Submitted:
28 April 2023
Posted:
28 April 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
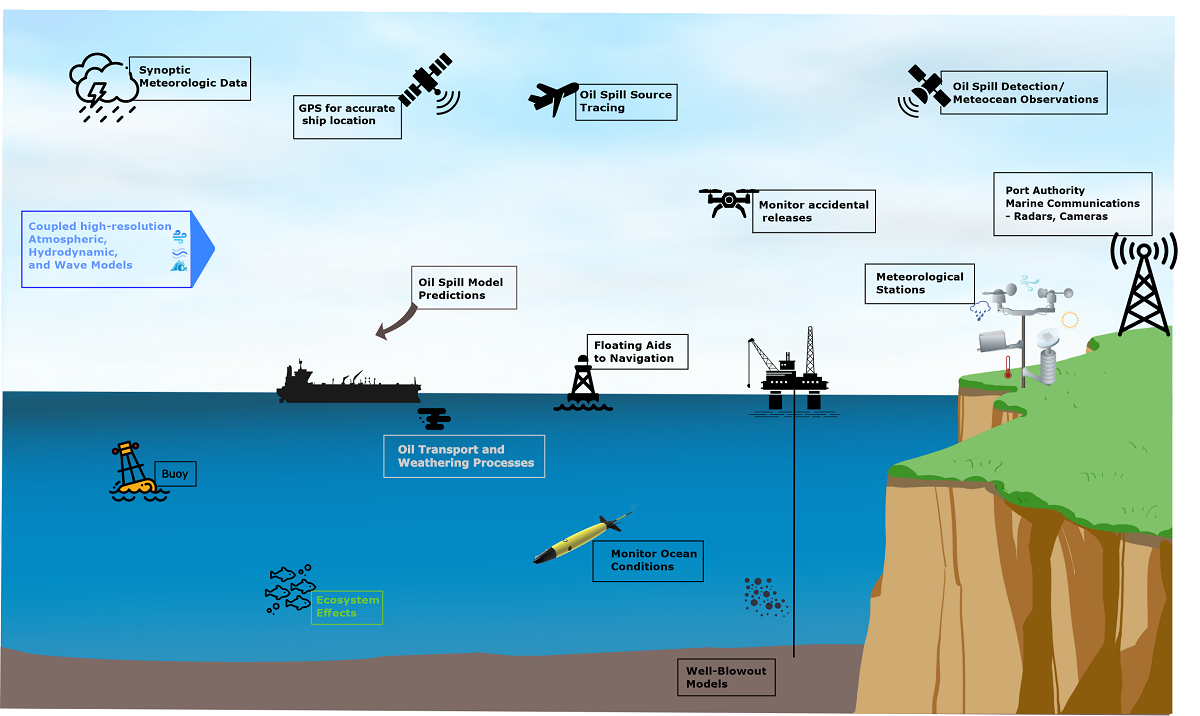
1. Introduction
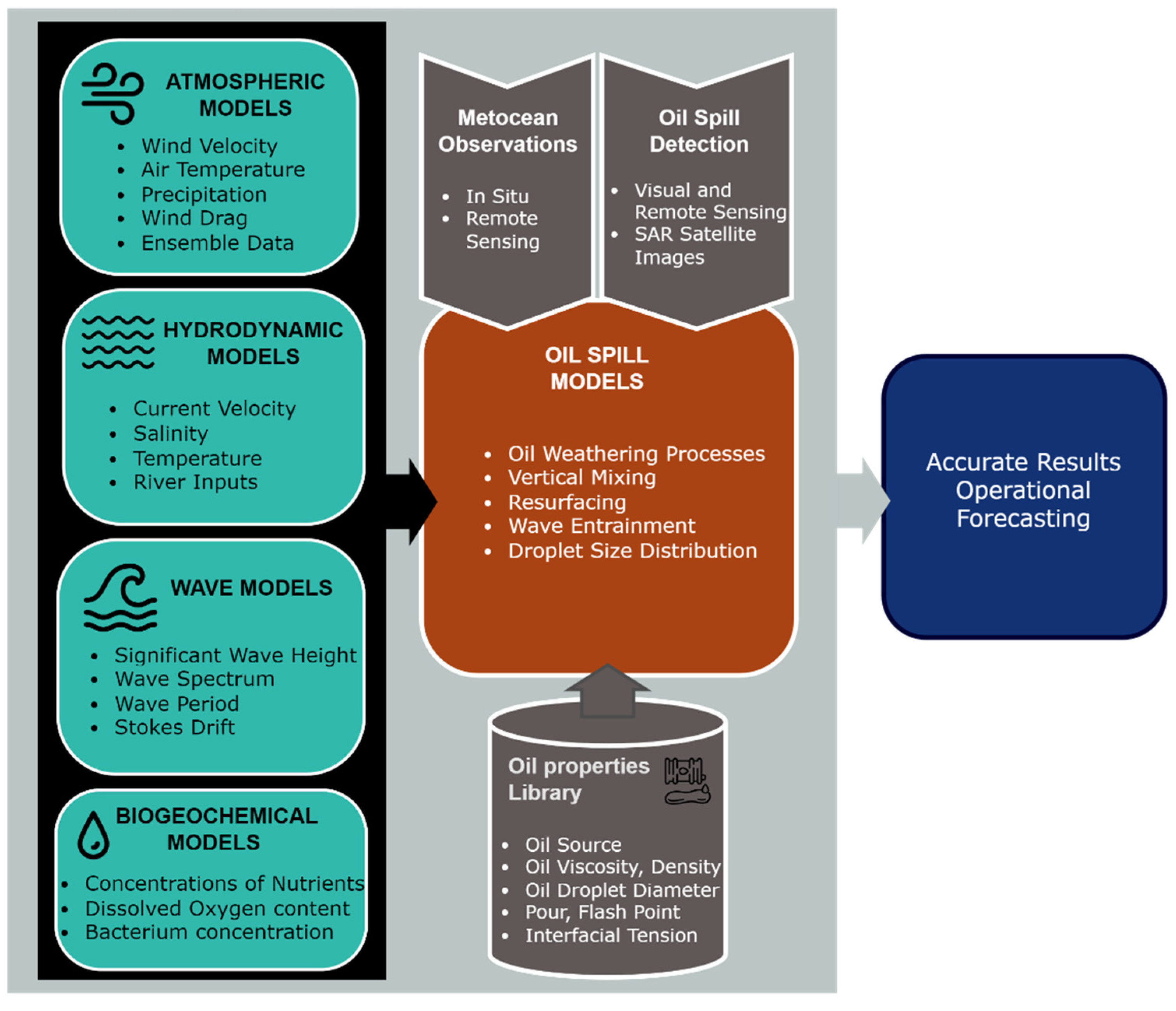
2. The Oil Spill Models
3. The Oil Spill Forcing Models
3.1. Wind Fields
| Wind | Provider | Geographical area | Spatial Resolution | Data Type | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Poseidon | HCMR | Mediterranean | ~5 km | Forecast | [106] |
| HIRLAM | AEMET | Western Mediterranean | ~ 15 km | Forecast | [108,112,113,114] |
| ARPEGE | Meteo-France | Mediterranean | ~10 km | Forecast | [108,118] |
| SKIRON | UOA | Mediterranean and Black Sea | ~5 and 10 km | Forecast | [53,102,120] [19,58,61,103,104,121] |
| MALTA/Maria ETA model | UOM | Central Mediterranean | ~4 km | Forecast | [108,109] |
| NAM | NOAA/NCEP | North America | 12km | Forecast | [66,86] |
| NARR | NOAA/NCEP | North America | 0.3° (32 km) | Reanalysis | [66,89,90] |
| NCOM AMSEAS | NOAA/FNMOC | Gulf of Mexico and Caribbean | 1/36° (~ 3km) | Hindcast | [74] |
| WRF | NCAR/NCEP | Regional | 0.15° (~16 km) | Forecast | [44] |
| NOGAPS | NOAA/United States Navy | Global | 0.5° (~56 km) | Forecast | [66,81] |
| CFSR | NOAA/NCEP | Global | 0.5° (~56 km) | Reanalysis | [66,77] |
| GFS | NOAA/NCEP | Global | 0.25° (~27 km) | Forecast | [50,69,70,71,83] |
| ERA5 | ECMWF | Global | 0.25° (~27 km) | Reanalysis | [42,51] |
| Era-Interim | ECMWF | Global | 0.125° (~12.5 km) | Reanalysis | [46,47,48,49,53,54,56,57] |
3.2. Hydrodynamics
| Hydrodynamics | Provider | Geographic Coverage | Spatial Resolution | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Poseidon Med Model | HCMR | Mediterranean | ~ 10 km | [19,108] |
| Poseidon Aegean Model | HCMR | Aegean Sea | ~ 3.5 km | [108] |
| CYPOM | CYCOFOS | Aegean-Levantine | ~ 2 km | [108,160,163] |
| WMED | CNR IAMC | Western Mediterranean | ~ 3.5 km | [19,108,156] |
| ALERMO | IASA | Eastern Mediterranean | ~ 3.5 km | [103,108,158] |
| MFS | INGV | Mediterranean | ~ 6.5 km | [19,108,163] |
| AFS | INGV | Adriatic Sea | ~ 2.2 km | [29,108] |
| PREVIMER MENOR | IFREMER | North Western Mediterranean | ~ 1.2 km | [19,108] |
| ΜΙΚΕ21 | DHI | Regional | - | [42] |
| CROCO | IRD | Regional | 1 km | [68] |
| NorShelf | Norwegian Meteorological Institute | Norwegian Shelf Sea | 2.4 km | [23] |
| SANIFS | CMCC-OPA | Mediterranean basin | 3 km | [56] |
| SHYFEM | ISMAR-CNR | Regional | 4 km, 1km |
[104,155] |
| NEMO | CMEMS | Mediterranean Global Global |
(1/24°) ~ 4 km (1/12°) ~ 9 km (1/4°)~27 km |
[50,54,55] [51,53,57] [69] |
| NGOM | NOAA- CSDL | North-eastern and Central GOM | 5-6 km | [66] |
| NCOM | NOAA FNMOC | American Seas and Alaska | 3 km | [66,74] |
| SABGOM | NCSU | GOM | ~ 5 km | [66] |
| IASROMS | NCSU | GOM | ~ 2 km | [66] |
| GLB-HYCOM | NOAA NRL | Global | 1/12° (~ 9 km) | [44,70] |
| GoM-HYCOM | NOAA NRL | GOM | (~ 4 km) | [66,67] |
| GoM-HYCOM | NOAA NRL | GOM | 1/50° (~ 2 km) | [46,47,49] |
| Fkeys-HYCOM | NOAA NRL | South Florida coastal, shelf areas and Straits of Florida | 1/100° (~ 1 km) | [46,48] |
3.3. Waves
| Wave system | Provider | Geographical area | Spatial Resolution | Data Type | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Poseidon WAM Cycle 4 Med | HCMR | Mediterranean | ~ 10 km | Forecast | [108,179] |
| Poseidon WAM Cycle 4 Aegean | HCMR | Aegean | ~ 3.5 km | Forecast | [108,179] |
| WAM4 | CYCOFOS | Mediterranean and Black Sea | ~ 5 km | Forecast | [19,108,181] |
| PdE-WAM | PdE | Western Mediterranean | ~ 8 km | Forecast | [108] |
| PREVIMER-MENOR-WW3 | IFREMER | Mediterranean | ~ 10 km | Forecast | [19,108] |
| MALTA/Maria WAMI | UOM | Central Mediterranean | ~ 12.5 km | Forecast | [108,109] |
| WAM Cycle 6, WAM 4.6.2 | CMEMS | Mediterranean | 1/24° (~ 4.5 km) | Forecast/Reanalysis | [50,176] |
| MFWAM | Meteo-France | Global | 1/12° (~9 km) | Forecast | [83,177] |
| WAVERYS | CMEMS | Global | 1/5° (~ 22 km) | Reanalysis | [51,172] |
| WAM | ECMWF | Global | 0.125° (~ 13 km) | Forecast | [23,46,47,48,49,185] |
4. Analysis of Selected Oil Spill Models, in terms of Boundary Forcing
4.1. Wind Fields
4.2. Hydrodynamics
4.3. Waves
4.4. Biogeochemical model
| Time period | SAR data | Currents | Waves | Wind | Sal/Temp | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 22/2/11-4/3/11 3-13/1/2011 5-15/1/2011 7-17/1/2011 (10 days) |
No | NorShelf model (2.4 km) | ECMWF (0.125°) | ECMWF (0.125°) | No | [23] |
| 20-27/5/2010 (7-days) 2-10/6/2010 (8 days) |
Yes | GoM-Hycom (1/50°) | ECMWF (0.125°) | (0.125°) | Only Salinity - GoM-HYCOM (1/50°) |
[47] |
| 2011-2016 (6 years) | No | GoM-Hycom (1/50°) | ECMWF (0.125°) | ECMWF (0.125°) | No | [46] |
| Feb. 2017 (5 days) August 2017 (5 days) |
Yes | GoM-Hycom (1/50°) | ECMWF (0.125°) | ECMWF (0.125°) | Only Salinity - GoM- HYCOM (1/50°) |
[49] |
| 2010-2017 (7 years) | No | GoM-Hycom (1/50°) | ECMWF (0.125°) | ECMWF (0.125°) | GoM- HYCOM (1/50°) | [48] |
| 25-30/10/2020 (5 days) | No | CMEMS- Mediterranean Forecast (1/24°) | CMEMS- Mediterranean Forecast (1/24°) | ) | CMEMS- Mediterranean Forecast (1/24°) | [50] |
| 20-23/07/2014 (3 days) 21-23/08/2014 (2 days) |
