Submitted:
24 April 2023
Posted:
25 April 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
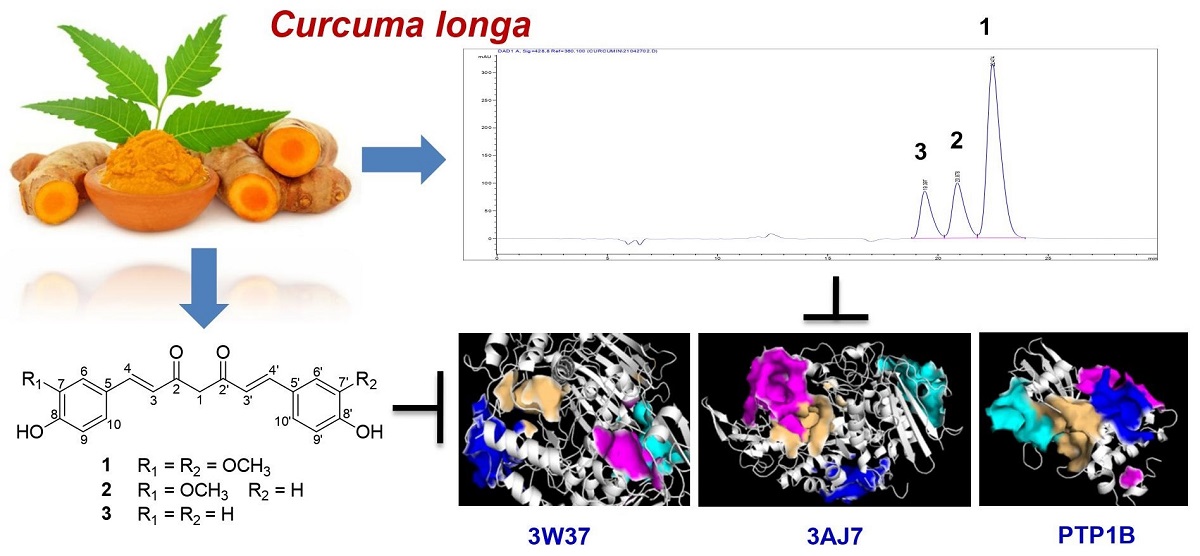
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Experimental Results
2.2. Computational Studies
| Compounds | 3W37 | 3AJ7 | PTP1B | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Site 1 | Site 2 | Site 3 | Site 4 | Site 1 | Site 2 | Site 3 | Site 4 | Site 1 | Site 2 | Site 3 | Site 4 | |
| 1 | -4.49 | -12.36 | -8.38 | -7.42 | -9.98 | -9.09 | -10.65 | -8.51 | -7.47 | -8.06 | -9.57 | -8.12 |
| 2 | -5.29 | -12.16 | -7.50 | -7.42 | -9.80 | -9.06 | -9.99 | -9.58 | -6.85 | -7.87 | -8.93 | -7.49 |
| 3 | -6.43 | -11.14 | -7.63 | -6.42 | -9.04 | -7.76 | -10.60 | -9.90 | -6.47 | -8.27 | -8.09 | -7.52 |
| Emodin | -4.65 | -6.99 | -6.25 | -5.83 | -7.53 | -7.16 | -7.90 | -7.74 | -6.03 | -7.07 | -11.31 | -5.51 |
| Ursolic acid | -5.27 | -7.36 | -3.70 | -6.20 | -8.81 | -8.01 | -7.68 | -8.80 | -7.43 | -7.28 | -12.37 | -5.98 |
| Acarbose | -6.61 | -12.22 | -6.06 | -12.78 | -13.15 | -12.46 | -12.72 | -13.24 | -12.22 | -8.60 | -12.75 | -10.59 |
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experimental Procedures
3.2. Plant Material
3.3. Extraction and Isolation
3.4. Spectral and Physical Data of Isolates
3.5. Inhibitory Assay on PTP1B
3.6. Inhibitory Assay on α-Glucosidase
3.7. Molecular Docking Studies
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Preethi, K.A.; Selvakumar, S.C.; Sekar, D. Diagnostic and Therapeutic Application of Exosomal microRNAs Inducing Inflammation in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2022, 42, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muntean, C.; Starcea, I.M.; Banescu, C. Diabetic kidney disease in pediatric patients: A current review. World J. Diabetes 2022, 13, 587–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, Z.J.; Yeh, J.M.; Reddy, C.L.; Gomber, A.; Ross, C.; Rittiphairoj, T.; Manne-Goehler, J.; Abdalla, A.T.; Abdullah, M.A.; Ahmed, A.; Ankotche, A.; Azad, K.; Bahendeka, S.; Baldé, N.; Jain, S.M.; Kalobu, J.C.; Karekezi, C.; Kol, H.; Prasannakumar, K.M.; Leik, S.K.; Mbanya, J.C.; Mbaye, M.N.; Niang, B.; Paturi, V.R.; Raghupathy, P.; Ramaiya, K.; Sethi, B.; Zabeen, B.; Atun, R. Estimating the total incidence of type 1 diabetes in children and adolescents aged 0-19 years from 1990 to 2050: a global simulation-based analysis. