Submitted:
25 June 2023
Posted:
27 June 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Basic Concepts of Cyberspace Map
2.1. Related Concepts of Cyberspace Map
2.2. Characteristics of Cyberspace Map
- With the basic characteristics of the map
- 2.
- Taking cyberspace as the expression object
- 3.
- A collection of multiple expressions
- 4.
- Unique information transmission
3. Conceptual Model of Cyberspace Map
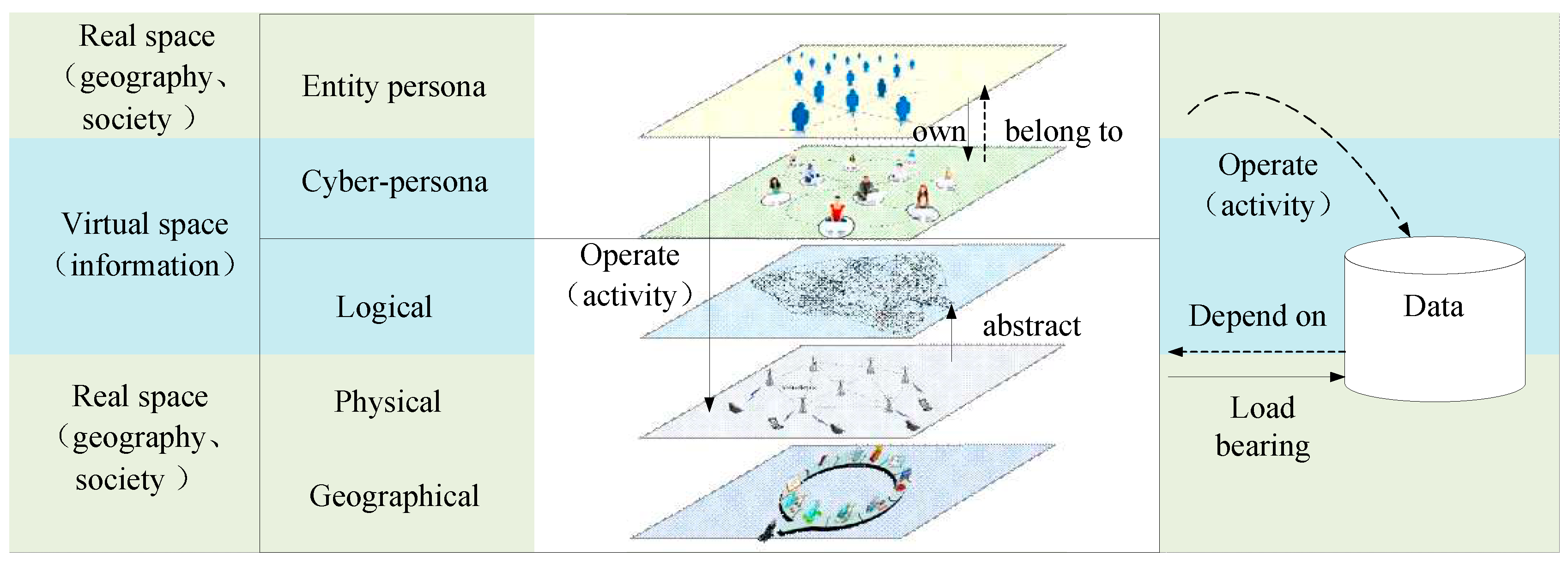
3.1. Object Space of Cyberspace Mapping
- Persona is the subject in cyberspace, which may be an individual or an organization or a group. It has subjective initiative and carries out purposeful activities in cyberspace through the operation of physical devices. The relationship between personae and facilities, data and operations are subject-object relationship.
