Submitted:
05 May 2023
Posted:
06 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
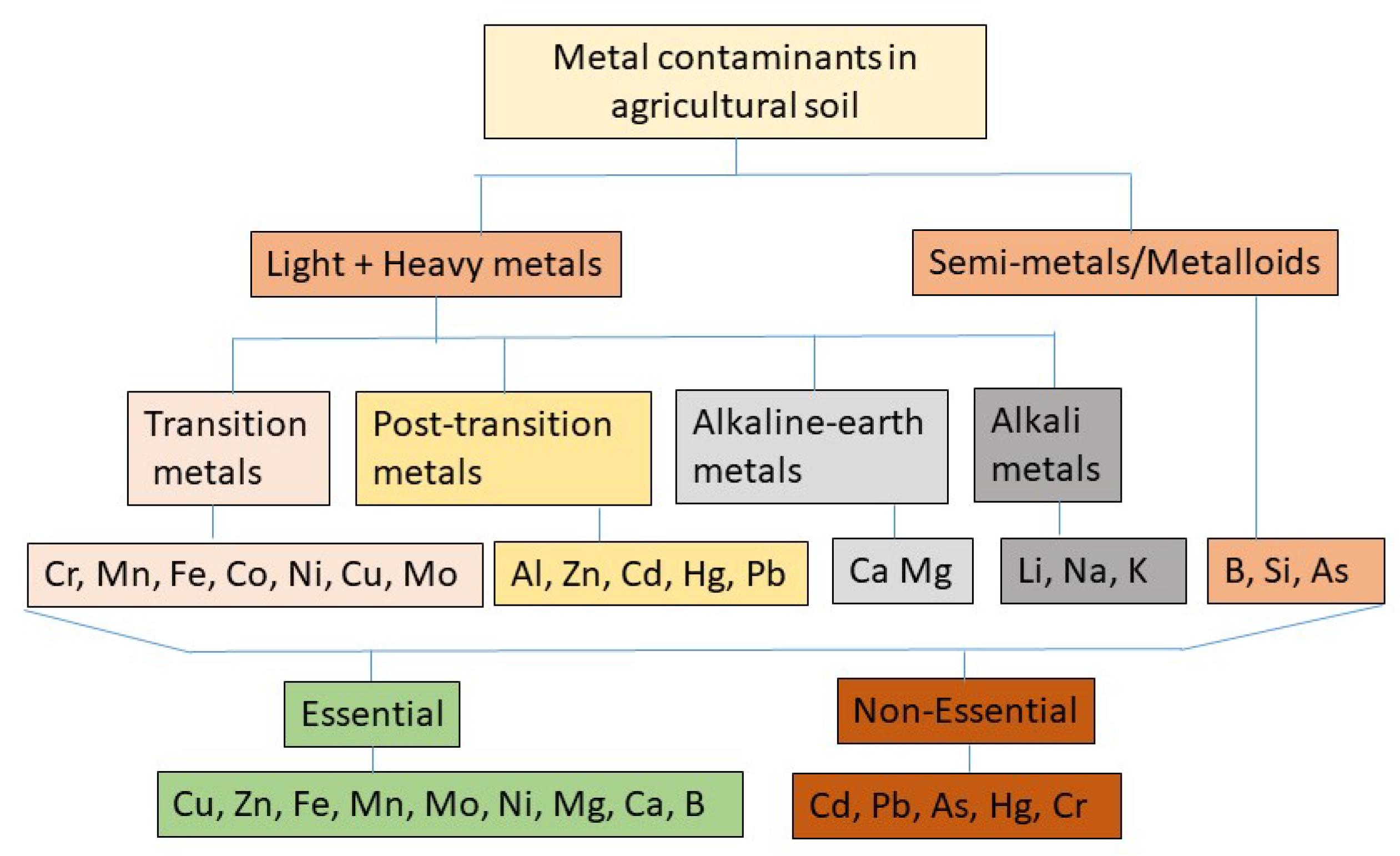
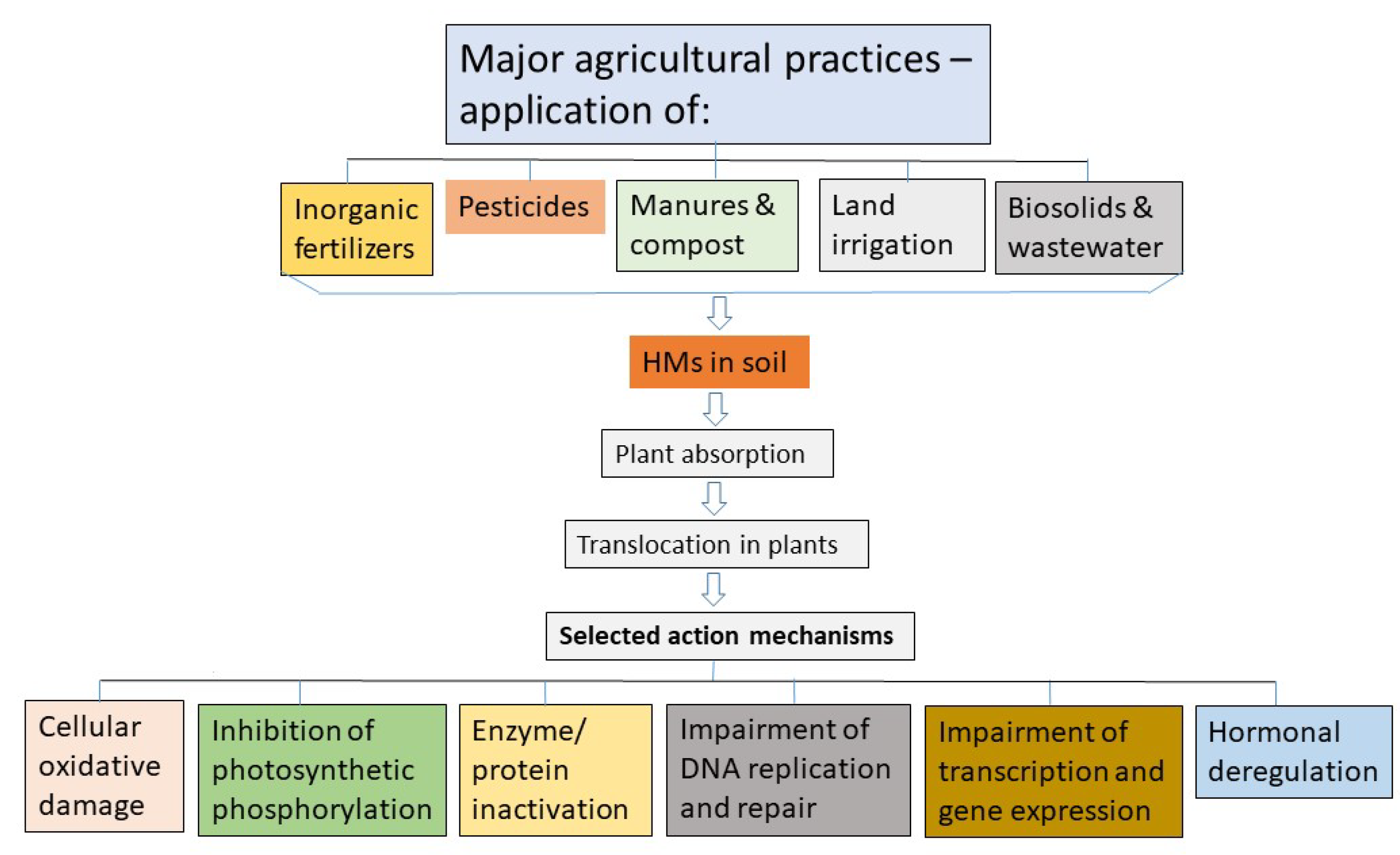
2. Sources of HM contamination in arable lands
2.1. Application of chemical fertilizers
2.2. Pesticide application
2.3. Application of livestock manures and compost
2.4. Application of sewage-sludge based biosolids.
2.5. Land Irrigation
3. Factors affecting HM interactions with crop plants.
3.1. Plant responses to HM toxicity
3.1.1. Plant type, growth stage, and growth conditions
3.1.2. Plant metabolic activities
3.1.3. Uptake, translocation, and bioaccumulation in plants
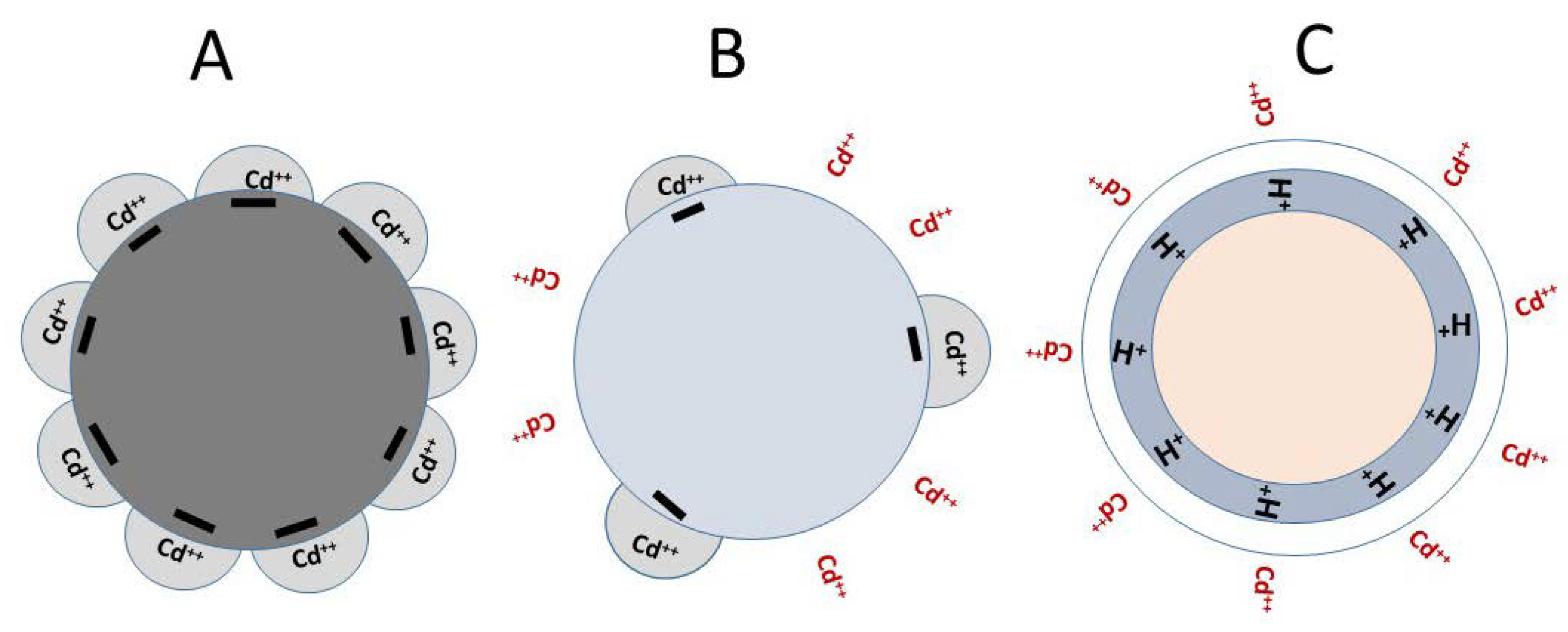
3.2. Occurrence and bioavailability of HMs
3.2.1. Hypothetical soil binding diagrams of HMs
3.2.2. HM precipitation in the soil—effect of pH
3.3. Rhizosphere chemistry and HM chelation
4. Key mechanisms of plant growth inhibition by HMs
4.1. Generation of oxidative stress
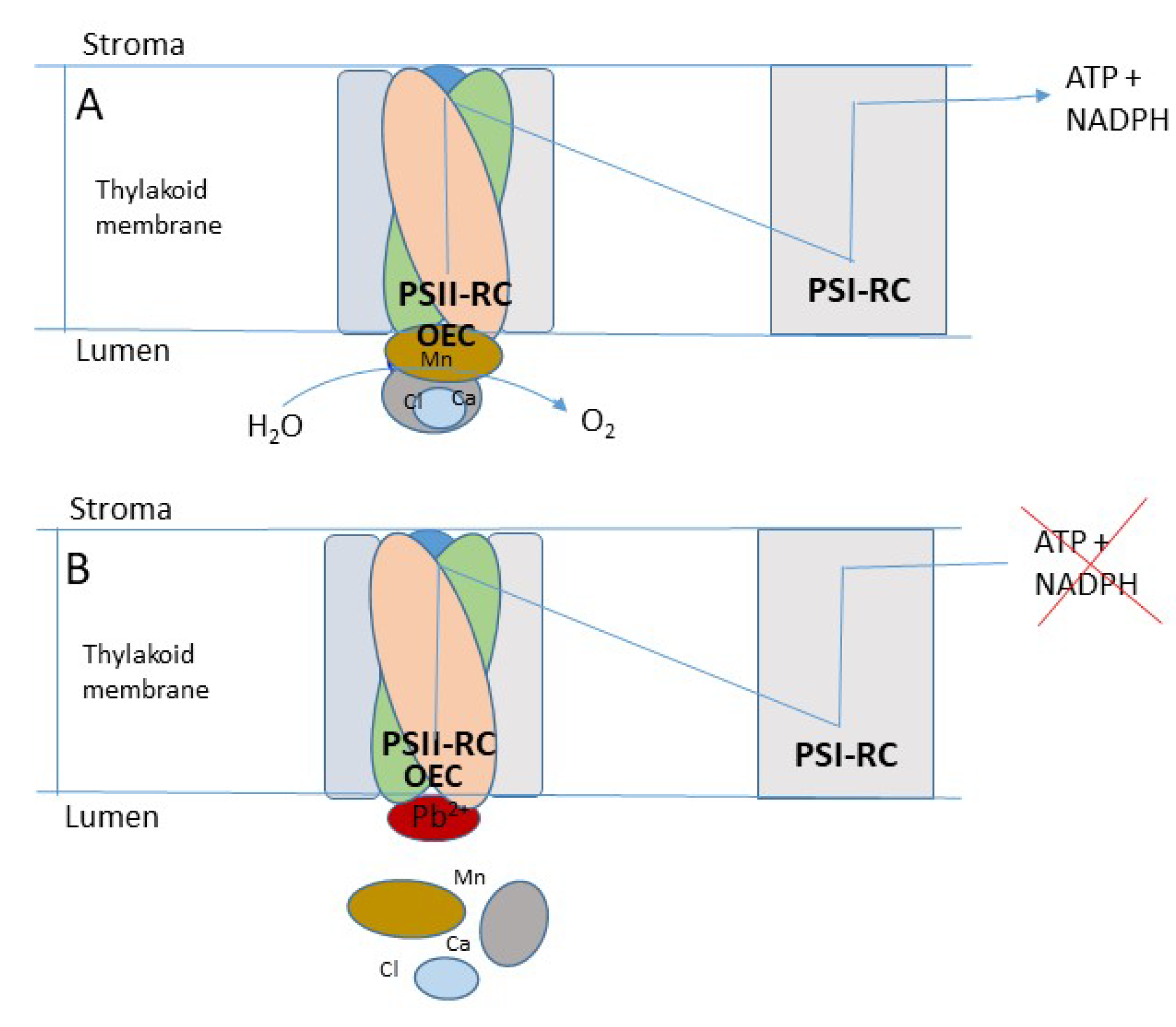
4.2. Inhibition of photosynthetic phosphorylation
4.3. Inactivation of enzyme activities
4.3.1. Inactivation of soil enzyme activities
4.3.2. Inactivation of plant enzyme activities
4.4. Genetic modifications
4.4.1. Effects on DNA metabolism
4.4.2. Effects on gene expression
4.5. Hormonal deregulation
4.6. Inhibition of soil microorganisms
5. Visual toxicity symptoms of HMs in plants
6. Conclusions and perspectives
Supplementary Materials
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pourret, O. , Hursthouse A. It’s Time to Replace the Term “Heavy Metals” with “Potentially Toxic Elements” When Reporting Environmental Research. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health, 2019, 16, 4446–4451. [Google Scholar]
- Maksymiec, W. Signaling responses in plants to heavy metal stress. Acta Physiol Plant. 2007, 29: 177–187.
- Shahid M., Khalid S., Abbas G., Shahid N., Nadeem M., Sabir M., Aslam M., Dumat C. Heavy Metal Stress and Crop Productivity. 2015. Hakeem, HR (ed.), Crop Prdo. Global Envi. Issues, Springer Inter. Publishing, Switzerland.
- Wuana, R.A. , Okieimen F.E. Heavy Metals in Contaminated Soils: A Review of Sources, Chemistry, Risks and Best Available Strategies for Remediation. Intern. Sch. Res. Net. Ecol 2011, 402647, 1-20.
- Ghori N.H., Ghori T., Hayat M.Q., Imadi S.R., Gul A., Altay V., Ozturk M. Heavy metal stress and responses in plants. Int. J. Envn. Sci. Tech. 2019. 16, 1807-1828.
- Ali, H. , Khan E., Ilahi I. Environmental Chemistry and Ecotoxicology of Hazardous Heavy Metals: Environmental Persistence, Toxicity, and Bioaccumulation. 2019. J. Chem 6730305, 1-14.
- Tóth, G. , Hermann T. , Da Silva M.R., Montanarella C. Heavy metals in agricultural soils of the European Union with implications for food safety. Envirn. Intern. 2016, 88, 299–309. [Google Scholar]
- Tiwari, S. , Lata C. Heavy Metal Stress, Signaling, and Tolerance Due to Plant-Associated Microbes: An Overview. 2018. CSIR-National Botanical Research Institute, Lucknow, India.
- Rai, P.K. , Leeb S.S., Zhangc, Tsangd UF, Kime KH. Heavy metals in food crops: Health risks, fate, mechanisms, and management. 2019. Environ. Inter. 2019 125, 365–385.
- Singh, S. , Parihar, P., Singh, R., Singh, V.P., and Prasad, SM. Heavy Metal Tolerance in Plants: Role of Transcriptomics, Proteomics, Metabolomics, and Ionomics. Front. Plant Sci. 2016. 6, 1143.
- Bashir K, Rasheed S, Kobayashi T, Seki M, Nishizawa NK. Regulating Subcellular Metal Homeostasis: The Key to Crop Improvement. 2016. Front. Plant Sci. 2016. 7, 1192, 1-9.
