Submitted:
09 June 2023
Posted:
12 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
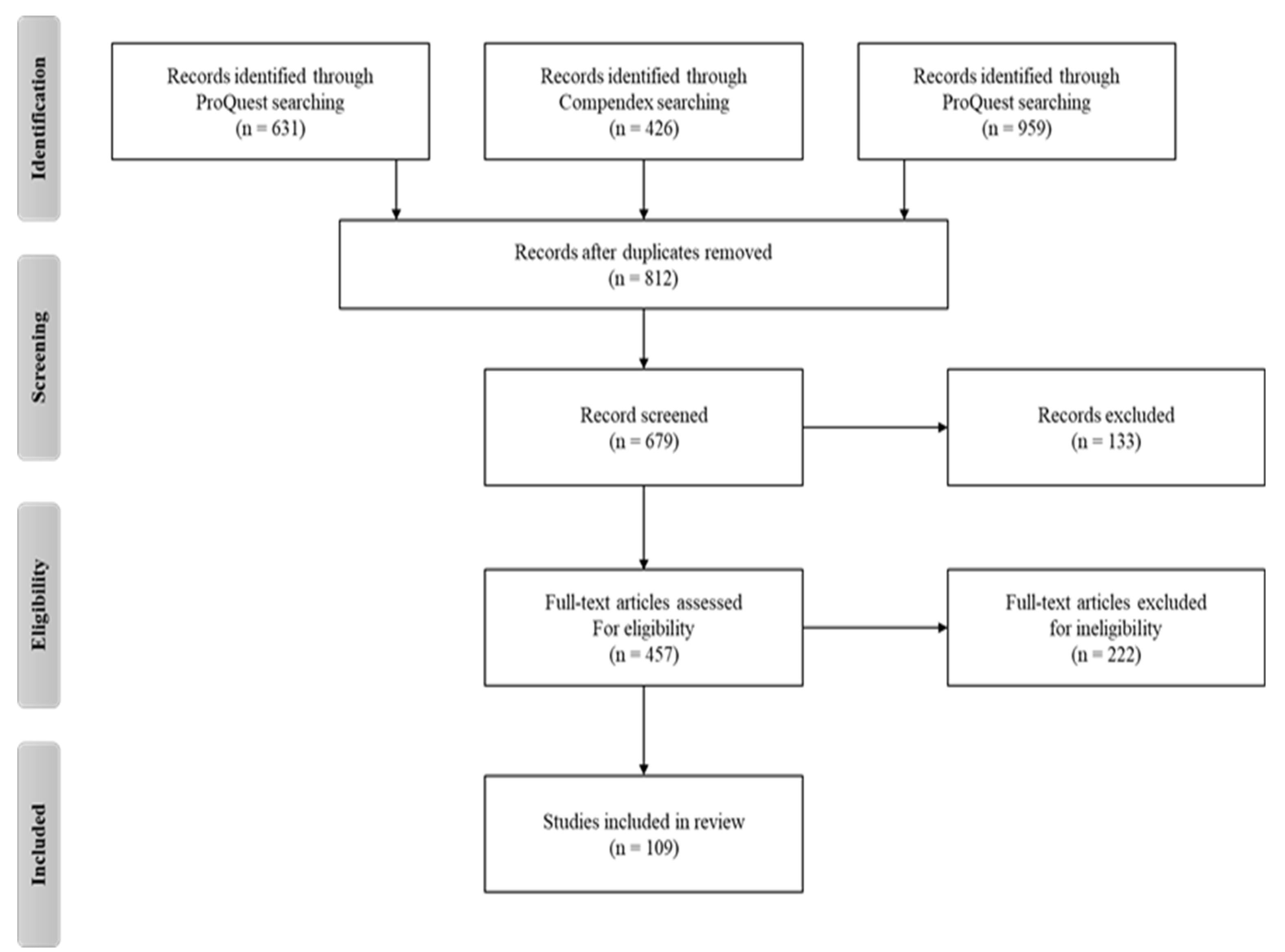
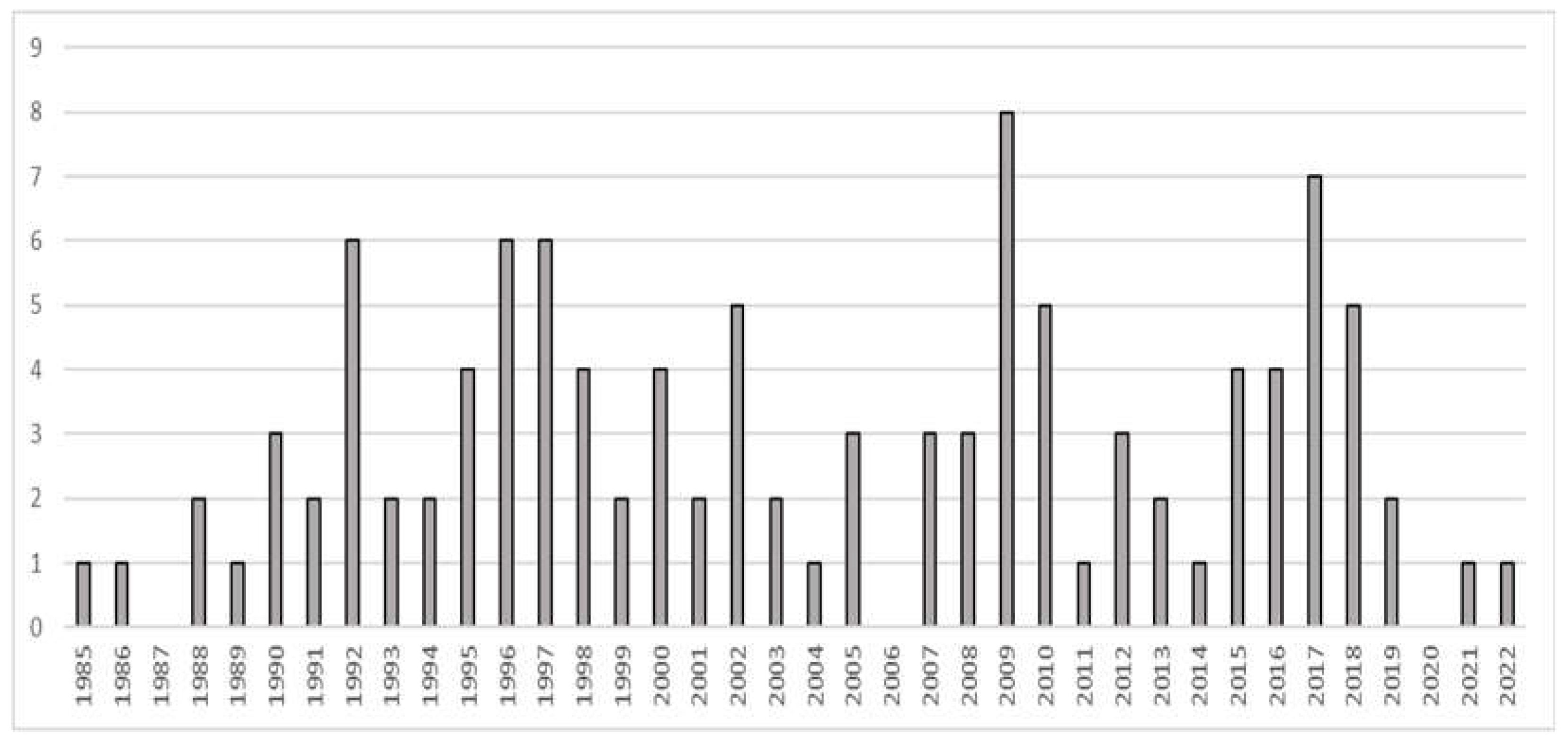
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
References
- Chung, W.; Swink, M. Patterns of Advanced Manufacturing Technology Utilization and Manufacturing Capabilities. Prod. Oper. Manag. 2009, 18, 533–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, I.; Small, M. Implementing advanced manufacturing technology: An integrated planning model. Omega 1994, 22, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, T.; Shankar, R.; Suhaib, M. A review of some issues and identification of some barriers in the implementation of FMS. Int. J. Flex. Manuf. Syst. 2007, 19, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millen, R.; Sohal, A.S. Planning processes for advanced manufacturing technology by large American manufacturers. Technovation 1998, 18, 741–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löfsten, H. and P. Lindelöf (2002). "Science Parks and the growth of new technology-based firms—academic-industry links, innovation and markets." Research policy 31(6): 859-876. [CrossRef]
- Chan, F.; Chan, M.; Lau, H.; Ip, R. Investment appraisal techniques for advanced manufacturing technology (AMT): a literature review. Integr. Manuf. Syst. 2001, 12, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gertler, M.S. "Being There": Proximity, Organization, and Culture in the Development and Adoption of Advanced Manufacturing Technologies. Econ. Geogr. 1995, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, M.H.; Yasin, M.M. Advanced manufacturing technology: Implementation policy and performance. J. Oper. Manag. 1997, 15, 349–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udoka, S.J.; Nazemetz, J.W. An empirically based analysis of the requirements for successful implementation of advanced manufacturing technology (AMT). Comput. Ind. Eng. 1990, 19, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, J.; Gunasekaran, A. Implementation of advanced manufacturing technology through industry-government-university co-operation in Taiwan. Comput. Ind. 1993, 22, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Singh, H.; Chandel, R. Exploring the key success factors of advanced manufacturing technology implementation in Indian manufacturing industry. J. Manuf. Technol. Manag. 2018, 29, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 12. Chan, F., et al. (2015). Barriers to advanced manufacturing technology in small-medium enterprises (SMEs) in Malaysia. 2015 International Symposium on Technology Management and Emerging Technologies (ISTMET), IEEE.
