Submitted:
03 May 2023
Posted:
04 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
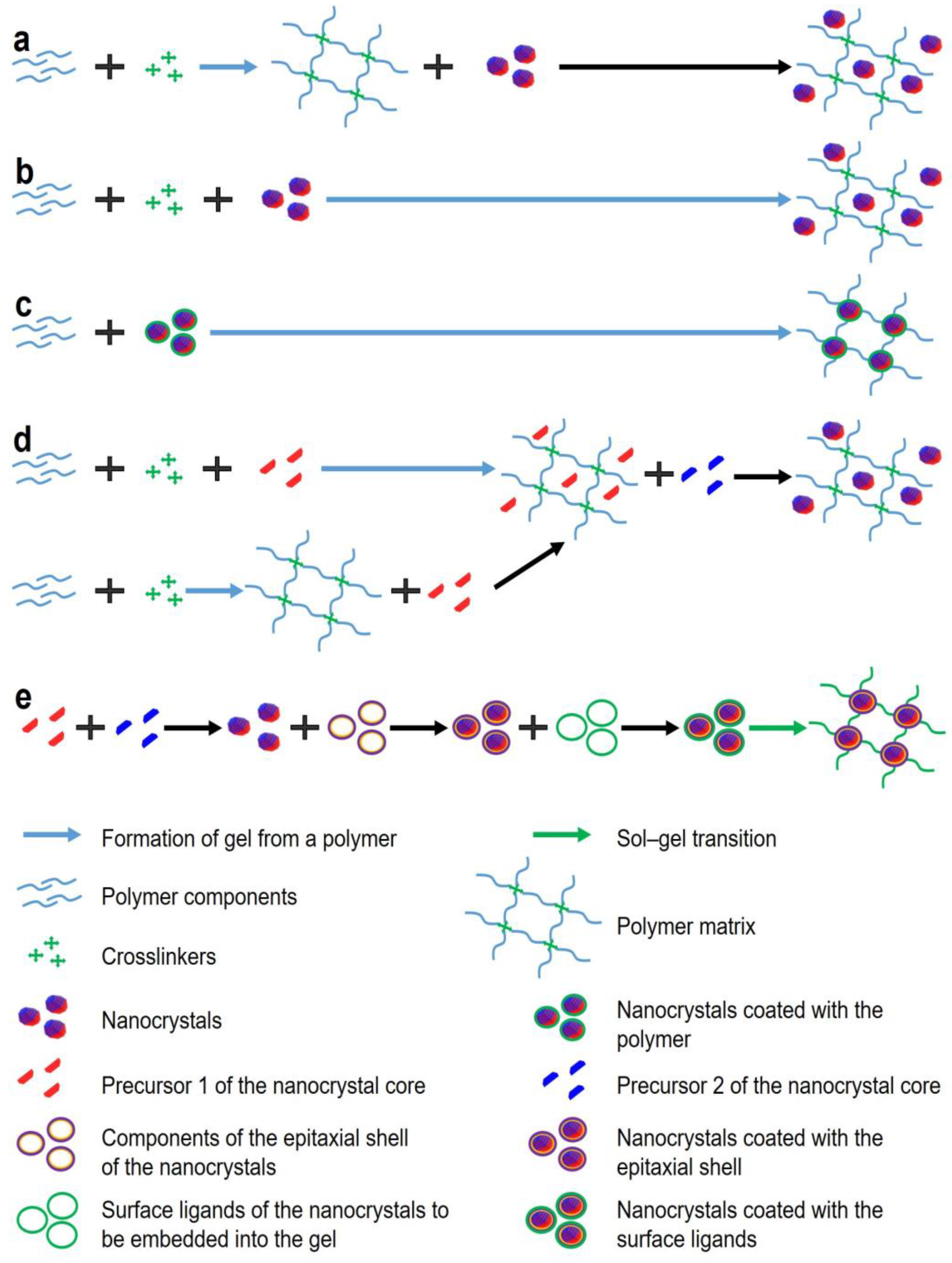
2. Methods for Obtaining Fluorescent Gels
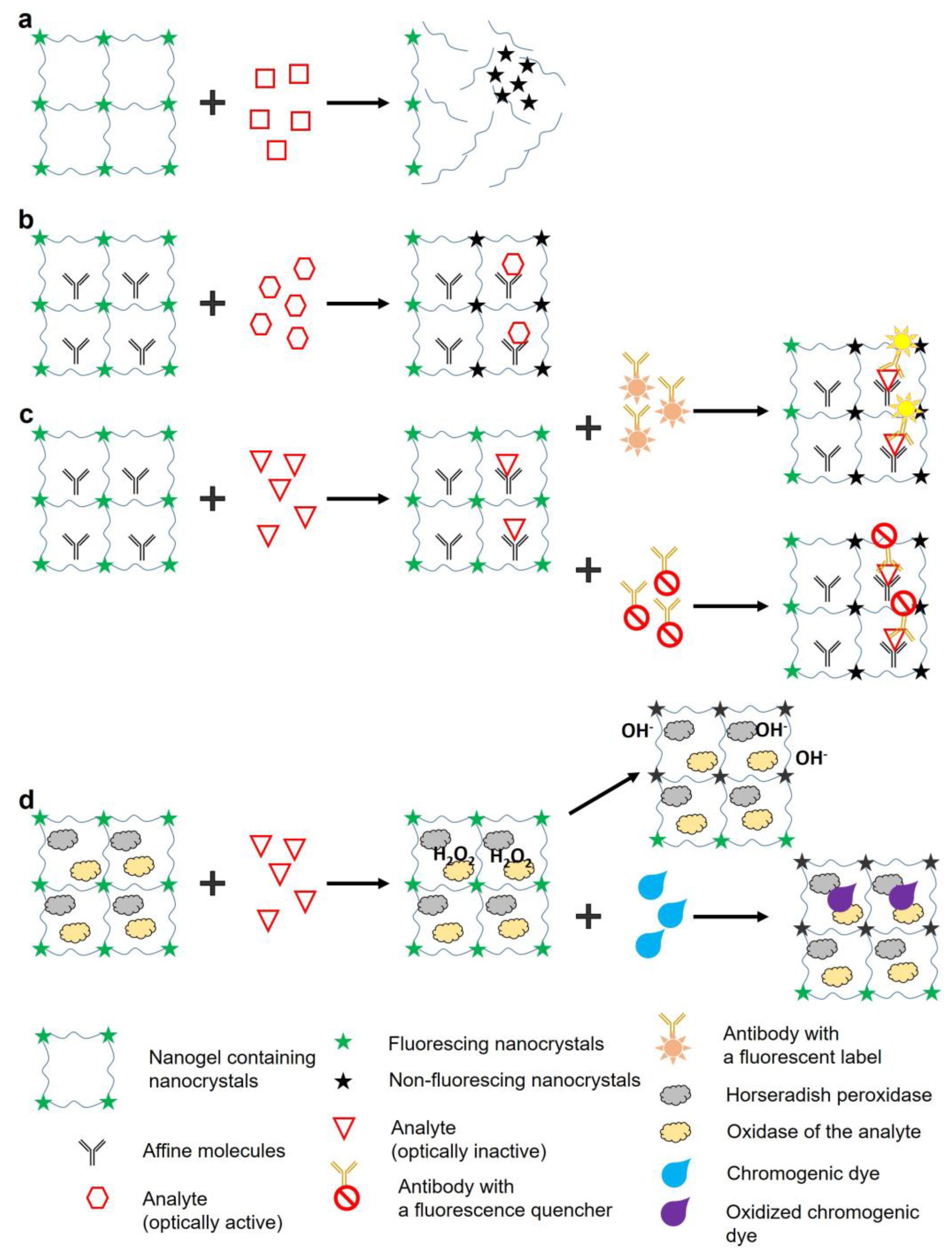
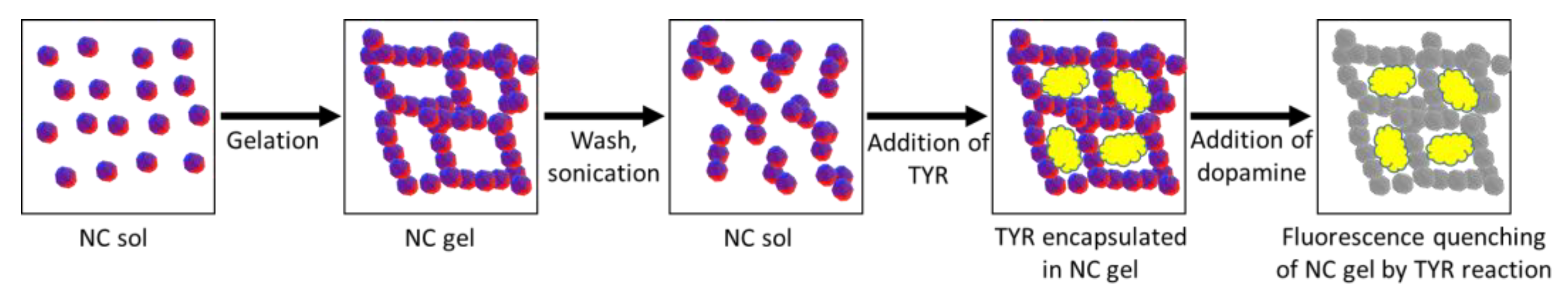
3. Methods of Analyte Detection Using Fluorescent Gels
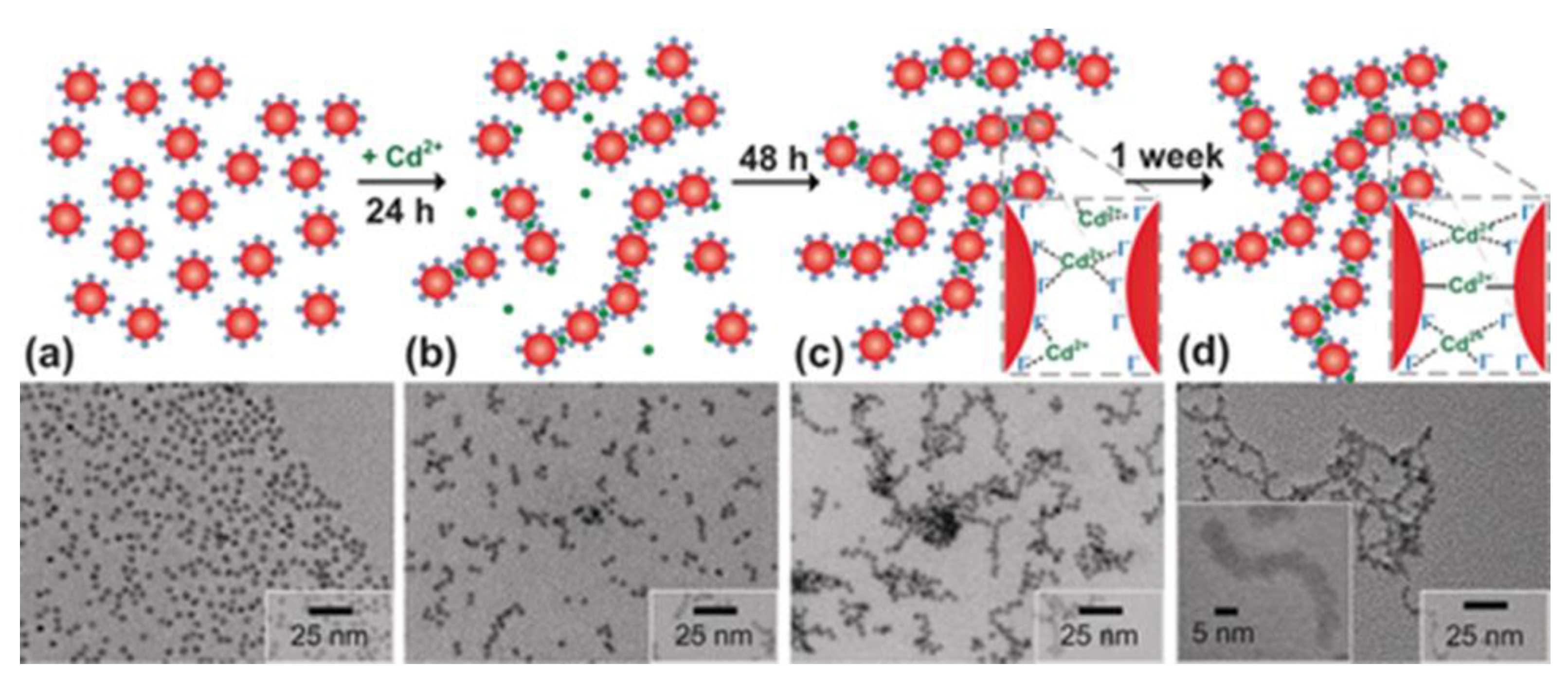
3. Gel Formation from Fluorescent Nanocrystals through Sol–Gel Phase Transition
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tu, R.; Zhang, Y.; Hua, E.; Bai, L.; Huang, H.; Yun, K.; Wang, M. Droplet-based microfluidic platform for high-throughput screening of Streptomyces. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annabestani, M.; Esmaeili-Dokht, P.; Fardmanesh, M. A novel, low cost, and accessible method for rapid fabrication of the modifiable microfluidic devices. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troy, T.; Jekic-McMullen, D.; Sambucetti, L.; Rice, B. Quantitative comparison of the sensitivity of detection of fluorescent and bioluminescent reporters in animal models. Mol. Imaging 2004, 3, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, P.Y.; Li, F.C.; Liu, M.H.; Chan, Y.H. Colorimetric and fluorescent dual-mode immunoassay based on plasmon-enhanced fluorescence of polymer dots for detection of PSA in whole blood. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 9841–9849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdullah Issa, M.; Abidin, Z. Sustainable development of enhanced luminescence polymer-carbon dots composite film for rapid Cd2+ removal from wastewater. Molecules 2020, 25, 3541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Huang, Z.-Z.; Weng, Y.; Tan, H. Pyrophosphate ion-responsive alginate hydrogel as an effective fluorescent sensing platform for alkaline phosphatase detection. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 11450–11453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guglielmi, M.; Martucci, A. Chapter 9: Semiconductor quantum dot-doped sol–gel materials. In Sol-Gel Derived Optical and Photonic Materials, Martucci, A., Santos, L., Estefanía Rojas Hernández, R., Almeida, R., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: 2020; pp. 209–226.
- Richter, A.; Paschew, G.; Klatt, S.; Lienig, J.; Arndt, K.-F.; Adler, H.-J.P. Review on hydrogel-based pH sensors and microsensors. Sensors 2008, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; He, C.; Chen, X. Hydrogels based on pH-responsive reversible carbon–nitrogen double-bond linkages for biomedical applications. Mater. Chem. Front. 