- Järup, L. Hazards of heavy metal contamination. British Medical Bulletin. 2003. 68, 167–182. [CrossRef]
- Sharma RK, Agrawal M, Marshall, FM. Atmospheric deposition of heavy metals (Cu, Zn, Cd and Pb) in Varanasi City, India. Environ. Monit. Assess 2008. 142, 269–278.
- Kumar, K. , Singh D.P., Barman S.C., Kumar N. Heavy Metal and Their Regulation in Plant System: An Overview. Chapter 2, Singh et al. (eds.), Plant Responses to Xenobiotics, Springer. Nature Singapore Pte Ltd. 2016. 19-38.
- Hasnine, M.T. , Huda M.E., Khatun R., Saadat A.H.M., Ahasan M., Akter S., Uddin M.F., Monika A.N., Rahman M.A., Ohiduzzaman M. Heavy Metal Contamination in Agric. Soil at DEPZA, Bangladesh. Envir. Ecol. Res. 2017. 5, 510-516.
- Ahmed, M. , Matsumoto M., Ozaki A., Thinh N.V., Kurosawa K. Heavy metal Contamination of Irrigation Water, Soil, and Vegetables and the Difference between Dry and Wet Seasons Near a Multi-Industry Zone in Bangladesh. Water 2019. 11, 583, 1-12.
- Arao T., Ishikawa S., Murakami M., Abe K., Maejima Y., Makino T. Heavy metal contamination of agricultural soil and countermeasures in Japan. Paddy Water Environ. 2010. 8, 247–257.
- Gebreyesus, S.T. Heavy Metals in Contaminated Soil: Sources & Washing through Chemical Extractants. Am. Sci. Res. J. Eng. Tech. Sci. (ASRJETS). 2014. 10, 54–60.
- Obinnaa, I.B. , and Ebere E.C. Water pollution by heavy metal and organic pollutants: Brief review of sources, effects, and progress on remediation with aquatic plants. Anal. Meth. Envirn. Chem. J. 2019,2, 25-38.
- Kumar, V. , Singh J., Kumar P. Heavy metals accumulation in crop plants: Sources, response mechanisms, stress tolerance and their effects. In: Kumar, V., Kumar, R., Singh, J. and Kumar, P. (eds) Contaminants in Agriculture and Environment: Health Risks and Remediation. Agro Environ Media, Haridwar, India, 2019. 1, 38-57.
- Ritche, H. , Roser M., Rosado P. Fertilizer consumption, 1961 to 2019. World in data. Source: Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations via the United States Department for Agriculture (USDA); 2022 (OurWorldInData.org). https://ourworldindata.org/fertilizers.
- Gimeno-Garcíaa, E.; Andreua, V.; Boluda, R. Heavy metals incidence in the application of inorganic fertilizers and pesticides to rice farming soils. Environ. Pollution. 1996. 92, 19–25.
- Mar, S.S. , Okazaki M., Motobayashi T. The influence of phosphate fertilizer application levels and cultivars on cadmium uptake by Komatsuna (Brassica rapa L. var. perviridis). Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2012. 58, 492—502.
- Wei, B. , Yu J. , Cao Z., Meng M., Yang L., Chen Q. The Availability and Accumulation of Heavy Metals in Greenhouse Soils Associated with Intensive Fertilizer Application. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2020, 17, 5359. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, E.Y. , Omueti J.A.I. Ogundayomi O. The Effect of Phosphate Fertilizer on Heavy Metal in soils and Amaranthus caudatus. Agric. Biol. J. N. Am., 2012. 3: 145-149.
- Zhuang, Z. , Mu H., Fu P., Wan Y., Yu Y., Wang Q., Li H. Accumulation of potentially toxic elements in agricultural soil and scenario analysis of Cd inputs by fertilization: A case study in Quzhou county. J. Environ. Mgmt. 2020, 269, 110797.
- Satarug, S. , Baker J.R., Urbenjapol S., Haswell-Elkins M., Reilly P.E.B., Williams D.J., Moore M.R. A global perspective on cadmium pollution and toxicity in non-occupationally exposed populations. Toxicol. Letters. 2003. 137, 65 – 83.