- Yu, N., et al. (2011). "Drivers and barriers for implementing advanced manufacturing technology in China's furniture industry: An exploratory study." Forest Products Journal 61(1): 83-91. [CrossRef]
- Singh, H. and J. Khamba (2009). "Evolving the barriers for enhancing the utilization level of advanced manufacturing technologies (AMTs) in Indian manufacturing industry." International Journal of Advanced Operations Management 1(2-3): 135-150. [CrossRef]
- Efstathiades, A.; A Tassou, S.; Oxinos, G.; Antoniou, A. Advanced manufacturing technology transfer and implementation in developing countries: The case of the Cypriot manufacturing industry. Technovation 2000, 20, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Co, H.C. Adoption and implementation of advanced manufacturing technology in Singapore. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 1997, 48, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marri, H. B., et al. (2007). "Implementation of advanced manufacturing technology in Pakistani small and medium enterprises: an empirical analysis." Journal of Enterprise Information Management 20(6): 726-739.
- Castrillón, I.D.; Cantorna, A.I.S. The effect of the implementation of advanced manufacturing technologies on training in the manufacturing sector. J. Eur. Ind. Train. 2005, 29, 268–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, A.M. Adopting advanced manufacturing technologies: Experience from Spain. J. Manuf. Syst. 1996, 15, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stock, G. N. and C. M. McDermott (2000). "Implementing advanced manufacturing technology: The role of organizational culture." Production & Inventory Management Journal 41(3): 66-66. [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Khamba, J. An empirical examination for enhancing the utilization level of advanced manufacturing technologies in India. J. Adv. Manag. Res. 2010, 7, 112–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H. and J. Khamba (2010). "Research Methodology for Effective Utilization of Advanced Manufacturing Technologies in Northern India Manufacturing Industry." IUP Journal of Operations Management 9.
- Small, M.H.; Yasin, M.M. Developing a framework for the effective planning and implementation of advanced manufacturing technology. Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 1997, 17, 468–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, M.; Åhlström, P.; Yalabik, B.; Mårtensson, P. Implementing advanced service technology in the public sector: an exploratory study of the relevance and limitations of insights from private sector manufacturing technology implementation. Prod. Plan. Control. 2012, 24, 916–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saberi, S.; Yusuff, R.M. Neural network application in predicting advanced manufacturing technology implementation performance. Neural Comput. Appl. 2010, 21, 1191–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efstathiades, A.; Tassou, S.; Antoniou, A. Strategic planning, transfer and implementation of Advanced Manufacturing Technologies (AMT). Development of an integrated process plan. Technovation 2002, 22, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, C.; Orr, S. Advanced manufacturing technology adoption—the German experience. Technovation 2005, 25, 711–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, A.J.; A Barton, R. Characterizing SME migration towards advanced manufacturing technologies. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B: J. Eng. Manuf. 2011, 226, 745–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narkhede, B. E. (2017). "Advance manufacturing strategy and firm performance: An empirical study in a developing environment of small-and medium-sized firms." Benchmarking: An International Journal 24(1): 62-101.
- Shani, A. (.; Grant, R.M.; Krishnan, R.; Thompson, E. Advanced Manufacturing Systems and Organizational Choice: Sociotechnical System Approach. Calif. Manag. Rev. 1992, 34, 91–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pao-Long, C. and S. S. Lung (2002). "Organizational changes for advanced manufacturing technology infusion: An empirical study." International Journal of Management 19(2): 206.
- Tesar, A. (1995). Advanced manufacturing: Technology and international competitiveness, Lawrence Livermore National Lab., CA (United States).