- Operation is a specific activity carried out by a persona in cyberspace and its impact on politics, economy, culture, society, military and other aspects. The activities in cyberspace are the expansion of human activities from social and geographical space to information space. From the macro scale, these activities include the operation and maintenance of cyberspace, service provision, supervision, attack defense, etc. from the micro scale, they are the specific operation processes of data creation, storage, replication, deletion, extraction, replacement, etc. Operation is the means and method of a persona's activities in cyberspace, which is related to the purpose and needs of the persona. Realize the impact of the persona 's activities in cyberspace on multiple spaces through operation: for physical facilities in real physical space, such as the destruction of facilities by virus; For virtual elements in the information space, for example, hackers' attacks on government websites made them unable to operate normally, so as to reduce the credibility of the government; For humanities and social space, for example, the spread of false information and, the creation of public opinion influence, etc. Through operation, roles form activities in various spaces, and the ultimate goal is to have an impact on things in real space.
- Data exists in virtual space and can be understood as assets in cyberspace. It cannot exist independently, relying on the existence of devices in the real geographical space, through device storage, transmission, etc. Data is dependent on facilities.
- Facilities exist in the real geographical space, which belongs to the physical part of cyberspace and is the material basis of cyberspace. The most important function is the carrier of data and also carries the activities of roles. Facilities are the direct objects and tools for the role to operate, and the role can only carry out activities in cyberspace through the operation of facilities.
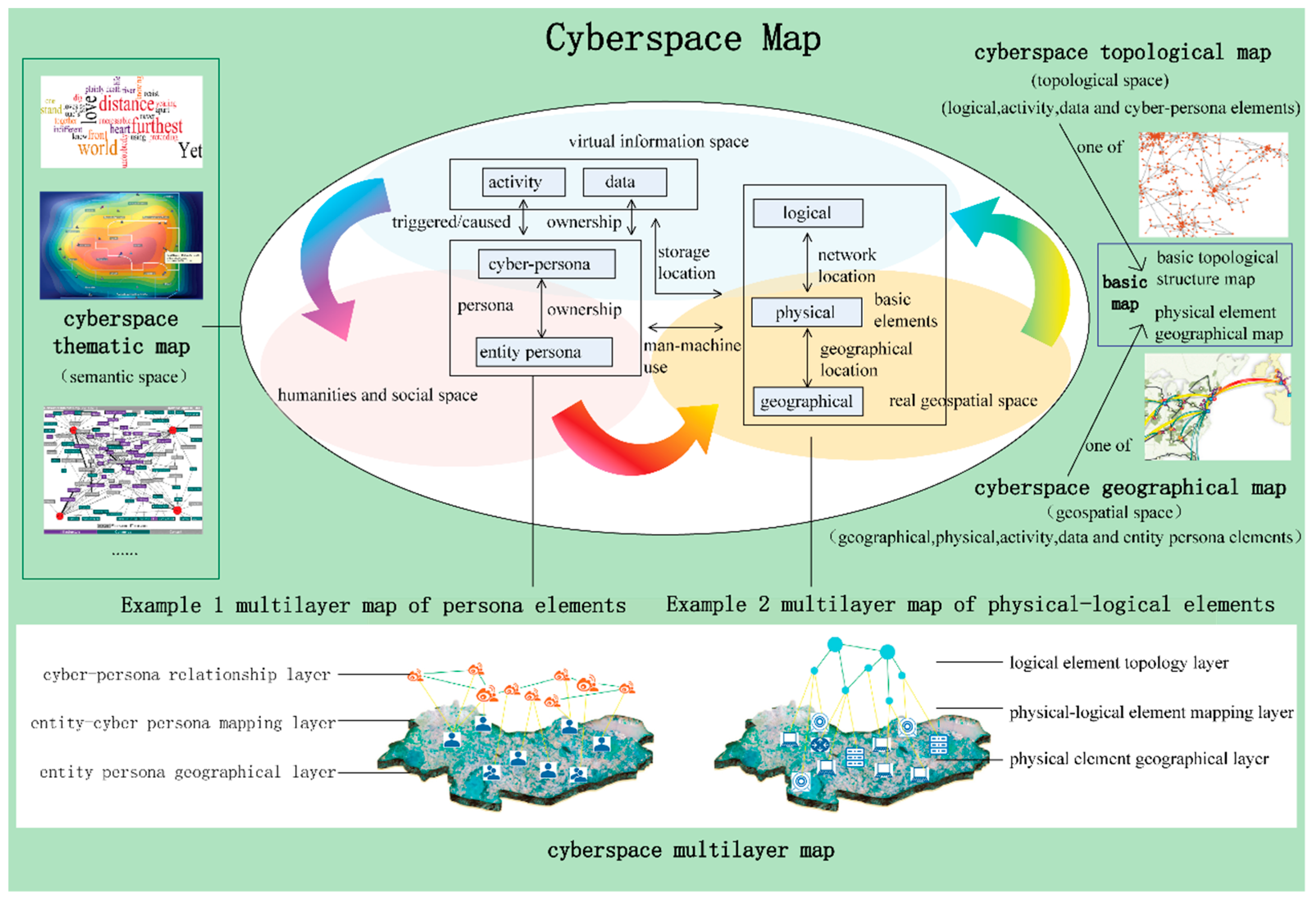
3.2. Conceptual Model of Cyberspace Map
3.2.1. Element-space association dimension
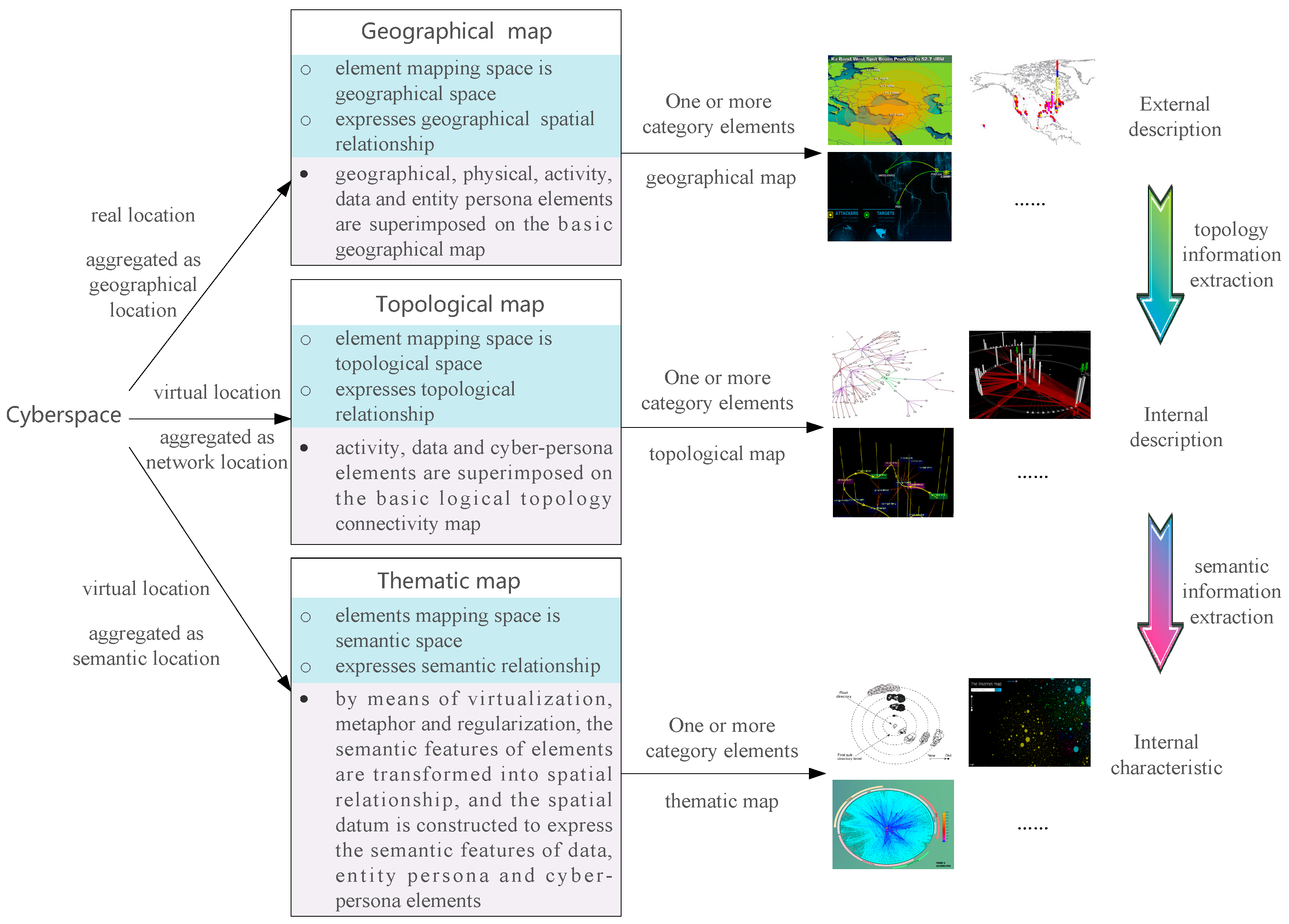
3.2.2. Element mapping dimension
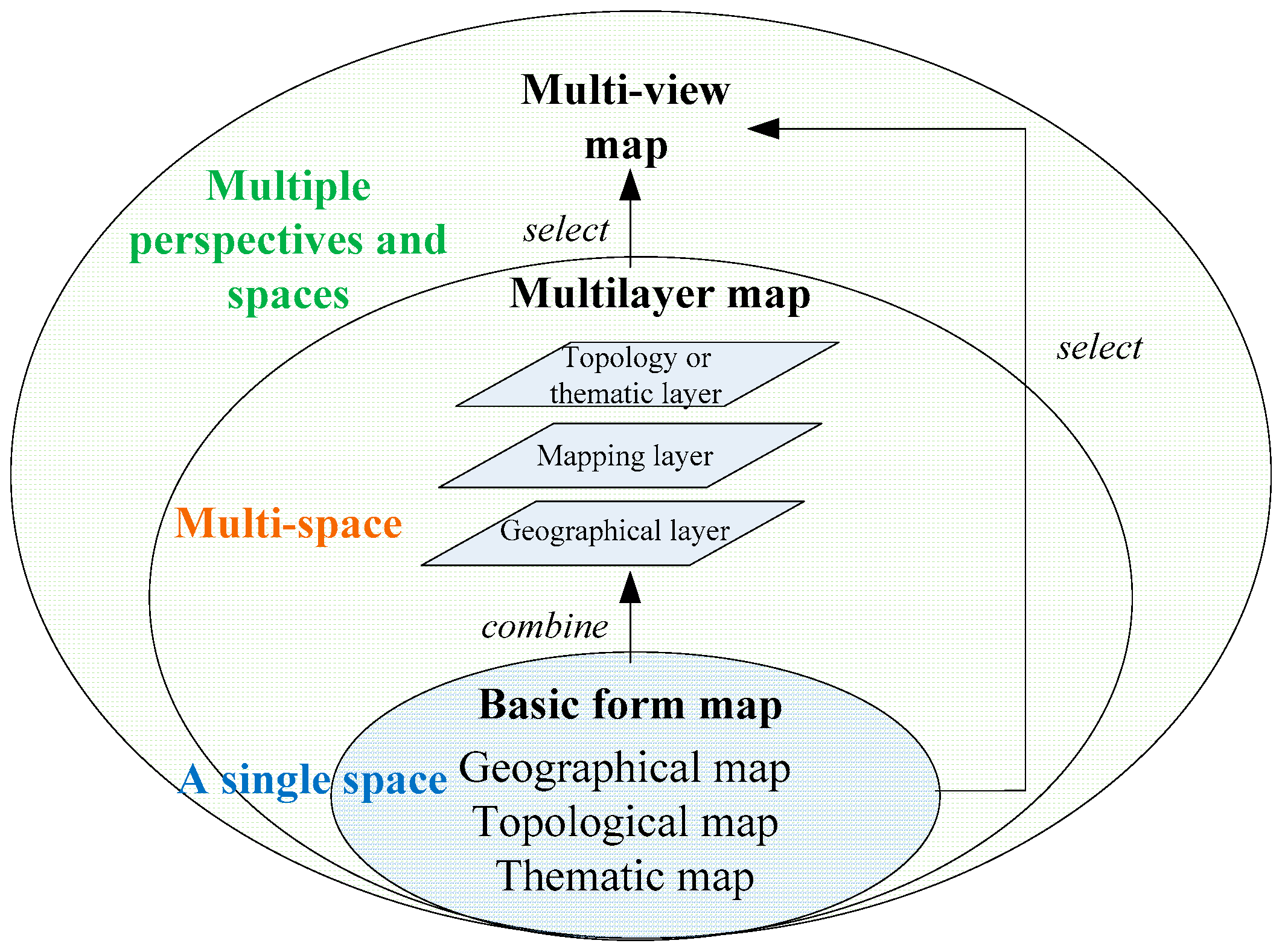
3.2.3. Map representation dimension
3.3. Elements Composition and Symbolization
- Geographical elements, physical elements and logical elements
- 2.
- Data elements
- 3.
- Persona elements
- 4.
- Activity elements
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, R.Z.; Ying, S. The Rejuvenation of Cartography in ICT Era. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica,2017,46,1274-1283. [CrossRef]
- Sargent, R.G. An Overview of Verification and Validation of Simulation Models. In Proceedings of the 1987 Winter Simulation Conference, Atlenta, Georgia, United State, 14-16 December 1987;pp.33-79. [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.Z.; Chen, Y.B.; Ying, S.; Lv, G.N.; Li, Z.L. Geographic Visualization of Pan-Map with the Context of Ternary Space. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2018,43,1603-1610. [CrossRef]
