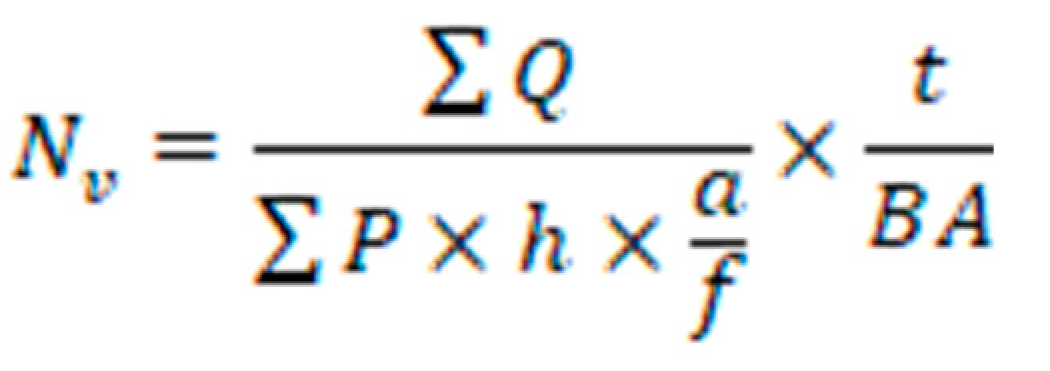1. Introduction
The Central Nervous System (CNS) comprises nerve cells and neuroglia susceptible to damage caused by various destructive factors (1-8). Methamphetamine (METH) was first manufactured during World War II (9). However, its illicit use and recreational consumption have become significant concerns in many countries. Despite its therapeutic applications in conditions like memory disorders, hyperactivity, narcolepsy, and obesity, it is being used illegally as a recreational drug (10-12). Research has indicated that this substance can have side effects on the respiratory, cardiovascular, and nervous systems (13, 14). Individuals who use METH are susceptible to experiencing a range of emotional and cognitive effects. These include euphoria, increased energy and alertness, increased physical and mental performance, hallucinations, paranoia, anxiety, and increased productivity (9, 11). Unfortunately, despite the documented reports of irreversible side effects associated with the misuse of this substance, its prevalence continues to rise, particularly among the younger population worldwide (15). Research studies have demonstrated that METH can disrupt the activities of neurotransmitters in the CNS, including dopamine, serotonin, and norepinephrine (16-18). Animal model studies have revealed that METH can release dopamine-containing vesicles stored within neurons and inhibit the enzyme monoamine oxidase (19). Abnormal activity has been reported in specific CNS areas affected by dopamine and serotonin regulation, such as the striatum, prefrontal cortex, caudate nucleus, anterior cingulate, and amygdala, which may contribute to the increased risk of depression and aggressive behaviours in METH users (20-22).
Furthermore, the degradation of dopaminergic neurons has also been observed following METH usage (23). METH's ability to induce neurotoxicity is well documented and occurs through multiple pathways, including increased production of reactive nitrogen and oxygen species, hypothermia, and induction of mitochondrial apoptosis (24-26). However, the precise mechanism underlying these activities is not fully understood (8). Neuroimaging studies investigating METH users have revealed alterations in both white and gray matter volume compared to healthy individuals in various regions of the CNS, including the cingulate, striatum, nucleus accumbens, hippocampus, parietal and occipital lobes, basal nuclei (22, 27-31). In addition to structural changes observed in the nervous system of individuals using METH, numerous studies have provided clear evidence of increased expression of oxidative stress, inflammatory, autophagy, and apoptosis markers in specific nervous system regions (13, 32-37). Previous investigations have confirmed that METH can elevate apoptotic markers such as BAX, caspase 3, 8, and 9 in the amygdala and hippocampus (38, 39). Neurotrophic factors play a crucial role in the development and functioning of the nervous system, particularly brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), which is associated with neuronal plasticity, survival, and neuroprotection (40). BDNF has a critical role in some parts of the CNS, which regulate cognition, emotions, and reward activities (41). Numerous studies have indicated alterations in BDNF levels under neuropathological conditions. Specifically, METH use has been shown to significantly decrease BDNF levels through the reduction of cAMP Response Element-Binding Protein (CREB) activities. Furthermore, disruption of normal AKT/GSk3 signaling pathways has been linked to METH use, which may contribute to the exacerbation of neurological and neurobehavioral symptoms (40, 42-44). Thus, in this investigation, we analyzed the overexpression of tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα) and examined alterations in the CREB/BDNF and Akt-1/GSK3 signaling pathways in postmortem amygdala samples obtained from individuals with a history of METH addiction.
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Sample preparation
A total of 20 male human brains, consisting of 10 control subjects and 10 individuals with a history of METH use, were obtained from the Iranian legal medicine organization in Tehran, Iran. Rigorous screening procedures were conducted to ensure the quality and validity of the samples, including verification of medical history, documentation of expiration, and examination of postmortem reports. The samples selected for this study were obtained from individuals with an average age of 38 ± 2 years at the time of death, and the entirety of the amygdala was included in the analysis.
The research procedures conducted in this study have received ethical approval from the Ethics Committee of Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences (SBMU) under the reference number IR.SBMU.RETECH.REC.1400.432. Three methods were employed to determine the presence of METH in the samples: Urine rapid test, High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC), and Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry (GC/MS). The urine rapid test utilized a Detect Diagnostics kit to identify 12 different types of drugs, including METH, cannabis, tramadol, morphine, and methadone. Initially, all samples underwent preparation for the preliminary examination. Protein extraction and isolation were performed by adjusting the pH using acidic, alkaline, and opioid solvents. Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC) was used as the preliminary screening method to detect the presence of drugs in the samples. If the TLC results were positive for the presence of the drug, further analysis was carried out using HPLC and GC/MS. If any drugs other than amphetamines were detected in the samples at this stage, the sample would be excluded from the study, as the presence of any other drugs could confound the results. Samples that yielded satisfactory results were accepted for further analysis. Following the initial preparation of the samples, METH in urine and stomach contents was examined. The presence of METH was detected by derivatizing it with heptafluorobutyric anhydride (HFBA), which allowed for the measurement of the METH or amphetamine derivative using GC/MS (33).