- Khorsheed, M.S.; A Al-Fawzan, M. Fostering university–industry collaboration in Saudi Arabia through technology innovation centers. Innovation 2014, 16, 224–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, N., et al. (2011). "Drivers and barriers for implementing advanced manufacturing technology in China's furniture industry: An exploratory study." Forest Products Journal 61(1): 83-91. [CrossRef]
- Bessant, J. The integration barrier; problems in the implementation of advanced manufacturing technology. Robotica 1985, 3, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, E. and D. Wield (1994). Implementing new technologies: innovation and the management of technology, Wiley Blackwell.
- Dimnik, T.; Johnston, D. Manufacturing managers and the adoption of advanced manufacturing technology. Omega 1993, 21, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H., et al. (2001). "Evaluating advanced manufacturing technology in Chinese state-owned enterprises: a survey and case studies." The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology 18(7): 528-536. [CrossRef]
- Swamidass, P.M.; Winch, G.W. Exploratory study of the adoption of manufacturing technology innovations in the USA and the UK. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2002, 40, 2677–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putterill, M.; Maguire, W.; Sohal, A.S. Advanced manufacturing technology investment: criteria for organizational choice and appraisal. Integr. Manuf. Syst. 1996, 7, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapitsyn, V.M.; Gerasimenko, O.A.; Andronova, L.N. Analysis of the status and trends of applications of advanced manufacturing technologies in Russia. Stud. Russ. Econ. Dev. 2017, 28, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourke, J., & Roper, S. (2016). AMT adoption and innovation: An investigation of dynamic and complementary effects. Technovation, 55, 42-55. [CrossRef]
- Saberi, S.; Yusu, R.M.; Zulkifli, N.; Ahma, M.M. Effective Factors on Advanced Manufacturing Technology Implementation Performance: A Review. J. Appl. Sci. 2010, 10, 1229–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, R.d.R.; de Lima, E.P.; da Costa, S.E.G. Identifying organizational requirements for the implementation of Advanced Manufacturing Technologies (AMT). J. Manuf. Syst. 2012, 31, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.-H.; Wang, T.-C. Measuring the success possibility of implementing advanced manufacturing technology by utilizing the consistent fuzzy preference relations. Expert Syst. Appl. 2009, 36, 4313–4320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, I. J. and M. H. Small (1996). "Planning for advanced manufacturing technology: a research framework." International Journal of Operations & Production Management 16(5): 4-24.
- da Costa, S.G.; de Lima, E.P. Advanced manufacturing technology adoption: an integrated approach. J. Manuf. Technol. Manag. 2008, 20, 74–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dangayach, G. and S. Deshmukh (2005). "Advanced manufacturing technology implementation: evidence from Indian small and medium enterprises (SMEs)." Journal of Manufacturing Technology Management 16(5): 483-496.
- Osola, J. Advanced manufacturing technology—the challenge. Comput. Eng. J. 1986, 3, 75–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eid, R. (2009). "Factors affecting the success of world class manufacturing implementation in less developed countries: The case of Egypt." Journal of Manufacturing Technology Management 20(7): 989-1008. [CrossRef]
- Chung, K. Deriving advantages from advanced manufacturing technology — an organizing paradigm. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 1991, 25, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teoi, A.Y.; Anholon, R.; da Silva, D.; Quelhas, O.L.G. Critical factors for the dimensional management system (DMS) implementation in manufacturing industries. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 88, 1053–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambasivarao, K. and S. Deshmukh (1995). "Selection and implementation of advanced manufacturing technologies: classification and literature review of issues." International Journal of Operations & Production Management 15(10): 43-62.
- Park, Y.-T. National systems of Advanced Manufacturing Technology (AMT): hierarchical classification scheme and policy formulation process. Technovation 2000, 20, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohal, A.S. A longitudinal study of planning and implementation of advanced manufacturing technologies. Int. J. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 1997, 10, 281–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwannapirom, S. and S. Lertputtarak (2008). "Across the boundary of advanced manufacturing technology transfer in auto-parts industry in Thailand." Universitatii Bucuresti. Analele. Seria Stiinte Economice si Administrative 2: 113.
- Percival, J.C. Complementarities Between Advanced Manufacturing Technologies. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2009, 56, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hynek, J., et al. (2009). "Problems associated with investment in advanced manufacturing technology from the management point of view." WSEAS Transactions on Systems 8(6): 753-762.
- Banakar, Z. and F. Tahriri (2010). "Justification and classification of issues for the selection and implementation of advanced manufacturing technologies." World Academy of Science, Engineering and Technology 65: 341-349.
