Submitted:
06 May 2023
Posted:
10 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
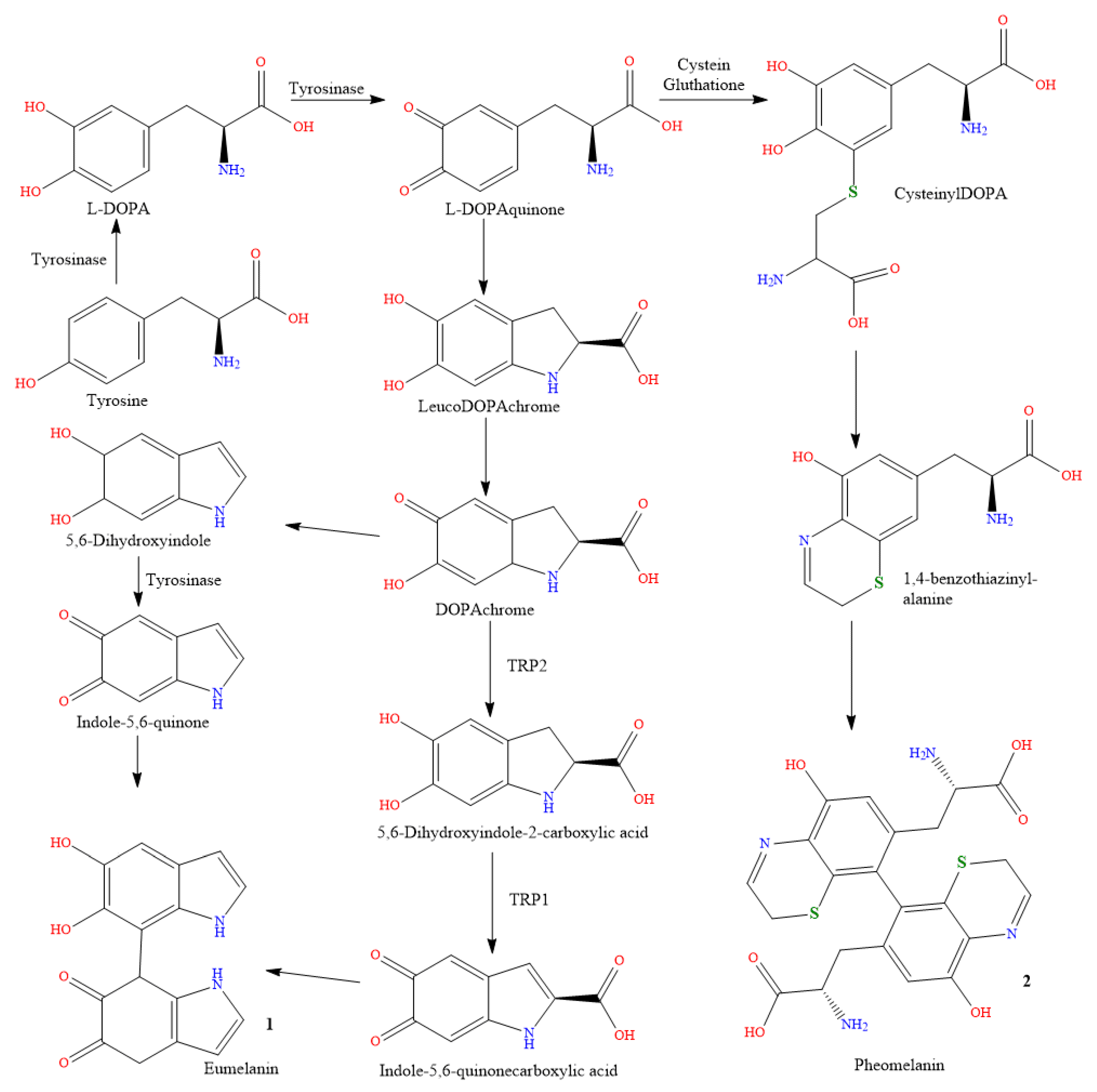
2. Causes of Skin Pigmentation
2.1. Genetics
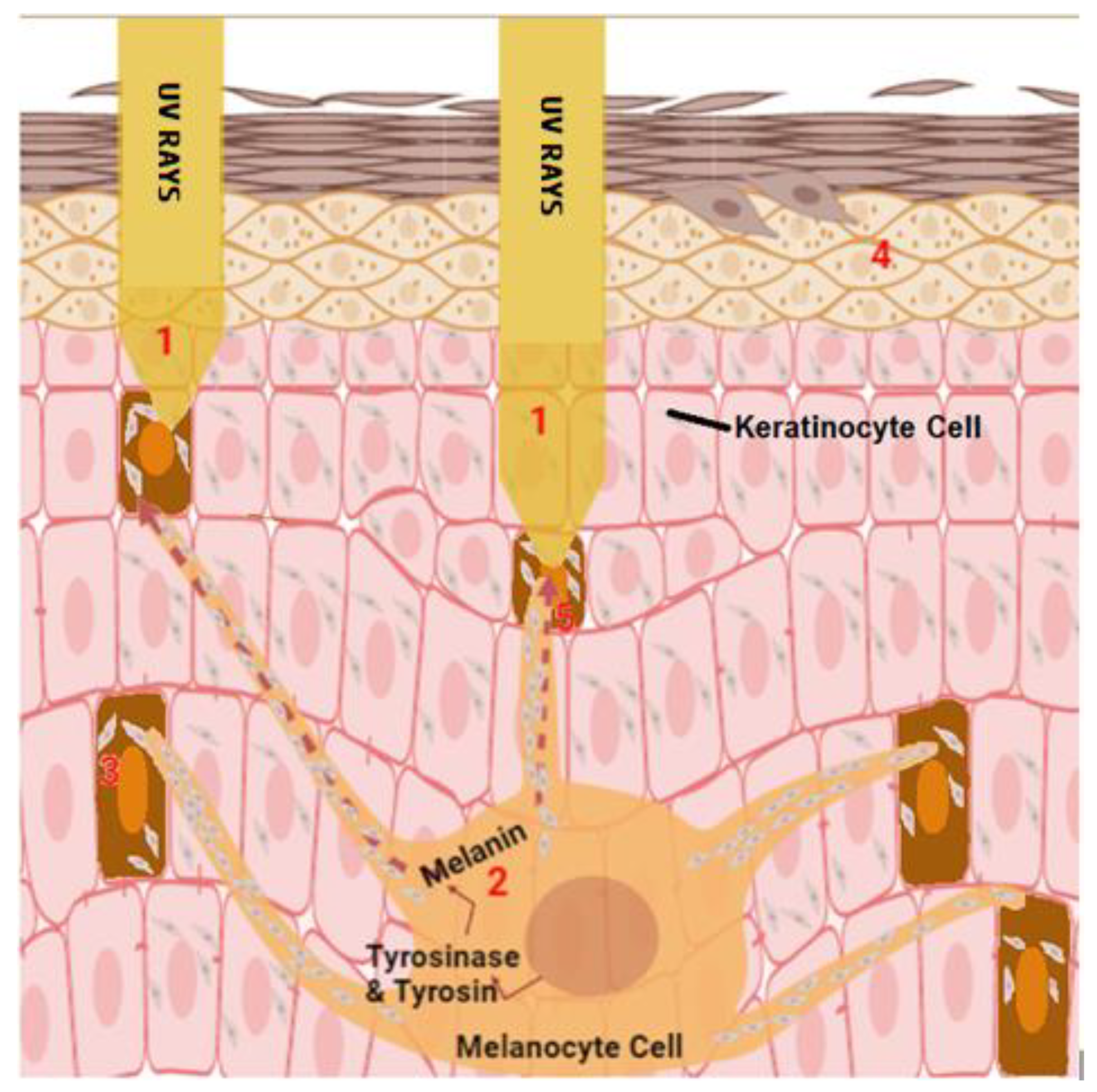
2.2. Sun Exposure
2.3. Medications
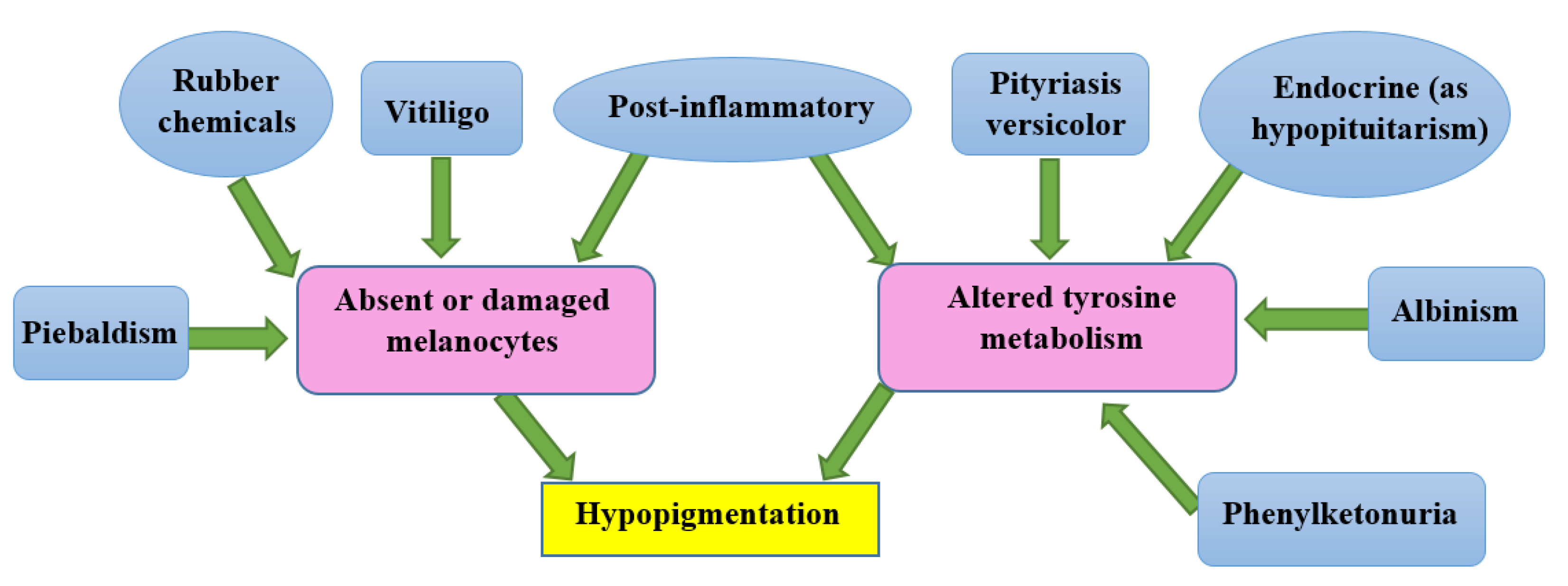
3. Types of pigmentation disorders
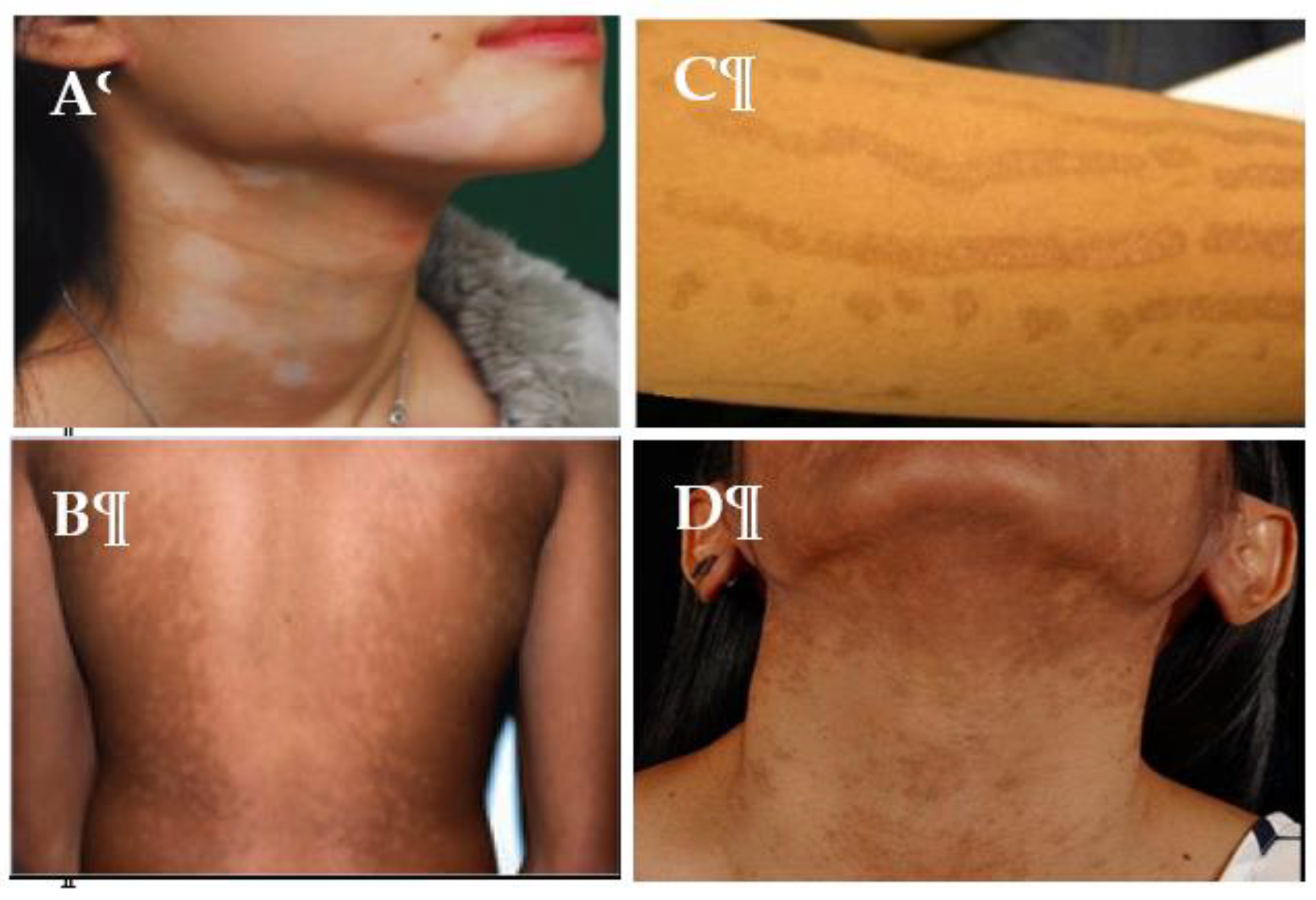
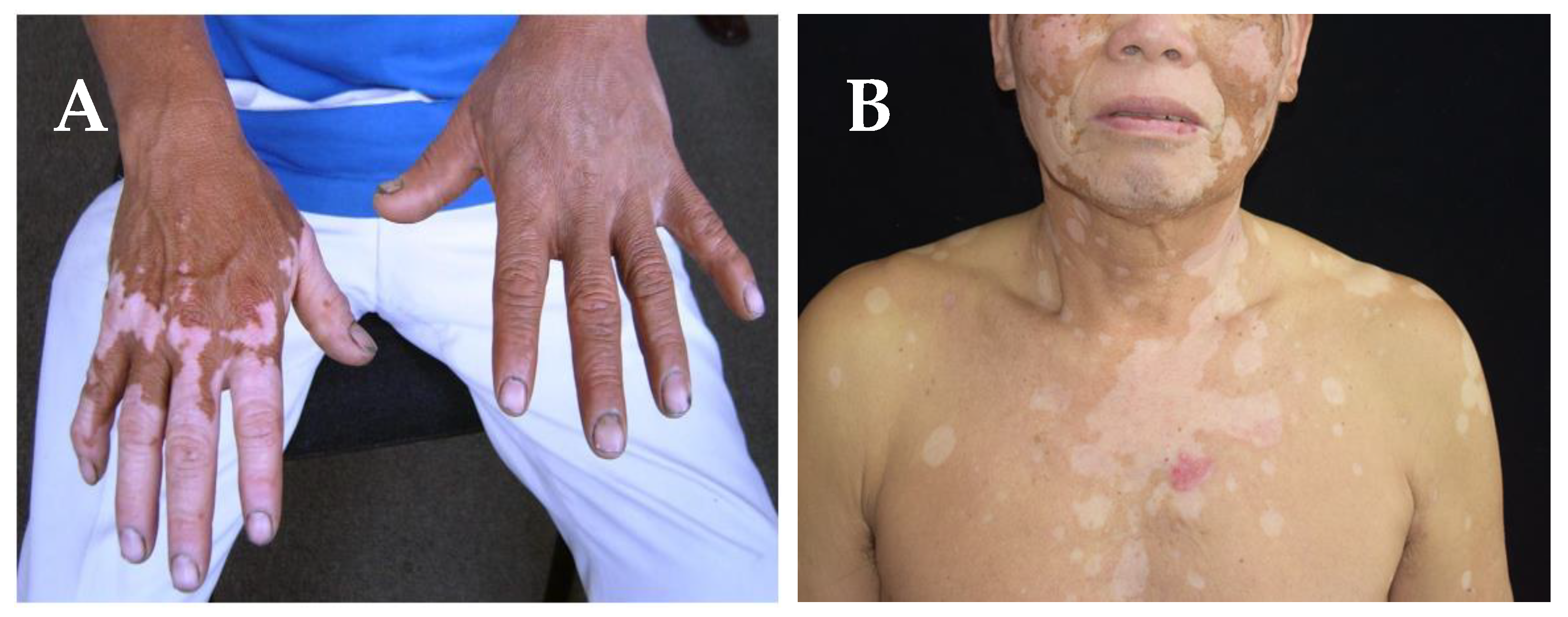
3.1. Causes of hypopigmentation
3.2. Causes of hyperpigmentation
4. Drugs for Treatment of Skin Pigmentation
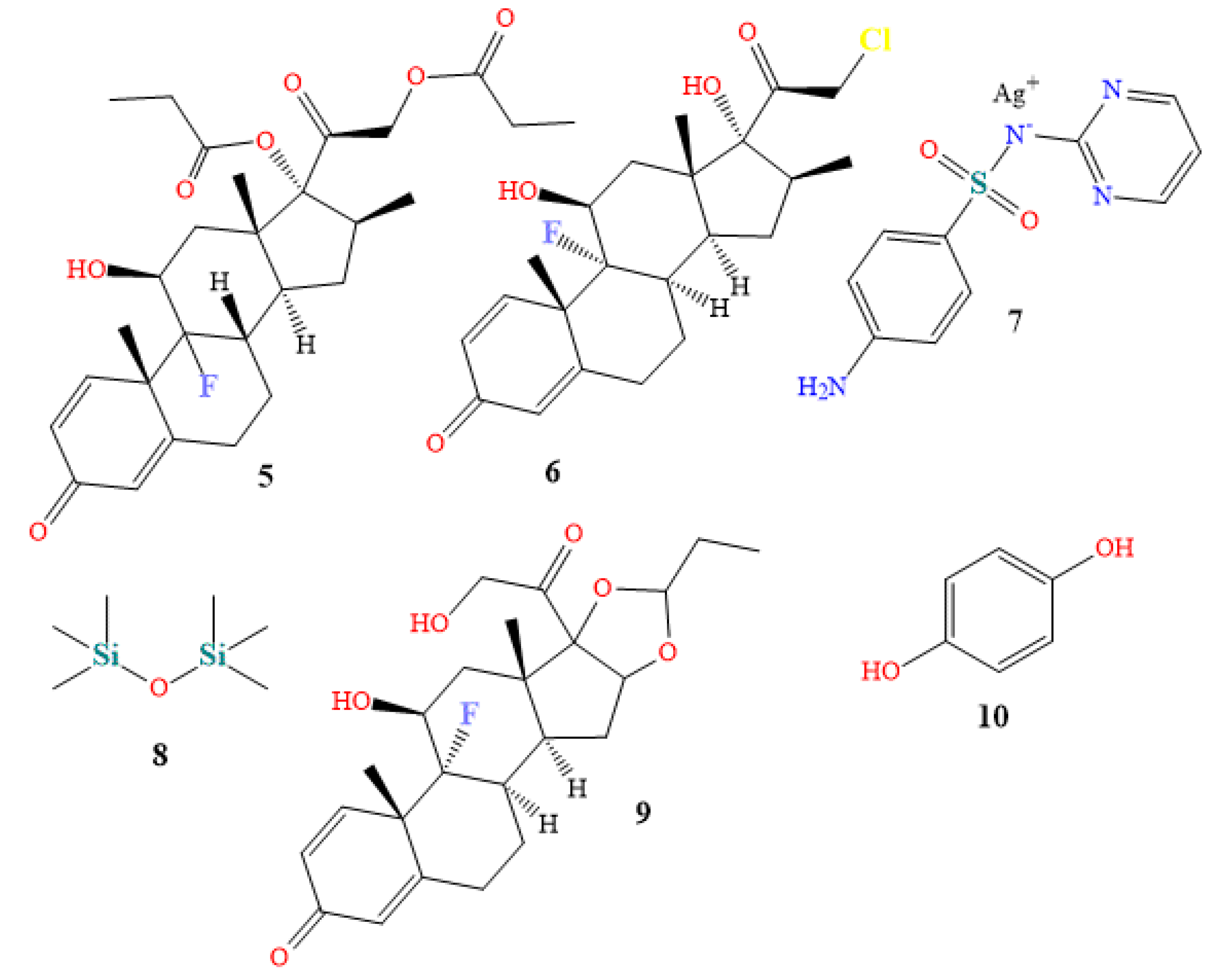
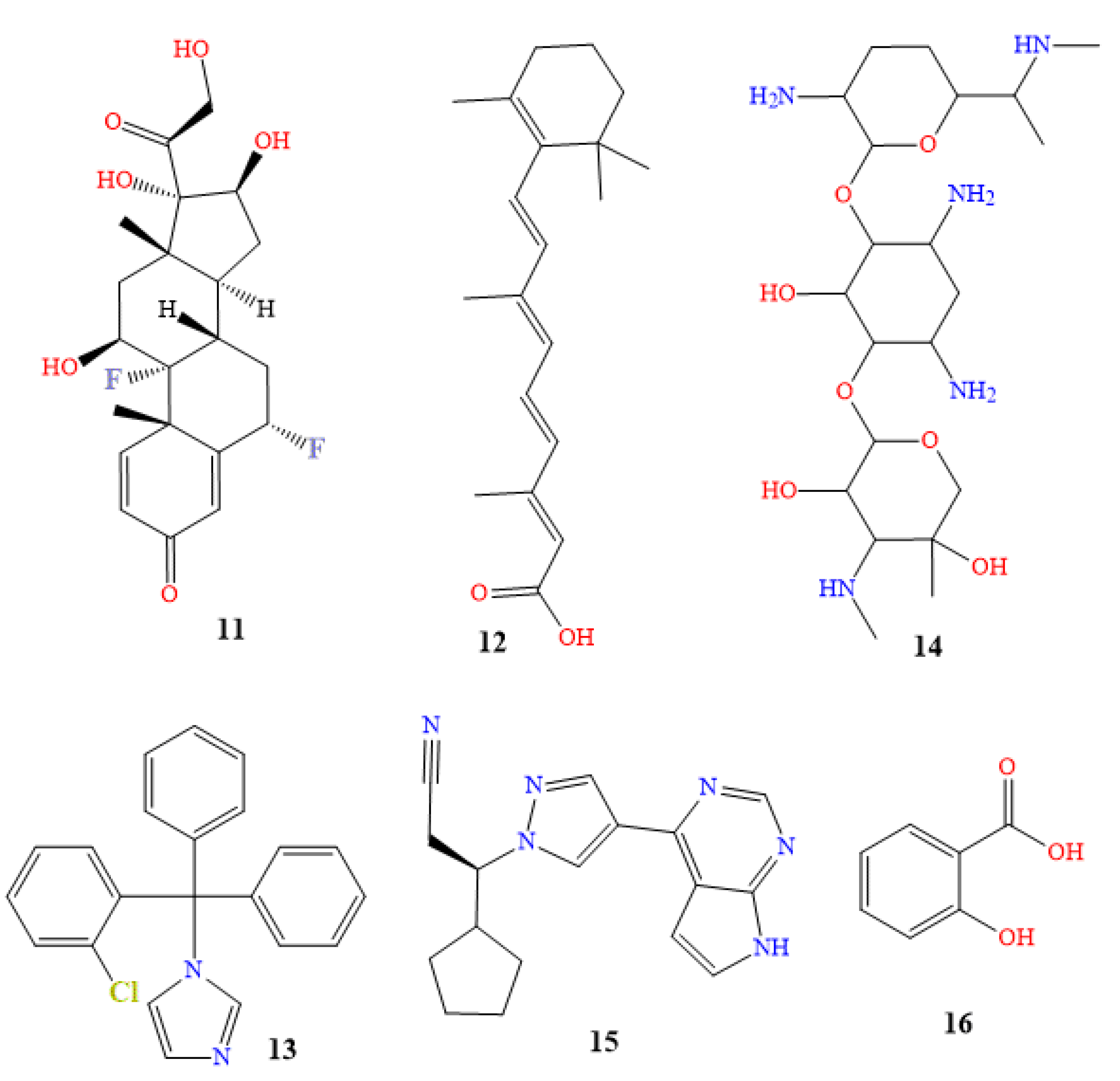
4.1. Oral Medications
4.2. Topical Creams
5. Natural hyperpigmentation treatment
6. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Del Bino, S.; Duval, C.; Bernerd, F. Clinical and Biological Characterization of Skin Pigmentation Diversity and Its Consequences on UV Impact. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, A.R.; Lin, M.; Granka, J.M.; Myrick, J.W.; Liu, X.; Sockell, A.; Atkinson, E.G.; Werely, C.J.; Möller, M.; Sandhu, M.S.; et al. An Unexpectedly Complex Architecture for Skin Pigmentation in Africans. Cell 2017, 171, 1340–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasti, T.H.; Timares, L. MC1R, Eumelanin and Pheomelanin: Their Role in Determining the Susceptibility to Skin Cancer. Photochem. Photobiol. 2015, 91, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solano, F. Photoprotection and Skin Pigmentation: Melanin-Related Molecules and Some Other New Agents Obtained from Natural Sources. Molecules 2020, 25, 1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polidori, C.; Jorge, A.; Ornosa, C. Eumelanin and pheomelanin are predominant pigments in bumblebee (Apidae:Bombus) pubescence. PeerJ 2017, 5, e3300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.; Zhai, P.