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2022, 10, 848–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Mathieu, C.; Berthelet, J.; Zhang, W.; Dupret, J.M.; Rodrigues Lima, F. Human Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B (PTP1B): From Structure to Clinical Inhibitor Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Dodd, G.T.; Tiganis, T. Protein Tyrosine Phosphatases in Hypothalamic Insulin and Leptin Signaling. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 36, 661–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behl, T.; Gupta, A.; Sehgal, A.; Albarrati, A.; Albratty, M.; Meraya, A.M.; Najmi, A.; Bhatia, S.; Bungau, S. Exploring protein tyrosine phosphatases (PTP) and PTP-1B inhibitors in management of diabetes mellitus. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 153, 113405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, M.; Gupta, S.J.; Chaudhary, A.; Garg, V.K. Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B inhibitors as antidiabetic agents - A brief review. Bioorg. Chem. 2017, 70, 267–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandi, S.; Saxena, M. Potential Inhibitors of Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase (PTP1B) Enzyme: Promising Target for Type-II Diabetes Mellitus. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2020, 20, 2692–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirsh, A.J.; Yao, S.Y.; Young, J.D.; Cheeseman, C.I. Inhibition of glucose absorption in the rat jejunum: A novel action of alpha-D-glucosidase inhibitors. Gastroenterology 1997, 113, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, H.; Honnda, Y. Amylases. In Encyclopedia of Microbiology, 3rd ed.; Academic Press, 2009; pp. 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Machado, G.C.; Eyles, J.P.; Ravi, V.; Hunter, D.J. Dietary supplements for treating osteoarthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Sports Med. 2018, 52, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bich, D.H.; Chung, D.Q.; Chuong, B.X.; Dong, N.T.; Dam, D.T.; Hien, P.V.; Lo, V.N.; Mai, P.D.; Man, P.K.; Nhu, D.T.; Tap, N.; Toan, T. The medicinal plants and medicinal animals in Vietnam, 1st ed.; Science and Technology Publishing House: Hanoi, Vietnam, 2006; pp. 383–391. [Google Scholar]
