forest areas decreased from 33.7% to 32.45% between 2008 and 2018 (
Figure 2), although other natural land uses, mostly shrubs, increased almost double (from 2.4% to 4.68%). Most of the deforestation affected to native forests during this period, and most of reforested and afforested areas in 2018 covered former agricultural land.
Fragmentation data showed that 61.48 km
2 of native forests were lost between 2008 and 2018, decreasing the number of patches and increasing the average size (
Table 3). The 2018+forestation scenario showed a large increase in the number of patches, but decreasing their average size, and also increased the number of patches compared to 2018, but not compared to 2008, with an average area close to the scenario of 2018.
The comparison between the scenarios 2018+forestation and 2018+ avoiding deforestation shows us that the area lost due to deforestation is greater than the afforested area (58 km2 of difference), this makes the dynamic a loss of forest, each time with less area, with a greater number of patches and smaller patches.
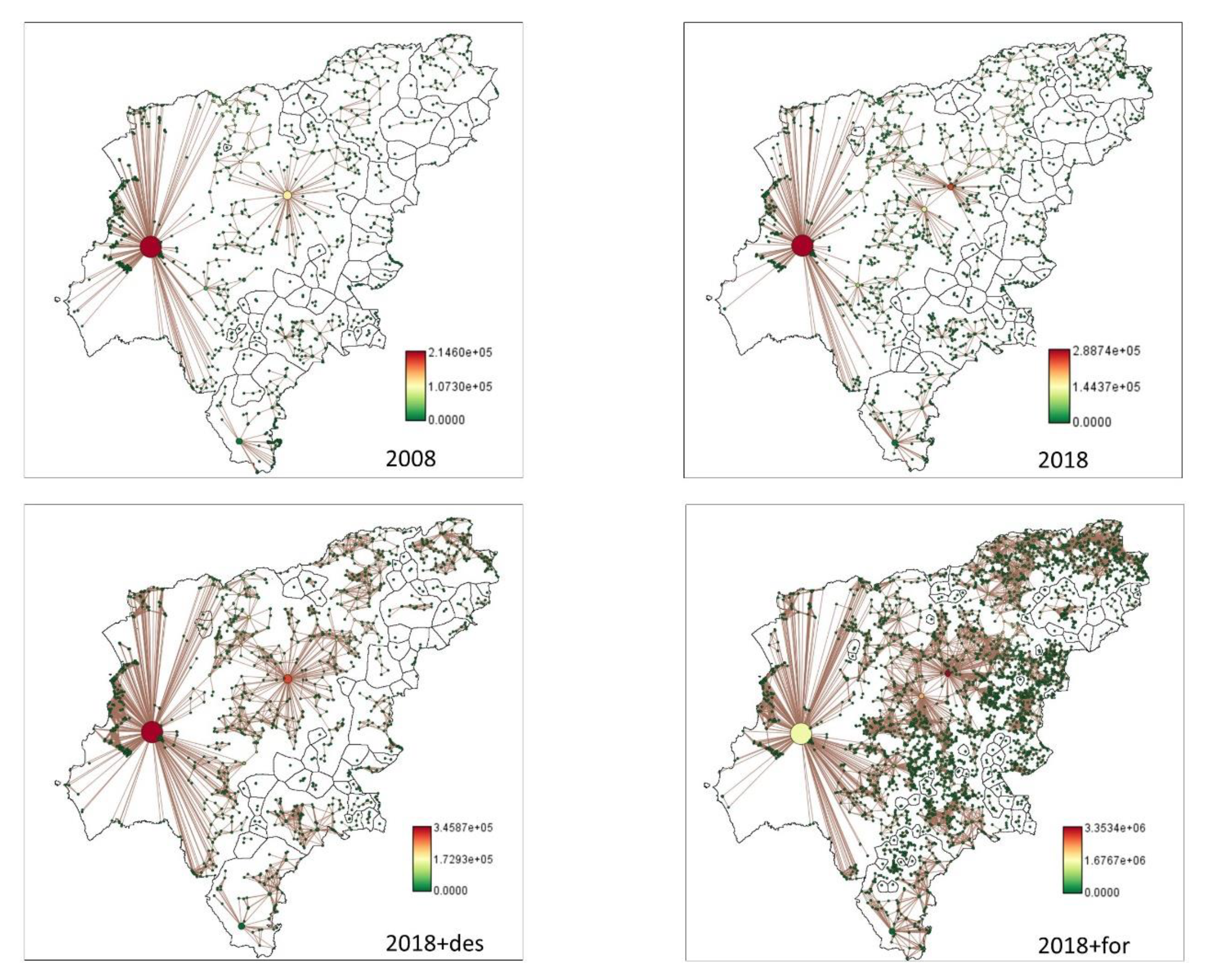
3.2. Connectivity analysis
The scenarios that presented better connectivity were those where forest areas increased (LUSES2018 + deforested and LUSES2018 + reforested). In this case, reforestation increased connectivity, even though LUSES2018 + reforested had less area than LUSES2018 + deforested, LUSES2018 + reforested presented better flux and CF (Table 5,
Figure 3).