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, B.; Yang, N.; Wang, M.; Xiao, Y.; Bao, G.; Wu, X. Morphological Characterization and Gene Expression Patterns for Melanin Pigmentation in Rex Rabbit. Biochem. Genet. 2019, 57, 734–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, S.H.; Lee, S.H. Sesamol decreases melanin biosynthesis in melanocyte cells and zebrafish: Possible involvement of MITF via the intracellular cAMP and p38/JNK signalling pathways. Exp. Dermatol. 2015, 24, 761–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madelaine, R.; Ngo, K.J.; Skariah, G.; Mourrain, P. Genetic deciphering of the antagonistic activities of the melanin-concentrating hormone and melanocortin pathways in skin pigmentation. PLOS Genet. 2020, 16, e1009244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdeslik, R.N.; Olinski, L.E.; Trieu, M.M.; Oprian, D.D.; Oancea, E. Human nonvisual opsin 3 regulates pigmentation of epidermal melanocytes through functional interaction with melanocortin 1 receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 11508–11517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horrell, E.M.W.; Boulanger, M.C.; D’orazio, J.A. Melanocortin 1 Receptor: Structure, Function, and Regulation. Front. Genet. 2016, 7, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suherlan, S., Fakih, T. M., & Effendi, D. H. (2021). Uji In-Silico Aktivitas Melanogenesis Senyawa Ternatin Bunga Kembang Telang (Clitoria ternatea) terhadap Reseptor Tirosinase. Prosiding Farmasi, 849-856.
