Submitted:
30 April 2023
Posted:
01 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
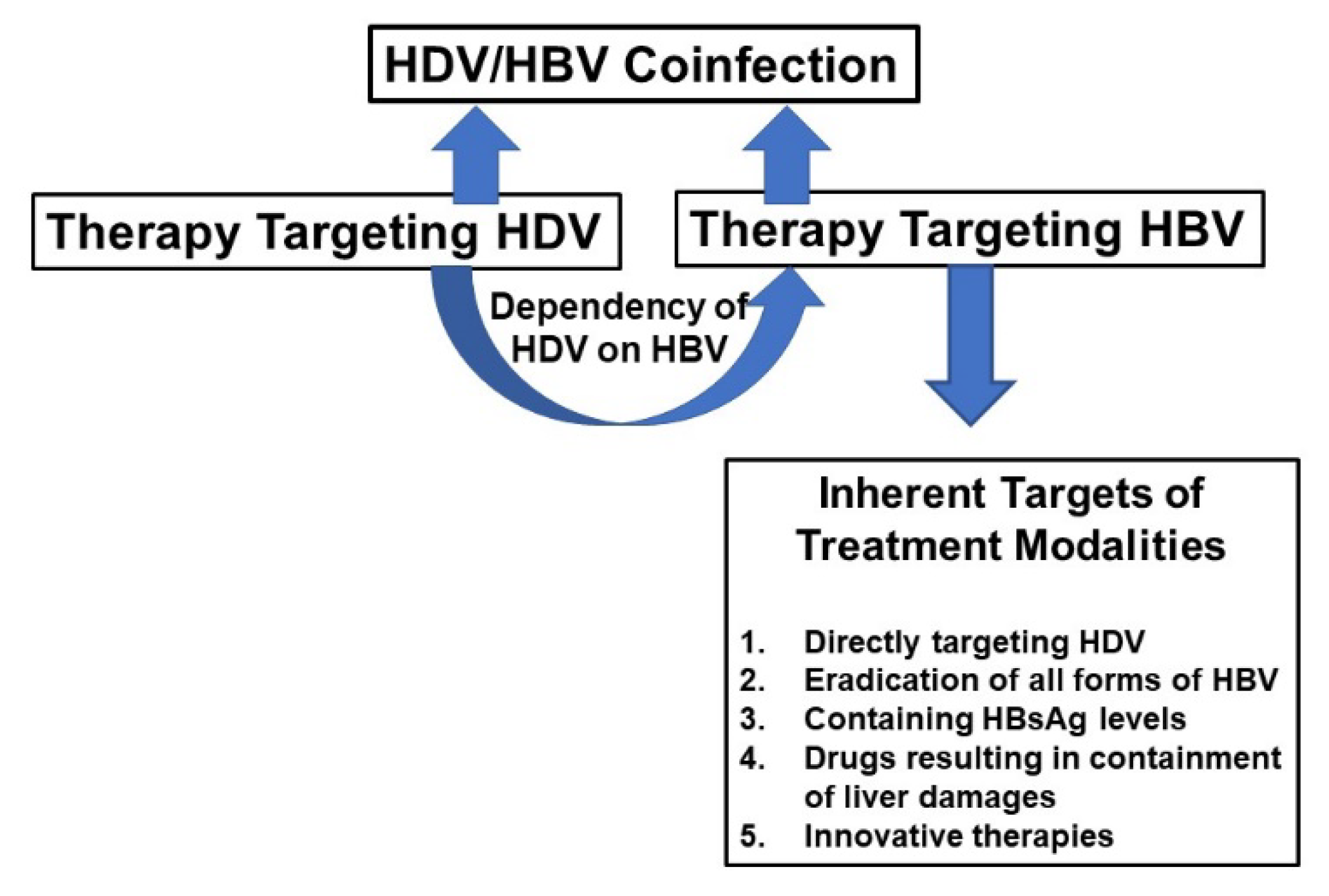
2. Characteristics of HDV/HBV coinfection
3. Ongoing therapeutic strategies against HDV
3.1. Fundamental aspects of therapy for HDV/HBV coinfection
3.2. Treatment of hepatitis delta patients with combination of IFNs with antiviral drugs
4. Fundamental logic of treatment of HBV/HDV coinfection and potentialities of commercially-available antiviral drugs
| 1. These drugs are not able to eradicate HBV. |
| 2. The effect of these drugs on cccDNA of HBV is almost negligible even after prolonged use. |
| 3. These drugs’ role in containing HBsAg and inducing seroconversion to antibody to HBsAg (anti-HBs) is insignificant. |
| 4. The immune modulatory capacities of these drugs are not enough to induce protective immunity to contain the pathological processes and control of viral replication and liver damages to satisfactory levels. |
5. Evolving therapies targeting the viruses
5.1. Therapies targeting entry of the virus to hepatocytes
5.2. HBsAg inhibition by nucleic acid polymers (NAP)
5.3. Prelylation-based therapy for HDV
5.4. Other evolving drugs for challenging HBV and HDV replication
6. What is expected from virus-targeting evolving drugs to contain HBV/HDV co-infection
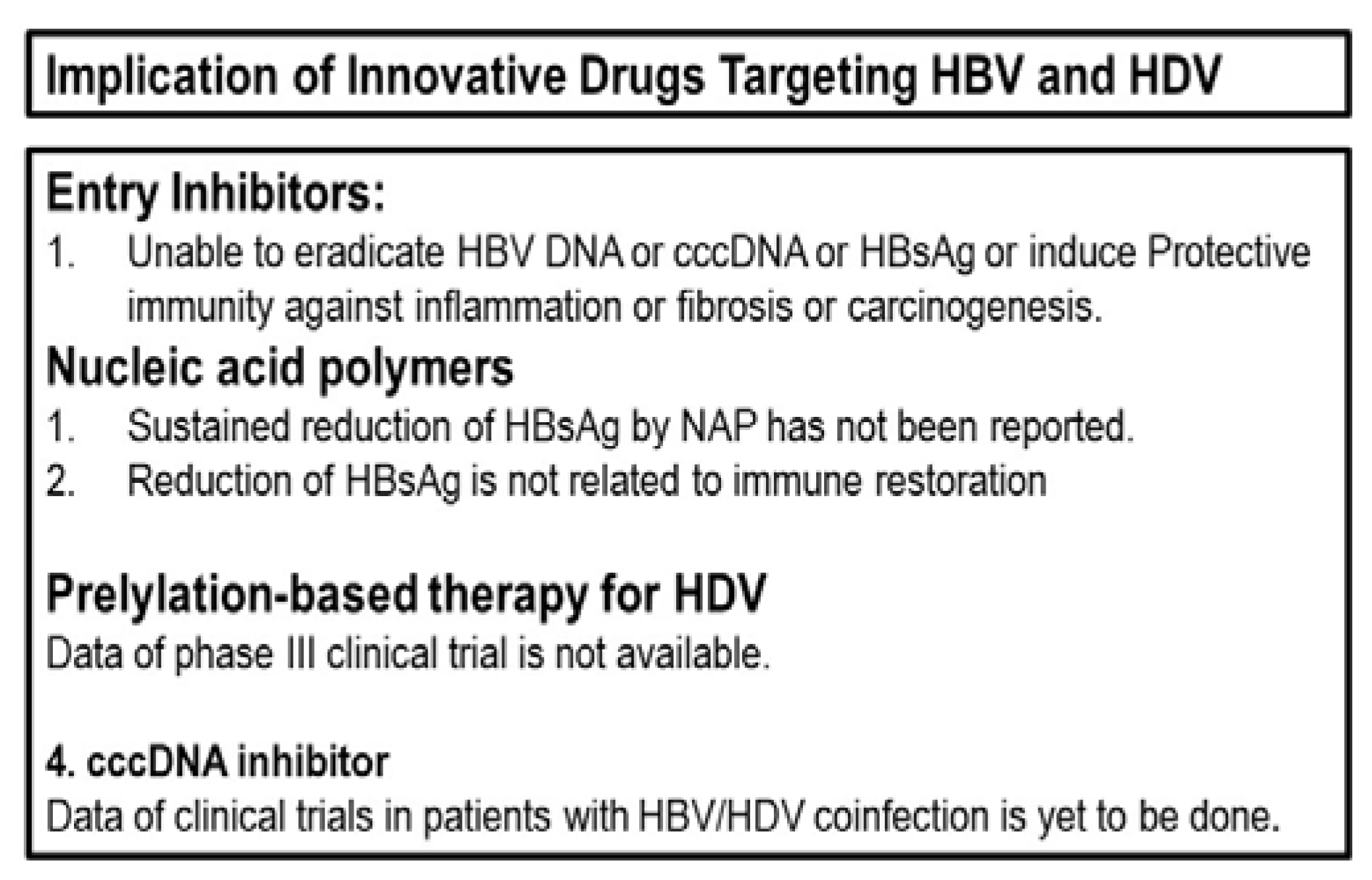
7. Logics behind the pessimistic view about commerciallly-avaaialble and evolving antiviral drugs for management of HBV/HDV co-infection
8. New modes of innovative therapy targeting the host immunity
9. A bird’s eye view regarding immune therapy for treating CHB patients
10. Development of antigen-specific immune therapy for CHB patients; Learning of the benches and translated to patients’ bedsides
11. Summation of the evolving therapies and their possible clinical implications to contain HBV/HDV coinfection
12. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Magnius, L.; Taylor, J.; Mason, W.S.; Sureau, C.; Deny, P.; Norder, H.; Ictv Report, C. ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Deltavirus. J. Gen. Virol. 2018, 99, 1565–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado-Mora, M.V.; Locarnini, S.; Rizzetto, M.; Pinho, J.R.R. An update on HDV: Virology, pathogenesis and treatment. Antivir. Ther. 2013, 18, 541–548, Sureau, C.; Negro F. The hepatitis delta virus: replication and pathogenesis. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64 (Suppl. S1), S102–S116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kos, A.; Dijkema, R.; Arnberg, A.C.; van der Meide, P.H.; Schellekens, H. The hepatitis delta (δ) virus possesses a circular RNA. Nature 1986, 323, 558–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seeger, C.; Mason, W.S. Hepatitis B virus biology. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2000, 64, 51–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hepatitis, B. World Health Organization. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-b (accessed on 25 April 2023).
