Submitted:
29 May 2023
Posted:
13 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. The different forms of Major CMTs
2.1. Demyelinated CMT
2.1.1. CMT1A (PMP22)
2.1.2. CMT1B (MPZ)
2.1.3. CMTX1 (GJB)
2.2. Axonal CMT
2.2.1. CMT2A (MFN2)
3. CMT treatment with compounds and drugs (Table 1)
3.1. Clinical research (previous and current)
3.1.1. Ascorbic acid
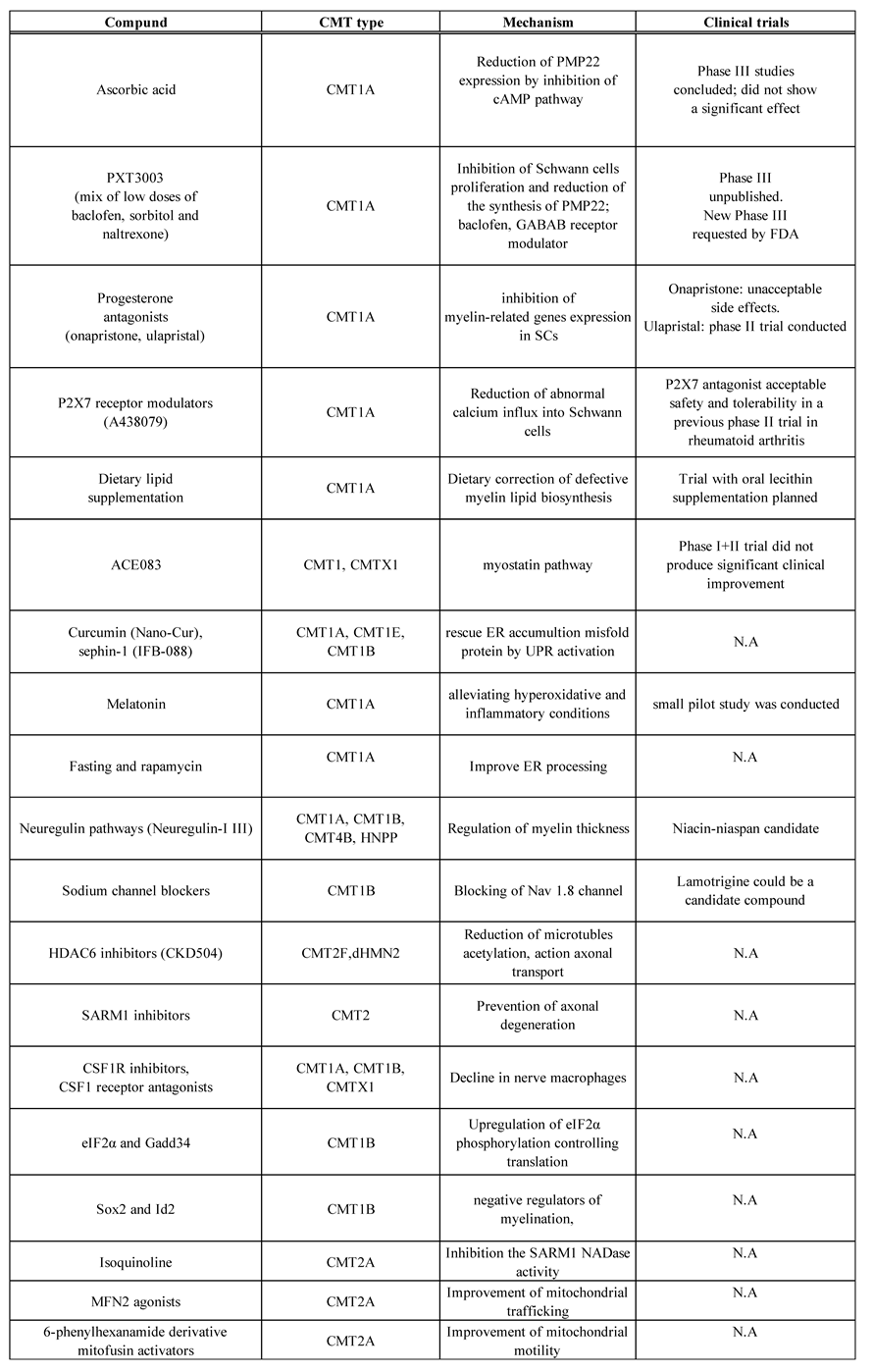
3.1.2. PXT3000
3.1.3. Progesterone receptor antagonist
3.1.4. ACE-083
3.1.5. P2X7 purinoreceptors
3.1.6. Lipid supplementation
3.2. Preclinical research
3.2.1. Neuregulin-1 type I (NRG1)
3.2.2. Curcumin
3.2.3. Sephin-1
3.2.4. Eukaryotic initiation factor 2-phosphorylation (eIF2α) and Gadd34
3.2.5. Melatonin
3.2.6. HDAC6 inhibitor
3.2.7. Fasting and rapamycin
3.2.8. Sox2 and Id2
3.2.9. Colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor inhibitor
3.2.10. Sodium channel blockers
3.2.11. SARM1 Pathway
3.2.12. MFN2 agonist and MFN1
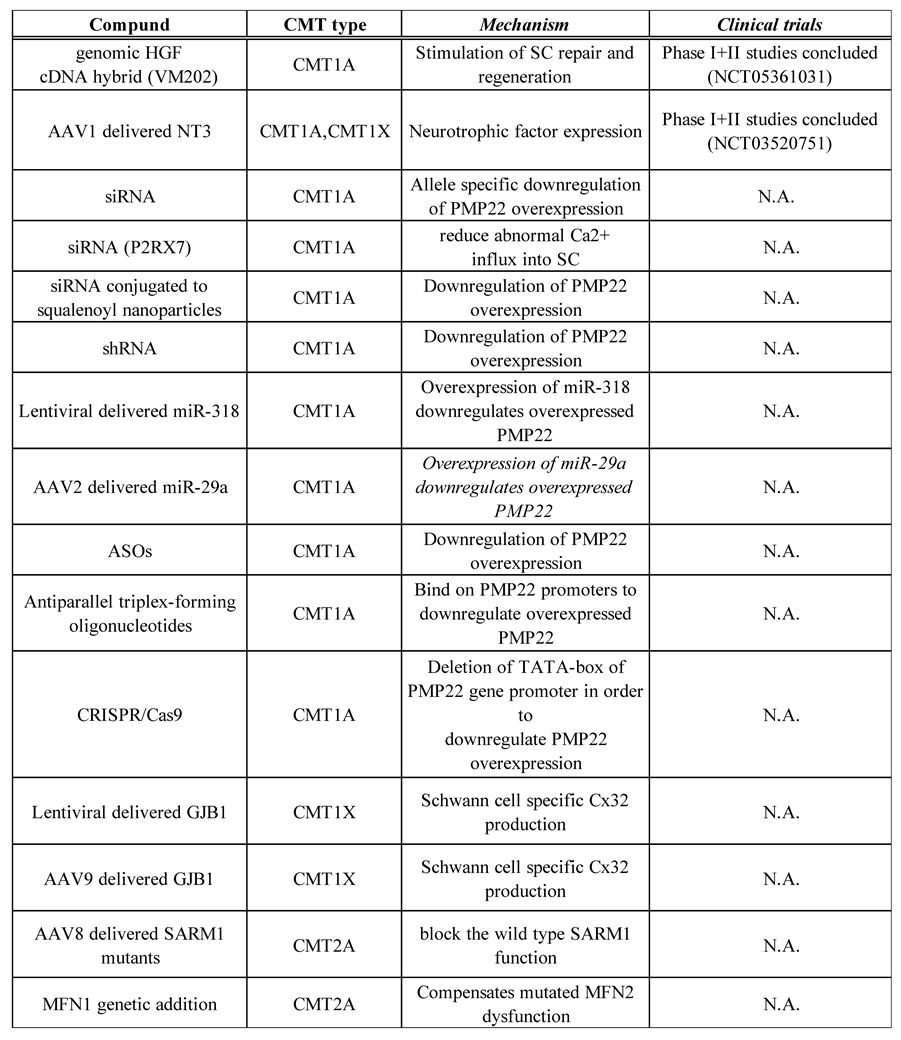
3.3. CMT treatment with gene-mediated therapy (Table 2)
3.3.1. Viral vector-based therapy and the growth factors neurotrophin 3
3.3.2. Gene silencing therapy
3.3.3. CRISPR/Cas9
3.3.4. Hepatocyte Growth factor: Engenesis®️ VM202
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stavrou, M.; Sargiannidou, I.; Georgiou, E.; Kagiava, A.; Kleopa, K.A. Emerging therapies for Charcot-Marie-Tooth inherited neuropathies. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22. [CrossRef]
- Pareyson, D.; Saveri, P.; Pisciotta, C. New developments in Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathy and related diseases. Curr Opin Neurol 2017, 30, 471–480. [CrossRef]
- Patzkó, A.; Shy, M.E. Update on Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep 2011, 11, 78–88. [CrossRef]
- Dyck, P.J.; Lambert, E.H. Lower motor and primary sensory neuron diseases with peroneal muscular atrophy. II. Neurologic, genetic, and electrophysiologic findings in various neuronal degenerations. Arch Neurol 1968, 18, 619–625. [CrossRef]
- Dyck, P.J.; Lambert, E.H. Lower motor and primary sensory neuron diseases with peroneal muscular atrophy. I. Neurologic, genetic, and electrophysiologic findings in hereditary polyneuropathies. Arch Neurol 1968, 18, 603–618. [CrossRef]
- Juneja, M.; Burns, J.; Saporta, M.A.; Timmerman, V. Challenges in modelling the Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathies for therapy development. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2019, 90, 58–67. [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, Y.; Takashima, H. Clinical genetics of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. J Hum Genet 2023, 68, 199–214. [CrossRef]
- Saporta, A.S.; Sottile, S.L.; Miller, L.J.; Feely, S.M.; Siskind, C.E.; Shy, M.E. Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease subtypes and genetic testing strategies. Ann Neurol 2011, 69, 22–33. [CrossRef]
- DiVincenzo, C.; Elzinga, C.D.; Medeiros, A.C.; Karbassi, I.; Jones, J.R.; Evans, M.C.; Braastad, C.D.; Bishop, C.M.; Jaremko, M.; Wang, Z.; Liaquat, K.; Hoffman, C.A.; York, M.D.; Batish, S.D.; Lupski, J.R.; Higgins, J.J. The allelic spectrum of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease in over 17,000 individuals with neuropathy. Mol Genet Genomic Med 2014, 2, 522–529. [CrossRef]
- Pisciotta, C.; Saveri, P.; Pareyson, D. Challenges in treating Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease and related neuropathies: Current management and future perspectives. Brain Sci 2021, 11. [CrossRef]
- Stavrou, M.; Sargiannidou, I.; Christofi, T.; Kleopa, K.A. Genetic mechanisms of peripheral nerve disease. Neurosci Lett 2021, 742, 135357. [CrossRef]
- Snipes, G.J.; Suter, U.; Welcher, A.A.; Shooter, E.M. Characterization of a novel peripheral nervous system myelin protein (PMP-22/SR13). J Cell Biol 1992, 117, 225–238. [CrossRef]