- Jablonski, N.G. The evolution of human skin pigmentation involved the interactions of genetic, environmental, and cultural variables. Pigment. Cell Melanoma Res. 2021, 34, 707–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ainger, S.A.; Jagirdar, K.; Lee, K.J.; Soyer, H.P.; Sturm, R.A. Skin Pigmentation Genetics for the Clinic. Dermatology 2017, 233, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; A McQuillan, M.; A Tishkoff, S. Evolutionary genetics of skin pigmentation in African populations. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2021, 30, R88–R97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kita, R.; Fraser, H.B. Local Adaptation of Sun-Exposure-Dependent Gene Expression Regulation in Human Skin. PLOS Genet. 2016, 12, e1006382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armenta, A.M.; Henkel, E.D.; Ahmed, A.M. Pigmentation Disorders in the Elderly. Drugs Aging 2019, 36, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adigun, C.G. Adverse Drug Reactions of the Lower Extremities. Clin. Podiatr. Med. Surg. 2016, 33, 397–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolaidou, E.; Katsambas, A.D. Pigmentation disorders: hyperpigmentation and hypopigmentation. Clin. Dermatol. 2014, 32, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhm, M. (2021). Disorders of Melanin Pigmentation. In Braun-Falco´ s Dermatology (pp. 1-35). Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
- Ma, E.Z.; Zhou, A.E.; Hoegler, K.M.; Khachemoune, A. Oculocutaneous albinism: epidemiology, genetics, skin manifestation, and psychosocial issues. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2022, 315, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federico, J. R., & Krishnamurthy, K. (2018). Albinism.
