1. Introduction
Scabies is one of the most common skin infestations in the world caused by the human itch mite, Sarcoptes scabiei var. hominis. It is estimated to affect more than 200 people worldwide, with a prevalence ranging between 0.2% and 71%. Scabies is endemic in underdeveloped and developing countries, although it could be considered as a re-emerging infectious disease also in developed settings, especially in crowded conditions. The most common sites of scabies outbreaks are nursing homes, prisons or childcare facilities. Nosocomial scabies outbreaks could represent a major public health problem, also due to high costs on healthcare systems [
1,
2].
Scabies is transmitted by direct and prolonged skin-to-skin contact with infected individuals, even if asymptomatic. Mite’s evolutionary cycle takes place entirely in man: after mating, the adult male remains on the skin while the female burrows into the epidermis, where she usually lives for 30 days laying her eggs. After few days, the eggs hatch and the larvae invade the skin, triggering a local inflammatory response with rash and intense itching, the most common symptom. Usually, in a primary infestation this reaction occurs after about four weeks by the contact with an infested individual [
3]. Scabies incubation period is estimated between 2 and 6 weeks, except for reinfections, where it’s shorter [
4].
When scabies affects immunocompromised, elderly or debilitated people it can lead to a more severe infestation called Norwegian or crusted scabies. This kind of infestation is more contagious because of the large number of mites colonizing patient’s skin (up to 2 millions of mites). People affected by crusted scabies can easily spread infestation either through short skin-to-skin direct contact or indirect contact with clothes, beds or infested fomites [
1].
Scabies outbreaks can be more frequent in healthcare settings, due to the clinical peculiarities of patients (e.g. physical or mental disability, advanced age, immunodeficiency), the duration of hospitalizations and the direct physical contact necessary for assistance. Most of outbreaks in healthcare settings are caused by unrecognized Norwegian scabies in hospitalized patients [
5]. Moreover, the diagnostic delay may underestimate the prevalence of scabies in these contexts [
6]. Usually, a lot of patients and healthcare workers (HCWs) are exposed to scabies, both in underdeveloped and developed countries. To date, there are no univocal recommendations on the prophylactic treatment or measures to prevent the transmission of scabies in close contacts [
7]. Similarly to what was observed during the COVID-19 pandemic, the implementation of the preventive protocols, aimed at a correct management of outbreaks, is crucial to limit the spread of infectious diseases among HCWs in healthcare settings [
8].
The aim of this retrospective observational study is to analyze a scabies outbreak in a large University Hospital in the South of Italy and to describe the results of an ad-hoc designated prevention protocol aimed at containing the spread of the infection among HCWs.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Setting and participants
The outbreak started on 11 October 2022, with a cluster of scabies cases in the Operative Unit (UO) of Internal Medicine (division F.). The observation period was between 11 October 2022 and 6 March 2023, considering the first case of scabies and the end of incubation period related to the last case detected (6 weeks starting from 22 January 2023). The ad-hoc designated preventive protocol was applied for all healthcare workers (HCWs, about 6000) working at the University Hospital of Bari, Apulia, Southern Italy. Ethical approval was not necessary because all medical examinations were performed according to Italian law on the protection of workers exposed to occupational risks (D.Lgs. 81/2008) and with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki, with scientific methods and for scientific purposes.
2.2. Case definitions
According to the 2020 International Alliance for the Control of Scabies (IACS) Consensus Criteria for the diagnosis of scabies, a “confirmed” case of scabies is defined as a patient who presents mites or mite products (e.g. eggs, faeces) visible by using a high-powered device and/or dermoscopy and/or light microscopy of skin samples [
9]. If mites or their products are not visible and other differential diagnosis are less likely than scabies, the diagnosis of scabies could also be “clinical” when the patient presents burrows and/or typical skin lesions in male genital area and/or in a typical distribution, with at least two anamnestic features (e.g. itch, close contact with a scabies case). Diagnosis of “suspected” scabies can be made if the patient presents typical skin lesions in a typical distribution, without any anamnestic features, or if he presents atypical skin lesions in atypical distribution, with at least two anamnestic features.
According to the European Guideline for the management of scabies, a scabies case could be considered cured if there are no sign or symptoms of scabies (e.g. absence of active skin lesions or nocturnal itching) within one week of starting therapy [
10].
2.3. Epidemiologic investigation and notification system
According to Italian law, all suspected or confirmed cases of scabies must be notified to the competent health authority [
11]. In this study, the epidemiological investigation was conducted by the UO of Hygiene and a report was also sent to the UO of Occupational Medicine to temporarily remove HCWs from work, according to the preventive protocol.