2.2. Tissue Preparation
The brain samples were carefully extracted from the skull and thoroughly rinsed to eliminate any traces of blood clots. To facilitate hematoxylin and eosin (H and E) staining, TUNEL assay, and immunohistochemistry analysis, the amygdala region of all brain samples was dissected by a skilled neuroanatomist and subsequently fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde for a period of one week. For the real-time PCR assay, the amygdala was also dissected and immediately stored at a temperature of -80 °C.
2.3. Real-time PCR
Total RNA was extracted from the samples using RNX-plus SinaClon (Tehran, Iran), and cDNA synthesis was performed using the RevertAid H Minus First Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Massachusetts, USA). The cDNA synthesis reaction involved the addition of 0.2 μg of Random Hexamer and 1 μg of total RNA. Subsequently, a mixture of 1 μl of each primer, 10 μl of SYBR Green Master Mix (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Massachusetts, USA), and 10 μl of dH2O was prepared, to which 2 μl of the sample cDNA was added. The real-time PCR reactions were carried out using an ABI device, with each sample analyzed in duplicate and repeated three times (n = 3). The data obtained were evaluated using the ∆∆Ct method (45). In the real-time PCR analysis, we employed a standardized protocol for the amplification process. The PCR reactions were carried out using a thermal cycler with the following conditions: an initial denaturation step at 95°C for 5 minutes, followed by a cycling protocol. Each cycle consisted of denaturation at 95°C for 30 seconds, annealing at a specific temperature for 30 seconds, and extension at 72°C for 30 seconds.
The number of cycles was set to 40, ensuring adequate amplification while minimizing non-specific products. A final extension step was performed at 72°C for 5 minutes to promote the complete extension of the amplified products. The real-time PCR process was carried out using suitable positive and negative controls, and a melting curve analysis was conducted at the end of the cycling protocol to verify the specificity of the amplified products.
2.4. Immunohistochemistry
After fixation with 4% paraformaldehyde, the brain sections were embedded in paraffin and sliced into 10 μm thick sections. Cryoprotective media containing 25% ethylene, 25% glycerin, and 0.05 M phosphate buffer was used to preserve the sections at -20 °C. The sections were deparaffinized using fresh xylene and then rehydrated through a series of graded alcohol concentrations (100%, 90%, and 70%). Subsequently, the sections were incubated in methanol with 0.3% hydrogen peroxide for 20 minutes to block endogenous peroxidase activity. Following that, the sections were incubated with primary antibodies (1:100) against CREB (Cell Signaling Biotech, Massachusetts, USA), BDNF (Cell Signaling Biotech, Massachusetts, USA), Akt-1 (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Texas, USA), GSK3 (Abcam, Cambridge, UK), RIPK3 (Abcam, Cambridge, UK), and TNF-α (Abcam, Cambridge, UK) at 4 °C overnight in a blocking buffer solution containing 1% bovine serum albumin (BSA) in PBS. After rinsing, the sections were incubated with a secondary antibody (goat anti-mouse, 1:100) (Abcam, Cambridge, UK) for 60 minutes. Finally, the sections were stained with DAPI (Abcam, Cambridge, UK). The stained sections were then analyzed using Image J software to measure the areas of positive immunoreactivity associated with the aforementioned antibodies. For this analysis, seven sections from each group (Meth and control) were selected, and adjustments were made before analyzing all sections (46, 47).
2.5. H&E and Nissl staining
The brain tissue was carefully dissected, and the amygdala was immersed in a 4% Paraformaldehyde solution. Subsequently, the amygdala tissue was embedded in paraffin blocks. The microtome was used to create sections with a thickness of 5 μm for general analysis and 25 μm for estimating the quantity and range of cells. Finally, the sections of the amygdala were stained using the Nissl and H & E staining procedures (32).
2.6. Stereological study
2.6.1. Number of neurons and glial cells
The optical dissector method was employed to ascertain the collective count of neurons and glial cells. Brain tissue sections were meticulously chosen through a systematic and uniformly random sampling approach. Images of these sections were overlaid with an impartial counting frame featuring clearly defined inclusion and exclusion boundaries. By adjusting the focal plane along the z-axis and subsequently connecting a microcator to the microscope's stage to measure the z-coordinate, nuclei of neurons and glial cells that came into the sharpest focus within the subsequent focal plane were identified for enumeration. The numerical density (NV) was calculated employing the following formula.
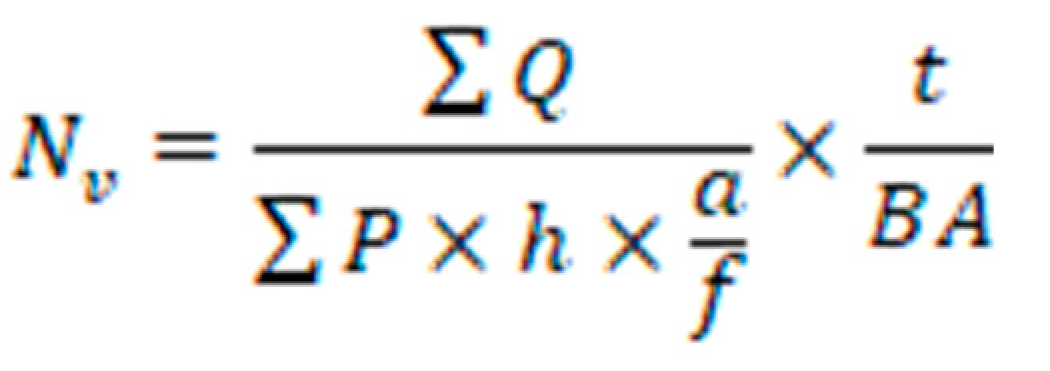
The variables ΣQ- and ΣP represent the calculated number of cells and the total number of microscopic fields, respectively. The parameters a/f, and h denotes the area per frame and the height of the director, respectively. Additionally, t represents the actual section thickness, and BA corresponds to the block advance of the microtome (33).