- Lee, D.; Kim, C.; Lee, J. Trichrome vitiligo in segmental type. Photodermatol. Photoimmunol. Photomed. 2011, 27, 111–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, J.P.; Batchelor, J.M. An approach to hypopigmentation. BMJ 2017, 356, i6534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silpa-Archa, N.; Kohli, I.; Chaowattanapanit, S.; Lim, H.W.; Hamzavi, I. Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation: A comprehensive overview: Epidemiology, pathogenesis, clinical presentation, and noninvasive assessment technique. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2017, 77, 591–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kallini, J.R.; Riaz, F.; Khachemoune, A. Tinea versicolor in dark-skinned individuals. Int. J. Dermatol. 2014, 53, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miazek, N., Michalek, I., Pawlowska-Kisiel, M., Olszewska, M., & Rudnicka, L. Pityriasis Alba—Common Disease, Enigmatic Entity: Up-to-Date Review of the Literature. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2015, 32, 786–791. [CrossRef]
- Jing, J.; Man, X.-Y. Vitiligo-like depigmentation in a patient treated with PD-1 antibody. BMJ 2021, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMichael, L. (2012). Skin camouflage. BMJ, 344.
- Sheth, P.; Shah, H.; Dave, J. Periorbital Hyperpigmentation: A Study of its Prevalence, Common Causative Factors and its Association with Personal Habits and Other Disorders. Indian J. Dermatol. 2014, 59, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.; Yin, L.; Smuda, C.; Batzer, J.; Hearing, V.J.; Kolbe, L. Molecular and histological characterization of age spots. Exp. Dermatol. 2016, 26, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxter, L.L.; Pavan, W.J. The etiology and molecular genetics of human pigmentation disorders. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Dev. Biol. 2012, 2, 379–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadalla, H. K. K., & Aradhya, S. (2011). Post acne hyperpigmentation: A brief review. Our Dermatol Online, 2(4), 230-231.
- Plensdorf, S.; Livieratos, M.; Dada, N. Pigmentation Disorders: Diagnosis and Management. Am Fam Physician. 2017, 96, 797–804.
- Woolery-Lloyd, H., & Kammer, J. N. (2011, September). Treatment of hyperpigmentation. In Seminars in cutaneous medicine and surgery (Vol. 30, No. 3, pp. 171-175). WB Saunders.
- Bala, H.R.; Lee, S.; Wong, C.; Pandya, A.; Rodrigues, M. Oral Tranexamic Acid for the Treatment of Melasma: A Review. Dermatol. Surg. 2018, 44, 814–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A. A., Al-Obaidi, Z. M. J., Raauf, A. M., & Mahmood, H. S. (2020). A Comparative, Randomized, Double-Blinded, and Vehicle-Controlled Study for the Reduction in Facial Pigmentation after Treatment with both Tranexamic Acid and Tranexamic Acid Ethyl Ester. Systematic Reviews in Pharmacy, 11(6), 563-567.
- Lee, D.H.; Oh, I.Y.; Koo, K.T.; Suk, J.M.; Jung, S.W.; Park, J.O.; Kim, B.J.; Choi, Y.M. Reduction in facial hyperpigmentation after treatment with a combination of topical niacinamide and tranexamic acid: a randomized, double-blind, vehicle-controlled trial. Ski. Res. Technol. 2013, 20, 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, A., Bhalla, M., & Sarkar, R. (2020). Tranexamic acid in melasma: a review. Pigment International, 7(1), 12. [CrossRef]
- Maeda, K. Mechanism of Action of Topical Tranexamic Acid in the Treatment of Melasma and Sun-Induced Skin Hyperpigmentation. Cosmetics 2022, 9, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKesey, J.; Tovar-Garza, A.; Pandya, A.G. Melasma Treatment: An Evidence-Based Review. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2019, 21, 173–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimes, P.; Ijaz, S.; Nashawati, R.; Kwak, D. New oral and topical approaches for the treatment of melasma. Int. J. Women's Dermatol. 2018, 5, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artzi, O.; Horovitz, T.; Bar-Ilan, E.; Shehadeh, W.; Koren, A.; Zusmanovitch, L.; Mehrabi, J.N.; Salameh, F.; Nelkenbaum, G.I.; Zur, E.; et al. The pathogenesis of melasma and implications for treatment. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2021, 20, 3432–3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taraz, M.; Niknam, S.; Ehsani, A.H. Tranexamic acid in treatment of melasma: A comprehensive review of clinical studies. Dermatol. Ther. 2017, 30, e12465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tse, T.W.; Hui, E. Tranexamic acid: an important adjuvant in the treatment of melasma. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2013, 12, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, R.; Mahajan, V.K.; Mehta, K.S.; Chauhan, P.S.; Rawat, R.; Shiny, T.N. Therapeutic efficacy and safety of oral tranexamic acid and that of tranexamic acid local infiltration with microinjections in patients with melasma: a comparative study. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2017, 42, 728–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.J.; Park, J.-Y.; Shibata, T.; Fujiwara, R.; Kang, H.Y. Efficacy and possible mechanisms of topical tranexamic acid in melasma. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2016, 41, 480–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sofen, B.; Prado, G.; Emer, J. Melasma and Post Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation: Management Update and Expert Opinion. 2016, 21. [Google Scholar]
- DEMİR, B., ÇİÇEK, D., BİLİK, L., AYDOĞDU, E. G., ARTAŞ, H., DEMİRPOLAT, N., & ERGİN, C. (2017). Oral isotretinoin induced pigmentation disorder: A case report. Firat Tip Derg, 22(3).
- Mysore, V.; Mahadevappa, O.H.; Barua, S.; Majid, I.; Viswanath, V.; Bhat, R.M.; Talwar, S.; Thurakkal, S.; Aurangabadkar, S.J.; Chatterjee, M.; et al. Standard guidelines of care: Performing procedures in patients on or recently administered with isotretinoin. J. Cutan. Aesthetic Surg. 2017, 10, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagatin, E., & Costa, C. S. (2020). The use of isotretinoin for acne–an update on optimal dosing, surveillance, and adverse effects. Expert review of clinical pharmacology, 13(8), 885-897. [CrossRef]
- Fallah, H.; Rademaker, M. Isotretinoin in the management of acne vulgaris: practical prescribing. Int. J. Dermatol. 2020, 60, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villani, A.; Nastro, F.; Di Vico, F.; Fabbrocini, G.; Annunziata, M.C.; Genco, L. Oral isotretinoin for acne: a complete overview. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2022, 21, 1027–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- pring, L. K., Krakowski, A. C., Alam, M., Bhatia, A., Brauer, J., Cohen, J., ... & Zaenglein, A. L. (2017). Isotretinoin and timing of procedural interventions: a systematic review with consensus recommendations. JAMA dermatology, 153(8), 802-809. [CrossRef]
- Chu, S.; Michelle, L.; Ekelem, C.; Sung, C.T.; Rojek, N.; Mesinkovska, N.A. Oral isotretinoin for the treatment of dermatologic conditions other than acne: a systematic review and discussion of future directions. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2020, 313, 391–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, D., Xue, H., Huang, S., He, S., Li, Y., Liu, J., ... & Zeng, W. (2022). A prospective, randomized, split-face study of concomitant administration of low-dose oral isotretinoin with 30% salicylic acid chemical peeling for the treatment of acne vulgaris in Asian population.
- Dréno, B.; Araviiskaia, E.; Kerob, D.; Andriessen, A.; Anfilova, M.; Arenbergerova, M.; Barrios, O.L.F.; Mokos, Z.B.; Haedersdal, M.; Hofmann, M.A.; et al. Nonprescription acne vulgaris treatments: Their role in our treatment armamentarium—An international panel discussion. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2020, 19, 2201–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rachmin, I.; Ostrowski, S.M.; Weng, Q.Y.; Fisher, D.E. Topical treatment strategies to manipulate human skin pigmentation. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2020, 153, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, S. K., & Ortonne, J. P. (1998). Pigmentation: dyschromia. In Textbook of cosmetic dermatology (pp. 391-415). Martin-Dunitz Ltd London.
- Yasir, M., Goyal, A., & Sonthalia, S. (2018). Corticosteroid adverse effects.
- Robert, C.; Hwu, W.-J.; Hamid, O.; Ribas, A.; Weber, J.S.; Daud, A.I.; Hodi, F.S.; Wolchok, J.D.; Mitchell, T.C.; Hersey, P.; et al. Long-term safety of pembrolizumab monotherapy and relationship with clinical outcome: A landmark analysis in patients with advanced melanoma. Eur. J. Cancer 2020, 144, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.H.; Bhutani, S.; Kim, C.H.; Irwin, M.R. Anti-inflammatory effects of melatonin: A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials. Brain, Behav. Immun. 2021, 93, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marathe, P.; Karekar, S.; Nagarajan, V.; Khopkar, U.; Chikhalkar, S.; Desai, P.; Dongre, M. Use of topical steroids in dermatology: A questionnaire based study. Indian Dermatol. Online J. 2020, 11, 725–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chadderdon, C., Gaston, R. G., Loeffler, B. J., & Lewis, D. (2017). Betamethasone Versus Ketorolac Injection for the Treatment of De Quervain's Tenosynovitis: A Double-Blind Randomized Clinical Trial: Level 1 Evidence. Journal of Hand Surgery, 42(9), S45-S46.
