Submitted:
18 April 2023
Posted:
19 April 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. H. pylori and Associated Diseases
2.1. Gastric Cancer
2.2. Peptic Ulcer Disease
2.3. Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue (MALT) Lymphoma
2.4. Extragastric Manifestations of H. pylori
3. H. pylori Virulence Factors and Cancer Mechanisms
3.1. Urease
3.2. Adhesins
3.3. CagA and the Pathogenicity Island
3.4. Vacuolating Toxin (VacA)
3.5. H. pylori Neutrophil activating protein (HP-NAP)
3.6. H. pylori γ-glutamyltranspeptidase (GGT)
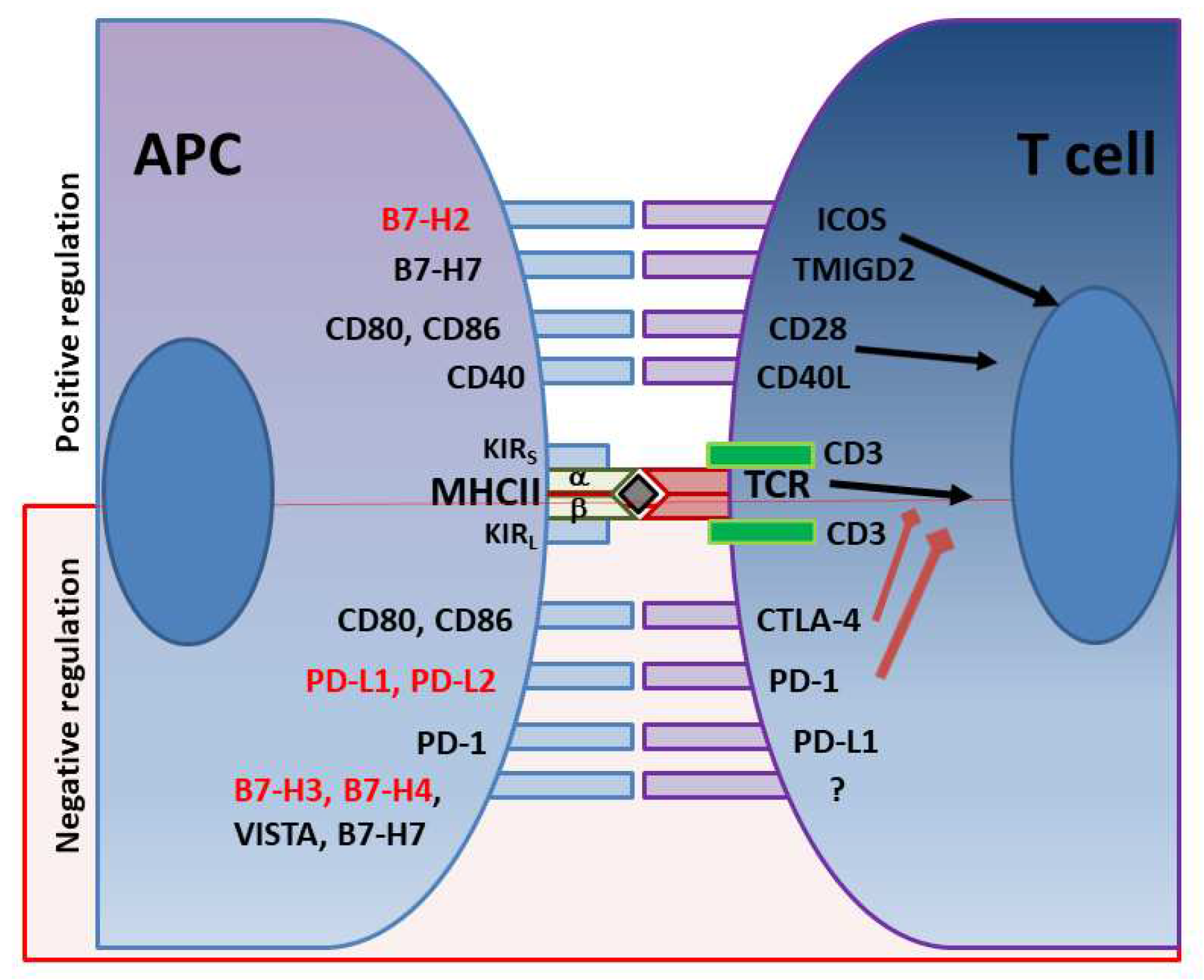
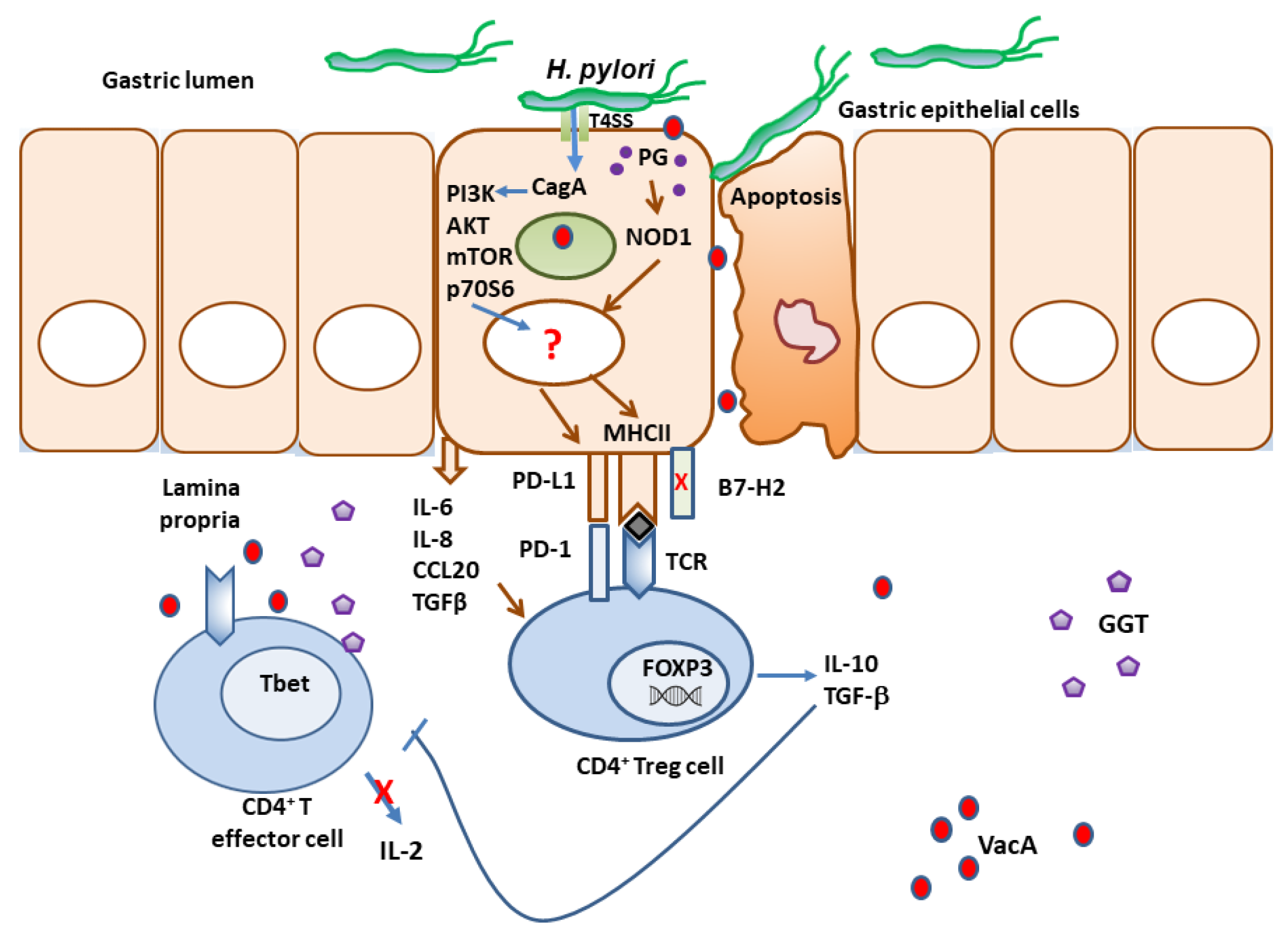
4. Immune Checkpoints in H. pylori Infection as Immune Escape Mechanisms
5. Conclusions and Future Directions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferlay, J.; Colombet, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Mathers, C.; Parkin, D.M.; Piñeros, M.; Znaor, A.; Bray, F. Estimating the global cancer incidence and mortality in 2018: GLOBOCAN sources and methods. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 144, 1941–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stomach (Gastric) Cancer Key Statistics.
