Submitted:
21 June 2023
Posted:
25 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Culture experiments
2.2. Electron and light microscopy
2.3. Study site and available water quality data
2.4. Analysis of polysaccharides
2.5. Statistical analysis
3. Results
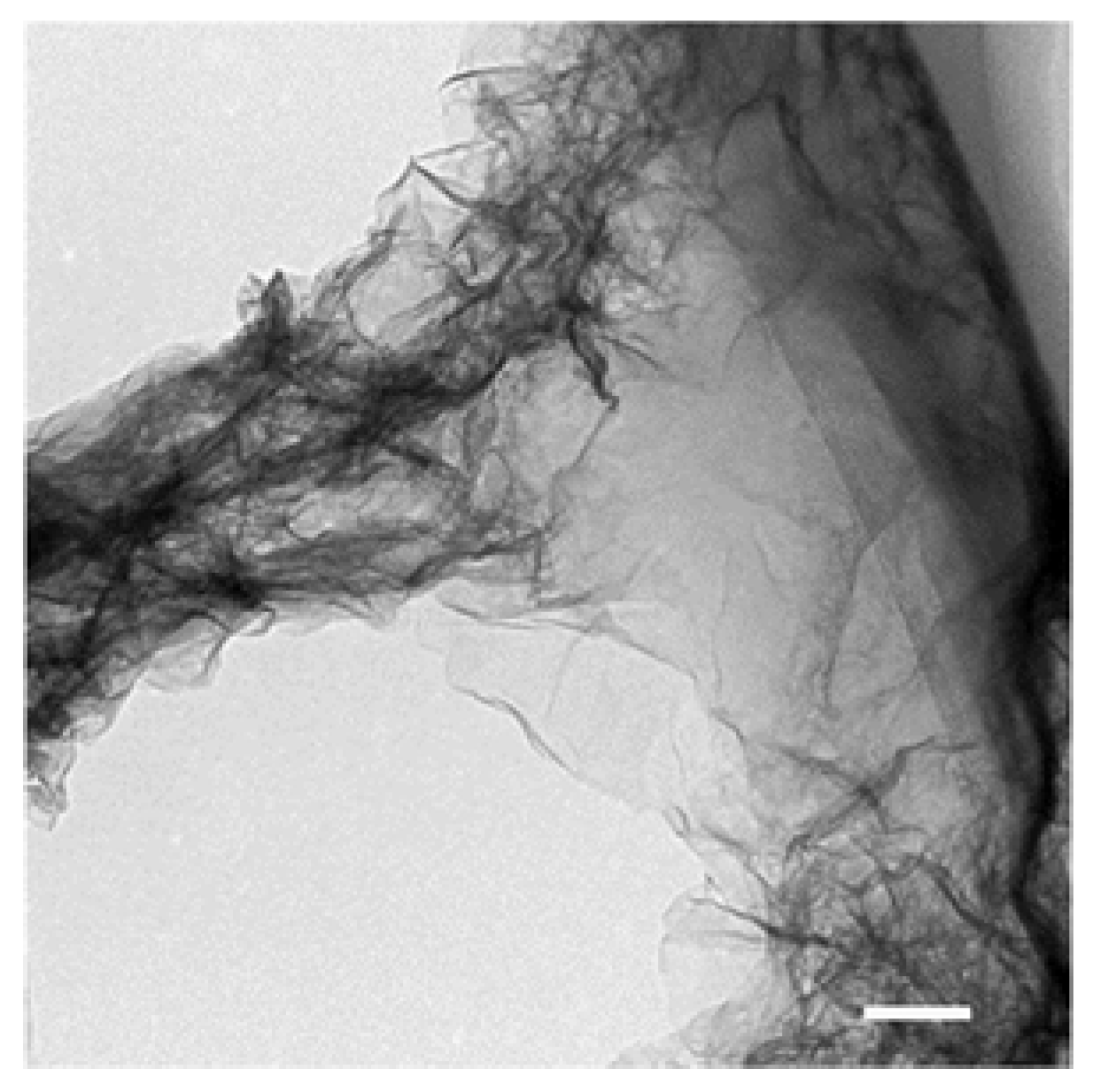
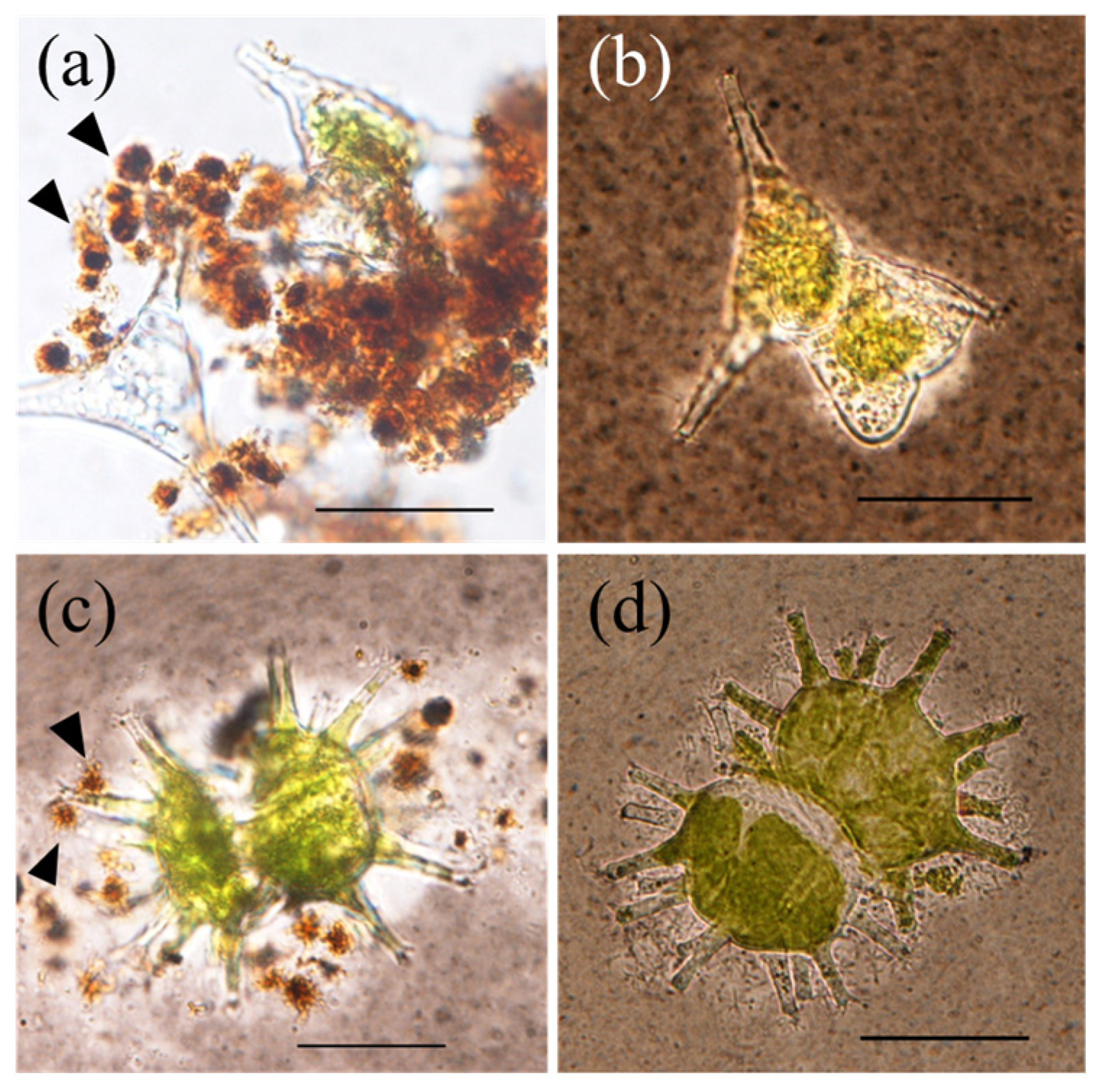
3.1. Filamentous Mn particle formation in laboratory model system
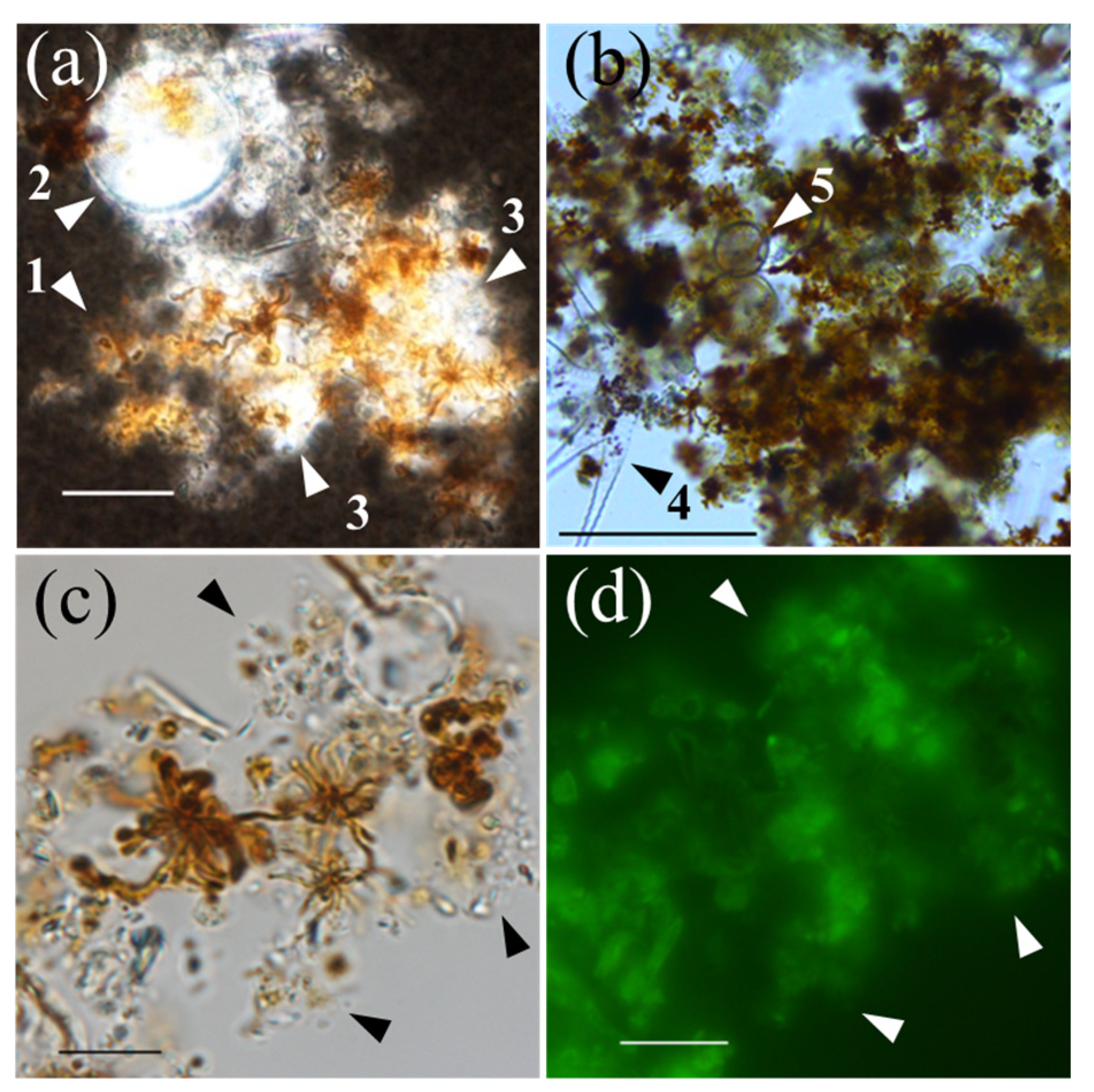
3.2. Filamentous Mn particles collected in the near-bottom layer of Lake Biwa
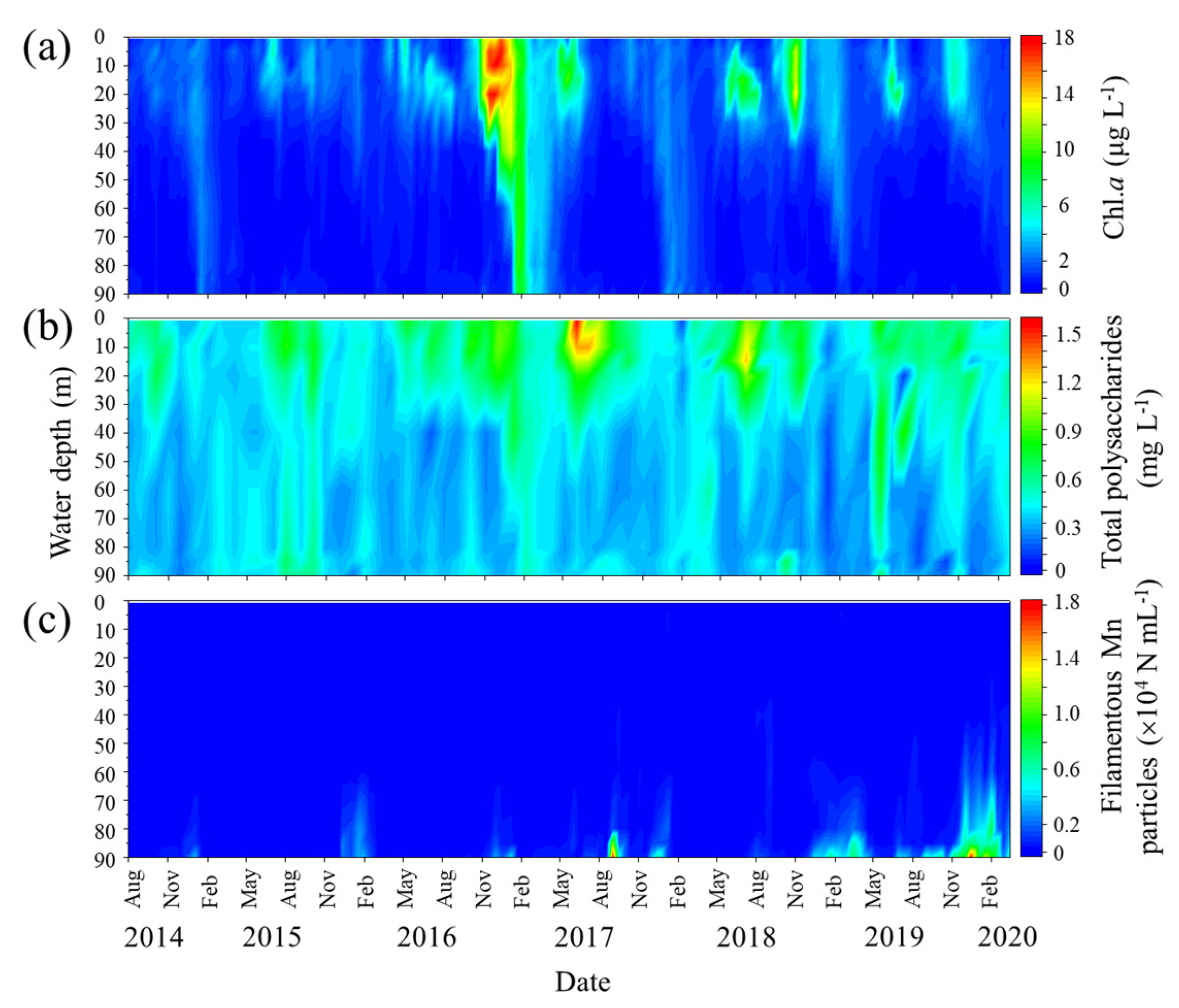
3.3. Distribution of polysaccharides in the water column of Lake Biwa
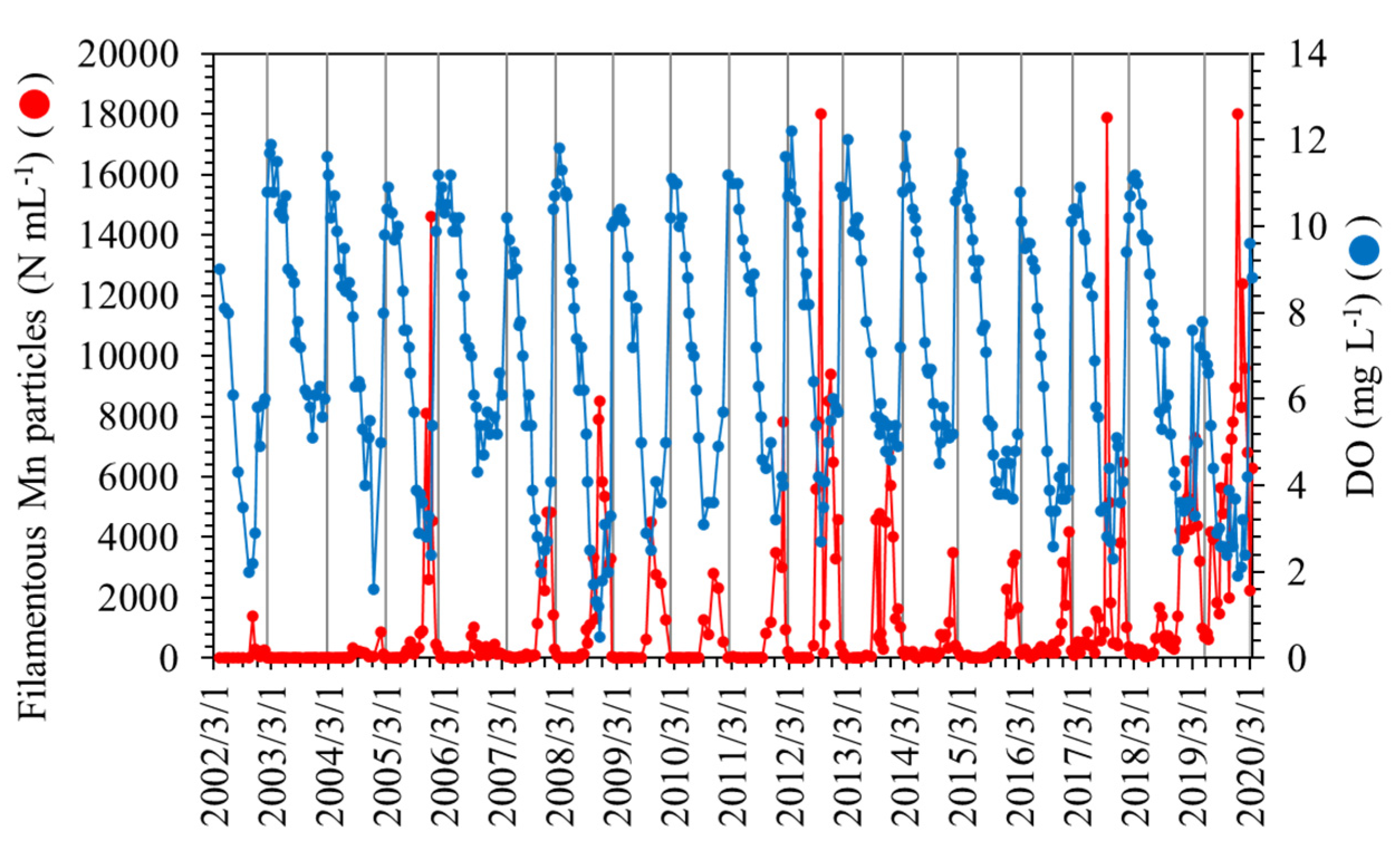
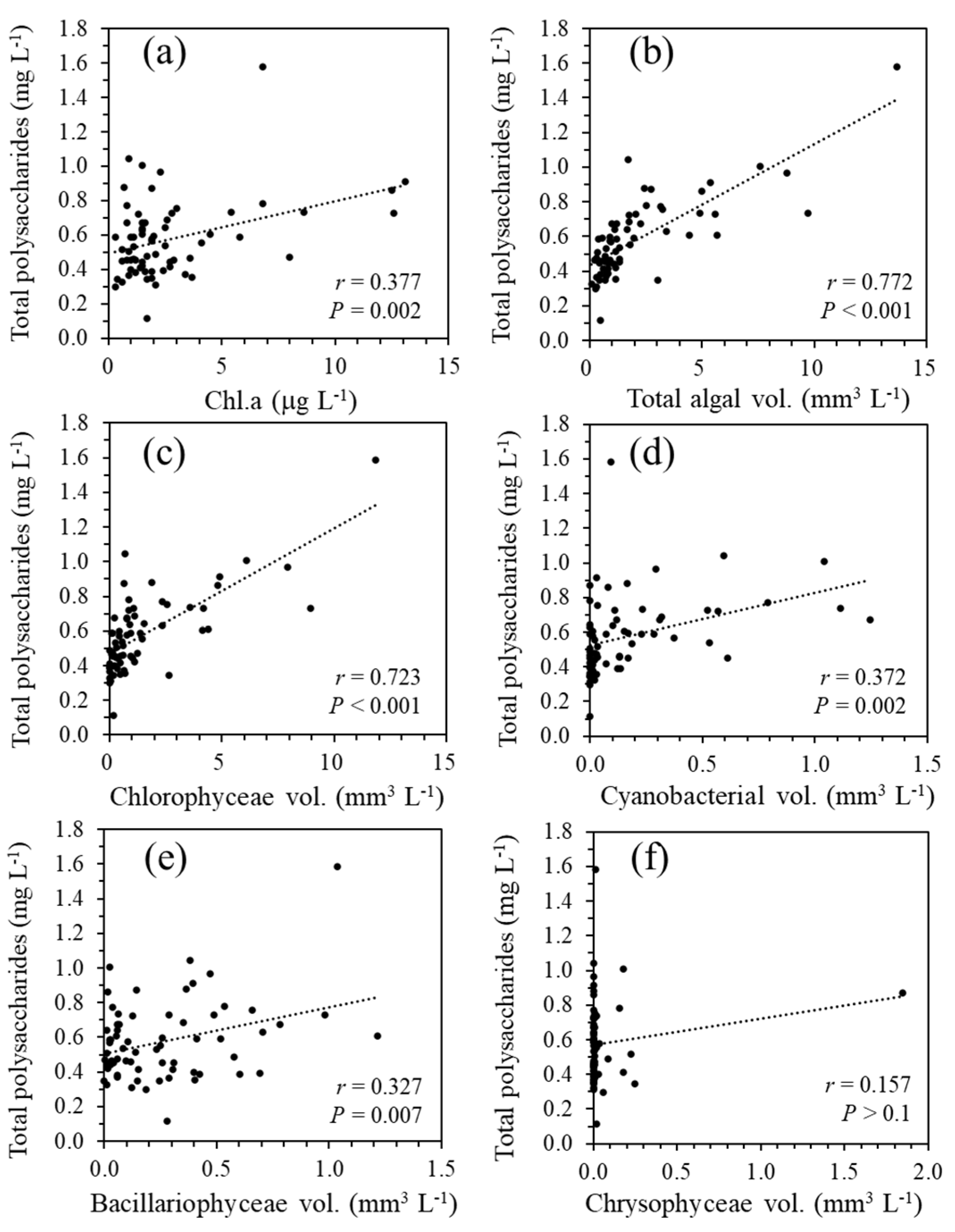
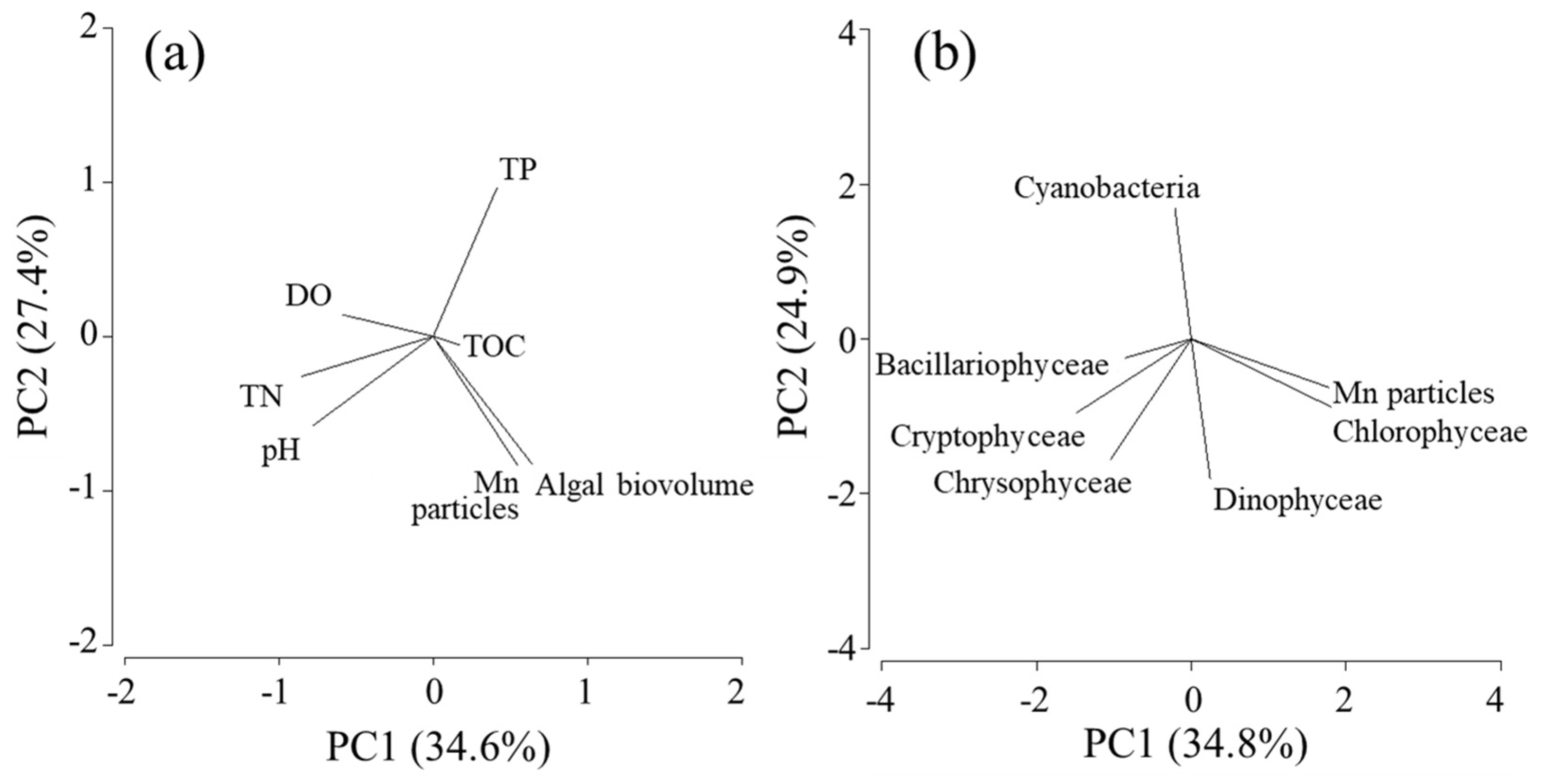
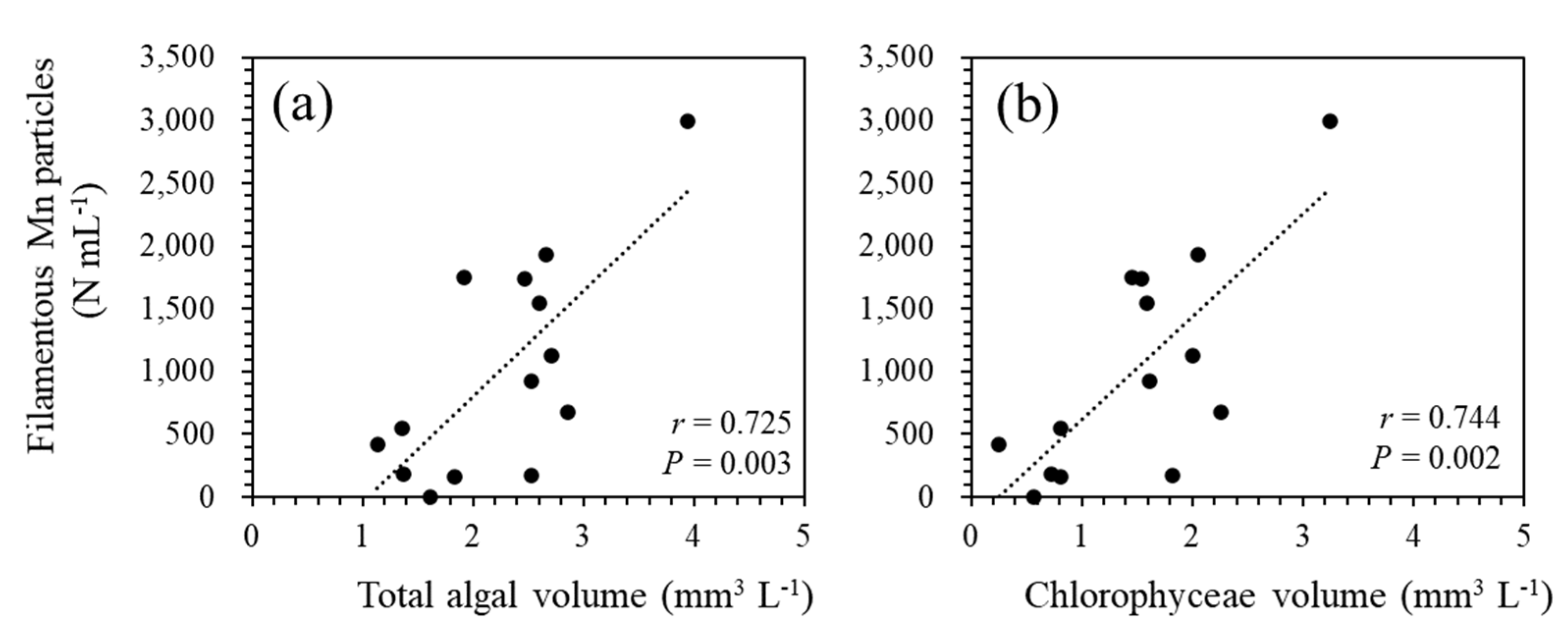
3.4. Correlation between filamentous Mn particles and the phytoplankton biovolume in the past 18 years
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tebo, B.M.; Bargar, J.R.; Clement, B.G.; Dick, G.J.; Murray, K. J.; Parker, D.; Verity, R.; Webb, S.M. Biogenic manganese oxides: properties and mechanisms of formation. Annu Rev Earth