- Patel, H.K.; Barot, B.S.; Parejiya, P.B.; Shelat, P.K.; Shukla, A. Topical delivery of clobetasol propionate loaded microemulsion based gel for effective treatment of vitiligo: Ex vivo permeation and skin irritation studies. Colloids Surfaces B: Biointerfaces 2013, 102, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khaitan, B.K.; Sindhuja, T. Autoimmunity in vitiligo: Therapeutic implications and opportunities. Autoimmun. Rev. 2021, 21, 102932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eleftheriadou, V.; Atkar, R.; Batchelor, J.; McDonald, B.; Novakovic, L.; Patel, J.V.; Ravenscroft, J.; Rush, E.; Shah, D.; Shah, R.; et al. British Association of Dermatologists guidelines for the management of people with vitiligo 2021. Br. J. Dermatol. 2021, 186, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Habet, K.; Kolli, S.S.; Pona, A.; Feldman, S.R. A review of topical corticosteroid sprays for the treatment of inflammatory dermatoses. Dermatol. Online J. 2019, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajinov, Z. Corticosteroid topical therapy range: Fluocinolone-acetonide gel. Galen. Med J. 2022, 1, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medici, S.; Peana, M.F.; Nurchi, V.M.; Zoroddu, M.A. Medical Uses of Silver: History, Myths, and Scientific Evidence. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 5923–5943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandyopadhyay, D. Topical antibacterials in dermatology. Indian J. Dermatol. 2021, 66, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhya, A.; Bain, J.; Dutta, G.; Hazra, A.; Majumdar, B.; Ray, O.; Ray, S.; Adhikari, S. Healing of burn wounds by topical treatment: A randomized controlled comparison between silver sulfadiazine and nano-crystalline silver. J. Basic Clin. Pharm. 2015, 6, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nethi, S.K.; Das, S.; Patra, C.R.; Mukherjee, S. Recent advances in inorganic nanomaterials for wound-healing applications. Biomater. Sci. 2019, 7, 2652–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, S.; Patil, A.; Prakash, C.; Kumari, H. Comparison of Intralesional Triamcinolone Acetonide, 5-Fluorouracil, and Their Combination in Treatment of Keloids. World J. Plast. Surg. 2018, 7, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Khan, H.; Sahibzada, M.N.; Paracha, M.M. Comparison of the efficacy of intralesional bleomycin versus intralesional triamcinolone acetonide in the treatment of keloids. Dermatol. Ther. 2019, 32, e13036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krithika, C.L.; Anand, S.N.; Subramani, G.P. Topical Curcumin and Triamcinolone Acetonide in Recurrent Minor Aphthous Ulcers: A Pilot Trial. J. Contemp. Dent. Pr. 2020, 21, 884–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwiatkowska, D.; Wicka, M.; Bulska, E.; Kaliszewski, P. Investigation of the Excretion of Triamcinolone Acetonide and Its Metabolite. Separations 2023, 10, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangion, S.E.; Mackenzie, L.; Roberts, M.S.; Holmes, A.M. Seborrheic dermatitis: topical therapeutics and formulation design. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2023, 185, 148–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atluri, K.; Manne, S.; Nalamothu, V.; Mantel, A.; Sharma, P.K.; Babu, R.J. Advances in Formulation and Therapeutic Strategies for the Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis. Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug Carr. Syst. 2023, 40, 1–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhu, S.; Klein, B.A.; Al-Hadlaq, M.; Chirravur, P.; Bajonaid, A.; Xu, Y.; Intini, R.; Hussein, M.; Vacharotayangul, P.; Sroussi, H.; et al. Oral lichen planus: comparative efficacy and treatment costs—a systematic review. BMC Oral Heal. 2022, 22, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakravan, F., Ghalayani, P., Emami, H., Isfahani, M. N., & Noorshargh, P. (2019). A novel formulation for radiotherapy-induced oral mucositis: Triamcinolone acetonide mucoadhesive film. Journal of research in medical sciences: the official journal of Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, 24. [CrossRef]
- Mangold, A. R., & Pittelkow, M. R. (2017). Lichen planus. Clinical and Basic Immunodermatology, 551-576.
- Nasrollahi, S.A.; Sabet, M.; Samadi, A.; Ayatollahi, A.; Yadangi, S.; Abels, C.; Firooz, A. Evaluation of the safety and efficacy of a triple combination cream (hydroquinone, tretinoin, and fluocinolone) for treatment of melasma in Middle Eastern skin. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2019, ume 12, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreher, F., Draelos, Z. D., Gold, M. H., Goldman, M. P., Fabi, S. G., & Puissegur Lupo, M. L. (2013). Efficacy of hydroquinone-free skin-lightening cream for photoaging. Journal of cosmetic dermatology, 12(1), 12-17. [CrossRef]
- Banihashemi, M.; Zabolinejad, N.; Jaafari, M.R.; Salehi, M.; Jabari, A. Comparison of therapeutic effects of liposomal Tranexamic Acid and conventional Hydroquinone on melasma. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2015, 14, 174–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pradhan, M.; Singh, D.; Murthy, S.N.; Singh, M.R. Design, characterization and skin permeating potential of Fluocinolone acetonide loaded nanostructured lipid carriers for topical treatment of psoriasis. Steroids 2015, 101, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treesirichod, A.; Chaithirayanon, S.; Chaikul, T.; Chansakulporn, S. The randomized trials of 10% urea cream and 0.025% tretinoin cream in the treatment of acanthosis nigricans. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2020, 32, 837–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagatin, E.; Gonçalves, H.D.S.; Sato, M.; Almeida, L.M.C.; Miot, H.A. Comparable efficacy of adapalene 0.3% gel and tretinoin 0.05% cream as treatment for cutaneous photoaging. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2018, 28, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nautiyal, A.; Wairkar, S. Management of hyperpigmentation: Current treatments and emerging therapies. Pigment. Cell Melanoma Res. 2021, 34, 1000–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraris, C.; Rimicci, C.; Garelli, S.; Ugazio, E.; Battaglia, L. Nanosystems in Cosmetic Products: A Brief Overview of Functional, Market, Regulatory and Safety Concerns. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usatine, R.P.; Tinitigan, M. Diagnosis and treatment of lichen planus. Am. Fam. Physician 2011, 84, 53–60. [Google Scholar]
- Korabiusz, K., Wawryków, A., Fabian-Danielewska, A., Stecko, M., Wilczyńska, A., Janik-Fuks, I., ... & Harasimowicz, J. (2019). Laser removal of tattoo-a case report. Journal of Education, Health and Sport, 9(6), 415-419.
- Doucette, K., Forster, S., & Marcus, A. (2018, April). Study to assess visual elimination of a novel otic gel (florfenicol, terbinafine, betamethasone acetate) in comparison to an otic solution (florfenicol, terbinafine, mometasone furoate) and an otic suspension (gentamicin sulfate, clotrimazole, mometasone furoate monohydrate) in dogs immediately after application to the ear canal. In BSAVA Congress Proceedings 2018 (pp. 489-489). BSAVA Library.
- Grammatikova, N. . Comparative Study of the Antimicrobial Activity of Combined Topical Medicinal Formulations of Betamethasone, Gentamicin, and Clotrimazole In Vitro. Pharm. Chem. J. 2020, 53, 971–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, L. K., Rajala-Schultz, P. J., & Lorch, G. (2018). Conductive hearing loss in four dogs associated with the use of ointment-based otic medications. Veterinary dermatology, 29(4), 341-e120. [CrossRef]
- Hikmatovich, I. N. (2023). Evaluation of the Efficacy of External Therapy in Sick Children with Alergodermatosis. Web of Semantic: Universal Journal on Innovative Education, 2(2), 50-54.
- Harris, J.E.; Rashighi, M.; Nguyen, N.; Jabbari, A.; Ulerio, G.; Clynes, R.; Christiano, A.M.; Mackay-Wiggan, J. Rapid skin repigmentation on oral ruxolitinib in a patient with coexistent vitiligo and alopecia areata (AA). J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2015, 74, 370–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosmarin, D.; Pandya, A.G.; Lebwohl, M.; Grimes, P.; Hamzavi, I.; Gottlieb, A.B.; Butler, K.; Kuo, F.; Sun, K.; Ji, T.; et al. Ruxolitinib cream for treatment of vitiligo: a randomised, controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet 2020, 396, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothstein, B.; Joshipura, D.; Saraiya, A.; Abdat, R.; Ashkar, H.; Turkowski, Y.; Sheth, V.; Huang, V.; Au, S.C.; Kachuk, C.; et al. Treatment of vitiligo with the topical Janus kinase inhibitor ruxolitinib. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2017, 76, 1054–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, A.; Rafique, W.; Owais, R.; Malik, F.; Ali, E. FDA approves Ruxolitinib (Opzelura) for Vitiligo Therapy: A breakthrough in the field of dermatology. Ann. Med. Surg. 2022, 81, 104499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shreberk-Hassidim, R.; Ramot, Y.; Zlotogorski, A. Janus kinase inhibitors in dermatology: A systematic review. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2017, 76, 745–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, S.; Kwa, M.; Gold, L.S.; Lim, H.W. Janus kinase inhibitors in dermatology: Part I. A comprehensive review. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2021, 86, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosmarin, D.; Passeron, T.; Pandya, A.G.; Grimes, P.; Harris, J.E.; Desai, S.R.; Lebwohl, M.; Ruer-Mulard, M.; Seneschal, J.; Wolkerstorfer, A.; et al. Two Phase 3, Randomized, Controlled Trials of Ruxolitinib Cream for Vitiligo. New Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 1445–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seneschal, J.; Wolkerstorfer, A.; Desai, S.R.; Grimes, P.; Ezzedine, K.; Kornacki, D.; Wei, S.; Butler, K.; Rosmarin, D. Efficacy and safety of ruxolitinib cream for the treatment of vitiligo by patient demographics and baseline clinical characteristics: Week 52 pooled subgroup analysis from two randomized phase 3 studies. Br. J. Dermatol. 2023, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sripathi, S. K., & Lalitha, P. (2016). Keratolytic Molecule Aided Inhibition of DNA Damage and Tyrosinase Activity of a Herbal Formulation. International Journal of BioSciences & Technology, 9(2).