- MacLachlan, J.H.; Cowie, B.C. Hepatitis B virus epidemiology. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2015, 5, a021410. [Google Scholar]
- Ganem, D.; Prince, A.M. Hepatitis B virus infection--natural history and clinical consequences. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 350, 1118–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbahrawy, A.; Atalla, H.; Alboraie, M.; Alwassief, A.; Madian, A.; El Fayoumie, M.; Tabll, A.A.; Aly, H.H. Recent advances in protective vaccines against hepatitis viruses: A narrative review. Viruses 2023, 15, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asselah, T.; Lada, O.; Moucari, R.; Martinot, M.; Boyer, N.; Marcellin, P. Interferon therapy for chronic hepatitis B. Clin. Liver Dis. 2007, 11, 839–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossi, G.; Viganò, M.; Loglio, A.; Lampertico, P. Hepatitis B virus long-term impact of antiviral therapy nucleot(s)ide analogues (NUCs). Liver. Int. 2017, 37, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoulim, F.; Lebossé, F.; Levrero, M. Current treatments for chronic hepatitis B virus infections. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2016, 18, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farci, P.; Niro, G.A. Clinical features of hepatitis D. Semin. Liver Dis. 2012, 32, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, H.; Zhong, G.; Xu, G.; He, W.; Jing, Z.; Gao, Z.; Huang, Y.; Qi, Y.; Peng, B.; Wang, H.; et al. Sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide is a functional receptor for human hepatitis B and D virus. Elife 2012, 3, e00049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, MM. RNA replication without RNA-dependent RNA polymerase: surprises from hepatitis delta virus. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 7951–7958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, M. RNA recombination in hepatitis delta virus: implications regarding the abilities of mammalian RNA polymerases. Virus Res. 2007, 127, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzetto, M.; Hoyer, B.; Canese, M.G.; Shih, J.W.; Purcell, R.H.; Gerin, J.L. Delta agent: association of δ antigen with hepatitis B surface antigen and RNA in serum of δ-infected chimpanzees. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 1980, 77, 6124–6128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lempp, F.A.; Ni, Y.; Urban, S. Hepatitis delta virus: insights into a peculiar pathogen and novel treatment options. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 13, 580–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hepatitis Delta. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-d (accessed on 5 April 2023).
- Huo, T.I.; Wu, J.C.; Lin, R.Y.; Sheng, W.Y.; Chang., F.Y.; Lee, S.D. Decreasing hepatitis D virus infection in Taiwan: an analysis of contributory factors. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 1997, 12, 747–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W, C.; Chen, T.K.; Han, H.F.; Lin, Y.C.; Huang, Y. M.; Kao, J.H.; Chen, P.J.; Liu, C.J. Investigating the prevalence and clinical effects of hepatitis delta viral infection in Taiwan. J Microbiol Immunol Infect 2021, 54, 902–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servant-Delmas, A. Le Ga, l.F.; Gallian, P.; Gordien, E.; Laperche, S. Increasing prevalence of HDV/HBV infection over 15 years in France. J. Clin. Virol. 2014, 59, 126–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Z.; Zhang, S.; Ou, X.; Li, S.; Ma, Z.; Wang, W.; Peppelenbosch, M.P.; Liu, J.; Pan, Q. Estimating the global prevalence, disease progression, and clinical outcome of hepatitis delta virus infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 221, 1677–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Center for Disease Control and Prevention. Hepatitis D Questions and Answers for Health Professionals. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/hdv/hdvfaq.htm#:~:text=Although%20HDV%20suppresses%20the%20replication,with%20HBV%20alone%20(2) (accessed on 5 April 2023).