- Sharma, A.; Dangayach, G.; Pathak, S. Implementation of advanced manufacturing technologies: experiences of Indian manufacturing companies. Int. J. Bus. Syst. Res. 2008, 2, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohal Amrik, S. (1992). "Implementing Advanced Manufacturing Technology: Factors Critical to Success." Logistics Information Management 5(1): 39-46.
- Storto, C.L. A double-DEA framework to support decision-making in the choice of advanced manufacturing technologies. Manag. Decis. 2018, 56, 488–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, K. L. L. and A. Seetharaman (2003). "Towards a better manufacturing sector: a perspective on the implementation of advanced manufacturing technology in Malaysia." International Journal of Management 20(4): 490.
- Leonard-Barton, D.; Deschamps, I. Managerial Influence in the Implementation of New Technology. Manag. Sci. 1988, 34, 1252–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, M.; Åhlström, P.; Yalabik, B.; Mårtensson, P. Implementing advanced service technology in the public sector: an exploratory study of the relevance and limitations of insights from private sector manufacturing technology implementation. Prod. Plan. Control. 2012, 24, 916–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beatty, C. Implementing advanced manufacturing technologies: Rules of the road. Long Range Plan. 1993, 26, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, P. Advanced technology design, people and organization: experience of Australian industrial collaboration. Integr. Manuf. Syst. 1996, 7, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zammuto, R. F. and E. J. O'Connor (1992). "Gaining advanced manufacturing technologies' benefits: The roles of organization design and culture." Academy of Management Review 17(4): 701-728. [CrossRef]
- Hayes, R.H.; Jaikumar, R. Requirements for successful implementation of new manufacturing technologies. J. Eng. Technol. Manag. 1991, 7, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Chen, I.; Chiang, D. Determining organizational structure choices in advanced manufacturing technology management. Omega 1997, 25, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDermott, C.M.; Stock, G.N. Organizational culture and advanced manufacturing technology implementation. J. Oper. Manag. 1999, 17, 521–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.A. Human issues influencing the successful implementation of advanced manufacturing technology. J. Eng. Technol. Manag. 1996, 13, 283–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaumont, N. , et al. (2002). "Do foreign-owned firms manage advanced manufacturing technology better?" International Journal of Operations & Production Management 22(7): 759-771.
- Gupta, A.; Prinzinger, J.; Messerschmidt, D.C. Role of organizational commitment in advanced manufacturing technology and performance relationship. Integr. Manuf. Syst. 1998, 9, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukathong, S.; Suksawang, P.; Naenna, T. Analyzing the importance of critical success factors for the adoption of advanced manufacturing technologies. Int. J. Eng. Bus. Manag. 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, Y.P. ; Yakimchuk Impact of advanced manufacturing technology on industrial relations: A comparative study. Eng. Manag. Int. 1989, 5, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Torre, P.; Álvarez, M.; Sarkis, J.; Adenso-Díaz, B. Barriers to the Implementation of Environmentally Oriented Reverse Logistics: Evidence from the Automotive Industry Sector. Br. J. Manag. 2010, 21, 889–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, M.H.; Yasin, M. Advanced manufacturing technology adoption and performance: the role of management information systems departments. Integr. Manuf. Syst. 2003, 14, 409–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, Y.K. A Comprehensive Bibliography on Justification of Advanced Manufacturing Technologies. Eng. Econ. 1992, 38, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- du Preez, W. B. and D. J. De Beer (2015). "Implementing the South African additive manufacturing technology roadmap-the role of an additive manufacturing centre of competence." South African Journal of Industrial Engineering 26(2): 85-92. [CrossRef]
- Ghobakhloo, M. Determinants of information and digital technology implementation for smart manufacturing. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2019, 58, 2384–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udo, G. J. and I. C. Ehie (1996). "Advanced manufacturing technologies: Determinants of implementation success." International Journal of Operations & Production Management 16(12): 6-26.
- Youssef, M.A.; Zairi, M. Benchmarking supplier partnerships in the context of advanced manufacturing technology implementation. Benchmarking Qual. Manag. Technol. 1996, 3, 4–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zairi, M. Supplier partnerships for effective advanced manufacturing technology implementation: a proposed model. Integr. Manuf. Syst. 1998, 9, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado, A. (2013). "Problems in the implementation process of advanced manufacturing technologies." The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology 64(1-4): 123-131. [CrossRef]
- Co, H. C., et al. (1998). "The human factor in advanced manufacturing technology adoption: an empirical analysis." International Journal of Operations & Production Management 18(1): 87-106.