- Taylor D R F. Developments in the Theory and Practice of CyberCartography. 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Oxford,UK,2014; PP.3-4. ISBN 9780444627179.
- Wang J.Y. Rethinking about the Information Age Cartography. Journal of Geomatics Science and Technology, 2013,30,229-333. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q. P. A survey on virtual reality. Sci China Ser F-Inf Sci, 2009,52,348-400. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Xiao, J.J. Survey on augmented virtual environment and augmented reality. SCIENTIA SINICA Informationis, 2015, 45, 157–180. [CrossRef]
- Pang, J.; Chen, G.X.; Song, G.F.; Zhang, X. Research and Application of Augmented Reality Map. Journal of Geomatics, 2021,46,130-134. [CrossRef]
- Ying, S.; Hou, S.Y.; Su, J.R.; Chen, Y.B.; Chen X.Y.; Guo R.Z. Characteristics of the Game Map.Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2020,45,1334-1343. [CrossRef]
- Ying, S.; Hou, S.Y.; Chen, Y.B.; Su, J.R. Virtuality and Reality of Game Maps. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2022,47,2085-2095. [CrossRef]
- Bin, J.; Ferjan J.O. Cybermap: the Map for Cyberspace. The Cartographic Journal, 1997, 34, 111-116. [CrossRef]
- Bin, J.; Ferjan J.O. Mapping cyberspace: visualising, analysing and exploring virtual worlds. The Cartographic Journal,2000,37,177-122. [CrossRef]