- Atafar, Z. , Mesdaghinia A., Nouri J., Homaee M., Yunesian M., Moghaddam M., Mahvi A.H. Effect of fertilizer application on soil heavy metal conc. Environ Monit Assess. 2010.160: 83–89.
- Al-Shawi, A.W. , Dahl R. The determination of cadmium and six other heavy metals in nitrate/phosphate fertilizer solution by ion chromatography. Anal. Chim. Acta, 1999. 391, 35–42.
- Samreen, S. , Kausar, S. Phosphorus Fertilizer: The Original and Commercial Sources. In: Phosphorus. 2019. Ed. Zhang T. InterTech Open. https://www.intechopen.com/chapters/64614.
- Paz, C.G. et al., Fertilizer Raw Materials. In: Chesworth, W. (eds) Encyclopedia of Soil Science. Encyclopedia of Earth Sciences Series. 2008. Springer, Dordrecht. [CrossRef]
- Luo L., Maa Y., Zhang S., Wei D., Zhu Y-G. An inventory of trace element inputs to agricultural soils in China. J. Environ. Mgmt. 2009. 90, 2524–2530.
- McNalley, P. Heavy Metals in Fertilizers. Data collection: MNDA. EH: Minnesota Dept. Health. 2020. https://www.health.state.mn.us/communities/environment/risk/studies/metals.html.
- Oerke, W.C. Crop losses to pests. J. Agric. Sci. 2006. 144, 31–43. [CrossRef]
- Tudi, M. , Ruan H. D., LiWang L.L., Sadler R., Connell D., Chu C., Phung D.T. Agriculture Development, Pesticide Application and Its Impact on the Environment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2021, 18, 1112. [Google Scholar]
- PPDB (Pesticides Properties Data Base). 2007. International Union of Pure and applied Chemistry, UPAC. http://sitem.herts.ac.uk/aeru/ppdb/en/atoz.htm.
- Lewis K.A., Tzilivakis J., Warner D, Green A. An international database for pesticide risk assessments and management. J. Human and Ecol. Risk Assess. 2016. 22, 1050–1064.
- Defarge, N. , de-Vendômois S., Séralinia GE. Toxicity of formulants and heavy metals in glyphosate-based herbicides and other pesticides. Toxicol. Reports. 2018. 5, 156–163.
- Alnuwaiser, M.A. An Analytical Survey of Trace Heavy Elements in Insecticides. Intern. J. Anal. Chem. 2019. 815 0793, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priyanka, P. , Kumar D.K., Yadav A., Yadav K. Nanobiotechnology and its application in agriculture and food production. Nanotech. Food, Agric. Envirn. 2020. 105-134.
- Wang H., Dong Y., Yang Y., Toor G.S., Zhang X. Changes in heavy metal contents in animal feeds and manures in an intensive animal production region of China. J. Environ. Sci. 2013, 25, 2435–2442.
- Liu, W.R. , Zenga D., She L., Su W.X., He D.C., Wua G.Y., Ma X.R., Jiang S., Jiang C.J., Ying G.G. Comparisons of pollution characteristics, emission situations, and mass loads for heavy metals in the manures of different livestock and poultry in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020.734, 139023.
- NAS (National Academy of Science). Arsenic: Medical and Biologic Effects of Environmental Pollutants. 5. Biologic Effects of Arsenic on Plants and Animals. 1977. 5, 1-332. Washington (DC): National Academies Press, US. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK231025/. 2310.
- Hu Y., Zhang W., Chen G., Cheng H., Tao S. Public health risk of trace metals in fresh chicken meat products on the food markets of a major production region in southern China. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 234, 667–676.
- Zhang F., Yanxia Li., Yang M., Wei L. Content of Heavy Metals in Animal Feeds and Manures from Farms of Different Scales in Northeast China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2012, 9, 2658–2668.
- Jensen J., Larsen M. M., Bak J. National monitoring study in Denmark finds increased and critical levels of copper and zinc in arable soils fertilized with pig slurry. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 214, 334–340.
- Lopes, C. , Herva M., Franco-Uría A., Roca E. Inventory of heavy metal content in organic waste applied as fertilizer in agriculture: evaluating the risk of transfer into the food chain. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2011; 18, 918e939. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao Y., Yan Z., Qin J. Effects of long-term cattle manure application on soil properties and soil heavy metals in corn seed production in NW China. Environ Sci. Pol. Res. 2014. 21, 7586–7595.
- Yang X.P., Li Q., Tang Z., Zhang W.W., Yu G.H., Shen Q.R., Zhao F.J. Heavy metal conc. and arsenic speciation in animal manure composts in China. Waste Mgmt. 2017. 64, 333–339.
- Zarcinas, B.A. , Ishak C.E., McLaughlin M.J., Cozens G. Heavy metals in soils and crops in southeast Asia. 1. Peninsular Malaysia. Environ. Geochem. Health. 2004. 26: 343–357.
- MDEQ bulletin. What are biosolids, how are they used, and are they safe? Water Resources Division, Michigan Department of Environmental Quality. 2014. 22014. https://www.michigan.gov/-/media/Project/Websites/egle/Documents/Programs/WRD/Biosolids/biosolids-what-how-safe.
- Kissel, K.E. , Rodriguez L., Paz J., Mitchell C., Patrick S., Zhang H., Fielder K., Morris L. Metal Conc. Standards for Land Application of Biosolids and Other By-Products in Georgia. Bulletin. 2017. 1353, 1-4 (Source: EPA: 40 CFR, Part 503).
- Silveira, M.L.A. , Alleoni L.R.F., Guilherme L.R.G. Biosolids and heavy metals in soils. Sci. Agric. 2003. 60, 64–111, 2003.
- McLaughlin, M.J. , Hamon R.E., McLaren R.G., Speir T.W., Rogers S.L. A bioavailability-based rationale for controlling metal and metalloid contamination of agric.land in Australia and New Zealand. Aust. J. Soil Res. 2000. 38, 1037–1086.
- EPA (Environmental Protection Agency). A Plain English Guide to the EPA Part 503 Biosolids Rule. 2023. EPA 40 CFR Part 503. https://www.epa.gov/biosolids/plain-english-guide-epa-part-503-biosolids-rule.
- Hossain, M.F. Arsenic contamination in Bangladesh. Agric. Ecosys. Environ. 2006. 113, 1–16.
- Hussain, M.M. , Hina A., Saeed A., Sabahat S., Jannat F., Aslam M. Impact of heavy metals on plants and animals in relation to sewage water: A Review. Sci. Tech. Dev. 2017. 36, 215-226.
- Berihun, B.T. , Amare D.E., Raju R.P., Ayele D.T., Dagne H. Determination of the Level of Metallic Contamination in Irrigation Vegetables, the Soil, and the Water in Gondar City, Ethiopia. Nutr. Dietary Suppl. 2021. 13, 1–7.
- Rai P.K., Tripathi B.D. Heavy metals in industrial wastewater, soil and vegetables in Lohta village, India. Toxic. Environ. Chem. 2007, 90, 247–257.
- Mohankumar, K. , Hariharan V., Rao N.P. Heavy Metal Contamination in Groundwater around Industrial Estate vs. Residential Areas in Coimbatore, India. J. Clinical Diag. Res. 2016. 10, BC05-BC07.
- Huq E.M., Su C., Lia J,, Sarven M.S. Arsenic enrichment and mobilization in the Holocene alluvial aquifers of Prayagpur of Southwestern Bangladesh. Intern. Biod. Biodeg. 2018, 128, 186–194.
- Ashfaque F., Inam A., Sahay S., Iqbal S. Influence of Heavy Metal Toxicity on Plant Growth, Metabolism and Its Alleviation by Phytoremediation - A Promising Technology. J. Agric. Ecol. Res. Inter. 2016. 6, 1-19 JAERI.23543.
- Rieuwerts, J.S. , Thornton I., Farago M.E., Ashmore M.R. Factors influencing metal bioavailability in soils: preliminary investigations for the development of a critical loads approach for metals. Chem. Spec. Bioavail. 1998. 10, 61-75.
- Jung, M.C. Heavy metal concentrations in soils and factors affecting metal uptake by plants in the vicinity of a Korean Cu-W Mine. Sensors. 2008. 8, 2413–2423. [CrossRef]
- Kacholi, D.S. , Sahu M. Levels and health risk assessment of heavy metals in soil, water, and vegetables of Dar es Salaam, Tanzania. J. Chem. 2018. 1402674.
- Njoku, K.L. , Nwani S. O. Phytoremediation of heavy metals contaminated soil from mechanic workshop and dumpsite using Amaranthus spinosus. Scien. African. 2022. 17, e01278.
- Ahn, Y. , Yun H. S., Pandi K., Park S., Ji M., Choi J. Heavy metal speciation with prediction model for heavy metal mobility and risk assessment in mine-affected soils. Environ. Sci. Poll. Res. Intern. 2020. 27, 3213– 3223.
- Maksymiec, W. , Baszynski T. Chlorophyll fluorescence in primary leaves of excess Cu-treated runner bean plants depends on their growth stages and the duration of Cu action. J Plant Physiol. 1996. 149, 196–200.
- Peralta-Videaa J.R., de la Rosaa G., Gonzalez J.H., Gardea-Torresdey J.L. Effects of the growth stage on the heavy metal tolerance of alfalfa plants. Adv. Environ. Res. 2004. 8, 679-685.
- Regassa, G. , Chandravanshi B. S. Levels of heavy metals in the raw and processed Ethiopian tobacco leaves. Springer Plus. 2016. 5, 232.
- Zayed, A. , Mel Lytle C., Qian J-H., Terry N. Chromium accumulation, translocation and chemical speciation in vegetable crops. Planta. 1998. 206: 293-299.
- Memon, A.R. Heavy Metal–Induced Gene Expression in Plants. In: Naeem, M., Ansari, A., Gill, S. (eds) Contaminants in Agriculture. 2020. Springer, Cham. [CrossRef]
- Shumaker, K.L. , Begonia G. Heavy Metal Uptake, Translocation, and Bioaccumulation Studies of Triticum aestivum Cultivated in Contaminated Dredged Materials. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2005, 2, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alaboudi, K.A. , Ahmed B., Brodie G. Phytoremediation of Pb and Cd contaminated soils by using sunflower (Helianthus annuus) plant. Annals Agric. Sci. 2018. 93, 123-127.
- Cu, N.X. Effect of Heavy Metals on Plant Growth and Ability to Use Fertilizing Substances to Reduce Heavy Metal Accumulation by Brassica Juncea. Global J. Sci. Front. Res. 2015. D Agric. Vet. 15, 1.0.
- Du, X. , Zhu Y-G., Liu Y-J., Zhao X-S. Uptake of mercury (Hg) by seedlings of rice (Oryza sativa L.) grown in solution culture and interactions with arsenate uptake. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2005. 54, 1–7.
- Satofuka, H.T. , Fukui M., Takagi H., Imanaka A.T. (2001). Metal-binding properties of phytochelatin-related peptides. J Inorg Biochem. 2001. 86, 595-602.
- Cobbett, C. , Goldsbrough P. (2002). Phytochelatins and metallothionines: Roles in Heavy Metal Detoxification and Homeostasis. Ann. Review Plant Biol. 2002. 53, 159.
- Yadav, S.K. Heavy metals toxicity in plants: An overview on the role of glutathione and phytochelatins in heavy metal stress tolerance of plants. SA J. Bot. 2010. 76, 167–179. [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.D. , Cheng Y., Kanwar M.K., Chu X-Y., Ahammed G.J., Qi Z-U. Responses of Plant Proteins to Heavy Metal Stress—A Review. 2017. Front. Plant Sci. 8, 1492.
