Submitted:
17 May 2023
Posted:
17 May 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Clinical case
3. Clinical efficacy of ICB in lymphomas
3.1. Classical Hodgkin lymphoma(cHL)
3.1.1. PD-1/PD-L1 ICB as monotherapy
3.1.2. PD-1/PD-L1 ICB in combination with chemotherapy
Frontline setting
Relapsed / refractory setting
3.1.3. PD-1/PD-L1 ICB combined with other agents
| Lymphoma Subtype | Studies | N | Study population | Therapy | ORR (%) | CR (%) | Median PFS(months) | Median OS (months) | Median follow-up (months) | Specificities |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Classical Hodgkin lymphoma (cHL) | Ansell 2015, [11,20] Phase 1 | 23 | R/R (prior ASCT or allo-SCT) | Nivolumab 3mg/kg q2wks* | 87 | 17 | NR† (86% at 6 months) | NR† | 21.5 | |
| Maruyama 2017, 2020, [21,22]Phase 2 | 17 | R/R (prior ASCT and BV) | Nivolumab 3mg/kg q2wks* | 88 | 31 | 11.7 (60% at 6 months) | NR (80% at 3-year) | 38.8 | ||
| KEYNOTE-013, Armand 2016, 2020 et al., [23,24], Phase 2B | 31 | R/R after BV failure | Pembrolizumab 10 mg/kg q2wks* | 58 | 19 | 11.4 (30% at 2 year) | NR(81% at 3-year) | 52.8 | ||
| CheckMate 205, Younes 2016, Armand 2018, Ansell 2021, [10,25,26,27], Cohort A, B, C, Phase 2 | 243 | R/R after:A. ASCT (n = 63)B. ASCT + BV (n = 80)C. BV + ASCT ± BV (n = 100) | Nivolumab 3 mg/kg q2wks* | 71 | 21 | 15 (18% at 5-year) | NR(71% at 5-year) | 58 | ||
| KEYNOTE-087, Ansell 2017, Chen 2019, Chen 2021, [12,28,29], Phase 2 | 210 | R/R after:A. ASCT + BV (n = 69)B. Salvage chemo + BV (n = 89) ( ineligibility for SCT owing to chemorefractory disease) C. ASCT (n = 60) | Pembrolizumab 200 mg q3wks* | 71 | 28 | 13.7 (14% at 5-year) | NR(71% at 5-year) | 62.9 | ||
| KEYNOTE-204, Kuruvilla 2021, [32], Phase 3 | 304 | R/R (ineligible or relapsed after ASCT) | Pembrolizumab 200 mg q3wks versus BV 1.8 mg/kg q3wks* | Pembrolizumab: 66BV: 54 | Pembrolizumab: 25BV: 24 | 13.2 (for pembrolizumab) 8.3 (for BV) | NA | 25.7 | ||
| JAVELIN Hodgkin trial, Herrera 2021, [43], Phase 1B | 31 | R/R (ineligible or relapsed after ASCT) | Avelumab with four dose levels and 2 dosing schedules (q2wks or q3wks) | 42 | 19 | 5.7 (18% at 1-year) | NA | NA | Dose levels/schedules: 70, 350, and 500 mg q2wks; 500 mg q3wks; 10 mg/kg q2wks | |
| Song 2019, Song 2022, [39,40], Phase 2 | 70 | R/R (ineligible or relapsed after ASCT) | Tislelizumab 200 mg q3wks* | 87 | 67 | 31.5 (41% at 3-year) | NR(85% at 3-year) | 33.8 | ||
| Song 2019, Wu 2021, [35,36], Phase 2 | 75 | R/R (ineligible or relapsed after ASCT) | Camrelizumab 200 mg q2wks* | 76 | 28 | 22.5 (67% at 1-year) | NR(83% at 3-year) | 36.2 | ||
| Nie 2019, Liu 2021, [37,38], Cohort 1 Phase 2 | 19 | R/R after more than 2 therapies lines, anti-PD1 naïve | Camrelizumab 200 mg q3wks monotherapy* | 90 | 32 | 15.5 (42% at 2-year) | NR (63% at 2-year) | 34.5 | ||
| ORIENT-1, Shi 2019, Su 2020, [33,34],Phase II | 96 | R/R after more than 2 therapies lines (including ASCT) | Sintilimab 200mg q2wks* | 80 | 29 | 18.6 (78% at 6 months) | NR(96% at 2-year) | 26.7 | ||
| Armand 2019, [62], Phase II | 30 | R/R after ASCT | Pembrolizumab 200 mg q3wks × 8 cycles as maintenance after ASCT | NA | NA | NR (82% at 18 months) | NR (100% at 18 months) | NA | ||
| Song 2022, [42], Phase I/II | 85 | R/R (including ASCT) | Penpulimab 200mg q2wks* (maximum of 24 months) | 89 | 47 | NR (72% at 1 year) | NR (100% at 18 months) | 15.8 | ||
| Lin 2022, [41], Phase II | 85 | R/R (including ASCT) | Zimberelimab (GLS-010) q2wks* (maximum of 24 months) | 91 | 33 | NR (78% at 1 year) | NR (99% at 1 year) | 15.8 | ||
| Follicular lymphoma (FL) | Barraclough 2019, Hawkes 2021, [110,111], Phase 2 | 39 | Newly diagnosed, stage III-IV, grade 1-3a FL | Nivolumab 240mg 2-weekly × 4 cyclesIf CR: N 240mg monotherapy × 4 cycles, maintenance N 480mg 4-weekly × 12 cycles If < CR: N 240mg + rituximab 375mg/m2 2-weekly × 4 cycles, maintenance N+R (N 480mg 4 weekly ×12 cycles; R 12 weekly × 8 cycles). | 92 | 54 | NR (72% at 1 year) | NR (96% at 1 year) | 17.5 | |
| CheckMate 140, Armand 2021, [86],Phase 2R/R | 92 | R/R (after failure of at least 2 prior lines of therapy) | Nivolumab 3 mg/kg q2wks* | 4 | 1 | 2.2 | NA | NA | minimal follow-up of 12 months | |
| Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) | Ansell 2019, [77],Phase 2 | 121 | R/R (ineligible or relapsed after ASCT) | Nivolumab 3 mg/kg q2wks* | 10 (all groups)‡ | 3 (all groups)§ | ASCT failed (n = 87):1.9 ASCT ineligible (n = 34): 1.4 | ASCT failed (n = 87):12.2 ASCT ineligible (n = 34): 5.8 | ASCT failed: 9 ASCT ineligible: 6 | |
| Primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma (PMBCL) | KEYNOTE-013, Zinzani 2017, Armand 2019, [14,80] Phase 1B | 21 | R/R PMBCL | Pembrolizumab 10mg/kg (n=11) 200 mg (n= 10) q3wks* | 48 | 33 | 10.4 | 31.4 | 29.1 | |
| KEYNOTE-170, Armand 2019, [14]Phase 2 | 53 | R/R PMBCL | Pembrolizumab 200 mg q3wks* | 45 | 13 | 5.5 | NR | 12.5 | ||
| Extranodal natural killer / T-cell lymphomas (ENKTL) | Kim 2020, [84],Phase 2 | 21 | R/R ENKTL | Avelumab 10 mg/kg q2wks* | 38 | 24 | 2.7 | NR | 15.7 | Response significantly associated with the expression of PD-L1 by tumor tissue |
| ORIENT-4, Tao 2021, [85],Phase 2 | 28 | R/R ENKTL | Sintilimab 200 mg q3wks* | 75 | 21 | NA | NR(79% at 2 year) | 30.4 | ||
| Hematologic malignancies | Lesokhin 2016, [76],Phase 1 | 81 | R/R B-cell lymphoma, TCL, MM (inclusive after ASCT) | Nivolumab 1 or 3mg/kg q2wks* | FL (n = 10): 40DLBCL (n = 11): 36TCL (n = 23): 17MM (n = 27): 4 | FL (n = 10): 10DLBCL (n = 11): 18TCL (n = 23): 0MM (n = 27): 4 | FL (n = 10): NRDLBCL (n = 11): 7TCL (n = 23): 10 MM (n = 27): 10 | NA | 16.7 | |
| Frigault 2020, [79],Phase 2 | 29 | R/R DLBCL + PMBCL after ASCT as maintenance | Pembrolizumab 200 mg q3wks × 8 cycles | N/A | 59% at 18 months | NR (59% at 18 months) | NR (93% at 18 months) | NA | ||
| Davids 2020, [78],Phase 1 | 28 | Relapsed hematologic malignancies after allo-SCT | Nivolumab 0.5-3 mg/kg q2wks* | 29 | 4 | 3.7 | 21.4 | 11 | ||
| Ding 2017, [19],Phase 2 | 25 | relapsed or progressive CLL (n=16) + CLL with RT (n=9) | Pembrolizumab 200mg q3wks* | CLL: 0RT: 44 | CLL: 0RT: 11 | CLL: 2.4RT: 5.4 | CLL: 4.3 RT: NR | 11 | ||
| Khodadoust 2020, [207], Phase 2 | 24 | R/R MF (n=9) and SS (n=15) | Pembrolizumab 2 mg/kg q3wks# | MF: 56SS: 27 | MF: 0SS: 7 | MF: 12 SS: 12 | MF: NRSS: NR | NA | ||
| Chong 2018, [100], Phase 1/2 | 12 | R/R B-cell NHL after CAR-T cells therapy | Pembrolizumab 200mg q3wks* | 27 | 9 | NA | NA | NA |
3.2. Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL)
3.2.1. PD-1/PD-L1 ICB as monotherapy
Aggressive NHL
Indolent B NHL
3.2.2. PD-1/PD-L1 ICB in combination with other agents
Aggressive NHL
Relapse / refractory setting
Indolent B NHL
Relapse / refractory setting
| Lymphoma subtype | Studies | N | Study population | Therapy | ORR (%) | CR (%) | Median PFS(months) | Median OS (months) | Median follow-up (months) | Specificities |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Classical Hodgkin lymphoma (cHL) | CheckMate 205, Ramchandren 2019, [44] Cohort D, Phase 2 | 51 | Untreated advanced stage | Nivolumab 240 mg q2wks × 4 doses followed by nivolumab-AVD × 6 cycles | 84 | 67 | NR (92% at 9 months) | NR (98% at 9 months) | 11.1 | |