2.4. Prevention and protection measures
In Italy, the management of scabies cases is still based on the indications given in the circular of the Ministry of Health of 13 March 1998, which requires isolation of cases for 24 hours from the start of treatment [
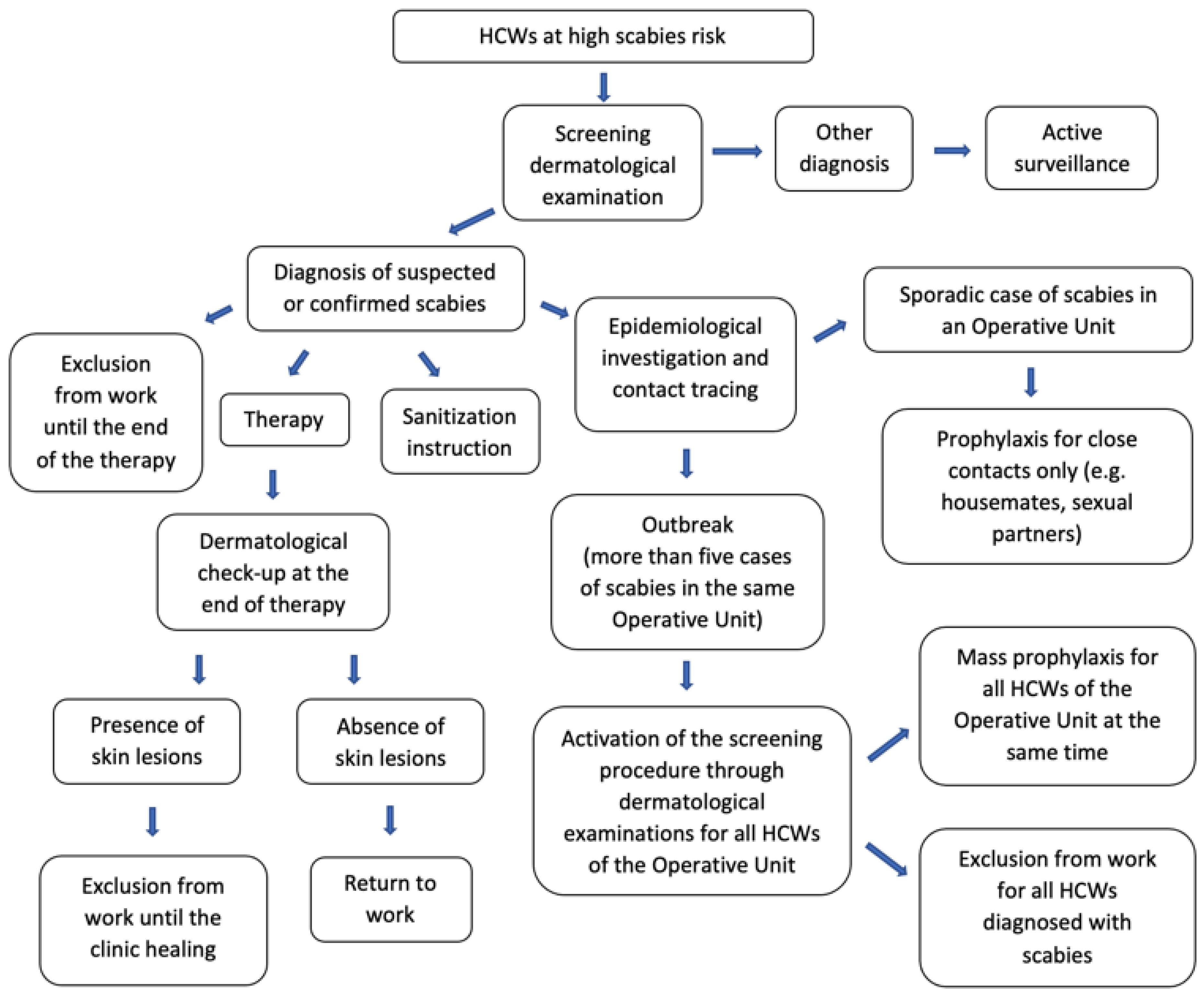
12]. In this study, the prevention protocol was designated by the UO of Occupational Medicine to limit the spread of scabies among HCWs (
Figure 1). As for all transmissible infectious diseases, the protocol was adapted considering the peculiar healthcare setting, in order to protect the health of both personnel and frail patients at high risk of comorbidity, similarly to what was observed during the COVID-19 pandemic [
13,
14].