2.7. Tunel assay
The Amygdala was then fixed and embedded in paraffin. Subsequently, sections were prepared and mounted on glass slides using gelatin. The samples underwent deparaffinization using Xylene to remove the paraffin. For the analysis of DNA fragmentation, TUNEL staining (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Massachusetts, USA) (green) was utilized, with DAPI serving as a nuclear counterstain (blue). Quantification of TUNEL-positive cells in the groups was performed using Image J software. This involved selecting seven images from each group, adjusting the threshold, and conducting analyses on all images (32).
2.8. Reactive oxygen species (ROS)
Brain tissue cells were isolated and subjected to trypsin-EDTA treatment. The cell suspension from the plates was then centrifuged at 1,400 x g for 5 minutes at 4 °C. To assess intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels, 2,7-dichlorofluorescein diacetate (DCFDA) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Massachusetts, USA) was added to the samples at a concentration of 20 μM, followed by incubation at 37 °C for 45 minutes. Subsequently, the samples were analyzed using a flow cytometer, with fluorescence intensity measured at 495 nm, to determine ROS levels. (48)
2.9. Glutathione disulphide content assessments and GSSG assay
The tissue samples were assessed for glutathione peroxidase (GPX) activity using a GPX test kit (Zellbio GmbH, Ronsee, Germany). The assay measured GPX activity in the entire sample by catalyzing the degradation of 1 μmol of mitochondrial glutathione (GSH) per minute. Aliquots of sample suspensions containing O-phthalaldehyde (OPA) and N-ethylmaleimide (NEM) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Massachusetts, USA) probes were collected from the incubation medium through centrifugation at 1,000 rpm for 1 minute (48).
2.10. SDS-PAGE Sample Prep and Gel Electrophoresis
For SDS-PAGE sample prep, homemade gels were utilized. Laemmli resolving gel was prepared by combining these components per 10mL: 3 mL 40% Acrylamide/Bis, 2.5 mL 1.5M Tris-HCl pH 8.8, 1 mL 10% SDS, 50 μL 10% APS, and 5 μL TEMED. Stacking gel was separately prepared per 2.5 mL with 0.25 mL 40% Acrylamide/Bis, 0.63 mL 0.5M Tris-HCl pH 6.8, 250 μL 10% SDS, 12.5 μL 10% APS, and 2.5 μL TEMED. Electrophoresis was performed using a running buffer containing 3 g Tris base, 14.4 g Glycine, and 1 g SDS dissolved in 1 L.
2.11. Immunoblotting
Samples were homogenized in lysis buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl pH 7.4, 150 mM NaCl, 5 mM EDTA, 10% glycerol, 1% Triton X-100, and additives). After heating and centrifugation, samples were mixed with 5x SDS loading buffer and separated on a 10% SDS-PAGE gel. Proteins were transferred to Immobilon®-PSQ PVDF Membrane (, MilliporeSigma, Massachusetts, USA) then incubated with primary antibodies (1:1000 dilution) overnight at 4℃. Secondary antibodies (1:10,000 dilution) were applied for 2 hours at room temperature. Membranes were exposed to Western Lightning Plus-ECL reagent (SuperSignalTM West Dura Extended Duration Substrate kit (Thermo Scientific Massachusetts, USA)) and analyzed using the ChemiDoc Imaging system (Bio-Rad, Texas, USA).
2.12. Statistical analysis
The data was analyzed using t-test in IBM SPSS Statistics Version 21, and the results were presented as mean ± standard deviation. Additionally, GraphPad Prism was utilized for data analysis.
3. Results
This study delved into the ramifications of chronic methamphetamine (METH) use on both gene expression and protein levels in postmortem human brains, mainly focusing on the amygdala. The distinctive profiles observed within the METH group were compared against those of a control group consisting of non-METH users.
3.1. Evaluation of the sample
Ten normal brains (control or non-METH group) were obtained from adult males with no history of drug use. The average age of the individuals was 38.2 ± 2.1 years. The individuals in the control group were male, with mean BMI of 24.4, and a brain volume of 1450.3±34.2 grams (mean ± SD). The ultimate cause of death for these individuals was attributed to factors such as myocardial infarcts or accidents. In contrast, the ten brains in the chronic METH user group belonged to individuals who were male, with a mean BMI of 18.8, and an average age of 38.1 ± 2.3 years. The brain volume of this group was measured to be 1310.6±52.5 grams (mean ± SD). The cause of death for these individuals was METH overdose, and they had a history of using METH for more than five years. The common methods of METH use among this group were smoking and intravenous (IV) injection. It is worth noting that none of the individuals had any neurodegenerative illnesses or a diagnosis of AIDS.
3.2. Real-time PCR
The analysis of qRT-PCR data was conducted using the Pfaffl method, a robust approach that accurately assesses gene expression levels. Significantly, within the METH group, a striking pattern emerged: certain genes displayed substantial upregulation in their expression levels, setting them in stark contrast to the control group. Notably, the genes GSK3, TNF-α, and RIPK3 demonstrated a marked increase in expression, underscoring the intricate impact of chronic METH exposure on these specific molecular pathways.