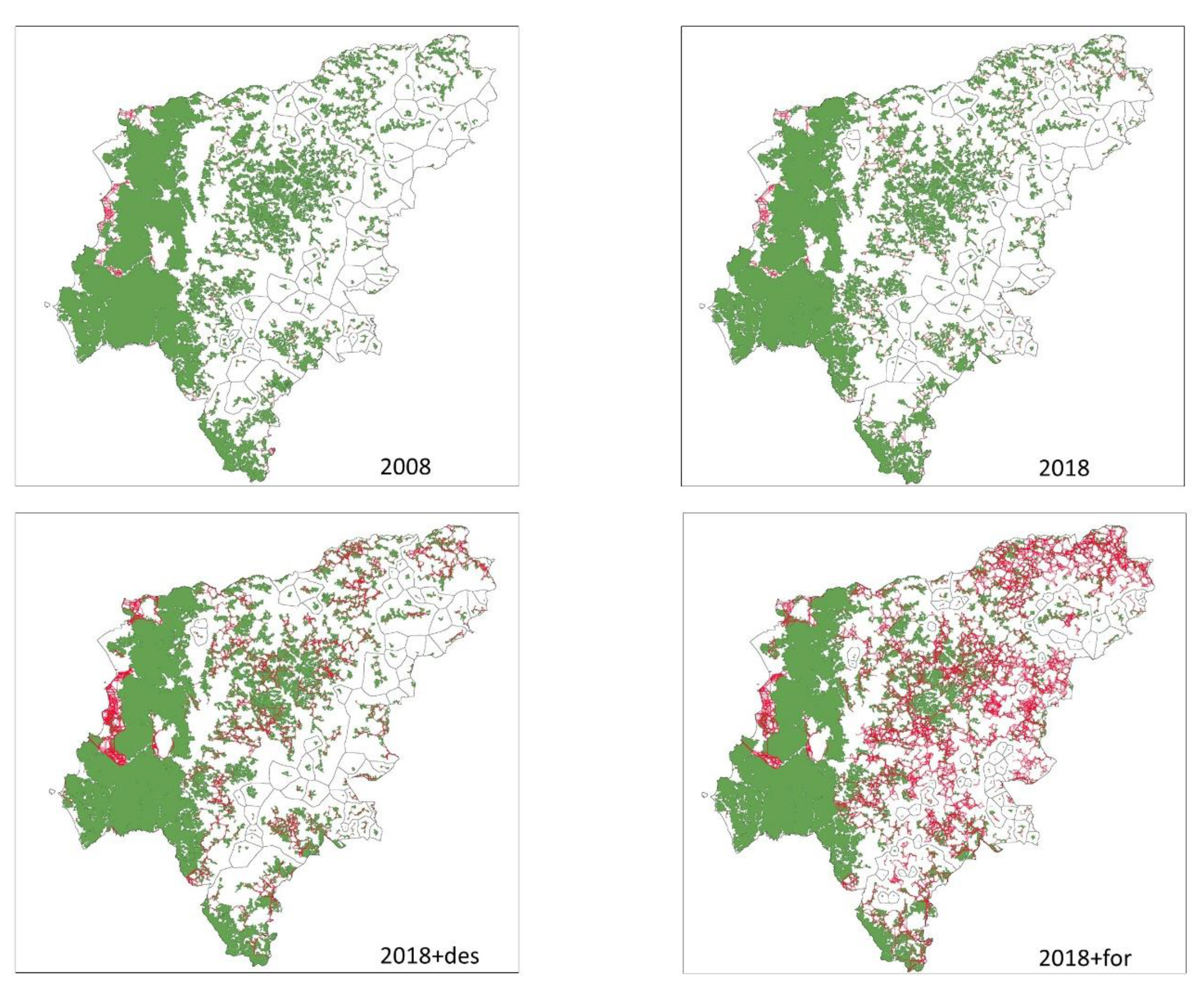
Links analysis showed that scenarios with increasing forest areas (LUSES2018 + deforested and LUSES2018 reforested) had higher number of links and distance. LUSES2018 + deforested scenario had 10 times a greater number of links than LUSES2008, reaching almost twice the distance in cost and four times more in distance in meters (Table 5 and
Figure 4).
Table 3.
Fragmentation metrics (number of patches, patch area and Total edge) in the Manabí province (Ecuador) for Land uses scenarios: 2008 (LUSES2008), 2018 (LUSES2018), 2018 avoiding deforestation (LUSES2018+def), and 2018 considering deforestation and reforestation (LUSES2018+ref).
Table 3.