- Ai, T.H. Maps Adaptable to Represent Spatial Cognition. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2008,12 ,347-354. [CrossRef]
- Ai, T.H. Development of Cartography Driven by Big Data. Journal of Geomatics, 2016,41,1-7. [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yang, F.; Wang, L.N.; Yu, X.K.; Fei, T.; Jiang, N. A Survey of Mapping Methods for Cyberspace. Journal of Geomatics Science and Technology,2019,36,620-626+631. [CrossRef]
- Taylor D R F. Cybercarotgraphy: Maps and mapping in the information era. Proceedings of the 18th ICA/ACI International Cartographic Conference. Stockholm,Sweden,23-27 June 1997;pp.23-27. [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Meng, L.Q. Research Progress and Prospect of Extended Reality and Geospatial Cognition.Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2022,47,2047-2053. [CrossRef]
- Munzner, T.; Burchard, P. Visualizing the Structure of the World Wide Web in 3D Hyperbolic Space. Proceedings of the first symposium on Virtual reality modeling language, San Diego CA, USA, 14-15 December 1995. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.Q.; Zhu, C.; Ding, Z.Y.; Liu,B.; Liu,Y. Map Modeling and Intelligence Terrain Analysis Method for Cyberspace.Journal of command and control,2022,8,294-302. [CrossRef]
- Gao, J. Let’s Take Another Look at Map. Bulletin of survey and mapping,2009,1,1-5. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/7161223.