No | CMEMS-Global Forecast (1/12°) | CMEMS-Global Reanalysis (1/5°) | No | [51] |
5. Conclusions and Recommendations
Future Outlook
- High-resolution wave models should be coupled to oil spill models, providing wave data (significant wave height, wave period, stokes drift velocity) with greater accuracy in the operational oil spill modeling.
- Biogeochemical processes, such as biodegradation, sedimentation, photo-oxidation should also be taken into account in operational oil spill scenarios, since these are very important in the prediction of the oil spill and in the environmental impacts in the marine field.
- Important OWPs, like biodegradation, need further improvement in their parametrization. For example, the biodegradation in OpenOil model takes into account only the sea surface temperature and it does not include parameters such as nutrients (phosphorus and nitrogen), dissolved oxygen content and number of bacteria.
- Emphasis should be given on the assessment of the accuracy of the oil spill models results, through the use of appropriate indicators that will compare and quantify the compatibility of the oil spill models against satellite SAR data.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Crain, C.M.; Halpern, B.S.; Beck, M.W.; Kappel, C.V. Understanding and Managing Human Threats to the Coastal Marine Environment. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 2009, 1162, 39–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, A.H.; Pavia, R.; Bostrom, A.; Leschine, T.M.; Starbird, K. Communication Practices for Oil Spills: Stakeholder Engagement During Preparedness and Response. Human and Ecological Risk Assessment 2015, 21, 667–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fingas, M.; Brown, C. Review of oil spill remote sensing. Marine Pollution Bulletin 2014, 83, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azevedo, A.; Oliveira, A.; Fortunato, A.B.; Zhang, J.; Baptista, A.M. A cross-scale numerical modeling system for management support of oil spill accidents. Marine Pollution Bulletin 2014, 80, 132–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafirakou, A. Oil Spill Dispersion Forecasting Models. In Monitoring of Marine Pollution; IntechOpen London, UK: 2019.
- Mishra, A.K.; Kumar, G.S. Weathering of Oil Spill: Modeling and Analysis. Aquatic Procedia 2015, 4, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keramea, P.; Spanoudaki, K.; Zodiatis, G.; Gikas, G.; Sylaios, G. Oil Spill Modeling: A Critical Review on Current Trends, Perspectives, and Challenges. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webler, T.; Lord, F. Planning for the Human Dimensions of Oil Spills and Spill Response. Environmental Management 2010, 45, 723–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Z.; You, F. Oil spill response planning with consideration of physicochemical evolution of the oil slick: A multiobjective optimization approach. Computers and Chemical Engineering 2011, 35, 1614–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, A.J.; Hope, M.J. Bayesian inference-based environmental decision support systems for oil spill response strategy selection. Marine Pollution Bulletin 2015, 96, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grubesic, T.H.; Wei, R.; Nelson, J. Optimizing oil spill cleanup efforts: A tactical approach and evaluation framework. Marine Pollution Bulletin 2017, 125, 318–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.E.; Stone, J.; Demes, K.; Piscitelli, M. Consequences of oil spills a review and framework for informing planning. Ecology and Society 2014, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Miller, J.; Wang, J.; Koley, S.S.; Katz, J. Size Distribution and Dispersion of Droplets Generated by Impingement of Breaking Waves on Oil Slicks. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans 2017, 122, 7938–7957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenning, R.J.; Robinson, H.; Bock, M.; Rempel-Hester, M.A.; Gardiner, W. Current practices and knowledge supporting oil spill risk assessment in the Arctic. Marine Environmental Research 2018, 141, 289–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barker, C.H.; Kourafalou, V.H.; Beegle-Krause, C.J.; Boufadel, M.; Bourassa, M.A.; Buschang, S.G.; Androulidakis, Y.; Chassignet, E.P.; Dagestad, K.-F.; Danmeier, D.G.; et al. Progress in Operational Modeling in Support of Oil Spill Response. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zodiatis, G.; Lardner, R.; Alves, T.M.; Krestenitis, Y.; Perivoliotis, L.; Sofianos, S.; Spanoudaki, K. Oil spill forecasting (prediction). Journal of Marine Research 2017, 75, 923–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaulding, M.L. State of the art review and future directions in oil spill modeling. Marine Pollution Bulletin 2017, 115, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zodiatis, G.; Lardner, R.; Spanoudaki, K.; Sofianos, S.; Radhakrishnan, H.; Coppini, G.; Liubartseva, S.; Kampanis, N.; Krokos, G.; Hoteit, I.; et al. Chapter 5 - Operational oil spill modelling assessments. In Marine Hydrocarbon Spill Assessments, Makarynskyy, O., Ed.; Elsevier: 2021; pp. 145–197.