- Adlkofer, K.; Martini, R.; Aguzzi, A.; Zielasek, J.; Toyka, K.V.; Suter, U. Hypermyelination and demyelinating peripheral neuropathy in Pmp22-deficient mice. Nat Genet 1995, 11, 274–280. [CrossRef]
- Fledrich, R.; Stassart, R.M.; Klink, A.; Rasch, L.M.; Prukop, T.; Haag, L.; Czesnik, D.; Kungl, T.; Abdelaal, T.A.; Keric, N.; Stadelmann, C.; Brück, W.; Nave, K.A.; Sereda, M.W. Soluble neuregulin-1 modulates disease pathogenesis in rodent models of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease 1A. Nat Med 2014, 20, 1055–1061. [CrossRef]
- Shy, M.E.; Jáni, A.; Krajewski, K.; Grandis, M.; Lewis, R.A.; Li, J.; Shy, R.R.; Balsamo, J.; Lilien, J.; Garbern, J.Y.; Kamholz, J. Phenotypic clustering in MPZ mutations. Brain 2004, 127, 371–384. [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, T.; Ando, M.; Okamoto, Y.; Yoshimura, A.; Higuchi, Y.; Hashiguchi, A.; Shiga, K.; Hayashida, A.; Hatano, T.; Ishiura, H.; Mitsui, J.; Hattori, N.; Mizuno, T.; Nakagawa, M.; Tsuji, S.; Takashima, H. Genetic spectrum of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease associated with myelin protein zero gene variants in Japan. Clin Genet 2021, 99, 359–375. [CrossRef]
- Scherer, S.S.; Kleopa, K.A. X-linked Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. J Peripher Nerv Syst 2012, 17(suppl 3), 9–13. [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.H.; Sakiyama, Y.; Hashiguchi, A.; Ando, M.; Okamoto, Y.; Yoshimura, A.; Higuchi, Y.; Takashima, H. Genetic and phenotypic profile of 112 patients with X-linked Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1. Eur J Neurol 2018, 25, 1454–1461. [CrossRef]
- Abrams, C.K.; Freidin, M.; Bukauskas, F.; Dobrenis, K.; Bargiello, T.A.; Verselis, V.K.; Bennett, M.V.; Chen, L.; Sahenk, Z. Pathogenesis of X-linked Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease: Differential effects of two mutations in connexin 32. J Neurosci 2003, 23, 10548–10558. [CrossRef]
- Yiu, E.M.; Geevasinga, N.; Nicholson, G.A.; Fagan, E.R.; Ryan, M.M.; Ouvrier, R.A. A retrospective review of X-linked Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease in childhood. Neurology 2011, 76, 461–466. [CrossRef]
- Siskind, C.; Feely, S.M.; Bernes, S.; Shy, M.E.; Garbern, J.Y. Persistent CNS dysfunction in a boy with CMT1X. J Neurol Sci 2009, 279, 109–113. [CrossRef]
- Feely, S.M.; Laura, M.; Siskind, C.E.; Sottile, S.; Davis, M.; Gibbons, V.S.; Reilly, M.M.; Shy, M.E. MFN2 mutations cause severe phenotypes in most patients with CMT2A. Neurology 2011, 76, 1690–1696. [CrossRef]
- Piscosquito, G.; Saveri, P.; Magri, S.; Ciano, C.; Di Bella, D.; Milani, M.; Taroni, F.; Pareyson, D. Mutational mechanisms in MFN2-related neuropathy: Compound heterozygosity for recessive and semidominant mutations. J Peripher Nerv Syst 2015, 20, 380–386. [CrossRef]
- Barbullushi, K.; Abati, E.; Rizzo, F.; Bresolin, N.; Comi, G.P.; Corti, S. Disease modeling and therapeutic strategies in CMT2A: State of the art. Mol Neurobiol 2019, 56, 6460–6471. [CrossRef]
- Kiepura, A.J.; Kochański, A. Charcot-Marie-Tooth type 1A drug therapies: Role of adenylyl cyclase activity and G-protein coupled receptors in disease pathomechanism. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars) 2018, 78, 198–209. [CrossRef]
- Kaya, F.; Belin, S.; Diamantidis, G.; Fontes, M. Ascorbic acid is a regulator of the intracellular cAMP concentration: Old molecule, new functions? FEBS Lett 2008, 582, 3614–3618. [CrossRef]
- Passage, E.; Norreel, J.C.; Noack-Fraissignes, P.; Sanguedolce, V.; Pizant, J.; Thirion, X.; Robaglia-Schlupp, A.; Pellissier, J.F.; Fontés, M. Ascorbic acid treatment corrects the phenotype of a mouse model of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. Nat Med 2004, 10, 396–401. [CrossRef]