- Farci, P.; Mandas, A.; Coiana, A.; Lai, M.E.; Desmet, V.; Van Eyken, P.; Gibo, Y.; Scaccbarozzi, S.; Criscuolo, D. Treatment of chronic hepatitis D with interferon alfa-2a. N Engl J Med 1994, 330, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heller, T.; Rotman, Y.; Koh, C. , Clark, S.; Haynes-Williams, V.; McBurney, R.; Schmid, P.; Albrecht, D.E.; Ghany, M.G.; Liang, T.J. et al. Long-term therapy of chronic delta hepatitis with peginterferon alfa. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2014, 40, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guedj, J.; Rotman, Y.; Cotler, S.J. Koh, C. ; Schmid, P,; Haynes-Williams, V.; Liang, T.J.; Liang, T. J.; Hoofnagle, J.H. et al. Understanding early serum hepatitis D virus and hepatitis B surface antigen kinetics during pegylated interferon-alpha therapy via mathematical modeling. Hepatology 2014, 60, 1902–1910. [Google Scholar]
- Gunsar F, Akarca US, Ersoz G, et al. Two-year interferon therapy with or without ribavirin in chronic delta hepatitis. Antivir Ther 2005, 10, 721–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niro, G.A.; Ciancio, A.; Gaeta, G.B.; Smedile, A.; Marrone, A.; Olivero, A.; Stanzione, M.; David, E.; Brancaccio, G.; Fontana, R.; et al. Pegylated interferon alpha-2b as monotherapy or in combination with ribavirin in chronic hepatitis delta. Hepatology 2006, 44, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaymakoglu, S.; Karaca, C.; Demir, K.; Poruroglu, A.; Badur, S.; Bozaci, M.; Besisik, F.; Bozaci, M.; Besisik, F.; Cakaloglu, Y.; et al. Alpha interferon and ribavirin combination therapy of chronic hepatitis D. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2005, 49, 1135–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheller, L.; Hilgard, G.; Anstasiou, O.; Dittmer, U.; Kahraman, A.; Wedemeyer, H.; Deterding, K. Poor clinical and virological outcome of nucleos(t)ide analogue monotherapy in HBV/HDV co-infected patients. Medicine 2021, 100, e26571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampertico, P. Discontinuation of nucleoside analogues in hepatitis B virus infection. Gastroenterol Hepatol 2013, 9, 656–668. [Google Scholar]
- Wolters, L.M.; van Nunen, A.B.; Honkoop, P.; Vossen, A. C.; Niesters, H.G.; Zondervan, P.E.; de Man, R.A. Lamivudine-high dose interferon combination therapy for chronic hepatitis B patients co-infected with the hepatitis D virus. J. Viral. Hepat. 2000, 7, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedemeyer H, Yurdaydin C, Ernst S, et al. 96 weeks of pegylated-interferon-alpha-2a plus tenofovir or placebo for the treatment of hepatitis delta: the HIDIT-2 study. Hepatology 2013, 58, 222A–223A.
- Wedemeyer, H.; Yurdaydin, C.; Hardtke, S.; Caruntu, F. A.; Curescu, M. G.; Yalcin, K.; Akarca, U. S.; Gurel, S.; Zeuzem, S.; et al. Peginterferon alfa-2a plus tenofovir disoproxil fumarate for hepatitis D (HIDIT-II): A randomised, placebo controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet Infect Dis. 2019, 19, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caredda, F.; d’Arminio Monforte, A.; Rossi, E.; Farci, P.; Smedile, A.; Tappero, G.; Moroni, M. Prospective study of epidemic Delta infection in drug addicts. Prog. Clin. Biol. Res. 1983, 143, 245–250. [Google Scholar]
- Smedile, A.; Farci, P.; Verme, G.; Caredda, F.; Cargnel, A.; Caporaso, N.; Dentico, P.; Trepo, C.; Opolon, P.; Gimson A, et al. Influence of Delta infection on severity of hepatitis B. Lancet 1982, 945–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smedile, A.; Dentico, P.; Zanetti, A.; Sagnelli, E.; Nordenfelt, E.; Actis, G.C; Rizzetto, M. Infection with the Delta agent in chronic HBsAg carriers. Gastroenterology 1981, 81, 992–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, M.I.; Deslauriers, M.; Andrews, C.W.; Tipples, G.A.; Walters, K.A.; Tyrrell, D.L.; Brown, N.; Condreay, L.D. Identification and characterization of mutations in hepatitis B virus resistant to lamivudine. Lamivudine Clinical Investigation Group. Hepatology 1998, 27, 1670–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angus, P.; Vaughan, R.; Xiong, S.; Yang, H.; Delaney, W.; Gibbs, C.; Brosgart, C.; Colledge, D.; Edwards, R.; Ayres, A.; et al. Resistance to adefovir dipivoxil therapy associated with the selection of a novel mutation in the HBV polymerase. Gastroenterology 2003, 125, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tenney, D.J.; Rose, R.E.; Baldick, C.J.; Pokornowski, K.A.; Eggers, B.J.; Fang, J.; Wichroski, M.J.; Xu, D.; Yang, J.; Wilber, R.B.; et al. Long-term monitoring shows hepatitis B virus resistance to entecavir in nucleoside-naive patients is rare through 5 years of therapy. Hepatology 2009, 49, 1503–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.L.; Wong, D.; Ip, P.; Kopaniszen, M.; Seto, W.K.; Fung, J.; Huang, F.Y.; Lee, B.; Cullaro, G.; Chong, C.K.; et al. Reduction of covalently closed circular DNA with long-term nucleos(t)ide analogue treatment in chronic hepatitis B. J. Hepatol. 2017, 66, 275–281. [Google Scholar]