- Tung, B.T.; Nham, D.T.; Hai, N.T.; Thu, D.K. Curcuma longa, the polyphenolic curcumin compound and pharmacological effects on liver. Dietary Interventions in Liver Disease; Academic Press: London, England, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Soleimani, V.; Sahebkar, A.; Hosseinzadeh, H. Turmeric (Curcuma longa) and its major constituent (curcumin) as nontoxic and safe substances. Phytother. Res. 2018, 32, 985–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karłowicz-Bodalska, K.; Han, S.; Freier, J.; Smolenski, M.; Bodalska, A. Curcuma longa as medicinal herb in the treatment of diabetic complications. Acta Pol. Pharm. 2017, 74, 605–610. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.M.; Li, Y.C.; Kong, L.D.; Hu, Q.H. Curcumin inhibits hepatic protein-tyrosine phosphatase 1B and prevents hypertriglyceridemia and hepatic steatosis in fructose-fed rats. Hepatology. 2010, 51, 1555–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostrzewa, T.; Przychodzen, P.; Gorska-Ponikowska, M.; Kuban-Jankowska, A. Curcumin and Cinnamaldehyde as PTP1B Inhibitors With Antidiabetic and Anticancer Potential. Anticancer Res. 2019, 39, 745–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostrzewa, T.; Wołosewicz, K.; Jamrozik, M.; Drzeżdżon, J.; Siemińska, J.; Jacewicz, D.; Górska-Ponikowska, M.; Kołaczkowski, M.; Łaźny, R.; Kuban-Jankowska, A. Curcumin and Its New Derivatives: Correlation between Cytotoxicity against Breast Cancer Cell Lines, Degradation of PTP1B Phosphatase and ROS Generation. Int J Mol Sci. 2021, 22, 10368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozkurt, O.; Kocaadam-Bozkurt, B.; Yildiran, H. Effects of curcumin, a bioactive component of turmeric, on type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications: an updated review. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 11999–12010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Yang, M.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, S.; Zhang, X. Curcumin protects islet beta cells from streptozotocin-induced type 2 diabetes mellitus injury via its antioxidative effects. Endokrynol Pol. 2022, 73, 942–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.Q.; Gu, T.T.; Wang, W.; Song, L.; Chen, T.Y.; Xue, Q.C.; Zhou, F.; Li, J.M.; Kong, L.D. Curcumin protects against fructose-induced podocyte insulin signaling impairment through upregulation of miR-206. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2015, 59, 2355–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- To, D.C.; Bui, T.Q.; Nhung, N.T.A.; Tran, Q.T.; Do, T.T.; Tran, M.H.; Hien, P.P.; Ngu, T.N.; Quy, P.T.; Nguyen, T.H.; Nguyen, H.T.; Nguyen, T.D.; Nguyen, P.H. On the Inhibitability of Natural Products Isolated from Tetradium ruticarpum towards Tyrosine Phosphatase 1B (PTP1B) and α-glucosidase (3W37): an in vitro and in silico Study. Molecules 2021, 26, 3691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galano, A.; Mazzone, G.; Alvarez-Diduk, R.; Marino, T.; Alvarez-Idaboy, J.R.; Russo, N. Free radicals induced oxidative stress at a molecular level: the current status, challenges and perspectives of computational chemistry based protocols. J. Mex. Chem. Soc. 2015, 7, 335–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galano, A.; Alvarez-Idaboy, J.R. Kinetics of Radical-Molecule Reactions in Aqueous Solution: A Benchmark Study of the Performance of Density Functional Methods. J. Comput. Chem. 2014, 35, 2019–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galano, A.; Alvarez-Idaboy, J.R. A Computational Methodology for Accurate Predictions of Rate Constants in Solution: Application to the Assessment of Primary Antioxidant Activity. J. Comput. Chem. 2013, 34, 2430–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tagami, T.; Yamashita, K.; Okuyama, M.; Mori, H.; Yao, M.; Kimura, A. Molecular basis for the recognition of long-chain substrates by plant & alpha-glucosidase. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 19296–19303. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yamamot, K.; Miyake, H.; Kusunoki, M.; Osaki, S. Crystal structures of isomaltase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae and in complex with its competitive inhibitor maltose. FEBS J. 2010, 277, 4205–4214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Wang, S.; Feng, J.; Xiao, Y.; Xue, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Liang, X. Structure elucidation and NMR assignments for curcuminoids from the rhizomes of Curcuma longa. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2009, 47, 902–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payton, F.; Sandusky, P.; Alworth, W.L. NMR Study of the Solution Structure of Curcumin. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayaprakasha, G.K.; Rao, L.J.M.; Sakariah, K.K. Improved HPLC Method for the Determination of Curcumin, Demethoxycurcumin, and Bisdemethoxycurcumin, J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 3668–3672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, H.L.; To, D.C.; Tran, M.H.; Do, T.T.; Nguyen, P.H. Natural PTP1B Inhibitors from Polygonum cuspidatum and Their 2-NBDG Uptake Stimulation. Nat Prod. Commun. 2020, 15, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Yu, J.; Chen, X.; Zhang, S.; Cai, Y.X.; Li, L. Curcumin as a mild natural α-glucosidase inhibitor: a study on its mechanism in vitro. International Journal of Food Science and Technology 2021, 57, 2689–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.Y.; Liu, R.R.; Shao, W.Y.; Mao, X.P.; Ma, L.; Gu, L.Q.; Huang, Z.S.; Chan, A.S.C. α-Glucosidase inhibition of natural curcuminoids and curcumin analogs. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2006, 41, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Lahham, S.; Jaradat, N.; Hamayel, A.; Assaassa, A.; Hammad, F.; Mosa, A.; Nafaa, F.; Chanim, M.; Dwikat, M.; Alqub, M.; Rahim, A.A.; Barquawi, A. Hexane extract of Curcuma longa L. inhibits the activities of key enzymes and pro- inflammatory adipokines linked to obesity. European Journal of Integrative Medicine 2021, 48, 101400–101408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.X.; Chen, X.; Chin, Y.X.; Zheng, J.K.; Lim, P.E.; Xue, C.H.; Tang, Q.J. Identification of curcumin as a potential α-glucosidase And dipeptidyl-peptidase 4 inhibitor: Molecular docking study, in vitro and in vivo biological evaluation. J. Food Biochem. 2021, 00, e13686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, G. Medicinal Chemistry: An Introduction; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Sessler, J.L.; Gale, P.A.; Cho, W.S. Anion Receptor Chemistry; Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho, A.A.; Andrade, L.N.; Batista, É.; Sousa, V.; De Sousa, D.P. Antitumor Phenylpropanoids Found in Essential Oils. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 392674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bezerra, D.P.; De Morais, M.C. The Dual Antioxidant/Prooxidant Effect of Eugenol and Its Action in Cancer Development and Treatment. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laskowski, R.; Rullmann, J.A.; MacArthur, M.; Kaptein,R. ; Thornton, J. AQUA and PROCHECK-NMR: Programs for checking the quality of protein structures solved by NMR. J. Biomol. NMR. 1996, 8, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, N.T.; Hai, N.T.; Han, P.T.N.; Huy, N.T.; Bay, M.V.; Quan, P.M.; Nam, P.C.; Vu, V.V.; Tung, N.S. Autodock Vina Adopts More Accurate Binding Poses but Autodock4 Forms Better Binding Affinity. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2019, 60, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, N.T.; Quang, H.D.; Van, V.T.; Nghi, D.H.; Cuong, N.M.; Cuong, T.D.; Toan, T.Q.; Giang, B.L.; Anh, N.T.H.; Mai, N.T.; Lan, N.T.; Chinh, L.V.; Quan, P.M. Design, synthesis, structure, in vitro cytotoxic activity evaluation and docking studies on target enzyme GSK-3β of new indirubin-3ʹ-oxime derivatives. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, Q.A.; Hang, N.T.T.; Quan, P.M.; Delfino, D.; Thao, D.T. Antiproliferative and antiinflammatory coxib–combretastatin hybrids suppress cell cycle progression and induce apoptosis of MCF7 breast cancer cells. Mol. Divers. 2020, 25, 2307–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
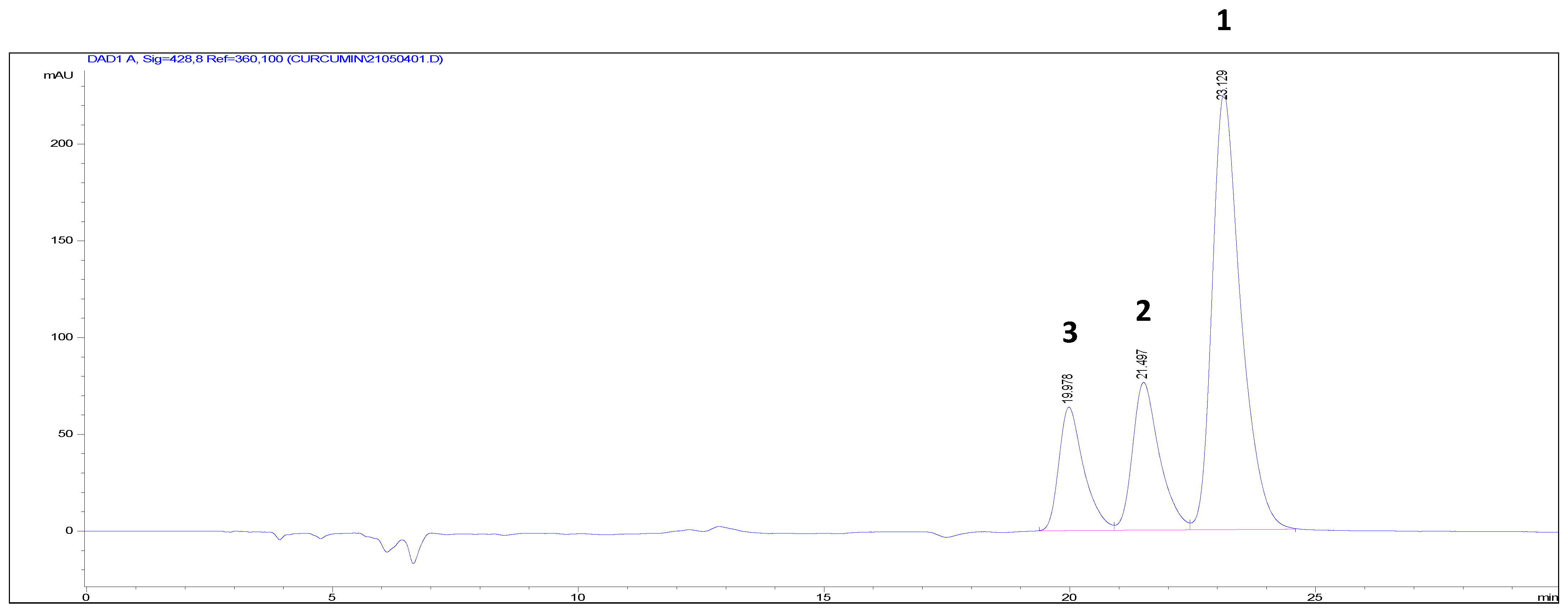
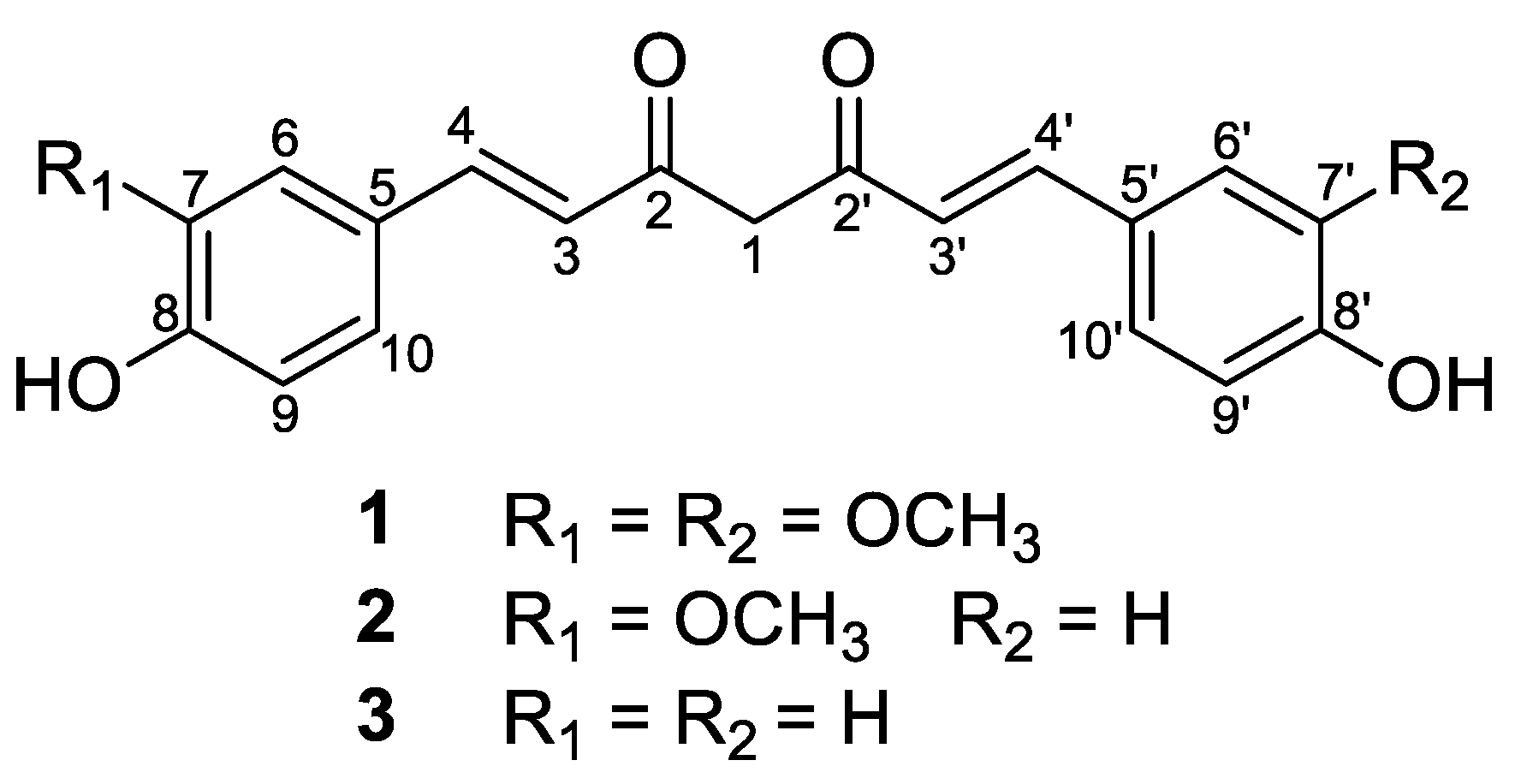
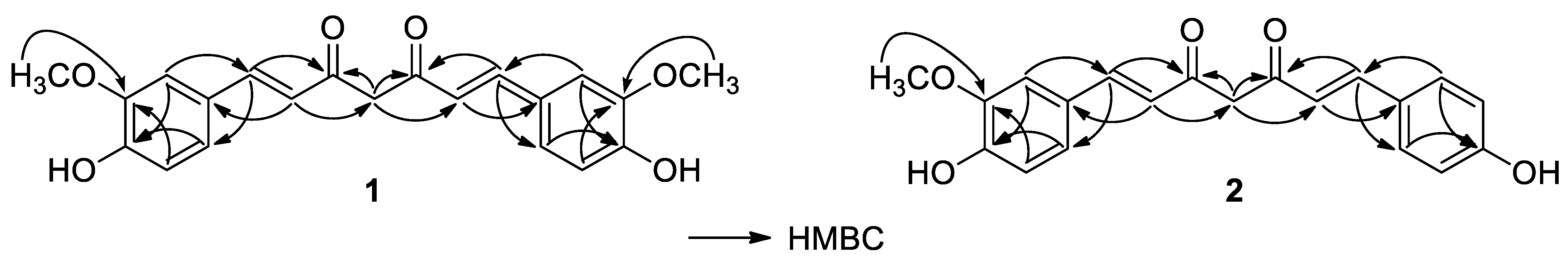
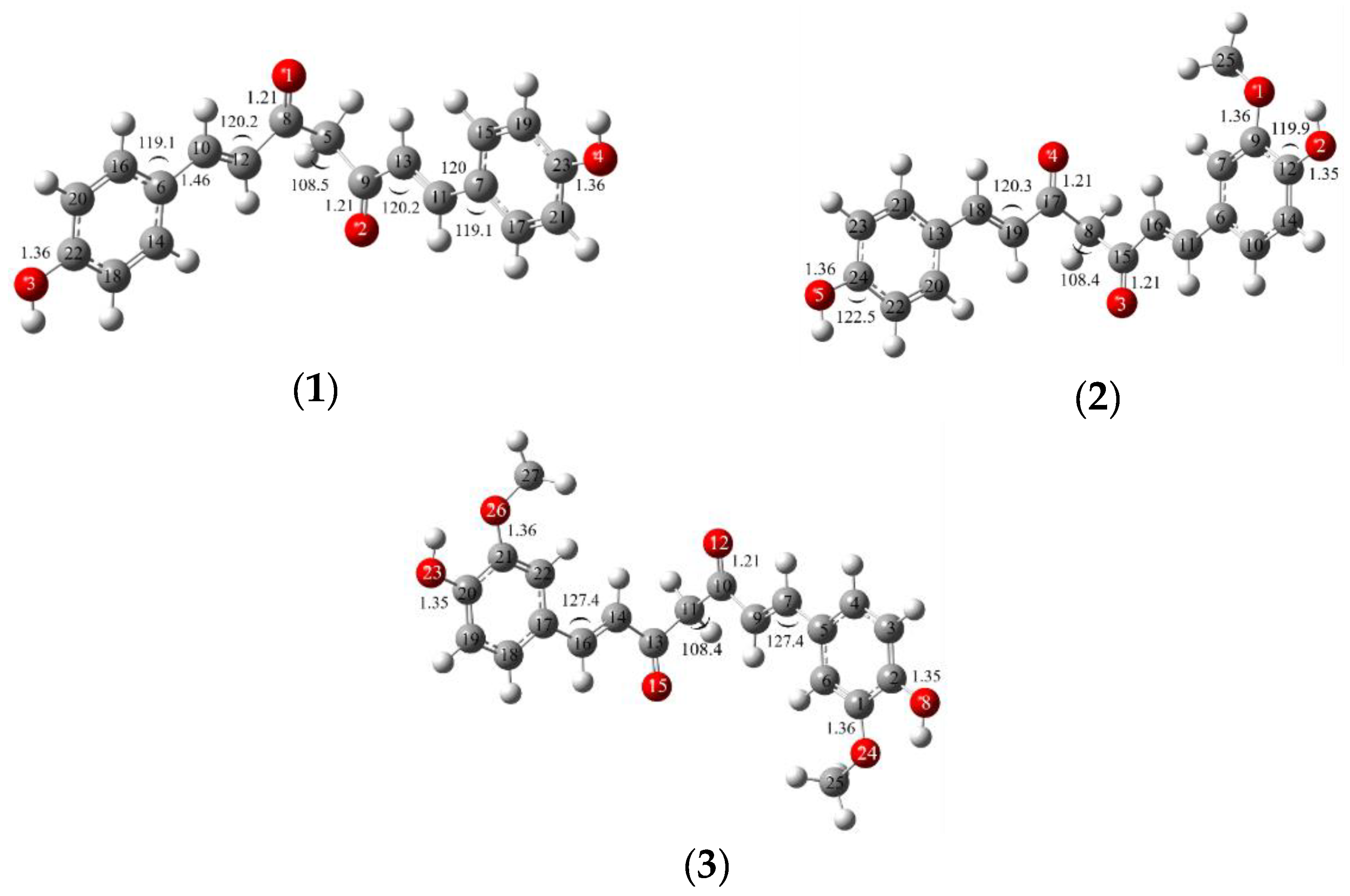
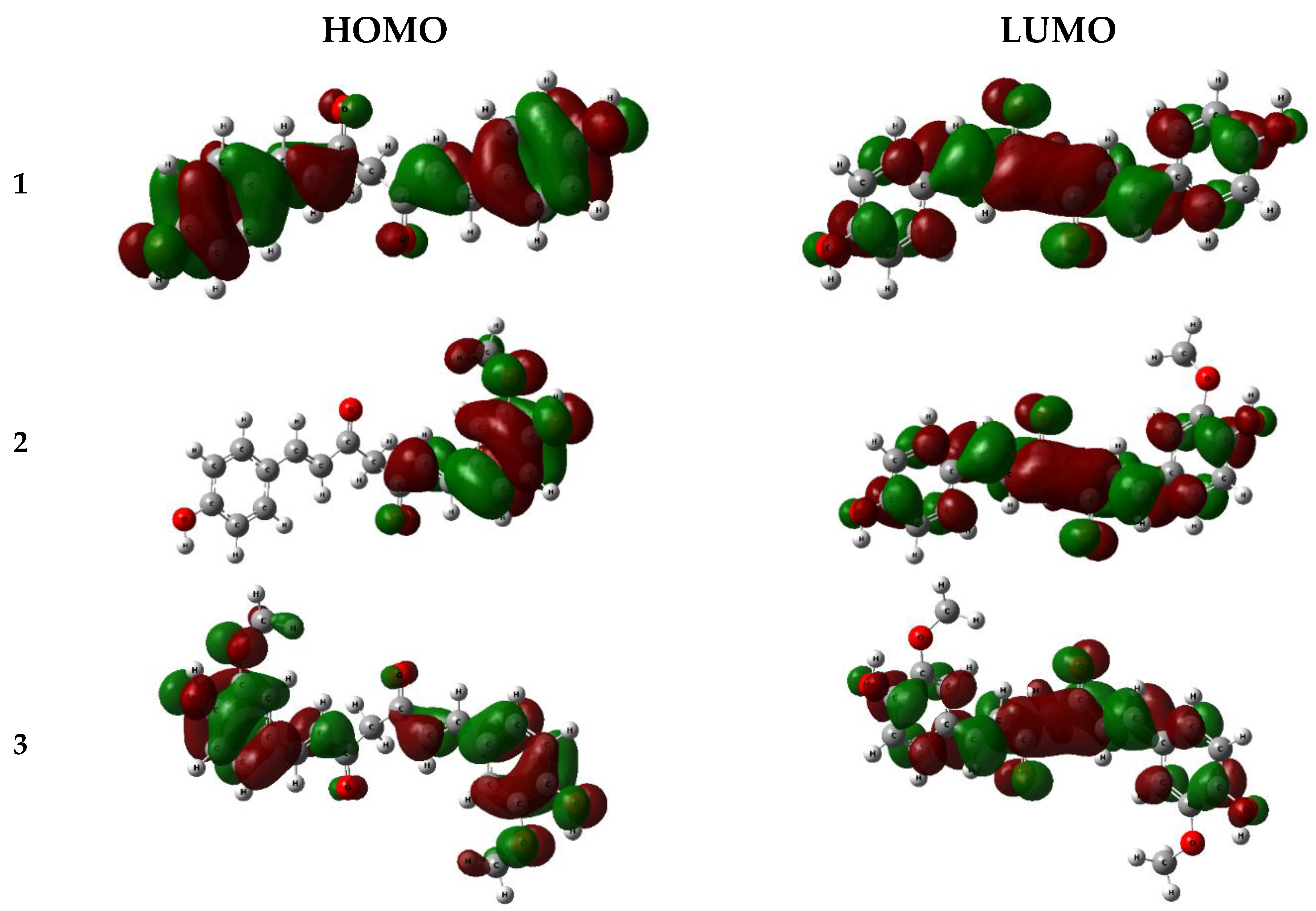
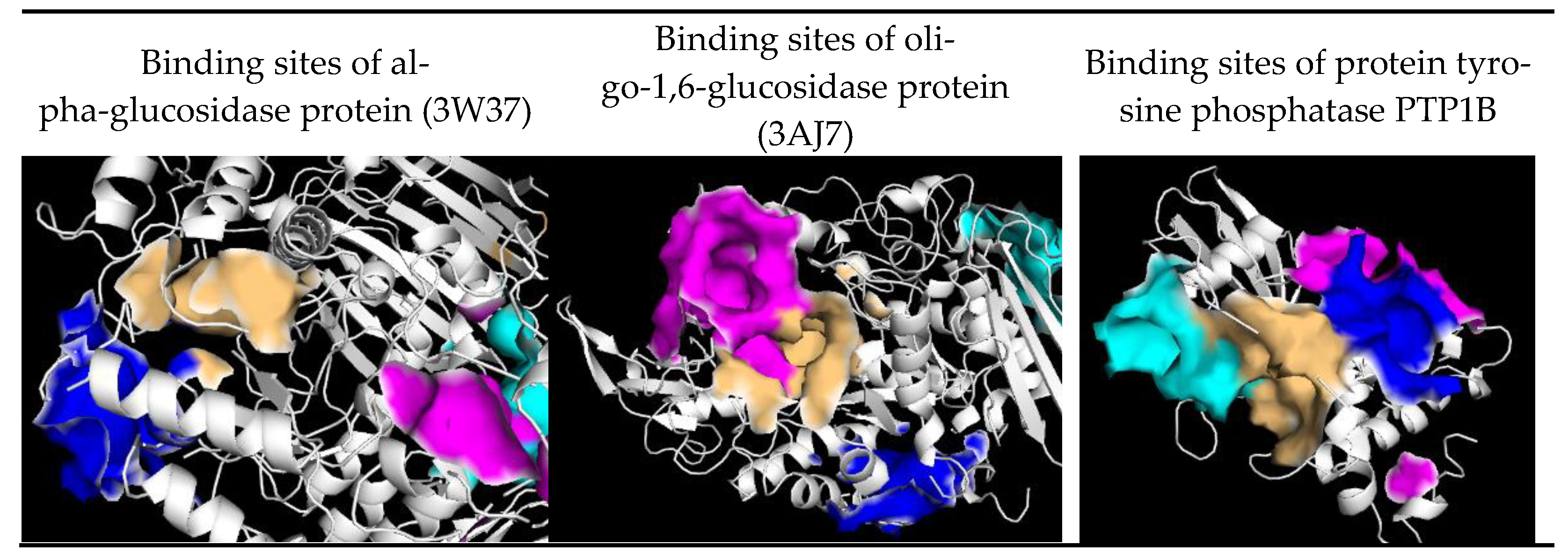
| Position | 1 | 2 | 3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δH (J in Hz) | δC | δH (J in Hz) | δC | δH (J in Hz) | δC | |
| 1 | 5.98 (2H, s) | 101.6 | 5.99 (2H, s) | 101.6 | 5.99 (2H, s) | 101.6 |
| 2 | 184.4 | 184.6 | 184.5 | |||
| 3 | 6.68 (1H, d, 16.2) | 122.1 | 6.69 (1H, d, 15.6) | 122.1 | 6.64 (1H, d, 15.6) | 121.7 |
| 4 | 7.58 (1H, d, 16.2) | 141.4 | 7.59 (1H, d, 15.6) | 141.4 | 7.58 (1H, d, 15.6) | 141.1 |
| 5 | 127.9 | 127.9 | 127.3 | |||
| 6 | 7.28 (1H, d, 1.8) | 111.6 | 7.29 (1H, d, 1.8) | 111.6 | 7.53 (1H, dd, 1.8, 7.8) | 130.8 |
| 7 | 148.9 | 148.9 | 6.88 (1H, dd, 1.8, 7.8) | 116.7 | ||
| 8 | 150.1 | 150.2 | 160.7 | |||
| 9 | 6.87 (1H, d, 7.8) | 116.3 | 6.86 (1H, d, 7.8) | 116.3 | 6.88 (1H, dd, 1.8, 7.8) | 116.7 |
| 10 | 7.14 (1H, dd, 1.8, 7.8) | 123.7 | 7.14 (1H, dd, 1.8, 7.8) | 123.8 | 7.53 (1H, dd, 1.8, 7.8) | 130.8 |
| 2′ | 184.4 | 184.4 | 184.5 | |||
| 3′ | 6.68 (1H, d, 16.2) | 122.1 | 6.64 (1H, d, 15.6) | 121.8 | 6.64 (1H, d, 15.6) | 121.7 |