- Grill, E. , Winnacker E.L., Zenk M.H.. Phytochelatins: The Principal Heavy Metal Complexing Peptides of Higher Plants. Science. 1985. 230, 674-676.
- Gril, E. , Winnacker E.L., Zenk M.H. Phytochelatins, a class of heavy-metal-binding peptides from plants, are functionally analogous to metallothioneins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 1987. 84, 439-443.
- Pal, R. , Rai J.P.N. Phytochelatins: Peptides Involved in Heavy Metal Detoxification. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2010. 160, 945–963.
- Jonak, J. , Nakagami H. , Hirt H. Heavy Metal Stress. Activation of Distinct Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Pathways by Copper and Cadmium. Plant Physiol. 2004, 136, 3276–3283. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xia, C. , Hong L., Yang Y., Yanping X., Xing H., Gang D. Protein Changes in Response to Lead Stress of Lead-Tolerant and Lead-Sensitive Industrial Hemp Using SWATH Technology. Genes. 2019. 10, 396.
- Thao, N.P. , Khan M. Q.R., Thu N.B.A., Hoang X.L.T., Asgher M., Khan N.A., Tran L.S.P. Role of Ethylene and Its Cross Talk with Other Signaling Molecules in Plant Responses to Heavy Metal Stress. Plant Physiol. 2015, 169, 73–84. [Google Scholar]
- Maksymiec, W. , Wianowska D. , Dawidowicz A.L., Radkiewicz S., Mardarowicz M., Krupa Z. The level of jasmonic acid in Arabidopsis thaliana and Phaseolus coccineus plants under heavy metal stress. J. Plant Physiol. 2005, 162, 1338–1346. [Google Scholar]
- Amari T., Ghnaya T., Abdelly C. Nickel, cadmium and lead phytotoxicity and potential of halophytic plants in heavy metal extraction. 2017, SA J. Bot. 111, 99–110.
- Yan, A. , Wang Y. , Tan S.N., Yusof L.K.M., Ghosh S., Chen1 Z. Phytoremediation: A Promising Approach for Revegetation of Heavy Metal-Polluted Land. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 359. [Google Scholar]
- Cho U-H. , Park J-O. Mercury-induced oxidative stress in tomato seedlings. Plant Sci. 2000, 156, 1–9.
- Jin, F. , Wang C. , Lin H.J., Shen Y.O., Zhang Z.M, Zhao M.J., Pan G.T. Heavy metal-transport proteins in plants: a review. NCBI. 2010, 21, 1875–82. [Google Scholar]
- Siddique, A.B. , Rahman M. M., Islam M.R., Naidu R. Varietal variation and formation of iron plaques on cadmium accumulation in rice seedling. Environ. Adv. 2021, 5, 100075. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, M.D. , Hasan M. M., Rahaman A., Haque P., Islam M.S., Rahman M.M. Translocation and bioaccumulation of trace metals from industrial effluent to locally grown vegetables and assessment of human health risk in Bangladesh. SN Applied Sci. 2020, 2, 1315. [Google Scholar]
- Bigdeli, M. , Seilsepour M. Investigation of Metals Accumulation in Some Vegetables Irrigated with Waste Water in Shahre Rey-Iran and Toxicological Implications. Am.-Eur. J. Agric. Environ. Sci., 2008, 4, 86–92. [Google Scholar]
- Kafle, A. , Timilsina A. , Gautam A., Adhikari K., Bhattarai A., Aryal N. Phytoremediation: Mechanisms, plant selection and enhancement by natural and synthetic agents. Environ. Adv. 2022, 8, 100203. [Google Scholar]
- Chen T-B. , Zheng Y-M., Lei M., Huang Z-C., Wu H-T., Chen H., Fan K-K., Yu K., Wu X., Tian Q-Z. Assessment of heavy metal pollution in surface soils of urban parks in Beijing, China. Chem. 2005, 60, 542–551.
- Islam, M.S. , Ahmed M. K., Raknuzzaman M., Mamun MHA., Islam M.K. Heavy metal pollution in surface water and sediment: A preliminary assessment of an urban river in a developing country. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 48, 282–291. [Google Scholar]
- Blake, L. , Goulding K. W.T. Effects of atmospheric deposition, soil pH and acidification on heavy metal contents in soils and vegetation of semi-natural ecosystems at Rothamsted Experimental Station, UK. Plant Soil. 2002, 240, 235–251. [Google Scholar]
- Soil Quality Indicators: pH - Soil Quality Information bulletin. USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service. 2011.
- Chuan, M.C. , Shu G. Y., Liu J.C. Solubility of heavy metals in a contaminated soil: Effects of redox potential and pH. Water Air Soil Pollut. 1996, 90, 543–556. [Google Scholar]
- Sanders, J.R. , McGrath S. P., Adams T.M. Zinc, copper and nickel concentrations in ryegrass grown on sludge-contaminated soils of different pH. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1986, 37, 961–968. [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin, M. Fertilizers and Soil Acidity. Fert. Tech. Res. bulletin. 2009. The Univ. of Adelaide, Australia.
- Giller, K.E. , Witter E. , Mcgarth S.P. Toxicity of heavy metals to microorganisms and microbial processes in agricultural soils: A review. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1998, 30, 1389–1414. [Google Scholar]
- Quenea, K. , Lamy, I. , Winterton, P., Bermond, A., Dumat, C. (2009). Interactions between metals and soil organic matter in various particle size fractions of soil contaminated with waste water. Geoderma. 2009, 1, 217–223. [Google Scholar]
- Gray, C.W. , Mclaren R. G. (2006). Soil factors affecting heavy metal solubility in some New Zealand soils. Water Air & Soil Pollution. 2006, 175, 3–14. [Google Scholar]
- McCauley, A. , Jones, C., and Olson-Rutz, K. Soil pH and organic matter. Nutrient management module No. 4449-8, 2017, 1-16.
- Reijonen, I. , Metzler. , Hartikainen H. Impact of soil pH and organic matter on the chemical bioavailability of vanadium species: The underlying basis for risk assessment. Environ. Pollution. 2016, 210, 371–379. [Google Scholar]
- Angelova, V. , Ivanova R., Pevicharova G., Ivanov K. Effect of organic amendments on heavy metals uptake by potato plants. 19th World Congress of Soil Science. 2010, Symposium 3.5.1. Heavy metal contaminated soil. 84-87.
- Cunningham, J.D. , Keeney, D. R., Ryan, J.A. (Phytotoxicity and Uptake of Metals Added to Soils as Inorganic Salts or in Sewage Sludge. J. Environ. Qual., 1975, 4, 455–460. [Google Scholar]
- Giordano, P.M. , Mays, D.A. Effect of land disposal applications of municipal wastes on crop yields and heavy metal uptake. Environ. Protect. Technol. Ser. 1977, EPA-600/2-77-014. USEPA, Washington, DC.
- McBride, M.B. Long-Term Biosolids Application on Land: Beneficial Recycling of Nutrients or Eutrophication of Agroecosystems? Soil Syst. 2022, 6, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadd, G.M. , Griffiths A. J. Microorganisms and Heavy Metal Toxicity. Microbial Ecol. 1978, 4, 303–317. [Google Scholar]
- Ayres, D.M., Davis, A.P., Gietka, P.M. Removing Heavy Metals from Wastewater. Engineering Research Center Report. Univ. of Maryland. 1994, 1-21.
- Prokkola, H. , Nurmesniemi, E-T. , Lassi, U. Removal of Metals by Sulphide Precipitation Using Na2S and HS Solution. Chem Eng., 2020, 4, 51, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Król, K. , Mizerna K. , Bożym M. An assessment of pH-dependent release and mobility of heavy metals from metallurgical slag. J. Hazard. Materials. 2020, 384, 121502. [Google Scholar]
- Gatiboni, L. , Hardy D. Soil Acidity and Liming for Agricultural Soils. SoilFacts. 2022 AG-439-50.
- Moreira, S.G. , Prochnow L. G., Pauletti V., Silva M.M., Kiehl J.C., Silva G.M.C. Effect of liming on micronutrient availability to soybean grown in soil under different lengths of time under no tillage. Acta Scient. Agro., 2017, 39, 89–97. [Google Scholar]
- Olego, M.A. , Quiroga M. J., Sánchez-García M., Cuesta M., Cara-Jiménez J., Garzón-Jimeno J.E. Effects of overliming on the nutritional status of grapevines with special reference to micronutrient content. OENO One. 2021, 1, 57–73. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang B., Wang, X.Q., Li X., Ni Y.Q., Li H.Y. Aluminum uptake and disease resistance in Nicotiana rustica leaves. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safety. 2010 73, 655–663.
- Sharma, P. , Dubey, R. S. Toxic heavy metals in plants. Braz. J. Plant Physiol. 2005, 17, 1677–9452. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, G. , Ma J. , Jiang M., Li J., Gao J., Qiao S., Zhao Z. (2019). The Mechanism of Plant Resistance to Heavy Metal. IOP Conference Series: Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 310, 052004 (GBEM2019). [Google Scholar]
- Fu, H. , Yu H. , Li T., Zhang X. Influence of cadmium stress on root exudates of high cadmium accumulating rice line (Oryza sativa L.). Ecotox. Environ. Safety. 2017, 150, 168. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J. , Shafi M., Wang Y., Wu L., Ye Z., Liu C., Zhong B., Guo H., He L., Liu D. Organic acid compounds in root exudation of Moso Bamboo (Phyllostachys pubescens ) and its bioactivity as affected by heavy metals. J. Environ Sci Pollut. Res Int, 2016. 23, 20977-20984.
- Caracciolo, A.B. , Terenzi V. Rhizosphere Microbial Communities and Heavy Metals. Microorganisms. 2021, 9, 1462. [Google Scholar]
- Gajewska, J. , Floryszak-Wieczorek J. , Sobieszczuk-Nowicka E., Mattoo A., Arasimowicz-Jelonek M. Fungal and oomycete pathogens and heavy metals: an inglorious couple in the environment. IMA Fungus. 2022, 13, 6. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hossain, Z. , Komatsu, S. Contribution of proteomic studies towards understanding plant heavy metal stress response. Front Plant Sci. 2013, 3, 310. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Argüello, J.M. , Raimunda, D., González-Guerrero, M. Metal Transport across Biomembranes: Emerging Models for a Distinct Chemistry. J. Biol. Chem. 2012. 287, 13510–13517.
- Aggarwal, A. , Sharma, L., Tripathi, B.N., Munjal, A.K., Baunthiyal, M., and Sharma, V. Metal Toxicity and Photosynthesis. In: Photosynthesis: Overviews on Recent Progress & Future Perspective. Chapter 16. 2014, pp. 229–236.