- Khan, A. and K. Nasser (2016). "Advanced manufacturing technologies for smart and competitive businesses." IUP Journal of Operations Management 15(3): 7.
- Szalavetz, A. The Environmental Impact of Advanced Manufacturing Technologies: Examples from Hungary. Central Eur. Bus. Rev. 2017, 6, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H. and J. Khamba (2008). "Evaluating the Barriers for Enhancing the Utilization Level of Advanced Manufacturing Technologies (AMTs) in Indian Manufacturing Industry." training 4: 22.
- Brandyberry, A.; Rai, A.; White, G.P. Intermediate Performance Impacts of Advanced Manufacturing Technology Systems: An Empirical Investigation*. Decis. Sci. 1999, 30, 993–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonsson, P. (2000). "An empirical taxonomy of advanced manufacturing technology." International Journal of Operations & Production Management 20(12): 1446-1474. [CrossRef]
- Wall, T.D.; Corbett, J.M.; Clegg, C.W.; Jackson, P.R.; Martin, R. Advanced manufacturing technology and work design: Towards a theoretical framework. J. Organ. Behav. 1990, 11, 201–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y., & Cecil, J. (2016). An Internet of Things (IoT)-based collaborative framework for advanced manufacturing. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 84, 1141-1152.
- Hottenstein, M.P.; Dean, J.W. Managing Risk in Advanced Manufacturing Technology. Calif. Manag. Rev. 1992, 34, 112–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, A. (2018). "Relationships between advanced manufacturing technologies, absorptive capacity, mass customization, time to market and financial and market performance: An empirical investigation." Asia-Pacific Journal of Business Administration 10(1): 2-20.
- Teng, K. L. L. and A. Seetharaman (2004). "The selection and management of cost justification techniques among advanced manufacturing technology companies in Malaysia." International Journal of Management 21(1): 45.
- Ghobakhloo, M.; Azar, A. Business excellence via advanced manufacturing technology and lean-agile manufacturing. J. Manuf. Technol. Manag. 2018, 29, 2–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, M.H. Planning, justifying and installing advanced manufacturing technology: a managerial framework. J. Manuf. Technol. Manag. 2007, 18, 513–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyori, G. M., & Ogola, J. M. (2015). Advanced manufacturing technology adoption in manufacturing companies in Kenya.
- Cheng, Y.; Matthiesen, R.; Farooq, S.; Johansen, J.; Hu, H.; Ma, L. The evolution of investment patterns on advanced manufacturing technology (AMT) in manufacturing operations: A longitudinal analysis. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2018, 203, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saliba, M. A., et al. (2017). "A study on the use of advanced manufacturing technologies by manufacturing firms in a small, geographically isolated, developed economy: the case of Malta." The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology 89(9-12): 3691-3707. [CrossRef]
- Dean Jr, J. W., et al. (1990). "Technical, economic and political factors in advanced manufacturing technology implementation." Journal of Engineering and Technology Management 7(2): 129-144. [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, E.B.; Uygun, Y. Strengthening advanced manufacturing innovation ecosystems: The case of Massachusetts. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2018, 136, 178–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjan, S.; Jha, V.K.; Pal, P. Application of emerging technologies in ERP implementation in Indian manufacturing enterprises: an exploratory analysis of strategic benefits. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 88, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- (Majchrzak, A. (1988). The human side of factory automation: Managerial and human resource strategies for making automation succeed, Jossey-Bass.
