Submitted:
27 April 2023
Posted:
28 April 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemistry
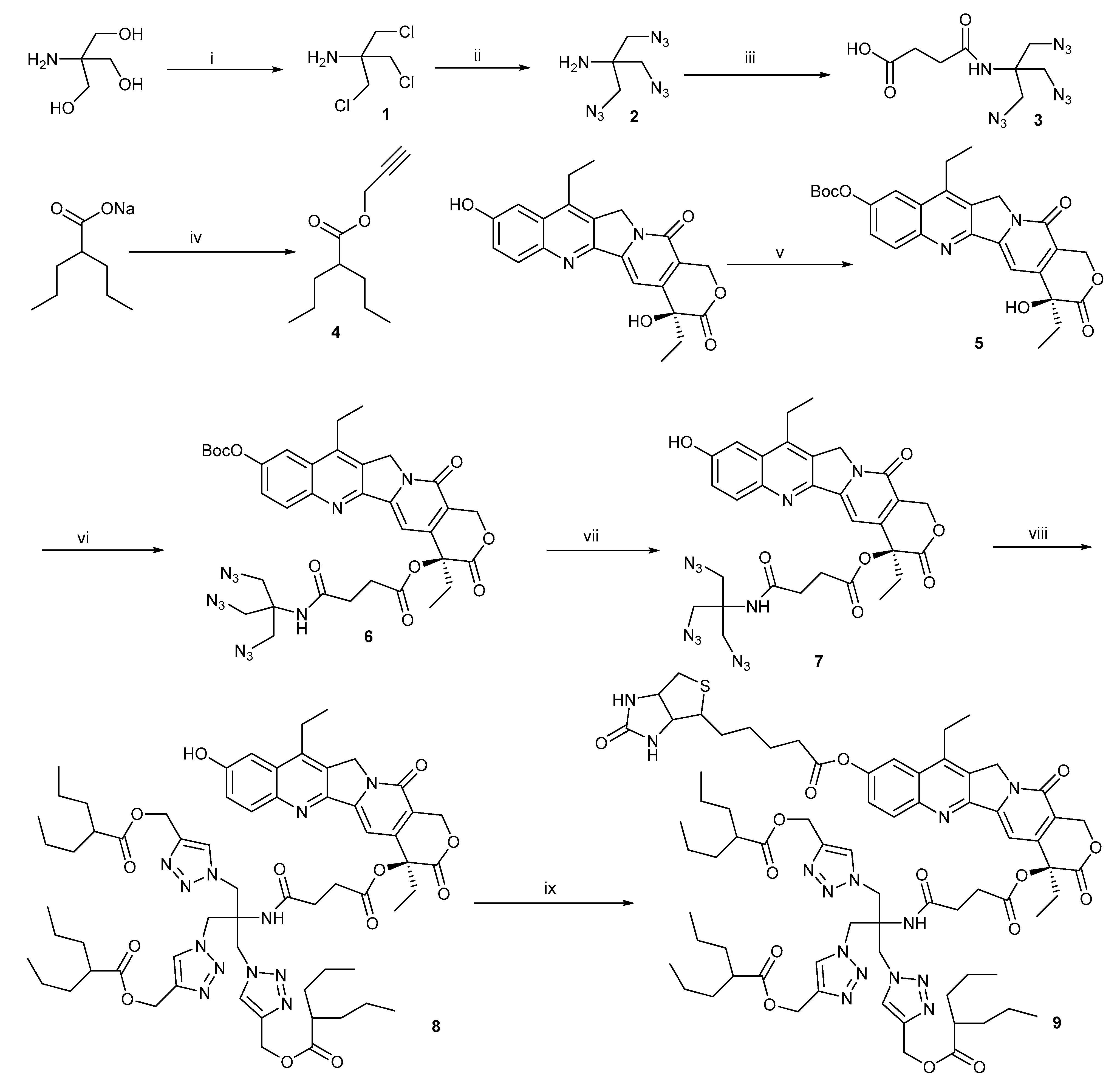
2.2. In Vitro Biological evaluation
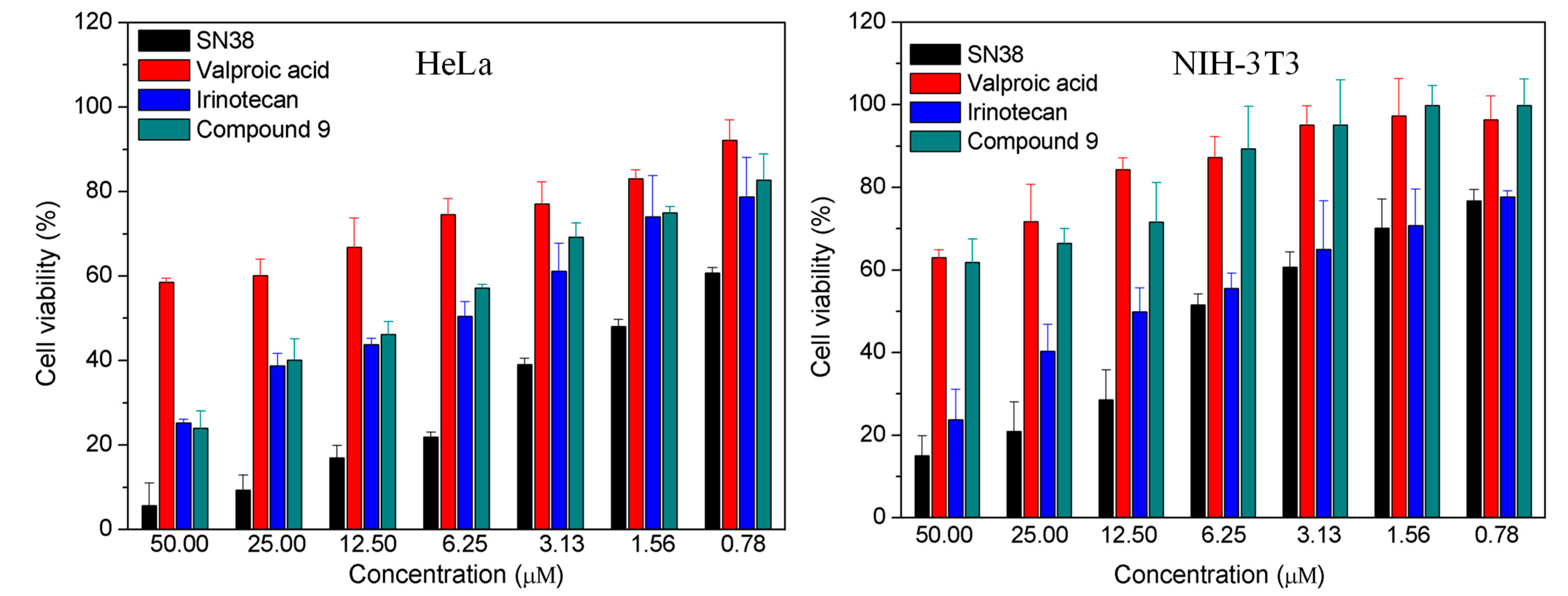
2.2.1. In Vitro Cytotoxicity
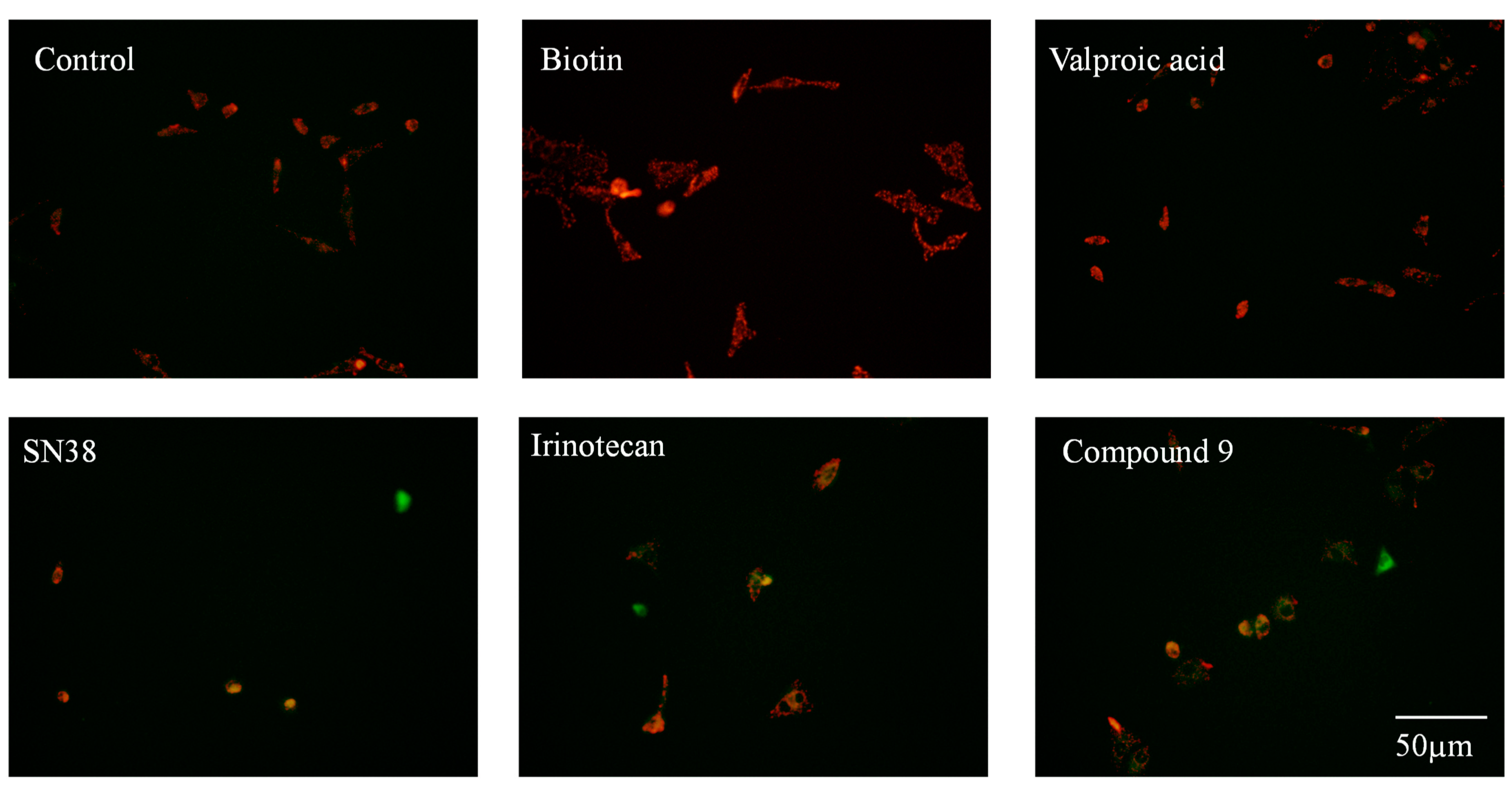
2.2.2. Mitochondrial Membrane Potential Analysis
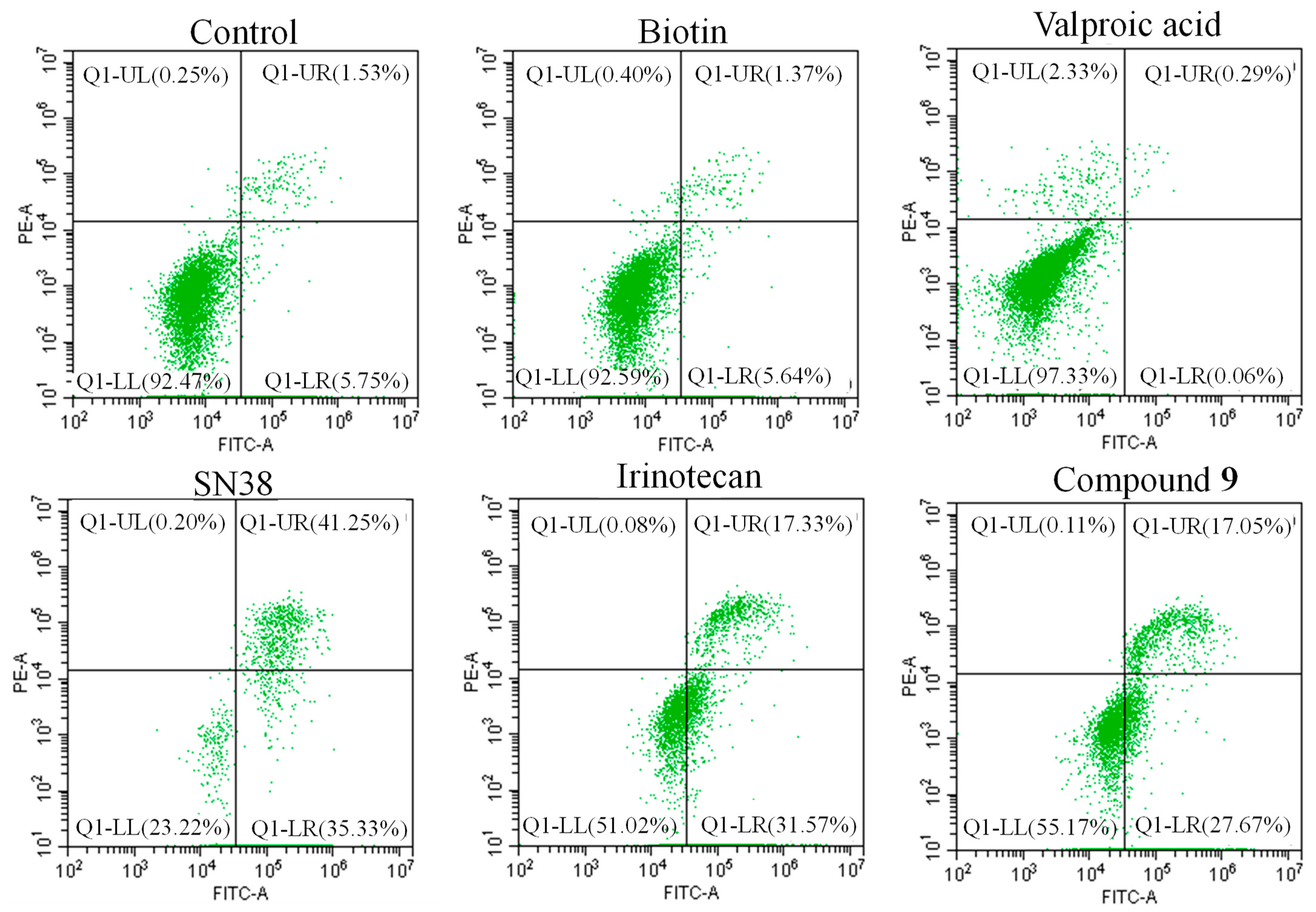
2.2.3. Apoptosis Study
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Synthesis of Compound 9
3.1.1. The Synthetic Route of Compound 1
3.1.2. The Synthetic Route of Compound 2
3.1.3. The Synthetic Route of Compound 3
3.1.4. The Synthetic Route of Compound 4
3.1.5. The Synthetic Route of Compound 5
3.1.6. The Synthetic Route of Compound 6 and 7
3.1.7. The Synthetic Route of Compound 8
3.1.8. The Synthetic Route of Compound 9
3.2. In Vitro Biological evaluation
3.2.1. In vitro cytotoxicity assay
3.2.2. Mitochondrial membrane potentials assay
3.2.3. Cell apoptosis assay
3.2.4. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martino, E.; Della Volpe, S.; Terribile, E.; Benetti, E.; Sakaj, M.; Centamore, A.; Sala, A.; Collina, S. The long story of camptothecin: From traditional medicine to drugs. Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry letters 2017, 27, 701–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocian, W.; Naumczuk, B.; Urbanowicz, M.; Sitkowski, J.; Bierczynska-Krzysik, A.; Bednarek, E.; Wiktorska, K.; Milczarek, M.; Kozerski, L. The Mode of SN38 Derivatives Interacting with Nicked DNA Mimics Biological Targeting of Topo I Poisons. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin-Encinas, E.; Selas, A.; Palacios, F.; Alonso, C. The design and discovery of topoisomerase I inhibitors as anticancer therapies. Expert Opinion on Drug Discovery 2022, 17, 581–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leppard, J.B.; Champoux, J.J. Human DNA topoisomerase I: relaxation, roles, and damage control. Chromosoma 2005, 114, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khaiwa, N.; Maarouf, N.R.; Darwish, M.H.; Alhamad, D.W.M.; Sebastian, A.; Hamad, M.; Omar, H.A.; Orive, G.; Al-Tel, T.H. Camptothecin's