- Xu, H. , Martinoia, E. , and Szabo, I. Organellar Channels and Transporters. Cell Calcium. 2015, 58, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Asati, A. , Pichhode M. , Nikhil K. Effect of Heavy Metals on Plants. Inter. J. Appl. Inno. Eng. Mgmt. 2016, 5, 56–66. [Google Scholar]
- Caroli, M.D. , Furini, A. , DalCorso, G., Rojas, M., Sansebastiano, G.P.D. Endomembrane Reorganization Induced by Heavy Metals. Plants. 2020, 9, 482, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Bernia, R. , Luyckxc, M. , Xu, X., Legay, S., Sergeant, K., Hausman, J-F. Lutts, S., Caia, S., Guerriero, G. Reactive oxygen species and heavy metal stress in plants. Environ. Expt. Bot. 2019, 161, 98–106. [Google Scholar]
- Tamás, L. , Mistrík, I. , Zelinová, V., 2017. Heavy metal-induced reactive oxygen species and cell death in barley root tip. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2017, 140, 34–40. [Google Scholar]
- Smeets, K. , Cuypers A. , Lambrechts A., Semane B., Hoet P., Van Laere A., Vangronsveld J. Induction of oxidative stress and antioxidative mechanisms in Phaseolus vulgaris after Cd application. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2005, 43, 437–444. [Google Scholar]
- van Assche, F. , Clijsters H. Effects of metals on enzyme activity in plants. Plant Cell Environ. 1990, 13, 195–206. [Google Scholar]
- Rucińiska-Sobkowiak, R. Oxidative stress in plants exposed to heavy metals. Postepy Biochem. 2010, 56: 191-200.
- Gjorgieva, D., Panovska, T.K., Ruskovska, T., BaIeva, K., Stafilov T. Influence of Heavy Metal Stress on Antioxidant Status and DNA Damage in Urtica dioica. BioMed Res. Intern. 2013, 276417, 1-6.
- Panda, S. , Chaudhury, I. , Khan, M. Heavy Metals Induce Lipid Peroxidation and Affect Antioxidants in Wheat Leaves. Biol. Plant. 2003, 46, 289–294. [Google Scholar]
- Gichner, T. , Patková Z. , Száková J,, Demnerová K. Toxicity and DNA damage in tobacco and potato plants growing on soil polluted with heavy metals. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safety. 2006, 65, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tamás, M.J. , Sharma, S. K., Ibstedt, S., Jacobson, S., Christen, P. 2014. Heavy Metals and Metalloids as a Cause for Protein Misfolding and Aggregation. Biomole. 2014, 4, 252–267. [Google Scholar]
- Kalaivanan, D. , Ganeshamurthy, A.N. Mechanisms of Heavy Metal Toxicity in Plants. Chapter In: Rao et al. (eds.), Abiotic Stress Physiology of Horticultural Crops. 2016, Springer, India.
- Salas-Moreno, M. , Contreras-Puentes, N. , Rodríguez-Cavallo, E., Jorrín-Novo, J., Marrugo-Negrete, J., Méndez-Cuadro, D. Protein Carbonylation as a Biomarker of Cd and Pb, Damage in Paspalum fasciculatum. Plants. 2019, 8, 513. [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann S, Serrano M. , L’Haridon F., Tjamos S.E., Metraux J-F. Reactive oxygen species and plant resistance to fungal pathogens. Phytochem. 2015, 112, 54–62.
- Dumanovic, J. , Nepovimova E., Natic M., Kuc K., Jac’evic V. The Significance of Reactive Oxygen Species and Antioxidant Defense System in Plants: A Concise Overview. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 552969.
- Sai Kachout, S. , Ben Mansoura, A. , Leclerc, J.C., Mechergui, R., Rejeb. M.N., Ouerghi, Z. Effects of heavy metals on antioxidant activities of Atriplex hortenesis and A. rosea. J. Environ. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 9, 444–457. [Google Scholar]
- Azevedo A, Rodriguez E. (2012). Phytotoxicity of Mercury in Plants: A Review. J. Bot. Article ID 848614, 1-6.
- Rashid, A., Popovic, R. Protective role of CaCl2 against Pb2+ inhibition in photosystem II. FEBS Lett. 1990, 271, 181-184.
- Rashid, A. , Bernier, M. , Pazdernick, L., Carpentier, R. Interaction of zinc with the donor side of photosystem II. Photosynth. Res. 1991, 30, 123–130. [Google Scholar]
- van Assche, F. , Clijsters, H. Multiple Effects of Heavy Metal Toxicity on Photosynthesis. In: Marcelle, R., Clijsters, H., van Poucke, M. (eds) Effects of Stress on Photosynthesis. Adv. Agric. Biotech. 1983, 3. Springer, Dordrecht.
- Rashid, A. , Camm, E. , Ekramoddoullah, A.K.M. Molecular mechanism of action of Pb++ and Zn++ on water oxidizing complex of photosystem II. FEBS Lett. 1994, 350, 296–298. [Google Scholar]
- Rashid, A. Carpentier, R. CaCl2 inhibition of H2O2 electron donation to PS II in submembrane preparations depleted in extrinsic polypeptides. FEBS Lett. 1989, 258, 331–334. [Google Scholar]
- Rashid, A. , Carpentier, R. The 16 and 23 kDa extrinsic polypeptides and the associated Ca++ and Cl- modify atrazine interaction with photosystem II core complex. Photosynth. Res. 1990, 24, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rashid, A. Popovic, R. Electron donation to photosystem II by DPC is inhibited by both the endogenous Mn-complex and by exogenous Mn ions. Biochem. Cell Biol. 1995, 73, 241–24. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Klob, W. , Kandler O. , Tanner W. The Role of Cyclic Photophosphorylation in Vivo. Plant Physiol. 1973, 51, 825–827. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, S.M. , Grover M., Kundu S., Desa S. Soil Enzymes. In book: Encyclopedia of Soil Science. 2017, Third Edition Chapter: Soil Enzymes. Publisher: Taylor & Francis. All rights reserved.
- Belyaeva, O.N. , Haynes R.J., Birukova O.A. Barley yield and soil microbial and enzyme activities as affected by contamination of two soils with lead, zinc or copper. Biol. Fert. Soils. 2005, 41: 85–94.
- Jaworska, H. , Lemanowicz J. Heavy metal contents and enzymatic activity in soils exposed to the impact of road traffic. Sci. Reports. 2019, 9, 19981. [Google Scholar]
- Aponte, A.N. , Meli P. , Butler B., Paolin J., Matus F.J., Merino K., Cornejo K., Kuzyakov Y. Meta-analysis of heavy metal effects on soil enzyme activities. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 737, 139744. [Google Scholar]
- Dick, R.P. Soil enzyme activities as integrative indicators of soil health. In: Pankhurst CE, Doube BM, Gupta VVSR (eds) Biological indicators of soil health. CAB, Wallingford. 1997, pp 121–156.
- Yeboah, J. , Shi, G. , Shi, W. Effect of Heavy Metal Contamination on Soil Enzymes Activities. J. Geosci. Environ. Prot. 2021, 9, 135–154. [Google Scholar]
- Ajsuvakova, O.P. , Tinkova, A., Aschner M., Rochae J.B.T., Michalkef B., Skalnayaa M.G., Skalny A.V., Butnariug M., Dadari M., Saracg J., Aaseth J., Bjørklundk G. Sulfhydryl groups as targets of Hg toxicity. Coord Chem Rev. 2020, 15; 417.
- Siborova, M. (1988). Cd2+ ions affect the quaternary structure of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase from barley leaves. Biochem. Physiol. 1988, 183, 371–378. [Google Scholar]
- Bielen, A. , Remans T. , Vangronsveld J., Cuypers A. The influence of metal stress on the availability and redox state of ascorbate, and possible interference with its cellular functions. Intern. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 6382–6413. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, M.A. , Piyatida, P., da Silva, J.A.T., Fujita, M. Molecular mechanism of heavy metal toxicity and tolerance in plants: central role of glutathione in detoxification of reactive oxygen species and methylglyoxal and in heavy metal chelation. J. Bot. 2012, 872875.
- De Filippis, L.F. , Pallaghy C.K. Heavy metals: Sources and biological effects. In: LC Rai, JP Gaur, CJ Soeder (eds.), Algae and Water Pollution. E. Schweizerbart’sche, Verlagsbuchhandlung, Stuttgart. 1994, 31-77.
- Hampp, R. , Ziegler H. , Ziegler I. Influence of Lead Ions on the Activity of Enzymes of the Reductive Pentose Phosphate Pathway. Biochem. Physiol. Pflanzen. 1973, 164, 588–595. [Google Scholar]
- Ernst, W.H.O. Biochemical aspects of cadmium in plants. In: Nriagu J.O. (ed) Cadmium in the environment, part 1. 1980, 639-653. New York: Wiley & Sons.
- Jain, S. , Muneerb M. , Guerriero G., Liu S., Vishwakarma K., Chauhan D., Dubey N., Tripathi D.K., Sharma S. Tracing the role of plant proteins in the response to metal toxicity: a comprehensive review. Plant Signal. Behav. 2018, 13, e1507401. [Google Scholar]
- Tsonev, T. , Lidon, F. J.C. Zinc in plants - An overview. Emir. J. Food Agric. 2012, 24, 322–333. [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton, J.W. , Kaltreider R. C., Bajenova O.V., lhnat M.A., McCaffrey J., Turpie B.W., Rowell E.E., Oh J., Nemeth M.J., Pesce C.A., Lariviere R. Molecular Basis for Effects of Carcinogenic Heavy Metals on Inducible Gene Expression. Environ. Health Persp. 1998, 106, Suppl 4. [Google Scholar]
- Badr, A. , El-Shazly H.H., Mohamed H.I. Plant Responses to Induced Genotoxicity and Oxidative Stress by Chemicals. Chapter, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Morales, M.E. , Rebecca J. , Derbes S., Catherine M.A., Ortego JC., Stark J., Deininger P.L., Roy-Engel A.S.M. Heavy Metal Exposure Influences Double Strand Break DNA Repair Outcomes. PLoS One. 2016, 11, e0151367. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, S. , Ma C. , Shi W., Liu W., Lu W., Liu O., Luo Z.B. Exogenous glutathione enhances cadmium accumulation and alleviates its toxicity in Populus × canescens. J. Tree Physiol. 2017, 37, 1697–1712. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, X.J. , Liu W. , Li Y.N., Sun X., Hai C.X., Hudson L.G., Liu K.J. Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 inhibition by arsenite promotes the survival of cells with unrepaired DNA lesions induced by UV exposure. Toxicol Sci. 2012, 127, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dutta, S. , Mitra, M. , Agarwal, P., Mahapatra, K., Sett, D.D.U., and Roy, S. Oxidative and genotoxic damages in plants in response to heavy metal stress and maintenance of genome stability. Plant Signal. Behav. 2018, 13, e1460048. [Google Scholar]
- Pourrut, B. , Jean, S. , Silvestre, J., and Pinelli, E. Lead-induced DNA damage in Vicia faba root cells: potential involvement of oxidative stress. Mutat. Res. 2011, 726, 123–128. [Google Scholar]
- Memon, A.R. , Zahirovic E. Genomics and transcriptomics analysis of Cu accumulator plant Brassica nigra L. J. Appl. Biol. Sci. 2014, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Verbruggen, N. , Juraniec, M. , Baliardini, C., Meyer, C.-L. Tolerance to cadmium in plants: The special case of hyperaccumulators. BioMetals. 2013, 26, 633–638. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, A. , Wang X. , Wu L, Wang F., Wu Z., Yang H., Chen Y., Wen D., Liu X. Silicon improves growth and alleviates oxidative stress in rice seedlings (Oryza sativa L.) by strengthening antioxidant defense and enhancing protein metabolism under arsanilic acid exposure. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safety. 2018, 158, 266–273. [Google Scholar]
- Gwozdz, E.A. , Przymusinski R. , Rucinska R., Deckert J. Plant cell responses to heavy metals: Molecular and physiological aspects. Acta Physiol. Plant. 1997, 19, 459–65. [Google Scholar]
- Rashid, A. Defense responses of plant cell wall non-catalytic proteins against pathogens. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2016, 94, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamás, L. , Mistrík, I. , Huttová, J., Halusková, L., Valentovicová, K., Zelinová, V. Role of reactive oxygen species-generating enzymes and H2O2 during Cd, Hg and osmotic stresses in barley root tip. Planta. 2010, 231, 221–231. [Google Scholar]
- Kuriakose, S.V. , Prasad, M. N.V. Cadmium stress affects seed Germination and seedling growth in Sorghum bicolor (L.) by changing the activities of hydrolyzing enzymes. Plant Growth Regul. 2008, 54, 143–156. [Google Scholar]
- Asami, T. , Nakagawa Y. Preface to the Special Issue: Brief review of plant hormones and their utilization in agriculture. J. Pestic Sci. 2018, 43, 154–158. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, V. , Ravindran P. , Kumar P.P. Plant hormone-mediated regulation of stress responses. Review. BMC Plant Biol. 2016, 16, 86. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, A. , Sidhu G. P.S., Araniti F., Bali A.S., Shahzad B., Tripathi D.K., Brestic M., Skalicky M., Landi M. The Role of Salicylic Acid in Plants Exposed to Heavy Metals. Molecules. 2020, 25, 540. [Google Scholar]
- Bücker-Neto, L. Paiva, A.L.S., Machado, R.D., Arenhart, R.A., Margis-Pinheiro, M. (2017). Interactions between plant hormones and heavy metals responses. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2027. 40, 373-386.