- Park, E.S.; Lee, A.R.; Kim, D.H.; Lee, J.H.; Yoo, J.J.; Ahn, S.H.; Sim, H.; Park, S.; Kang, H.S.; Won, J.; et al. Identification of a quadruple mutation that confers tenofovir resistance in chronic hepatitis B patients. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 1093–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Zhong, G.; Xu, G.; He, W.; Jing, Z.; Gao, Z.; Huang, Y.; Qi, Y.; Peng, B.; Wang, H.; et al. Sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide is a functional receptor for human hepatitis B and D virus. eLife 2012, 1, e00049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelke, M.; Mills, K.; Seitz, S.; Simon, P.; Gripon, P.; Schnolzer, M.; Urban, S. Characterization of a hepatitis B and hepatitis delta virus receptor binding site. Hepatology 2006, 43, 750–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, H.; Wang, C. Key factors for “Fishing” NTCP as functional receptor for HBV and HDV. Viruses 2023, 15, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wedemeyer, H.; Bogomolov, P.; Blank, A.; Allweiss, L.; Dandri-Petersen, M.; Bremer, B.; Voronkova, N.; Schöneweis, K.; Pathil, A.; Burhenne, J.; et al. GS-005-Final results of a multicenter, open-label phase 2b clinical trial to assess safety and efficacy of Myrcludex B in combination with Tenofovir in patients with chronic HBV/HDV co-infection. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, S3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedemeyer, H.; Aleman, S.; Andreone, P.; Blank, A.; Brunetto, M.; Bogomolov, P.; Chulanov, V.; Geyvandova, N.; Hilgard, G.; Mamonova, N.; et al. Late breaker posters-2730: Bulevirtide monotherapy at low and high dose in patients with chronic hepatitis delta: 24 weeks interim data of the phase 3 MYR301 study. J. Hepatol. 2021, 75, S294. [Google Scholar]
- Asselah, T.; Arama, S.S.; Bogomolov, P.; Bourliere, M.; Fontaine, H.; Gherlan, G.S.; Gorodin, V.; Hilleret, M.N.; Lazar, L.; Mamonova, N.; et al. OS-2717: Safety and efficacy of bulevirtide monotherapy and in combination with Peginterferon alfa-2a in patients with chronic hepatitis delta: 24 weeks interim data of MYR204 Phase 2b study. J. Hepatol. 2021, 75, S291. [Google Scholar]
- Bogomolov, P.; Alexandrov, A.; Voronkova, N.; Macievich, M.; Kokina, K.; Petrachenkova, M.; Lehr, T.; Lempp, F.A.; Wedemeyer, H.; Haag, M.; et al. Treatment of chronic hepatitis D with the entry inhibitor myrcludex B: First results of a phase Ib/IIa study. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 490–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferenci P, Reiberger T, Jachs M. Treatment of Chronic Hepatitis D with Bulevirtide-A Fight against Two Foes-An Update. Cells. 2022, 11, 3531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaillant, A. Nucleic acid polymers: Broad spectrum antiviral activity, antiviral mechanisms and optimization for the treatment of hepatitis B and hepatitis D infection. Antivir. Res. 2016, 133, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaillant, A.; Juteau, J.-M.; Lu, H.; Liu, S.; Lackman-Smith, C.; Ptak, R.; Jiang, S. Phosphorothioate oligonucleotides inhibit human immunodeficiency virus type 1 fusion by blocking gp41 core formation. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 1393–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazinet, M.; Pantea, V.; Placinta, G.; Moscalu, I.; Cebotarescu, V.; Cojuhari, L.; Jimbei, P.; Iarovoi, L.; Smesnoi, V.; Musteata, T.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of 48Weeks REP 2139 or REP 2165, Tenofovir Disoproxil, and Pegylated Interferon Alfa-2a in Patients with Chronic HBV Infection Naive to Nucleos(t)ide Therapy. Gastroenterology 2020, 8, 2180–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einav, S.; Glenn, J.S. Prenylation inhibitors: a novel class of antiviral agents. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2003, 52, 883–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bordier, B.B.; Marion, P.L.; Ohashi, K.; Kay, M. A.; Greenberg, H. B.; Cassy, J. L.; Glenn, J.S. A prenylation inhibitor prevents production of infectious hepatitis delta virus particles. J Virol. 