journey from discovery to WHO Essential Medicine: Fifty years of promise. Eur J Med Chem 2021, 223, 113639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cronin, A.; Barnes, J.; Pedersen, J.; Heathcote, D.; Collins, T. Mitigating exacerbation of Irinotecan-induced gastrointestinal toxicity in combination with an ATM inhibitor in the rat. Toxicology Letters 2016, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venditto, V.J.; Simanek, E.E. Cancer Therapies Utilizing the Camptothecins: A Review of the in Vivo Literature. Molecular pharmaceutics 2010, 7, 307–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bala, V.; Rao, S.; Li, P.; Wang, S.; Prestidge, C.A. Lipophilic Prodrugs of SN38: Synthesis and in Vitro Characterization toward Oral Chemotherapy. Molecular pharmaceutics 2016, 13, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Wu, X.; Li, T.; Wu, Y.; Song, L.; Zhang, W.; Yin, L.; Wu, Y.; Han, W.; Yang, Y. An esterase-activatable prodrug formulated liposome strategy: potentiating the anticancer therapeutic efficacy and drug safety. Nanoscale Advances 2022, 4, 952–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Liu, X.; Wang, H.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Li, K.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Shen, Y.; Sui, M. A nanotherapeutic strategy to overcome chemoresistance to irinotecan/7-ethyl-10-hydroxy-camptothecin in colorectal cancer. Acta Biomater 2022, 137, 262–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.Y.; Zhao, H.Y.; Lei, H.; Yuan, B.; Mao, S.; Xin, M.; Zhang, S.Q. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of 10-Substituted Camptothecin Derivatives with Improved Water Solubility and Activity. ChemMedChem 2021, 16, 1000–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Xie, F.; Xiao, D.; Xu, X.; Su, Z.; Wang, Y.; Fan, S.; Zhou, X.; Li, S. Synthesis and evaluation of highly releasable and structurally stable antibody-SN-38-conjugates. Drug Deliv 2021, 28, 2603–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Shen, Q.; Gao, Y.; Wang, L.; Fang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Lu, W. Design, Synthesis, and