- De Dominicis, M.; Bruciaferri, D.; Gerin, R.; Pinardi, N.; Poulain, P.M.; Garreau, P.; Zodiatis, G.; Perivoliotis, L.; Fazioli, L.; Sorgente, R.; et al. A multi-model assessment of the impact of currents, waves and wind in modelling surface drifters and oil spill. Deep-Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography 2016, 133, 21–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dearden, C.; Culmer, T.; Brooke, R. Performance Measures for Validation of Oil Spill Dispersion Models Based on Satellite and Coastal Data. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering 2022, 47, 126–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisano, A.; De Dominicis, M.; Biamino, W.; Bignami, F.; Gherardi, S.; Colao, F.; Coppini, G.; Marullo, S.; Sprovieri, M.; Trivero, P.; et al. An oceanographic survey for oil spill monitoring and model forecasting validation using remote sensing and in situ data in the Mediterranean Sea. Deep-Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography 2016, 133, 132–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Hénaff, M.; Kourafalou, V.H. Mississippi waters reaching South Florida reefs under no flood conditions: synthesis of observing and modeling system findings. Ocean Dynamics 2016, 66, 435–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röhrs, J.; Dagestad, K.F.; Asbjørnsen, H.; Nordam, T.; Skancke, J.; Jones, C.E.; Brekke, C. The effect of vertical mixing on the horizontal drift of oil spills. Ocean Science 2018, 14, 1581–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaulding, M.L. A state-of-the-art review of oil spill trajectory and fate modeling. Oil and Chemical Pollution 1988, 4, 39–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagestad, K.F.; Röhrs, J.; Breivik, O.; Ådlandsvik, B. OpenDrift v1.0: A generic framework for trajectory modelling. Geoscientific Model Development 2018, 11, 1405–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lardner, R.; Zodiatis, G.; Loizides, L.; Demetropoulos, A. An operational oil spill model for the Levantine Basin(Eastern Mediterranean Sea; 1011-4289; International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA): Monaco, 5-6 October, 1988 1998; pp. 542–543. [Google Scholar]
- Lardner, R.; Zodiatis, G. MEDSLIK oil spill model recent developments. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly, Vienna, Austria, 17-22 April, 2016; pp. EPSC2016–16240.
- De Dominicis, M.; Pinardi, N.; Zodiatis, G.; Lardner, R. MEDSLIK-II, a Lagrangian marine surface oil spill model for short-term forecasting – Part 1: Theory. Geosci. Model Dev. 2013, 6, 1851–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Dominicis, M.; Pinardi, N.; Zodiatis, G.; Archetti, R. MEDSLIK-II, a Lagrangian marine surface oil spill model for short-term forecasting – Part 2: Numerical simulations and validations. Geosci. Model Dev. 2013, 6, 1871–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCay, D.F. Development and application of damage assessment modeling: Example assessment for the North Cape oil spill. Marine Pollution Bulletin 2003, 47, 341–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCay, D.F.; Li, Z.; Horn, M.; Crowley, D.; Spaulding, M.; Mendelsohn, D.; Turner, C. Modeling oil fate and subsurface exposure concentrations from the Deepwater Horizon oil spill. In Proceedings of the 39th AMOP Technical Seminar on Environmental Contamination and Response, Ottawa, Canada; 2016; pp. 115–150. [Google Scholar]
- Beegle-Krause, C.J. General NOAA oil modeling environment (GNOME): A new spill trajectory model. 2005 International Oil Spill Conference, IOSC 2005 2005, 2001, 3277–3283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelenke, B.; O'Connor, C.; Barker, C.H.; Beegle-Krause, C.J.; Eclipse, L. General NOAA Operational Modeling Environment (GNOME) technical documentation. 2012.
- Duran, R.; Romeo, L.; Whiting, J.; Vielma, J.; Rose, K.; Bunn, A.; Bauer, J. Simulation of the 2003 Foss Barge - Point Wells Oil Spill: A Comparison between BLOSOM and GNOME Oil Spill Models. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 2018, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowley, D.; Mendelsohn, D.; Mulanaphy, N.W.; Li, Z.; Spaulding, M. Modeling Subsurface Dispersant Applications for Response Planning and Preparation. International Oil Spill Conference Proceedings 2014, 2014, 933–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spaulding, M.; Mendelsohn, D.; Crowley, D.; Li, Z.; Bird, A. DRAFT Technical Reports for Deepwater Horizon Water Column Injury Assessment: WC_TR. 13: Application of OILMAP DEEP to the Deepwater Horizon Blowout. DWH NRDA Water Column Technical Working Group Report. Prepared for National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration by RPS ASA, South Kingstown, RI 2015, 2879, 386–386. [Google Scholar]
- Spaulding, M.; Li, Z.; Mendelsohn, D.; Crowley, D.; French-McCay, D.; Bird, A. Application of an Integrated Blowout Model System, OILMAP DEEP, to the Deepwater Horizon (DWH) Spill. Marine Pollution Bulletin 2017, 120, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, J.R.; Grubesic, T.H.; Sim, L.; Rose, K.; Graham, J. Approach for assessing coastal vulnerability to oil spills for prevention and readiness using GIS and the Blowout and Spill Occurrence Model. Ocean and Coastal Management 2015, 112, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, L.H. Blowout and spill occrrence model. 2013, 1-90.
- Murray, K.J.; Boehm, P.D.; Prince, R.C. The Importance of Understanding Transport and Degradation of Oil and Gasses from Deep-Sea Blowouts. In Deep Oil Spills, Murawski, S.A., Ainsworth, C.H., Gilbert, S., Hollander, D.J., Paris, C.B., Schlüter, M., Wetzel, D.L., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2020; pp. 86–106. [Google Scholar]
- Benard, L.D.; Mohd Tuah, P. Bioremediation of petroleum hydrocarbons in seawater: Oil spill plume modelling approaches. In Microbial Action on Hydrocarbons, Kumar, V., Kumar, M., Prasad, R., Eds.; Springer Singapore: Singapore, 2019; pp. 35–62. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Chen, Q.; Zheng, C.; Han, Z.; Cai, B.; Liu, Y. Oil spill modeling of Chengdao oilfield in the Chinese Bohai Sea. Ocean Engineering 2022, 255, 111422–111422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacharias, D.C.; Rezende, K.F.O.; Fornaro, A. Offshore petroleum pollution compared numerically via algorithm tests and computation solutions. Ocean Engineering 2018, 151, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacharias, D.C.; Gama, C.M.; Harari, J.; da Rocha, R.P.; Fornaro, A. Mysterious oil spill on the Brazilian coast – Part 2: A probabilistic approach to fill gaps of uncertainties. Marine Pollution Bulletin 2021, 173, 113085–113085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GitHub. OpenDrift. Available online: https://github.com/OpenDrift/opendrift/ (accessed on 25 February 2022).