Conversely, a contrasting trend was observed for other pivotal genes. The genes CREB, BDNF, and Akt-1, recognized for their essential roles in neural function and plasticity, exhibited a discernible reduction in expression within the METH group. This bidirectional alteration in gene expression emphasizes the multifaceted influence of METH on the molecular landscape of the brain, encompassing both upregulation and downregulation of critical players.
The molecular changes extended to genes intimately associated with apoptotic processes. Genes such as Caspase 3 and Bax, key orchestrators of apoptosis, showcased heightened expression within the METH group. This heightened expression potentially hints at the activation of apoptotic pathways in response to chronic METH exposure. In contrast, the anti-apoptotic gene Bcl2 displayed diminished expression, further supporting the notion of METH-induced apoptotic perturbations. An intriguing aspect of this gene expression profile is the augmentation of autophagy-associated genes within the METH group. The genes LC3 and ATG5, intricately involved in autophagy, exhibited enhanced expression. This observation suggests a potential activation of autophagy pathways, likely as an adaptive response to METH-induced cellular stress. This multifaceted gene expression landscape, as depicted in Figure 1, offers a glimpse into the intricate molecular changes taking place within the context of chronic METH exposure. The varying responses of different genes underscore the complexity of METH's impact on neural circuits, potentially contributing to the diverse behavioral and cognitive alterations associated with chronic substance use.
3.3. Immunohistochemistry result
The intricate protein landscape within the amygdala samples was meticulously examined, with a focused lens on key players like CREB, BDNF, Akt-1, GSK3, TNF-α, and RIPK3. The investigation, conducted within the context of METH exposure, unveiled a series of striking alterations in protein expression, shedding light on the profound impact of this substance on neural physiology. Foremost, the examination of CREB, a transcription factor intricately involved in neural plasticity, revealed a notable reduction in its protein expression within the METH-exposed group (METH group: 8.60 ± 1.80, control group: 48.30 ± 3.80). This reduction potentially underscores the METH-induced perturbation of molecular pathways governing neural adaptation and synaptic plasticity, implicating CREB's role in the broader spectrum of neural responses to chronic METH exposure (figure 2).
In tandem, the assessment of BDNF, a neurotrophic factor indispensable for neuronal survival and growth, unraveled a significant decrease in protein expression within the METH-exposed group (METH group: 12.59 ± 6.14, control group: 49.75 ± 4.52). This observation potentially echoes the neural consequences of chronic METH use, hinting at compromised neurotrophic support and potential impacts on neuronal health (figure 3).
A noteworthy finding emerged from the investigation of Akt-1, a kinase central to cell survival and proliferation. The METH group displayed a pronounced reduction in Akt-1 protein expression (METH group: 15.95 ± 4.03, control group: 47.71 ± 2.17), potentially highlighting the impairment of essential cell signaling cascades and cellular responses within the amygdala due to prolonged METH exposure (figure 4).
The protein expression analysis of RIPK3, a regulator of cell death and inflammation, illuminated an intriguing rise within the METH-exposed group (METH group: 44.71 ± 7.97, control group: 21.40 ± 9.73). This elevation potentially underscores the intricate balance between survival and programmed cell death, offering insight into the interplay between METH-induced neural stress and cellular response pathways (figure 5).
In striking contrast, the protein expression of GSK3, a kinase implicated in various cellular processes, demonstrated a significant increase within the METH-exposed group (METH group: 46.66 ± 4.74, control group: 9.28 ± 2.38). This increase potentially hints at the intricate interplay between chronic METH exposure and cellular regulatory mechanisms, as GSK3's altered expression might contribute to the observed structural and functional changes in the amygdala (figure 6).
The examination of TNF-α, a pro-inflammatory cytokine, unveiled a marked elevation in protein expression within the METH group (METH group: 58.57 ± 8.44, control group: 16.56 ± 9.32). This inflammation-associated protein's increased presence might signify an inflammatory response triggered by METH exposure, potentially linking neural inflammation to the observed changes in neuronal structure and function (figure 7).
In collective resonance, the dynamic protein expression changes across these pivotal molecules, as illustrated in Figure 2-7, provide a nuanced perspective on the intricate molecular mechanisms underpinning the neural consequences of chronic METH exposure. These findings intricately connect to METH's broader impact on neural plasticity, inflammation, and cell survival, offering invaluable insights into the complex landscape of substance-induced neural alterations.
3.4. Tunel assay
In our investigation, we meticulously quantified all apoptotic cells. DAPI staining enabled the precise identification of cellular nuclei, while Tunel staining facilitated the detection of apoptotic cells (Figure 8). Notably, a substantial rise in apoptotic cells was observed in the METH group, highlighting the notable impact of METH exposure on apoptotic cell levels.
3.5. GPX Activation, GSSG, ROS
In our study, we delved into oxidative stress's intricate realm by measuring ROS production, GSSG levels, and GPX activity. We aimed to unravel the balance between harmful reactive oxygen species (ROS) and protective antioxidant mechanisms. The results we unearthed painted a vivid picture of the impact of METH exposure. We discovered a significant escalation in ROS formation and GSSG levels within the METH group. These findings resemble the red flags of heightened oxidative stress – a condition where the equilibrium between cellular damage and repair becomes disrupted.
On the contrary, when we scrutinized the activity of GPX, a pivotal antioxidant enzyme responsible for curbing oxidative damage, a stark decline was evident compared to the control group (Figure 9). This collective data, vividly depicted in Figure 9, signifies that the METH group experienced an intensified state of oxidative stress, with ROS and GSSG surges surpassing the norm. Additionally, the dwindling GPX activity underscores the struggle of the cellular defence system against oxidative onslaught. Our comprehensive findings enhance our understanding of the multifaceted effects of METH exposure on oxidative stress dynamics.