| NIVAHL Trial, Bröckelmann2022, [45], Phase 2 | 109 | Untreated early stage and unfavorable | Groupe 1: Nivolumab 240 mg q2wks + AVD × 4 cyclesGroupe 2:Nivolumab × 4 cycles monotherapy, nivolumab-AVD × 2 cycles, AVD only × 2 cycles, followed by 30-Gy involved-site radiotherapy | 96 | 87 | NA1: 100% at 1-year2: 98% at 1-year | NA1: 100% at 1-year2: 100% at 1-year | 13 | ||
| Cheson 2020, [50] Phase 2 | 46 | Untreated, > 60 years old or younger and ineligible for chemotherapy | Nivolumab 3 mg/kg + BV 1.8 mg/kg q3wks × 8 cycles | 61 | 48 | 18.3 | NR | 21.2 | ||
| Allen 2021, [46], Phase 2 | 30 | Untreated early unfavorable and advanced-stage | Pembrolizumab 200 mg q3wks for 3 cycles, AVD × 4-6 cycles | 100 | NA | NR | NR | 22.5 | ||
| Nie 2019, Liu 2021 et al., [37,38], Cohort 1 combination, Phase 2 | 67 | R/R after more than 2 therapies lines | Cohort 1 combination; anti-PD1 naïve: (n=42): decitabine (10 mg/d, days 1 to 5) plus camrelizumab 200mg q3wks*Cohort 2 (n=25); anti-PD1 resistant: decitabine plus camrelizumab* | 1: 952: 52 | 1: 712: 28 | 1: 89% at 1-year2: 59% at 1-year | 1: 63% at 2-year2: NA | 34.5 | ||
| Herrera 2019, Mei 2022, [53,54], Phase 2 | 43 | R/R first salvage therapy and bridge to ASCT | Nivolumab 3 mg/kg q2wks × 6 cycles +/- ICE. PET-CT after C3 and C6. After C6, pts in CR: ASCT, not in CR: N-ICE for 2 cycles | 93 | 91 | NA(72% at 2-year) | NA (95% at 2-year) | NA | Among 9 patients who received N-ICE: ORR 100%, CR 89% | |
| Bryan 2021, [55], Phase 2 | 42 | R/R prior to ASCT | Pembrolizumab 200mg q2wks + ICE × 2 cycles, stem cell mobilization/collection, pembrolizumab 200mg × 1 cycle | 97 | NA | 26.9 (88% at 2-year) | NR(95% at 2-year) | 27 | ||
| Diefenbach 2020, [66], Phase 1/2 | 64 | R/R | BV 1.8 mg/kg + ipilimumab 3 mg/kg or nivolumab 3 mg/kg or nivolumab 3 mg/kg and ipilimumab 1 mg/kg* | BV + Ipi76 BV + Nivo89 BV + Ipi/Nivo82 | BV + Ipi57BV + Nivo61BV + Ipi/Nivo73 | BV + Ipi14.4 (61% at 1 year)BV + NivoNR (70% at 1 year)BV + Ipi/NivoNR (80% at 1 year) | NR | BV + Ipi: 31.2BV + Nivo: 28.8BV + Ipi/Nivo: 20.4 | ||
| Sermer 2020, Sermer 2021, [67,68], Phase 2 | 22 | R/R (heavily pretreated, previous ICB therapy accepted) | Entinostat 5-7 mg orally q1wks + pembrolizumab 200mg q3wks | 86 | 45 | NA (72% at 1 year) | NA | 8.4 | ||
| Lepik 2020, [61], Phase 2 | 30 | R/R after Nivolumab monotherapy | Nivolumab 3 mg/kg on D1,14 + bendamustine (90 mg/m2) on D1, 2 of a 28-day cycle for up to 3 cycles | 87 | 57 | 10.2 (23% at 2 year) | NA(97% at 2 year) | 25 | ||
| Herrera 2018, Advani 2021, [51,52] Phase 1/2 | 62 | R/R in initial salvage therapy before ASCT | BV + Nivolumab 3 mg/kg q3wks × 4 cycles | 82 | 61 | NR (77% at 3 year) | NR (93% at 3 year) | 34.3 | ||
| Moskowitz 2021, [56], Phase 2 | 38 | R/R after first line therapy, prior to ASCT | Pembrolizumab 200 mg + GVD q3wks × 2-4 cycles | 100 | 95 | NA | NA | 13.5 | ||
| Ansell 2019, Bartlett 2020, [69,70], Phase 1B | 24 | R/R, CD30 positive, 3-7 prior lines of therapy including BV | Pembrolizumab 200 mg q3wks + AFM13 dose escalation schedules | 83 | 37 | NA (77% at 6 months) | NA | NA | ||
| Dave 2022, [71], Phase 1 | 10 | R/R inclusive after ASCT, allo-SCT, BV, prior ICB) (n=8 active disease, n=2 adjuvant after ASCT) | TAA-Ts + Nivolumabin 6 patients* | 1 CR7 SD at 3 months | 41 (adjuvant arm) and 12.6 (active disease arm) | Nivolumab priming impacted TAA-T recognition and persistence. | ||||
| CheckMate 039, Ansell 2016, Armand 2021, [64,65], Phase 1B | 52 | R/R after ≥2 prior lines of therapy, independent of ASCT | Nivolumab 3 mg/kg + ipilimumab 1 mg/kg q3wks or nivolumab 3 mg/kg + lirilumab 3 mg/kg q4wks* | Nivo/Ipi:(n = 31)74 Nivo/Liri (n = 21): 76 | Nivo/Ipi:(n = 31)23Nivo/Liri: (n = 21):24 | Nivo/Ipi: NRNivo/Liri:NR | NA | Nivo/Ipi : 18Nivo/Liri: 11 | ||
| Timmerman 2022, [75], Phase I/II (cohort 2) | 29 | R/R after anti-PD1 therapy | Favezelimab 800mg q3wks + pembrolizumab 20mmg q3wks for up to 35 cycles | 31 | 7 | 9 (39% at 1 year) | 26 (91% at 1 year) | N/A | ||
| Follicular lymphoma (FL) | Younes 2017, Younes 2022, [112,113]Phase 1/2 | 40 | FL grade 1, 2 or 3a disease requiring therapy | Obinutuzumab 1000 mg on days 1, 8 and 15 of cycle 1 and day 1 of cycles 2-6, bendamustine 90 mg/m2 on days 1 and 2 of cycles 1-6, and atezolizumab 840 mg on days 1 and 15 of cycles 2-6 (28-day cycles).Maintenance in pts with CR or PR consisted of obinu 1000 mg on day 1 of every other month and atezo 840 mg on days 1 and 2 of each month* | NA | 75% | NA (81% at 3 year) | NA (89% at 3 year) | 40.4 | Grade 5 (fatal) adverse events reported in five patients |
| Westin 2014, [116], Phase 2 | 30 | Relapsed FL rituximab sensible | Rituximab 375 mg/m2 weekly for 1 cycle + pidilizumab 3 mg/kg q4wks for 12 doses | 66 | 52 | 18.8 | NA | 15.4 | ||
| Nastoupil 2017, Nastoupil 2022, [114,115],Phase 2 | 30 | Relapsed FL rituximab sensible | Pembrolizumab 200 mg q3wks for up to 16 cycles + rituximab 375 mg/m2 weekly for 1 cycle | 67 | 50 | 12.6 | NR (97% at 3 year) | 35 | ||
| Morschhauser 2021, [117],Phase 1B/2 | 32 | R/R FL (grade 1–3a) | Obinutuzumab 1000 mg + atezolizumab 840 mg + lenalidomide 15mg (in the expansion phase) or 20mg × 6 cycles, if CR/PR/SD maintenance* | 78 (at the end of the induction) | 72 (at the end of the induction) | NA (68% at 3 year) | NA (90% at 3 year) | 30 (lenalidomide 15mg)14.2 (lenalidomide 20mg) | ||
| Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) | Younes 2018, Younes 2019,[89,90],Phase 1/2 | 40 | Untreated advanced DLBCL | atezolizumab 1200mg q3wks + R-CHOP × 8 cycles | NA | 78 | NA (75% at 2 year) | NA (86% at 2 year) | 21.3 | |
| Smith 2020, [91],Phase 1 | 30 | Untreated DLBCL or grade 3b FL | Pembrolizumab 200 mg + R-CHOP q3wks × 6 cycles | 90 | 77 | NA (83% at 2 year) | NA (84% at 2 year) | 25.5 | ||
| Nowakowski 2022, [92],Phase 2 | 37 | High-risk DLBCL (IPI ≥3/NCCN-IPI ≥4) | Durvalumab 1125mg q3wks+ R-CHOP × 6-8 cycles, then durvalumab consolidation* | 97 | 68 | NA (68% at 1 year) | NA | NA | ||
| Palomba 2022,[103],Phase 1B | 43 | R/R DLBCL | Atezolizumab 1200 mg + tazemetostat 800 mg orally twice daily q3wks | 16 | 7 | 2 | 13 | 23.7 | ||
| ZUMA 6, Jacobson 2020, [97],Phase 1/2 | 28 | R/R DLBCL | Atezolizumab 1200mg + KTE-C19 (axi-cel) | 75 | 46 | NR | NR | 10.2 | ||
| PORTIA trial, Jäger 2021, [99],Phase 1B | 12 | R/R DLBCL | Pembrolizumab q3wks for up to 6 doses either days +15, +8, or –1 of tisagenlecleucel | Days+15: 50 Days+825 Days-125 | Days+15: 0Days+8 25Days-125 | NA | NA | 4 | ||
| Witzig 2019, [94],Phase 1/2 | 61 | R/R DLBCL | Pembrolizumab 200mg q3wks + acalabrutinib 100mg BID* | 26 | 7 | 1.9 | NA | NA | ||
| Alexander trial, Osborne 2020, [102],Phase 1 | 29 | R/R DLBCL | Pembrolizumab 200mg q3wks + AUTO3 (bispecific CAR T targeting CD19/22) | 69 | 52 | NA | NA | NA | ||
| Primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma (PMBCL) | CheckMate 436, Zinzani 2019, Zinzani 2021, [107,108],Phase 2 | 30 | R/R PMBCL | Nivolumab 240 mg and BV 1.8 mg/kg q3wks* | 73 | 37 | 26 (56% at 1 and 2 year) | NR (76% at 2 year) | 11.1 | |