- Androulidakis, Y.; Kourafalou, V.; Robert Hole, L.; Le Hénaff, M.; Kang, H. Pathways of Oil Spills from Potential Cuban Offshore Exploration: Influence of Ocean Circulation. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hole, L.R.; Dagestad, K.-F.; Röhrs, J.; Wettre, C.; Kourafalou, V.H.; Androulidakis, Y.; Kang, H.; Le Hénaff, M.; Garcia-Pineda, O. The DeepWater Horizon Oil Slick: Simulations of River Front Effects and Oil Droplet Size Distribution. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 2019, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hole, L.R.; de Aguiar, V.; Dagestad, K.F.; Kourafalou, V.H.; Androulidakis, Y.; Kang, H.; Le Hénaff, M.; Calzada, A. Long term simulations of potential oil spills around Cuba. Marine Pollution Bulletin 2021, 167, 112285–112285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourafalou, V.; Justic, D.; Androulidakis, Y.; Bracco, A. From the deep ocean to the coasts and estuaries through the shelf: linking coastal response to a deep blow-out. International Oil Spill Conference Proceedings 2021, 2021, 685087–685087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keramea, P.; Kokkos, N.; Gikas, G.D.; Sylaios, G. Operational Modeling of North Aegean Oil Spills Forced by Real-Time Met-Ocean Forecasts. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devis Morales, A.; Rodríguez Rubio, E.; Rincón Martínez, D. Numerical modeling of oil spills in the Gulf of Morrosquillo, Colombian Caribbean. CT&F - Ciencia, Tecnología y Futuro 2022, 12, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasselmann, K. On the spectral dissipation of ocean waves due to white capping. Boundary-Layer Meteorology 1974, 6, 107–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepp Neves, A.A.; Pinardi, N.; Navarra, A.; Trotta, F. A General Methodology for Beached Oil Spill Hazard Mapping. Frontiers in Marine Science 2020, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liubartseva, S.; Smaoui, M.; Coppini, G.; Gonzalez, G.; Lecci, R.; Cretì, S.; Federico, I. Model-based reconstruction of the Ulysse-Virginia oil spill, October–November 2018. Marine Pollution Bulletin 2020, 154, 111002–111002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kampouris, K.; Vervatis, V.; Karagiorgos, J.; Sofianos, S. Oil spill model uncertainty quantification using an atmospheric ensemble. Ocean Science 2021, 17, 919–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liubartseva, S.; Federico, I.; Coppini, G.; Lecci, R. Stochastic oil spill modeling for environmental protection at the Port of Taranto (southern Italy). Marine Pollution Bulletin 2021, 171, 112744–112744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siqueira, P.G.S.C.; Silva, J.A.M.; Gois, M.L.B.; Duarte, H.O.; Moura, M.C.; Silva, M.A.; Araújo, M.C. Numerical simulations of potential oil spills near Fernando de Noronha archipelago. In Trends in Maritime Technology and Engineering Volume 2; CRC Press: London, 2022; pp. 273–282. [Google Scholar]
- Zodiatis, G.; Coppini, G.; Peña, J.; Benjumeda, P.; Sepp-Neves, A.A.; Lardner, R.; Liubartseva, S.; Soloviev, D.; Scuro, M.; Viola, F. Operational response to the Syrian oil pollution crisis in 2021. May 01, 2022, 2022; pp. EGU22–1098.
- Alves, T.M.; Kokinou, E.; Zodiatis, G.; Lardner, R.; Panagiotakis, C.; Radhakrishnan, H. Modelling of oil spills in confined maritime basins: The case for early response in the Eastern Mediterranean Sea. Environmental Pollution 2015, 206, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zodiatis, G.; Liubartseva, S.; Loizides, L.; Pellegatta, M.; Coppini, G.; Lardner, R.; Kallos, G.; Kalogeri, C.; Bonarelli, R.; Sepp Neves, A.A.; et al. CMEMS AND CYCOFOS ASSESSING THE POLLUTION RISK FROM THE LEVIATHAN OFFSHORE PLATFORM IN THE EASTERN MEDITERRANEAN SEA CMEMS ET CYCOFOS : ÉVALUATION DU RISQUE DE POLLUTION DE LA PLATE-FORME OFFSHORE LEVIATHAN EN MER MÉDITERRANÉE ORIENTALE. In Proceedings of the 9th EuroGOOS International conference, Brest, France, 2021; 2021-05-03; pp. 169–177. [Google Scholar]
- Liubartseva, S.; Zodiatis, G.; Coppini, G.; Sepp Neves, A.A.; Peña, J.; Benjumeda, P.; Lecci, R.; Soloviev, D. Operational simulations of a Mediterranean oil spill in February 2021. May 01, 2022, 2022; pp. EGU22–2276.
- Lardner, R.; Zodiatis, G.; Hayes, D.; Pinardi, N. Application of the MEDSLIK oil spill model to the Lebanese spill of July 2006. In Proceedings of the European Group of Experts on satellite monitoring of sea based oil pollution, European Communities ISSN, Brussels, Belgium; 2006; pp. 1018–5593. [Google Scholar]
- Zodiatis, G.; Lardner, R.; Solovyov, D.; Panayidou, X.; De Dominicis, M. Predictions for oil slicks detected from satellite images using MyOcean forecasting data. Ocean Sci. 2012, 8, 1105–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoteit, I.; Abualnaja, Y.; Afzal, S.; Ait-El-Fquih, B.; Akylas, T.; Antony, C.; Dawson, C.; Asfahani, K.; Brewin, R.J.; Cavaleri, L.; et al. Towards an End-to-End Analysis and Prediction System for Weather, Climate, and Marine Applications in the Red Sea. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society 2021, 102, E99–E122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, M.; Spaulding, M. Drift current under the action of wind and waves; Canada, 1993; pp. 587–615.
- French-McCay, D.P.; Spaulding, M.L.; Crowley, D.; Mendelsohn, D.; Fontenault, J.; Horn, M. Validation of Oil Trajectory and Fate Modeling of the Deepwater Horizon Oil Spill. Frontiers in Marine Science 2021, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French-McCay, D.P.; Jayko, K.; Li, Z.; Spaulding, M.L.; Crowley, D.; Mendelsohn, D.; Horn, M.; Isaji, T.; Kim, Y.H.; Fontenault, J.; et al. Oil fate and mass balance for the Deepwater Horizon oil spill. Marine Pollution Bulletin 2021, 171, 112681–112681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nugroho, D.; Pranowo, W.S.; Gusmawati, N.F.; Nazal, Z.B.; Rozali, R.H.B.; Fuad, M.A.Z. The application of coupled 3d hydrodynamic and oil transport model to oil spill incident in karawang offshore, indonesia. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science 2021, 925, 012048–012048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, I.M.; Chantsev, V.Y. Simulating oil spill movement and behavior: a case study from the Gulf of Suez, Egypt. Modeling Earth Systems and Environment 2022, 8, 4553–4562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, B.; Das, M.; Pradhan, C. Trajectory modelling for hypothetical oil spill in Odisha offshore, India. Journal of Earth System Science 2022, 131, 205–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, I.M.; Chantsev, V.Y. Modeling marine oil spill trajectory and fate off Hurghada, Red Sea coast, Egypt. Egyptian Journal of Aquatic Biology and Fisheries 2022, 26, 41–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, L.; Graham, J.; Rose, K.; Duran, R.; Nelson, J.; Umhoefer, J.; Vielma, J. Developing a Comprehensive Deepwater Blowout and Spill Model; 2015; pp. 48–48.
- Lehr, W.; Jones, R.; Evans, M.; Simecek-Beatty, D.; Overstreet, R. Revisions of the ADIOS oil spill model. Environmental Modelling and Software 2002, 17, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grubesic, T.H.; Nelson, J.R. Estimating potential oil spill trajectories and coastal impacts from near-shore storage facilities: A case study of FSO Nabarima and the Gulf of Paria. International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction 2022, 78, 103117–103117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Nadiga, S.; Thiaw, C.; Wang, J.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Q.; Van den Dool, H.M.; Pan, H.L.; Moorthi, S.; Behringer, D.; et al. The NCEP Climate Forecast System. Journal of Climate 2006, 19, 3483–3517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuka, D.R.; Walter, M.T.; MacAlister, C.; Degaetano, A.T.; Steenhuis, T.S.; Easton, Z.M. Using the Climate Forecast System Reanalysis as weather input data for watershed models. Hydrological Processes 2014, 28, 5613–5623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meza-Padilla, R.; Enriquez, C.; Appendini, C.M. Rapid assessment tool for oil spill planning and contingencies. Marine Pollution Bulletin 2021, 166, 112196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brian, K.; Ben, B.; Charles, L. A case study of consensus modelling for tracking oil spills. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science 2010, 11, 012025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brushett, B.A.; King, B.A.; Lemckert, C.J. Evaluation of met-ocean forecast data effectiveness for tracking drifters deployed during operational oil spill response in Australian waters. Journal of Coastal Research 2011, 991–994. [Google Scholar]
- Le Hénaff, M.; Kourafalou, V.H.; Paris, C.B.; Helgers, J.; Aman, Z.M.; Hogan, P.J.; Srinivasan, A. Surface Evolution of the Deepwater Horizon Oil Spill Patch: Combined Effects of Circulation and Wind-Induced Drift. Environmental Science & Technology 2012, 46, 7267–7273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaz, A.C.; Faillettaz, R.; Paris, C.B. A Coupled Lagrangian-Earth System Model for Predicting Oil Photooxidation. Frontiers in Marine Science 2021, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NOAA. Global Forecast System (GFS). Available online: https://www.ncei.noaa.gov/products/weather-climate-models/global-forecast (accessed on 15 November 2022).