| 4′ | 7.58 (1H, d, 16.2) | 141.4 | 7.57 (1H, d, 15.6) | 141.2 | 7.58 (1H, d, 15.6) | 141.1 |
| 5′ | 127.9 | 127.3 | 127.3 | |||
| 6′ | 7.28 (1H, d, 1.8) | 111.6 | 7.52 (1H, dd, 1.8, 6.6) | 130.9 | 7.53 (1H, dd, 1.8, 7.8) | 130.8 |
| 7′ | 148.9 | 6.87 (1H, dd, 1.8, 6.6) | 116.8 | 6.88 (1H, dd, 1.8, 7.8) | 116.7 | |
| 8′ | 150.1 | 160.8 | 160.7 | |||
| 9′ | 6.87 (1H, d, 7.8) | 116.3 | 6.87 (1H, dd, 1.8, 6.6) | 116.8 | 6.88 (1H, dd, 1.8, 7.8) | 116.7 |
| 10′ | 7.14 (1H, dd, 1.8, 7.8) | 123.7 | 7.52 (1H, dd, 1.8, 6.6) | 130.9 | 7.53 (1H, dd, 1.8, 7.8) | 130.8 |
| 7-OCH3 | 3.89 (3H, s) | 56.2 | 3.89 (3H, s) | 56.3 | ||
| 7′-OCH3 | 3.89 (3H, s) | 56.2 | ||||
| Compounds | PTP1B | α-glucosidase |
|---|---|---|
| IC50, µM | IC50, µM | |
| Curcumin (1) | 37.8 ± 1.4 | 78.2 ± 0.2 |
| Demethoxycurcumin (2) | 45.3 ± 0.7 | 82.4 ± 0.8 |
| Bisdemethoxycurcumin (3) | 72.6 ± 1.1 | 90.6 ± 1.0 |
| Emodina | 7.6 ± 0.1 | - |
| Ursolic acida | 4.3 ± 0.4 | - |
| Acarboseb | - c | 147.2 ± 1.0 |
| Compounds | EHOMO (eV) | ELUMO (eV) | ∆EGAP = ELUMO − EHOMO | I=− EHOMO | A = −ELUMO | χ=(I+A)/2 |
μ =−χ = −(∂E/∂N)v® |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | -7.298 | -1.581 | 5.717 | 7.298 | 1.581 | 4.439 | -4.439 |
| 2 | -7.298 | -1.574 | 5.724 | 7.298 | 1.574 | 4.436 | -4.436 |
| 3 | -7.525 | -1.563 | 5.962 | 7.525 | 1.563 | 4.544 | -4.544 |
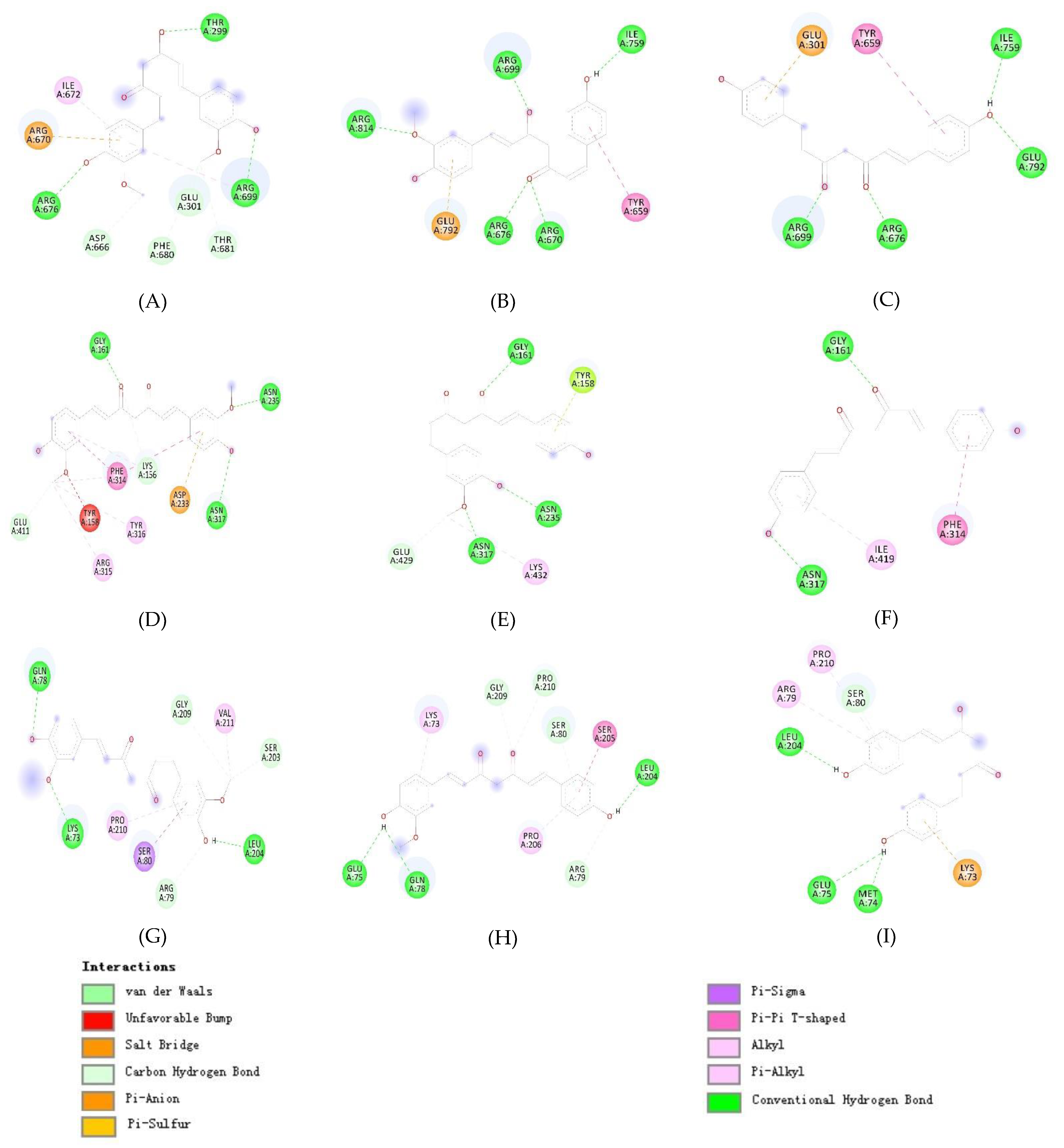
| Site | Residues of 3W37 | Residues of 3AJ7 | Residues of PTP1B |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Tyr360, Phe367, Pro395, Ile396, Leu397, Ile454, Phe457, Arg458, Ile463, Ile466 | Asp69, Tyr72, His112, Lys156, Ser157, Tyr158, Phe159, Leu177, Phe178, Gln182, Arg213, Asp307, Thr310, Ser311, Pro312, Leu313, Phe314, Arg315, Tyr316, His351, Asp352, Gln353, Glu411, Ile440, Arg442, Arg446 | Arg24, Ala27, Ser28, Asp29, Phe30, Pro31, Cys32, Lys36, Asp48, Val49, Phe52, Ile219, Arg254, Arg257, Met258, Gly259, GLn262 |
| 2 | Glu301, Tyr659, Thr662, Leu663, Asp666, Arg670, Ile672, Arg676, Ile697, Gly698, Arg699, Gly700, Ile701, Ile754, Asn758, Ile759, Val760, Ala761, Thr790, Gly&91, Glu792 | Val369, Ile370, Lys373, Pro488, Asn489, Ser490, Asn493, Phe494, Glu497, Leu561, Glu562, Phe593, Gly564, Asn565, Tyr566, Pro567, Lys568, Val571 | Ala35, Lys36, Leu37, Pro38, Asn40, Lys41, Asn44, Arg45, Tyr46, Arg47, Asp48, Val49,Ser50 |