| Multiple hematologic malignancies | CheckMate 039, Ansell 2016, Armand 2021, [64,65], Phase 1B | 78 | R/R hematologic malignancies (≥2 prior lines of therapy) independent of ASCT | Nivolumab 3 mg/kg + ipilimumab 1 mg/kg q3wks or nivolumab 3 mg/kg + lirilumab 3 mg/kg q4wks* | Nivo/Ipi: B-NHL(n = 16)19 T-NHL (n=11): 9Nivo/Liri B-NHL (n = 32): 13 T-NHL (n=11): 22 | Nivo/Ipi: B-NHL(n = 16)6T-NHL (n=11): 0Nivo/Liri B-NHL (n = 32):3T-NHL (n=11): 0 | Nivo/Ipi: B-NHL(n = 16)1 T-NHL (n=11): 2Nivo/Liri B-NHL (n = 32): 1T-NHL (n=11): 6 | NA | Nivo/Ipi : 18Nivo/Liri: 11 | |
| Younes 2019, [93],Phase 1/2A | 141 | R/R CLL, SLL, FL, DLBCL | Ibrutinib + nivolumab 3 mg/kg q2wks* | CLL/SLL (n = 36):61, FL (n = 40):33, DLBCL (n = 45):36RT (n = 20):65 | CLL/SLL (n = 36):0FL (n = 40):10DLBCL (n = 45):16RT (n = 20):10 | CLL/SLL (n = 36): NRFL (n = 40):9.1 DLBCL (n = 45):2.6 RT (n = 20):5.0 | CLL/SLL (n = 36): NRFL (n = 40):NRDLBCL (n = 45):13.5 RT (n = 20): 10.3 | 19.7 | ||
| Palomba 2022, [105],Phase 1B | 49 | R/R FL + R/R DLBCL | Atezolizumab 1200 mg + obinutuzumab 1000 mg | FL (n = 26): 54DLBCL(n = 23): 17 | FL (n = 26):23DLBCL(n = 23): 4 | FL (n = 26): 9 DLBCL(n = 23): 3 | FL (n = 26): NADLBCL (n = 23): 9 | NA | ||
| Jain 2016, Jain 2018, [118,119],Phase 2(cohort 1) | 28 | R/R FL + RT | Nivolumab 3 mg/kg q2wks × 24 cycles + ibrutinib 420 mg* | FL (n=5): 60RT (n = 23): 43 | FL (n=5): 0RT (n = 23): 35 | FL (n=5): NRRT (n = 23): NA | FL (n=5): NRRT (n = 23): 13.8 | NA | ||
| LYSA trial, Herbaux 2020, Herbaux 2021, [87,104], Phase 2 | 136 | R/R DLBCL (cohort 1) and R/R iNHL (FL + MZL) (cohort 2) | Obinutuzumab 1 g × 8 cycles + atezolizumab 1.2 g q3wks × 24 cycles + venetoclax 800mg/j (on D8) × 24 cycles | DLBCL (n=58):24FL (n=58):54MZL (n=20): 67 | DLBCL (n=58):18FL (n=58):30MZL (n=20):17 | NA | NA | DLBCL: 9FL: 14.5MZL: 11.9 | ||
| Hutchings 2019, [106],Phase 1B | 36 | R/R B- NHL (DLBCL, transformed FL, MCL, PMBCL, LPL, iNHL) | Atezolizumab 1200mg + CD-20-TCB antibody (RG6026) q3wks | 36 | 17 | NA | NA | NA | Ongoing trial | |
| KEYNOTE-155, Gregory 2022, [95],Phase 1B | 72 | R/R hematologic malignancies | Pembrolizumab 200 q3wks + dinaciclib (dose escalation)* | CLL (n = 17): 29 DLBCL (n = 38): 21 MM (n = 17): 0 | CLL (n = 17): 0DLBCL (n = 38): 11MM (n = 17): 0 | CLL (n = 17): 5.2 DLBCL (n = 38): 2.1 MM (n = 17): 1.6 | CLL (n = 17): 21.7 DLBCL (n = 38): 7.9 MM (n = 17): 10.5 | NA | Dinaciclib dose levels (7 mg/m2, 10 mg/m2, 14mg/m2) | |
| Herrera 2020, [96],Phase 1/2 | 61 | R/R FL + R/R DLBCL | Durvalumab 10 mg/kg q2wks + ibrutinib 560mg once daily (dosing according to phase 1B)* | FL (n=29): 26 Non-GCB DLBCL (n=16): 38GCB-DLBCL (n=16): 13 | FL (n=29): 4Non-GCB DLBCL (n=16): 31GCB-DLBCL (n=16): 6 | FL (n=29): 10.2 Non-GCB DLBCL (n=16): 4.1GCB-DLBCL (n=16): 2.9 | FL (n=29): NR Non-GCB DLBCL (n=16): 7.3GCB-DLBCL (n=16): 5.5 | FL: 17DLBCL: 17.5 | ||
| Hirayama 2020, [101],Phase 1 | 13 | R/R B-cell NHL | Durvalumab dose escalation up to 10 doses + JCAR014 (CD19-specific 4-1BB-costimulated CAR-T cells) | 50 | 42 | NA | NA | NA | Durvalumab dose escalation ongoing | |
| Panayiotidis 2022, [88],Phase 2 | 55 | R/R MCL, WM, MZL | Atezolizumab + obinutuzumab (MCL+WM) or rituximab (MZL) | MCL (n = 30): 17WM (n = 4): 0MZL (n = 21): 43 | NA | NA | NA | NA | ||
| Sang 2022, [72], Phase II | 12 | R/R CD30+ lymphoma (9 cHL, 1 angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma (AITL), 2 gray zone lymphoma) | Cohort 1: 106/kg of CD30 CAR-Ts Cohort 2: 107/kg of CD30 CAR-Ts Cohort 3: 107/kg of CD30 CAR-Ts + anti-PD-1 antibody q3wks starting 14 days after CAR-T cell infusion† | 92(Cohort 1&2: 86%; Cohort 3: 100%) | 70 (Cohort 1&2: 27%; Cohort 3: 80%) | 45 | 70 | 21.5 | Anti-PD1 treatment not mentionned |
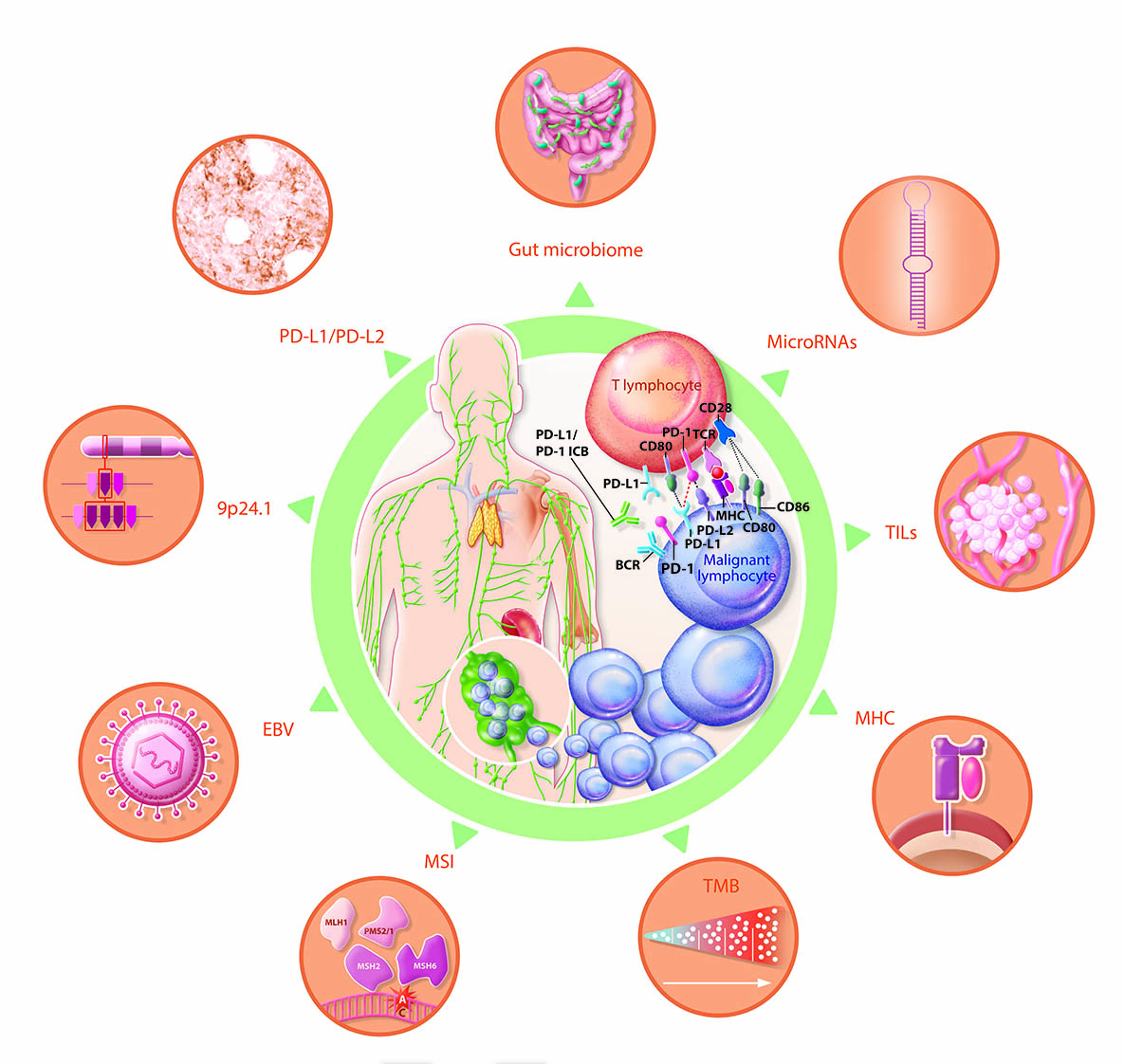
4. Predictive biomarkers of response to ICB in lymphoma
4.1. Tissue expression and plasma levels of PD-Ls
4.1.2. PD-L1 expression
4.1.2. PD-L2 expression
4.2.9. p24.1 gene alterations
4.3. Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) and JAK/STAT signaling pathway
4.4. Tissue tumor mutational burden (TMB) and plasma tumor mutational burden (pTMB)
4.5. MSI and d-MMR
4.6. MHC expression
4.7. Intra-tumoral CD8+ T lymphocyte infiltrate density
4.8. MicroRNAs
4.9. Gut microbiome
5. Conclusion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goodman AM, Kato S, Bazhenova L, Patel SP, Frampton GM, Miller V, et al. Tumor Mutational Burden as an Independent Predictor of Response to Immunotherapy in Diverse Cancers. Mol Cancer Ther. 2017 Nov;16(11):2598–608.
- Arneth, B. Tumor Microenvironment. Medicina (Mex). 2019 Dec 30;56(1):15.
- Armengol M, Santos JC, Fernández-Serrano M, Profitós-Pelejà N, Ribeiro ML, Roué G. Immune-Checkpoint Inhibitors in B-Cell Lymphoma. Cancers. 2021 Jan 8;13(2):214.
- Petitprez F, Meylan M, de Reyniès A, Sautès-Fridman C, Fridman WH. The Tumor Microenvironment in the Response to Immune Checkpoint Blockade Therapies. Front Immunol. 2020 ;11:784. 7 May.
- Pardoll, DM. The blockade of immune checkpoints in cancer immunotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2012 Apr;12(4):252–64.
- Kyi C, Postow MA. Immune checkpoint inhibitor combinations in solid tumors: opportunities and challenges. Immunotherapy. 2016 Jun;8(7):821–37.
- et al. Gravelle et al. - 2017 - Mechanisms of PD-1PD-L1 expression and prognostic.pdf.
- Keir ME, Butte MJ, Freeman GJ, Sharpe AH. PD-1 and Its Ligands in Tolerance and Immunity. Annu Rev Immunol. 2008 Apr 1;26(1):677–704.
- Xie W, Medeiros LJ, Li S, Yin CC, Khoury JD, Xu J. PD-1/PD-L1 Pathway and Its Blockade in Patients with Classic Hodgkin Lymphoma and Non-Hodgkin Large-Cell Lymphomas. Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 2020 Aug;15(4):372–81.
- Younes A, Santoro A, Shipp M, Zinzani PL, Timmerman JM, Ansell S, et al. Nivolumab for classical Hodgkin’s lymphoma after failure of both autologous stem-cell transplantation and brentuximab vedotin: a multicentre, multicohort, single-arm phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016 Sep;17(9):1283–94.
- Ansell S, Armand P, Timmerman JM, Shipp MA, Bradley Garelik MB, Zhu L, et al. Nivolumab in Patients (Pts) with Relapsed or Refractory Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma (R/R cHL): Clinical Outcomes from Extended Follow-up of a Phase 1 Study (CA209-039). Blood. 2015 Dec 3;126(23):583–583.
- Chen R, Zinzani PL, Fanale MA, Armand P, Johnson NA, Brice P, et al. Phase II Study of the Efficacy and Safety of Pembrolizumab for Relapsed/Refractory Classic Hodgkin Lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2017 Jul 1;35(19):2125–32.
- Ok CY, Young KH. Targeting the programmed death-1 pathway in lymphoid neoplasms. Cancer Treat Rev. 2017 Mar;54:99–109.
- Armand P, Rodig S, Melnichenko V, Thieblemont C, Bouabdallah K, Tumyan G, et al. Pembrolizumab in Relapsed or Refractory Primary Mediastinal Large B-Cell Lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2019 Dec 1;37(34):3291–9.
- Nayak L, Iwamoto FM, LaCasce A, Mukundan S, Roemer MGM, Chapuy B, et al. PD-1 blockade with nivolumab in relapsed/refractory primary central nervous system and testicular lymphoma. Blood. 2017 Jun 8;129(23):3071–3.