Planet Sci 2004, 32, 287–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Huangfu, X.; Ma, C.; Liu, Z. Sequestration and oxidation of heavy metals mediated by Mn(II) oxidizing microorganisms in the aquatic environment. Chemosphere 2023, 329, 138594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lienemann, C.P.; Taillefert, M.; Perret, D.; Gaillard, J.F. Association of cobalt and manganese in aquatic systems: chemical and microscopic evidence. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 1997, 61, 1437–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taillefert, M.; Macgregor, B.J.; Gaillard, J.F.; Lienemann, C.P.; Stahl, D.A. Evidence for a dynamic cycle between Mn and Co in the water column of a stratified lake. Environ Sci Technol 2002, 36, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neretin, L.N.; Pohl, C.; Jost, G.; Leipe, T.; Pollehne, F. Manganese cycling in the Gotland Deep, Baltic Sea. Mar Chem 2003, 82, 125–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellwig, O.; Leipe, T.; März, C.; Glockzin, M.; Pollehne, F.; Schnetger, B.; Yakushev, E.V.; Böttcher, M.E.; Brumsack, H.J. A new particulate Mn-Fe-P-shuttle at the redoxcline of anoxic basins. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 2010, 74, 7100–7115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, S.; Blomqvist, S.; Ingri, J. Distribution of dissolved and suspended particulate molybdenum, vanadium, and tungsten in the Baltic Sea. Mar Chem 2017, 196, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ossa, O. F.; Hofmann, A.; Wille, M.; Spangenberg, J.E.; Bekker, A.; Poulton, S.W.; Eickmann, B.; Schoenberg, R. Aerobic iron and manganese cycling in a redox-stratified Mesoarchean epicontinental sea. Earth Planet Sci Lett 2018, 500, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henkel, J.V.; Schulz-Vogt, H.N.; Dellwig, O.; Pollehne, F.; Schott, T.; Meeske, C.; Beier, S.; Jürgens, K. Biological manganese-dependent sulfide oxidation impacts elemental gradients in redox-stratified systems: indications from the Black Sea water column. ISME J 2022, 16, 1523–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, E.; Perry, R.S.; Staley, J.T. Characterization, distribution, and significance of Metallogenium in Lake Washington. Microb