2002, 76, 10465–10472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yurdaydin, C.; Keskin, O.; Yurdcu, E.; Çali¸skan, A.; Önem, S.; Karakaya, F.; Kalkan, Ç.; Karatayli, E.; Karatayli, S.; Choong, I.; et al. A phase 2 dose-finding study of lonafarnib and ritonavir with or without interferon alpha for chronic delta hepatitis. Hepatology 2022, 75, 1551–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yurdaydin, C.; Keskin, O.; Kalkan, Ç.; Karakaya, F.; Çali¸skan, A.; Karatayli, E.; Karatayli, S.; Bozdayi, A.M.; Koh, C.; Heller, T.; et al. Optimizing lonafarnib treatment for the management of chronic delta hepatitis: The LOWR HDV-1 study. Hepatology 2018, 67, 1224–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, K.; Canini, L.; Dahari, H.; Zhao, X.; Uprichard, S. L.; Hayness-Williams, V.; Winters, M.A.; Subramanya, GCooper, S. L.; Pinto, P; et al. Oral prenylation inhibition with lonafarnib in chronic hepatitis D infection: a proof-of-concept randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 2A trial. Lancet Infect Dis. 2015, 15, 1167–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thi, E.P.; Dhillon, A.P.; Ardzinski, A.; Bidirici-Ertekin, L.; Cobarrubias, K.D.; Cuconati, A.; Kondratowicz, A.S.; Kwak, K.; Li, A.H.L.; Miller, A.; et al. ARB-1740, a RNA Interference Therapeutic for Chronic Hepatitis B Infection. ACS Infect. Dis. 2019, 5, 725–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verrier, E.R.; Weiss, A.; Bach, C.; Heydmann, L.; Turon-Lagot, V.; Kopp, A.; El Saghire, H.; Crouchet, E.; Pessaux, P.; Garcia, T.; et al. Combined small molecule and loss-of-function screen uncovers estrogen receptor alpha and CAD as host factors for HDV infection and antiviral targets. Gut 2020, 69, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhum, Q.; Zhang, J.D.; Zhang, Y.; Ni, X.; Xiang, K.; Jiang, J.; Li, B.; Yu, Y.; Hu, H.; et al. Discovery of a first-in-class orally available HBV cccDNA inhibitor. J Hepatol. 2023, 78, 742–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, R.; Li, Q.; Woodson, M.E.; Gasonoo, M.; Meyers, M.J.; Tavis, J.E. Efficient inhibition of hepatitis B virus (HBV) replication and cccDNA formation by HBV ribonuclease H inhibitors during infection. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2021, 65, e014602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allweiss, L.; Dandri, M. The Role of cccDNA in HBV Maintenance. Viruses 2017, 9, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Fraga, R.S.; Vaisberg, V.V.; Alfaia Mendes, L.C.; Carrilho, F. J.; Ono, S.K. Adverse events of nucleos(t)ide analogues for chronic hepatitis B: a systematic review. J Gastroenterol. 2020, 55, 496–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhat, S.A.; Kazim, S.N. HBV cccDNA-A Culprit and stumbling block for the hepatitis B virus infection: Its presence in hepatocytes perplexed the possible mission for afunctional cure. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 24066–24081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guidotti, L.G.; Chisari, F.V. Immunobiology and pathogenesis of viral hepatitis. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2006, 1, 23–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eddleston, A.L.; Mondelli, M. Immunopathological mechanisms of liver cell injury in chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J. Hepatol. 1986, 3 (Suppl. 2), S17–S23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilg, H.; Vogel, W.; Tratkiewicz, J.; Aulizky, W.E.; Herold, M.; Gruber, M.; Geissler, D.; Umalauft, F.; Judmaier, G.; Schwuelra, U. Pilot study of natural human interleukin-2 in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Immunomodulatory and antiviral effects. J Hepatol. 1993, 19, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artillo, S.; Pastore, G.; Alberti, A.; Milella, M.; Santantonio, T.; Fattovitch, G.; Guistina, G.; Ryff, J.C.; Chaneac, M.; Bartolome, J.; et al. Double-blind, randomized controlled trial of interleukin-2 treatment of chronic hepatitis B. J. Med. Virol. 1998, 54, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreño, V.; Zeuzem, S.; Hopf, U.; Marcellin, P.; Cooksley, W.G.; Fevery, J.; Diuago, M.; Reddy, R.; Peters, M.; Rittweger, K.; et al. A phase I/II study of recombinant human interleukin-12 in patients with chronic hepatitis B. J. Hepatol. 2000, 32, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín, J.; Quiroga, J.A.; Bosch, O.; Carreño, V. Changes in cytokine production during therapy with granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology 1994, 20, 1156–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Moreno, M.; García, R.; Rua, M.J.; Serrano, B.; Moraleda, G.; Feijoo, E.; Bartolome, J.; Ortiz, F.; Castillo, I.; Carreno, V. Levamisole and interferon in children with chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology 1993, 18, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhat, B.A.; Marinos, G.; Daniels, H.M.; Naoumov, N.V.; Williams, R. Evaluation of efficacy and safety of thymus humoral factor-gamma 2 in the management of chronic hepatitis B. J Hepatol. 