- Zhou H, Xu-Monette ZY, Xiao L, Strati P, Hagemeister FB, He Y, et al. Prognostic factors, therapeutic approaches, and distinct immunobiologic features in patients with primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma on long-term follow-up. Blood Cancer J. 2020 ;10(5):49. 4 May.
- Riemersma SA, Oudejans JJ, Vonk MJ, Dreef EJ, Prins FA, Jansen PM, et al. High numbers of tumour-infiltrating activated cytotoxic T lymphocytes, and frequent loss of HLA class I and II expression, are features of aggressive B cell lymphomas of the brain and testis. J Pathol. 2005 Jul;206(3):328–36.
- Chen X, Song X, Li K, Zhang T. FcγR-Binding Is an Important Functional Attribute for Immune Checkpoint Antibodies in Cancer Immunotherapy. Front Immunol. 2019 Feb 26;10:292.
- Ding W, LaPlant BR, Call TG, Parikh SA, Leis JF, He R, et al. Pembrolizumab in patients with CLL and Richter transformation or with relapsed CLL. Blood. 2017 Jun 29;129(26):3419–27.
- Ansell SM, Lesokhin AM, Borrello I, Halwani A, Scott EC, Gutierrez M, et al. PD-1 Blockade with Nivolumab in Relapsed or Refractory Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2015 Jan 22;372(4):311–9.
- Maruyama D, Hatake K, Kinoshita T, Fukuhara N, Choi I, Taniwaki M, et al. Multicenter phase II study of nivolumab in Japanese patients with relapsed or refractory classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Cancer Sci. 2017 May;108(5):1007–12.
- Maruyama D, Terui Y, Yamamoto K, Fukuhara N, Choi I, Kuroda J, et al. Final results of a phase II study of nivolumab in Japanese patients with relapsed or refractory classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2020 Oct 22;50(11):1265–73.
- Armand P, Shipp MA, Ribrag V, Michot JM, Zinzani PL, Kuruvilla J, et al. Programmed Death-1 Blockade With Pembrolizumab in Patients With Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma After Brentuximab Vedotin Failure. J Clin Oncol. 2016 Nov 1;34(31):3733–9.
- Armand P, Kuruvilla J, Michot JM, Ribrag V, Zinzani PL, Zhu Y, et al. KEYNOTE-013 4-year follow-up of pembrolizumab in classical Hodgkin lymphoma after brentuximab vedotin failure. Blood Adv. 2020 Jun 23;4(12):2617–22.
- Armand P, Engert A, Younes A, Fanale M, Santoro A, Zinzani PL, et al. Nivolumab for Relapsed/Refractory Classic Hodgkin Lymphoma After Failure of Autologous Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation: Extended Follow-Up of the Multicohort Single-Arm Phase II CheckMate 205 Trial. J Clin Oncol. 2018 ;36(14):1428–39. 10 May.
- Armand P, Engert A, Younes A, Lee HJ, Santoro A, Zinzani PL, et al. Nivolumab for Relapsed or Refractory Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma (cHL) after Autologous Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation (auto-HCT): Extended Follow-up of the Phase 2 Single-Arm CheckMate 205 Study. Blood. 2018 Nov 29;132(Supplement 1):2897–2897.
- Ansell S, Bröckelmann P, von Keudell G, Lee HJ, Santoro A, Zinzani PL, et al. HL-398: Five-Year Overall Survival from the CheckMate 205 Study of Nivolumab for Relapsed or Refractory (R/R) Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma (cHL). Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2021 Sep;21:S373–4.
- Chen R, Zinzani PL, Lee HJ, Armand P, Johnson NA, Brice P, et al. Pembrolizumab in relapsed or refractory Hodgkin lymphoma: 2-year follow-up of KEYNOTE-087. Blood. 2019 Oct 3;134(14):1144–53.
- Armand P, Zinzani PLL, Lee HJ, Johnson N, Brice P, Radford J, et al. Five-Year Follow-up of Keynote-087: Pembrolizumab Monotherapy in Relapsed/Refractory Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma (R/R cHL). Blood. 2021 Nov 5;138(Supplement 1):1366–1366.
- Zinzani PL, Chen R, Armand P, Johnson NA, Brice P, Radford J, et al. Pembrolizumab monotherapy in patients with primary refractory classical hodgkin lymphoma who relapsed after salvage autologous stem cell transplantation and/or brentuximab vedotin therapy: KEYNOTE-087 subgroup analysis. Leuk Lymphoma. 2020 Mar 20;61(4):950–4.
- Vaddepally RK, Kharel P, Pandey R, Garje R, Chandra AB. Review of Indications of FDA-Approved Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors per NCCN Guidelines with the Level of Evidence. Cancers. 2020 Mar 20;12(3):738.
- Kuruvilla J, Ramchandren R, Santoro A, Paszkiewicz-Kozik E, Gasiorowski R, Johnson NA, et al. Pembrolizumab versus brentuximab vedotin in relapsed or refractory classical Hodgkin lymphoma (KEYNOTE-204): an interim analysis of a multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2021 Apr;22(4):512–24.
- Shi Y, Su H, Song Y, Jiang W, Sun X, Qian W, et al. Safety and activity of sintilimab in patients with relapsed or refractory classical Hodgkin lymphoma (ORIENT-1): a multicentre, single-arm, phase 2 trial. Lancet Haematol. 2019 Jan;6(1):e12–9.
- Su H, Song Y, Jiang W, Sun X, Qian W, Zhang W, et al. Sintilimab for relapsed/refractory classical Hodgkin’s lymphoma: Long-term follow-up on the multicenter, single-arm phase II ORIENT-1 study. J Clin Oncol. 2020 ;38(15_suppl):8034–8034. 20 May.
- Song Y, Wu J, Chen X, Lin T, Cao J, Liu Y, et al. A Single-Arm, Multicenter, Phase II Study of Camrelizumab in Relapsed or Refractory Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Dec 15;25(24):7363–9.
- Wu J, Song Y, Chen X, Lin T, Cao J, Liu Y, et al. Camrelizumab for relapsed or refractory classical Hodgkin lymphoma: Extended follow-up of the multicenter, single-arm, Phase 2 study. Int J Cancer. 2022 Mar 15;150(6):984–92.
- Nie J, Wang C, Liu Y, Yang Q, Mei Q, Dong L, et al. Addition of Low-Dose Decitabine to Anti–PD-1 Antibody Camrelizumab in Relapsed/Refractory Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2019 Jun 10;37(17):1479–89.
- Liu Y, Wang C, Li X, Dong L, Yang Q, Chen M, et al. Improved clinical outcome in a randomized phase II study of anti-PD-1 camrelizumab plus decitabine in relapsed/refractory Hodgkin lymphoma. J Immunother Cancer. 2021 Apr;9(4):e002347.
- Song Y, Gao Q, Zhang H, Fan L, Zhou J, Zou D, et al. Treatment of relapsed or refractory classical Hodgkin lymphoma with the anti-PD-1, tislelizumab: results of a phase 2, single-arm, multicenter study. Leukemia. 2020 Feb;34(2):533–42.
- Song Y, Gao Q, Zhang H, Fan L, Zhou J, Zou D, et al. Tislelizumab for Relapsed/Refractory Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma: 3-Year Follow-up and Correlative Biomarker Analysis. Clin Cancer Res. 2022 Mar 15;28(6):1147–56.
- Lin N, Zhang M, Bai H, Liu H, Cui J, Ke X, et al. Efficacy and safety of GLS-010 (zimberelimab) in patients with relapsed or refractory classical Hodgkin lymphoma: A multicenter, single-arm, phase II study. Eur J Cancer. 2022 Mar;164:117–26.
- Song Y, Zhou K, Jin C, Qian Z, Hou M, Fan L, et al. Penpulimab for Relapsed or Refractory Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma: A Multicenter, Single-Arm, Pivotal Phase I/II Trial (AK105-201). Front Oncol. 2022 Jul 7;12:925236.
- Herrera AF, Burton C, Radford J, Miall F, Townsend W, Santoro A, et al. Avelumab in relapsed/refractory classical Hodgkin lymphoma: phase 1b results from the JAVELIN Hodgkins trial. Blood Adv. 2021 Sep 14;5(17):3387–96.
- Ramchandren R, Domingo-Domènech E, Rueda A, Trněný M, Feldman TA, Lee HJ, et al. Nivolumab for Newly Diagnosed Advanced-Stage Classic Hodgkin Lymphoma: Safety and Efficacy in the Phase II CheckMate 205 Study. J Clin Oncol. 2019 Aug 10;37(23):1997–2007.
- Bröckelmann PJ, Goergen H, Keller U, Meissner J, Ordemann R, Halbsguth TV, et al. Efficacy of Nivolumab and AVD in Early-Stage Unfavorable Classic Hodgkin Lymphoma: The Randomized Phase 2 German Hodgkin Study Group NIVAHL Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2020 Jun 1;6(6):872.
- Allen PB, Savas H, Evens AM, Advani RH, Palmer B, Pro B, et al. Pembrolizumab followed by AVD in untreated early unfavorable and advanced-stage classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood. 2021 Mar 11;137(10):1318–26.
- Johnson P, Federico M, Kirkwood A, Fosså A, Berkahn L, Carella A, et al. Adapted Treatment Guided by Interim PET-CT Scan in Advanced Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2016 Jun 23;374(25):2419–29.
- Evens AM, Carter J, Loh KP, David KA. Management of older Hodgkin lymphoma patients. Hematology. 2019 Dec 6;2019(1):233–42.
- Moccia AA, Aeppli S, Güsewell S, Bargetzi M, Caspar C, Brülisauer D, et al. Clinical characteristics and outcome of patients over 60 years with Hodgkin lymphoma treated in Switzerland. Hematol Oncol. 2021 Apr;39(2):196–204.
- Cheson BD, Bartlett NL, LaPlant B, Lee HJ, Advani RJ, Christian B, et al. Brentuximab vedotin plus nivolumab as first-line therapy in older or chemotherapy-ineligible patients with Hodgkin lymphoma (ACCRU): a multicentre, single-arm, phase 2 trial. Lancet Haematol. 2020 Nov;7(11):e808–15.
- Herrera AF, Moskowitz AJ, Bartlett NL, Vose JM, Ramchandren R, Feldman TA, et al. Interim results of brentuximab vedotin in combination with nivolumab in patients with relapsed or refractory Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood. 2018 Mar 15;131(11):1183–94.
- Advani RH, Moskowitz AJ, Bartlett NL, Vose JM, Ramchandren R, Feldman TA, et al. Brentuximab vedotin in combination with nivolumab in relapsed or refractory Hodgkin lymphoma: 3-year study results. Blood. 2021 Aug 12;138(6):427–38.
- Herrera AF, Chen RW, Palmer J, Tsai NC, Mei M, Popplewell LL, et al. PET-Adapted Nivolumab or Nivolumab Plus ICE As First Salvage Therapy in Relapsed or Refractory Hodgkin Lymphoma. Blood. 2019 Nov 13;134(Supplement_1):239–239.
- Mei MG, Lee HJ, Palmer JM, Chen R, Tsai NC, Chen L, et al. Response-adapted anti-PD-1–based salvage therapy for Hodgkin lymphoma with nivolumab alone or in combination with ICE. Blood. 2022 Jun 23;139(25):3605–16.
- Locke J. Bryan, MD. 229 Pembrolizumab (PEM) Added to ICE Chemotherapy Results in High Complete Metabolic Response Rates in Relapsed/Refractory Classic Hodgkin Lymphoma (cHL): A Multi-Institutional Phase II Trial. 2021 Dec 11.