Ecol 1980, 6, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maki, J.S.; Tebo, B.M.; Palmer, F.E.; Nealson, K.H.; Staley, J.T. The abundance and biological activity of manganese-oxidizing bacteria and Metallogenium-like morphotypes in Lake Washington, USA. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 1987, 45, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sternbeck, J. Manganese cycling in a eutrophic lake -rates and pathways. Aquat Geochem 1996, 1, 399–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuta, S.; Ikegaya, H.; Hashimoto, H.; Ichise, S.; Kohno, T.; Miyata, N.; Takada, J. Formation of filamentous Mn oxide particles by the alphaproteobacterium Bosea sp. strain BIWAKO-01. Geomicrobiol J 2015, 32, 666–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakharova, Y.R.; Parfenova, V.V.; Granina, L.Z.; Kravchenko, O.S.; Zemskaya, T.I. Distribution of iron- and manganese-oxidizing bacteria in the bottom sediments of Lake Baikal. Inland Water Biol, 2010; 3, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrlich, H.L.; Newman, D.K. Geomicrobiology of manganese. In Geomicrobiology, 5th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, USA, 2009; pp. 347–420. [Google Scholar]
- Miyajima, T. Production of Metallogenium-like particles by heterotrophic manganese-oxidizing bacteria collected from a lake. Arch Microbiol 1992, 158, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leppard, G.G. The characterization of algal and microbial mucilages and their aggregates in aquatic ecosystems. Sci Total Environ 1995, 165, 103–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passow, U. Transparent exopolymer particles (TEP) in aquatic environments. Prog Oceanogr 2002, 55, 287–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mari, X.; Passow, U.; Migon, C.; Burd, A.B.; Legendre, L. Transparent exopolymer particles: effects on carbon cycling in the ocean. Prog Oceanogr 2017, 151, 13–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, T.; Viner-Mozzini, Y. Abundance and characteristics of polysaccharide and proteinaceous particles in Lake Kinneret. Aquat Microb Ecol 2001, 24, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, F.; Malfatti, F. Microbial structuring of marine ecosystems. Nat Rev Microbiol 2007, 5, 