- Sun, Z.W.; Lu, Z.; Wang, Y. The Geography of Cyberspace: Review and Prospect. Advances in Earth Science, 2007, 22,1005-1011. [CrossRef]
- Kellerman A. Cyberspace Classification and Cognition-Information and Communications Cyberspaces. Journal of Urban Technology. 2008,14,5-32. [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.J. Analysis on The Security of Cyberspace Cognitive Domain in China.Southeast Communication,2017,7,84-85. [CrossRef]
- Fang, B.X. Define Cyberspace Security. Chinese Journal of Network and Information Security,2018,4,1-5. [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.Z.; Chen, Y.B.; Zhao, Z.G.;He,B.;Lv,G.N.;Li,Z.L.;Ying,S.;Ma,D. A Theoretical Framework for the Study of Pan-Maps. Journal of Geomatics, 2021, 46,9-15. [CrossRef]
- Fang, B.X. Research on the Cyberspace Sovereignty. 1st ed.;Science Press: Beijing,China,2017;pp.33-34. ISBN9787030542557.
- U.S. Army Training and Doctrine Command. The United States Army’s Cyberspace Operations Concept Capability Plan 2016-2028. US Army Training and Doctrine Command Pamphlet,2010(525) ,1-72. http://www.tradoc.army.mil/tpubs/regndx.htm.
- Craig, D.; Don, B. CyberCOP: Cyber Situational Awareness Demonstration Tool. Ottawa, Canada: Defence Research and Development Canada, 2019. http://www.solananetworks.com.
- Gao, C.D.; Guo, Q.Q.; Jiang, D.;Wang,Z.B.;Fang,C.L.;Hao,M.M. Theoretical basis and technical methods of cyberspace geography. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 2019,29,1949-1964. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, G.X.; Jiang, B.C.;Zhang,L.T.;Ma,L. A Review of visualization methods of Cyberspace Map.Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2022,47,2113-2122. [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Y. Cartography in the Age of Spatiotemporal Big Data. Acta Geodaeticaet Cartographica Sinica,2017,46,1226-1237. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.Y.; Zhou, C.H.; Wo, W.; Hu, T.; Liu, H.Q.; Gao, X.W. Preliminary Study on Conception and Key Technologies of the Location-based Pan-Information Map. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2015, 40, 285-295. [CrossRef]
- Martin, D.; Rob K. Atlas of cyberspace. 1st ed.; Pearson Education Limited: London Great Britain ,2001; pp.104+118. ISBN: 0-201-74575-5.
- Guo, R.Z.; Chen, Y.B.; Zhao, Z.G.; Han, D.Z.; Ma, D.; Ying, S.; Di, P.; Ke, W.Q.; Fan, Y. Scientific Concept and Representation Framework of Maps in the ICT Era. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2022,47,1978-1987. [CrossRef]
- FIREEYR CYBER. Available online: https://threatmap.checkpoint.com/. (accessed on 14 December 2020).
- Pv4 AS Core: Visualizing IPv4 Internet Topology at a Macroscopic Scale in 2007. Available online: https://www.caida.org/research/topology/as_core_network/2007/. (accessed on 14 December 2020).