- Ferlay, J.; Colombet, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Parkin, D.M.; Piñeros, M.; Znaor, A.; Bray, F. Cancer statistics for the year 2020: An overview. Int. J. Cancer 2021, 149, 778–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Infection with Helicobacter pylori. IARC Monogr Eval. Carcinog. Risks Hum 61, 177–240.
- Hooi, J.K.Y.; Lai, W.Y.; Ng, W.K.; Suen, M.M.Y.; Underwood, F.E.; Tanyingoh, D.; Malfertheiner, P.; Graham, D.Y.; Wong, V.W.S.; Wu, J.C.Y.; et al. Global Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori Infection: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Gastroenterology 2017, 153, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, B.J.; Warren, J.R. Unidentified curved bacilli in the stomach of patients with gastritis and peptic ulceration. Lancet 1984, 1, 1311–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correa, P. A human model of gastric carcinogenesis. 1988, 48, 3554–60.
- Ma, J.; Shen, H.; Kapesa, L.; Zeng, S. Lauren classification and individualized chemotherapy in gastric cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 11, 2959–2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plummer, M. , Franceschi, S., Vignat, J., Forman, D. and De Martel, C. (2015) Global burden of gastric cancer attributable to Helicobacter pylori. Int J Cancer, Int J Cancer 136, 487–490.
- Schistosomes, liver flukes and Helicobacter pylori. IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. Lyon, 7-. IARC Monogr Eval Carcinog Risks Hum, Various 61, 1. 14 June.
- Jemal, A. , Bray, F. ( CA Cancer J Clin 61, 69–90.
- Holcombe, C. Helicobacter pylori: the African enigma. Gut 1992, 33, 429–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agha, A. and Graham, D. Y. (2005) Evidence-based examination of the African enigma in relation to Helicobacter pylori infection. Scand J Gastroenterol 40.
- Bamford, K.B.; Fan, X.; Crowe, S.E.; Leary, J.F.; Gourley, W.K.; Luthra, G.K.; Brooks, E.G.; Graham, D.Y.; Reyes, V.E.; Ernst, P.B. Lymphocytes in the human gastric mucosa during Helicobacter pylori have a T helper cell 1 phenotype. Gastroenterology 1998, 114, 482–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, J.G.; Beck, P.; Dangler, C.A.; Whary, M.T.; Wang, T.C.; Shi, H.N.; Nagler-Anderson, C. Concurrent enteric helminth infection modulates inflammation and gastric immune responses and reduces helicobacter-induced gastric atrophy. Nat. Med. 2000, 6, 536–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Z. , Feng, Y., Muthupalani, S., Eurell, L. L., Taylor, N. S., Whary, M. T. and Fox, J. G. (2011) Coinfection with enterohepatic helicobacter species can aeliorate or promote Helicobacter pylori-induced gastric pathology in C57BL/6 Mice. Infect Immun 79, 3861–3871.
- Singh, K.; Ghoshal, U.C. Causal role of Helicobacter pylori infection in gastric cancer: An Asian enigma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 12, 1346–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Yamaoka, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Matha, I.; Gao, X. A Comprehensive Sequence and Disease Correlation Analyses for the C-Terminal Region of CagA Protein of Helicobacter pylori. PLOS ONE 2009, 4, e7736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaoka, Y. , Kodama, T., Kashima, K., Graham, D. Y. and Sepulveda, A. R. (1998) Variants of the 3’ region of the cagA gene in Helicobacter pylori isolates from patients with different H. pylori-associated diseases. J. Clin. Microbiol 36, 2258–2263.
- Correa, P.; Cuello, C.; Duque, E.; Burbano, L.C.; Garcia, F.T.; Bolanos, O.; Brown, C.; Haenszel, W. Gastric Cancer in Colombia. III. Natural History of Precursor Lesions 2. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1976, 57, 1027–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaturvedi, R.; de Sablet, T.; Asim, M.; Piazuelo, M.B.; Barry, D.P.; Verriere, T.G.; Sierra, J.C.; Hardbower, D.M.; Delgado, A.G.; Schneider, B.G.; et al. Increased Helicobacter pylori-associated gastric cancer risk in the Andean region of Colombia is mediated by spermine oxidase. Oncogene 2014, 34, 3429–3440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bravo, L. E. , Van Doorn, L. J., Realpe, J. L. and Correa, P. (2002) Virulence-associated genotypes of Helicobacter pylori: Do they explain the African enigma? American Journal of Gastroenterology 97.
- Kodaman, N.; Pazos, A.; Schneider, B.G.; Piazuelo, M.B.; Mera, R.; Sobota, R.S.; Sicinschi, L.A.; Shaffer, C.L.; Romero-Gallo, J.; de Sablet, T.; et al. Human and Helicobacter pylori coevolution shapes the risk of gastric disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2014, 111, 1455–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakhti, S. Z. , Raei, N., Latifi-Navid, S., Zahri, S. and Yazdanbod, A. (2019) Inverse relationship between cagG-positive Helicobacter pylori status and risk of gastric ulcer. Br J Biomed Sci 76.
- Sverdén, E. , Agréus, L., Dunn, J. M. and Lagergren, J. (2019) Peptic ulcer disease. BMJ, British Medical Journal Publishing Group 367.
- Lau, J. Y. , Sung, J., Hill, C., Henderson, C., Howden, C. W. and Metz, D. C. (2011) Systematic review of the epidemiology of complicated peptic ulcer disease: incidence, recurrence, risk factors and mortality. Digestion, Digestion 84, 102–113.
- Lanas, A. and Chan, F. K. L. (2017, ) Peptic ulcer disease. The Lancet, Lancet Publishing Group. 5 August.