- Arif, T. Salicylic acid as a peeling agent: a comprehensive review. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2015, ume 8, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Jiang, R.; Zhou, J.; Xu, X.; Sun, Z.; Li, J.; Chen, X.; Li, Z.; Yan, X.; Zhao, D.; et al. Salicylic acid in ginseng root alleviates skin hyperpigmentation disorders by inhibiting melanogenesis and melanosome transport. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 910, 174458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colantonio, S.; Rivers, J.K. Botanicals With Dermatologic Properties Derived From First Nations Healing: Part 2—Plants and Algae. J. Cutan. Med. Surg. 2016, 21, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnes, J.B.; Usatine, R.P. Management of external genital warts. Am. Fam. Physician 2014, 90.
- Lu, J.; Cong, T.; Wen, X.; Li, X.; Du, D.; He, G.; Jiang, X. Salicylic acid treats acne vulgaris by suppressing AMPK/SREBP1 pathway in sebocytes. Exp. Dermatol. 2019, 28, 786–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeoh, S. C., & Goh, C. F. (2021). Topical delivery of salicylates. Drug delivery and translational research, 1-21. [CrossRef]
- Ogbechie-Godec, O.A.; Elbuluk, N. Melasma: an Up-to-Date Comprehensive Review. Dermatol. Ther. 2017, 7, 305–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufman, B.P.; Aman, T.; Alexis, A.F. Postinflammatory Hyperpigmentation: Epidemiology, Clinical Presentation, Pathogenesis and Treatment. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2018, 19, 489–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanlayavattanakul, M.; Lourith, N. Plants and Natural Products for the Treatment of Skin Hyperpigmentation – A Review. Planta Medica 2018, 84, 988–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollinger, J.C.; Angra, K.; Halder, R.M. Are Natural Ingredients Effective in the Management of Hyperpigmentation? A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Aesthetic Dermatol. 2018, 11, 28–37. [Google Scholar]
- Panzella, L.; Napolitano, A. Natural and Bioinspired Phenolic Compounds as Tyrosinase Inhibitors for the Treatment of Skin Hyperpigmentation: Recent Advances. Cosmetics 2019, 6, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimes, P.; Bhawan, J.; Howell, M.; Desai, S.; Coryell, E.; Einziger, M.; Simpson, A.; Yaroshinsky, A.; McCraw, T. Histopathological Changes Induced by Malassezin: A Novel Natural Microbiome Indole for Treatment of Facial Hyperpigmentation. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2022, 21, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nautiyal, A.; Wairkar, S. Management of hyperpigmentation: Current treatments and emerging therapies. Pigment. Cell Melanoma Res. 2021, 34, 1000–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karadas, F.; Erdoğan, S.; Kor, D.; Oto, G.; Uluman, M. The Effects of Different Types of Antioxidants (Se, Vitamin E and Carotenoids) in Broiler Diets on the Growth Performance, Skin Pigmentation and Liver and Plasma Antioxidant Concentrations. Braz. J. Poult. Sci. 2016, 18, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucock, M.D. The evolution of human skin pigmentation: A changing medley of vitamins, genetic variability, and UV radiation during human expansion. Am. J. Biol. Anthr. 2022, 180, 252–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rembe, J.-D.; Fromm-Dornieden, C.; Stuermer, E.K. Effects of Vitamin B Complex and Vitamin C on Human Skin Cells: Is the Perceived Effect Measurable? Adv. Ski. Wound Care 2018, 31, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farzanfar, S.; Kouzekonan, G.S.; Mirjani, R.; Shekarchi, B. Vitamin B12-loaded polycaprolacton/gelatin nanofibrous scaffold as potential wound care material. Biomed. Eng. Lett. 2020, 10, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vivcharenko, V.; Wojcik, M.; Przekora, A. Cellular Response to Vitamin C-Enriched Chitosan/Agarose Film with Potential Application as Artificial Skin Substitute for Chronic Wound Treatment. Cells 2020, 9, 1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrios-Garay, K.; Toledano-Serrabona, J.; Gay-Escoda, C.; Sánchez-Garcés, M. Clinical effect of vitamin C supplementation on bone healing: A systematic review. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Y Cirugía Bucal 2022, 27, e205–e215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Niaimi, F.; Zhen Chiang, N.Y. Topical Vitamin C and the Skin: Mechanisms of Action and Clinical Applications. J. Clin. aesthetic Dermatol. 2017, 10, 14–17. [Google Scholar]
- Ravetti, S.; Clemente, C.; Brignone, S.; Hergert, L.; Allemandi, D.; Palma, S. Ascorbic Acid in Skin Health. Cosmetics 2019, 6, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, K. Y., Song, H. J., & Kim, D. C. (2022). Effect of alpha-tocopheryl acetate, retinyl palmitate, and phytantriol on hair protection. Journal of Applied Biological Chemistry, 65(4), 307-312.
- Santos, J. S., Tavares, G. D., & Barradas, T. N. (2021). Vitamin E and derivatives in skin health promotion. In Vitamin E in Health and Disease-Interactions, Diseases and Health Aspects. IntechOpen.
- Putranti, A.R.; Hendradi, E.; Primaharinastiti, R. Effectivity and physicochemical stability of nanostructured lipid carrier coenzyme q10 in different ratio of lipid alfa cetyl palmitate and alpha tocopheryl acetate as carrier. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2017, 10, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panichakul, T.; Rodboon, T.; Suwannalert, P.; Tripetch, C.; Rungruang, R.; Boohuad, N.; Youdee, P. Additive Effect of a Combination of Artocarpus lakoocha and Glycyrrhiza glabra Extracts on Tyrosinase Inhibition in Melanoma B16 Cells. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.K.; Pathak, U.; Medhi, M.; Mastinu, A.; Sikarwar, M.S.; Mishra, P. Botanical, Chemical and Pharmacological Properties of Artocarpus lakoocha (Monkey Fruit): A Review. Agric. Rev. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, S.; Shoaib, R.; Khan, S.; Masood, A. Phytochemicals; Targeted-Based Therapeutic Approaches for Pigmentation Disorders. Open Access Indones. J. Med Rev. 2023, 3, 368–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughn, A.R.; Clark, A.K.; Sivamani, R.K.; Shi, V.Y. Natural Oils for Skin-Barrier Repair: Ancient Compounds Now Backed by Modern Science. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2018, 19, 103–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkic, A.; Stappen, I. Essential Oils and Their Single Compounds in Cosmetics—A Critical Review. Cosmetics 2018, 5, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.A.; Galgut, J.M.; Choudhary, R.K. On The Novel Action of Melanolysis by a Leaf Extract of Aloe vera and Its Active Ingredient Aloin, Potent Skin Depigmenting Agents. Planta Medica 2012, 78, 767–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gad, H.A.; Roberts, A.; Hamzi, S.H.; Gad, H.A.; Touiss, I.; Altyar, A.E.; Kensara, O.A.; Ashour, M.L. Jojoba Oil: An Updated Comprehensive Review on Chemistry, Pharmaceutical Uses, and Toxicity. Polymers 2021, 13, 1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, Y.; Ma, S.; Tominaga, T.; Yokoyama, K.; Kitatani, K.; Horikawa, K.; Suzuki, K. Acute Effects of Transdermal Administration of Jojoba Oil on Lipid Metabolism in Mice. Medicina 2019, 55, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaak, J.; Staib, P. An updated review on efficacy and benefits of sweet almond, evening primrose and jojoba oils in skin care applications. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2021, 44, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturtevant, D.; Lu, S.; Zhou, Z.-W.; Shen, Y.; Wang, S.; Song, J.-M.; Zhong, J.; Burks, D.J.; Yang, Z.-Q.; Yang, Q.-Y.; et al. The genome of jojoba ( Simmondsia chinensis ): A taxonomically isolated species that directs wax ester accumulation in its seeds. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaay3240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasr, M., Abdel-Hamid, S., H Moftah, N., Fadel, M., & A Alyoussef, A. (2017). Jojoba oil soft colloidal nanocarrier of a synthetic retinoid: preparation, characterization and clinical efficacy in psoriatic patients. Current drug delivery, 14(3), 426-432.
- Sánchez, M.; Avhad, M.R.; Marchetti, J.M.; Martínez, M.; Aracil, J. Jojoba oil: A state of the art review and future prospects. Energy Convers. Manag. 2016, 129, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoharan, S., Vishnupriya, V., & Gayathri, R. (2016). Phytochemical analysis and in vitro antioxidant activity of jojoba oil. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Research, 8(6), 512.
- Goik, U.; Goik, T.; Załęska, I. The Properties and Application of Argan Oil in Cosmetology. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2019, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phong, C.; Lee, V.; Yale, K.; Sung, C.; Mesinkovska, N. Coconut, Castor, and Argan Oil for Hair in Skin of Color Patients: A Systematic Review. J. Drugs Dermatol. JDD 2022, 21, 751–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charrouf, Z.; Guillaume, D. The argan oil project: going from utopia to reality in 20 years. OCL 2018, 25, D209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, C.d.S.; Bonafé, G.A.; Santos, J.C.; Martinez, C.A.R.; Ortega, M.M.; Ribeiro, M.L. The Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Licorice (Glycyrrhiza glabra)-Derived Compounds in Intestinal Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, Y.-J.; Son, D.-H.; Chung, T.-H.; Lee, Y.-J. A Review of the Pharmacological Efficacy and Safety of Licorice Root from Corroborative Clinical Trial Findings. J. Med. Food 2020, 23, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohiuddin, A. K. (2019). Skin lightening & management of hyperpigmentation. Pharma Sci Anal Res J, 2(2), 180020.