- Moskowitz AJ, Shah G, Schöder H, Ganesan N, Drill E, Hancock H, et al. Phase II Trial of Pembrolizumab Plus Gemcitabine, Vinorelbine, and Liposomal Doxorubicin as Second-Line Therapy for Relapsed or Refractory Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2021 Oct 1;39(28):3109–17.
- Geoerger B, Zwaan CM, Marshall LV, Michon J, Bourdeaut F, Casanova M, et al. Atezolizumab for children and young adults with previously treated solid tumours, non-Hodgkin lymphoma, and Hodgkin lymphoma (iMATRIX): a multicentre phase 1–2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2020 Jan;21(1):134–44.
- Moskowitz CH, Nademanee A, Masszi T, Agura E, Holowiecki J, Abidi MH, et al. Brentuximab vedotin as consolidation therapy after autologous stem-cell transplantation in patients with Hodgkin’s lymphoma at risk of relapse or progression (AETHERA): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. The Lancet. 2015 May;385(9980):1853–62.
- Schmitz N, Pfistner B, Sextro M, Sieber M, Carella AM, Haenel M, et al. Aggressive conventional chemotherapy compared with high-dose chemotherapy with autologous haemopoietic stem-cell transplantation for relapsed chemosensitive Hodgkin’s disease: a randomised trial. The Lancet. 2002 Jun;359(9323):2065–71.
- Crump, M. Management of Hodgkin Lymphoma in Relapse after Autologous Stem Cell Transplant. Hematology. 2008 Jan 1;2008(1):326–33.
- Lepik KV, Mikhailova NB, Kondakova EV, Zalyalov YR, Fedorova LV, Tsvetkova LA, et al. A Study of Safety and Efficacy of Nivolumab and Bendamustine (NB) in Patients With Relapsed/Refractory Hodgkin Lymphoma After Nivolumab Monotherapy Failure. HemaSphere. 2020 Jun;4(3):e401.
- Armand P, Chen YB, Redd RA, Joyce RM, Bsat J, Jeter E, et al. PD-1 blockade with pembrolizumab for classical Hodgkin lymphoma after autologous stem cell transplantation. Blood. 2019 Jul 4;134(1):22–9.
- Wolchok JD, Kluger H, Callahan MK, Postow MA, Rizvi NA, Lesokhin AM, et al. Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab in Advanced Melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2013 Jul 11;369(2):122–33.
- Ansell S, Gutierrez ME, Shipp MA, Gladstone D, Moskowitz A, Borello I, et al. A Phase 1 Study of Nivolumab in Combination with Ipilimumab for Relapsed or Refractory Hematologic Malignancies (CheckMate 039). Blood. 2016 Dec 2;128(22):183–183.
- Armand P, Lesokhin A, Borrello I, Timmerman J, Gutierrez M, Zhu L, et al. A phase 1b study of dual PD-1 and CTLA-4 or KIR blockade in patients with relapsed/refractory lymphoid malignancies. Leukemia. 2021 Mar;35(3):777–86.
- Diefenbach CS, Hong F, Ambinder RF, Cohen JB, Robertson MJ, David KA, et al. Ipilimumab, nivolumab, and brentuximab vedotin combination therapies in patients with relapsed or refractory Hodgkin lymphoma: phase 1 results of an open-label, multicentre, phase 1/2 trial. Lancet Haematol. 2020 Sep;7(9):e660–70.
- Sermer DJ, Vardhana S, Biggar E, Moskowitz AJ, Joffe E, Khan N, et al. Interim Efficacy Analysis of a Phase II Study Demonstrates Promising Activity of the Combination of Pembrolizumab (PEM) and Entinostat (ENT) in Relapsed and Refractory (R/R) Hodgkin Lymphoma (HL). Blood. 2021 Nov 5;138(Supplement 1):2447–2447.
- Sermer DJ, Vardhana SA, Ames A, Biggar E, Moskowitz AJ, Batlevi CL, et al. Early data from a phase II trial investigating the combination of pembrolizumab (PEM) and entinostat (ENT) in relapsed and refractory (R/R) Hodgkin lymphoma (HL). J Clin Oncol. 2020 ;38(15_suppl):e20018–e20018. 20 May.
- Ansell SM, Bartlett NL, Chen RW, Herrera A, Domingo-Domenech E, Mehta A, et al. Investigating safety and preliminary efficacy of AFM13 plus pembrolizumab in patients with relapsed/refractory Hodgkin lymphoma after brentuximab vedotin failure. Hematol Oncol. 2019 Jun;37:177–8.
- Bartlett NL, Herrera AF, Domingo-Domenech E, Mehta A, Forero-Torres A, Garcia-Sanz R, et al. A phase 1b study of AFM13 in combination with pembrolizumab in patients with relapsed or refractory Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood. 2020 Nov 19;136(21):2401–9.
- Dave H, Terpilowski M, Mai M, Toner K, Grant M, Stanojevic M, et al. Tumor-associated antigen–specific T cells with nivolumab are safe and persist in vivo in relapsed/refractory Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood Adv. 2022 Jan 25;6(2):473–85.
- Sang W, Wang X, Geng H, Li T, Li D, Zhang B, et al. Anti-PD-1 Therapy Enhances the Efficacy of CD30-Directed Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell Therapy in Patients With Relapsed/Refractory CD30+ Lymphoma. Front Immunol. 2022 Apr 1;13:858021.
- Wang H, Kaur G, Sankin AI, Chen F, Guan F, Zang X. Immune checkpoint blockade and CAR-T cell therapy in hematologic malignancies. J Hematol OncolJ Hematol Oncol. 2019 Dec;12(1):59.
- Li AM, Hucks GE, Dinofia AM, Seif AE, Teachey DT, Baniewicz D, et al. Checkpoint Inhibitors Augment CD19-Directed Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) T Cell Therapy in Relapsed B-Cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Blood. 2018 Nov 29;132(Supplement 1):556–556.
- Timmerman J, Lavie D, Johnson NA, Avigdor A, Borchmann P, Andreadis C, et al. Favezelimab (anti–LAG-3) plus pembrolizumab in patients with relapsed or refractory (R/R) classical Hodgkin lymphoma (cHL) after anti–PD-1 treatment: An open-label phase 1/2 study. J Clin Oncol. 2022 Jun 1;40(16_suppl):7545–7545.
- Lesokhin AM, Stephen M. Ansell, Armand P, Scott EC, Halwani A, Gutierrez M, et al. Nivolumab in Patients With Relapsed or Refractory Hematologic Malignancy: Preliminary Results of a Phase Ib Study. J Clin Oncol. 2016 Aug 10;34(23):2698–704.
- Ansell SM, Minnema MC, Johnson P, Timmerman JM, Armand P, Shipp MA, et al. Nivolumab for Relapsed/Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma in Patients Ineligible for or Having Failed Autologous Transplantation: A Single-Arm, Phase II Study. J Clin Oncol. 2019 Feb 20;37(6):481–9.
- Davids MS, Kim HT, Costello C, Herrera AF, Locke FL, Maegawa RO, et al. A multicenter phase 1 study of nivolumab for relapsed hematologic malignancies after allogeneic transplantation. Blood. 2020 Jun 11;135(24):2182–91.
- Frigault MJ, Armand P, Redd RA, Jeter E, Merryman RW, Coleman KC, et al. PD-1 blockade for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma after autologous stem cell transplantation. Blood Adv. 2020 Jan 14;4(1):122–6.
- Zinzani PL, Ribrag V, Moskowitz CH, Michot JM, Kuruvilla J, Balakumaran A, et al. Safety and tolerability of pembrolizumab in patients with relapsed/refractory primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma. Blood. 2017 Jul 20;130(3):267–70.
- Michot JM, Armand P, Ding W, Ribrag V, Christian B, Marinello P, et al. KEYNOTE-170: Phase 2 study of pembrolizumab in patients with relapsed/refractory primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma (rrPMBCL) or relapsed or refractory Richter syndrome (rrRS). Ann Oncol. 2016 Nov;27:viii15.
- Khodadoust MS, Rook AH, Porcu P, Foss F, Moskowitz AJ, Shustov A, et al. Pembrolizumab in Relapsed and Refractory Mycosis Fungoides and Sézary Syndrome: A Multicenter Phase II Study. J Clin Oncol. 2020 Jan 1;38(1):20–8.
- Kwong YL, Chan TSY, Tan D, Kim SJ, Poon LM, Mow B, et al. PD1 blockade with pembrolizumab is highly effective in relapsed or refractory NK/T-cell lymphoma failing l-asparaginase. Blood. 2017 Apr 27;129(17):2437–42.
- Kim SJ, Lim JQ, Laurensia Y, Cho J, Yoon SE, Lee JY, et al. Avelumab for the treatment of relapsed or refractory extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma: an open-label phase 2 study. Blood. 2020 Dec 10;136(24):2754–63.
- Tao R, Fan L, Song Y, Hu Y, Zhang W, Wang Y, et al. Sintilimab for relapsed/refractory extranodal NK/T cell lymphoma: a multicenter, single-arm, phase 2 trial (ORIENT-4). Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021 Dec;6(1):365.
- Armand P, Janssens A, Gritti G, Radford J, Timmerman J, Pinto A, et al. Efficacy and safety results from CheckMate 140, a phase 2 study of nivolumab for relapsed/refractory follicular lymphoma. Blood. 2021 Feb 4;137(5):637–45.
- Herbaux C, Ghesquieres H, Bouabdallah R, Guidez S, Gyan E, Gressin R, et al. Atezolizumab + obinutuzumab + venetoclax in patients with relapsed or refractory indolent non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma (R/R iNHL): Primary analysis of a phase 2 trial from LYSA. J Clin Oncol. 2021 ;39(15_suppl):7544–7544. 20 May.
- Panayiotidis P, Tumyan G, Thieblemont C, Ptushkin VV, Marin-Niebla A, García-Sanz R, et al. A phase-II study of atezolizumab in combination with obinutuzumab or rituximab for relapsed or refractory mantle cell or marginal zone lymphoma or Waldenström’s macroglobulinemia. Leuk Lymphoma. 2022 Apr 16;63(5):1058–69.
- Younes A, Burke JM, Cheson B, Diefenbach C, Ferrari S, Hahn U, et al. Safety and Efficacy of Atezolizumab in Combination with Rituximab Plus CHOP in Previously Untreated Patients with Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL): Primary Analysis of a Phase I/II Study. Blood. 2018 Nov 29;132(Supplement 1):2969–2969.
- Younes A, Burke JM, Cheson BD, Diefenbach C, Ferrari S, Hahn UH, et al. Safety and Efficacy of Atezolizumab in Combination with Rituximab Plus CHOP in Previously Untreated Patients with Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL): Updated Analysis of a Phase I/II Study. Blood. 2019 Nov 13;134(Supplement_1):2874–2874.
- Smith SD, Till BG, Shadman MS, Lynch RC, Cowan AJ, Wu QV, et al. Pembrolizumab with R-CHOP in previously untreated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: potential for biomarker driven therapy. Br J Haematol. 2020 Jun;189(6):1119–26.
- Nowakowski GS, Willenbacher W, Greil R, Larsen TS, Patel K, Jäger U, et al. Safety and efficacy of durvalumab with R-CHOP or R2-CHOP in untreated, high-risk DLBCL: a phase 2, open-label trial. Int J Hematol. 2022 Feb;115(2):222–32.