Fragmentation metrics (number of patches, patch area and Total edge) in the Manabí province (Ecuador) for Land uses scenarios: 2008 (LUSES2008), 2018 (LUSES2018), 2018 avoiding deforestation (LUSES2018+def), and 2018 considering deforestation and reforestation (LUSES2018+ref).
| Scenario |
Overall area (km2) |
Number of patches |
Patch area |
ED = Patch perimeter / Patch area |
| |
|
|
Average |
Median |
S.D |
Average |
Median |
S.D |
| LUSES2008 |
1614.54 |
1600 |
1.01 |
0.01 |
23.80 |
1809.59 |
77.78 |
56280.65 |
| LUSES2018 |
1553.06 |
1434 |
1.08 |
0.05 |
24.21 |
215.85 |
28.21 |
1895.71 |
| LUSES2018+ref |
1623.46 |
3340 |
0.49 |
0.02 |
16.23 |
109.91 |
31.17 |
1245.31 |
| LUSES2018+def |
1681.79 |
1581 |
1.06 |
0.02 |
24.85 |
1651.67 |
44.44 |
56493.51 |
Table 4.
Connectivity metrics (Flux, F; Probability of Connectivity, PC; Number of Components, NC; and Current Flow CF) in the Manabí province (Ecuador) for Land uses scenarios: 2008 (LUSES2008), 2018 (LUSES2018), 2018 avoiding deforestation (LUSES2018+def), and 2018 avoiding deforestation and reforestation (LUSES2018+ref).
Table 4.
Connectivity metrics (Flux, F; Probability of Connectivity, PC; Number of Components, NC; and Current Flow CF) in the Manabí province (Ecuador) for Land uses scenarios: 2008 (LUSES2008), 2018 (LUSES2018), 2018 avoiding deforestation (LUSES2018+def), and 2018 avoiding deforestation and reforestation (LUSES2018+ref).
| |
Scenario |
| Metric |
2008 |
2018 |
2018+def |
2018+ref |
| F |
4.14E+11 |
5.01E+11 |
6.08E+11 |
1.23E+12 |
| EC |
1.14E+09 |
1.14E+09 |
1.25E+09 |
1.19E+09 |
| PC |
0.01383299 |
0.01384695 |
0.01669168 |
0.015178734 |
| NC |
57 |
63 |
55 |
55 |
| CF (Average) |
3488.34 |
7467.24 |
5791.91 |
64658.92 |
| CF (patch with higher CF) |
214596.13 |
288738.98 |
345865.63 |
3353361.40 |
Figure 3.
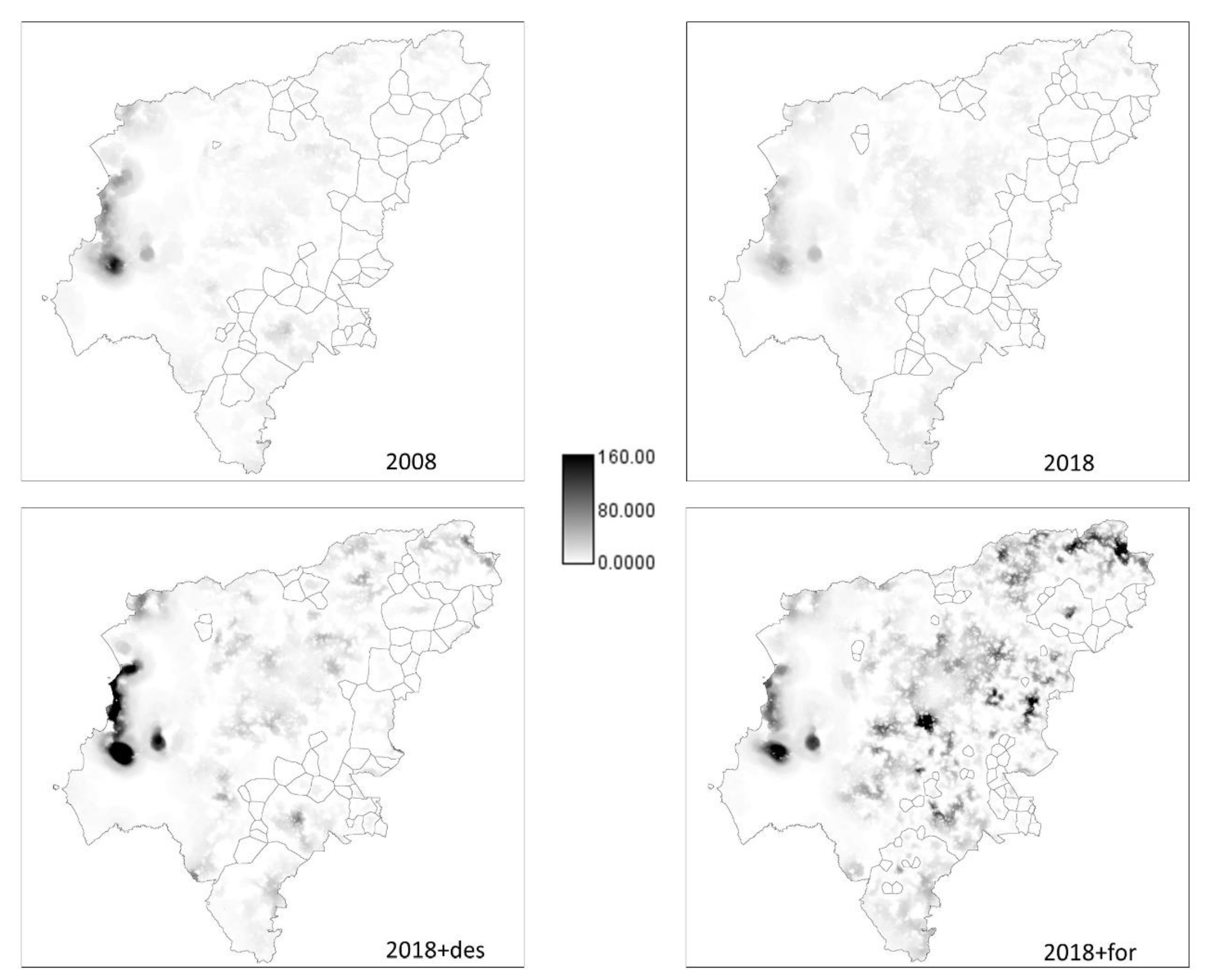
Current flow metric in the Manabí province (Ecuador) for Land uses scenarios: 2008 (LUSES2008), 2018 (LUSES2018), 2018 avoiding deforestation (LUSES2018+def), and 2018 considering deforestation and reforestation (LUSES2018+for). Components (areas outlined in black), connections between the patches (the size of the line indicates the connectivity, the thicker indicates more connectivity) and connectivity of the patch (color of the circle) are shown.