- Zhang, X.; Cheng, L.; Zhang, F.; Wu, J.; Li, S.; Liu, J.; Chu, S.; Xia, N.; Min, K.; Zuo, X.; et al. Evaluation of multi-source forcing datasets for drift trajectory prediction using Lagrangian models in the South China Sea. Applied Ocean Research 2020, 104, 102395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NCEP, G. 0. 25 Degree Global Forecast Grids Historical Archive. ds084. 1. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skamarock, W.C.; Klemp, J.B.; Dudhia, J.; Gill, D.O.; Liu, Z.; Berner, J.; Wang, W.; Powers, J.G.; Duda, M.G.; Barker, D.M. A description of the advanced research WRF model version 4. National Center for Atmospheric Research: Boulder, CO, USA 2019, 145, 145. [Google Scholar]
- Lichiheb, N.; Hicks, B.B.; Myles, L. An evaluation of meteorological data prediction over Washington, D.C.: Comparison of DCNet observations and NAM model outputs. Urban Climate 2023, 48, 101410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukovsky, M.S.; Karoly, D.J. A Brief Evaluation of Precipitation from the North American Regional Reanalysis. Journal of Hydrometeorology 2007, 8, 837–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ainsworth, C.H.; Chassignet, E.P.; French-McCay, D.; Beegle-Krause, C.J.; Berenshtein, I.; Englehardt, J.; Fiddaman, T.; Huang, H.; Huettel, M.; Justic, D.; et al. Ten years of modeling the Deepwater Horizon oil spill. Environmental Modelling & Software 2021, 142, 105070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French-McCay, D.; Crowley, D.; Rowe, J.J.; Bock, M.; Robinson, H.; Wenning, R.; Walker, A.H.; Joeckel, J.; Nedwed, T.J.; Parkerton, T.F. Comparative Risk Assessment of spill response options for a deepwater oil well blowout: Part 1. Oil spill modeling. Marine Pollution Bulletin 2018, 133, 1001–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesinger, F.; DiMego, G.; Kalnay, E.; Mitchell, K.; Shafran, P.C.; Ebisuzaki, W.; Jović, D.; Woollen, J.; Rogers, E.; Berbery, E.H.; et al. North American Regional Reanalysis. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society 2006, 87, 343–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feehan, C.J.; Sharp, W.C.; Miles, T.N.; Brown, M.S.; Adams, D.K. Larval influx of Diadema antillarum to the Florida Keys linked to passage of a Tortugas Eddy. Coral Reefs 2019, 38, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ECMWF. European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts. Available online: https://www.ecmwf.int/en/ forecasts/accessing-forecasts (accessed on 25 November 2022).
- Zhang, L.; Shi, H.; Wang, Z.; Yu, H.; Yin, X.; Liao, Q. Comparison of Wind Speeds from Spaceborne Microwave Radiometers with In Situ Observations and ECMWF Data over the Global Ocean. Remote Sensing 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehard, B.; Malardel, S.; Dörnbrack, A.; Kaifler, B.; Kaifler, N.; Wedi, N. Comparing ECMWF high-resolution analyses with lidar temperature measurements in the middle atmosphere. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society 2018, 144, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haiden, T.; Janousek, M.; Bidlot, J.; Ferranti, L.; Prates, F.; Vitart, F.; Bauer, P.; Richardson, D.S. Evaluation of ECMWF forecasts, including the 2016 resolution upgrade; European Centre for Medium Range Weather Forecasts Reading, UK: 2016.
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; et al. The ERA5 global reanalysis. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dee, D.P.; Uppala, S.M.; Simmons, A.J.; Berrisford, P.; Poli, P.; Kobayashi, S.; Andrae, U.; Balmaseda, M.A.; Balsamo, G.; Bauer, P.; et al. The ERA-Interim reanalysis: Configuration and performance of the data assimilation system. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society 2011, 137, 553–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrisford, P.; Dee, D.; Poli, P.; Brugge, R.; Fielding, K.; Fuentes, M.; Kallberg, P.; Kobayashi, S.; Uppala, S.; Simmons, A. The ERA-Interim Archive Version 2.0; 1; ECMWF: Shinfield Park, Reading, 2009; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- ECMWF. ERA Interim, Daily, European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts. Available online: https://apps.ecmwf.int/datasets/data/interim-fulldaily/ (accessed on 15 November 2022).
- Black, T.L. The New NMC Mesoscale Eta Model: Description and Forecast Examples. Weather and Forecasting 1994, 9, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesinger, F.; Chou, S.C.; Gomes, J.L.; Jovic, D.; Bastos, P.; Bustamante, J.F.; Lazic, L.; Lyra, A.A.; Morelli, S.; Ristic, I.; et al. An upgraded version of the Eta model. Meteorology and Atmospheric Physics 2012, 116, 63–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallos, G.; Nickovic, S.; Papadopoulos, A.; Jovic, D.; Kakaliagou, O.; Misirlis, N.; Boukas, L.; Mimikou, N.; Sakellaridis, G.; Papageorgiou, J. The regional weather forecasting system SKIRON: An overview. 1997, 1997; p. 17.
- Zafirakou-Koulouris, A.; Koutitas, C.; Sofianos, S.; Mantziafou, A.; Tzali, M.; Dermissi, S.C. Oil spill dispersion forecasting with the aid of a 3D simulation model. Journal of Physical Science and Application 2012, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Ribotti, A.; Antognarelli, F.; Cucco, A.; Falcieri, M.F.; Fazioli, L.; Ferrarin, C.; Olita, A.; Oliva, G.; Pes, A.; Quattrocchi, G.; et al. An Operational Marine Oil Spill Forecasting Tool for the Management of Emergencies in the Italian Seas. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering 2019, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, R.; Biton, E.; Brokovich, E.; Kark, S.; Levin, N. Oil spill contamination probability in the southeastern Levantine basin. Marine Pollution Bulletin 2015, 91, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadopoulos, A.; Katsafados, P.; Kallos, G.; Nickovic, S. The Weather Forecasting System for Poseidon - an Overview. Journal of Atmospheric & Ocean Science 2002, 8, 219–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annika, P.; George, T.; George, P.; Konstantinos, N.; Costas, D.; Koutitas, C. The Poseidon Operational Tool for the Prediction of Floating Pollutant Transport. Marine Pollution Bulletin 2001, 43, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zodiatis, G.; De Dominicis, M.; Perivoliotis, L.; Radhakrishnan, H.; Georgoudis, E.; Sotillo, M.; Lardner, R.W.; Krokos, G.; Bruciaferri, D.; Clementi, E.; et al. The Mediterranean Decision Support System for Marine Safety dedicated to oil slicks predictions. Deep Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography 2016, 133, 4–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drago, A.; Azzopardi, J.; Gauci, A.P.; Tarasova, R.; Bruschi, A. Assessing the offshore wave energy potential for the Maltese Islands. 2013.