- Younes A, Brody J, Carpio C, Lopez-Guillermo A, Ben-Yehuda D, Ferhanoglu B, et al. Safety and activity of ibrutinib in combination with nivolumab in patients with relapsed non-Hodgkin lymphoma or chronic lymphocytic leukaemia: a phase 1/2a study. Lancet Haematol. 2019 Feb;6(2):e67–78.
- Witzig TE, Maddocks KJ, De Vos S, Lyons RM, Edenfield WJ, Sharman JP, et al. Phase 1/2 trial of acalabrutinib plus pembrolizumab (Pem) in relapsed/refractory (r/r) diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL). J Clin Oncol. 2019 ;37(15_suppl):7519–7519. 20 May.
- Gregory GP, Kumar S, Wang D, Mahadevan D, Walker P, Wagner-Johnston N, et al. Pembrolizumab plus dinaciclib in patients with hematologic malignancies: the phase 1b KEYNOTE-155 study. Blood Adv. 2022 Feb 22;6(4):1232–42.
- Herrera AF, Goy A, Mehta A, Ramchandren R, Pagel JM, Svoboda J, et al. Safety and activity of ibrutinib in combination with durvalumab in patients with relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma or diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Am J Hematol. 2020 Jan;95(1):18–27.
- Jacobson CA, Westin JR, Miklos DB, Herrera AF, Lee J, Seng J, et al. Abstract CT055: Phase 1/2 primary analysis of ZUMA-6: Axicabtagene ciloleucel (Axi-Cel) in combination With atezolizumab (Atezo) for the treatment of patients (Pts) with refractory diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL). In: Tumor Biology [Internet]. American Association for Cancer Research; 2020 [cited 2021 Oct 3]. p. CT055–CT055. Available from: http://cancerres.aacrjournals.org/lookup/doi/10.1158/1538-7445.AM2020-CT055.
- Cao Y, Lu W, Sun R, Jin X, Cheng L, He X, et al. Anti-CD19 Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cells in Combination With Nivolumab Are Safe and Effective Against Relapsed/Refractory B-Cell Non-hodgkin Lymphoma. Front Oncol. 2019 Aug 19;9:767.
- Jäger U, Worel N, McGuirk J, Riedell PA, Fleury I, Borchmann P, et al. Safety and efficacy of tisagenlecleucel (tisa-cel) plus pembrolizumab (pembro) in patients (pts) with relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (r/r DLBCL): Updated analysis of the phase 1b PORTIA study. J Clin Oncol. 2021 ;39(15_suppl):e19537–e19537. 20 May.
- Chong EA, Svoboda J, Dwivedy Nasta S, Landsburg DJ, Winchell N, Napier E, et al. Sequential Anti-CD19 Directed Chimeric Antigen Receptor Modified T-Cell Therapy (CART19) and PD-1 Blockade with Pembrolizumab in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory B-Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas. Blood. 2018 Nov 29;132(Supplement 1):4198–4198.
- Hirayama AV, Gauthier J, Hay KA, Sheih A, Cherian S, Chen X, et al. Efficacy and Toxicity of JCAR014 in Combination with Durvalumab for the Treatment of Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Aggressive B-Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. Blood. 2018 Nov 29;132(Supplement 1):1680–1680.
- Osborne W, Marzolini M, Tholouli E, Ramakrishnan A, Bachier CR, McSweeney PA, et al. Phase I Alexander study of AUTO3, the first CD19/22 dual targeting CAR T cell therapy, with pembrolizumab in patients with relapsed/refractory (r/r) DLBCL. J Clin Oncol. 2020 ;38(15_suppl):8001–8001. 20 May.
- Palomba ML, Cartron G, Popplewell L, Ribrag V, Westin J, Huw LY, et al. Combination of Atezolizumab and Tazemetostat in Patients With Relapsed/Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: Results From a Phase Ib Study. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2022 Jul;22(7):504–12.
- Herbaux C, Casasnovas O, Feugier P, Damaj G, Bouabdallah R, Guidez S, et al. Atezolizumab + obinutuzumab + venetoclax in patients with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell Lymphomas (R/R DLBCL): Primary analysis of a phase II trial from LYSA. J Clin Oncol. 2020 ;38(15_suppl):8053–8053. 20 May.
- Palomba ML, Till BG, Park SI, Morschhauser F, Cartron G, Marks R, et al. Combination of Atezolizumab and Obinutuzumab in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Follicular Lymphoma and Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: Results from a Phase 1b Study. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2022 Jul;22(7):e443–51.
- Hutchings M, Gritti G, Sureda A, Terol MJ, Dyer MJ, Iacoboni G, et al. CD20-TCB, a Novel T-Cell-Engaging Bispecific Antibody, Can be Safely Combined with the Anti-PD-L1 Antibody Atezolizumab in Relapsed or Refractory B-Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. Blood. 2019 Nov 13;134(Supplement_1):2871–2871.
- Zinzani PL, Santoro A, Gritti G, Brice P, Barr PM, Kuruvilla J, et al. Nivolumab Combined With Brentuximab Vedotin for Relapsed/Refractory Primary Mediastinal Large B-Cell Lymphoma: Efficacy and Safety From the Phase II CheckMate 436 Study. J Clin Oncol. 2019 Nov 20;37(33):3081–9.
- Zinzani PL, Santoro A, Gritti G, Brice P, Barr PM, Kuruvilla J, et al. Nivolumab plus brentuximab vedotin for relapsed/refractory primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma: Extended follow-up from the phase 2 CheckMate 436 study. Hematol Oncol. 2021 Jun;39(S2):hon.51_2879.
- Cai J, Liu P, Huang H, Li Y, Ma S, Zhou H, et al. Combination of anti-PD-1 antibody with P-GEMOX as a potentially effective immunochemotherapy for advanced natural killer/T cell lymphoma. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020 Dec;5(1):289.
- Barraclough A, Chong G, Gilbertson M, Grigg A, Churilov L, Fancourt T, et al. Immune Priming with Single-Agent Nivolumab Followed By Combined Nivolumab & Rituximab Is Safe and Efficacious for First-Line Treatment of Follicular Lymphoma; Interim Analysis of the “1st FLOR” Study. Blood. 2019 Nov 13;134(Supplement_1):1523–1523.
- Hawkes EA, Lee ST, Chong G, Gilbertson M, Grigg A, Churilov L, et al. Immune priming with nivolumab followed by nivolumab and rituximab in first-line treatment of follicular lymphoma: The phase 2 1st FLOR study. J Clin Oncol. 2021 ;39(15_suppl):7560–7560. 20 May.
- Anas Younes, MD, Burke M. John, Catherine S Diefenbach, Silvia Ferrari, Cyrus Kahn, Jeffrey P. Sharman, MD, Monica Tani, Chaitra S. Ujjani, MD, Umberto Vitolo, MD, Sam Yuen, Paul Woodard, Kirsten Mundt, Günter Fingerle-Rowson, Surya Chitra, Gila Sellam, Rodica Morariu-Zamfir, Michael Gilbertson. Safety and Efficacy of Atezolizumab in Combination with Obinutuzumab and Bendamustine in Patients with Previously Untreated Follicular Lymphoma: An Interim Analysis. Blood (2017) 130 (Supplement 1): 481.
- Younes A, Burke JM, Diefenbach CS, Ferrari S, Khan C, Sharman JP, et al. Safety and efficacy of atezolizumab with obinutuzumab and bendamustine in previously untreated follicular lymphoma. Blood Adv. 2022 Mar 31;bloodadvances.2021006131.
- Nastoupil LJ, Westin JR, Fowler NH, Fanale MA, Samaniego F, Oki Y, et al. Response rates with pembrolizumab in combination with rituximab in patients with relapsed follicular lymphoma: Interim results of an on open-label, phase II study. J Clin Oncol. 2017 ;35(15_suppl):7519–7519. 20 May.
- Nastoupil LJ, Chin CK, Westin JR, Fowler NH, Samaniego F, Cheng X, et al. Safety and activity of pembrolizumab in combination with rituximab in relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma. Blood Adv. 2022 Feb 22;6(4):1143–51.
- Westin JR, Chu F, Zhang M, Fayad LE, Kwak LW, Fowler N, et al. Safety and activity of PD1 blockade by pidilizumab in combination with rituximab in patients with relapsed follicular lymphoma: a single group, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014 Jan;15(1):69–77.
- Morschhauser F, Ghosh N, Lossos IS, Palomba ML, Mehta A, Casasnovas O, et al. Obinutuzumab-atezolizumab-lenalidomide for the treatment of patients with relapsed/refractory follicular lymphoma: final analysis of a Phase Ib/II trial. Blood Cancer J. 2021 Aug;11(8):147.
- Jain N, Basu S, Thompson PA, Ohanian M, Ferrajoli A, Pemmaraju N, et al. Nivolumab Combined with Ibrutinib for CLL and Richter Transformation: A Phase II Trial. Blood. 2016 Dec 2;128(22):59–59.
- Jain N, Ferrajoli A, Basu S, Thompson PA, Burger JA, Kadia TM, et al. A Phase II Trial of Nivolumab Combined with Ibrutinib for Patients with Richter Transformation. Blood. 2018 Nov 29;132(Supplement 1):296–296.
- Jeong AR, Ball ED, Goodman AM. Predicting Responses to Checkpoint Inhibitors in Lymphoma: Are We Up to the Standards of Solid Tumors? Clin Med Insights Oncol. 2020 Jan;14:117955492097636.
- Garcia-Diaz A, Shin DS, Moreno BH, Saco J, Escuin-Ordinas H, Rodriguez GA, et al. Interferon Receptor Signaling Pathways Regulating PD-L1 and PD-L2 Expression. Cell Rep. 2017 May;19(6):1189–201.
- Cha JH, Chan LC, Li CW, Hsu JL, Hung MC. Mechanisms Controlling PD-L1 Expression in Cancer. Mol Cell. 2019 Nov;76(3):359–70.
- Daud AI, Wolchok JD, Robert C, Hwu WJ, Weber JS, Ribas A, et al. Programmed Death-Ligand 1 Expression and Response to the Anti–Programmed Death 1 Antibody Pembrolizumab in Melanoma. J Clin Oncol. 2016 Dec 1;34(34):4102–9.
- Borghaei H, Paz-Ares L, Horn L, Spigel DR, Steins M, Ready NE, et al. Nivolumab versus Docetaxel in Advanced Nonsquamous Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N Engl J Med. 2015 Oct 22;373(17):1627–39.
- Rosenberg JE, Hoffman-Censits J, Powles T, van der Heijden MS, Balar AV, Necchi A, et al. Atezolizumab in patients with locally advanced and metastatic urothelial carcinoma who have progressed following treatment with platinum-based chemotherapy: a single-arm, multicentre, phase 2 trial. The Lancet. 2016 May;387(10031):1909–20.
- Saleh RR, Scott JL, Meti N, Perlon D, Fazelzad R, Ocana A, et al. Prognostic Value of Programmed Death Ligand-1 Expression in Solid Tumors Irrespective of Immunotherapy Exposure: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Mol Diagn Ther. 2022 Mar;26(2):153–68.
- Center for Devices and Radiological Health, List of Cleared or Approved Companion Diagnostic Devices (In Vitro and Imaging Tools). FDA (2019). Available online at: /medical-devices/vitro-diagnostics/list-cleared-or-approved-companion-diagnostic-devices-vitro-and-imaging-tools.