- The Internet Map. Available online: http://internet-map.net/. (accessed on 14 December 2020).
- Wang, X.L. On Social Space. Degree of Doctor, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China, May 2010.
- He, Z.Y.; Song, Y.; Li, L.Y. Cartography. 1st ed.; Wuhan University Press: Wuhan, China,2016; pp.173.ISBN9787307181847.
- Zhang, L. Research on the Technologies of Expression and Analysis for the Cyberspace Surveying and Mapping. Degree of Master, Information Engineering University: Zhengzhou, China, June 2018.
- Wang, Y.X. Research on the Method and Technology of Cyberspace Relation and Node Map Information Visualization. Degree of Master, Information Engineering University: Zhengzhou, China, June 2020.
- Zhang, Z. The Research on Theory of Cybermap. Degree of Master, Information Engineering University: Zhengzhou, China, June 2012.
- Erick, D. M.; Charles, A. M. Operational Graphics for Cyberspace. Joint Force Quarterly, 2017,85,42-49.
- Chen, T.M. General Course on Cyberspace Security. 1st ed.; Post & Telecom Press: Beijing, China, 2019; pp.3.ISBN9787115507754.
- Wang, Q.; Li, F.J.; Zhou, Q. Architecture and Key Technologies of Cyberspace Security. Journal of Nanjing University of Science and Technology,2019,43,495-504. [CrossRef]


| Concept | Definition |
|---|---|
| Cyber/Web cartography | Cybercartography was formally defined as "the organization, presentation, analysis, and communication of spatially referenced information on a wide variety of topics of interest and use to society in an interactive, dynamic, multimedia, multisensory, and multidisciplinary format" [4]. |
| Web cartography is the further development of digital cartography. In the network environment, government, enterprises and volunteers mapping coexist. It is an information flow or assembly line integrating multi-source mapping data acquisition, processing (production) and service. The overall efficiency is improved, and the main service mode is to provide network-based electronic map services [5]. | |
| Extended reality map |
Based on computer science and relevant scientific technologies, virtual reality (VR) produces a digital environment in which visual perception, sense of hearing, and sense of touch are highly similar to those of actual environment within a certain range. With the help of necessary equipment to interact and interfere with objects in a digital environment, users may have feelings and experiences corresponding to those in the actual environment. VR is a scientific technology for understanding or simulating the nature[6]. |
| The virtual environment and the real environment are matched and synthesized to achieve enhancement. The technology of overlaying 3D virtual objects to real world display is called augmented reality (AR) [7]. | |
| Augmented reality map is a map based on video spatialization, which integrates virtual and reality for real-time geographic information visualization and intelligent geographic analysis through computer vision technology [8]. | |
| Game map | Game map is the representative of the virtual space map. It’s the digital expression of physics and society of the game world itself, including game base map and scene map. The game base map is often shown as eagle eye mode map or the environment map of the whole game. The game scene is the main activity place of the character, and the scene expression can be two-dimensional or three-dimensional [9,10]. |
| Cyberspace/cyber map | Cybermaps, as special maps for cyberspace, have been used as a tool for understanding various aspects of cyberspace. It can be simply defined as the map for visualizing numerous aspects of cyberspace, for instance, physical locations of cyberspace, traffic situation and so on[11,12]. |
| Cyberspace map is a visual expression of things, phenomena and processes in cyberspace. It is a form of mental map for cognition and navigation of virtual space [13,14]. | |
| Cyberspace map is a kind of visualization expression technology of cyberspace and its elements based on cartography method and combined with visualization related theories and methods[15]. | |
| Pan-map | Pan-map is the extension and expansion of the traditional standard map. It is a comprehensive expression of the ternary space of geography, social humanities and information. It is a generalized map expression that analyzes the characteristics of the ternary space objects through map language, image thinking and spatial thinking, and realizes the functions of information acquisition, transmission and cognition between people, people and objects, and objects [3]. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