Figure 3.
Current flow metric in the Manabí province (Ecuador) for Land uses scenarios: 2008 (LUSES2008), 2018 (LUSES2018), 2018 avoiding deforestation (LUSES2018+def), and 2018 considering deforestation and reforestation (LUSES2018+for). Components (areas outlined in black), connections between the patches (the size of the line indicates the connectivity, the thicker indicates more connectivity) and connectivity of the patch (color of the circle) are shown.
Figure 4.
Forest patches (green), links between the patches (red) and components (areas delimited by black lines) in the Manabí province (Ecuador) for Land uses scenarios: 2008 (LUSES2008), 2018 (LUSES2018), 2018 avoiding deforestation (LUSES2018+def), and 2018 avoiding deforestation and reforestation (LUSES2018+for).
Figure 4.
Forest patches (green), links between the patches (red) and components (areas delimited by black lines) in the Manabí province (Ecuador) for Land uses scenarios: 2008 (LUSES2008), 2018 (LUSES2018), 2018 avoiding deforestation (LUSES2018+def), and 2018 avoiding deforestation and reforestation (LUSES2018+for).
Table 5.
Number of links, distance in cost and meters of the links generated in the 4 scenarios.
Table 5.
Number of links, distance in cost and meters of the links generated in the 4 scenarios.
| |
Number of links |
Distance in cost |
Distance in meters |
| |
|
Average |
Median |
S.D |
Average |
Median |
S.D |
| 2008 |
1487 |
42.32 |
25.56 |
40.89 |
385.40 |
254.56 |
363.08 |
| 2018 |
1922 |
47.59 |
31.00 |
43.11 |
408.56 |
254.56 |
386.36 |
| 2018+for |
18430 |
96.89 |
103.34 |
46.74 |
1247.94 |
1026.40 |
918.51 |
| 2018+des |
6001 |
84.83 |
87.91 |
49.70 |
1520.34 |
1301.54 |
1170.28 |
When considering only the 2018+avoiding deforestation scenario, connectivity increased for the reference vertebrate species in the west part of the Manabí province (
Figure 5). On the other hand, for the reforestation scenario (LUSES2018 + reforested) the number of links also increased on central and extreme northeast areas (areas where most of the reforestation was done) (
Figure 5).
4. Discussion
National reforestation programs are a frequent policy in rural areas of the Tropic to reduce poverty and increase biodiversity [
43]. In recent decades, balance between economic growth and ecological preservation has become a pressing issue in Ecuador [
44]. Thus, forest plantations have been promoted as an essential part of rural development and it is likely that there will be ongoing pressure to establish additional plantations. Our findings suggest that forest plantations increase fragmentation but may contribute to landscape connectivity between habitat patches in dry tropical forests. Forest plantations provide new links to native fragments in both agricultural and forestry landscapes at the cost of adding higher fragmentation in terms of edge availability and number of patches. The increase in edge forest habitat might be relevant for generalist species but might limit the suitability of forest patches for species strictly associated with Ecuadorian dry forests.