- Guo H, Ding Q, Gong Y, Gilcrease MZ, Zhao M, Zhao J, et al. Comparison of three scoring methods using the FDA-approved 22C3 immunohistochemistry assay to evaluate PD-L1 expression in breast cancer and their association with clinicopathologic factors. Breast Cancer Res. 2020 Dec;22(1):69.
- Kulangara K, Hanks DA, Waldroup S, Peltz L, Shah S, Roach C, et al. Development of the combined positive score (CPS) for the evaluation of PD-L1 in solid tumors with the immunohistochemistry assay PD-L1 IHC 22C3 pharmDx. J Clin Oncol. 2017 ;35(15_suppl):e14589–e14589. 20 May.
- Mok TSK, Wu YL, Kudaba I, Kowalski DM, Cho BC, Turna HZ, et al. Pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy for previously untreated, PD-L1-expressing, locally advanced or metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer (KEYNOTE-042): a randomised, open-label, controlled, phase 3 trial. The Lancet. 2019 May;393(10183):1819–30.
- Chen C, Liu S, Jiang X, Huang L, Chen F, Wei X, et al. Tumor mutation burden estimated by a 69-gene-panel is associated with overall survival in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2021 Dec;10(1):20.
- Qiu L, Zheng H, Zhao X. The prognostic and clinicopathological significance of PD-L1 expression in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: a meta-analysis. BMC Cancer. 2019 Dec;19(1):273.
- Shu Z, Minghui Z, Yu Z, Hongxue M, Yan W, Yupeng L, et al. The prognostic value of programmed cell death ligand 1 expression in non-Hodgkin lymphoma: a meta-analysis. Cancer Biol Med. 2018;15(3):290.
- Veldman J, Alsada ZND, Berg A, Plattel WJ, Diepstra A, Visser L. Soluble PD-L1 is a promising disease biomarker but does not reflect tissue expression in classic Hodgkin lymphoma. Br J Haematol. 2021 May;193(3):506–14.
- Shen H, Ji Y, Zhou D, Zhang Y, Wang W, Sun J, et al. Soluble programmed death-ligand 1 are highly expressed in peripheral T-cell lymphoma: a biomarker for prognosis. Hematology. 2019 Jan 1;24(1):392–8.
- Cho I, Lee H, Yoon SE, Ryu KJ, Ko YH, Kim WS, et al. Serum levels of soluble programmed death-ligand 1 (sPD-L1) in patients with primary central nervous system diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. BMC Cancer. 2020 Dec;20(1):120.
- Takamori S, Takada K, Azuma K, Jogo T, Shimokawa M, Toyokawa G, et al. Prognostic Impact of Programmed Death-Ligand 2 Expression in Primary Lung Adenocarcinoma Patients. Ann Surg Oncol. 2019 Jun;26(6):1916–24.
- Shinchi Y, Komohara Y, Yonemitsu K, Sato K, Ohnishi K, Saito Y, et al. Accurate expression of PD-L1/L2 in lung adenocarcinoma cells: A retrospective study by double immunohistochemistry. Cancer Sci. 2019 Sep;110(9):2711–21.
- Green MR, Monti S, Rodig SJ, Juszczynski P, Currie T, O’Donnell E, et al. Integrative analysis reveals selective 9p24.1 amplification, increased PD-1 ligand expression, and further induction via JAK2 in nodular sclerosing Hodgkin lymphoma and primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma. Blood. 2010 Oct 28;116(17):3268–77.
- Tobin JWD, Keane C, Gunawardana J, Mollee P, Birch S, Hoang T, et al. Progression of Disease Within 24 Months in Follicular Lymphoma Is Associated With Reduced Intratumoral Immune Infiltration. J Clin Oncol. 2019 Dec 1;37(34):3300–9.
- Mottok A, Hung SS, Chavez EA, Woolcock B, Telenius A, Chong LC, et al. Integrative genomic analysis identifies key pathogenic mechanisms in primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma. Blood. 2019 Sep 5;134(10):802–13.
- Shi M, Roemer MGM, Chapuy B, Liao X, Sun H, Pinkus GS, et al. Expression of Programmed Cell Death 1 Ligand 2 (PD-L2) Is a Distinguishing Feature of Primary Mediastinal (Thymic) Large B-cell Lymphoma and Associated With PDCD1LG2 Copy Gain. Am J Surg Pathol. 2014 Dec;38(12):1715–23.
- Chapuy B, Roemer MGM, Stewart C, Tan Y, Abo RP, Zhang L, et al. Targetable genetic features of primary testicular and primary central nervous system lymphomas. Blood. 2016 Feb 18;127(7):869–81.
- Godfrey J, Tumuluru S, Bao R, Leukam M, Venkataraman G, Phillip J, et al. PD-L1 gene alterations identify a subset of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma harboring a T-cell–inflamed phenotype. Blood. 2019 ;133(21):2279–90. 23 May.
- Wang Y, Wenzl K, Manske MK, Asmann YW, Sarangi V, Greipp PT, et al. Amplification of 9p24.1 in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identifies a unique subset of cases that resemble primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma. Blood Cancer J. 2019 Sep;9(9):73.
- Igarashi T, Teramoto K, Ishida M, Hanaoka J, Daigo Y. Scoring of PD-L1 expression intensity on pulmonary adenocarcinomas and the correlations with clinicopathological factors. ESMO Open. 2016;1(4):e000083.
- Roemer MGM, Advani RH, Ligon AH, Natkunam Y, Redd RA, Homer H, et al. PD-L1 and PD-L2 Genetic Alterations Define Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma and Predict Outcome. J Clin Oncol. 2016 Aug 10;34(23):2690–7.
- Liu J, Hamrouni A, Wolowiec D, Coiteux V, Kuliczkowski K, Hetuin D, et al. Plasma cells from multiple myeloma patients express B7-H1 (PD-L1) and increase expression after stimulation with IFN-γ and TLR ligands via a MyD88-, TRAF6-, and MEK-dependent pathway. Blood. 2007 Jul 1;110(1):296–304.
- Karachaliou N, Gonzalez-Cao M, Crespo G, Drozdowskyj A, Aldeguer E, Gimenez-Capitan A, et al. Interferon gamma, an important marker of response to immune checkpoint blockade in non-small cell lung cancer and melanoma patients. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2018 Jan 1;10:175883401774974.
- Luo Y, Liu Y, Wang C, Gan R. Signaling pathways of EBV-induced oncogenesis. Cancer Cell Int. 2021 Dec;21(1):93.
- Ang KK, Harris J, Wheeler R, Weber R, Rosenthal DI, Nguyen-Tân PF, et al. Human Papillomavirus and Survival of Patients with Oropharyngeal Cancer. N Engl J Med. 2010 Jul;363(1):24–35.
- Seiwert TY, Burtness B, Mehra R, Weiss J, Berger R, Eder JP, et al. Safety and clinical activity of pembrolizumab for treatment of recurrent or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (KEYNOTE-012): an open-label, multicentre, phase 1b trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016 Jul;17(7):956–65.
- Wang H, Zhao Q, Zhang Y, Zhang Q, Zheng Z, Liu S, et al. Immunotherapy Advances in Locally Advanced and Recurrent/Metastatic Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Its Relationship With Human Papillomavirus. Front Immunol. 2021 Jul 8;12:652054.
- Kim SJ, Hyeon J, Cho I, Ko YH, Kim WS. Comparison of Efficacy of Pembrolizumab between Epstein-Barr Virus‒Positive and ‒Negative Relapsed or Refractory Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas. Cancer Res Treat. 2019 Apr 15;51(2):611–22.
- Biggi AFB, Elgui de Oliveira D. The Epstein-Barr Virus Hacks Immune Checkpoints: Evidence and Consequences for Lymphoproliferative Disorders and Cancers. Biomolecules. 2022 Mar 4;12(3):397.
- Satou A, Nakamura S. EBV-positive B-cell lymphomas and lymphoproliferative disorders: Review from the perspective of immune escape and immunodeficiency. Cancer Med. 2021 Oct;10(19):6777–85.
- Ligeti K, Müller LP, Müller-Tidow C, Weber T. Risk factors, diagnosis, and management of posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorder: improving patient outcomes with a multidisciplinary treatment approach. Transpl Res Risk Manag. 2017 Jan;Volume 9:1–14.
- Steiner Raphael et al. Low 5-year cumulative incidence of post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorders after solid organ transplantation in Switzerland. Swiss Med Wkly [Internet]. 2018 Mar 8 [cited 2022 Oct 1];148(910). Available from: http://doi.emh.ch/smw.2018.14596.
- Tse E, Zhao WL, Xiong J, Kwong YL. How we treat NK/T-cell lymphomas. J Hematol OncolJ Hematol Oncol. 2022 Dec;15(1):74.
- Kiyasu J, Miyoshi H, Hirata A, Arakawa F, Ichikawa A, Niino D, et al. Expression of programmed cell death ligand 1 is associated with poor overall survival in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood. 2015 Nov 5;126(19):2193–201.
- Strickler JH, Hanks BA, Khasraw M. Tumor Mutational Burden as a Predictor of Immunotherapy Response: Is More Always Better? Clin Cancer Res. 2021 Mar 1;27(5):1236–41.
- Snyder A, Makarov V, Merghoub T, Yuan J, Zaretsky JM, Desrichard A, et al. Genetic Basis for Clinical Response to CTLA-4 Blockade in Melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2014 Dec 4;371(23):2189–99.
- Rizvi NA, Hellmann MD, Snyder A, Kvistborg P, Makarov V, Havel JJ, et al. Mutational landscape determines sensitivity to PD-1 blockade in non–small cell lung cancer. Science. 2015 Apr 3;348(6230):124–8.
- Klempner SJ, Fabrizio D, Bane S, Reinhart M, Peoples T, Ali SM, et al. Tumor Mutational Burden as a Predictive Biomarker for Response to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Review of Current Evidence. The Oncologist [Internet]. 2020 Jan [cited 2021 Nov 3];25(1). Available from: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1634/theoncologist.2019-0244. 2019.
- Marcus L, Fashoyin-Aje LA, Donoghue M, Yuan M, Rodriguez L, Gallagher PS, et al. FDA Approval Summary: Pembrolizumab for the Treatment of Tumor Mutational Burden–High Solid Tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 2021 Sep 1;27(17):4685–9.
- Galanina N, Bejar R, Choi M, Goodman A, Wieduwilt M, Mulroney C, et al. Comprehensive Genomic Profiling Reveals Diverse but Actionable Molecular Portfolios across Hematologic Malignancies: Implications for Next Generation Clinical Trials. Cancers. 2018 Dec 21;11(1):11.
- Ricciuti B, Wang X, Alessi JV, Rizvi H, Mahadevan NR, Li YY, et al. Association of High Tumor Mutation Burden in Non–Small Cell Lung Cancers With Increased Immune Infiltration and Improved Clinical Outcomes of PD-L1 Blockade Across PD-L1 Expression Levels. JAMA Oncol [Internet]. 2022 Jun 16 [cited 2022 Aug 8]; Available from: https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamaoncology/fullarticle/2793565. 2793.
- Chalmers ZR, Connelly CF, Fabrizio D, Gay L, Ali SM, Ennis R, et al. Analysis of 100,000 human cancer genomes reveals the landscape of tumor mutational burden. Genome Med. 2017 Dec;9(1):34.
- Wienand K, Chapuy B, Stewart C, Dunford AJ, Wu D, Kim J, et al. Genomic analyses of flow-sorted Hodgkin Reed-Sternberg cells reveal complementary mechanisms of immune evasion. Blood Adv. 2019 Dec 10;3(23):4065–80.