- Pareyson, D.; Reilly, M.M.; Schenone, A.; Fabrizi, G.M.; Cavallaro, T.; Santoro, L.; Vita, G.; Quattrone, A.; Padua, L.; Gemignani, F.; Visioli, F.; Laurà, M.; Radice, D.; Calabrese, D.; Hughes, R.A.; Solari, A.; CMT-TRIAAL; CMT-TRAUK groups Ascorbic acid in Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1A (CMT-TRIAAL and CMT-TRAUK): A double-blind randomised trial. Lancet Neurol 2011, 10, 320–328. [CrossRef]
- Gess, B.; Baets, J.; De Jonghe, P.; Reilly, M.M.; Pareyson, D.; Young, P. Ascorbic acid for the treatment of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2015, 2015, CD011952. [CrossRef]
- Pisciotta, C.; Saveri, P.; Pareyson, D. Updated review of therapeutic strategies for Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease and related neuropathies. Expert Rev Neurother 2021, 21, 701–713. [CrossRef]
- Chumakov, I.; Milet, A.; Cholet, N.; Primas, G.; Boucard, A.; Pereira, Y.; Graudens, E.; Mandel, J.; Laffaire, J.; Foucquier, J.; Glibert, F.; Bertrand, V.; Nave, K.A.; Sereda, M.W.; Vial, E.; Guedj, M.; Hajj, R.; Nabirotchkin, S.; Cohen, D. Polytherapy with a combination of three repurposed drugs (PXT3003) down-regulates Pmp22 over-expression and improves myelination, axonal and functional parameters in models of CMT1A neuropathy. Orphanet J Rare Dis 2014, 9, 201. [CrossRef]
- Attarian, S.; Young, P.; Brannagan, T.H.; Adams, D.; Van Damme, P.; Thomas, F.P.; Casanovas, C.; Tard, C.; Walter, M.C.; Péréon, Y.; Walk, D.; Stino, A.; de Visser, M.; Verhamme, C.; Amato, A.; Carter, G.; Magy, L.; Statland, J.M.; Felice, K. A double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized trial of PXT3003 for the treatment of Charcot-Marie-Tooth type 1A. Orphanet J Rare Dis 2021, 16, 433. [CrossRef]
- Désarnaud, F.; Do Thi, A.N.; Brown, A.M.; Lemke, G.; Suter, U.; Baulieu, E.E.; Schumacher, M. Progesterone stimulates the activity of the promoters of peripheral myelin protein-22 and protein zero genes in Schwann cells. J Neurochem 1998, 71, 1765–1768. [CrossRef]
- Magnaghi, V.; Ballabio, M.; Roglio, I.; Melcangi, R.C. Progesterone derivatives increase expression of Krox-20 and Sox-10 in rat Schwann cells. J Mol Neurosci 2007, 31, 149–157. [CrossRef]
- Melcangi, R.C.; Magnaghi, V.; Cavarretta, I.; Zucchi, I.; Bovolin, P.; D'Urso, D.; Martini, L. Progesterone derivatives are able to influence peripheral myelin protein 22 and P0 gene expression: Possible mechanisms of action. J Neurosci Res 1999, 56, 349–357. [CrossRef]
- Sereda, M.W.; Meyer zu Hörste, G.; Suter, U.; Uzma, N.; Nave, K.A. Therapeutic administration of progesterone antagonist in a model of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease (CMT-1A). Nat Med 2003, 9, 1533–1537. [CrossRef]
- Thomas, F.P.; Brannagan, T.H., 3rd; Butterfield, R.J.; Desai, U.; Habib, A.A.; Herrmann, D.N.; Eichinger, K.J.; Johnson-Cl, N.E.; Karam, C.; Pestronk, A.; et al. Randomized Phase 2 Study of ACE-083 in Patients With Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease. Neurology 2022, 98, e2356–2367. [CrossRef]
- Sociali, G.; Visigalli, D.; Prukop, T.; Cervellini, I.; Mannino, E.; Venturi, C.; Bruzzone, S.; Sereda, M.W.; Schenone, A. Tolerability and efficacy study of P2X7 inhibition in experimental Charcot-Marie-Tooth type 1A (CMT1A) neuropathy. Neurobiol Dis 2016, 95, 145–157. [CrossRef]
- Keystone, E.C.; Wang, M.M.; Layton, M.; Hollis, S.; McInnes, I.B.; D1520C00001 Study Team Clinical evaluation of the efficacy of the P2X7 purinergic receptor antagonist AZD9056 on the signs and symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis in patients with active disease despite treatment with methotrexate or sulphasalazine. Ann Rheum Dis 2012, 71, 1630–1635. [CrossRef]
- Küllenberg, D.; Taylor, L.A.; Schneider, M.; Massing, U. Health effects of dietary phospholipids. Lipids Health Dis 2012, 11, 3. [CrossRef]