- Al-Hakimi, A.M.A. Modification of cadmium toxicity in pea seedlings by kinetin. Plant Soil Environ. 2007, 53:129-135.
- El-Monem, A.M.S. , Farghal I. I., Sofy M.R. Role of gibberellic acid in abolishing the detrimental effects of Cd and Pb on broad bean and lupin plants. Res. J. Agric Biol Sci. 2009, 5, 6–13. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.F. , Wang Z. W., Dong F., Lei G.J., Shi Y.Z., Li G.X., Zheng S.J. Exogenous auxin alleviates cadmium toxicity in Arabidopsis thaliana by stimulating synthesis of hemicellulose 1 and increasing the cadmium fixation capacity of root cell walls. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 263, 98–403. [Google Scholar]
- Agami, R.A. , Mohamed G. F. Exogenous treatment with indole-3-acetic acid and salicylic acid alleviates cadmium toxicity in wheat seedlings. Ecotox. Environ. Safety. 2013, 94, 164–171. [Google Scholar]
- Ahammed, G.J. , Choudhury, S. P., Chen, S., Xia, X., Shi, K., Zhou, Y., and Yu, J. Role of brassinosteroids in alleviation of phenanthrene–cadmium co-contamination-induced photosynthetic inhibition and oxidative stress in tomato. J. Expt. Bot. 2013, 64, 199–213. [Google Scholar]
- Hayat, S. , Ali B. , Hasan S.A., Ahmad A. Brassinosteroid enhanced the level of antioxidants under cadmium stress in Brassica juncea. Environ Exp Bot. 2007, 60, 33–41. [Google Scholar]
- Hasan, S.A. , Hayat, S. , Ahmad, A. Brassinosteroids protect photosynthetic machinery against the cadmium induced oxidative stress in two tomato cultivars. Chem. 2011, 84, 1446–1451. [Google Scholar]
- Vishwakarma, K. , Upadhyay N. , Kumar N., Yadav G., Singh J., Mishra R.K., Kumar V., Verma R., Upadhyay R.G., Pandey M., Sharma S. Abscisic Acid Signaling and Abiotic Stress Tolerance in Plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 161. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, S. , Kumar V. Responses of wild type and abscisic acid mutants of Arabidopsis thaliana to cadmium. J. Plant Physiol. 2002, 159, 1323–1327. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, B. , Deng F. , Chen G., Chen X., Gao W., Long L., Xia L., Chen Z-H. Evolution of Abscisic Acid Signaling for Stress Responses to Toxic Metals and Metalloids. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 909. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.Q. , Sesin V. , Kisiala A., Emery R.J.N. Phytohormonal Roles in Plant Responses to Heavy Metal Stress: Implications for Using Macrophytes in Phytoremediation of Aquatic Ecosystems. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2021, 40, 7–22. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, H.B. , Sofy M.R., Almoneafy A.A., Abdelhamid M.T., Basit A., Sofy A.R., Lone R., El-Enain M.M.A. Role of Microorganisms in Managing Soil Fertility and Plant Nutrition in Sustainable Agriculture. Chapter 4; 2021. In: H. I. Mohamed et al. (eds.), PGP Microbes for Sustainable Biotic and Abiotic Stress Mgmt. Springer Nature; Switzerland AG.
- Shah, K.K. , Tripathi S. , Shrestha T.J., Modi B., Paudel N., Das B.D. Role of soil microbes in sustainable crop production and soil health: A review. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2021, 13, 109–118. [Google Scholar]
- Gikas, P. Kinetic responses of activated sludge to individual and joint nickel (Ni(II)) and cobalt (Co(II)) - an isobolographic approach. J. Hazard. Materials. 2007, 143, 246–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gikas, P. Single and combined effects of nickel (Ni(II)) and cobalt (Co(II)) ions on activated sludge and on other aerobic microorganisms: J. Hazard. Materials. 2008, 159, 187–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y. , Fan J. , Zhu W., Amombo E., Lou Y., Chen L., Fu J. Effect of Heavy Metals Pollution on Soil Microbial Diversity and Bermudagrass Genetic Variation. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 755. [Google Scholar]
- Abdu, N. , Abdullahi A. A., Abdulkadir A. Heavy metals and soil microbes. Environ Chem Lett. 2017, 15, 65–84. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y. , Narayanan M. , Shi X., Chen X., Li Z., Natarajan D., Ma Y. Plant growth-promoting bacteria in metal contaminated soil: Current perspectives on remediation mechanisms. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 966226. [Google Scholar]
- González Henao, S. , Ghneim-Herrera T. (2021) Heavy Metals in Soils and the Remediation Potential of Bacteria Associated With the Plant Microbiome. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 604216. [Google Scholar]
- Nwachukwu, O.I. , Pulford, I. D. Microbial respiration as an indication of metal toxicity in contaminated organic materials and soil. J. Hazard. Materials. 2011, 185, 1140–1147. [Google Scholar]
- Kizilkaya, R. , Akin, T. , Bayrakli, B., Salam, M. Microbiological characteristics of soils contaminated with heavy metals, Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2004, 40, 95–102. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, D. Effects of heavy metals on soil microbial community. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 113, 012009; IOP Publishing, IOP Conf Series. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, S.S. , Tuteja, N. Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant Machinery in abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2010, 48, 909–930. [Google Scholar]
- Chibuike, G. U. , and Obiora, S. C. Heavy metal polluted soils: effect on plants and bioremediation methods. Appl. Environ. Soil Sci. 2014, 752708.
- Koike, S.T. , Subbara K. V., Davis R.M., Turini T.A. (2003). Vegetable diseases caused by plant pathogens. ANR Pub. 2003, 8099, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Sanogo, S. Microbial clicks and combobulation: integrating microbes without passports and visas for managing soilborne diseases. Arch. Phytopath. Plant Prot. 2020, 53, 691–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, A. , Hwang S. F., Ahmed H.U., Turnbull1 G.D., Strelkov S.F. Gossen B.D. Effects of soil-borne Rhizoctonia solani on canola seedlings after application of glyphosate herbicide. Canadian J. Plant Sci. 2013, 93, 97–107. [Google Scholar]
- Rashid, A. , Sharma P., Evans, I. Plant bioassay techniques for detecting and identifying herbicide residues in soil. Agri-Facts: Practical information for Alberta’s Agriculture Industry. Agdex # 609-1, 2001. Edmonton, Alberta, Canada.
- Yamada, M. , Malambane G. , Yamada S., Suharsono S., Tsujimoto H., Moseki B., Akashi K. Differential physiological responses and tolerance to potentially toxic elements in biodiesel tree Jatropha curcas. Sci. Reports. 2018, 8, 1635. [Google Scholar]
- Gill, S.S. , Hasanuzzaman, M. , Nahar, K., Macovei A., Tuteja N. Importance of nitric oxide in cadmium stress tolerance in crop plants. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 63, 254–261. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- López-Millán, A.F. , Sagardoy R. , Solanas M., Abadía A., Abadía J. Cadmium toxicity in tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum) plants grown in hydroponics. Environ. Expt. Bot. 2009, 65, 376–385. [Google Scholar]
- DalCorso, G. , Farinati S. , Furini A. Regulatory networks of Cd stress in plants. Plant Signal. Behav. 2010, 5, 663–667. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, S. , Li M. , Zuo J., Jiang W., Liu, D. Cadmium effects on mineral accumulation, antioxidant defense system and gas exchange in cucumber. Z. Agric. 2016, 102, 193–200. [Google Scholar]
- Rizwan, M. , Ali, S. , Adrees, M., Rizvi, H., Zia-ur-Rehman, M., Hannan, F., Qayyum, M.F., Hafeez, F., Ok, Y.S. Cadmium stress in rice: toxic effects, tolerance mechanisms, and mgmt: a review. Env. Sci. Poll. Res. 2016, 23, 17859–17879. [Google Scholar]
- Ullah, I. , Mateen A. , Ahmad A., Munir I., Iqbal A., Alghamdi K.M.S., Al-Solami H.M., Siddiqui M.F. Heavy metal ATPase genes expression induced by endophytic bacteria, AI001, and AI002” mediate cadmium translocation and phytoremediation. Environ. Poll. 2022, 293, 118508. [Google Scholar]
- Haider, F.U. , Liqun, C. , Coulter, J.A., Alam S., Cheema A.S., Wu J., Zhang R., Wenjun M., Farooq M. Cadmium toxicity in plants: Impacts and remediation strategies. Ecotox. Environ. Safety. 2021, 211, 111887. [Google Scholar]
- Nagajyoti, P.C. , Lee, K. D., Sreekanth T.M.V. Heavy metals, occurrence, and toxicity for plants: a review. Environ Chem. Lett. 2010, 8, 199–216. [Google Scholar]
- Glinska, S. , Michlewska, S. , Gapinska, M., Seliger, P., Bartosiewicz, R. The effect of EDTA and EDDS on lead uptake and localization in hydroponically grown Pisum sativum L. Acta Physiol Plant. 2014, 36, 399–408. [Google Scholar]
- Aslam, M. , Aslam A. , Sheraz M., Ali B., Ulhassan Z., Najeeb U., Zhou Z., Gill R.A. Lead Toxicity in Cereals: Mechanistic Insight Into Toxicity, Mode of Action, and Management. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 11, 587785. [Google Scholar]
- Gautam, M. , Sengar R. S., Chaudhary R., Sengar K., Garg S. Possible cause of inhibition of seed germination in rice by heavy metals Pb and Hg. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2010, 92, 1111–1119. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, M.A. , Uddin, M. N., Sarwar, A.K.M.G. Toxicity of arsenic on germination and seedling growth of rice. J. Bang. Soc. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2007, 4, 153–156. [Google Scholar]
- Abbas, G. , Murtaza B. , Bibi I., Shahid M., Niazi N.K., Khan, M.A., Amjad A., Hussain M., Natasha. Arsenic Uptake, Toxicity, Detoxification, and Speciation in Plants: Physiological, Biochemical, and Molecular Aspects. Int. J. Environ. Pub. Health Res. 2018, 15, 59, 1–45. [Google Scholar]
- Imran, M.A. , Sajid, Z. A., Chaudhry, M.N.. Arsenic (As) Toxicity to Germination and Vegetative Growth of Sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.). Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2015, 24, 1993–2002. [Google Scholar]
- Das, I. , Ghosh K. , Das D., Das S.K. Assessment of arsenic toxicity in rice plants in areas of West Bengal. Chem. Spec. Bioavail. 2013, 25, 201–108. [Google Scholar]
- Huq, S.M.I. , Parvin K. , Rahman R., Joardar J.C. Response of cowpea (Vigna sinensis to Arsenic. Canadian J. Pure. Appl. Sci. 2009, 3, 897–902. [Google Scholar]
- Patra, M. , Sharma, M. Mercury Toxicity in Plants. Bot. Review. 2000, 66, 379–422. [Google Scholar]
- Cargnelutti, D. , Tabaldi L. A., Spanevello R.M., Jucoski G.O., Battisti V., Redin M., Linares C.E.B., Dressler V.L., Flores M.M., Nicoloso F.T., Morsch V.M., Schetinger, M.R.C. Mercury toxicity induces oxidative stress in growing cucumber seedlings. Chem. 2006, 65, 999–1006. [Google Scholar]
- Marrugo, J. , Hernández J. , Pinedo-Hernández J., Montes E, Sergi D. Mercury uptake and effects on growth in Jatropha curcas. J. Environ. Sci. 2016, 48, 120–125. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, H.P. , Mahajan P. , Kaur S., Batish D.R., Kohli R.K. Chromium toxicity and tolerance in plants. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2013, 11, 229–254. [Google Scholar]
- Amin, H. , Arain B. A., Amin F., Surhio M.A. Phytotoxicity of Chromium on Germination, Growth and Biochemical Attributes of Hibiscus esculentus L. Am. J. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, 2431–2439. [Google Scholar]
- Samantaray, S. , Rout G. R., Das P. Role of Cr on plant growth and metabolism. Acta Physiol. Plant. 1998, 20, 201–212. [Google Scholar]
- Stambulska, U. , Bayliak M.M., Lushchak V.I. Chromium(VI) Toxicity in Legume Plants: Modulation Effects of Rhizobial Symbiosis. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 803121.