Biological Evaluation of HSP90 Inhibitor-SN38 Conjugates for Targeted Drug Accumulation. Journal of medicinal chemistry 2020, 63, 5421–5441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botta, L.; Filippi, S.; Zippilli, C.; Cesarini, S.; Bizzarri, B.M.; Cirigliano, A.; Rinaldi, T.; Paiardini, A.; Fiorucci, D.; Saladino, R.; et al. Artemisinin Derivatives with Antimelanoma Activity Show Inhibitory Effect against Human DNA Topoisomerase 1. ACS medicinal chemistry letters 2020, 11, 1035–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verza, F.A.; Das, U.; Fachin, A.L.; Dimmock, J.R.; Marins, M. Roles of Histone Deacetylases and Inhibitors in Anticancer Therapy. Cancers 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Autin, P.; Blanquart, C.; Fradin, D. Epigenetic Drugs for Cancer and microRNAs: A Focus on Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors. Cancers (Basel) 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckschlager, T.; Plch, J.; Stiborova, M.; Hrabeta, J. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors as Anticancer Drugs. Int J Mol Sci 2017, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molife, L.R.; de Bono, J.S. Belinostat: clinical applications in solid tumors and lymphoma. Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs 2011, 20, 1723–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnock-Jones, K.P. Panobinostat: First Global Approval. Drugs 2015, 75, 695–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wong, C.H.; Loong, H.H.F. Synergistic activities of the histone deacetylase inhibitors with conventional cytotoxic chemotherapies in angiosarcomas. Invest New Drugs 2022, 40, 868–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cincinelli, R.; Musso, L.; Artali, R.; Guglielmi, M.B.; La Porta, I.; Melito, C.; Colelli, F.; Cardile, F.; Signorino, G.; Fucci, A.; et al. Hybrid topoisomerase I and HDAC inhibitors as dual action anticancer agents. PLoS One 2018, 