- Fledrich, R.; Abdelaal, T.; Rasch, L.; Bansal, V.; Schütza, V.; Brügger, B.; Lüchtenborg, C.; Prukop, T.; Stenzel, J.; Rahman, R.U.; Hermes, D.; Ewers, D.; Möbius, W.; Ruhwedel, T.; Katona, I.; Weis, J.; Klein, D.; Martini, R.; Brück, W.; Müller, W.C.; Bonn, S.; Bechmann, I.; Nave, K.A.; Stassart, R.M.; Sereda, M.W. Targeting myelin lipid metabolism as a potential therapeutic strategy in a model of CMT1A neuropathy. Nat Commun 2018, 9, 3025. [CrossRef]
- Scapin, C.; Ferri, C.; Pettinato, E.; Zambroni, D.; Bianchi, F.; Del Carro, U.; Belin, S.; Caruso, D.; Mitro, N.; Pellegatta, M.; Taveggia, C.; Schwab, M.H.; Nave, K.A.; Feltri, M.L.; Wrabetz, L.; D’Antonio, M. Enhanced axonal neuregulin-1 type-III signaling ameliorates neurophysiology and hypomyelination in a Charcot-Marie-Tooth type 1B mouse model. Hum Mol Genet 2019, 28, 992–1006. [CrossRef]
- Bolino, A.; Piguet, F.; Alberizzi, V.; Pellegatta, M.; Rivellini, C.; Guerrero-Valero, M.; Noseda, R.; Brombin, C.; Nonis, A.; D'Adamo, P.; Taveggia, C.; Previtali, S.C. Niacin-mediated Tace activation ameliorates CMT neuropathies with focal hypermyelination. EMBO Mol Med 2016, 8, 1438–1454. [CrossRef]
- Anand, P.; Kunnumakkara, A.B.; Newman, R.A.; Aggarwal, B.B. Bioavailability of curcumin: Problems and promises. Mol Pharm 2007, 4, 807–818. [CrossRef]
- Khajavi, M.; Inoue, K.; Wiszniewski, W.; Ohyama, T.; Snipes, G.J.; Lupski, J.R. Curcumin treatment abrogates endoplasmic reticulum retention and aggregation-induced apoptosis associated with neuropathy-causing myelin protein zero-truncating mutants. Am J Hum Genet 2005, 77, 841–850. [CrossRef]
- Khajavi, M.; Shiga, K.; Wiszniewski, W.; He, F.; Shaw, C.A.; Yan, J.; Wensel, T.G.; Snipes, G.J.; Lupski, J.R. Oral curcumin mitigates the clinical and neuropathologic phenotype of the trembler-J mouse: A potential therapy for inherited neuropathy. Am J Hum Genet 2007, 81, 438–453. [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, Y.; Pehlivan, D.; Wiszniewski, W.; Beck, C.R.; Snipes, G.J.; Lupski, J.R.; Khajavi, M. Curcumin facilitates a transitory cellular stress response in trembler-J mice. Hum Mol Genet 2013, 22, 4698–4705. [CrossRef]
- Patzkó, A.; Bai, Y.; Saporta, M.A.; Katona, I.; Wu, X.; Vizzuso, D.; Feltri, M.L.; Wang, S.; Dillon, L.M.; Kamholz, J.; Kirschner, D.; Sarkar, F.H.; Wrabetz, L.; Shy, M.E. Curcumin derivatives promote Schwann cell differentiation and improve neuropathy in R98C CMT1B mice. Brain 2012, 135, 3551–3566. [CrossRef]
- Ndong Ntoutoume, G.M.A.; Granet, R.; Mbakidi, J.P.; Brégier, F.; Léger, D.Y.; Fidanzi-Dugas, C.; Lequart, V.; Joly, N.; Liagre, B.; Chaleix, V.; Sol, V. Development of curcumin-cyclodextrin/cellulose nanocrystals complexes: New anticancer drug delivery systems. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 2016, 26, 941–945. [CrossRef]
- Caillaud, M.; Msheik, Z.; Ndong-Ntoutoume, G.M.; Vignaud, L.; Richard, L.; Favreau, F.; Faye, P.A.; Sturtz, F.; Granet, R.; Vallat, J.M.; Sol, V.; Desmoulière, A.; Billet, F. Curcumin-cyclodextrin/cellulose nanocrystals improve the phenotype of Charcot-Marie-Tooth-1A transgenic rats through the reduction of oxidative stress. Free Radic Biol Med 2020, 161, 246–262. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Podojil, J.R.; Kunjamma, R.B.; Jones, J.; Weiner, M.; Lin, W.; Miller, S.D.; Popko, B. Sephin1, which prolongs the integrated stress response, is a promising therapeutic for multiple sclerosis. Brain 2019, 142, 344–361. [CrossRef]
- Scapin, C.; Ferri, C.; Pettinato, E.; Bianchi, F.; Del Carro, U.; Feltri, M.L.; Kaufman, R.J.; Wrabetz, L.; D'Antonio, M. Phosphorylation of eIF2alpha promotes Schwann cell differentiation and myelination in CMT1B mice with activated UPR. J Neurosci 2020, 40, 8174–8187. [CrossRef]
- Chahbouni, M.; López, M.D.S.; Molina-Carballo, A.; de Haro, T.; Muñoz-Hoyos, A.; Fernández-Ortiz, M.; Guerra-Librero, A.; Acuña-Castroviejo, D. Melatonin treatment reduces oxidative damage and normalizes plasma pro-inflammatory cytokines in patients suffering from Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathy: A pilot study in three children. Molecules 2017, 22. [CrossRef]