- Kimyon, R.S.; Liou, Y.L.; Schlarbaum, J.P.; Warshaw, E.M. Allergic Contact Dermatitis to Licorice Root Extract. Dermatitis® 2019, 30, 227–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, J.M.; Accioly, J.; Kitchen, N. Double Blind, Placebo Controlled Evaluation of a Novel Skin Lightening Agent. J. Drugs Dermatol. JDD 2018, 17, 113–115. [Google Scholar]
- Dhariwala, M.Y.; Ravikumar, P. An overview of herbal alternatives in androgenetic alopecia. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2019, 18, 966–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, L., & Lio, P. (2020). Turmeric, curcumin, and curcuminoids: a dermatologic review. Clinical Focus, 38-42.
- Vo, T. S., Vo, T. T. B. C., Vo, T. T. T. N., & Lai, T. N. H. (2021). Turmeric (Curcuma longa L.): Chemical components and their effective clinical applications. Journal of the Turkish Chemical Society Section A: Chemistry, 8(3), 883-898.
- Firmansyah, D.; Sumiwi, S.A.; Saptarini, N.M.; Levita, J. Curcuma longa extract inhibits the activity of mushroom tyrosinase and the growth of murine skin cancer B16F10 cells. J. Herbmed Pharmacol. 2022, 12, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooqui, R.K.; Kaurav, M.; Kumar, M.; Sudheesh, M.S.; Pandey, R.S. Permeation enhancer nanovesicles mediated topical delivery of curcumin for the treatment of hyperpigmentation. J. Liposome Res. 2022, 32, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akter, J., Islam, M. Z., Hossain, M. A., & Takara, K. (2021). Anti-tyrosinase properties of different species of turmeric and isolation of active compounds from Curcuma amada. Medicinal Chemistry Research, 30, 1669-1676.
- Rodríguez-Cid, L.; Qian, W.; Iribarra-Araya, J.; Etcheverry-Berríos. ; Martínez-Olmos, E.; Choquesillo-Lazarte, D.; Sañudo, E.C.; Roubeau, O.; López-Periago, A.M.; González-Campo, A.; et al. Broadening the scope of high structural dimensionality nanomaterials using pyridine-based curcuminoids. Dalton Trans. 2021, 50, 7056–7064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaughn, A.R.; Clark, A.K.; Notay, M.; Sivamani, R.K. Randomized Controlled Pilot Study of Dietary Supplementation with Turmeric or Herbal Combination Tablets on Skin Barrier Function in Healthy Subjects. J. Med. Food 2018, 21, 1260–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kallis, P.J.; Price, A.; Dosal, J.R.; Nichols, A.J.; Keri, J. A Biologically Based Approach to Acne and Rosacea. J. Drugs Dermatol. JDD 2018, 17, 611–617. [Google Scholar]
- Song, X.-C.; Canellas, E.; Wrona, M.; Becerril, R.; Nerin, C. Comparison of two antioxidant packaging based on rosemary oleoresin and green tea extract coated on polyethylene terephthalate for extending the shelf life of minced pork meat. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2020, 26, 100588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, R., Rashidlamir, A., Ashtary-Larky, D., Wong, A., Alipour, M., Motevalli, M. S., ... & Zouhal, H. (2020). Does green tea extract enhance the anti-inflammatory effects of exercise on fat loss?. British journal of clinical pharmacology, 86(4), 753-762. [CrossRef]
- Gaweł-Bęben, K.; Kukula-Koch, W.; Hoian, U.; Czop, M.; Strzępek-Gomółka, M.; Antosiewicz, B. Characterization of Cistus × incanus L. and Cistus ladanifer L. Extracts as Potential Multifunctional Antioxidant Ingredients for Skin Protecting Cosmetics. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, G.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, N.; Li, H.; Feng, Y. Green Tea and Epigallocatechin Gallate (EGCG) for the Management of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Diseases (NAFLD): Insights into the Role of Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Mechanism. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodges, J.K.; Sasaki, G.Y.; Bruno, R.S. Anti-inflammatory activities of green tea catechins along the gut–liver axis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: lessons learned from preclinical and human studies. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2020, 85, 108478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaikul, P.; Sripisut, T.; Chanpirom, S.; Ditthawutthikul, N. Anti-skin aging activities of green tea (Camelliasinensis (L) Kuntze) in B16F10 melanoma cells and human skin fibroblasts. Eur. J. Integr. Med. 2020, 40, 101212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, S.; Sherje, A.P. Development of resveratrol and green tea sunscreen formulation for combined photoprotective and antioxidant properties. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 60, 102000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkelman, W.J. Aromatherapy, botanicals, and essential oils in acne. Clin. Dermatol. 2018, 36, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patidar, K. (2018). Unmet Need and Challenges of Skin Aging by Herbal Anti-aging Cosmeceuticals: An Overview. Asian Journal of Pharmaceutics (AJP), 12(02).
- Phasha, V.; Senabe, J.; Ndzotoyi, P.; Okole, B.; Fouche, G.; Chuturgoon, A. Review on the Use of Kojic Acid—A Skin-Lightening Ingredient. Cosmetics 2022, 9, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeedi, M.; Eslamifar, M.; Khezri, K. Kojic acid applications in cosmetic and pharmaceutical preparations. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 110, 582–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khezri, K.; Saeedi, M.; Morteza-Semnani, K.; Akbari, J.; Hedayatizadeh-Omran, A. A promising and effective platform for delivering hydrophilic depigmenting agents in the treatment of cutaneous hyperpigmentation: kojic acid nanostructured lipid carrier. Artif. Cells, Nanomedicine, Biotechnol. 2021, 49, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Park, T.J.; Ikram, M.; Ahmad, S.; Ahmad, R.; Jo, M.G.; Kim, M.O. Antioxidative and Anti-inflammatory Effects of Kojic Acid in Aβ-Induced Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2021, 58, 5127–5140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zilles, J. C., Dos Santos, F. L., Kulkamp-Guerreiro, I. C., & Contri, R. V. (2022). Biological activities and safety data of kojic acid and its derivatives: A review. Experimental dermatology, 31(10), 1500-1521.
- Bakhouche, I.; Aliat, T.; Boubellouta, T.; Gali, L.; Şen, A.; Bellik, Y. Phenolic contents and in vitro antioxidant, anti-tyrosinase, and anti-inflammatory effects of leaves and roots extracts of the halophyte Limonium delicatulum. South Afr. J. Bot. 2021, 139, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.-X.; Liang, J.-X.; Liu, L.-L.; Shi, F.-C.; Jia, X.-W.; Li, M.-H.; Xu, C.-P. Novel kojic acid derivatives with anti-inflammatory effects from Aspergillus versicolor. Fitoterapia 2021, 154, 105027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gust, P. J., & Luke, J. D. (2016). Kojic acid. Journal of the Dermatology Nurses' Association, 8(5), 338-340.