- Chapuy B, Stewart C, Dunford AJ, Kim J, Wienand K, Kamburov A, et al. Genomic analyses of PMBL reveal new drivers and mechanisms of sensitivity to PD-1 blockade. Blood. 2019 Dec 26;134(26):2369–82.
- Cho J, Yoon SE, Kim SJ, Ko YH, Kim WS. Comparison of tumor mutation burden of 300 various non-Hodgkin lymphomas using panel based massively parallel sequencing. BMC Cancer. 2021 Dec;21(1):972.
- Russano M, Napolitano A, Ribelli G, Iuliani M, Simonetti S, Citarella F, et al. Liquid biopsy and tumor heterogeneity in metastatic solid tumors: the potentiality of blood samples. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020 Dec;39(1):95.
- Zhu G, Guo YA, Ho D, Poon P, Poh ZW, Wong PM, et al. Tissue-specific cell-free DNA degradation quantifies circulating tumor DNA burden. Nat Commun. 2021 Dec;12(1):2229.
- Roschewski M, Dunleavy K, Pittaluga S, Moorhead M, Pepin F, Kong K, et al. Circulating tumour DNA and CT monitoring in patients with untreated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: a correlative biomarker study. Lancet Oncol. 2015 May;16(5):541–9.
- Shi Y, Su H, Song Y, Jiang W, Sun X, Qian W, et al. Circulating tumor DNA predicts response in Chinese patients with relapsed or refractory classical hodgkin lymphoma treated with sintilimab. EBioMedicine. 2020 Apr;54:102731.
- Zhou H, Du X, Zhao T, Ouyang Z, Liu W, Deng M, et al. Distribution and influencing factors of tumor mutational burden in different lymphoma subtypes. J Clin Oncol. 2019 ;37(15_suppl):e19053–e19053. 20 May.
- Li K, Luo H, Huang L, Luo H, Zhu X. Microsatellite instability: a review of what the oncologist should know. Cancer Cell Int. 2020 Dec;20(1):16.
- Le DT, Durham JN, Smith KN, Wang H, Bartlett BR, Aulakh LK, et al. Mismatch repair deficiency predicts response of solid tumors to PD-1 blockade. Science. 2017 Jul 28;357(6349):409–13.
- Gatalica Z, Vranic S, Xiu J, Swensen J, Reddy S. High microsatellite instability (MSI-H) colorectal carcinoma: a brief review of predictive biomarkers in the era of personalized medicine. Fam Cancer. 2016 Jul;15(3):405–12.
- Tian T, Li J, Xue T, Yu B, Li X, Zhou X. Microsatellite instability and its associations with the clinicopathologic characteristics of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Cancer Med. 2020 Apr;9(7):2330–42.
- Wieczorek M, Abualrous ET, Sticht J, Álvaro-Benito M, Stolzenberg S, Noé F, et al. Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) Class I and MHC Class II Proteins: Conformational Plasticity in Antigen Presentation. Front Immunol [Internet]. 2017 Mar 17 [cited 2021 Nov 3];8. Available from: http://journal.frontiersin.org/article/10.3389/fimmu.2017.00292/full. 0029.
- Hazini A, Fisher K, Seymour L. Deregulation of HLA-I in cancer and its central importance for immunotherapy. J Immunother Cancer. 2021 Aug;9(8):e002899.
- Rodig SJ, Gusenleitner D, Jackson DG, Gjini E, Giobbie-Hurder A, Jin C, et al. MHC proteins confer differential sensitivity to CTLA-4 and PD-1 blockade in untreated metastatic melanoma. Sci Transl Med. 2018 Jul 18;10(450):eaar3342.
- Roemer MGM, Advani RH, Redd RA, Pinkus GS, Natkunam Y, Ligon AH, et al. Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma with Reduced β 2 M/MHC Class I Expression Is Associated with Inferior Outcome Independent of 9p24.1 Status. Cancer Immunol Res. 2016 Nov;4(11):910–6.
- Weber JS, Gibney G, Sullivan RJ, Sosman JA, Slingluff CL, Lawrence DP, et al. Sequential administration of nivolumab and ipilimumab with a planned switch in patients with advanced melanoma (CheckMate 064): an open-label, randomised, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016 Jul;17(7):943–55.
- Piersma SJ, Jordanova ES, van Poelgeest MIE, Kwappenberg KMC, van der Hulst JM, Drijfhout JW, et al. High Number of Intraepithelial CD8+ Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes Is Associated with the Absence of Lymph Node Metastases in Patients with Large Early-Stage Cervical Cancer. Cancer Res. 2007 Jan 1;67(1):354–61.
- Matias Autio, Suvi-Katri Leivonen, Oscar Brück, Satu Mustjoki, Judit Mészáros Jørgensen, Marja-Liisa Karjalainen-Lindsberg, et al. Immune cell constitution in the tumor microenvironment predicts the outcome in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Haematologica. 2020 Feb 20;106(3):718–29.
- Leivonen SK, Pollari M, Brück O, Pellinen T, Autio M, Karjalainen-Lindsberg ML, et al. T-cell inflamed tumor microenvironment predicts favorable prognosis in primary testicular lymphoma. Haematologica. 2019 Feb;104(2):338–46.
- Wu H, Tang X, Kim HJ, Jalali S, Pritchett JC, Villasboas JC, et al. Expression of KLRG1 and CD127 defines distinct CD8 + subsets that differentially impact patient outcome in follicular lymphoma. J Immunother Cancer. 2021 Jul;9(7):e002662.
- Nygren L, Wasik AM, Baumgartner-Wennerholm S, Jeppsson-Ahlberg Å, Klimkowska M, Andersson P, et al. T-Cell Levels Are Prognostic in Mantle Cell Lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2014 Dec 1;20(23):6096–104.
- Alonso-Álvarez S, Vidriales MB, Caballero MD, Blanco O, Puig N, Martin A, et al. The number of tumor infiltrating T-cell subsets in lymph nodes from patients with Hodgkin lymphoma is associated with the outcome after first line ABVD therapy. Leuk Lymphoma. 2017 ;58(5):1144–52. 4 May.
- Maimela NR, Liu S, Zhang Y. Fates of CD8+ T cells in Tumor Microenvironment. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2019;17:1–13.
- Li F, Li C, Cai X, Xie Z, Zhou L, Cheng B, et al. The association between CD8+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and the clinical outcome of cancer immunotherapy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. eClinicalMedicine. 2021 Nov;41:101134.
- Hammond, SM. An overview of microRNAs. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2015 Jun;87:3–14.
- Fuertes T, Ramiro AR, de Yebenes VG. miRNA-Based Therapies in B Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. Trends Immunol. 2020 Oct;41(10):932–47.
- Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG, Ambs S, Cimmino A, Petrocca F, et al. A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines cancer gene targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2006 Feb 14;103(7):2257–61.
- Ji Q, Jiang T, Su J, Zhang S, Li C, Yang X, et al. Serum miR-21 predicts the prognosis of patients with primary gastrointestinal diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Acta Biochim Pol [Internet]. 2022 Jun 12 [cited 2022 Aug 12]; Available from: https://ojs.ptbioch.edu.pl/index.php/abp/article/view/5816.
- Li J, Fu R, Yang L, Tu W. miR-21 expression predicts prognosis in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015;8(11):15019–24.
- Li J, Zhai XW, Wang HS, Qian XW, Miao H, Zhu XH. Circulating MicroRNA-21, MicroRNA-23a, and MicroRNA-125b as Biomarkers for Diagnosis and Prognosis of Burkitt Lymphoma in Children. Med Sci Monit Int Med J Exp Clin Res. 2016 Dec 19;22:4992–5002.
- Mao X, Sun Y, Tang J. Serum miR-21 is a diagnostic and prognostic marker of primary central nervous system lymphoma. Neurol Sci. 2014 Feb;35(2):233–8.
- Xi J, Huang Q, Wang L, Ma X, Deng Q, Kumar M, et al. miR-21 depletion in macrophages promotes tumoricidal polarization and enhances PD-1 immunotherapy. Oncogene. 2018 Jun;37(23):3151–65.
- Gopalakrishnan V, Spencer CN, Nezi L, Reuben A, Andrews MC, Karpinets TV, et al. Gut microbiome modulates response to anti–PD-1 immunotherapy in melanoma patients. Science. 2018 Jan 5;359(6371):97–103.
- Matson V, Fessler J, Bao R, Chongsuwat T, Zha Y, Alegre ML, et al. The commensal microbiome is associated with anti–PD-1 efficacy in metastatic melanoma patients. Science. 2018 Jan 5;359(6371):104–8.
- Liu X, Chen Y, Zhang S, Dong L. Gut microbiota-mediated immunomodulation in tumor. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021 Dec;40(1):221.
- Hwang SR, Higgins A, Castillo Almeida NE, LaPlant B, Maurer MJ, Ansell SM, et al. Effect of antibiotic use on outcomes in patients with Hodgkin lymphoma treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors. Leuk Lymphoma. 2021 Jan 2;62(1):247–51.
- Casadei B, Guadagnuolo S, Barone M, Turroni S, Argnani L, Brigidi P, et al. Gut Microbiota Role in Response to Checkpoint Inhibitor Treatment in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory B-Cell Hodgkin Lymphoma: The MICRO-Linf Study. Blood. 2021 Nov 5;138(Supplement 1):2957–2957.
- Khodadoust MS, Rook AH, Porcu P, Foss F, Moskowitz AJ, Shustov A, et al. Pembrolizumab in Relapsed and Refractory Mycosis Fungoides and Sézary Syndrome: A Multicenter Phase II Study. J Clin Oncol. 2020 Jan 1;38(1):20–8.
- Burtness B, Harrington KJ, Greil R, Soulières D, Tahara M, de Castro G, et al. Pembrolizumab alone or with chemotherapy versus cetuximab with chemotherapy for recurrent or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (KEYNOTE-048): a randomised, open-label, phase 3 study. The Lancet. 2019 Nov;394(10212):1915–28.
- Fuchs CS, Doi T, Jang RW, Muro K, Satoh T, Machado M, et al. Safety and Efficacy of Pembrolizumab Monotherapy in Patients With Previously Treated Advanced Gastric and Gastroesophageal Junction Cancer: Phase 2 Clinical KEYNOTE-059 Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2018 ;4(5):e180013. 10 May.
| Target | Name | Pharmaceutical company | Isotype | Approval status | Year Indication |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PD-1 | Nivolumab (Opdivo®) Pembrolizumab (Keytruda®) Tislelizumab (BGB-A317) Camrelizumab (AiRuiKa™) Sintilimab (Tyvyt®) Zimberelimab (AB122) Penpulimab (AK105) |
Bristol-Myers Squibb Merck BeiGene Hengrui Innovent Biologics, Eli Lilly Gloria Biosciences, Arcus Biosciences, Taiho Pharmaceutical Co Akeso Biopharma |
IgG4 S228P IgG4 S228P IgG4mut, FcyR null IgG4 S228P IgG4 κ IgG4 IgG1, FcyR null |
FDA / EMA [25,64] FDA / EMA [23,28,81] China NMPA [39] China NMPA [35] China NMPA [33] China NMPA [41] China NMPA [42] |
2018, cHL 2018, cHL, PMBCL 2019, cHL 2019, cHL 2018, cHL 2021, cHL 2021, cHL |
| PD-L1 | Atezolizumab (Tecentriq®) Avelumab (Bavencio®) |
Roche Merck KGaA/Pfizer |
IgG1mut, FcyR null IgG1 |
- - |
- - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