- d'Ydewalle, C.; Krishnan, J.; Chiheb, D.M.; Van Damme, P.; Irobi, J.; Kozikowski, A.P.; Vanden Berghe, P.; Timmerman, V.; Robberecht, W.; Van Den Bosch, L. HDAC6 inhibitors reverse axonal loss in a mouse model of mutant HSPB1-induced Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. Nat Med 2011, 17, 968–974. [CrossRef]
- Simões-Pires, C.; Zwick, V.; Nurisso, A.; Schenker, E.; Carrupt, P.A.; Cuendet, M. HDAC6 as a target for neurodegenerative diseases: What makes it different from the other HDACs? Mol Neurodegener 2013, 8, 7. [CrossRef]
- Ha, N.; Choi, Y.I.; Jung, N.; Song, J.Y.; Bae, D.K.; Kim, M.C.; Lee, Y.J.; Song, H.; Kwak, G.; Jeong, S.; Park, S.; Nam, S.H.; Jung, S.C.; Choi, B.O. A novel histone deacetylase 6 inhibitor improves myelination of Schwann cells in a model of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1A. Br J Pharmacol 2020, 177, 5096–5113. [CrossRef]
- Bali, P.; Pranpat, M.; Bradner, J.; Balasis, M.; Fiskus, W.; Guo, F.; Rocha, K.; Kumaraswamy, S.; Boyapalle, S.; Atadja, P.; Seto, E.; Bhalla, K. Inhibition of histone deacetylase 6 acetylates and disrupts the chaperone function of heat shock protein 90: A novel basis for antileukemia activity of histone deacetylase inhibitors. J Biol Chem 2005, 280, 26729–26734. [CrossRef]
- Picci, C.; Wong, V.S.C.; Costa, C.J.; McKinnon, M.C.; Goldberg, D.C.; Swift, M.; Alam, N.M.; Prusky, G.T.; Shen, S.; Kozikowski, A.P.; Willis, D.E.; Langley, B. HDAC6 inhibition promotes alpha-tubulin acetylation and ameliorates CMT2A peripheral neuropathy in mice. Exp Neurol 2020, 328, 113281. [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yu, M.; Fu, S.; Liu, D.; Tan, Y. Role of selective histone deacetylase 6 inhibitor ACY-1215 in cancer and other human diseases. Front Pharmacol 2022, 13, 907981. [CrossRef]
- Ravi, B.; Antonellis, A.; Sumner, C.J.; Lieberman, A.P. Genetic approaches to the treatment of inherited neuromuscular diseases. Hum Mol Genet 2019, 28, R55–R64. [CrossRef]
- Madorsky, I.; Opalach, K.; Waber, A.; Verrier, J.D.; Solmo, C.; Foster, T.; Dunn, W.A., Jr; Notterpek, L. Intermittent fasting alleviates the neuropathic phenotype in a mouse model of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. Neurobiol Dis 2009, 34, 146–154. [CrossRef]
- Rangaraju, S.; Verrier, J.D.; Madorsky, I.; Nicks, J.; Dunn, W.A., Jr; Notterpek, L. Rapamycin activates autophagy and improves myelination in explant cultures from neuropathic mice. J Neurosci 2010, 30, 11388–11397. [CrossRef]
- Nicks, J.; Lee, S.; Harris, A.; Falk, D.J.; Todd, A.G.; Arredondo, K.; Dunn, W.A., Jr; Notterpek, L. Rapamycin improves peripheral nerve myelination while it fails to benefit neuromuscular performance in neuropathic mice. Neurobiol Dis 2014, 70, 224–236. [CrossRef]
- Florio, F.; Ferri, C.; Scapin, C.; Feltri, M.L.; Wrabetz, L.; D'Antonio, M. Sustained expression of negative regulators of myelination protects Schwann cells from dysmyelination in a Charcot-Marie-Tooth 1B mouse model. J Neurosci 2018, 38, 4275–4287. [CrossRef]
- Klein, D.; Patzkó, Á.; Schreiber, D.; van Hauwermeiren, A.; Baier, M.; Groh, J.; West, B.L.; Martini, R. Targeting the colony stimulating factor 1 receptor alleviates two forms of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease in mice. Brain 2015, 138, 3193–3205. [CrossRef]
- Rosberg, M.R.; Alvarez, S.; Krarup, C.; Moldovan, M. An oral NaV1.8 blocker improves motor function in mice completely deficient of myelin protein P0. Neurosci Lett 2016, 632, 33–38. [CrossRef]
- Moldovan, M.; Pisciotta, C.; Pareyson, D.; Krarup, C. Myelin protein zero gene dose dependent axonal ion-channel dysfunction in a family with Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. Clin Neurophysiol 2020, 131, 2440–2451. [CrossRef]