4.1. Land uses changes and fragmentation
It is generally accepted that land uses changes affect biodiversity levels modifying the dynamics of animal and vegetal populations and their long-term viability [
44]. Fragmentation relies on the structural complexity of the land uses matrix, modifying the dispersion capability for species in the landscapes. According to our results, reforestation activities resulted in a more compact network with more fragmentation (i.e. increasing number of patches). Those effects were more concentrated along areas with native forests remnants. Areas with dominant agricultural uses maintained high values of fragmentation metrics [
45]. Our results are consistent with previous findings, showing that forest plantation expansion may increase forest habitat but also increased fragmentation [
46]. This contrasting pattern may lead to perceive that the current shift from marginal tropical agricultural lands to plantations will have a negative effect on the flora, fauna and some Ecosystem Services [
47] . However, the presence of remnants patches of forests, as part of an interdependent forest net, can act as safeguarded areas contributing to the landscape arrangement [
48]. Forest plantations may increase this dispersion availability in fragmented landscapes, with plantations serving as steppingstones. On this case, generalist species can easily move across a landscape because they don't need specific habitat conditions, prefer open spaces or more edges, or have a larger home range or higher dispersion capability than specialist species [
49].
Our results also show that the forest area is decreasing, and reforestation efforts are not enough to reduce the high rates of deforestation suffered in the study area. Ecuador is one of the South American countries with the highest deforestation rate. The coast of Ecuador presents highly fragmented and very little protected ecosystems [
24,
50]. It is essential to stop deforestation, since if this trend continues, a highly fragmented ecosystem will be formed, with very small patches, harming species that have a high area requirement or forest specialists.
4.2. Connectivity
To provide insights into the interaction of forest plantations within heterogeneous landscapes, numerous studies have examined changes in landscape pattern and connectivity [
51]. Landscape connectivity of dominant land uses changed significantly over time in Manabí province (i.e., class types and surface of land uses) as result of forest plantations despite relatively constant dominance of agricultural cover. When we compared connectivity in scenarios considering only deforestation and reforestation, we found that forest plantations contribute to link native forest fragments, which have a middle to high conservation value and occupy less territory. Thus, as we initially stated in our hypothesis, forest plantations have contributed to improve connectivity, as well as the preservation of native forest remains.
Maintaining or restoring connectivity between fragmented habitats or plots has been suggested as the key to countering many of the negative consequences of fragmentation. Connected habitats more effectively preserve species and ecological functions. According to our result, in areas with complex land uses, connectivity due to forest plantations experienced the greatest relative increase associated proximity to natural vegetation areas and natural reserve boundaries. Despite being small, reforestation can act as stepping stones to connect patches with larger surfaces [
52,
53].
This information is important because many key species have connectivity requirements. Jaguarundi (
Puma yagouaroundi) habits less human-influenced landscapes and is very sensitive to habitat loss and disturbed areas [
54]. As a result, they face a greater risk of extinction [
55]. Our research revealed that changes in connectivity due to forest plantations may generate critical landscape connections for jaguarundi. In this instance, the species would benefit from the use of reforestation strategies that preserve or improve landscape connectivity in the study area. Habitat connections between strictly Protected Areas and the mosaics of forest plantations could contribute to species conservation. Threatened species receive priority in conservation planning because, among other factors, their populations are declining due to habitat fragmentation [
48]. Many species have long distance movement in the landscape, but others are less mobile and need “forest islands” to move around and spread out across the land uses matrix [
49].
4.3. Prioritization of forest plantations to improve connectivity
Forest plantations may contribute to restore connectivity among natural areas. Forest plantations may contribute to prioritize connectivity and safeguard local threatened species [
51]. A multi-taxa plantation framework, as the example presented here, may allowed to establish various networks of connected habitat based on the landscape-optimized movement corridor for key-species and threatened species in forest management in Ecuador. We presented a network of corridors under the current afforestation program in Ecuador and identified potential corridors that combine various current land uses. Because they have the potential to improve the impact of forest plantations in terms of biodiversity, these findings are relevant to the National Forest Plantation Program. First, native forest fragments have high conservation value, and plantations can improve their connectivity by incorporating spatial structural complexity for specialist species with dispersal ability across the landscape [
49]. Second, even though technical viability of this multi-species plantation framework needs to be further evaluated, it provides preliminary evidence of contributing to improve corridor networks ensuring the persistence of species with distinct habitat preferences, sensitivity to native forest replacement, and movement capacity. To avoid clearing of native forests within the potential corridors that could be used in the connectivity network, forest plantation and forest management must include biological corridors as a methodological task in their planning [
56]. As a result, the preservation of landscape elements that make a more significant contribution to landscape connectivity should be a top priority for the sustainable planning of forestry landscapes in Ecuador. By specifying the effects of plantations on the landscape-scale movement of multiple species, the temporal dynamic of natural and planted forestry landscapes must be considered, and focal species should be identified. Also, the socio-ecological framework of forestry of rural communities is not well understood. Therefore, by (1) restoring habitat, forestry could contribute to the improvement of threatened species' population viability; 2) connectivity in the landscape to avoid detrimental effects on these populations. Promoting sustainable forest plantations may contribute to establishing a link between forest sustainability and conservation biology, as well as the care and protection of endangered and endemic species.