First, a risk assessment was carried out, defining HCWs at high scabies risk as subjects working in UOs with more than five confirmed cases of scabies, close contacts of a confirmed case of scabies, or HCWs with signs and symptoms of the disease.
According to the protocol, all cases of HCWs at high scabies risk were subject to active surveillance and underwent a screening dermatological examination at the UO of Dermatology.
All scabies cases were treated by applying topical Permethrin 5% cream or benzyl benzoate 30% lotion all over the body for 10 hours, for three consecutive days, repeating the treatment after one week. Therapy-refractory cases were also treated with oral Ivermectin. It was also recommended to treat close contacts (e.g. people living in the same house or sharing the same bed) at the same time [
10].
Although national and international recommendations suggest a 24-hour absence from work from the start of therapy a rapid and more aggressive response to institutional outbreaks is equally recommended [
12,
15]. Therefore, our protocol established that all infested HCWs were suspended from work for the whole duration of treatment, until definitive healing. At the end of treatment, all HCWs infested underwent a medical check-up at UOs of Dermatology and Occupational Medicine, in order to certify the absence of skin lesions and to allow the return to work.
All cases were also instructed to wash sheets, blankets and clothes at 60°C or more, or to close them into a plastic bag or cellophane, without using for a week to avoid reinfestations.
All Directors of Operating Units with reported scabies cases were also requested to identify all possible contacts among HCWs or patient and to ensure the cleaning of all surfaces or furnishings (e.g. rooms, bathrooms, padded furniture) using a vacuum cleaner or to close all non-washable items in a plastic bag or cellophane for a few days.
According to the European Guideline for the management of scabies, in case of epidemical outbreaks, mass prophylactic treatment was extended to all contacts, even if not close (level of evidence Ib; grade A recommendation) [
10,
16]. In our protocol, mass prophylactic treatment was established for all HCWs working in UOs with more than five confirmed cases of scabies. A single dose of topical Permethrin 5% cream was used as prophylaxis, applied on the same day by all HCWs.
2.5. Statistical analysis
Continuous variables are reported as mean ± standard deviation (SD) and range, and categorical variables as proportions. The chi-square test was used to compare proportion between groups. The Skewness and kurtosis test was conducted to evaluate the normality of the continuous variables; a normalization model was set for not normally distributed variables, the t student for independent data test was performed to compare continuous variables between groups.
To analyse the determinants of scabies, a multivariate logistic regression model was built; the variables age, sex (male vs. female), UOs (Internal Medicine F. vs. other), job category, BMI, smoke habit, use of alcohol, allergies, and chronic conditions were considered as determinants. The adjusted Odds Ratios (aORs) were calculated, as well as 95%CIs. The Hosmer-Lemeshow’s chi-squared test was used to evaluate the goodness-of-fit of the multivariate logistic regression model.
A two-sided p-value < 0.05 was considered an indicator of statistical significance for all tests. An anonymized data analysis was performed using the STATA MP17 software.
3. Results
3.1. Scabies cases: prevalence and distribution
Table 1 shows the time trend of the spread of the infection. Overall, scabies cases were observed in 8 UOs: Internal Medicine divisions F. (n=13) and B. (n=1), Pneumology (n=1), Emergency Medicine and Surgery (n=1), Transfusion Medicine (n=1), Pediatric Oncology (n=1), Rheumatology (n=1) and Cardiac Surgery (n=2).
In the observation period, 183 HCWs at high scabies risk were subjected to screening dermatological examinations: 161 (88%) were negative, 21 (11.5%) were found to be diagnostic for scabies and 1 (0.5%) was diagnosed for other parasitosis. Prophylactic therapy with topical Permethrin 5% cream was also indicated for 39 asymptomatic HCWs (21.3% of all dermatological examinations).
The prevalence of scabies infestation in the 8 UOs with at least one case was 2.6% (21/800 HCWs). Among scabies cases, there were 8 physicians (5 male, 3 female), 7 nurses (2 male, 5 female) and 6 other HCWs (4 male, 2 female). The average age was 37.8 years, although it was lower in females than in males (33.9 years vs. 41.3 years) and in physicians than in other HCWs (29.75 years for physicians vs. 39.43 years for nurses vs. 46.5 years for other HCWs).
The average length of the infestation period was 31 days (range 8 – 48 days).