- Abd Rahman, A. and D. Bennett (2009). "Advanced manufacturing technology adoption in developing countries: The role of buyer-supplier relationships." Journal of Manufacturing Technology Management 20(8): 1099-1118. [CrossRef]
- Siegel, D.; Waldman, D.; Youngdahl, W. The adoption of advanced manufacturing technologies: human resource management implications. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 1997, 44, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkuika, G.L.F.N.; Yiqun, X. Quantitative Evaluation and Optimization Path of Advanced Manufacturing Development Policy Based on the PMC–AE Index Model. Int. J. Glob. Bus. Competitiveness 2022, 17, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, T.; Feng, T.; Ye, C. Advanced Manufacturing Technologies and Green Innovation: The Role of Internal Environmental Collaboration. Sustainability 2016, 8, 1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Tang, R.; Ji, Y.; Liu, F.; Gao, L.; Huisingh, D. Impact of advanced manufacturing on sustainability: An overview of the special volume on advanced manufacturing for sustainability and low fossil carbon emissions. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 161, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Search Phase | ProQuest | Compendex | Google Scholar | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All articles contain at least one of the following keywords in their abstract or title: AMT AND Critical factors, AMT AND Challenges, AMT AND Barriers, AMT AND Adoption, and AMT AND Implementation. | 1,282 | 864 | 1,822 | |
| All articles contain at least one of the additional keywords in their abstract or title: country, economy, company, organization, sector, and industry. | 206 | 127 | 346 | |
| All articles with substantively relevant text (fit for purpose) | 122 | 104 | 231 | |
| All articles with effectively relevant text (fit for purpose) | 41 | 33 | 35 | 109 |
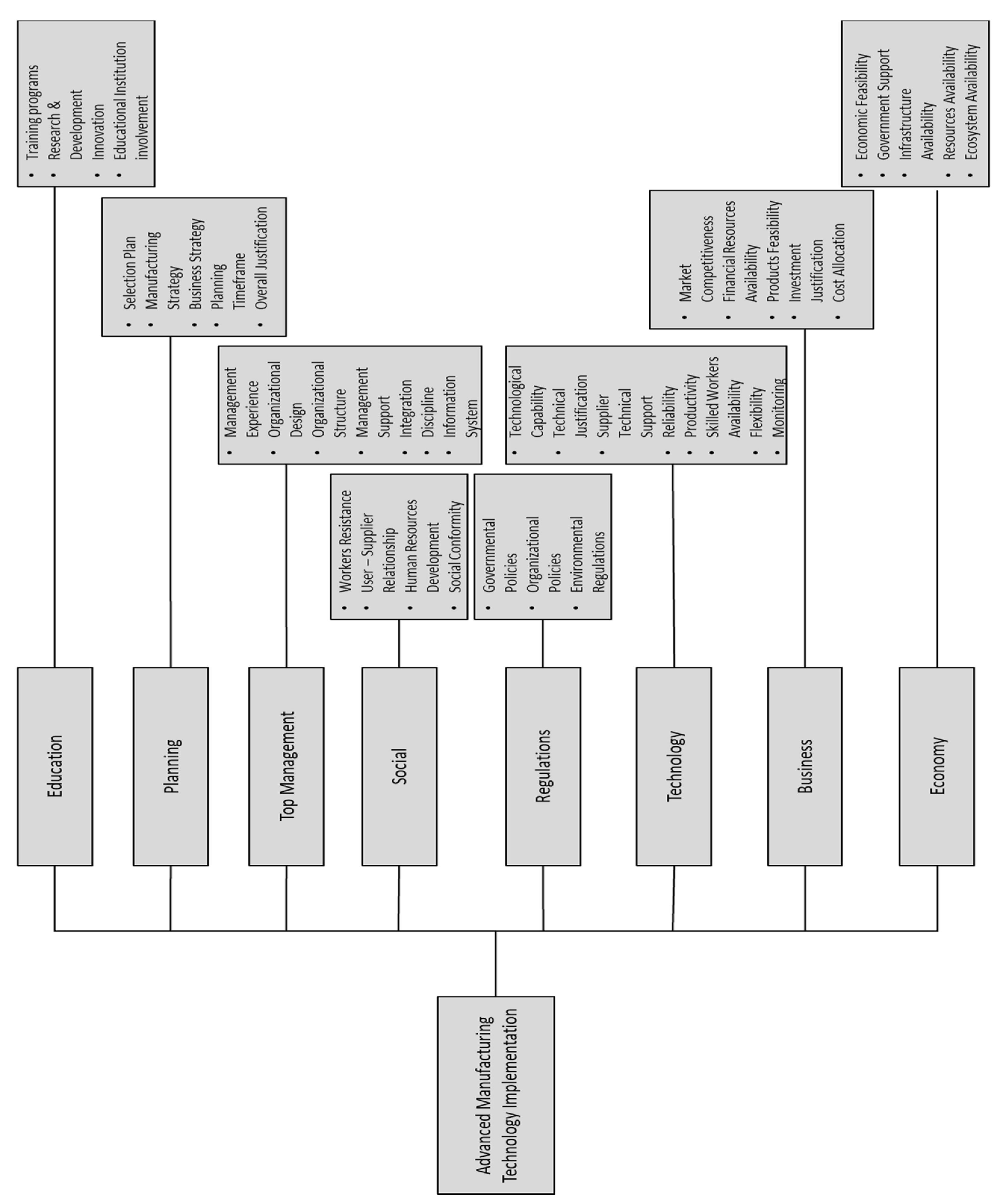
| Category | Number of studies | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Education | 5 | 5% |
| Planning | 6 | 6% |
| Management | 32 | 29% |
| Technology | 13 | 12% |
| Business | 12 | 11% |
| Economy | 13 | 12% |
| Regulations | 5 | 5% |
| Social | 10 | 9% |
| Mix | 13 | 12% |
| Total | 109 |
| Country | Number of studies |
|---|---|
| Australia | 3 |
| Brazil | 3 |
| Canada | 3 |
| China | 3 |
| Cyprus | 2 |
| Czech Republic | 1 |
| Egypt | 1 |
| Germany | 1 |
| Hong Kong | 2 |
| Hungary | 1 |
| India | 11 |
| Iran | 2 |
| Italy | 1 |
| Kenya | 1 |
| Malaysia | 7 |
| Malta | 1 |
| Mexico | 1 |
| New Zealand | 1 |
| Pakistan | 2 |
| Russia | 1 |
| Saudi Arabia | 3 |
| Singapore | 3 |
| South Africa | 1 |