- Searle, T.; Al-Niaimi, F.; Ali, F.R. The top 10 cosmeceuticals for facial hyperpigmentation. Dermatol. Ther. 2020, 33, e14095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohno, Y.; Kondo, S.; Tajima, K.; Shibata, T.; Itoh, T. Effect of Phlorotannins Isolated From Eisenia bicyclis on Melanogenesis in Mouse B16 Melanoma Cells. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2021, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phang, S.J.; Teh, H.X.; Looi, M.L.; Arumugam, B.; Fauzi, M.B.; Kuppusamy, U.R. Phlorotannins from brown algae: a review on their antioxidant mechanisms and applications in oxidative stress-mediated diseases. J. Appl. Phycol. 2023, 35, 867–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jesumani, V.; Du, H.; Aslam, M.; Pei, P.; Huang, N. Potential Use of Seaweed Bioactive Compounds in Skincare—A Review. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Yang, A.; Wang, J.; Huang, D.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Qu, Q.; Ma, W.; Xiong, R.; Zhu, M.; et al. Potential application of natural bioactive compounds as skin-whitening agents: A review. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2022, 21, 6669–6687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-N.; Yang, H.-M.; Kang, S.-M.; Ahn, G.; Roh, S.W.; Lee, W.; Kim, D.; Jeon, Y.-J. Whitening Effect of Octaphlorethol A Isolated from Ishige foliacea in an In Vivo Zebrafish Model. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 25, 448–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.-H.; Kang, N.; Kim, E.-A.; Heo, S.-J.; Moon, S.-H.; Jeon, B.-T.; Jeon, Y.-J. Antidiabetogenic and antioxidative effects of octaphlorethol a isolated from the brown algae Ishige foliacea in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2014, 23, 1261–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thawabteh, A.M.; Swaileh, Z.; Ammar, M.; Jaghama, W.; Yousef, M.; Karaman, R.; Bufo, S.A.; Scrano, L. Antifungal and Antibacterial Activities of Isolated Marine Compounds. Toxins 2023, 15, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernando, I.P.S.; Sanjeewa, K.K.A.; Samarakoon, K.W.; Kim, H.-S.; Gunasekara, U.K.D.S.S.; Park, Y.-J.; Abeytunga, D.T.U.; Lee, W.W.; Jeon, Y.-J. The potential of fucoidans from Chnoospora minima and Sargassum polycystum in cosmetics: antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, skin-whitening, and antiwrinkle activities. J. Appl. Phycol. 2018, 30, 3223–3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kok, J.M.-L.; Jee, J.-M.; Chew, L.-Y.; Wong, C.-L. The potential of the brown seaweed Sargassum polycystum against acne vulgaris. J. Appl. Phycol. 2016, 28, 3127–3133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenço-Lopes, C., Fraga-Corral, M., Soria-Lopez, A., Nuñes-Estevez, B., Barral-Martinez, M., Silva, A., ... & Prieto, M. A. (2022). Fucoxanthin’s optimization from Undaria pinnatifida using conventional heat extraction, bioactivity assays and in silico studies. Antioxidants, 11(7), 1296. [CrossRef]
- Park, E.-J.; Choi, J.-I. Melanogenesis inhibitory effect of low molecular weight fucoidan from Undaria pinnatifida. J. Appl. Phycol. 2017, 29, 2213–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-H.; Kang, S.-M.; Ko, S.-C.; Lee, D.-H.; Jeon, Y.-J. Octaphlorethol A, a novel phenolic compound isolated from a brown alga, Ishige foliacea, increases glucose transporter 4-mediated glucose uptake in skeletal muscle cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 420, 576–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-N.; Yang, H.-M.; Kang, S.-M.; Ahn, G.; Roh, S.W.; Lee, W.; Kim, D.; Jeon, Y.-J. Whitening Effect of Octaphlorethol A Isolated from Ishige foliacea in an In Vivo Zebrafish Model. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 25, 448–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lajis, A.F.B.; Ariff, A.B. Discovery of new depigmenting compounds and their efficacy to treat hyperpigmentation: Evidence from in vitro study. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2019, 18, 703–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haggag, Y.A.; Elrahman, A.A.A.; Ulber, R.; Zayed, A. Fucoidan in Pharmaceutical Formulations: A Comprehensive Review for Smart Drug Delivery Systems. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, B.; Chen, K.; Tong, Z.; Chen, L.; Chen, Q.; Su, J. Advances in Fucoxanthin Research for the Prevention and Treatment of Inflammation-Related Diseases. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natsume, C.; Aoki, N.; Aoyama, T.; Senda, K.; Matsui, M.; Ikegami, A.; Tanaka, K.; Azuma, Y.-T.; Fujita, T. Fucoxanthin Ameliorates Atopic Dermatitis Symptoms by Regulating Keratinocytes and Regulatory Innate Lymphoid Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Jimenez, A.; Teruel-Puche, J.A.; Berna, J.; Rodriguez-Lopez, J.N.; Tudela, J.; Garcia-Ruiz, P.A.; Garcia-Canovas, F. Characterization of the action of tyrosinase on resorcinols. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2016, 24, 4434–4443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.-J.; Lin, C.-C.; Lu, T.-M.; Li, J.-H.; Chen, I.-S.; Kuo, Y.-H.; Ko, H.-H. Chemical constituents derived from Artocarpus xanthocarpus as inhibitors of melanin biosynthesis. Phytochemistry 2015, 117, 424–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamahara, M.; Sugimura, K.; Kumagai, A.; Fuchino, H.; Kuroi, A.; Kagawa, M.; Itoh, Y.; Kawahara, H.; Nagaoka, Y.; Iida, O.; et al. Callicarpa longissima extract, carnosol-rich, potently inhibits melanogenesis in B16F10 melanoma cells. J. Nat. Med. 2015, 70, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustapha, N.; Bzéouich, I.M.; Ghedira, K.; Hennebelle, T.; Chekir-Ghedira, L. Compounds isolated from the aerial part of Crataegus azarolus inhibit growth of B16F10 melanoma cells and exert a potent inhibition of the melanin synthesis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2015, 69, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, J.H.; Nam, D.-Y.; Lee, D.-U. Valencene from the Rhizomes of Cyperus rotundus Inhibits Skin Photoaging-Related Ion Channels and UV-Induced Melanogenesis in B16F10 Melanoma Cells. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 1091–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, K. S., Lee, J. Y., Hyun, S. K., Kim, B. W., & Kwon, H. J. (2015). Juniperus chinensis and the functional compounds, cedrol and widdrol, ameliorate α-melanocyte stimulating hormone-induced melanin formation in B16F10 cells. Food Science and Biotechnology, 24, 611-618.
- de Freitas, M.M.; Fontes, P.R.; Souza, P.M.; William Fagg, C.; Neves Silva Guerra, E.; de Medeiros Nóbrega, Y.K.; Silveira, D.; Fonseca-Bazzo, Y.; Simeoni, L.A.; Homem-de-Mello, M.; et al. Extracts of Morus nigra L. Leaves Standardized in Chlorogenic Acid, Rutin and Isoquercitrin: Tyrosinase Inhibition and Cytotoxicity. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanlayavattanakul, M.; Lourith, N.; Chaikul, P. Jasmine rice panicle: A safe and efficient natural ingredient for skin aging treatments. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 193, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lourith, N.; Kanlayavattanakul, M.; Chingunpitak, J. Development of sunscreen products containing passion fruit seed extract. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallam, A.; Mira, A.; Ashour, A.; Shimizu, K. Acetylcholine esterase inhibitors and melanin synthesis inhibitors from Salvia officinalis. Phytomedicine 2016, 23, 1005–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srisayam, M.; Weerapreeyakul, N.; Barusrux, S.; Kanokmedhakul, K. Antioxidant, antimelanogenic, and skin-protective effect of sesamol. 2014, 65, 69–79. [Google Scholar]
- Diwakar, G.; Rana, J.; Saito, L.; Vredeveld, D.; Zemaitis, D.; Scholten, J. Inhibitory effect of a novel combination of Salvia hispanica (chia) seed and Punica granatum (pomegranate) fruit extracts on melanin production. Fitoterapia 2014, 97, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourith, N.; Kanlayavattanakul, M.; Chaikul, P.; Chansriniyom, C.; Bunwatcharaphansakun, P. In vitro and cellular activities of the selected fruits residues for skin aging treatment. An. Da Acad. Bras. De Ciências 2017, 89, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Class | Generic name | Brand names ® | Dosage form |
|---|---|---|---|
| Topical steroids | Betamethasone | Etnovate, Diprolene, Luxiq, Beta-Val, Diprolene AF | Cream, gel, ointment, lotion |
| Clobetasol | Dermovate, Clobex, Olux, Olux-E, Temovate, Clobevate, Clodan, Cormax, Cormax Scalp, Embeline, Embeline E, Impeklo, Tovet | Solution, spray, ointment, gel, foam, lotion, cream, shampoo | |
| Triamcinolone acetonide | DermasilkRx SDS Pak, Dermasorb TA , DermaWerx SDS Pak, Kenalog , Oralone , Trianex , Triderm | Cream, ointment | |
| Topical anti-infectives | Silver topical | SilvaSorb, Aceso Ag, Solox | Cream, gel, foam |
| Topical steroids with anti-infectives | Dimethicone and triamcinolone topical | Yaliira Pak, Ellzia Pak, TriaDime-80, TriHeal-80 | Creams, shampoos, powders, gels |
| Topical depigmenting agents | Fluocinolone, hydroquinone and tretinoin topical | Tri-Luma, Triderma | Cream |
| Hydroquinone topical | Melquin HP, Alera, EpiQuin Micro, Esoterica, Hydro-Q, Melamin, Melpaque HP, Nuquin HP, AMBI Fade, Blanche, Esoterica Nighttime, Glytone, Lustra-Ultra, Melamin-C, NeoStrata HQ Skin Lightening, Olivia Quido, Fade cream, Remergent HQ | Cream | |
| Topical keratolytics | Salicylic acid topical | Bensal HP, KeralytGel, Salex, Acnex, Aliclen, DHS Salicylic Acid 3%, Durasal, Keralyt Shampoo, Stri-Dex, Akurza, DermalZone, Dr Scholl's, Fostex, Freezeone, Rayasal, Salvax, Stridex, | Liquid, soap, cream, lotion, foam |
| Podophyllum resin topical | Podocon-25, Podofin, Pododerm | Topical solution | |
| Podofilox topical | Condylox | Topical gel, topical solution |
| Name of plant | Family | Growth place | Active compounds |
|---|---|---|---|
| Angelica sinensis [194] | Apiaceae | East Asia | 4-ethylresorcinol, 4-ethylphenol, 1-tetradecalnol |
| Artocarpus [195] | Moraceae | Southeast Asia | Artocarpin, cudraflavone C, artocarpanone |
| Callicarpa longissima [196] | Lamiaceae | Southeast Asia | Carnosol |
| Crataegus azarolus [197] | Rosaceae | European | Ursolic acid, hyperoside, virtexin-2″-O-rhamnoside |
| Cyperus rotundus [198] | Cyperaceae | Africa, France, Austria, southern Asia | Valencene, camphene, carryophyllene oxide |
| Juniperus chinensis [199] | Cupressaceae | China, Myanmar, Russian, Korea | Widdrol |
| Morus nigra [200] | Moraceae | Iberian Peninsula | Isoquercitrin, rutin, chlorogenic acid |
| Oryza sativa [201] | Poaceae | China | p-coumaric, ferulic |
| Passiflora edulis [202] | Passifloraceae | Brazil, Paraguay, Argentina | Piceatannol, resveratrol, quercetin |
| Salvia officinalis [203] | Lamiaceae | Mediterranean region | 7a-methoxyrosmanol, isorosmanol |
| Sesamum indicum [204] | Pedaliaceae | Africa, India | Sesamol |
| Punica granatum [205] | Lythraceae | Mediterranean | Punicalgin |
| Litchi chinensis [206] | Sapindaceae | China, India, Bangladesh, Vietnam, Thailand, Malaysia, Indonesia, Pakistan, Cambodia, Bangladesh, Himalayas | Rosmarinc acid, gallic acid |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