3.2. Characteristics of the sample and risk factors of scabies
The characteristics of the sample of HCWs at high risk, per group, (scabies, n° 21) vs. control (non-scabies, n°162), are reported in
Table 2.
The multivariate regression model showed a statistically significant association between the diagnosis of scabies and allergy to dust mites (aOR=8.0; 95%CI=1.1-58.3), allergy to other antigens (aOR=0.05; 95%CI=0.01-0.57) and being a nurse (aOR=7.1; 95%CI=1.7-29.9) or other HCW than physician (aOR=9.1; 95%CI=1.8-46.2). No associations were found between the diagnosis of scabies and age, sex, BMI, smoke habit, alcohol, diabetes, hypertension and cardiovascular diseases (
Table 3).
3.3. The index case and outbreak reconstruction
The index case (IC) was identified through epidemiological investigation carried out by the UO of Hygiene. IC was an elderly man hospitalized in the UO of Internal Medicine F. from 27 July to 17 August 2022. During the hospitalization, the patient showed itchy skin lesions and was initially diagnosed with a suspected allergic reaction to drugs. After two months, IC underwent several medical examinations at the same UO, complaining about the persistence of skin lesions and finally, on 12 October, was directed to a dermatological examination which allowed the two-months-delayed scabies diagnosis.
The first scabies case among HCWs (a male physician) was detected on 11 October 2022 in the same UO that had initially assisted the IC. In the following days other 7 cases were diagnosed (8 cases overall in the UO of Internal Medicine F.). On 24 October 2022, was detected the first scabies case in another UO (UO of Pulmonology). The epidemiological investigation revealed that the HCW had close contacts with colleagues working in the UO of Internal Medicine F. (the two wards were in the same floor), who were later diagnosed with scabies (he did not take prophylaxis because he was off work and unaware of the hospital outbreak).
According to the preventive protocol, due to the high number of scabies cases (more than five) in the UO of Internal Medicine F., all HCWs underwent a screening dermatological examination. Overall, from 9 November 2022 to 6 December 2022, 152 HCWs working in the Operative Unit of Internal Medicine F. were submitted to screening specialistic examination: 3 (2%) were diagnosed with scabies (two of them shared the same house) and none of the remaining 149 HCWs (88%) showed signs or symptoms of scabies at the time of the examination. The preventive protocol also required all HCWs to apply a single prophylactic dose of Permethrin 5% topical cream at the same time, on the so-called "P-day" (day of prophylaxis), established on 20 November 2022.
From the P-day to 22 January 2023 there were only few sporadic scabies cases in several different UOs.
4. Discussion
The prevalence of scabies in healthcare setting could be underreported, often due to diagnostic delay and the presence of elderly immunocompromised in acute or long-term care facilities, with significant economic implications related to pharmaceutical costs, lost working days or closures of hospital wards [
6,
17,
18].
In our hospital, after the recognition of the scabies outbreak, a preventive protocol was urgently set up thanks to a multidisciplinary approach (cooperation between the Operative Units of Occupational Medicine, Hygiene and Dermatology). Setting up a multidisciplinary team is the first recognized step towards an effective approach to the outbreak [
19]. A crucial role within our protocol was also played by the massive information of patients and staff, as well as by a careful risk assessment aimed at selecting the HCWs with high scabies risk to be sent to dermatological screening for any eventual therapeutic treatment. A HCW at high scabies risk was defined as a subject working in a UO with more than five confirmed cases of scabies, a close contact of a confirmed case of scabies, or a HCW with signs and symptoms of the disease. This approach has made it possible to contain the costs of massive prophylaxis which, on the contrary, would have become necessary in the absence of a risk assessment.
Our protocol also provided stricter criteria for the suspension from work of HCWs diagnosed with scabies (whole duration of the therapy and clinical recovery ascertained by medical examination before readmission to work) than national and international recommendations, which indicate suspension from work for only 24 hours from the beginning of the therapy [
12,
16].
These preventive measures allowed us to obtain a low prevalence of scabies (2.6%, 21/800) in the UOs with at least one case of scabies and a lowest prevalence (0.35%, 21/6000) considering all HCWs in the University Hospital of Bari. Moreover, the duration of our outbreak was shortened (14.7 weeks) and with the exception of the Internal Medicine UO, the other UOs reported only sporadic cases, with no further clusters. Supporting our results, literature data on the prevalence and duration of nosocomial scabies outbreaks showed that average number of HCWs diagnosed with scabies per outbreak is 39 (range 6-278) and the average duration of outbreaks is 14.5 weeks (range 4-52 weeks) [
17].