782–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callieri, C.; Corno, G.; Contesini, M.; Fontaneto, D.; Bertoni, R. Transparent expolymer particles (TEP) are driven by chlorophyll a and mainly confined to the euphotic zone in a deep subalpine lake. Inland Waters 2017, 7, 118–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.-M. Non-surface attached bacterial aggregates: a ubiquitous third lifestyle. Front Microbiol 2020, 11, 557035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyajima, T. Biological manganese oxidation in a lake. I. Occurrence and distribution of Metallogenium sp., and its kinetic properties. Arch Hydrobiol 1992, 124, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuta, S.; Yoshida, M.; Okamoto, T.; Wakabayashi, T.; Ichise, S.; Aoki, S.; Kono, T.; Miyajima, T. Morphological variations of a manganese-oxidizing microorganism Metallogenium observed in the developmental process of cultures collected from Lake Biwa waters. Jpn J Limnol 2007, 68, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, K.; Furuta, S.; Nakajima, T. Microbes as indicator species in low oxygen environments. In Lake Biwa. Interactions between nature and people; Kawanabe, H., Nishino, M., Maehata, M., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, Netherlands, 2012; pp. 231–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M.; Ichimura, T. Fresh- and salt-water forms of Spirulina platensis in axenic cultures. Bull Jpn Soc Phycol 1977, 25, 371–377. [Google Scholar]
- Giroldo, D.; Vieira, A.A.H.; Paulshn, B.S. Microbial degradation of extracellular polysaccharides released by a tropical strain of Staurastrum orbiculare (Zygnematophyceae). Phycologia 2005, 44, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boogerd, F.C.; de Vrind, J.P.M. Manganese oxidation by Leptothrix discophora. J Bacteriol 1987, 169, 489–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikegaya, H.; Nakase, T.; Iwata, K.; Tsuchida, H.; Sonobe, S.; Shimmen, T. Studies on conjugation of Spirogyra using monoclonal culture. J Plant Res 2012, 125, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiga Prefecture (2023) Annual Reports on the Environment. Shiga Prefecture, Japan. Available on https://www.pref.shiga.lg.jp/ippan/kankyoshizen/kankyou/11319.html.