- El-Omar, E.; Oien, K.; El-Nujumi, A.; Gillen, D.; Wirz, A.; Dahill, S.; Williams, C.; Ardill, J.; McColl, K. Helicobacter pylori infection and chronic gastric acid hyposecretion. Gastroenterology 1997, 113, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isaacson, P.G.; Du, M. Gastrointestinal lymphoma: where morphology meets molecular biology. J. Pathol. 2005, 205, 255–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Elios, M.M.; Amedei, A.; Manghetti, M.; Costa, F.; Baldari, C.T.; Quazi, A.S.; Telford, J.L.; Romagnani, S.; del Prete, G. Impaired T-cell regulation of B-cell growth in Helicobacter pylori–related gastric low-grade MALT lymphoma. Gastroenterology 1999, 117, 1105–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussell, T. , Isaacson, P. G., Crabtkee, J. E. and Spencer, J. O. (1996) Helicobacter p ylori-specific tumour-infiltrating T cells provide contact-dependent help for the growth of malignant B cells in low-grade gastric lymphoma of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue. Journal of Pathology 178, 122–127.
- Parsonnet, J.; Hansen, S.; Rodriguez, L.; Gelb, A.B.; Warnke, R.A.; Jellum, E.; Orentreich, N.; Vogelman, J.H.; Friedman, G.D. Helicobacter pylori Infection and Gastric Lymphoma. New Engl. J. Med. 1994, 330, 1267–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruskone-Fourmestraux, A.; Fischbach, W.; Aleman, B.M.P.; Boot, H.; Du, M.Q.; Megraud, F.; Montalban, C.; Raderer, M.; Savio, A.; Wotherspoon, A.; et al. EGILS consensus report. Gastric extranodal marginal zone B-cell lymphoma of MALT. Gut 2011, 60, 747–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zullo, A.; Hassan, C.; Cristofari, F.; Andriani, A.; De Francesco, V.; Ierardi, E.; Tomao, S.; Stolte, M.; Morini, S.; Vaira, D. Effects of Helicobacter pylori Eradication on Early Stage Gastric Mucosa–Associated Lymphoid Tissue Lymphoma. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 8, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J. Z. , Li, J. Y., Wu, T. F., Xu, J. H., Huang, C. Z., Cheng, D., Chen, Q. K. and Yu, T. (2017) Helicobacter pylori Infection Is Associated with Type 2 Diabetes, Not Type 1 Diabetes: An Updated Meta-Analysis. Gastroenterol Res Pract, Hindawi Limited 2017.
- Upala, S. , Sanguankeo, A., Saleem, S. A. and Jaruvongvanich, V. (2017) Effects of Helicobacter pylori eradication on insulin resistance and metabolic parameters: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol, Lippincott Williams and Wilkins 29, 153–159.
- Liu, J. , Wang, F. and Shi, S. (2015) Helicobacter pylori Infection Increase the Risk of Myocardial Infarction: A Meta-Analysis of 26 Studies Involving more than 20,000 Participants. Helicobacter, John Wiley & Sons, Ltd 20, 176–183.
- Xu, M.-Y.; Cao, B.; Yuan, B.-S.; Yin, J.; Liu, L.; Lu, Q.-B. Association of anaemia with Helicobacter pylori infection: a retrospective study. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13434–13434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satoh, T. , Pandey, J. P., Okazaki, Y., Asahi, A., Kawakami, Y., Ikeda, Y. and Kuwana, M. (2009) Single nucleotide polymorphism of interleukin-1beta associated with Helicobacter pylori infection in immune thrombocytopenic purpura. Tissue Antigens, Tissue Antigens 73, 353–357.
- Shen, X. , Yang, H., Wu, Y., Zhang, D. and Jiang, H. (2017) Meta-analysis: Association of Helicobacter pylori infection with Parkinson’s diseases. Helicobacter, John Wiley & Sons, Ltd 22, e12398.
- Chung, S.J.; Lim, S.H.; Choi, J.; Kim, D.; Kim, Y.S.; Park, M.J.; Yim, J.Y.; Kim, J.S.; Cho, S.-H.; Jung, H.C.; et al. Helicobacter pylori Serology Inversely Correlated With the Risk and Severity of Reflux Esophagitis inHelicobacter pylori Endemic Area: A Matched Case-Control Study of 5,616 Health Check-Up Koreans. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2011, 17, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; Hu, J.; Wang, X.; Ren, M.; Lu, G.; Lu, X.; Zhang, D.; He, S. The Effect of Helicobacter pylori Eradication in Patients with Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Studies. Dig. Dis. 2020, 38, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islami, F. and Kamangar, F. (2008) Helicobacter pylori and Esophageal Cancer Risk -- A Meta-Analysis. Cancer Prev Res (Phila), NIH Public Access 1, 329.
- Chen, Y.; Blaser, M.J. Helicobacter pyloriColonization Is Inversely Associated with Childhood Asthma. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 198, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Elios, M.M.; Amedei, A.; Codolo, G.; Del Prete, G.; de Bernard, M. The effect of Helicobacter pylori on asthma and allergy. J. Asthma Allergy 2010, 3, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, N.; Nasrallah, E.; Khoury, C.; Mansour, B.; Abu Zuher, L.; Asato, V.; Muhsen, K. Associations of Helicobacter pylori seropositivity and gastric inflammation with pediatric asthma. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2020, 55, 2236–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karttunen, R.; Andersson, G.; Poikonen, K.; Kosunen, T.U.; Karttunen, T.; Juutinen, K.; Niemelä, S. Helicobacter pylori induces lymphocyte activation in peripheral blood cultures. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1990, 82, 485–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amedei, A.; Cappon, A.; Codolo, G.; Cabrelle, A.; Polenghi, A.; Benagiano, M.; Tasca, E.; Azzurri, A.; D’elios, M.M.; Del Prete, G.; et al. The neutrophil-activating protein of Helicobacter pylori promotes Th1 immune responses. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 1092–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, V. E. and Beswick, E. J. (2007) Helicobacter pylori neutrophil activating protein’s potential as tool in therapeutic immune modulation. Expert Opin Ther Pat 17.
- Lundgren, A. , Suri-Payer, E., Enarsson, K., Svennerholm, A. M. and Lundin, B. S. (2003) Helicobacter pylori-specific CD4+ CD25high regulatory T cells suppress memory T-cell responses to H. pylori in infected individuals. Infect. Immun 71, 1755–1762.
- Beswick, E.J.; Pinchuk, I.V.; Earley, R.B.; Schmitt, D.A.; Reyes, V.E. Role of Gastric Epithelial Cell-Derived Transforming Growth Factor β in Reduced CD4 + T Cell Proliferation and Development of Regulatory T Cells during Helicobacter pylori Infection. Infect. Immun. 2011, 79, 2737–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beswick, E. J. , Pinchuk, I. V, Earley, R. B., Schmitt, D. A. and Reyes, V. E. (2011) The Role of Gastric Epithelial Cell-Derived TGF-{beta} in Reduced CD4+ T Cell Proliferation and Development of Regulatory T Cells during Helicobacter pylori Infection 1. Infect. Immun 79, 2737–2745.
- Lundgren, A. , Stromberg, E., Sjoling, A., Lindholm, C., Enarsson, K., Edebo, A., Johnsson, E., Suri-Payer, E., Larsson, P., Rudin, A., et al. (2005) Mucosal FOXP3-expressing CD4+ CD25high regulatory T cells in Helicobacter pylori-infected patients. Infect. Immun 73, 523–531.
- Wang, S. K. , Zhu, H. F., He, B. S., Zhang, Z. Y., Chen, Z. T., Wang, Z. Z. and Wu, G. L. (2007) CagA+ H. pylori infection is associated with polarization of T helper cell immune responses in gastric carcinogenesis. World Journal of Gastroenterology : WJG, Baishideng Publishing Group Inc 13, 2923.