3.6. Stereological analysis of the amygdala
The amygdala central nuclei were subjected to H&E and Cresyl violet staining in the study groups. Our observations revealed that neuronal vacuolation and gliosis were notably more severe in the METH group compared to the control group. Stereological analysis of neuron and glial cell numbers was performed on both groups. The METH group exhibited a significant decrease in the number of neurons and a marked increase in the number of glial cells compared to the control group (P < 0.001) (Figure 10).
The histological examination of the amygdala central nuclei revealed significant findings in the study groups. Specifically, H&E and Cresyl violet staining indicated a distinct pattern of structural changes within the METH group compared to the control group. Neuronal vacuolation and gliosis were particularly pronounced in the METH group, signifying a considerable disruption in the microarchitecture of the central nucleus of the amygdala.
The amygdala is renowned for its pivotal role in processing and regulating emotions, particularly those related to fear, stress, and social interactions. The central nuclei of the amygdala, being integral components of this intricate neural circuitry, play a crucial role in orchestrating responses to emotional stimuli and contributing to emotional learning and memory. The observed neuronal vacuolation and gliosis in the METH group could potentially indicate underlying neuroinflammatory processes or disturbances in neural connectivity within this vital region. The subsequent stereological analysis, which quantified the numbers of neurons and glial cells, offers valuable insights into the potential functional implications of these structural alterations. Notably, the METH group displayed a substantial reduction in the number of neurons alongside a marked increase in glial cell numbers compared to the control group (P < 0.001) (Figure 10). This perturbed balance between neurons and glial cells could potentially disrupt the intricate information processing within the amygdala, impacting various functions such as emotional regulation, fear conditioning, and the interpretation of social cues.
Furthermore, the connection between these structural modifications and the functional role of the amygdala extends to broader behavioral outcomes. Dysregulation of the amygdala has been implicated in various psychiatric disorders, encompassing anxiety, depression, and addiction. The pronounced structural changes observed within the central nucleus of the amygdala in the METH group may significantly contribute to the observed behavioral and emotional dysregulation often associated with individuals with a history of METH use.
To conclude, the observed structural changes in the central nucleus of the amygdala, marked by neuronal vacuolation and gliosis, underscore the intricate interplay between structural alterations and their potential functional repercussions. These findings offer insights into the potential neural mechanisms underpinning METH-induced alterations in emotion and behavior and underscore the amygdala's essential role in emotional processing and its susceptibility to perturbations stemming from substance-related factors.
3.7. Immunoblotting
After using immunoblotting, we checked the levels of proteins—important molecules in our study. This helped us understand how things work in response to METH exposure, building on what we found through real-time PCR. In simple terms, in the group exposed to METH, we saw that certain proteins such as GSK3, TNF-α, and RIPK3 were higher compared to the control group. This suggests that METH might be causing certain pathways or processes to get more active. On the other hand, some key proteins like CREB, BDNF, and Akt-1 were lower in the METH group compared to the control group. This might mean that METH affects how these proteins work, possibly changing how cells communicate or function (Figure 11).
4. Discussion
METH is a widely known nervous system stimulant that has been extensively studied for its therapeutic effects on various diseases. However, the misuse and uncontrolled use of METH have become a growing concern due to its high potential for abuse and illegal nature (8). Previous research has clearly demonstrated the detrimental impact of METH on the CNS, leading to various neurological and behavioral disorders such as delirium, paranoia, anxiety, depression, memory impairment, hallucinations, and poor concentration among METH users (11). Although several hypotheses have been proposed, the exact molecular mechanisms underlying METH-induced neurological effects are still not fully understood. Increased production of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species, induction of autophagy and apoptosis, elevated levels of inflammatory factors, and mitochondrial dysfunction are believed to play a role (13, 38). Specifically, disruption of dopaminergic and serotonergic neurons has been linked to METH's neurological effects (49). Our study investigated the effects of METH on the amygdala and revealed significant alterations in various parameters. We observed a significant reduction in GPX activation and downregulation of BDNF, CREB, and Akt-1 expression/levels. Additionally, we noted a marked increase in the levels of GSSG, ROS, RIPK3, GSK3, and the inflammatory factor TNF-α in the postmortem amygdala of METH users compared to the control group. These findings align with previous studies suggesting that METH disrupts ion channels, leading to increased intracellular calcium levels, mitochondrial dysfunction, impaired energy metabolism, and excessive production of reactive oxygen species, ultimately interfering with the antioxidant system in neural cells (13, 49, 50).
In pathological states of the nervous system, astrocytes and microglia undergo hypertrophy and hyperactivation, resulting in the overproduction of inflammatory factors and subsequent neuroinflammation (49). The combination of these factors ultimately leads to the destruction of nerve cells and the development of irreversible neurological defects in METH users (27).
Our findings are consistent with earlier research showing significant increases in GSSG, malondialdehyde (MDA), GSK3, and TNF-α in METH users, along with a notable decrease in GSH levels and an increase in GSSG and ROS in the amygdala (13, 34) (38). Although apoptosis, autophagy, and inflammation have been proposed as potential mechanisms for the adverse effects of METH on the CNS, the exact molecular mechanisms and signaling pathways involved have not been fully elucidated (34, 38).