- Mesinger, F.; Janjić, Z.I.; Ničković, S.; Gavrilov, D.; Deaven, D.G. The Step-Mountain Coordinate: Model Description and Performance for Cases of Alpine Lee Cyclogenesis and for a Case of an Appalachian Redevelopment. Monthly Weather Review 1988, 116, 1493–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eerola, K. Twenty-One Years of Verification from the HIRLAM NWP System. Weather and Forecasting 2013, 28, 270–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navascués, B.; Calvo, J.; Morales, G.; Santos, C.; Callado, A.; Cansado, A.; Cuxart, J.; Díez, M.; del Río, P.; Escribà, P.; et al. Long-term verification of HIRLAM and ECMWF forecasts over Southern Europe: History and perspectives of Numerical Weather Prediction at AEMET. Atmospheric Research 2013, 125-126, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castanedo, S.; Perez-Diaz, B.; Abascal, A.J.; Cardenas, M.; Olabarrieta, M.; Medina, R.; Receveur, J.; Evrard, E.; Guyomarch, J. A HIGH RESOLUTION OPERATIONAL OIL SPILL MODEL AT SANTANDER BAY (SPAIN): IMPLEMENTATION AND VALIDATION. International Oil Spill Conference Proceedings 2014, 2014, 516–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castanedo, S.; Medina, R.; Losada, I.J.; Vidal, C.; Méndez, F.J.; Osorio, A.; Juanes, J.A.; Puente, A. The Prestige Oil Spill in Cantabria (Bay of Biscay). Part I: Operational Forecasting System for Quick Response, Risk Assessment, and Protection of Natural Resources. Journal of Coastal Research 2006, 22, 1474–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Déqué, M.; Dreveton, C.; Braun, A.; Cariolle, D. The ARPEGE/IFS atmosphere model: a contribution to the French community climate modelling. Climate Dynamics 1994, 10, 249–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, P. FORECASTING OIL SPILL DRIFT AT METEO-FRANCE. International Oil Spill Conference Proceedings 1997, 1997, 990–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yessad, K. Basics about ARPEGE/IFS, ALADIN and AROME in the cycle 40 of ARPEGE/IFS. Meteo-France/CNRM Technical Notes 2013.
- Declerck, A.; Ourmières, Y.; Molcard, A. Assessment of the coastal dynamics in a nested zoom and feedback on the boundary current: the North-Western Mediterranean Sea case. Ocean Dynamics 2016, 66, 1529–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radice, C.; Brogniez, H.; Kirstetter, P.E.; Chambon, P. Novel assessment of numerical forecasting model relative humidity with satellite probabilistic estimates. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2022, 22, 3811–3825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepp Neves, A.A.; Pinardi, N.; Martins, F. IT-OSRA: applying ensemble simulations to estimate the oil spill risk associated to operational and accidental oil spills. Ocean Dynamics 2016, 66, 939–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickovic, S.; Kallos, G.; Papadopoulos, A.; Kakaliagou, O. A model for prediction of desert dust cycle in the atmosphere. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres 2001, 106, 18113–18129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CMEMS. Global Ocean 1/12° Physics Analysis and Forecast updated Daily, Copernicus Marine Service. [CrossRef]
- CMEMS. Mediterranean Sea Physics Analysis and Forecast, Copernicus Marine Service. [CrossRef]
- Clementi, E.; Chiara Goglio, A.; Aydogdu, A.; Pistoia, J.; Escudier, R.; Drudi, M.; Grandi, A.; Mariani, A.; Lyubartsev, V.; Lecci, R.; et al. The new Mediterranean Sea analysis and forecasting system including tides: description and validation. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly Conference Abstracts, 2021; pp. EGU21–13531–EGU13521–13531. [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson, D.; Müller, S.A.; Sévellec, F. Tracking water masses using passive-tracer transport in NEMO v3.4 with NEMOTAM: application to North Atlantic Deep Water and North Atlantic Subtropical Mode Water. Geosci. Model Dev. 2020, 13, 2031–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lea, D.J.; Mirouze, I.; Martin, M.J.; King, R.R.; Hines, A.; Walters, D.; Thurlow, M. Assessing a new coupled data assimilation system based on the met office coupled atmosphere-land-ocean-sea ice model. Monthly Weather Review 2015, 143, 4678–4694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilskie, M.V.; Hagen, S.C.; Alizad, K.; Medeiros, S.C.; Passeri, D.L.; Needham, H.F.; Cox, A. Dynamic simulation and numerical analysis of hurricane storm surge under sea level rise with geomorphologic changes along the northern Gulf of Mexico. Earth's Future 2016, 4, 177–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumberg, A.F.; Mellor, G.L. A Description of a Three-Dimensional Coastal Ocean Circulation Model. In Three-Dimensional Coastal Ocean Models; Coastal and Estuarine Sciences; 1987; pp. 1–16.
- Metzger, E.J.; Smedstad, O.M.; Thoppil, P.G.; Hurlburt, H.E.; Cummings, J.A.; Wallcraft, A.J.; Zamudio, L.; Franklin, D.S.; Posey, P.G.; Phelps, M.W.; et al. US Navy Operational Global Ocean and Arctic Ice Prediction Systems. Oceanography 2014, 27, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chassignet, E.P.; Hurlburt, H.E.; Smedstad, O.M.; Halliwell, G.R.; Hogan, P.J.; Wallcraft, A.J.; Bleck, R. Ocean prediction with the Hybrid Coordinate Ocean Model (HYCOM). Ocean Weather Forecasting: An Integrated View of Oceanography 2006, 22, 413–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chassignet, E.P.; Srinivasan, A. Data Assimilative Hindcast for the Gulf of Mexico. US Dept. of the Interior, Bureau of Ocean Energy Management, Headquarters, Sterling, VA 2015, OCS Study, 46 p.
- Androulidakis, Y.; Kourafalou, V.; Le Hénaff, M.; Kang, H.S.; Sutton, T.; Chen, S.; Hu, C.; Ntaganou, N. Offshore Spreading of Mississippi Waters: Pathways and Vertical Structure Under Eddy Influence. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans 2019, 124, 5952–5978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourafalou, V.; Androulidakis, Y.; Le Hénaff, M.; Kang, H.S. The Dynamics of Cuba Anticyclones (CubANs) and Interaction With the Loop Current/Florida Current System. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans 2017, 122, 7897–7923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourafalou, V.H.; Androulidakis, Y.S.; Kang, H.; Smith, R.H.; Valle-Levinson, A. Physical connectivity between Pulley Ridge and Dry Tortugas coral reefs under the influence of the Loop Current/Florida Current system. Progress in Oceanography 2018, 165, 75–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, K.H.; He, R. Coastal upwelling in the South Atlantic Bight: A revisit of the 2003 cold event using long term observations and model hindcast solutions. Journal of Marine Systems 2010, 83, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.; He, R.; Fennel, K.; Cai, W.J.; Lohrenz, S.; Hopkinson, C. Modeling ocean circulation and biogeochemical variability in the Gulf of Mexico. Biogeosciences 2013, 10, 7219–7234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambon, J.B.; He, R. Development of the Coupled Northwest Atlantic Prediction System (CNAPS). , 2016, 2016; pp. PO14B–2775. 01 February.
- Chao, Y.; Li, Z.; Farrara, J.; McWilliams, J.C.; Bellingham, J.; Capet, X.; Chavez, F.; Choi, J.K.; Davis, R.; Doyle, J.; et al. Development, implementation and evaluation of a data-assimilative ocean forecasting system off the central California coast. Deep-Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography 2009, 56, 100–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oddo, P.; Bonaduce, A.; Pinardi, N.; Guarnieri, A. Sensitivity of the Mediterranean Sea level to atmospheric pressure and free surface elevation numerical formulation in NEMO. Geoscientific Model Development 2014, 7, 3001–3015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonani, M.; Pinardi, N.; Dobricic, S.; Pujol, I.; Fratianni, C. A high-resolution free-surface model of the Mediterranean Sea. Ocean Science 2008, 4, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrarin, C.; Bajo, M.; Umgiesser, G. Model-driven optimization of coastal sea observatories through data assimilation in a finite element hydrodynamic model (SHYFEM v. 7565). Geoscientific Model Development 2021, 14, 645–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umgiesser, G.; Ferrarin, C.; Cucco, A.; De Pascalis, F.; Bellafiore, D.; Ghezzo, M.; Bajo, M. Comparative hydrodynamics of 10 Mediterranean lagoons by means of numerical modeling. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans 2014, 119, 2212–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaeta, M.G.; Samaras, A.G.; Federico, I.; Archetti, R.; Maicu, F.; Lorenzetti, G. A coupled wave-3-D hydrodynamics model of the Taranto Sea (Italy): A multiple-nesting approach. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences 2016, 16, 2071–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinardi, N.; Allen, I.; Demirov, E.; De Mey, P.; Korres, G.; Lascaratos, A.; Le Traon, P.Y.; Maillard, C.; Manzella, G.; Tziavos, C. The Mediterranean ocean forecasting system: First phase of implementation (1998-2001). Annales Geophysicae 2003, 21, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federico, I.; Pinardi, N.; Coppini, G.; Oddo, P.; Lecci, R.; Mossa, M. Coastal ocean forecasting with an unstructured grid model in the southern Adriatic and northern Ionian seas. Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences 2017, 17, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röhrs, J.; Sperrevik, A.K.; Christensen, K.H. NorShelf: A reanalysis and data-assimilative forecast model for the Norwegian Shelf Sea; 2018; pp. 1–42.