5. Conclusions
Our results indicate that reforestation activities in the Manabí province during the last decades has increased fragmentation but may contribute to landscape connectivity between native forest patches in dry tropical forests. We suggest that the new forest plantations patches can be used for native fauna as steppingstones to colonize other native forest areas at the cost of adding higher fragmentation in terms of edge availability and number of patches.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.Q.G., R.M.N-C. and C.A.R.; methodology, R.M.N-C., C.A.R., A.Q.G.; formal analysis, C.A.R., A.Q.G., R.M.N-C., P.G.M.; investigation, C.A.R., A.Q.G., R.M.N-C.; resources, UNESUM.; data curation, A.Q.G.; writing—original draft preparation, R.M.N-C., A.Q.G., C.A.R., P.G.M.; writing—review and editing, all authors; supervision, R.M.N-C.,; project administration, A.Q.G.; funding acquisition, A.Q.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received financial support from the State University of the South of Manabí, the researcher's own funds. and support from the ERSAF Group - UCO - Campus Rabanales/Cordoba Spain.
Data Availability Statement
And the data generated by the authors from these original layers are available by request to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We appreciate the support provided by the Provincial GAD of Manabí, to the Ministry of the environment zone 4; Zone 4 Ministry of Agriculture, to the Cantonal GADs of the southern zone of Manabí (provided field information), to students from UNESUM (validation of data in the territory). We are grateful for the institutional support of the University of Córdoba. Special thanks for the support of Rafael M Navarro Cerrillo, Carlos Rivas and Pablo Gonzalez (Members of the ERSAF Research Group), for the direction and data support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Holl, Karen D Research Directions in Tropical Forest Restoration1. Ann. Mo. Bot. Gard. 2017, 102, 237–250. [CrossRef]
- Bremer, L.L.; Farley, K.A. Does Plantation Forestry Restore Biodiversity or Create Green Deserts? A Synthesis of the Effects of Land-Use Transitions on Plant Species Richness. Biodivers. Conserv. 2010, 19, 3893–3915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawson, S.M.; Brin, A.; Brockerhoff, E.G.; Lamb, D.; Payn, T.W.; Paquette, A.; Parrotta, J.A. Plantation Forests, Climate Change and Biodiversity. Biodivers. Conserv. 2013, 22, 1203–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driscoll, D.A.; Banks, S.C.; Barton, P.S.; Lindenmayer, D.B.; Smith, A.L. Conceptual Domain of the Matrix in Fragmented Landscapes. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2013, 28, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horák, J.; Brestovanská, T.; Mladenović, S.; Kout, J.; Bogusch, P.; Halda, J.P.; Zasadil, P. Green Desert?: Biodiversity Patterns in Forest Plantations. For. Ecol. Manag. 2019, 433, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaño-Villa, G.J.; Estevez, J.V.; Guevara, G.; Bohada-Murillo, M.; Fontúrbel, F.E. Differential Effects of Forestry Plantations on Bird Diversity: A Global Assessment. For. Ecol. Manag. 2019, 440, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iezzi, M.E.; Di Bitetti, M.S.; Martínez Pardo, J.; Paviolo, A.; Cruz, P.; De Angelo, C. Forest Fragments Prioritization Based on Their Connectivity Contribution for Multiple Atlantic Forest Mammals. Biol. Conserv. 2022, 266, 109433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brockerhoff, E.G.; Jactel, H.; Parrotta, J.A.; Ferraz, S.F.B. Role of Eucalypt and Other Planted Forests in Biodiversity Conservation and the Provision of Biodiversity-Related Ecosystem Services. For. Ecol. Manag. 2013, 301, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpato, G.H.; Prado, V.M.; dos Anjos, L. What Can Tree Plantations Do for Forest Birds in Fragmented Forest Landscapes? A Case Study in Southern Brazil. For. Ecol. Manag. 2010, 260, 1156–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, J.; Lindenmayer, D.B. Landscape Modification and Habitat Fragmentation: A Synthesis. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2007, 16, 265–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardiner, R.; Bain, G.; Hamer, R.; Jones, M.E.; Johnson, C.N. Habitat Amount and Quality, Not Patch Size, Determine Persistence of a Woodland-Dependent Mammal in an Agricultural Landscape. Landsc. Ecol. 2018, 33, 1837–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ries, L.; Fletcher, R.J.; Battin, J.; Sisk, T.D. Ecological Responses to Habitat Edges: Mechanisms, Models, and Variability Explained. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2004, 35, 491–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewers, R.M.; Didham, R.K. Continuous Response Functions for Quantifying the Strength of Edge Effects. J. Appl. Ecol. 2006, 43, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas, C.A.; Guerrero-Casado, J.; Navarro-Cerillo, R.M. Deforestation and Fragmentation Trends of Seasonal Dry Tropical Forest in Ecuador: Impact on Conservation. For. Ecosyst. 2021, 8, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plan Nacional de Desarrollo 2017-2021 Toda Una Vida | SITEAL. Available online: https://siteal.iiep.unesco.org/bdnp/280/plan-nacional-desarrollo-2017-2021-toda-vida (accessed on 9 December 2022).