| 3 | Tyr319, Pro658, Tyr661, Gln763, Arg773, Phe777, Leu793, Phe794, Leu795, Asp796, Trp841 | Lys156, Ser157, Tyr158, Phe159, Gly160, Gly161, Asp233, Asn235, Ser236, Thr237, Trp238, Ser311, Leu313, Phe314, Asn317, Asn415, Ala418, Ile419, Glu422, His423, Glu428, Glu429, Lys432 | Leu71, Lys73, Met74, Glu75, Ala77, Gln78, Arg79, Ser80, Ser203, Leu204, Ser205, Pro206, His208, Gly209, Pro210, Val211, Leu233, Lys237 |
| 4 | Tys331, Arg332, Asp333, Ile358, Asp359,Tyr360, Met361, Asp362, Ala363, Phe364, Asp370, His373, Phe374, Arg629 | Lys, Trp15, Asn259, Ile262, Glu271, Ile272, Met273, Thr274, Tyr289, Thr290, Ser291, Ala292, Arg294, His295, Glu296, Leu297, Ser298, Asp341, Cys342, Trp343 | Lys73, Met74, Glu75, Glu76, Ala77, Thr230, Leu234, Lys248, Val249, Glu252, Lys255, Phe256 |
| Compounds | 3W37 | 3AJ7 | PTP1B | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H-bond | Van der Waals interaction | H-bond | Van der Waals interaction | H-bond | Van der Waals interaction | |
| 1 | Thr299, Arg676, Arg699 | Glu301, Asp666, Arg670, Ile672, Phe680, Thr681 | Gly161, Asn235, Asn317 | Lys156, Tyr158, Asp233, Phe314, Arg315, Tyr316, Glu411 | Lys73, Gln78, Leu204 | Arg79, Ser80, Ser203, Gly209, Pro210, Val211 |
| 2 | Arg670, Arg676, Arg699, Ile759, Arg814 | Tyr659, Glu792 | Gly161, Asn235, Asn317 | Tyr158, Glu429, Lys432 | Glu75, Gln78, Leu204 | Lys73, Arg79, Ser80, Ser205, Pro206, Gly209, Pro210 |
| 3 | Arg676, Arg699, Ile759, Glu792 | Glu301, Tyr659 | Gly161, Asn317 | Phe314, Ile419 | Met74, Glu75, Leu204 | Lys73, Arg79, Ser80, Pro210 |
| Site | 3W37 | 3AJ7 | PTP1B | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grid box center | |||||||||
| x | y | z | x | y | z | x | y | z | |
| 1 | -2.783 | -20.139 | -14.192 | 16.920 | -10.869 | 19.269 | -27.669 | 40.981 | -8.880 |
| 2 | 16.542 | -28.867 | -41.997 | 28.176 | 16.748 | -0.427 | -23.809 | 30.047 | -16.569 |
| 3 | 8.457 | -41.335 | -37.723 | 15.262 | -21.012 | 13.686 | -34.929 | 32.542 | 9.157 |
| 4 | -13.147 | -11.244 | -19.031 | 12.365 | 10.215 | 30.416 | -34.929 | 42.799 | 5.639 |
| Grid box size | |||||||||
| x | y | Z | x | y | Z | x | y | Z | |
| 1 | 50 | 55 | 50 | 74 | 64 | 70 | 66 | 55 | 50 |
| 2 | 68 | 52 | 70 | 50 | 60 | 55 | 60 | 40 | 40 |
| 3 | 55 | 55 | 55 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 68 | 55 |
| 4 | 55 | 50 | 65 | 60 | 60 | 60 | 55 | 50 | 50 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