- Shchepetkin, A.F.; McWilliams, J.C. The regional oceanic modeling system (ROMS): a split-explicit, free-surface, topography-following-coordinate oceanic model. Ocean Modelling 2005, 9, 347–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debreu, L.; Marchesiello, P.; Penven, P.; Cambon, G. Two-way nesting in split-explicit ocean models: Algorithms, implementation and validation. Ocean Modelling 2012, 49-50, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Fox-Kemper, B.; Zhu, J.; Dong, C. Application of Symmetric Instability Parameterization in the Coastal and Regional Ocean Community Model (CROCO). Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems 2021, 13, e2020MS002302–e002020MS002302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penven, P.; Marchesiello, P.; Debreu, L.; Lefèvre, J. Software tools for pre- and post-processing of oceanic regional simulations. Environmental Modelling and Software 2008, 23, 660–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, I.R.; Bach, H.K. MIKE 21: a modelling system for estuaries, coastal waters and seas. Environmental Software 1992, 7, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhi, M. MIKE 21 & MIKE 3 flow model FM, hydrodynamic and transport module, scientific documentation. DHI Water & Environment 2017.
- Symonds, A.M.; Vijverberg, T.; Post, S.; van der Spek, B.-J.; Henrotte, J.; Sokolewicz, M. COMPARISON BETWEEN MIKE 21 FM, DELFT3D AND DELFT3D FM FLOW MODELS OF WESTERN PORT BAY, AUSTRALIA. Coastal Engineering Proceedings 2017, 1, currents–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burchard, H.; Petersen, O. Models of turbulence in the marine environment —a comparative study of two-equation turbulence models. Journal of Marine Systems 1999, 21, 29–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cucco, A.; Sinerchia, M.; Ribotti, A.; Olita, A.; Fazioli, L.; Perilli, A.; Sorgente, B.; Borghini, M.; Schroeder, K.; Sorgente, R. A high-resolution real-time forecasting system for predicting the fate of oil spills in the Strait of Bonifacio (western Mediterranean Sea). Marine Pollution Bulletin 2012, 64, 1186–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cucco, A.; Daniel, P. Numerical Modeling of Oil Pollution in the Western Mediterranean Sea. In Oil Pollution in the Mediterranean Sea: Part I: The International Context, Carpenter, A., Kostianoy, A.G., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2018; pp. 255–274. [Google Scholar]
- Korres, G.; Nitti, K.; Perivoliotis, L.; Tsiaras, K.; Papadopoulos, A.; Triantafyllou, G.; Hoteit, I.; Abdullah, K. Forecasting the Aegean Sea hydrodynamics within the POSEIDON-II operational system. Journal of Operational Oceanography 2010, 3, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zodiatis, G.; Coppini, G.; Perivoliotis, L.; Lardner, R.; Alves, T.; Pinardi, N.; Liubartseva, S.; De Dominicis, M.; Bourma, E.; Sepp Neves, A.A. Numerical Modeling of Oil Pollution in the Eastern Mediterranean Sea. In Oil Pollution in the Mediterranean Sea: Part I: The International Context, Carpenter, A., Kostianoy, A.G., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2018; pp. 215–254. [Google Scholar]
- Zodiatis, G.; Lardner, R.; Lascaratos, A.; Georgiou, G.; Korres, G.; Syrimis, M. High resolution nested model for the Cyprus, NE Levantine Basin, eastern Mediterranean Sea: implementation and climatological runs. Ann. Geophys. 2003, 21, 221–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zodiatis, G.; Lardner, R.; Nikolaidis, M.; Sofianos, S.; Vervantis, V.; Zhuk, E.; Spanoudaki, K.; Kampanis, N.; Kallos, G.; Sylaios, G. The new CYCOFOS forecasting at coastal, sub-regional and regional scales in the Mediterranean and the Black Sea. , 2021, 2021; pp. EGU21–2392. 01 April.
- Pinardi, N.; Coppini, G. Preface "Operational oceanography in the Mediterranean Sea: the second stage of development". Ocean Sci. 2010, 6, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oddo, P.; Pinardi, N.; Zavatarelli, M. A numerical study of the interannual variability of the Adriatic Sea (2000–2002). Science of The Total Environment 2005, 353, 39–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppini, G.; De Dominicis, M.; Zodiatis, G.; Lardner, R.; Pinardi, N.; Santoleri, R.; Colella, S.; Bignami, F.; Hayes, D.R.; Soloviev, D.; et al. Hindcast of oil-spill pollution during the Lebanon crisis in the Eastern Mediterranean, July–August 2006. Marine Pollution Bulletin 2011, 62, 140–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clementi, E.; Oddo, P.; Gerasimos, K.; Drudi, M.; Pinardi, N. Coupled wave-ocean modelling system in the Mediterranean Sea; 2013.
- Korres, G.; Lascaratos, A. A one-way nested eddy resolving model of the Aegean and Levantine basins: implementation and climatological runs. Ann. Geophys. 2003, 21, 205–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonani, M.; Teruzzi, A.; Gerasimos, K.; Pinardi, N.; Crise, A.; Adani, M.; Oddo, P.; Dobricic, S.; Fratianni, C.; Drudi, M.; et al. The Mediterranean Monitoring and Forecasting Centre, a component of the MyOcean system; 2011.
- Garreau, P.; Garnier, V.; Schaeffer, A. Eddy resolving modelling of the Gulf of Lions and Catalan Sea. Ocean Dynamics 2011, 61, 991–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaeffer, A.; Garreau, P.; Molcard, A.; Fraunié, P.; Seity, Y. Influence of high-resolution wind forcing on hydrodynamic modeling of the Gulf of Lions. Ocean Dynamics 2011, 61, 1823–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Group, T.W. The WAM Model—A Third Generation Ocean Wave Prediction Model. Journal of Physical Oceanography 1988, 18, 1775–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ECMWF. Wave Forecasts. Available online: http://apps.ecmwf.int/mars-catalogue/?class=od&stream=wave (accessed on 15 November 2022).
- CMEMS. Global Ocean Waves Reanalysis WAVERYS. [CrossRef]
- Law-Chune, S.; Aouf, L.; Dalphinet, A.; Levier, B.; Drillet, Y.; Drevillon, M. WAVERYS: a CMEMS global wave reanalysis during the altimetry period. Ocean Dynamics 2021, 71, 357–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aouf, L.; Dalphinet, A.; Hauser, D.; Delaye, L.; Tison, C.; Chapron, B.; Hermozo, L.; Tourain, C. On the assimilation of CFOSAT wave data in the wave model MFWAM: Verification phase. In Proceedings of the International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS); 2019; pp. 7959–7961. [Google Scholar]
- Ferry, N.; Parent, L.; Garric, G.; Barnier, B.; Jourdain, N.C. Mercator global Eddy permitting ocean reanalysis GLORYS1V1: Description and results. Mercator-Ocean Quarterly Newsletter 2010, 34, 15–27. [Google Scholar]
- CMEMS. Mediterranean Sea Waves Analysis and Forecast, Copernicus Marine Service. [CrossRef]
- Korres, G.; Ravdas, M.; Zacharioudaki, A.; Denaxa, D.; Sotiropoulou, M. Mediterranean sea waves analysis and forecast (CMEMS MED-Waves, MedWAM3 system)(Version 1)[Data set]. Copernicus Monitoring Environment Marine Service (CMEMS). Epub ahead of print. [CrossRef]
- Ardhuin, F.; Rogers, E.; Babanin, A.V.; Filipot, J.F.; Magne, R.; Roland, A.; van der Westhuysen, A.; Queffeulou, P.; Lefevre, J.M.; Aouf, L.; et al. Semiempirical dissipation source functions for ocean waves. Part I: Definition, calibration, and validation. Journal of Physical Oceanography 2010, 40, 1917–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CMEMS. Global Ocean Waves Analysis and Forecast. [CrossRef]
- Korres, G.; Papadopoulos, A.; Katsafados, P.; Ballas, D.; Perivoliotis, L.; Nittis, K. A 2-year intercomparison of the WAM-Cycle4 and the WAVEWATCH-III wave models implemented within the Mediterranean Sea. Mediterranean Marine Science 2011, 12, 129–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zodiatis, G.; Lardner, R.; Hayes, D.R.; Georgiou, G.; Sofianos, S.; Skliris, N.; Lascaratos, A. Operational ocean forecasting in the Eastern Mediterranean: implementation and evaluation. Ocean Sci. 2008, 4, 31–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zodiatis, G.; Galanis, G.; Nikolaidis, A.; Radhakrishnan, H.; Emmanouil, G.; Nikolaidis, G.; Lardner, R.; Sofianos, S.; Stylianou, S.; Nikolaidis, M. Downscaling the Copernicus CMEMS Med-MFC in the Eastern Mediterranean: The new CYCOFOS forecasting systems at regional and sub-regional scales. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the Eight EuroGOOS International Conference, Bergen, Norway, 3-5 October 2017, 2017; pp. 305–310.