- Shankar, S. , Shanker, U., Shikha. Arsenic contamination of groundwater: A Review of sources, prevalence, health risks, and strategies for mitigation. Sci. World J. 2014, 304524.
- Oliveira, H. Chromium as an Environmental Pollutant: Insights on Induced Plant Toxicity. J. Bot. 2012, 375843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolaou, K.E. , Chatzistathis T. , Theocharis S., Argiriou A., Koundouras S., Zioziou E. Effects of Chromium Toxicity on Physiological Performance and Nutrient Uptake in Two Grapevine Cultivars (Vitis vinifera L.) Growing on Own Roots or Grafted onto Different Rootstocks. Hort. 2022, 8, 493. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, J. , Yan L. , Li G., Sadiq M., Rahim N., Wu J., Ma W., Xu G., Du M. Effects of conservation tillage strategies on soil physicochemical indicators and N2O emission under spring wheat monocropping systems. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 7066. [Google Scholar]
- He, Z. , Shentu J. , Yang X., Baligar V.C., Zhang T., Stoffella P.J. Heavy Metal Contamination of Soils: Sources, Indicators, and Assessment. J. Environ. Indicators. 2015, 9, 17–18. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, L. , Xu Z. , Ren M., Guo Q., Hua X., Hua G., Wand H., Peng P. Source identification of eight hazardous heavy metals in agricultural soils of Huizhou, Guangdong Province, China. Ecotox. Environ. Safety. 2012, 78, 2–8. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R. , Wu H. , Ding J., Fu, W., Gan L., Li Y. Mercury pollution in vegetables, grains and soils from areas surrounding coal-fired power plants. Sci. Reports. 2017, 7, 46545. [Google Scholar]
- Codex Alimentarius Commission. FAO- WHO. CF/14 INF/1; 2021.
| Fertilizers | Cadmium content (mg Kg−1) | |
|---|---|---|
| Based on product | Based on P content | |
| Complete fertilizer | 23–29 | 418–527 |
| Single superphosphate | 16–26 | 186–302 |
| Superphosphate | 13–34 | 151–395 |
| Rock phosphate | 7.2–47 | 54–303 |
| High analysis fertilizer | <0.6–5.6 | 15–118 |
| Double superphosphate | <0.6–12 | <3.6–72 |
| Triple superphosphate | 0.8–7.0 | 24–35 |
| Mono-ammonium phosphate | 1.8–8.1 | 12–37 |
| Di-ammonium phosphate | 4.3–6.6 | 22–28 |
| Elements | MAX | MIN | Fold difference |
|---|---|---|---|
| mg Kg−1 soil | |||
| Cadmium | 0.65 | 0.06 | 10.8 |
| Copper | 171.5 | 21.0 | 8.2 |
| Nickel | 36.9 | 28.7 | 1.3 |
| Lead | 38.0 | 20.5 | 1.9 |
| Zinc | 433 | 71.9 | 6 |
| Chemical name | Formula | HM elements |
|---|---|---|
| Insecticides | ||
| Aluminium phosphide | AIP | Al |
| Aluminium silicate | Al₂Si₂O₇ | Al |
| Arsenic acid | H₃AsO₄ | As |
| Copper acetoarsenite | C₄H₆As₆Cu₄O₁₆ | As, Cu |
| Copper oxide | Cu₂O | Cu |
| Copper carbonate | CH₂Cu₂O | Cu |
| Copper naphthenate | C₂₂H₁₄CuO₄ | Cu |
| Lead arsenate | AsHO₄Pb | As, Pb |
| Lithium perfluorooctane sulfonate | C₈F₁₇LiO₃S | Li |
| Sodium meta-arsenite | NaAsO2 | As |
| Fungicide | ||
| Copper oxide | CuO | Cu |
| Copper bis(3-phenylsalicylate) | C₂₆H₁₈CuO₆ | Cu |
| Copper abietate | C₄0H₅₈CuO₄ | Cu |
| Copper acetate | Cu₂(CH₃COO)₄ | Cu |
| Copper carbonate | CH₂Cu₂O | Cu |
| Copper chloride | CuCl₂ | Cu |
| Copper hydroxide | H₂O₂Cu | Cu |
| Copper naphthenate | C₂₂H₁₄CuO₄ | Cu |
| Copper oxychloride | (ClCu₂H₃O₃)₂ | Cu |
| Copper sulphate | CuSO4-Ca(OH)2 | Cu |
| Mercuric oxide | HgO | Hg |
| Mercurous chloride | Hg₂Cl₂ | Hg |
| Methoxyethylmercury chloride | C₃H₇ClHgO | Hg |
| Methoxyethylmercury acetate | C₅H₁0HgO₃ | Hg |
| Phenyl mercuric acetate | C₈H₈O₂Hg | Hg |
| Phenylmercury chloride | C₆H₅ClHg | Hg |
| Phenylmercury nitrate | C₆H₅HgNO₃ | Hg |
| Sodium arsenite | NaAsO₂ | As |
| Zinc borate | ZnB3O4(OH)3 | Zn, B |
| Zinc oxide | ZnO | Zn |
| Zineb | C₄H₆N₂S₄Zn | Zn |
| Herbicides | ||
| Arsenic acid | H₃AsO₄ | As |
| Calcium arsenate | As₂Ca₃O₈ | As |
| Sodium arsenite | NaAsO₂ | As |
| Cacodylic acid | (CH3)2AsO(OH) | As |
| Rodenticides | ||
| Barium carbonate | BaCO3 | Ba |
| Zinc phosphide | Zn3P2 | Zn |
| Thallium sulfate | Tl2SO4 | Tl |
| Defoliants | ||
| Sodium dichromate | Na2Cr2O7 | Cr |
| Zinc chloride | ZnCl2 | Zn |
| Mercuric chloride | HgCl2 | Hg |
| Trade name | Technical name | Metal impurities (ppb)* |
|---|---|---|
| Insecticides | Defarge et al., [38] | |
| Pyrinex® | Chorpyriphos | As (390), Cr (800), Ni (1200) |
| Polysect® | Acetamipride | Ni (50) |
| Fungicides | Defarge et al., [38] | |
| Eyetak® | Prochloraze | As (200), Co (90), Cr (200), Ni (190), Pb (12) |
| Folpan® | Folpet | As (260), Cr (2000), Ni (1200) |
| Maronee® | Tebuconazole | As (90), Co (50), Cr (100) |
| Opus® | Epoxiconazole | Cr (90), Ni (60) |
| Pictor® | Boscalid | As (300), Co (275), Cr (1000), Ni (600) |
| Teldor® | Fenhexamid | As (575), Cr (800), Ni (800) |
| Herbicides | Defarge et al., [38] | |
| R 3+® | Glyphosate based formulations | As (375), Co (50), Cr (175), Ni (20) |
| R Bioforce® | As (260), Cr (200), Ni (120) | |
| R Express® | As (60) | |
| R GT+® | As (450), Co (150), Cr (100), Ni (50), Pb (10) | |
| R WeatherMax® | As (500), Cr (100), Ni (20), Pb (10) | |
| Bayer GC® | As (75), Co (60), Cr, (110) Ni (20) | |
| Clinic EV® | As (400), Co (90), Cr (150), Ni (20) | |
| Glyfos® | As (200), Cr (1100), Ni (50), Pb (30) | |
| Glyphogan® | As (320), Co (125, Cr (100), Ni (40) | |
| Pavaprop-G® | Cr (110), N (190) | |
| Radical Tech+® | As (270), Co (70), Cr (50), Ni (50) | |
| Lonpar® | 2,4-D | As (160), Cr (150), Ni (180) |
| Matin® | Isoproturon | As (100), Cr (100), Ni (30), Pb (25) |
| Starane® | Fluoroxypyr | As (75), Cr (250), Ni (100), Pb (100) |
| Insecticides | Alnuwaiser [39] | |
| Sniper® | Fipronil | Zn (506), Cu (423), Cr (746), Co (275), Pb (88) |
| CyperCel® | Cypermethrin | Zn (2389), Cu (669), Cr (373), Co (18), Pb (807) |
| CyperSafe® | Cypermethrin | Zn (968), Cu (464), Cr (10), Co (6), Pb (119) |
| Scope 60® | Asaybrmthrin | Zn (527), Cu (539), Cr (437), Co (23), Pb (39) |
| Brodor® | Permethrin | Zn (10), Cr (16), Pb (186) |
| Clash® | Acephate + Buprofezin | Zn (1078), Cr (73), Co (39), Pb (1316) |
| Acefed® | Mithomail | Cu (19), Cr (48), Co (4), Pb (121) |
| Lanid® | - | Cu (128), Cr (60), Pb (98) |
| Probalt® | - | Cu (179), Cr (85), Co (25), Pb (46) |
| Nourcam® | - | - |
| Madar® | - | Zn (10), Cu (66), Cr (16), Co (10), |
| PifPaf® | - | Cu (110), Co (5), Thallium, Tl (19), Pb (12) |
| Paygon® | - | Zn (52), Tl (15), Pb (19) |
| Source | Level | Zn | Cu | Pb | Cd | Cr | Hg | As | Ni |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pig | MAX | 4639 | 1288 | 23 | 60 | 85 | 0.3 | 89 | 19 |
| MIN | 100 | 73 | 0.3 | 0.04 | 3.5 | 0.0 | 0.01 | 4.7 | |
| FD | 46 | 18 | 77 | 1500 | 24 | - | 8900 | 4.0 | |
| Chicken | MAX | 578 | 314 | 33 | 4.1 | 251 | 0.5 | 23 | 39 |
| MIN | 166 | 18 | 3.0 | 0.03 | 4.0 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 5.2 | |
| FD | 3.5 | 17 | 11 | 137 | 63 | 25 | 460 | 7.5 | |
| Duck | MAX | 682 | 199 | 41 | 2.5 | 64 | 0.07 | 6.8 | 16 |
| MIN | 98 | 35 | 4.5 | 0.3 | 7.0 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 8.4 | |
| FD | 7.0 | 5.7 | 9.1 | 8.3 | 9.1 | 2.3 | 680 | 1.9 | |
| Poultry | MAX | 682 | 314 | 41 | 4.1 | 251 | 0.5 | 23 | 39 |
| MIN | 77 | 15 | 2.0 | 0.03 | 2.5 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 5.2 | |
| FD | 8.9 | 21 | 21 | 137 | 100 | 25 | 2300 | 7.5 | |
| Cattle | MAX | 816 | 174 | 32 | 3.4 | 79 | 0.6 | 6.3 | 19 |
| MIN | 49 | 12 | 1.6 | 0.04 | 0.8 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 4.2 | |
| FD | 17 | 15 | 20 | 85 | 99 | 30 | 630 | 4.5 | |
| Sheep | MAX | 431 | 215 | 20 | 1.4 | 22 | 2.4 | 2.6 | 12 |
| MIN | 42 | 8.4 | 1.7 | 0.3 | 8.0 | 0.2 | 0.6 | 1.2 | |
| FD | 10 | 26 | 12 | 4.7 | 2.8 | 12 | 4.3 | 10 |