13, e0205018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, R.; Miyanishi, K.; Kubo, T.; Hamaguchi, K.; Osuga, T.; Tanaka, S.; Ohnuma, H.; Murase, K.; Takada, K.; Nagayama, M.; et al. Synergistic antitumor effect of histone deacetylase class IIa inhibitor with lenvatinib in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol Int, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovejero-Sanchez, M.; Asensio-Juarez, G.; Gonzalez, M.; Puebla, P.; Vicente-Manzanares, M.; Pelaez, R.; Gonzalez-Sarmiento, R.; Herrero, A.B. Panobinostat Synergistically Enhances the Cytotoxicity of Microtubule Destabilizing Drugs in Ovarian Cancer Cells. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Q.; Yu, X.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Su, M.; Zhou, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, Y.; Lu, W. A series of camptothecin prodrugs exhibit HDAC inhibition activity. Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry 2018, 26, 4706–4715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, G.Y.; Wang, L.B.; Kang, J.H.; Wang, J.M. Curcumin p38-dependently enhances the anticancer activity of valproic acid in human leukemia cells. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 2010, 41, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.T.; Lai, H.C.; Lee, H.Y.; Lin, W.H.; Chang, C.C.; Chu, T.Y.; Lin, Y.W.; Lee, K.D.; Yu, M.H. Valproic acid resensitizes cisplatin-resistant ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Science 2008, 99, 1218–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna-Palencia, G.R.; Correa-Basurto, J.; Vasquez-Moctezuma, I. Valproic acid as a sensitizing agent for cancer treatment. Gaceta Medica De Mexico 2019, 155, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanaei, M.; Kavoosi, F. Profound Inhibitory and Apoptotic Effects of Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor Valproic Acid on Different Cancers. Crescent Journal of Medical and Biological Sciences 2019, 6, 441–448. [Google Scholar]