- Mestecky, J. The common mucosal immune system and current strategies for induction of immune responses in external secretions. J. Clin. Immunol. 1987, 7, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayar, R. , Shirvani, J. S., Hajian -Tilaki, K., Vosough, Z. and Ranaei, M. (2019) The negative association between inflammatory bowel disease and Helicobacter pylori seropositivity. Caspian J Intern Med, Caspian J Intern Med 10, 217–222.
- Castanõ-Rodríguez, N. , Kaakoush, N. O., Lee, W. S. and Mitchell, H. M. (2017) Dual role of Helicobacter and Campylobacter species in IBD: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Gut, BMJ Publishing Group 66, 235–249.
- Ewe, K.; Schwartz, S.; Petersen, S.; Press, A.G. Inflammation Does Not Decrease Intraluminal pH in Chronic Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1999, 44, 1434–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes, V. E. , Almanza, R. J. and Ye, G. (1998) Helicobacter pylori: A Trojan horse in the gastric environment? Mucosal Immunology Update 5, 68–70.
- Beswick, E. J. , Suarez, G. and Reyes, V. E. (2006) H. pylori and host interactions that influence pathogenesis. World J Gastroenterol 12.
- Suarez, G. , Reyes, V. E. and Beswick, E. J. (2006) Immune response to H. pylori. World J Gastroenterol 12.
- Reyes, V. E. , Suárez, G., Sierra, J. C. and Beswick, E. J. (2009) Helicobacter pylori. Vaccines for Biodefense and Emerging and Neglected Diseases.
- Alzahrani, S. , Lina, T. T., Gonzalez, J., Pinchuk, I. V., Beswick, E. J. and Reyes, V. E. (2014) Effect of Helicobacter pylori on gastric epithelial cells. World J Gastroenterol 20.
- Lina, T. T. , Alzahrani, S., Gonzalez, J., Pinchuk, I. V., Beswick, E. J. and Reyes, V. E. (2014) Immune evasion strategies used by Helicobacter pylori. World J Gastroenterol 20.
- Ha, N.-C.; Oh, S.-T.; Sung, J.Y.; Cha, K.A.; Lee, M.H.; Oh, B.-H. Supramolecular assembly and acid resistance of Helicobacter pylori urease. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2001, 8, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mobley, H. The role of Helicobacter pylori urease in the pathogenesis of gastritis and peptic ulceration. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 1996, 10, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- E Dunn, B.; Phadnis, S.H. Structure, function and localization of Helicobacter pylori urease. . 1999, 71, 63–73. [Google Scholar]
- E Dunn, B.; Vakil, N.B.; Schneider, B.G.; Miller, M.M.; Zitzer, J.B.; Peutz, T.; Phadnis, S.H. Localization of Helicobacter pylori urease and heat shock protein in human gastric biopsies. Infect. Immun. 1997, 65, 1181–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phadnis, S.H.; Parlow, M.H.; Levy, M.; Ilver, D.; Caulkins, C.M.; Connors, J.B.; E Dunn, B. Surface localization of Helicobacter pylori urease and a heat shock protein homolog requires bacterial autolysis. Infect. Immun. 1996, 64, 905–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.; Gunasena, H.; Cheng, Z.; Espejo, R.; Crowe, S.E.; Ernst, P.B.; Reyes, V.E. Helicobacter pylori Urease Binds to Class II MHC on Gastric Epithelial Cells and Induces Their Apoptosis. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 1918–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Crowe, S.E.; Behar, S.; Gunasena, H.; Ye, G.; Haeberle, H.; Van Houten, N.; Gourley, W.K.; Ernst, P.B.; Reyes, V.E. The Effect of Class II Major Histocompatibility Complex Expression on Adherence of Helicobacter pylori and Induction of Apoptosis in Gastric Epithelial Cells: A Mechanism for T Helper Cell Type 1–mediated Damage. J. Exp. Med. 1998, 187, 1659–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrera, C.; Espejo, R.; E Reyes, V. Differential glycosylation of MHC class II molecules on gastric epithelial cells: Implications in local immune responses. Hum. Immunol. 2002, 63, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X. J. , Gunasena, H., Gonzales, M., Almanza, R., Cheng, Z., Ye, G., Barrera, C., Crowe, S. E., Ernst, P. B. and Reyes, V. E. (1998) Class II MHC molecules on gastric epithelial cells act as receptors for Helicobacter pylori urease and signal apoptosis of the epithelium. FASEB Journal 12.
- Beswick, E. J. J. , Pinchuk, I. V. V, Minch, K., Suarez, G., Sierra, J. C. C., Yamaoka, Y. and Reyes, V. E. E. (2006) The Helicobacter pylori Urease B Subunit Binds to CD74 on Gastric Epithelial Cells and Induces NF-{kappa}B Activation and Interleukin-8 Production. Infect. Immun 74, 1148–1155.
- Beswick, E.J.; Bland, D.A.; Suarez, G.; Barrera, C.A.; Fan, X.; Reyes, V.E. Helicobacter pyloriBinds to CD74 on Gastric Epithelial Cells and Stimulates Interleukin-8 Production. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 2736–2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boren, T. , Falk, P., Roth, K. A., Larson, G. and Normark, S. (1993) Attachment of Helicobater pylori to human gastric epithelium mediated by blood group antigens. Science (1979) 262, 1892–1895.
- Sheu, B.-S.; Sheu, S.-M.; Yang, H.-B.; Huang, A.-H.; Wu, J.-J. Host gastric Lewis expression determines the bacterial density of Helicobacter pylori in babA2 genopositive infection. Gut 2003, 52, 927–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujimoto, S. , Olaniyi Ojo, O., Arnqvist, A., Yih Wu, J., Odenbreit, S., Haas, R., Graham, D. Y. and Yamaoka, Y. (2007) Helicobacter pylori BabA Expression, Gastric Mucosal Injury, and Clinical Outcome. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, NIH Public Access 5, 49.
- Sheu, S.-M.; Sheu, B.-S.; Chiang, W.-C.; Kao, C.-Y.; Wu, H.-M.; Yang, H.-B.; Wu, J.-J. H. pylori clinical isolates have diverse babAB genotype distributions over different topographic sites of stomach with correlation to clinical disease outcomes. BMC Microbiol. 2012, 12, 89–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaoka, Y. , Kwon, D. H. and Graham, D. Y. (2000) A M(r) 34,000 proinflammatory outer membrane protein (oipA) of Helicobacter pylori. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A 97, 7533–7538.
- Lu, H.; Wu, J.Y.; Beswick, E.J.; Ohno, T.; Odenbreit, S.; Haas, R.; Reyes, V.E.; Kita, M.; Graham, D.Y.; Yamaoka, Y. Functional and Intracellular Signaling Differences Associated with the Helicobacter pylori AlpAB Adhesin from Western and East Asian Strains. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 6242–6254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odenbreit, S.; Till, M.; Hofreuter, D.; Faller, G.; Haas, R. Genetic and functional characterization of the alpAB gene locus essential for the adhesion of Helicobacter pylori to human gastric tissue. Mol. Microbiol. 1999, 31, 1537–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odenbreit, S.; Faller, G.; Haas, R. Role of the AlpAB proteins and lipopolysaccharide in adhesion of Helicobacter pylori to human gastric tissue. Int. J. Med Microbiol. 2002, 292, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdavi, J. , Sondén, B. ( NIH Public Access 297, 573.