| South Korea | 1 |
| Spain | 3 |
| Sweden | 3 |
| Taiwan | 3 |
| Thailand | 3 |
| UK | 8 |
| USA | 34 |
| Critical Factor | References |
|---|---|
| Training programs | [6,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22] |
| Research and development | [12,14,17,18,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33] |
| Innovation | [3,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42] |
| Educational institutions involvement | [10,33] |
| Critical Factor | References |
|---|---|
| Selection Plan | [2,4,6,16,23,26,35,43,44,46,47,48,49,50,51,52] |
| Manufacturing Strategy | [2,9,11,36,43,44,51,53,54,55,56,57] |
| Business Strategy | [2,23,40,45,49,50,51,55,58,59,60,61] |
| Planning Timeframe | [4,12,23,46,47,62] |
| Overall Justification | [2,4,12,44,58,63] |
| Critical Factor | References |
|---|---|
| Organizational Design | [11,24,36,47,63,67,68] |
| Organizational Structure | [11,12,13,16,22,31,44,47,64,69,70] |
| Organizational Culture | [9,13,17,20,25,58,68,71] |
| Management Support | [2,3,9,16,17,19,24,28,50,52,55,56,59,61,64,67,69,71,72,73,74,75,85] |
| Integration | [12,59,66,76] |
| Information System | [9,29,30,38,77,78] |
| Critical Factor | References |
|---|---|
| Technological Capability | [1,3,9,12,23,35,50,67] |
| Technical Justification | [2,22,24,25,43,49,59,62,63,79,80,81] |
| Supplier Technical Support | [12,15,45,56,67,73,82,83,84] |
| Reliability | [2,3,9,16,17,19,24,28,50,52,55,56,59,61,64,67,69,71,72,73,74,75,85] |
| Productivity | [13,37,51,58,59,63,72,86,87,88] |
| Flexibility | [2,14,18,22,23,26,59,71,72,76,86,89,90] |
| Monitoring | [2,23,25,26,29,38,43,60,62,69,70,74,90,91,92,93,98] |
| Critical Factor | References |
|---|---|
| Market Competitiveness | [9,26,27,32,37,48,49,55,58,59,60,71,87,90,94,95,96,97] |
| Financial Resources Availability | [12,16,38,48,56,67] |
| Products Feasibility | [3,4,39,44,48,49,62,82,95,96] |
| Investment Justification | [5,6,39,44,55,58,63,67,69,85,96,98,99,100] |
| Cost Allocation | [3,12,13,53,58,77,82,96] |
| Critical Factor | References |
|---|---|
| Economic Feasibility | [25,32,63,79,80,101] |
| Government Support | [5,10,12,32,101,102] |
| Infrastructure Availability | [5,12,14,15,22,39,43,46,53,54,85,91] |
| Resources Availability | [5,17,60,85,88,102] |
| Ecosystem Availability | [39,50,60,67,80,103,104] |
| Critical Factor | References |
|---|---|
| Workers Resistance | [3,4,9,12,13,14,17,43,44,45,55,66,72,76,105] |
| User–Supplier Relationship | [7,9,15,26,45,46,61,67,69,73,83,84,85,106] |
| Human Resources Development | [11,15,17,18,22,25,43,56,59,61,67,72,98,107] |
| Social Conformity | [3,59,71,76,92,102,105] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