- Harper, K.A.; Macdonald, S.E.; Burton, P.J.; Chen, J.; Brosofske, K.D.; Saunders, S.C.; Euskirchen, E.S.; Roberts, D.; Jaiteh, M.S.; Esseen, P.-A. Edge Influence on Forest Structure and Composition in Fragmented Landscapes. Conserv. Biol. 2005, 19, 768–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prefectura de Imbabura Plan de Forestación y Reforestación de La Provincia de Imbabura. Available online: https://www.imbabura.gob.ec/phocadownloadpap/K-Planes-programas/CONGOPE%20PLAN%20FORESTAL.pdf (accessed on 9 December 2022).
- Consejo Provincial de Manabí Plan de Ordenamiento Territorial de Manabi_2030_v1.1. Available online: https://www.manabi.gob.ec/wp-content/uploads/2022/09/PDOT_Manabi_2030_v1.1..pdf (accessed on 11 January 2023).
- Prentice, K.C. Bioclimatic Distribution of Vegetation for General Circulation Model Studies. J. Geophys. Res. Atmospheres 1990, 95, 11811–11830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentry, A.H. Species Richness and Floristic Composition of Choco Region Plant Communities. Caldasia 1986, 15, 71–91. [Google Scholar]
- Mosandl, R.; Günter, S.; Stimm, B.; Weber, M. Ecuador Suffers the Highest Deforestation Rate in South America. In Gradients in a Tropical Mountain Ecosystem of Ecuador; Beck, E., Bendix, J., Kottke, I., Makeschin, F., Mosandl, R., Eds.; Estudios Ecológicos; Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg, 2008; ISBN 978-3-540-73526-7. [Google Scholar]
- Ministerio del Ambiente Evaluación Nacional Forestal. Protocolo para el Procesamiento del Mapa Densidades de Carbono para Estratos Boscosos del Ecuador Continental con Imágenes Modis y Landsat 2014. <b>2014</b>, 32. Ministerio del Ambiente Evaluación Nacional Forestal. Protocolo para el Procesamiento del Mapa Densidades de Carbono para Estratos Boscosos del Ecuador Continental con Imágenes Modis y Landsat 2014. 2014, 32.
- Peralvo, M.; Delgado, J. Metodología Para La Generación Del Mapa de Deforestación Histórica. Quito Minist. Ambiente CONDESAN 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Rivas, C.A.; Navarro-Cerillo, R.M.; Johnston, J.C.; Guerrero-Casado, J. Dry forest is more threatened but less protected than evergreen forest in Ecuador’s coastal region. Environ. Conserv. 2020, 47, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGarigal, K. FRAGSTATS: Spatial Pattern Analysis Program for Quantifying Landscape Structure; U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Pacific Northwest Research Station, 1995; 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Minor, E.S.; Urban, D.L. Graph Theory as a Proxy for Spatially Explicit Population Models in Conservation Planning. Ecol. Appl. 2007, 17, 1771–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivas, C. A. , Guerrero-Casado, J., & Navarro-Cerillo, R. M. Deforestation and fragmentation trends of seasonal dry tropical forest in Ecuador: impact on conservation. For. Ecosyst. 2021; 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Foltête, J.-C.; Clauzel, C.; Vuidel, G. A Software Tool Dedicated to the Modelling of Landscape Networks. Environ. Model. Softw. 2012, 38, 316–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. Joint Research Centre. Institute for Environment and Sustainability. Forest Landscape in Europe: Pattern, Fragmentation and Connectivity.; Publications Office: LU, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- de la Sancha, N.U.; Boyle, S.A.; McIntyre, N.E. Identifying Structural Connectivity Priorities in Eastern Paraguay’s Fragmented Atlantic Forest. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 16129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scriven, S.A.; Carlson, K.M.; Hodgson, J.A.; McClean, C.J.; Heilmayr, R.; Lucey, J.M.; Hill, J.K. Testing the Benefits of Conservation Set-Asides for Improved Habitat Connectivity in Tropical Agricultural Landscapes. J. Appl. Ecol. 2019, 56, 2274–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giordano, A.J. Ecology and Status of the Jaguarundi Puma Yagouaroundi: A Synthesis of Existing Knowledge. Mammal Rev. 2016, 46, 30–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro Cerrillo, R.M.; Esteves Vieira, D.J.; Ochoa-Gaona, S.; de Jong, B.H.J.; del Mar Delgado Serrano, M. Land Cover Changes and Fragmentation in Mountain Neotropical Ecosystems of Oaxaca, Mexico under Community Forest Management. J. For. Res. 2019, 30, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meurant, M.; Gonzalez, A.; Doxa, A.; Albert, C.H. Selecting Surrogate Species for Connectivity Conservation. Biol. Conserv. 2018, 227, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, S.P.; Wilson, K.A.; Meijaard, E.; Watts, M.; Dennis, R.; Christy, L.; Possingham, H.P. Influence of a Threatened-Species Focus on Conservation Planning. Conserv. Biol. 2010, 24, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saura, S.; Torné, J. Conefor Sensinode 2.2: A Software Package for Quantifying the Importance of Habitat Patches for Landscape Connectivity. Environ. Model. Softw. 2009, 24, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foltête, J.-C.; Clauzel, C.; Vuidel, G.; Tournant, P. Integrating Graph-Based Connectivity Metrics into Species Distribution Models. Landsc. Ecol. 2012, 27, 557–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saura, S.; Estreguil, C.; Mouton, C.; Rodríguez-Freire, M. Network Analysis to Assess Landscape Connectivity Trends: Application to European Forests (1990–2000). Ecol. Indic. 2011, 11, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saura, S.; Pascual-Hortal, L. A New Habitat Availability Index to Integrate Connectivity in Landscape Conservation Planning: Comparison with Existing Indices and Application to a Case Study. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2007, 83, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urban, D.; Keitt, T. Landscape Connectivity : A Graph-Theoretic Perspective. Ecology 2001, 82, 1205–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LANDSCAPE CONNECTIVITY: A GRAPH-THEORETIC PERSPECTIVE - Urban - 2001 - Ecology - Wiley Online Library. Available online: https://esajournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1890/0012-9658%282001%29082%5B1205%3ALCAGTP%5D2.0.CO%3B2?casa_token=4yxZX952lBEAAAAA%3AYyqGm4smRIL-X_PD1y3kWUIc9i8-10YIIGCpCTEaxtAn--ytZzlC0KyGuaFiMcSsP9V8HeOBUgSbOxfj (accessed on 11 January 2023).