- Walz, A.; Odenbreit, S.; Mahdavi, J.; Borén, T.; Ruhl, S. Identification and characterization of binding properties of Helicobacter pylori by glycoconjugate arrays. Glycobiology 2005, 15, 700–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirmo, S. , Kelm, S., Schauer, R., Nilsson, B. and Wadström, T. (1996) Adhesion of Helicobacter pylori strains to α-2,3-linked sialic acids. Glycoconj J, Kluwer Academic Publishers 13, 1005–1011.
- Backert, S. , Tegtmeyer, N. and Fischer, W. (2015) Composition, structure and function of the Helicobacter pylori cag pathogenicity island encoded type IV secretion system. Future Microbiol 10.
- Hatakeyama, M. Structure and function of Helicobacter pylori CagA, the first-identified bacterial protein involved in human cancer. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B 2017, 93, 196–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan-Türköz, B. , Jiménez-Soto, L. F., Dian, C., Ertl, C., Remaut, H., Louche, A., Tosi, T., Haas, R. and Terradot, L. (2012) Structural insights into Helicobacter pylori oncoprotein CagA interaction with β1 integrin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109.
- Jiménez-Soto, L.F.; Kutter, S.; Sewald, X.; Ertl, C.; Weiss, E.; Kapp, U.; Rohde, M.; Pirch, T.; Jung, K.; Retta, S.F.; et al. Helicobacter pylori Type IV Secretion Apparatus Exploits β1 Integrin in a Novel RGD-Independent Manner. PLOS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatakeyama, M. Helicobacter pylori CagA and Gastric Cancer: A Paradigm for Hit-and-Run Carcinogenesis. Cell Host Microbe 2014, 15, 306–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higashi, H.; Tsutsumi, R.; Fujita, A.; Yamazaki, S.; Asaka, M.; Azuma, T.; Hatakeyama, M. Biological activity of the Helicobacter pylori virulence factor CagA is determined by variation in the tyrosine phosphorylation sites. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2002, 99, 14428–14433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueiredo, C. , Machado, J. C. and Yamaoka, Y. (2005) Pathogenesis of Helicobacter pylori Infection. Helicobacter 10 Suppl 1, 14–20.
- Churin, Y.; Al-Ghoul, L.; Kepp, O.; Meyer, T.F.; Birchmeier, W.; Naumann, M. Helicobacter pylori CagA protein targets the c-Met receptor and enhances the motogenic response. J. Cell Biol. 2003, 161, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, M.; Mimuro, H.; Kiga, K.; Fukumatsu, M.; Ishijima, N.; Morikawa, H.; Nagai, S.; Koyasu, S.; Gilman, R.H.; Kersulyte, D.; et al. Helicobacter pylori CagA Phosphorylation-Independent Function in Epithelial Proliferation and Inflammation. Cell Host Microbe 2009, 5, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mimuro, H.; Suzuki, T.; Tanaka, J.; Asahi, M.; Haas, R.; Sasakawa, C. Grb2 Is a Key Mediator of Helicobacter pylori CagA Protein Activities. Mol. Cell 2002, 10, 745–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco, A. T. , Johnston, E., Krishna, U., Yamaoka, Y., Israel, D. A., Nagy, T. A., Wroblewski, L. E., Piazuelo, M. B., Correa, P. and Peek Jr., R. M. (2008) Regulation of gastric carcinogenesis by Helicobacter pylori virulence factors. Cancer Res 68, 379–387.
- Saadat, I. , Higashi, H., Obuse, C., Umeda, M., Murata-Kamiya, N., Saito, Y., Lu, H., Ohnishi, N., Azuma, T., Suzuki, A., et al. (2007) Helicobacter pylori CagA targets PAR1/MARK kinase to disrupt epithelial cell polarity. Nature 447, 330–333.
- Murata-Kamiya, N. , Kurashima, Y., Teishikata, Y., Yamahashi, Y., Saito, Y., Higashi, H., Aburatani, H., Akiyama, T., Peek Jr., R. M., Azuma, T., et al. (2007) Helicobacter pylori CagA interacts with E-cadherin and deregulates the beta-catenin signal that promotes intestinal transdifferentiation in gastric epithelial cells. Oncogene.
- Palrasu, M.; Zaika, E.; Paulrasu, K.; Gokulan, R.C.; Suarez, G.; Que, J.; El-Rifai, W.; Peek, R.M.; Garcia-Buitrago, M.; Zaika, A.I. Helicobacter pylori pathogen inhibits cellular responses to oncogenic stress and apoptosis. PLOS Pathog. 2022, 18, e1010628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohnishi, N.; Yuasa, H.; Tanaka, S.; Sawa, H.; Miura, M.; Matsui, A.; Higashi, H.; Musashi, M.; Iwabuchi, K.; Suzuki, M.; et al. Transgenic expression of Helicobacter pylori CagA induces gastrointestinal and hematopoietic neoplasms in mouse. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 1003–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viala, J.; Chaput, C.; Boneca, I.G.; Cardona, A.; E Girardin, S.; Moran, A.P.; Athman, R.; Mémet, S.; Huerre, M.R.; Coyle, A.J.; et al. Nod1 responds to peptidoglycan delivered by the Helicobacter pylori cag pathogenicity island. Nat. Immunol. 2004, 5, 1166–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grubman, A. , Kaparakis, M. ( regulates direct killing of Helicobacter pylori by antimicrobial peptides 94. Cell Microbiol 12, 626–639.
- Suarez, G.; Romero-Gallo, J.; Piazuelo, M.B.; Wang, G.; Maier, R.J.; Forsberg, L.S.; Azadi, P.; Gomez, M.A.; Correa, P.; Peek, R.M. Modification of Helicobacter pylori Peptidoglycan Enhances NOD1 Activation and Promotes Cancer of the Stomach. Cancer Res 2015, 75, 1749–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorbara, M.T.; Ellison, L.K.; Ramjeet, M.; Travassos, L.H.; Jones, N.L.; Girardin, S.E.; Philpott, D.J. The Protein ATG16L1 Suppresses Inflammatory Cytokines Induced by the Intracellular Sensors Nod1 and Nod2 in an Autophagy-Independent Manner. Immunity 2013, 39, 858–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, C. G. , Feng, Y., Xu, S., Taylor, N. S., Kinsel, M., Dewhirst, F. E., Paster, B. J., Greenwell, M., Levine, G., Rogers, A., et al. (2002) Helicobacter cetorum sp. nov., a Urease-positive Helicobacter species isolated from dolphins and whales. J Clin Microbiol 40.