- Gerdts, J.; Brace, E.J.; Sasaki, Y.; DiAntonio, A.; Milbrandt, J. SARM1 activation triggers axon degeneration locally via NAD⁺ destruction. Science 2015, 348, 453–457. [CrossRef]
- Gerdts, J.; Summers, D.W.; Milbrandt, J.; DiAntonio, A. Axon self-destruction: New links among SARM1, MAPKs, and NAD+ metabolism. Neuron 2016, 89, 449–460. [CrossRef]
- Summers, D.W.; Frey, E.; Walker, L.J.; Milbrandt, J.; DiAntonio, A. DLK activation synergizes with mitochondrial dysfunction to downregulate axon survival factors and promote SARM1-dependent axon degeneration. Mol Neurobiol 2020, 57, 1146–1158. [CrossRef]
- Loreto, A.; Hill, C.S.; Hewitt, V.L.; Orsomando, G.; Angeletti, C.; Gilley, J.; Lucci, C.; Sanchez-Martinez, A.; Whitworth, A.J.; Conforti, L.; Dajas-Bailador, F.; Coleman, M.P. Mitochondrial impairment activates the Wallerian pathway through depletion of NMNAT2 leading to SARM1-dependent axon degeneration. Neurobiol Dis 2020, 134, 104678. [CrossRef]
- Geisler, S.; Huang, S.X.; Strickland, A.; Doan, R.A.; Summers, D.W.; Mao, X.; Park, J.; DiAntonio, A.; Milbrandt, J. Gene therapy targeting SARM1 blocks pathological axon degeneration in mice. J Exp Med 2019, 216, 294-303. [CrossRef]
- Hughes, R.O.; Bosanac, T.; Mao, X.; Engber, T.M.; DiAntonio, A.; Milbrandt, J.; Devraj, R.; Krauss, R. Small molecule SARM1 inhibitors recapitulate the SARM1-/- phenotype and allow recovery of a metastable pool of axons fated to degenerate. Cell Rep 2021, 34, 108588. [CrossRef]
- Detmer, S.A.; Chan, D.C. Complementation between mouse Mfn1 and Mfn2 protects mitochondrial fusion defects caused by CMT2A disease mutations. J Cell Biol 2007, 176, 405–414. [CrossRef]
- Misko, A.L.; Sasaki, Y.; Tuck, E.; Milbrandt, J.; Baloh, R.H. Mitofusin2 mutations disrupt axonal mitochondrial positioning and promote axon degeneration. J Neurosci 2012, 32, 4145–4155. [CrossRef]
- Rocha, A.G.; Franco, A.; Krezel, A.M.; Rumsey, J.M.; Alberti, J.M.; Knight, W.C.; Biris, N.; Zacharioudakis, E.; Janetka, J.W.; Baloh, R.H.; Kitsis, R.N.; Mochly-Rosen, D.; Townsend, R.R.; Gavathiotis, E.; Dorn, G.W. MFN2 agonists reverse mitochondrial defects in preclinical models of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 2A. Science 2018, 360, 336–341. [CrossRef]
- Dang, X.; Zhang, L.; Franco, A.; Li, J.; Rocha, A.G.; Devanathan, S.; Dolle, R.E.; Bernstein, P.R.; Dorn, G.W., 2nd Discovery of 6-phenylhexanamide derivatives as potent stereoselective mitofusin activators for the treatment of mitochondrial diseases. J Med Chem 2020, 63, 7033–7051. [CrossRef]
- Franco, A.; Dang, X.; Walton, E.K.; Ho, J.N.; Zablocka, B.; Ly, C.; Miller, T.M.; Baloh, R.H.; Shy, M.E.; Yoo, A.S.; Dorn, G.W. Burst mitofusin activation reverses neuromuscular dysfunction in murine CMT2A. eLife 2020, 9. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Carmona, S.; Muhammad, A.K.M.G.; Bell, S.; Landeros, J.; Vazquez, M.; Ho, R.; Franco, A.; Lu, B.; Dorn, G.W., 2nd; Wang, S.; Lutz, C.M.; Baloh, R.H. Restoring mitofusin balance prevents axonal degeneration in a Charcot-Marie-Tooth type 2A model. J Clin Invest 2019, 129, 1756–1771. [CrossRef]
- Sargiannidou, I.; Kagiava, A.; Bashiardes, S.; Richter, J.; Christodoulou, C.; Scherer, S.S.; Kleopa, K.A. Intraneural GJB1 gene delivery improves nerve pathology in a model of X-linked Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. Ann Neurol 2015, 78, 303–316. [CrossRef]
- Kagiava, A.; Karaiskos, C.; Richter, J.; Tryfonos, C.; Lapathitis, G.; Sargiannidou, I.; Christodoulou, C.; Kleopa, K.A. Intrathecal gene therapy in mouse models expressing CMT1X mutations. Hum Mol Genet 2018, 27, 1460–1473. [CrossRef]
- Kagiava, A.; Richter, J.; Tryfonos, C.; Karaiskos, C.; Heslegrave, A.J.; Sargiannidou, I.; Rossor, A.M.; Zetterberg, H.; Reilly, M.M.; Christodoulou, C.; Kleopa, K.A. Gene replacement therapy after neuropathy onset provides therapeutic benefit in a model of CMT1X. Hum Mol Genet 2019, 28, 3528–3542. [CrossRef]