Previous studies have highlighted the neuroprotective effects of factors such as CREB, BDNF, and Akt-1 in the CNS, promoting neuronal regeneration, survival, and growth (51). Impairment in CREB regulation has been linked to programmed cell death, ROS production, and neurodegeneration (52). In light of this, we conducted a comprehensive analysis of the potential signaling pathways, namely CREB/BDNF and Akt-1/GSK-3, that may be disrupted in the amygdala of individuals using METH. Consistent with previous studies, our findings provide further evidence of significant downregulation in the expression/levels of BDNF, CREB, and Akt-1 (both total and phosphorylated forms) while demonstrating a noteworthy increase in GSK-3 levels (40-42). We observed significant alterations in multiple parameters in the amygdala of METH users. These include elevated levels of inflammatory cytokine TNF-α, increased GSSG, ROS, and GSK3 levels, and notable downregulation of BDNF, CREB, and Akt-1. These changes are consistent with previous research, suggesting that METH disrupts ion channels, impairs mitochondrial function, and interferes with the antioxidant system in neural cells. Furthermore, our study aligns with previous findings regarding the hypertrophy and hyperactivation of astrocytes and microglia in pathological nervous system states. These processes contribute to the overproduction of inflammatory factors and subsequent neuroinflammation, ultimately leading to irreversible neurological defects in METH users.
Our results also support earlier studies reporting significant increases in GSSG, MDA, GSK3, and TNF-α, along with a decrease in GSH levels in the amygdala of METH users. While apoptosis, autophagy, and inflammation have been proposed as potential mechanisms, further research is required to fully elucidate the molecular mechanisms and signaling pathways involved in METH-induced CNS damage. Previous research has highlighted the neuroprotective effects of factors such as CREB, BDNF, and Akt-1, which promote neuronal regeneration, survival, and growth in the CNS. Impairment in CREB regulation has been associated with programmed cell death, ROS production, and neurodegeneration.
By examining the potential signaling pathways disrupted in the amygdala of METH users, namely CREB/BDNF and Akt-1/GSK-3, our study provides further evidence of the significant downregulation of BDNF, CREB, and Akt-1, as well as an increase in GSK-3 levels. These findings contribute to our understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying METH-induced neurotoxicity. In summary, our study enhances the knowledge surrounding the detrimental effects of METH on the amygdala. By shedding light on previously unknown mechanisms and providing valuable insights into the impact of METH on the brain, our findings contribute to developing targeted interventions and therapeutic strategies to mitigate the harmful effects of METH use on the CNS.
Conclusions:
In conclusion, our study expands our understanding of the detrimental effects of METH on the CNS, particularly in the amygdala. METH misuse and uncontrolled use have been associated with various neurological and behavioral disorders. While the exact molecular mechanisms of METH-induced neurotoxicity remain incompletely understood, our findings provide valuable insights into the underlying mechanisms.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The collection and preservation of all brains in this study were carried out in strict accordance with the principles outlined in the Declaration of Helsinki. The research protocols employed in this study were reviewed and approved by the Ethics Committee of Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences (IR.SBMU.RETECH.REC.1400.432).
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the funding support provided by the Hearing Disorders Research Center at Loghman Hakim Hospital, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran. Additionally, we extend our appreciation to the Iranian legal organization for their assistance.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest related to this study.
References
- Behl T, Makkar R, Sehgal A, Singh S, Sharma N, Zengin G, Bungau S, Andronie-Cioara FL, Munteanu MA, Brisc MC, Uivarosan D. Current trends in neurodegeneration: Cross talks between oxidative stress, cell death, and inflammation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2021, 22, 7432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahmasebinia, F. and S. Emadi. Effects of clioquinol on the aggregation of beta-amyloid peptides in the presence and absence of metal ions and astrocyte-mediated inflammation. in european journal of immunology 2016. wiley-blackwell 111 river st, hoboken 07030-5774, nj usa.
- Pourgholaminejad, A. , F. Tahmasebinia, The Role of Th17 Cells in Immunopathogenesis of Neuroinflammatory Disorders. Neuroimmune Diseases: From Cells to the Living Brain 2019, p. 83.
- Mahmoudiasl, G., Abbaszadeh, H., Rezaei-Tavirani, M., Abdollahifar, M., Khoramgah, M., Niknazar, S., Roozbahany, N.. Nod-like receptor protein 3 and nod-like receptor protein 1 inflammasome activation in the hippocampal region of postmortem METH chronic user. Bratislavske lekarske listy 2019, 120, 769–776.
- Khoshsirat, S., Khoramgah, M. S., Mahmoudiasl, G.-R., Rezaei-Tavirani, M., Abdollahifar, M.-A., Tahmasebinia, F., Abbaszadeh, H. A.. LC3 and ATG5 overexpression and neuronal cell death in the prefrontal cortex of postmortem chronic METH users. Journal of Chemical Neuroanatomy 2020, 107, 101802.
- Rasti Boroojeni F, Mashayekhan S, Abbaszadeh HA, Ansarizadeh M, Khoramgah MS, Rahimi Movaghar V. Bioinspired nanofiber scaffold for differentiating bone marrow-derived neural stem cells to oligodendrocyte-like cells: design, fabrication, and characterization. International Journal of Nanomedicine 2020, 2, 3903–3920. [Google Scholar]
- Cadet, J.L. and I.N. Krasnova, Molecular bases of methamphetamine-induced neurodegeneration. International review of neurobiology 2009, 88, 101–119.
- İvecen, B. and O. GOKDEMIR, Methamphetamine Addiction. dahuder medical journal 2022, 2, 98–101. [CrossRef]
- Prakash MD, Tangalakis K, Antonipillai J, Stojanovska L, Nurgali K, Apostolopoulos V. Methamphetamine: effects on the brain, gut and immune system. Pharmacological research. 2017, 120, 60–67. [Google Scholar]
- Chavda V, Chaurasia B, Umana GE, Tomasi SO, Lu B, Montemurro N. Narcolepsy—A Neuropathological Obscure Sleep Disorder: A Narrative Review of Current Literature. Brain Sciences 2022, 12, 1473. [Google Scholar]
- Rusyniak, D.E. Neurologic manifestations of chronic methamphetamine abuse. Psychiatric Clinics 2013, 36, 261–275. [Google Scholar]
- Compton, W.M., N.D. Volkow.Abuse of prescription drugs and the risk of addiction. Drug and alcohol dependence 2006, 83, S4–S7.