| Elements | Maximum permissible level (mg Kg−1) | Cumulative loading rate (Kg ha−1) | Monthly average concentrations (mg Kg−1) | Annual loading rate (Kg ha−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| As | 75 | 41 | 41 | 2.0 |
| Cd | 85 | 39 | 39 | 1.9 |
| Cr | 3000 | 3000 | 1200 | 150 |
| Cu | 4300 | 1500 | 1500 | 75 |
| Pb | 840 | 300 | 300 | 15 |
| Hg | 57 | 17 | 17 | 0.9 |
| Ni | 420 | 420 | 420 | 21 |
| Se | 100 | 100 | 36 | 5.0 |
| Zn | 7500 | 2800 | 2800 | 140 |
| Elements | Cr | Cu | Zn | As | Cd | Pb | Ni | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mg L−1 | ||||||||
| Max level (FD)* |
2.13 (21.3) |
4.62 (23.1) |
15.20 (7.6) |
0.52 (5.2) |
0.02 (2.0) |
1.15 (0.2) |
- | Ahmed et al., [16] |
| Max level (FD) |
0.94 (9.4) |
0.61 (3.1) |
0.86 (0.4) |
- |
0.04 (4.0) |
0.19 (0.04) |
0.12 (0.6) |
Berihun et al., [58] |
| FAO limit | 0.10 | 0.20 | 2.00 | 0.10 | 0.01 | 5.00 | 0.20 | |
| Crop Species |
HMs elements |
Conc. (mg Kg−1 soil) |
Height (cm) | Dry wt. (g) | Yield | Refs | ||
| Shoot | Root | Shoot | Root | g/plot | Alaboudi et al., [74]* | |||
| Helianthus annuus |
Pb | 0 | 53 | 34 | 4.3 | 2.5 | - | |
| 80 | 28 | 10 | 2.6 | 1.7 | - | |||
| 200 | 15 | 2 | 1.5 | 0.8 | - | |||
| Cd | 0 | 53 | 34 | 3.9 | 2.4 | - | ||
| 80 | 16 | 6 | 1.1 | 0.6 | - | |||
| 200 | 9 | 1.7 | 0.8 | 0.2 | - | |||
| Brassica Juncea |
Cu | 0 | 20 | - | - | - | 70 | Cu [75]** |
| 100 | 15 | - | - | - | 50 | |||
| 200 | 13 | - | - | - | 33 | |||
| Pb | 0 | 20 | - | - | - | 70 | ||
| 100 | 13 | - | - | - | 35 | |||
| 200 | 11 | - | - | - | 31 | |||
| Zn | 0 | 20 | - | - | 70 | |||
| 300 | 17 | - | - | 64 | ||||
| 500 | 16 | - | - | 44 | ||||
| Oryza Sativa |
Hg | mg L−1 nutrient solution | Pot−1 | Pot−1 | Du et al., [76]*** | |||
| 0 | - | - | 0.52 | 0.19 | - | |||
| 0.5 | - | - | 0.28 | 0.17 | - | |||
| 1.0 | - | - | 0.22 | 0.12 | - | |||
| 2.5 | - | - | 0.17 | 0.08 | - | |||
| Physiological parameters* | Kinetin (µM) | Cadmium (µM) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 25 | 50 | ||
| Chla/Chlb content (%) | 0 20 |
100 114/112 |
73/72 158/149 |
48/44 139/129 |
| Photosynthesis rate (%) | 0 20 |
100 124 |
88 146 |
42 80 |
| Soluble sugars content (%) | 0 20 |
100 180 |
67 226 |
49 249 |
| Soluble proteins content (%) | 0 20 |
100 72 |
119 61 |
133 50 |
| Amino acid content (%) | 0 20 |
100 132 |
73 179 |
65 200 |
| Toxicity symptoms observed in some studies involving multiple plant/crop species | References for review |
|---|---|
| Cadmium (Cd2+): solubility in water—high; mobility in soil colloids—high; bioavailability in soil—high; translocability in plants—high, toxicity in plants—highly lethal | |
| Chlorosis, wilting, leaf epinasty, stunting of plant growth. | Gill et al., [217] |
| Growth inhibition, leaf chlorosis and necrosis, and root browning. | López-Millán et al., [218] |
| Leaf rolling and chlorosis | DalCorso et al., [219] |
| Leaf chlorosis with green coloration around veins; leaf rolling, and growth stunting. | Sun et al., [220] |
| Reduction in seed germination, plant growth, biomass accumulation, and crop quality. | Rizwan et al., [221] |
| Chlorosis on newly expanded leaves, root growth inhibition. | Yamada et al., [216] |
| Growth stunting, chlorosis, root tip browning, and plant death. | Kumar et al., [20] |
| Stunting of growth, leaf chlorosis, reduction in fresh and dry biomass, plant death. | Ullah et al., [222] |
| Reduction in seed germination, shoot and root growth. | Chibuike and Obiora, [211] |
| Chlorosis, growth stunting, and necrosis. | Haider et al., [223] |
| Stunting of plant growth and blackening of roots. | Sharma and Dubey, [120] |
| Lead (Pb2+): solubility in water—low; mobility in soil colloids—poor; bioavailability in soil—limited; translocability in plants—restricted; toxicity in plants—moderately lethal | |
| Inhibition of seed germination, early seedling growth, root and stem elongation, and leaf expansion. | Nagajyoti et al., [224] |
| Inhibition of seedling growth and secondary root growth. | Glinska et al., [225] |
| Inhibition of seed germination, seedling growth, root and stem elongation, and leaf expansion. | Asati et al., [130] |
| Inhibition of seed germination, seedling development, root elongation. | Tiwari and Lata, [8] |
| Stunting of shoot and root growth. | Kumar et al., [20] |
| Plant growth inhibition. | Xia et al., [85] |
| Inhibition of seed germination, root and shoot biomass, root elongation, and cell death. | Aslam et al., [226] |
| Inhibition of germination and seedling growth. | Gautam et al., [227] |
| Inhibition of seed germination, seedling height, number of roots per plant, and dry matter production. | Hossain et al., [228] |
| Arsenic (As3+ As5+): solubility in water—high; mobility in soil colloids—high; bioavailability in soil—high; translocability in plants—high, toxicity in plants—lethal | |
| Reduction in leaf and root growth, wilting and violet coloration of leaves. | Abbas et al., [229] |
| Reduction in shoot and root length, and number of leaves per plant. | Imran et al., [230] |
| Reddening of tips, blades, margins, and midribs followed by yellowing of entire leaves. | Das et al., [231] |
| Shortening of plant height, premature shedding of leaves, and reduction in the number and size of nodules. | Huq et al., [232] |
| Reduction in leaf area, leaf fresh weight, fruit yield, seed germination, seedling height, and dry matter production; stunting of growth; chlorosis and wilting. | Asati et al., [130] |
| Reduction in seed germination, seedling height, leaf area, dry matter production, crop yield; chlorosis and wilting. | Chibuike and Obiora, [211] |
| Mercury (Hg2+): solubility in water—low; mobility in soil colloids—low; bioavailability in soil—moderate; translocability in plants—limited, toxicity in plants—moderately lethal | |
| Abnormal germination, hypertrophy of root and coleoptile, inhibition of seedling growth. | Patra and Sharma, [233] |
| Reduction in germination, plant height, tiller and panicle production, biomass accumulation, and yield; chlorosis. | Chibuike and Obiora, [211] |
| Decrease in both root and shoot biomass. | Du et al., [76] |
| Inhibition of seed germination, shoot and root length, and fresh and dry matter production. | Gautam et al., [227] |
| Reduction in seed germination, embryo growth, primary root elongation. | Azevedo and Rodriguez, [146] |
| Inhibition of root and shoot biomass. | Cargnelutti et al., [234] |
| Inhibition of plant growth, biomass production, and leaf area. | Marrugo-Negrere et al., [235] |
| Inhibition of germination, seedling growth and development, biomass accumulation; leaf chlorosis and necrosis. | Singh et al., [236] |
| Chromium (Cr3+ Cr6+): solubility in water—moderate; mobility in soil colloids—moderate; bioavailability in soil—moderate; translocability in plants—restricted; toxicity in plants—moderately lethal | |
| Inhibition of root and plant growth; leaf chlorosis. | Sharma et al., [186] |
| Inhibition of seed germination, root and shoot growth; reduction of plant biomass. | Asati et al., [130] |
| Inhibition of seed germination, seedling and plant growth. | Amin et al., [237] |
| Growth retardation, root discoloration. | Yamada et al., [216] |
| Chlorosis, necrosis; reduction in dry wight, nodulation, crop yield; inhibition of plant growth, root length | Samantaray et al., [238] |
| Inhibition of seed germination and seedling development and reduction of plant biomass and crop yield. | Stambulska et al., [239] |
| Inhibition of germination, root and shoot growth, dry matter production, and yield. | Shanker et al., [240] |
| Decrease in seed germination, reduction in growth, and yield. | Oliveira, [241] |
| Leaf interveinal chlorosis and root browning. | Nikolaou et al., [242] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