- Kagiava, A.; Sargiannidou, I.; Theophilidis, G.; Karaiskos, C.; Richter, J.; Bashiardes, S.; Schiza, N.; Nearchou, M.; Christodoulou, C.; Scherer, S.S.; Kleopa, K.A. Intrathecal gene therapy rescues a model of demyelinating peripheral neuropathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2016, 113, E2421–E2429. [CrossRef]
- Schiza, N.; Georgiou, E.; Kagiava, A.; Médard, J.J.; Richter, J.; Tryfonos, C.; Sargiannidou, I.; Heslegrave, A.J.; Rossor, A.M.; Zetterberg, H.; Reilly, M.M.; Christodoulou, C.; Chrast, R.; Kleopa, K.A. Gene replacement therapy in a model of Charcot-Marie-Tooth 4C neuropathy. Brain 2019, 142, 1227–1241. [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Kwak, G.; Kim, H.J.; Park, H.T.; Choi, B.O.; Hong, Y.B. miR-381 attenuates peripheral neuropathic phenotype caused by overexpression of PMP22. Exp Neurobiol 2019, 28, 279–288. [CrossRef]
- Sahenk, Z.; Galloway, G.; Clark, K.R.; Malik, V.; Rodino-Klapac, L.R.; Kaspar, B.K.; Chen, L.; Braganza, C.; Montgomery, C.; Mendell, J.R. AAV1.NT-3 gene therapy for charcot-marie-tooth neuropathy. Mol Ther 2014, 22, 511–521. [CrossRef]
- Serfecz, J.; Bazick, H.; Al Salihi, M.O.; Turner, P.; Fields, C.; Cruz, P.; Renne, R.; Notterpek, L. Downregulation of the human peripheral myelin protein 22 gene by miR-29a in cellular models of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. Gene Ther 2019, 26, 455–464. [CrossRef]
- Morelli, K.H.; Griffin, L.B.; Pyne, N.K.; Wallace, L.M.; Fowler, A.M.; Oprescu, S.N.; Takase, R.; Wei, N.; Meyer-Schuman, R.; Mellacheruvu, D.; Kitzman, J.O.; Kocen, S.G.; Hines, T.J.; Spaulding, E.L.; Lupski, J.R.; Nesvizhskii, A.; Mancias, P.; Butler, I.J.; Yang, X.L.; Hou, Y.M.; Antonellis, A.; Harper, S.Q.; Burgess, R.W. Allele-specific RNA interference prevents neuropathy in Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 2D mouse models. J Clin Invest 2019, 129, 5568–5583. [CrossRef]
- Sahenk, Z.; Ozes, B. Gene therapy to promote regeneration in Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. Brain Res 2020, 1727, 146533. [CrossRef]
- Ozes, B.; Myers, M.; Moss, K.; McKinney, J.; Ridgley, A.; Chen, L.; Bai, S.; Abrams, C.K.; Freidin, M.M.; Mendell, J.R.; Sahenk, Z. AAV1.NT-3 gene therapy for X-linked Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathy type 1. Gene Ther 2022, 29, 127–137. [CrossRef]
- Kagiava, A.; Karaiskos, C.; Richter, J.; Tryfonos, C.; Jennings, M.J.; Heslegrave, A.J.; Sargiannidou, I.; Stavrou, M.; Zetterberg, H.; Reilly, M.M.; Christodoulou, C.; Horvath, R.; Kleopa, K.A. AAV9-mediated Schwann cell-targeted gene therapy rescues a model of demyelinating neuropathy. Gene Ther 2021, 28, 659–675. [CrossRef]
- Sahenk, Z.; Nagaraja, H.N.; McCracken, B.S.; King, W.M.; Freimer, M.L.; Cedarbaum, J.M.; Mendell, J.R. NT-3 promotes nerve regeneration and sensory improvement in CMT1A mouse models and in patients. Neurology 2005, 65, 681–689. [CrossRef]
- Yalvac, M.E.; Amornvit, J.; Chen, L.; Shontz, K.M.; Lewis, S.; Sahenk, Z. AAV1.NT-3 gene therapy increases muscle fiber diameter through activation of mTOR pathway and metabolic remodeling in a CMT mouse model. Gene Ther 2018, 25, 129–138. [CrossRef]
- Jessen, K.R.; Mirsky, R. Schwann cells and their precursors emerge as major regulators of nerve development. Trends Neurosci 1999, 22, 402–410. [CrossRef]
- McTigue, D.M.; Horner, P.J.; Stokes, B.T.; Gage, F.H. Neurotrophin-3 and brain-derived neurotrophic factor induce oligodendrocyte proliferation and myelination of regenerating axons in the contused adult rat spinal cord. J Neurosci 1998, 18, 5354–5365. [CrossRef]
- Meier, C.; Parmantier, E.; Brennan, A.; Mirsky, R.; Jessen, K.R. Developing Schwann cells acquire the ability to survive without axons by establishing an autocrine circuit involving insulin-like growth factor, neurotrophin-3, and platelet-derived growth factor-BB. J Neurosci 1999, 19, 3847–3859. [CrossRef]