- Reyrat, J.-M.; Lanzavecchia, S.; Lupetti, P.; de Bernard, M.; Pagliaccia, C.; Pelicic, V.; Charrel, M.; Ulivieri, C.; Norais, N.; Ji, X.; et al. 3D imaging of the 58 kda cell binding subunit of the Helicobacter pylori cytotoxin. J. Mol. Biol. 1999, 290, 459–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClain, M.S.; Iwamoto, H.; Cao, P.; Vinion-Dubiel, A.D.; Li, Y.; Szabo, G.; Shao, Z.; Cover, T.L. Essential Role of a GXXXG Motif for Membrane Channel Formation by Helicobacter pylori Vacuolating Toxin. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 12101–12108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Rivera, C.; Gangwer, K.A.; McClain, M.S.; Eli, I.M.; Chambers, M.G.; Ohi, M.D.; Lacy, D.B.; Cover, T.L. Reconstitution of Helicobacter pylori VacA Toxin from Purified Components. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 5743–5752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, V.J.; Ivie, S.E.; McClain, M.S.; Cover, T.L. Functional Properties of the p33 and p55 Domains of the Helicobacter pylori Vacuolating Cytotoxin. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 21107–21114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, V.R.; Patel, H.K.; Kostolansky, S.S.; Ballivian, R.A.; Eichberg, J.; Blanke, S.R. Sphingomyelin Functions as a Novel Receptor for Helicobacter pylori VacA. PLOS Pathog. 2008, 4, e1000073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricci, V. , Galmiche, A., Doye, A., Necchi, V., Solcia, E. and Boquet, P. (2000) High cell sensitivity to Helicobacter pylori VacA toxin depends on a GPI-anchored protein and is not blocked by inhibition of the clathrin-mediated pathway of endocytosis. Mol Biol Cell 11.
- Oldani, A.; Cormont, M.; Hofman, V.; Chiozzi, V.; Oregioni, O.; Canonici, A.; Sciullo, A.; Sommi, P.; Fabbri, A.; Ricci, V.; et al. Helicobacter pylori Counteracts the Apoptotic Action of Its VacA Toxin by Injecting the CagA Protein into Gastric Epithelial Cells. PLOS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauthier, N. C. , Monzo, P., Gonzalez, T., Doye, A., Oldani, A., Gounon, P., Ricci, V., Cormont, M. and Boquet, P. (2007) Early endosomes associated with dynamic F-actin structures are required for late trafficking of H. pylori VacA toxin. Journal of Cell Biology 177.
- Yamasaki, E. , Wada, A., Kumatori, A., Nakagawa, I., Funao, J., Nakayama, M., Hisatsune, J., Kimura, M., Moss, J. and Hirayama, T. (2006) Helicobacter pylori vacuolating cytotoxin induces activation of the proapoptotic proteins Bax and Bak, leading to cytochrome c release and cell death, independent of vacuolation. J Biol Chem, J Biol Chem 281, 11250–11259.
- Galmiche, A.; Rassow, J.; Doye, A.; Cagnol, S.; Chambard, J.; Contamin, S.; de Thillot, V.; Just, I.; Ricci, V.; Solcia, E.; et al. The N-terminal 34 kDa fragment of Helicobacter pylori vacuolating cytotoxin targets mitochondria and induces cytochrome c release. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 6361–6370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, P.; Luo, Z.-Q.; Blanke, S.R. Helicobacter pylori vacuolating cytotoxin A (VacA) engages the mitochondrial fission machinery to induce host cell death. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2011, 108, 16032–16037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atherton, J. C. , Cao, P., Peek, R. M., Tummuru, M. K. R., Blaser, M. J. and Cover, T. L. (1995) Mosaicism in vacuolating cytotoxin alleles of Helicobacter pylori. Association of specific vacA types with cytotoxin production and peptic ulceration. J Biol Chem, J Biol Chem 270, 17771–17777.
- Bakhti, S. Z. , Latifi-Navid, S., Mohammadi, S., Zahri, S., Bakhti, F. S., Feizi, F., Yazdanbod, A. and Siavoshi, F. (2016) Relevance of Helicobacter pylori vacA 3’-end Region Polymorphism to Gastric Cancer. Helicobacter, Helicobacter 21, 305–316.
- Soyfoo, D.M.; Doomah, Y.H.; Xu, D.; Zhang, C.; Sang, H.-M.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Zhang, G.-X.; Jiang, J.-X.; Xu, S.-F. New genotypes of Helicobacter Pylori VacA d-region identified from global strains. BMC Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClain, M. S. , Cao, P., Iwamoto, H., Vinion-Dubiel, A. D., Szabo, G., Shao, Z. and Cover, T. L. (2001) A 12-amino-acid segment, present in type s2 but not type s1 Helicobacter pylori VacA proteins, abolishes cytotoxin activity and alters membrane channel formation. J Bacteriol 183.
- Wang, H.-J.; Kuo, C.-H.; Yeh, A.A.M.; Chang, P.C.L.; Wang, W.-C. Vacuolating Toxin Production in Clinical Isolates of Helicobacter pylori with Different vacA Genotypes. J. Infect. Dis. 1998, 178, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basso, D.; Zambon, C.; Letley, D.P.; Stranges, A.; Marchet, A.; Rhead, J.L.; Schiavon, S.; Guariso, G.; Ceroti, M.; Nitti, D.; et al. Clinical Relevance of Helicobacter pylori cagA and vacA Gene Polymorphisms. Gastroenterology 2008, 135, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogueira, C.; Figueiredo, C.; Carneiro, F.; Gomes, A.T.; Barreira, R.; Figueira, P.; Salgado, C.; Belo, L.; Peixoto, A.; Bravo, J.C.; et al. Helicobacter pylori Genotypes May Determine Gastric Histopathology. Am. J. Pathol. 2001, 158, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugimoto, M.; Zali, M.R.; Yamaoka, Y. The association of vacA genotypes and Helicobacter pylori-related gastroduodenal diseases in the Middle East. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2009, 28, 1227–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, W.-L.; Yeh, Y.-C.; Sheu, B.-S. The impacts of H. pylori virulence factors on the development of gastroduodenal diseases. J. Biomed. Sci. 2018, 25, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, C.; Olivares, A.; Torres, E.; Yilmaz, O.; Cohen, H.; Perez-Perez, G. Diversity of VacA Intermediate Region among Helicobacter pylori Strains from Several Regions of the World. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 690–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, X.; Fernandez, T.; Burroni, D.; Pagliaccia, C.; Atherton, J.C.; Reyrat, J.-M.; Rappuoli, R.; Telford, J.L. Cell Specificity of Helicobacter pylori Cytotoxin Is Determined by a Short Region in the Polymorphic Midregion. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 3754–3757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, G.; Forster, S.; Irving, A.; Tate, M.; Ferrero, R.L.; Hertzog, P.; Frøkiær, H.; Kaparakis-Liaskos, M. Helicobacter pylori VacA Suppresses Lactobacillus acidophilus-Induced Interferon Beta Signaling in Macrophages via Alterations in the Endocytic Pathway. Mbio 2013, 4, e00609–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, P.-Y.; Jones, N.L. Helicobacter pylori strains expressing the vacuolating cytotoxin interrupt phagosome maturation in macrophages by recruiting and retaining TACO (coronin 1) protein. Cell. Microbiol. 2003, 5, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, M. K. , Joo, S. K., Jin, Y. L., Kim, Y. J., Youn, H. J., In, Y. K., Young, J. C., Oh, Y. K., Kim, N., Hyun, C. J., et al. (2007) Vacuolating Cytotoxin in Helicobacter pylori Water-Soluble Proteins Upregulates Chemokine Expression in Human Eosinophils via Ca2+ Influx, Mitochondrial Reactive Oxygen Intermediates, and NF-κB Activation. Infect Immun, American Society for Microbiology (ASM) 75, 3373.