As regards to the characteristics of scabies cases, our results are in line with the literature in showing a significant association between scabies infection and being a nurse or having an allergy to dust mites [
17,
20]. According to literature data, our study also showed no statistically significant association between having chronic diseases (e.g., diabetes, hypertension and cardiovascular diseases) and scabies [
21]. Finally, a literature review by Dobner et al. showed an association between obesity and skin infections rates [
22]. In contrast with this finding our study showed no statistical associations between scabies diagnosis and BMI or age.
Our study has some limitations, including its retrospective design. The potential diagnostic delay, due to the extended incubation period and the individual variability of clinical manifestations of the infestation could have led to an underestimation of scabies cases. Moreover, dermatological screening was carried out only for high risk HCWs, according to risk assessment and epidemiological investigation. On the one hand this attitude could have led to an underdiagnosis but, on the other, it allowed to save financial resources and time to be reserved for the treatment of cases and their clinical evaluation for readmission to work, representing one of the strengths of the study. Finally, an important point that would further improve the management of scabies outbreak in hospital settings is the strengthening of the interactions and shared data network between hospitals and local health authorities. Concerning this, as reported in literature, some symptomatic HCWs consult the general practitioner rather than the occupational health service or hospital dermatologists, generating a greater probability of misdiagnosis and compromising contact tracing procedures [
23]. Nevertheless, coordinated actions to control scabies at a global level are crucial, since scabies outbreaks are likely to increase in the near future as a result of an ageing population and increasing population density in urban areas [
24,
25].
5. Conclusions
The specific approach to scabies outbreaks in healthcare settings has gained increasing importance in management and treatment guidelines, although there is no globally accepted strategy, as well as, there are still different issues to be addressed. Within this context, our study shows our experience of how a nosocomial scabies outbreak was contained through the rapid implementation of prevention protocol and measures that allowed to limit the spread of the infestation among HCWs, the duration of the outbreak and the economic burden related, in particular, to HCWs absence from work.
Nevertheless, the strengthening of the interactions between the hospital and territorial care networks is necessary to guarantee a more optimal management of hospital outbreaks and to limit missing diagnoses. Further studies may increase our knowledge on the best approach to an emerging and recurrent issue in hospital institutions and reviews of these outbreaks and their approach could also be used in other working contexts than the healthcare one.
Author Contributions
CF: ST, LV: Conceptualisation, Supervision and Project administration. SS, LDM, AC: Validation, Writing - original draft and Writing - review & editing. FPB: Software and Statistical Analysis. PS, GD, PR, FA, SZ, GG: Investigation and Data Curation. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The patients were informed that data from the research protocol would be treated in an anonymous manner based on scientific methods and for scientific purposes in accordance with the principles of the Helsinki Declaration. Ethical approval is not necessary because all medical and instrumental examinations were performed according to Italian laws concerning the protection of workers exposed to occupational risks (D. Lgs. 81/2008).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Global Health, Division of Parasitic Diseases and Malaria. Parasites – Scabies. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/parasites/scabies/index.html (accessed on 30 March 2023).
- World Health Organization. Newsroom, Fact sheets, Details, Scabies. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/scabies (accessed on 30 March 2023).
- Scanni, G. The Mite-Gallery Unit: A New Concept for Describing Scabies through Entodermoscopy. Trop Med Infect Dis. 2019, 4(1), 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedoya Del Campillo, A.; Lleopart, N.; ChQR, G.; Álvarez, M.; Montilla, M.; Martínez-Carpio, P.A. Intervention protocol to improve scabies control in enclosed communities: a case report. Rev Esp Sanid Penit. 2021, 23(1), 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; O'Grady, S.; Muller, M.P. Rapid control of a scabies outbreak at a tertiary care hospital without ward closure. Am J Infect Control. 2012, 40(5), 451–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouvresse, Sophiea; Chosidow, Oliviera. Scabies in healthcare settings. Current Opinion in Infectious Diseases 2010, 23(2), p 111-118. [CrossRef]
- FitzGerald, D.; Grainger, R.J.; Reid, A. Interventions for preventing the spread of infestation in close contacts of people with scabies. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014, (2), CD009943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Maria, L.; Sponselli, S.; Caputi, A.; Pipoli, A.; Giannelli, G. ; Delvecchio, G et al. Comparison of Three Different Waves in Healthcare Workers during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Retrospective Observational Study in an Italian University Hospital. J Clin Med. 3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelman, D.; Yoshizumi, J.; Hay, R.J.; Osti, M.; Micali, G.; Norton, S.; et al. The 2020 International Alliance for the Control of Scabies Consensus Criteria for the Diagnosis of Scabies. Br J Dermatol. 2020, 183(5), 808–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salavastru, C.M.; Chosidow, O.; Boffa, M.J.; Janier, M.; Tiplica, G.S. European guideline for the management of scabies. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2017, 31(8), 1248–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Official Gazette of the Italian Republic. Italian Ministry of Health. Decreto 15 dicembre 1990. Sistema informativo delle malattie infettive e diffusive. (GU Serie Generale n.6 del 08-01-1991). Available online: https://www.gazzettaufficiale.it/atto/serie_generale/caricaDettaglioAtto/originario?atto.dataPubblicazioneGazzetta=1991-01-08&atto.codiceRedazionale=091A0055 (accessed on 30 March 2023).