- Kishimoto, N.; Ichise, S.; Suzuki, K.; Yamamoto, C. Analysis of long-term variation in phytoplankton biovolume in the northern basin of Lake Biwa. Limnology 2013, 14, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichise, S.; Ikegaya, H.; Furuta, S.; Fujiwara, N.; Ikeda, S.; Kishimoto, N.; Nishimura, O. Analysis of long-term variation of phytoplankton biovolume and gelatinous sheath volume in Lake Biwa. Jpn J Water Treat Biol 2013, 49, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashima, Y.; Shimizu, A.; Maruo, M.; Sohrin, Y. Trace elements influenced by environmental changes in Lake Biwa: I Seasonal variations under suboxic hypolimnion conditions during 2007 and 2009. Limnology 2016, 17, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, T.A.; Melvin, E.H. Determination of dextran with anthrone. Anal Chem 1953, 25, 1656–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, T. Measuring β-glucan deposition in plant cell walls. In Plant fibers. Modern methods of plant analysis; Linskens, H.F., Jackson, J.F., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1989; pp. 138–160. [Google Scholar]
- Lefkowitz, J.P. , Rouff, A.A.; Elzinga, E.J. Influence of pH on the reductive transformation of birnessite by aqueous Mn(II). Environ Sci Technol 2013, 47, 10364–10371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, L.L.; Aguilar, C.; Nealson, K.H. Manganese oxidation in pH and O2 microenvironments produced by phytoplankton. Limnol Oceanogr 1988, 33, 352–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knauer, K.; Jabusch, T.; Sigg, L. Manganese uptake and Mn(II) oxidation by the alga Scenedesmus subspicatus. Aquat Sci 1999, 61, 44–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Wang, S.; Tai, Y.; Tao, R.; Dai, Y.; Guo, J.; Yang, Y.; Duan, S. Biogenic manganese oxides generated by green algae Desmodesmus sp. WR1 to improve bisphenol A removal. J Hazard Mater 2017, 339, 310–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaput, D.L.; Fowler, A.J.; Seo, O.; Duhn, K.; Hansel, C.M.; Santelli, C.M. Mn oxide formation by phototrophs: spatial and temporal patterns, with evidence of an enzymatic superoxide-mediated pathway. Sci Rep 2019, 9, 18244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, L.Y.; Jones, G.; Alexander, B.; Elmund, K.; Wright-Jones, C.; Nealson, K.H. Intriguing microbial diversity associated with metal-rich particles from a freshwater reservoir. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 2002, 42, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robbins, E.I.; Corley, T.L. Microdynamics and seasonal changes in manganese oxide epiprecipitation in Pinal Creek, Arizona. Hydrobiologia 2005, 534, 165–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keim, C.N.; Nalini Jr., H. A.; de Lena, J.C. Manganese oxide biominerals from freshwater environments in Quadrilatero Ferrifero, Minas Gerais, Brazil. Geomicrobiol J 2015, 32, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glockzin, M.; Pollehne, F.; Dellwig, O. Stationary sinking velocity of authigenic manganese oxides at pelagic redoxclines. Mar Chem 2014, 160, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vicente, I.; Ortega-Retuerta, E.; Romera, O.; Morales-Baquero, R.; Reche, I. Contribution of transparent exopolymer particles to carbon sinking flux in an oligotrophic reservoir. Biogeochemistry 2009, 96, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Retuerta, E.; Duarte, C.M.; Reche, I. Significance of bacterial activity for the distribution and dynamics of transparent exopolymer particles in the Mediterranean Sea. Microb Ecol 2010, 59, 808–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayakawa, K. Seasonal variations and dynamics of dissolved carbohydrates in Lake Biwa. Org Geochem 2004, 35, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urabe, J.; Nakanishi, M.; Kawabata, K. Contribution of metazoan plankton to the cycling of nitrogen and phosphorus in Lake Biwa. Limnol Oceanogr 1995, 40, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohrin, Y.; Nakashima, Y.; Maruo, M. Trace elements influenced by environmental changes in Lake Biwa: II. Chemical variations in the hypolimnion over the last half-century. Limnology 2016, 17, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takamatsu, T.; Kawashima, M.; Koyama, M. The role of Mn2+-rich hydrous manganese oxide in the accumulation of arsenic in lake sediments. Water Res 1985, 19, 1029–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiyama, M.; Hori, T.; Kihara, S.; Matsui, M. Geochemical behavior of trace elements in Lake Biwa. Limnology 2005, 6, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