- Supajatura, V.; Ushio, H.; Wada, A.; Yahiro, K.; Okumura, K.; Ogawa, H.; Hirayama, T.; Ra, C. Cutting Edge: VacA, a Vacuolating Cytotoxin of Helicobacter pylori, Directly Activates Mast Cells for Migration and Production of Proinflammatory Cytokines. J. Immunol. 2002, 168, 2603–2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oertli, M. , Noben, M., Engler, D. B., Semper, R. P., Reuter, S., Maxeiner, J., Gerhard, M., Taube, C. and Muller, A. (2013) Helicobacter pylori gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase and vacuolating cytotoxin promote gastric persistence and immune tolerance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A 110, 3047–3052.
- Boncristiano, M.; Paccani, S.R.; Barone, S.; Ulivieri, C.; Patrussi, L.; Ilver, D.; Amedei, A.; D’Elios, M.M.; Telford, J.L.; Baldari, C.T. The Helicobacter pylori Vacuolating Toxin Inhibits T Cell Activation by Two Independent Mechanisms. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 198, 1887–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebert, B.; Fischer, W.; Weiss, E.; Hoffmann, R.; Haas, R. Helicobacter pyloriVacuolating Cytotoxin Inhibits T Lymphocyte Activation. Science 2003, 301, 1099–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molinari, M.; Salio, M.; Galli, C.; Norais, N.; Rappuoli, R.; Lanzavecchia, A.; Montecucco, C. Selective Inhibition of Ii-dependent Antigen Presentation by Helicobacter pylori Toxin VacA. J. Exp. Med. 1998, 187, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, L.-A.H.; Schlesinger, L.S.; Kang, B. Virulent Strains of Helicobacter pylori Demonstrate Delayed Phagocytosis and Stimulate Homotypic Phagosome Fusion in Macrophages. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 191, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanotti, G.; Papinutto, E.; Dundon, W.G.; Battistutta, R.; Seveso, M.; Del Giudice, G.; Rappuoli, R.; Montecucco, C. Structure of the Neutrophil-activating Protein from Helicobacter pylori. J. Mol. Biol. 2002, 323, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satin, B. , Del, G. G., Della V, B., Dusi, S., Laudanna, C., Tonello, F., Kelleher, D., Rappuoli, R., Montecucco, C. and Rossi, F. (2000) The neutrophil-activating protein (HP-NAP) of Helicobacter pylori is a protective antigen and a major virulence factor. J. Exp. Med 191, 1467–1476.
- Evans Jr., D. J., Evans, D. G., Takemura, T., Nakano, H., Lampert, H. C., Graham, D. Y., Granger, D. N. and Kvietys, P. R. (1995) Characterization of a Helicobacter pylori neutrophil-activating protein. Infect. Immun 63, 2213–2220.
- Marnett, L. J. (2000) Oxyradicals and DNA damage. Carcinogenesis.
- Fu, H. W. (2014) Helicobacter pylori neutrophil-activating protein: From molecular pathogenesis to clinical applications. World J Gastroenterol 20.
- Montemurro, P.; Nishioka, H.; Dundon, W.G.; de Bernard, M.; Del Giudice, G.; Rappuoli, R.; Montecucco, C. The neutrophil-activating protein (HP-NAP) of Helicobacter pylori is a potent stimulant of mast cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 2002, 32, 671–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polenghi, A.; Bossi, F.; Fischetti, F.; Durigutto, P.; Cabrelle, A.; Tamassia, N.; Cassatella, M.A.; Montecucco, C.; Tedesco, F.; de Bernard, M. The Neutrophil-Activating Protein of Helicobacter pylori Crosses Endothelia to Promote Neutrophil Adhesion In Vivo. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 1312–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, S.-H.; Hong, Z.-W.; Chen, C.-C.; Chang, H.-W.; Fu, H.-W. Helicobacter pylori Neutrophil-Activating Protein Directly Interacts with and Activates Toll-like Receptor 2 to Induce the Secretion of Interleukin-8 from Neutrophils and ATRA-Induced Differentiated HL-60 Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castanheira, F.V.S.; Kubes, P. Neutrophils and NETs in modulating acute and chronic inflammation. Blood 2019, 133, 2178–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oleastro, M.; Ménard, A. The Role of Helicobacter pylori Outer Membrane Proteins in Adherence and Pathogenesis. Biology 2013, 2, 1110–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, M.; Jin, C.; Yu, D.; Eriksson, F.; Essand, M. Vector-Encoded Helicobacter pylori Neutrophil-Activating Protein Promotes Maturation of Dendritic Cells with Th1 Polarization and Improved Migration. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 2287–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, M. , Bolz, C., Revez, J., Javed, S., El-Najjar, N., Anderl, F., Hyytiäinen, H., Vuorela, P., Gerhard, M. and Hänninen, M. L. (2012) Evidence for conserved function of γ-glutamyltranspeptidase in Helicobacter genus. PLoS One 7.
- Suzuki, H.; Kumagai, H. [Gamma-glutamyltranspeptidase from Escherichia coli K-12]. . 1989, 61, 491–6. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shibayama, K. , Wachino, J. I., Arakawa, Y., Saidijam, M., Rutherford, N. G. and Henderson, P. J. F. (2007) Metabolism of glutamine and glutathione via gamma-glutamyltranspeptidase and glutamate transport in Helicobacter pylori: possible significance in the pathophysiology of the organism. Mol Microbiol, Mol Microbiol 64, 396–406.
- Shibayama, K. , Wachino, J. I., Arakawa, Y., Saidijam, M., Rutherford, N. G. and Henderson, P. J. F. (2007) Metabolism of glutamine and glutathione via γ-glutamyltranspeptidase and glutamate transport in Helicobacter pylori: Possible significance in the pathophysiology of the organism. Mol Microbiol 64, 396–406.
- McGovern, K. J. , Blanchard, T. G., Gutierrez, J. A., Czinn, S. J., Krakowka, S. and Youngman, P. (2001) γ-glutamyltransferase is a Helicobacter pylori virulence factor but is not essential for colonization. Infect Immun 69.
- Chevalier, C. , Thiberge, J. M., Ferrero, R. L. and Labigne, A. (1999) Essential role of Helicobacter pylori gamma-glutamyltranspeptidase for the colonization of the gastric mucosa of mice. Mol Microbiol, Mol Microbiol 31, 1359–1372.
- Kim, K. M. , Lee, S. G., Park, M. G., Song, J. Y., Kang, H. L., Lee, W. K., Cho, M. J., Rhee, K. H., Youn, H. S. and Baik, S. C. (2007) Gamma-glutamyltranspeptidase of Helicobacter pylori induces mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in AGS cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, Biochem Biophys Res Commun 355, 562–567.
- Valenzuela, M.; Bravo, D.; Canales, J.; Sanhueza, C.; Díaz, N.; Almarza, O.; Toledo, H.; Quest, A.F.G. Helicobacter pylori–Induced Loss of Survivin and Gastric Cell Viability Is Attributable to Secreted Bacterial Gamma-Glutamyl Transpeptidase Activity. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 208, 1131–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-M.; Lee, S.-G.; Kim, J.-M.; Kim, D.-S.; Song, J.-Y.; Kang, H.-L.; Lee, W.-K.; Cho, M.-J.; Rhee, K.-H.; Youn, H.-S.; et al. Helicobacter pylori γ-glutamyltranspeptidase induces cell cycle arrest at the G1-S phase transition. J. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, M.; Ling, S.S.M.; Lui, S.Y.; Yeoh, K.G.; Ho, B. Helicobacter pylori γ-Glutamyl Transpeptidase Is a Pathogenic Factor in the Development of Peptic Ulcer Disease. Gastroenterology 2010, 139, 564–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busiello, I. , Acquaviva, R., Di Popolo, A., Blanchard, T. G., Ricci, V., Romano, M. and Zarrilli, R. (2004) Helicobacter pyloriγ-glutamyltranspeptidase upregulates COX-2 and EGF-related peptide expression in human gastric cells. Cell Microbiol, John Wiley & Sons, Ltd 6, 255–267.