- Wawruszak, A.; Halasa, M.; Okon, E.; Kukula-Koch, W.; Stepulak, A. Valproic Acid and Breast Cancer: State of the Art in 2021. Cancers (Basel) 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wang, L.; Cheng, Z.; Yang, B.; Yu, J.; Chen, Y.; Lu, W. SN38-based albumin-binding prodrug for efficient targeted cancer chemotherapy. J Control Release 2021, 339, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Che, R.; Lu, W. Enhanced cellular uptake efficiency of DCM probes or SN38 conjugating with phenylboronic acids. Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry 2020, 28, 115377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Zhang, J.; Jin, X.; Liu, L.; Tian, X. Folate Receptor Targeting and Cathepsin B-Sensitive Drug Delivery System for Selective Cancer Cell Death and Imaging. ACS medicinal chemistry letters 2020, 11, 1514–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Hwang, D.; Choi, M.; Lee, S.; Kang, S.; Lee, Y.; Kim, S.; Chung, J.; Jon, S. Antibody-Assisted Delivery of a Peptide-Drug Conjugate for Targeted Cancer Therapy. Molecular pharmaceutics 2019, 16, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrikopoulou, A.; Zografos, E.; Liontos, M.; Koutsoukos, K.; Dimopoulos, M.A.; Zagouri, F. Trastuzumab Deruxtecan (DS-8201a): The Latest Research and Advances in Breast Cancer. Clin Breast Cancer 2021, 21, e212–e219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koo, S.; Bobba, K.N.; Cho, M.Y.; Park, H.S.; Won, M.; Velusamy, N.; Hong, K.S.; Bhuniya, S.; Kim, J.S. Molecular Theranostic Agent with Programmed Activation for Hypoxic Tumors. ACS Applied Bio Materials 2019, 2, 4648–4655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jangili, P.; Won, M.; Kim, S.J.; Chun, J.; Shim, I.; Kang, C.; Ren, W.X.; Kim, J.S. Binary Drug Reinforced First Small-Molecule-Based Prodrug for Synergistic Anticancer Effects. ACS Applied Bio Materials 2019, 2, 3532–3539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, H.; Xu, X.; Chen, J.; Li, L.; Wang, J.; Fang, T.; Zhou, L.; Wang, H.; Zheng, S. Rational design of multifunctional small-molecule prodrugs for simultaneous suppression of cancer cell growth and metastasis in vitro and in vivo. Chemical communications 2016, 52, 5601–5604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Wu, J.; Xie, K.; Fang, T.; Chen, C.; Xie, H.; Zhou, L.; Zheng, S. Precise Engineering of Prodrug Cocktails into Single Polymeric Nanoparticles for Combination Cancer Therapy: Extended and Sequentially Controllable Drug Release. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2017, 9, 10567–10576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Zhang, W.; He, R.; Ismail, M.; Ling, L.; Yao, C.; Fu, Z.; Li, X. Dual 7-ethyl-10-hydroxycamptothecin conjugated phospholipid prodrug assembled liposomes with in vitro anticancer effects. Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry 2017, 25, 3247–3258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Groot, F.; Busscher, G.; Aben, R.; Scheeren, H. Novel 20-carbonate linked prodrugs of camptothecin and 9-aminocamptothecin designed for activation by tumour-associated plasmin. Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry letters 2002, 12, 2371–2376. [Google Scholar]
- Fam, K.T.; Collot, M.; Klymchenko, A.S. Probing biotin receptors in cancer cells with rationally designed fluorogenic squaraine dimers. Chemical Science 2020, 11, 8240–8248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, X.Y.; Huo, F.J.; Yue, Y.K.; Chen, T.G.; Yin, C.X. Cancer cell recognition by a Cys-reactive turn-on significant enhanced fluorescent emission targeting biotin receptors. Sensors and Actuators B-Chemical 2020, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiti, S.; Paira, P. Biotin conjugated organic molecules and proteins for cancer therapy: A review. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2018, 145, 206–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoury, A.; Sakoff, J.A.; Gilbert, J.; Karan, S.; Gordon, C.P.; Aldrich-Wright, J.R. Potent Platinum(IV) Prodrugs That Incorporate a Biotin Moiety to Selectively Target Cancer Cells. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perumal, D.; Golla, M.; Pillai, K.S.; Raj, G.; Krishna, P.K.A.; Varghese, R. Biotin-decorated NIR-absorbing nanosheets for targeted photodynamic cancer therapy. Organic & biomolecular chemistry 2021, 19, 2804–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.M.; Luo, Y.; Du, C.H.; Wu, L.; Wang, Y.K.; Chen, Y.D.; Li, S.Q.; Jiang, X.; Xie, Y.M. Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel SN38-glucose conjugate for colorectal cancer treatment. Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry letters 2023, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Fu, W.; Zhu, L.-Z.; Liu, X.-F.; Li, L.; Peng, L.-Z.; Kai, G.-Y.; Liu, Y.-Q.; Zhang, Z.-J.; Xu, C.-R. Anti-tumor effects and mechanism of a novel camptothecin derivative YCJ100. Life sciences 2022, 311, 121105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.R.; Yin, R.J.; Dai, X.F.; Wu, G.Z.; Qi, X.; Li, J.; Jiang, T. Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of novel 7-substituted 10,11-methylenedioxy-camptothecin derivatives against drug-resistant small-cell lung cancer in vitro and in vivo. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2022, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, M.; Guo, Y.; Cui, Z.; Li, T.; Luo, D.; Xu, B.; Huang, C.; Guo, J.; et al. A Mitochondria-Targeted Phenylbutyric Acid Prodrug Confers Drastically Improved Anticancer Activities. Journal of medicinal chemistry 2022, 65, 9955–9973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, Y.H.; Shreeve, J.M. 1,3-Diazido-2-(azidomethyl)-2-propylammonium salts. Inorg Chem 2009, 48, 8431–8438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, K.K.; Ghosh, A.K.; Hajra, A. Late-stage ortho-C-H alkenylation of 2-arylindazoles in aqueous medium by Manganese(i)-catalysis. RSC Adv 2022, 12, 19412–19416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Lu, W. Co-Prodrugs of 7-Ethyl-10-hydroxycamptothecin and Vorinostat with in Vitro Hydrolysis and Anticancer Effects. ACS Omega 2019, 5, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Lee, Y.; Kang, S.; Choi, M.; Lee, S.; Kim, S.; Gujrati, V.; Kim, J.; Jon, S. Self-assembled nanoparticles comprising aptide-SN38 conjugates for use in targeted cancer therapy. Nanotechnology 2016, 27, 48LT01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).