- Downey, L.A. and J.M. Loftis.Altered energy production, lowered antioxidant potential, and inflammatory processes mediate CNS damage associated with abuse of the psychostimulants MDMA and methamphetamine. European journal of pharmacology 2014, 727, 125–129. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varner KJ, Ogden BA, Delcarpio J, Meleg-Smith S. Cardiovascular responses elicited by the “binge” administration of methamphetamine. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 2002, 301, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tehrani AM, Boroujeni ME, Aliaghaei A, Feizi MA, Safaralizadeh R. Methamphetamine induces neurotoxicity-associated pathways and stereological changes in prefrontal cortex. Neuroscience letters 2019, 712, 134478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkow ND, Chang L, Wang GJ, Fowler JS, Leonido-Yee M, Franceschi D, Sedler MJ, Gatley SJ, Hitzemann R, Ding YS, Logan J. Association of dopamine transporter reduction with psychomotor impairment in methamphetamine abusers. American Journal of Psychiatry 2001, 158, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrestha P, Katila N, Lee S, Seo JH, Jeong JH, Yook S. Methamphetamine induced neurotoxic diseases, molecular mechanism, and current treatment strategies. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2022, 154, 113591. [Google Scholar]
- Hong SJ, Zhang D, Zhang LH, Yang P, Wan J, Yu Y, Wang TH, Feng ZT, Li LH, Yew DT. Expression of dopamine transporter in the different cerebral regions of methamphetamine-dependent rats. Human & Experimental Toxicology 2015, 34, 707–717. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan J, Lv R, Brašić JR, Han M, Liu X, Wang Y, Zhang G, Liu C, Li Y, Deng Y. Dopamine transporter dysfunction in Han Chinese people with chronic methamphetamine dependence after a short-term abstinence. Psychiatry Research: Neuroimaging. 2014, 221, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- London, E.D., et al., Mood disturbances and regional cerebral metabolic abnormalities inrecently abstinent methamphetamine abusers. Archives of general psychiatryn 2004, 61, 73–84. [CrossRef]
- Moszczynska A, Fitzmaurice P, Ang L, Kalasinsky KS, Schmunk GA, Peretti FJ, Aiken SS, Wickham DJ, Kish SJ. Why is parkinsonism not a feature of human methamphetamine users? Brain 2004, 127, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson PM, Hayashi KM, Simon SL, Geaga JA, Hong MS, Sui Y, Lee JY, Toga AW, Ling W, London ED. Structural abnormalities in the brains of human subjects who use methamphetamine. Journal of Neuroscience 2004, 24, 6028–6036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, D.B. and J.P. O’Callaghan, Elevated environmental temperature and methamphetamine neurotoxicity. Environmental research 2003, 92, 48–53. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayanthi S, Deng X, Ladenheim B, McCoy MT, Cluster A, Cai NS, Cadet JL. Calcineurin/NFAT-induced up-regulation of the Fas ligand/Fas death pathway is involved in methamphetamine-induced neuronal apoptosis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2005, 102, 868–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiyatkin, E.A. and H.S. Sharma, Permeability of the blood–brain barrier depends on brain temperature. Neuroscience 2009, 161, 926–939. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nopparat C, Porter JE, Ebadi M, Govitrapong P. The mechanism for the neuroprotective effect of melatonin against methamphetamine-induced autophagy. Journal of pineal research 2010, 49, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang X, Chen YY, Shen Y, Cao X, Li A, Liu Q, Li Z, Zhang LB, Dai W, Tan T, Arias-Carrion O. Methamphetamine abuse impairs motor cortical plasticity and function. Molecular psychiatry 2017, 22, 1274–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salo R, Fassbender C, Buonocore MH, Ursu S. Behavioral regulation in methamphetamine abusers: an fMRI study. Psychiatry Research: Neuroimaging 2013, 211, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales AM, Lee B, Hellemann G, O’Neill J, London ED. Gray-matter volume in methamphetamine dependence: cigarette smoking and changes with abstinence from methamphetamine. Drug and alcohol dependence 2012, 125, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jernigan TL, Gamst AC, Archibald SL, Fennema-Notestine C, Mindt MR, Marcotte TL, Heaton RK, Ellis RJ, Grant I. Effects of methamphetamine dependence and HIV infection on cerebral morphology. American Journal of Psychiatry 2005, 162, 1461–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves J, Baptista S, Martins T, Milhazes N, Borges F, Ribeiro CF, Malva JO, Silva AP. Methamphetamine-induced neuroinflammation and neuronal dysfunction in the mice hippocampus: preventive effect of indomethacin. European Journal of Neuroscience 2010, 31, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshsirat S, Khoramgah MS, Mahmoudiasl GR, Rezaei-Tavirani M, Abdollahifar MA, Tahmasebinia F, Darabi S, Niknazar S, Abbaszadeh HA. LC3 and ATG5 overexpression and neuronal cell death in the prefrontal cortex of postmortem chronic methamphetamine users. Journal of Chemical Neuroanatomy 2020, 107, 101802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirakabad FS, Khoramgah MS, Abdollahifar MA, Tehrani AS, Rezaei-Tavirani M, Niknazar S, Tahmasebinia F, Mahmoudiasl GR, Khoshsirat S, Abbaszadeh HA. NUPR1-CHOP experssion, autophagosome formation and apoptosis in the postmortem striatum of chronic methamphetamine user. Journal of Chemical Neuroanatomy 2021, 114, 101942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roohbakhsh, A., K. Shirani, and G. Karimi, Methamphetamine-induced toxicity: The role of autophagy? Chemico-biological interactions 2016, 260, 163–167. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mata MM, Napier TC, Graves SM, Mahmood F, Raeisi S, Baum LL. Methamphetamine decreases CD4 T cell frequency and alters pro-inflammatory cytokine production in a model of drug abuse. European journal of pharmacology 2015, 752, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GR, Mahmoudiasl, Abbaszadeh HA, Abdollahifar MA, Khoramgah MS, and Roozbahany NA. "Nod-like receptor protein 3 and nod-like receptor protein 1 inflammasome activation in the hippocampal region of postmortem methamphetamine chronic user. Bratislava Medical Journal 2019, 120, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Kohno M, Loftis JM, Huckans M, Dennis LE, McCready H, Hoffman WF. The relationship between interleukin-6 and functional connectivity in methamphetamine users. Neuroscience letters 2018, 677, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo D, Huang X, Xiong T, Wang X, Zhang J, Wang Y, Liang J. Molecular mechanisms of programmed cell death in methamphetamine-induced neuronal damage. Frontiers in Pharmacology 2022, 13, 980340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu CW, Ping YH, Yen JC, Chang CY, Wang SF, Yeh CL, Chi CW, Lee HC. Enhanced oxidative stress and aberrant mitochondrial biogenesis in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells during methamphetamine induced apoptosis. Toxicology and applied pharmacology 2007, 220, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gholami M, Hozuri F, Abdolkarimi S, Mahmoudi M, Motaghinejad M, Safari S, Sadr S. Pharmacological and molecular evidence of neuroprotective curcumin effects against biochemical and behavioral sequels caused by methamphetamine: Possible function of CREB-BDNF signaling pathway. Basic and Clinical Neuroscience 2021, 12, 325. [Google Scholar]
- Motaghinejad M, Motevalian M, Babalouei F, Abdollahi M, Heidari M, Madjd Z. Possible involvement of CREB/BDNF signaling pathway in neuroprotective effects of topiramate against methylphenidate induced apoptosis, oxidative stress and inflammation in isolated hippocampus of rats: molecular, biochemical and histological evidences. Brain research bulletin 2017, 132, 82–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motaghinejad M, Mashayekh R, Motevalian M, Safari S. The possible role of CREB-BDNF signaling pathway in neuroprotective effects of minocycline against alcohol-induced neurodegeneration: molecular and behavioral evidences. Fundamental & Clinical Pharmacology 2021, 35, 113–130. [Google Scholar]
- Feizipour S, Sobhani S, Mehrafza S, Gholami M, Motaghinejad M, Motevalian M, Safari S, Davoudizadeh R. Selegiline acts as neuroprotective agent against methamphetamine-prompted mood and cognitive related behavior and neurotoxicity in rats: Involvement of CREB/BDNF and Akt/GSK3 signal pathways. Iranian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences 2020, 23, 606. [Google Scholar]
- Keshavarzi S, Kermanshahi S, Karami L, Motaghinejad M, Motevalian M, Sadr S. Protective role of metformin against methamphetamine induced anxiety, depression, cognition impairment and neurodegeneration in rat: the role of CREB/BDNF and Akt/GSK3 signaling pathways. Neurotoxicology 2019, 72, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darabi S, Noori-Zadeh A, Rajaei F, Abbaszadeh HA, Bakhtiyari S, Roozbahany NA. SMER28 attenuates dopaminergic toxicity mediated by 6-hydroxydopamine in the rats via modulating oxidative burdens and autophagy-related parameters. Neurochemical Research 2018, 43, 2313–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darabi SH, Tiraihi T, Noori-Zadeh A, Rajaei F, Darabi L, Abbaszadeh H. Creatine and retinoic acid effects on the induction of autophagy and differentiation of adipose tissue-derived stem cells into GABAergic-like neurons. Journal of Babol university of medical sciences 2017, 19, 41–49. [Google Scholar]
- Abbaszadeh HA, Tiraihi T, Delshad AR, Zadeh MS, Taheri T. Bone marrow stromal cell transdifferentiation into oligodendrocyte-like cells using triiodothyronine as a inducer with expression of platelet-derived growth factor α as a maturity marker. Iranian biomedical journal 2013, 17, 62. [Google Scholar]
- Moghimi N, Eslami Farsani B, Ghadipasha M, Mahmoudiasl GR, Piryaei A, Aliaghaei A, Abdi S, Abbaszadeh HA, Abdollahifar MA, Forozesh M. COVID-19 disrupts spermatogenesis through the oxidative stress pathway following induction of apoptosis. Apoptosis 2021, 26, 415–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaerzadeh F, Streit WJ, Heysieattalab S, Khoshbouei H. Methamphetamine neurotoxicity, microglia, and neuroinflammation. Journal of neuroinflammation 2018, 15, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Castellano P, Nwagbo C, Martinez LR, Eugenin EA. Methamphetamine compromises gap junctional communication in astrocytes and neurons. Journal of neurochemistry 2016, 137, 561–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayr, B. M. Montminy, Transcriptional regulation by the phosphorylation-dependent factor CREB. Nature reviews Molecular cell biology 2001, 2, 599–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang G, Li J, Peng Y, Shen B, Li Y, Liu L, Wang C, Xu Y, Lin S, Zhang S, Tan Y. Ginsenoside Rb1 attenuates methamphetamine (METH)-induced neurotoxicity through the NR2B/ERK/CREB/BDNF signalings in vitro and in vivo models. Journal of Ginseng Research 2022, 46, 426–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).