- Nagy, T.A.; Frey, M.R.; Yan, F.; Israel, D.A.; Polk, D.B.; Peek, R.M. Helicobacter pyloriRegulates Cellular Migration and Apoptosis by Activation of Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase Signaling. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 199, 641–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murayama, Y.; Miyagawa, J.; Shinomura, Y.; Kanayama, S.; Isozaki, K.; Yamamori, K.; Mizuno, H.; Ishiguro, S.; Kiyohara, T.; Miyazaki, Y.; et al. Significance of the association between heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor and CD9 in human gastric cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2002, 98, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, F. , Grabowska, A. M., Clarke, P. A., Whelband, E., Robinson, K., Argent, R. H., Tobias, A., Kumari, R., Atherton, J. C. and Watson, S. A. (2010) Helicobacter pylori potentiates epithelial:mesenchymal transition in gastric cancer: Links to soluble HB-EGF, gastrin and matrix metalloproteinase-7. Gut 59.
- Shi, H. , Qi, C., Meng, L., Yao, H., Jiang, C., Fan, M., Zhang, Q., Hou, X. and Lin, R. (2021) Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells promote Helicobacter pylori-associated gastric cancer progression by secreting thrombospondin-2. Cell Prolif 54.
- Wang, Z.; Wang, W.; Shi, H.; Meng, L.; Jiang, X.; Pang, S.; Fan, M.; Lin, R. Gamma-glutamyltransferase of Helicobacter pylori alters the proliferation, migration, and pluripotency of mesenchymal stem cells by affecting metabolism and methylation status. J. Microbiol. 2022, 60, 627–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, L.; Shi, H.; Wang, Z.; Fan, M.; Pang, S.; Lin, R. The Gamma-glutamyltransferase gene of Helicobacter pylori can promote gastric carcinogenesis by activating Wnt signal pathway through up-regulating TET1. Life Sci. 2021, 267, 118921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmees, C. , Prinz, C., Treptau, T., Rad, R., Hengst, L., Voland, P., Bauer, S., Brenner, L., Schmid, R. M. and Gerhard, M. (2007) Inhibition of T-cell proliferation by Helicobacter pylori gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase. Gastroenterology 132, 1820–1833.
- Gerhard, M.; Schmees, C.; Voland, P.; Endres, N.; Sander, M.; Reindl, W.; Rad, R.; Oelsner, M.; Decker, T.; Mempel, M.; et al. A Secreted Low--Molecular-Weight Protein From Helicobacter pylori Induces Cell-Cycle Arrest of T Cells. Gastroenterology 2005, 128, 1327–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fassi Fehri, L. , Koch, M., Belogolova, E., Khalil, H., Bolz, C., Kalali, B., Mollenkopf, H. J., Beigier-Bompadre, M., Karlas, A., Schneider, T., et al. (2010) Helicobacter pylori induces miR-155 in T cells in a cAMP-Foxp3-dependent manner. PLoS One 5.
- Hori, S.; Nomura, T.; Sakaguchi, S. Control of Regulatory T Cell Development by the Transcription Factor Foxp3. Science 2003, 299, 1057–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandulski, A. , Wex, T., Kuester, D., Peitz, U., Gebert, I., Roessner, A. and Malfertheiner, P. (2008) Naturally occurring regulatory T cells (CD4+, CD25high, FOXP3+) in the antrum and cardia are associated with higher H. pylori colonization and increased gene expression of TGF-beta1. Helicobacter, Helicobacter 13, 295–303.
- Ohue, Y. and Nishikawa, H. (2019) Regulatory T (Treg) cells in cancer: Can Treg cells be a new therapeutic target? Cancer Sci., Division of Cancer Immunology, Research Institute/Exploratory Oncology Research & Clinical Trial Center (EPOC), National Cancer Center, Tokyo, Japan Division of Cancer Immunology, Research Institute/Exploratory Oncology Research & Clinical Trial Center (E 110, 2080–2089.
- Lina, T. T. , Alzahrani, S., House, J., Yamaoka, Y., Sharpe, A. H., Rampy, B. A., Pinchuk, I. V. and Reyes, V. E. (2015) Helicobacter pylori cag pathogenicity island’s role in B7-H1 induction and immune evasion. PLoS One 10.
- Das, S.; Suarez, G.; Beswick, E.J.; Sierra, J.C.; Graham, D.Y.; Reyes, V.E. Expression of B7-H1 on Gastric Epithelial Cells: Its Potential Role in Regulating T Cells during Helicobacter pylori Infection. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 3000–3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beswick, E. J. J. , Pinchuk, I. V. V, Das, S., Powell, D. W. W. and Reyes, V. E. E. (2007) B7-H1 Expression on Gastric Epithelial Cells after Helicobacter pylori Exposure Promotes the Development of CD4+ CD25+ FoxP3+ Regulatory T Cells. Infect. Immun 75, 4334–4341.
- Lina, T. T. , Pinchuk, I. V., House, J., Yamaoka, Y., Graham, D. Y., Beswick, E. J. and Reyes, V. E. (2013) CagA-dependent downregulation of B7-H2 expression on gastric mucosa and inhibition of Th17 responses during Helicobacter pylori infection. Journal of Immunology 191.
- Hou, J.; Yu, Z.; Xiang, R.; Li, C.; Wang, L.; Chen, S.; Li, Q.; Chen, M.; Wang, L. Correlation between infiltration of FOXP3+ regulatory T cells and expression of B7-H1 in the tumor tissues of gastric cancer. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2014, 96, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shigemori, T.; Toiyama, Y.; Okugawa, Y.; Yamamoto, A.; Yin, C.; Narumi, A.; Ichikawa, T.; Ide, S.; Shimura, T.; Fujikawa, H.; et al. Soluble PD-L1 Expression in Circulation as a Predictive Marker for Recurrence and Prognosis in Gastric Cancer: Direct Comparison of the Clinical Burden Between Tissue and Serum PD-L1 Expression. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2018, 26, 876–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Böger, C. , Behrens, H. M., Krüger, S., Röcken, C., Boger, C., Behrens, H. M., Kruger, S. and Rocken, C. (2017) The novel negative checkpoint regulator VISTA is expressed in gastric carcinoma and associated with PD-L1/PD-1: A future perspective for a combined gastric cancer therapy? Oncoimmunology, Taylor and Francis Inc., Department of Pathology, Christian-Albrechts-University, Kiel, Germany Department of Pathology, Christian-Albrechts-University, Kiel, Germany Department of Pathology, Christian-Albrechts-University, Kiel, Germany Department of Pathology, Christian-Albrech 6, e1293215.
- Lina, T.T.; Gonzalez, J.; Pinchuk, I.V.; Beswick, E.J.; Reyes, V.E. Helicobacter pylori Elicits B7-H3 Expression on Gastric Epithelial Cells: Implications in Local T Cell Regulation and Subset Development During Infection. Clin. Oncol. Res. 2019, 2, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).