- Sterne, G.D.; Brown, R.A.; Green, C.J.; Terenghi, G. Neurotrophin-3 delivered locally via fibronectin mats enhances peripheral nerve regeneration. Eur J Neurosci 1997, 9, 1388–1396. [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Chang, E.H.; Koo, O.J.; Jwa, D.H.; Mo, W.M.; Kwak, G.; Moon, H.W.; Park, H.T.; Hong, Y.B.; Choi, B.O. Pmp22 mutant allele-specific siRNA alleviates demyelinating neuropathic phenotype in vivo. Neurobiol Dis 2017, 100, 99–107. [CrossRef]
- Boutary, S.; Caillaud, M.; El Madani, M.; Vallat, J.M.; Loisel-Duwattez, J.; Rouyer, A.; Richard, L.; Gracia, C.; Urbinati, G.; Desmaële, D.; Echaniz-Laguna, A.; Adams, D.; Couvreur, P.; Schumacher, M.; Massaad, C.; Massaad-Massade, L. Squalenoyl siRNA PMP22 nanoparticles are effective in treating mouse models of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1 A. Commun Biol 2021, 4, 317. [CrossRef]
- Gautier, B.; Hajjar, H.; Soares, S.; Berthelot, J.; Deck, M.; Abbou, S.; Campbell, G.; Ceprian, M.; Gonzalez, S.; Fovet, C.M.; Schütza, V.; Jouvenel, A.; Rivat, C.; Zerah, M.; François, V.; Le Guiner, C.; Aubourg, P.; Fledrich, R.; Tricaud, N. AAV2/9-mediated silencing of PMP22 prevents the development of pathological features in a rat model of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease 1 A. Nat Commun 2021, 12, 2356. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.T.; Damle, S.; Ikeda-Lee, K.; Kuntz, S.; Li, J.; Mohan, A.; Kim, A.; Hung, G.; Scheideler, M.A.; Scherer, S.S.; Svaren, J.; Swayze, E.E.; Kordasiewicz, H.B. PMP22 antisense oligonucleotides reverse Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1A features in rodent models. J Clin Invest 2018, 128, 359–368. [CrossRef]
- Pantera, H.; Moran, J.J.; Hung, H.A.; Pak, E.; Dutra, A.; Svaren, J. Regulation of the neuropathy-associated Pmp22 gene by a distal super-enhancer. Hum Mol Genet 2018, 27, 2830–2839. [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Lee, J.Y.; Song, D.W.; Bae, H.S.; Doo, H.M.; Yu, H.S.; Lee, K.J.; Kim, H.K.; Hwang, H.; Kwak, G.; Kim, D.; Kim, S.; Hong, Y.B.; Lee, J.M.; Choi, B.O. Targeted PMP22 TATA-box editing by CRISPR/Cas9 reduces demyelinating neuropathy of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1A in mice. Nucleic Acids Res 2020, 48, 130–140. [CrossRef]
- Henry, T.D.; Hirsch, A.T.; Goldman, J.; Wang, Y.L.; Lips, D.L.; McMillan, W.D.; Duval, S.; Biggs, T.A.; Keo, H.H. Safety of a non-viral plasmid-encoding dual isoforms of hepatocyte growth factor in critical limb ischemia patients: A phase I study. Gene Ther 2011, 18, 788–794. [CrossRef]
- Ko, K.R.; Lee, J.; Lee, D.; Nho, B.; Kim, S. Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) promotes peripheral nerve regeneration by activating repair Schwann cells. Sci Rep 2018, 8, 8316. [CrossRef]
- Sufit, R.L.; Ajroud-Driss, S.; Casey, P.; Kessler, J.A. Open label study to assess the safety of VM202 in subjects with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Frontotemporal Degener 2017, 18, 269–278. [CrossRef]
- Kessler, J.A.; Shaibani, A.; Sang, C.N.; Christiansen, M.; Kudrow, D.; Vinik, A.; Shin, N.; VM202 study group M.s. Gene therapy for diabetic peripheral neuropathy: A randomized, placebo-controlled phase III study of VM202, a plasmid DNA encoding human hepatocyte growth factor. Clin Transl Sci 2021, 14, 1176–1184. [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Hwang, H.Y.; Cho, K.R.; Park, E.A.; Lee, W.; Paeng, J.C.; Lee, D.S.; Kim, H.K.; Sohn, D.W.; Kim, K.B. Intramyocardial transfer of hepatocyte growth factor as an adjunct to CABG: Phase I clinical study. Gene Ther 2013, 20, 717–722. [CrossRef]
- Rossor, A.M.; Shy, M.E.; Reilly, M.M. Are we prepared for clinical trials in Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease? Brain Res 2020, 1729, 146625. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