- Italian Ministry of Health. Circolare n.4 of 13 marzo 1998 Protocollo 400.3/26/1189. MISURE DI PROFILASSI PER ESIGENZE DI SANITA’ PUBBLICA. Provvedimenti da adottare nei confronti di soggetti affetti da alcune malattie infettive e nei confronti di loro conviventi o contatti. Available online: https://www.trovanorme.salute.gov.it/norme/dettaglioAtto?id=25185 (accessed on 30 March 2023).
- Vimercati, L.; De Maria, L.; Quarato, M.; Caputi, A.; Stefanizzi, P.; Gesualdo, L.; et al. COVID-19 hospital outbreaks: Protecting healthcare workers to protect frail patients. An Italian observational cohort study. Int J Infect Dis. 2021, 102, 532–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Maria, L.; Sponselli, S.; Caputi, A.; Stefanizzi, P.; Pipoli, A.; Giannelli, G.; Delvecchio, G.; Tafuri, S.; Inchingolo, F.; Migliore, G.; Bianchi, F.P.; Boffetta, P.; Vimercati, L. SARS-CoV-2 Breakthrough Infections in Health Care Workers: An Italian Retrospective Cohort Study on Characteristics, Clinical Course and Outcomes. J Clin Med. [CrossRef]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Parasites – Scabies. Prevention & Control. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/parasites/scabies/prevent.html (accessed on 30 March 2023).
- Romani, L.; Whitfeld, M.J.; Koroivueta, J.; Kama, M.; Wand, H.; Tikoduadua, L.; et al. Mass Drug Administration for Scabies Control in a Population with Endemic Disease. N Engl J Med. 2015, 373(24), 2305–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vorou, R.; Remoudaki, H.D.; Maltezou, H.C. Nosocomial scabies. J Hosp Infect. 2007, 65(1), 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, N.; Guedes, P.M.; Norton, P.; Azevedo, F.; Lisboa, C. Dois Surtos de Escabiose num Hospital Terciário em Portugal [Two Scabies Outbreaks at a Tertiary Care Hospital in Portugal]. Acta Med Port. [CrossRef]
- Stoevesandt, J.; Carlé, L.; Leverkus, M.; Hamm, H. Control of large institutional scabies outbreaks: institutional scabies outbreaks. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2012;10:637–47. [CrossRef]
- Arlian, L.G.; Morgan, M.S. A review of Sarcoptes scabiei: past, present and future. Parasit Vectors. 2017, 10(1), 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karaca Ural, Z.; Çatak, B.; Ağaoğlu, E. Prevalence of Scabies in the Covid-19 Pandemic Period and Determination of Risk Factors for Scabies: a Hospital-Based Cross-Sectional Study in Northeast Turkey. Acta Parasitol. 2022, 67(2), 802–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobner, J.; Kaser, S. Body mass index and the risk of infection - from underweight to obesity. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2018, 24(1), 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capobussi, M.; Sabatino, G.; Donadini, A.; Tersalvi, C.A.; Castaldi, S. Control of scabies outbreaks in an Italian hospital: an information-centered management strategy. Am J Infect Control. 2014, 42(3), 316–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hay, R.J.; Steer, A.C.; Chosidow, O.; Currie, B.J. Scabies: a suitable case for a global control initiative. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2013, 26, 107–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelman, D.; Steer, A.C. Diagnosis, treatment, and control of scabies: can we do better? Lancet Infect Dis. 2018, 18, 822–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).