- Sammut, S.; Gauci, R.; Drago, A.; Gauci, A.; Azzopardi, J. Pocket beach sediment: A field investigation of the geodynamic processes of coarse-clastic beaches on the Maltese Islands (Central Mediterranean). Marine Geology 2017, 387, 58–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolman, H. User manual and system documentation of WAVEWATCH III version 3.14. MMAB Contribution 2009, 166, 311. [Google Scholar]
- Pleskachevsky, A.; Tings, B.; Wiehle, S.; Imber, J.; Jacobsen, S. Multiparametric sea state fields from synthetic aperture radar for maritime situational awareness. Remote Sensing of Environment 2022, 280, 113200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, P. The wave model. Meteorological Training Course Lecture Series 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Spanoudaki, K. Mathematical modelling of oil spill fate and transport in the marine environment incorporating biodegradation kinetics of oil droplets. , 2016, 2016; pp. EPSC2016–13155. 01 April.
- Zheng, Y.; Bourassa, M.A.; Hughes, P. Influences of Sea Surface Temperature Gradients and Surface Roughness Changes on the Motion of Surface Oil: A Simple Idealized Study. Journal of Applied Meteorology and Climatology 2013, 52, 1561–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, I.C.; Toro-Farmer, G.; Diercks, A.R.; Schwing, P.; Muller-Karger, F.; Murawski, S.; Hollander, D.J. Large-scale deposition of weathered oil in the Gulf of Mexico following a deep-water oil spill. Environmental Pollution 2017, 228, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Area | Oil spill Model | Forcing Wind Field | Hydrodynamics | Waves | Oil Weathering Processes | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Norwegian Sea | OpenOil | ECMWF (0.1°) | NorShelf model (2.4 km, hourly) | ECMWF (0.125°, 12-hourly) | Evaporation, emulsification, dispersion, beaching, vertical mixing, resurfacing | [23] |
| Gulf of Mexico | OpenOil | ECMWF (0.125°, 6-hourly) | GoM-HYCOM (1/50°) | ECMWF (0.125°,12-hourly) | Evaporation, emulsification, dispersion, beaching, vertical mixing, resurfacing | [47] |
| Italian Seas | MEDSLIK-II | SKIRON (10 km, hourly) | SHYFEM (4 km, 1 km, hourly) | - | Evaporation, emulsification, dispersion, spreading, beaching | [104] |
| Northern Atlantic | MEDSLIK-II | ECMWF (0.125°, 6-hourly) | CMEMS-Global (1/12°, hourly) | - | Evaporation, emulsification, dispersion, spreading, beaching | [53] |
| Northwestern Med Sea | MEDSLIK-II | ECMWF (0.125°, 6-hourly) | CMEMS Med MFC (1/24°, hourly) | Jonswap wave spectrum | Evaporation, emulsification, dispersion, spreading, beaching | [54] |
| GoM and Cuban coast | OpenOil | ECMWF (0.125°, 3-hourly) | GoM-HYCOM (1/50°, 6-hourly) FKEYS-HYCOM (1/100°, 6-hourly) | ECMWF (0.125°,12-hourly) | Evaporation, emulsification, dispersion, beaching, vertical mixing, resurfacing | [46] |
| Gulf of Mexico | OpenOil | ECMWF (0.125°, 6-hourly) | GoM-HYCOM (1/50°, daily) | ECMWF (0.125°, 12-hourly) | Evaporation, emulsification, dispersion | [49] |
| Gulf of Mexico | OILMAPDEEP/SIMAP | ) | GoM-HYCOM (1/25°, 3-hourly) with ADCP currents | - | Evaporation, emulsification, dispersion, spreading, beaching, dissolution, sedimentation, biodegradation | [67] |
| Gulf of Mexico | SIMAP | NOAA-NARR (0.3°, 3-hourly) CFSR (0.5°, hourly) NAM (12km, hourly) NOGAPS (0.5°, 6-hourly) |
GoM-HYCOM Reanalysis (1/25°, 3-hourly) GoM-HYCOM Real-time (1/25°, hourly) SABGOM (5 km, 3-hourly) IAS ROMS (6 km, hourly) NCOM Real Time (3km, 3-hourly) NGOM (5-6 km, 3-hourly) |
- | Evaporation, emulsification, dispersion, spreading, beaching, dissolution, sedimentation, biodegradation, photo-oxidation. | [66] |
| Indonesia | GNOME | constant | CMEMS-Global (1/12°, hourly) and CROCO (1km) | ECMWF (0.125°, 12-hourly) and CROCO (1km) | - | [68] |
| Aegean Sea | MEDSLIK-II | ECMWF (~9 km, ~18 km, hourly) | CMEMS Med MFC (1/24°, hourly) | Ekman | Evaporation, emulsification, dispersion, spreading, beaching | [55] |
| Cuban coast | OpenOil | ECMWF (0.125°, 3-hourly) | GoM-HYCOM (1/50°, daily) FKEYS-HYCOM (1/100°, 6-hourly) |
ECMWF (0.125°, 12-hourly) | Evaporation, emulsification, dispersion, beaching, vertical mixing, resurfacing | [48] |
| Southern Italy | MEDSLIK-II | ECMWF (0.125°, 6-hourly) | SANIFS (3km in open sea, 100 m in coastal waters, 20 m in target area, hourly) | Johnswap wave spectrum | Evaporation, emulsification, dispersion, spreading, beaching | [56] |
| Brazilian Coast | STFM | WRF (0.15°, hourly) | GLB-HYCOM (1/12°, 3-hourly) | - | Evaporation, emulsification, dispersion | [44] |
| SE Levantine |
MEDSLIK and MEDSLIK II | SKIRON (5 km, hourly) ECMWF (0.125°, 6-hourly) |
CYCOFOS (2km, 6-hourly) CMEMS Med MFC (1/24°, hourly) |
- | Evaporation, emulsification, dispersion, spreading, beaching | [61] |
| Thracian Sea | OpenOil | NOAA-GFS (0.25°, 3-hourly) | CMEMS Med MFC (1/24°, hourly) | Evaporation, emulsification, dispersion, beaching, vertical mixing, resurfacing, Biodegradation | [50] | |
| Brazilian Coast | MEDSLIK-II | ECMWF (0.125°, 6-hourly) | CMEMS-Global Forecast (1/12°, hourly) | Johnswap wave spectrum | Evaporation, emulsification, dispersion, spreading, beaching | [57] |
| Gulf of Suez, Egypt | GNOME | ) | GLO-CPL Copernicus (1/4°, hourly) | - | Evaporation, emulsification, dispersion, spreading, beaching | [69] |
| Gulf of Paria Venezuela |
BLOSOM | NCOM – AMSEAS (3 km, 3-hourly) | NCOM – AMSEAS 3 km, 3-hourly) | - | Evaporation, emulsification, dispersion, spreading, beaching | [74] |
| Odisha offshore India | GNOME | NOAA NCEP-GFS (0.25°, 3-hourly) | GLB-HYCOM (1/12°, 3-hourly) | - | Evaporation, emulsification, dispersion, spreading, beaching | [70] |
| Chinese Bohai Sea | MIKE 21/3 OS FM | ) | MIKE21 | - | Evaporation, emulsification, dispersion | [42] |
| Colombian Caribbean |
OpenOil | ) | CMEMS-Global Forecast (1/12°, hourly) | CMEMS-Global Reanalysis (1/5°, 3-hourly) | Evaporation, emulsification, dispersion, beaching, vertical mixing, resurfacing, Biodegradation | [51] |
| Red Sea, Egypt | GNOME | ) | CMEMS-Global Forecast (1/12°, hourly) | - | Evaporation, emulsification, spreading, dispersion, beaching | [71] |
| NE Levantine | MEDSLIK and MEDSLIK II |
SKIRON (5km, hourly) ECMWF (0.125°, 6-hourly) |
CYCOFOS (2km, 6-hourly) CMEMS Med MFC (1/24°) |
- | Evaporation, emulsification, dispersion, spreading, beaching | [58] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