2018, 2, 1765–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, H.; Maruyama, H.; Akita, Y.; Arai, F. Hydrogel Fluorescence microsensor with fluorescence recovery for prolonged stable temperature measurements. Sensors 2019, 19, 5247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Sukker, I.; Müller, M.; Schönherr, H. Selective discrimination of key enzymes of pathogenic and nonpathogenic bacteria on autonomously reporting shape-encoded hydrogel patterns. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 5175–5184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wu, C.; Hu, X.; Lu, Y.; Wang, G.; Yu, F.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y. Flexible and self-healing electrochemical hydrogel sensor with high efficiency toward glucose monitoring. Biosens. Bioelectr. 2020, 155, 112105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, Y.; Hedenqvist, M.S.; Chen, C.; Cai, C.; Li, H.; Liu, H.; Fu, J. Multifunctional conductive hydrogels and their applications as smart wearable devices. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 2561–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Missirlis, D.; Baños, M.; Lussier, F.; Spatz, J.P. Facile and Versatile method for micropatterning poly(acrylamide) hydrogels using photocleavable comonomers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 3643–3652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Xue, B.; Qin, M.; Cao, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, W. Printable fluorescent hydrogels based on self-assembling peptides. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kar, T.; Patra, N. Pyrene-based fluorescent supramolecular hydrogel: scaffold for nanoparticle synthesis. J. Phys. Org. Chem. 2020, 33, e4026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Jin, X.; Ashrafzadeh Afshar, E.; Taher, M.A.; Xia, C.; Joo, S.-W.; Mashifana, T.; Vasseghian, Y. Simple turn-off fluorescence sensor for determination of raloxifene using gold nanoparticles stabilized by chitosan hydrogel. Chemosphere 2022, 305, 135392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, Q.; Wang, H.; Wang, G.; Shen, H. Quantum dots-loaded self-healing gels for versatile fluorescent assembly. Nanomaterials 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisanic, T.R., 2nd; Zhang, Y.; Wang, T.H. Quantum dots in diagnostics and detection: principles and paradigms. Analyst 2014, 139, 2968–2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, S.C.; Nath, S.S. Size-dependent fluorescence in CdSe quantum dots. Emerg. Mater. Res. 2012, 1, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montón, H.; Nogués, C.; Rossinyol, E.; Castell, O.; Roldán, M. QDs versus Alexa: Reality of promising tools for immunocytochemistry. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2009, 7, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.Y.; Zheng, S.Y.; Du, C.; Ling, J.; Zhu, C.N.; Wang, Y.J.; Wu, Z.L.; Zheng, Q. Carbon dot/poly(methylacrylic acid) nanocomposite hydrogels with high toughness and strong fluorescence. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2020, 2, 1043–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Liao, Q.; Xu, Z.; Li, H.; Zheng, L.; Fu, H. Embedding perovskite nanocrystals into a polymer matrix for tunable luminescence probes in cell imaging. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1604382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, W.; Cui, Y. Synthesis of Polymeric nanocomposite hydrogels containing the pendant ZnS nanoparticles: approach to higher refractive index optical polymeric nanocomposites. Macromolecules 2018, 51, 2672–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Li, Q.; Wen, W.; Hu, L.; He, W.; Liu, H. Cadmium sulfide quantum dots/poly(acrylic acid-co-acrylic amide) composite hydrogel synthesized by gamma irradiation. Rad. Phys. Chem. 2018, 145, 130–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Yang, G.; Yuan, Z.; Ji, X.; Kong, F.; Huang, B.; Dionysiou, D.D.; Chen, J. Hydrogel as a miniature hydrogen production reactor to enhance photocatalytic hydrogen evolution activities of CdS and ZnS quantum dots derived from modified gel crystal growth method. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 373, 814–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaponik, N.; Wolf, A.; Marx, R.; Lesnyak, V.; Schilling, K.; Eychmüller, A. Three-dimensional self-assembly of thiol-capped CdTe nanocrystals: Gels and aerogels as building blocks for nanotechnology. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 4257–4262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Li, H.; Hao, H.; Chen, Y.; Dong, C.; Wang, G. β-Cyclodextrin functionalized Mn-doped ZnS quantum dots for the chiral sensing of tryptophan enantiomers11Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available: pH effect on the PL intensity of the as-synthesized β-CD-Mn-ZnS QDs, PL spectra of β-CD-Mn-ZnS QDs/Trp enantiomers at different equilibration time and UV-vis spectra of the mixture of Trp enantiomers and β-CD at various standing time. See doi: 10.1039/C4PY00618F. Polym. Chem. 2015, 6, 591–598. [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, S. Highly selective and sensitive detection of mercuric ion based on a visual fluorescence method. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 9792–9801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cayuela, A.; Soriano, M.L.; Kennedy, S.R.; Steed, J.W.; Valcárcel, M. Fluorescent carbon quantum dot hydrogels for direct determination of silver ions. Talanta 2016, 151, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Pacheco, A.; Del Río Castillo, A.E.; Martín, C.; Herrero, M.A.; Merino, S.; García Fierro, J.L.; Díez-Barra, E.; Vázquez, E. Graphene quantum dot–aerogel: From nanoscopic to macroscopic fluorescent materials. Sensing polyaromatic compounds in water. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 18192–18201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Li, L.; Luo, F.; Qiu, B.; Lin, Z.; Guo, L. Ratiometric fluorescent hydrogel test kit for on-spot visual detection of nitrite. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 1252–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, S.; Nandi, S.; Jelinek, R. Carbon-dot–hydrogel for enzyme-mediated bacterial detection. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 588–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Rosenzweig, Z. Luminescent CdS quantum dots as selective ion probes. Ana. Chem. 2002, 74, 5132–5138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surana, K.; Bhattacharya, B. Fluorescence quenching by Förster resonance energy transfer in carbon–cadmium sulfide core-shell quantum dots. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 32749–32753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Xing, M.; Wu, Q. Green synthesis of fluorescent carbon dots/hydrogel nanocomposite with stable Fe3+ sensing capability. J. Alloys Comp. 2019, 790, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truskewycz, A.; Beker, S.A.; Ball, A.S.; Murdoch, B.; Cole, I. Incorporation of quantum carbon dots into a PVP/ZnO hydrogel for use as an effective hexavalent chromium sensing platform. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1099, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, B.; Mandani, S.; Thakur, N.; Sarma, T.K. Cd(II)–nucleobase supramolecular metallo-hydrogels for in situ growth of color tunable CdS quantum dots. Soft Matter 2018, 14, 5715–5720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrmann, A.; Kaufmann, L.; Dey, P.; Haag, R.; Schedler, U. Bioorthogonal in situ hydrogels based on polyether polyols for new biosensor materials with high sensitivity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 11382–11390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aloraefy, M.; Pfefer, T.J.; Ramella-Roman, J.C.; Sapsford, K.E. In vitro evaluation of fluorescence glucose biosensor response. Sensors 2014, 14, 12127–12148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourreza, N.; Ghomi, M. A novel metal enhanced fluorescence bio probe for insulin sensing based on poly vinyl alcohol-borax hydrogel functionalized by Ag dots. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 251, 609–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Hu, N.; Peng, J.; Chen, L.; Weng, J. Ultrasensitive detection of mitochondrial DNA mutation by graphene oxide/DNA hydrogel electrode. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 6905–6913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Grazon, C.; Sensharma, P.; Nguyen, T.T.; Feng, Y.; Chern, M.; Baer, R.C.; Varongchayakul, N.; Cook, K.; Lecommandoux, S.; et al. Hydrogel-Embedded Quantum Dot-Transcription Factor Sensors for Quantitative Progesterone Detection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 43513–43521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, M.-J.; Park, S.-Y. Carbon-dot-based ratiometric fluorescence glucose biosensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 282, 719–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Li, H.; Mujtaba Mari, G.; Yu, X.; Yu, W.; Wen, K.; Ke, Y.; Shen, J.; Wang, Z. Fluorescence immunoassay based on the inner-filter effect of carbon dots for highly sensitive amantadine detection in foodstuffs. Food Chem. 2019, 294, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsson, A.; Ekblad, T.; Andersson, O.; Liedberg, B. Photografted poly(ethylene glycol) matrix for affinity interaction studies. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, I.Y.; Kim, J.S.; Choi, B.R.; Lee, K.; Lee, H. Hydrogel based biosensors for in vitro diagnostics of biochemicals, proteins, and genes. Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2017, 6, 1601475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Wolf, L.K.; Georgiadis, R.M. Secondary structure effects on DNA hybridization kinetics: a solution versus surface comparison. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, 3370–3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welch, N.G.; Scoble, J.A.; Muir, B.W.; Pigram, P.J. Orientation and characterization of immobilized antibodies for improved immunoassays (Review). Biointerphases 2017, 12, 02D301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, B.; Huang, S.; Ge, F.; Luo, Y.; Jia, D.; Dai, Y. 3D antibody immobilization on a planar matrix surface. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 28, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Wen, D.; Gaponik, N.; Eychmüller, A. Enzyme-encapsulating quantum dot hydrogels and xerogels as biosensors: multifunctional platforms for both biocatalysis and fluorescent probing. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 976–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Guo, W.; Wang, E. Utilizing a CdTe quantum dots-enzyme hybrid system for the determination of both phenolic compounds and hydrogen peroxide. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 1141–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Zeng, Y.; Qi, Y.; Zhou, T.; Shi, G. A novel electrochemical sensor for determination of dopamine based on AuNPs@SiO2 core-shell imprinted composite. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 38, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linkov, P.A.; Vokhmintcev, K.V.; Samokhvalov, P.S.; Nabiev, I.R. Ultrasmall quantum dots for fluorescent bioimaging in vivo and in vitro. Optics Spectrosc. 2017, 122, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandi, D.; Mansingh, S.; Behera, A.; Parida, K. Calculation of relative fluorescence quantum yield and Urbach energy of colloidal CdS QDs in various easily accessible solvents. J. Luminesc. 2021, 231, 117792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neo, D.C.J.; Goh, W.P.; Lau, H.H.; Shanmugam, J.; Chen, Y.F. CuInS2 Quantum Dots with Thick ZnSexS1–x Shells for a Luminescent Solar Concentrator. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 3, 6489–6496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Shi, Q.; Fu, S.; Song, J.; Xia, H.; Du, D.; Lin, Y. Efficient synthesis of MCu (M = Pd, Pt, and Au) aerogels with accelerated gelation kinetics and their high electrocatalytic activity. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 8779–8783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anupama, K.; Paul, T.; Ann Mary, K.A. Solid-state fluorescent selenium quantum dots by a solvothermal-assisted sol–gel route for curcumin sensing. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 21525–21533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arachchige, I.U.; Brock, S.L. Sol–Gel Methods for the assembly of metal chalcogenide quantum dots. Accounts Chem. Res. 2007, 40, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arachchige, I.U.; Brock, S.L. Highly luminescent quantum-dot monoliths. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 1840–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewa-Rahinduwage, C.C.; Silva, K.L.; Brock, S.L.; Luo, L. Quantum dot assembly driven by electrochemically generated metal-ion crosslinkers. Chem. Mater. 2021, 33, 4522–4528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matter, F.; Luna, A.L.; Niederberger, M. From colloidal dispersions to aerogels: How to master nanoparticle gelation. Nano Today 2020, 30, 100827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesnyak, V.; Voitekhovich, S.V.; Gaponik, P.N.; Gaponik, N.; Eychmüller, A. CdTe nanocrystals capped with a tetrazolyl analogue of thioglycolic acid: Aqueous synthesis, characterization, and metal-assisted assembly. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 4090–4096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Q.; Brock, S.L. Porous CdTe nanocrystal assemblies: ligation effects on the gelation process and the properties of resultant aerogels. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 50 20, 9985–9992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gacoin, T.; Lahlil, K.; Larregaray, P.; Boilot, J.P. Transformation of CdS colloids: sols, gels, and precipitates. J. Phys. Chem. B 2001, 105, 10228–10235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.