1995, 23, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woltman, A.M.; Ter Borg, M.J.; Binda, R.S.; Sprengers, D.; E von Blomberg, B.M.; Scheper, R.J.; Hayashi, K.; Nishi, N.; Boosnstra, A.; van der Molen, R.; et al. Alpha-galactosylceramide in chronic hepatitis B infection: results from a randomized placebo-controlled Phase I/II trial. Antivir Ther. 2009, 14, 809–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iino, S.; Toyota, J.; Kumada, H.; Kiyosawa, K.; Kakumu, S.; Suzuki, E.; Martins, E.B. The efficacy and safety of thymosin alpha-1 in Japanese patients with chronic hepatitis B; results from a randomized clinical trial. J. Viral. Hepat. 2005, 12, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, J.; Zhuang, L.; Cheng, H.-Y.; Yan, S.M.; Yu, L.; Huang, J.H.; Huang, M.L.; Ma, Y.L.; Chongsuvivatwong, V.; Sriplung, H.; et al. Efficacy of thymosin alpha-1 and interferon alpha in treatment of chronic viral hepatitis B: a randomized controlled study. World J Gastroenterol. 2006, 12, 6715–6721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maini, M.K.; Boni, C.; Lee, C.K.; Larrubia, J.R.; Reignat, S.; Ogg, G.S.; King, A.S.; Herberg, J.; Gilson, R.; Alisa, A.; et al. The role of virus-specific CD8(+) cells in liver damage and viral control during persistent hepatitis B virus infection. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 191, 1269–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertoletti, A.; Le Bert, N. Immunotherapy for Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection. Gut Liver 2018, 12, 497–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoletti, A.; Maini, M.K.; Ferrari, C. The host-pathogen interaction during HBV infection: immunological controversies. Antivir Ther. 2010, 15 Suppl. 3, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pol, S.; Driss, F.; Michel, M.L.; Nalpas, B.; Berthelot, P.; Brechot, C. Specific vaccine therapy in chronic hepatitis B infection. Lancet 1994, 344, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senturk, H.; Tabak, F.; Akdogan, M.; Erdem, L.; Mert, A.; Ozaras, R.; Sander, E.; Ozbay, G.; Badur, S. Therapeutic vaccination in chronic hepatitis B. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2002, 17, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Y.; Zhang, X.X.; Yao, X.; Jiang, J.-H.; Xie, Y.-H.; Yuan, Z.-H.; Wen, Y.-M. Serum HbeAg sero-conversion correlated with decrease of HbsAg and HBV DNA in chronic hepatitis B patients treated with a therapeutic vaccine. Vaccine 2010, 28, 8169–8174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalcin, K.; Acar, M.; Degertekin, H. Specific hepatitis B vaccine therapy in inactive HbsAg carriers: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Infection 2003, 31, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.-M.; Wu, X.-H.; Hu, D.-C.; Zhang, Q.-P.; Guo, S.-Q. Hepatitis B vaccine and anti-HBs complex as approach for vaccine therapy. Lancet 1995, 345, 1575–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.Z.; Zhao, K.; Guo, L.M.; Li, L.J.; Xie, Q.; Ren, H.; Zhang, J.M.; Xu, M.; Wang, H.F.; Huang, W.X.; et al. A randomized con-trolled phase Iib trial of antigen-antibody immunogenic complex therapeutic vaccine in chronic hepatitis B patients. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.Z.; Wang, X.Y.; Shen, X.L.; Gong, G.Z.; Ren, H.; Guo, L.M.; Sun, A.M.; Xu, M.; Li, L.J.; Guo, X.H.; et al. Results of a phase III clinical trial with an HBsAg-HBIG immunogenic complex therapeutic vaccine for chronic hepatitis B patients: Experiences and findings. J. Hepatol. 2013, 59, 450–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontaine, H.; Kahi, S.; Chazallon, C.; Bourgine, M.; Varaut, A.; Buffet, C.; Godon, O.; Meritet, J.F.; Saidi, Y.; Michel, M.L.; et al. Anti-HBV DNA vaccination does not prevent relapse after discontinuation of analogues in the treatment of chronic hepatitis B: A randomised trial-ANRS HB02 VAC-ADN. Gut 2015, 64, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancini-Bourgine, M.; Fontaine, H.; Bréchot, C.; Pol, S.; Michel, M.L. Immunogenicity of a hepatitis B DNA vaccine administered to chronic HBV carriers. Vaccine 2006, 24, 4482–4489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cova, L. Present and future DNA vaccines for chronic hepatitis B treatment. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2017, 17, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavenaugh, J.S.; Awai, D.; Mendy, M.; Hill, A.V.S.; Whittle, H.; McConkey, S. J. Partially randomized, non-blinded trial of DNA and MVA therapeutic vaccines based on hepatitis B virus surface protein for chronic HBV infection. Plos One 2011, 6, e14626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Li, Y.G.; Zhang, D.Z.; Wang, Z.Y.; Zeng, W.Q.; Shi, X.F.; Ren, H. Therapeutic effect of autologous dendritic cell vaccine on patients with chronic hepatitis B: A clinical study. World J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 11, 1806–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbar, S.M.; Furukawa, S.; Horiike, N.; Abe, M.; Hiasa, Y.; Onji, M. Safety and immunogenicity of hepatitis B surface antigen-pulsed dendritic cells in patients with chronic hepatitis B. J. Viral Hepat. 2011, 18, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Li, J.; Chen, R.L.; Nie, L.; Huang, J.; Liu, Z.W.; Luo, L.; Yan, X.J. Autologus dendritic cell vaccine for chronic hepatitis B carriers: A pilot, open label, clinical trial in human volunteers. Vaccine 2010, 28, 2497–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbar, S.M.; Chen, S.; Al-Mahtab, M.; Abe, M.; Hiasa, Y.; Onji, M. Strong and multi-antigen specific immunity by hepatitis B core antigen (HBcAg)-based vaccines in a murine model of chronic hepatitis B: HBcAg is a candidate for a therapeutic vaccine against hepatitis B virus. Antiviral Res. 2012, 96, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Mahtab, M.; Akbar, S.M.F.; Aguilar, J.C.; Uddin, H.; Khan, S.I.; Rahman, S. Therapeutic potential of a combined hepatitis B virus surface and core antigen vaccine in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Hepatol. Int. 2013, 7, 981–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Mahtab, M.; Akbar, S.M.F.; Aguilar, J.C.; Guillen, G.; Penton, E.; Tuero, A.; Yoshida, O.; Hiasa, Y.; Onji, M. Treatment of chronic hepatitis B naïve patients with a therapeutic vaccine containing HBs and HBc antigens (a randomized, open and treat-ment-controlled phase III clinical trial). PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0201236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbar, S.M.F.; Al Mahtab, M.; Aguilar, J.C.; Yoshida, O.; Penton, E.; Guillen, G.; Hiasa, Y. Sustained antiviral and liver protection by a nasal therapeutic vaccine (NASVAC), containing both HBsAg and HBcAg) in patients with chronic hepatitis B; 2-year follow-up of phase III clinical trial. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbar, S.M.F.; Al Mahtab, M.; Aguilar, J.C.; Yoshida, O.; Khan, S.; Penton, E.; Gerardo, G.N.; Hiasa, Y. The Safety and Efficacy of a Therapeutic Vaccine for Chronic Hepatitis B: A Follow-Up Study of Phase III Clinical Trial. Vaccines 2021, 10, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Mahtab, M.; Akbar, S.M.F.; Aguilar, J.C.; Yoshida, O.; Khan, S.; Guillen, G.; Hiasa, Y. Safety profile, antiviral capacity, and liver protection of a nasal therapeutic vaccine in patients with chronic hepatitis B: Five-year-follow-up outcomes after the end of treatment. Front Med (Lausanne), 2023, 10, 1032531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, O.; Akbar, S.M.F.; Imai, Y.; Sanada, T.; Tsukiyama-Kohara, K.; Miyazaki, T.; Kamishita, T.; Miyake, T.; Tokumoto, Y.; Hikita, H et al. Intranasal therapeutic vaccine containing HBsAg and HBcAg for patients with chronic hepatitis B; 18 months follow-up results of phase IIa clinical study. Hepatol Res 2023, 53, 196–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lok, A.S.; Pan, C.Q.; Han, S-H.B.; Trinh, H.N.; Fessel, W.J.; Rodell, T.; Massetto, B.; Lin, L.; Gaggar, A.; Subramanian, M.; et al. Randomized phase II study of GS-4774 as a therapeutic vaccine in virally suppressed patients with chronic hepatitis B. J. Hepatol 2016, 65, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| 1. HBsAg-positivity precedes the detection of HDV DNA |
| 2. HDV may suppress HBV replication following superinfection. |
| 3.The pathogenic mechanisms and liver damage are related to factors like “HBV/HDV” superinfection or “HBV/HDV” coinfection. |
| 4. In the case of “coinfection” replication of both viruses may be contained |
| 5. However, in the case of HDV infection in existing HBV chronic-infected subjects, there may be severe forms of liver damage and their progression to complications |
| 6. HDV does not have its own RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RDRP); however, HBV is endowed with its own RDRP, and thus therapeutic strategies would be complex to contain these two viruses in the same run. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