- Girardet, X.; Foltête, J.-C.; Clauzel, C. Designing a Graph-Based Approach to Landscape Ecological Assessment of Linear Infrastructures. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2013, 42, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holl, K.D. Research Directions in Tropical Forest Restoration. Ann. Mo. Bot. Gard. 2017, 102, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proyecto: Programa Nacional de Reforestación Con Fines de Conservación Ambiental, Protección de Cuencas Hidrográficas y Beneficios Alternos CUP: - PDF Free Download. Available online: https://docplayer.es/204935700-Proyecto-programa-nacional-de-reforestacion-con-fines-de-conservacion-ambiental-proteccion-de-cuencas-hidrograficas-y-beneficios-alternos-cup.html (accessed on 13 December 2022).
- Pliscoff, P.; Simonetti, J.A.; Grez, A.A.; Vergara, P.M.; Barahona-Segovia, R.M. Defining Corridors for Movement of Multiple Species in a Forest-Plantation Landscape. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 23, e01108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Coomes, D.A.; Gibson, L.; Hu, G.; Liu, J.; Luo, Y.; Wu, C.; Yu, M. Forest Fragmentation in China and Its Effect on Biodiversity. Biol. Rev. 2019, 94, 1636–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, D.P.; Socolar, J.B.; Mills, S.C.; Burivalova, Z.; Koh, L.P.; Wilcove, D.S. Conservation of Tropical Forests in the Anthropocene. Curr. Biol. 2019, 29, R1008–R1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martensen, A.C.; Ribeiro, M.C.; Banks-Leite, C.; Prado, P.I.; Metzger, J.P. Associations of Forest Cover, Fragment Area, and Connectivity with Neotropical Understory Bird Species Richness and Abundance. Conserv. Biol. 2012, 26, 1100–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeley, A.T.H.; Beier, P.; Jenness, J.S. Connectivity Metrics for Conservation Planning and Monitoring. Biol. Conserv. 2021, 255, 109008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lessmann, J.; Muñoz, J.; Bonaccorso, E. Maximizing Species Conservation in Continental Ecuador: A Case of Systematic Conservation Planning for Biodiverse Regions. Ecol. Evol. 2014, 4, 2410–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarabon, S.; Dutoit, T.; Isselin-Nondedeu, F. Pooling Biodiversity Offsets to Improve Habitat Connectivity and Species Conservation. J. Environ. Manage. 2021, 277, 111425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, L.P.; Sabatino, M.C.; Jaimes, F.R.; Saura, S. Landscape Connectivity and the Role of Small Habitat Patches as Stepping Stones: An Assessment of the Grassland Biome in South America. Biodivers. Conserv. 2017, 26, 3465–3479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siqueira, F.F.; de Carvalho, D.; Rhodes, J.; Archibald, C.L.; Rezende, V.L.; van den Berg, E. Small Landscape Elements Double Connectivity in Highly Fragmented Areas of the Brazilian Atlantic Forest. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa, C. C. , Trigo, T. C., Tirelli, F. P., da Silva, L. G., Eizirik, E., Queirolo, D., de Freitas, T. R. Geographic distribution modeling of the margay (Leopardus wiedii) and jaguarundi (Puma yagouaroundi): a comparative assessment. J. Mammal. 2018; 99, 252–262. [Google Scholar]
- Giordano, A. J. Ecology and status of the jaguarundi Puma yagouaroundi: A synthesis of existing knowledge. Mamm. Rev. 2016, 46(1), 30–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFadden, T.N.; Dirzo, R. Opening the Silvicultural Toolbox: A New Framework for Conserving Biodiversity in Chilean Timber Plantations. For. Ecol. Manag. 2018, 425, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).