-J.; Wang, H.; Zhou, Q.-H.; You, Y.-Z. Reversible and multisensitive quantum dot gels. Macromolecules 2011, 44, 4306–4312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saez Cabezas, C.A.; Ong, G.K.; Jadrich, R.B.; Lindquist, B.A.; Agrawal, A.; Truskett, T.M.; Milliron, D.J. Gelation of plasmonic metal oxide nanocrystals by polymer-induced depletion attractions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2018, 115, 8925–8930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayevich, V.; Cai, B.; Benad, A.; Haubold, D.; Sonntag, L.; Gaponik, N.; Lesnyak, V.; Eychmüller, A. 3D assembly of all-inorganic colloidal nanocrystals into gels and aerogels. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 6334–6338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaponik, N.; Talapin, D.V.; Rogach, A.L.; Hoppe, K.; Shevchenko, E.V.; Kornowski, A.; Eychmüller, A.; Weller, H. Thiol-capping of CdTe nanocrystals: An alternative to organometallic synthetic routes. J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106, 7177–7185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewa-Rahinduwage, C.C.; Geng, X.; Silva, K.L.; Niu, X.; Zhang, L.; Brock, S.L.; Luo, L. Reversible electrochemical gelation of metal chalcogenide quantum dots. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 12207–12215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanan, J.L.; Brock, S.L. CdS aerogels: Effect of concentration and primary particle size on surface area and opto-electronic properties. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesnyak, V.; Wolf, A.; Dubavik, A.; Borchardt, L.; Voitekhovich, S.V.; Gaponik, N.; Kaskel, S.; Eychmüller, A. 3D assembly of semiconductor and metal nanocrystals: Hybrid CdTe/Au structures with controlled content. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 13413–13420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Liu, Y.; Tang, J.; Tang, W. Surface ligands engineering of semiconductor quantum dots for chemosensory and biological applications. Mater. Today 2017, 20, 360–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moya, M.L.; Alonzo, L.F.; George, S.C. Microfluidic device to culture 3D in vitro human capillary networks. In Biomimetics and Stem Cells: Methods and Protocols, Vunjak-Novakovic, G., Turksen, K., Eds.; Springer New York: New York, NY, 2014; pp. 21–27.
- Park, D.; Lee, J.; Lee, Y.; Son, K.; Choi, J.W.; Jeang, W.J.; Choi, H.; Hwang, Y.; Kim, H.-Y.; Jeon, N.L. Aspiration-mediated hydrogel micropatterning using rail-based open microfluidic devices for high-throughput 3D cell culture. Scientific Reports 2021, 11, 19986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




