1. Introduction
Digital transformation has become a vital aspect in many fields of life, including e-sports businesses, because it is the basis of supporting flexible and adaptive changes in operational processes and information systems (Parviainen et al., 2017); leads to improved efficiency and productivity (Toanca, 2016); makes it easy to enter new markets (Pereira et al., 2022); recognizes the emergence of threats and opportunities caused by the dynamism and rapid change of the business environment (Toanca, 2016); leads to automating processes, reduces costs and improves decision-making (Rupeika-Apoga et al., 2022); causes innovation (Rupeika-Apoga et al., 2022); follows strategic change (Ji & Li, 2022); improves the customer experience (Carrijo et al., 2021) and ultimately improves the value proposition for the customer and creates new revenue channels (Romanova &Shvalev, 2023).
Therefore, many industries have taken steps in this direction in order to gain the benefits of these developments. Meanwhile, the sports industry has been one of the greatest users of these new technologies due to the ever-growing need for using digital solutions (Ratten, 2020), so that digital transformation has become the main priority of 80% of sports companies around the world (Vandenhouweele, 2020). For example, GoPro initially offered a camera that was suitable for filming action sports, then this company reached millions of people around the world by using its brand and taking advantage of social media and providing user-friendly software (Brodie et al., 2017). Such digital innovations are not limited to social media, National Football League (NFL) CEO Roger Goodell also introduced the NFL's roadmap to enhance the in-stadium experience using digital technologies (Boorstin, 2019). Stadium operators are beginning to digitize their stadiums by offering smartphone applications that allow spectators, media and other stakeholders such as sponsors to communicate with each other and create value. For example, the San Francisco 49ers app provides an opportunity for fans to order food and drinks, communicate with other fans, access real-time statistics, and see traffic patterns inside and outside the stadium (Horbel et al. al., 2021). This means that sports businesses are increasingly trying to create new ideas and have come to the conclusion that new technologies will help them develop products and services (Ratten, 2020).
Nevertheless, the researches show that the adoption of digital transformations has not always been accompanied by success. Many companies, especially sports businesses, have avoided entering this field (Osterrieder et al. ., 2020) or their digital transformation process has slowed down (Teker et al., 2022) due to the chaotic conditions resulting from fundamental changes in the organizations, the nature of uncertainty, the lack of transparency in terms of the consequences, the high costs of investment (Bannikov et al., 2022; Osterrieder et al., 2020), employee resistance to change (Teker et al., 2022), lack of digital skills among employees (Teker et al., 2022), doubts about the safety and effective management of data (Jewapatarakul&Ueasangkomsate, 2022), cyber security, changing the way customers interact and compliance with regulations (Jewapatarakul&Ueasangkomsate, 2022; Phuong, 2022; Teker et al., 2022). As an explanation, I should say that, Kairon et al. have a different opinion, they believe that strategy, not technology, drives digital transformation, therefore they have suggested that businesses should focus on developing a clear digital strategy that is aligned with their overall business strategy and must create the organizational capabilities needed to effectively implement this strategy (Kane et al., 2015). In addition, Brown believes that the lack of knowledge about the various dimensions of this phenomenon and the factors related to it and also the lack of a guidelines to direct the organizations are the main reasons for this failure. They suggest maturity models as a guideline (Brown & Brown, 2019), because digital maturity is a systematic method for the digital transformation of the businesses (Kane et al., 2017) and shows the achievements that the organizations have reached by making digital attempts so far, the way the organization adapts to this environment and get ready to compete in this digital environment (Carrijo). et al., 2021).
However, there is no clear and specific framework that describes the concepts and general guidelines of digital transformation maturity (Egodawele et al., 2022; Korachi&Bounabat, 2019). Between 70% and 95% of all digital transformation projects fail due to the large and varied challenges that organizations face during digital transformation processes (Merten et al., 2022). Most models provide an incomplete picture of digital maturity, most of the existing models of digital maturity are only dedicated to the field of production (Teichert, 2019). On the other hand, in developing countries, there are challenges such as digital skills, lack of digital skills (Gorokhova, 2021), legal complexity, insufficient funding (Safonov et al., 2022), obstacles to successful implementation (Syed & Bandara, 2019), lack of context-dependent policy etc. which prevent the successful implementation of digital transformation maturity in the businesses (Hicks, 2021). Therefore, it is necessary to develop a framework which is capable of guiding businesses towards digital transformation in a desired way. Such a framework seems to be much more valuable in e-sports businesses, because in e-sport businesses digital transformation requires specific capabilities and enablers just like other businesses, but unlike them, digital transformation maturity models in e-sport businesses have not been customized with the specific goals and needs of these businesses. On the other hand, they do not have a clear picture and a deep understanding of the maturity of digital transformation, because basically most of the researches conducted have an industrial background. In addition, in the field of sports management, theoretical contributions regarding the potentials and consequences of digitalization are still limited (Ströbel et al., 2021).
Therefore, it is necessary to design a framework for the maturity of digital transformation in electronic sports businesses in developing countries, and in this regard, this study has three objectives: 1) to identify the capabilities of digital transformation maturity in electronic sports businesses, 2) to identify achievements of maturity of digital transformation in e-sports businesses and 3) to identify maturity levels of digital transformation in e-sports businesses. Achieving these goals can help online sports businesses manage digital transformations and also provide systematic insight into the requirements of the success of digital transformation in eSports businesses. It can also guide the mentioned businesses to adopt a coherent and integrated digital strategy. Additionally, it contributes to the existing literature on the maturity of digital transformation in eSports businesses.
2. Literature review
2.1. Digital transformation
In the research literature, digitization, digitalization and digital transformation are concepts that are sometimes used interchangeably, even though these concepts do not have a single definition (Mertens & Wiener, 2018; Riedl et al., 2017). Meantime, digitalization is the process of converting analog information into digital encoded information (Tilson et al., 2010), which was formed with the widespread emergence of computers (Stegmann et al., 2021). Digitalization is a phenomenon that describes the use of digital technologies, for example when companies use computers to facilitate work processes and do not adopt them only for the traditional uses (Legner et al., 2017). Therefore, digitalization is related to the use of digital technologies in organizational settings and increasing the workforce (Stegmann et al., 2021). On the other hand, digital transformation is a radical process of change that is carried out using the pre-introduced innovations (Hinings et al., 2018; Skog et al., 2018). Also, digital transformation is the process of imposing changes in the use of digital technologies or the development of new digital business models and a dramatic change in the functioning of an organization or a country centered on transformative technologies (Fitzgerald et al., 2014; Kane et al., 2015; Verhoef et al., 2021). In addition, it means the integration of digital technologies in all the different segments of a business, which changes the working procedures and provides value for the customers (Zhai et al., 2022). Therefore, in this study, what we mean by digital transformation in electronic sports businesses is a cultural, organizational and operational change which is identified by the intelligent integration of digital technologies, processes and competencies at all levels and the convergence function of them in a strategic direction. The results of a case study show that the number of published studies emphasizing digital transformation in sports marketing has increased since 2016 (37 articles) and reached its peak in 2020 (91 articles). Most of the studies have been published in sports communication journals (International Journal of Sports Communication: 46 articles; Communication and Sports: 29 articles). Most of the studies have used a quantitative (123 articles) or qualitative (116 articles) approach, and more than half of the studies have been published in the United States of America (147 articles), and these studies are related to sports media, electronic sports. , fantasy sports and other digital innovations (such as smartphone applications) (Stegmann et al., 2021). And there was no research that examined the digital transformation in specific with an emphasis on electronic sports businesses. However, in the few studies conducted by Yang and his colleagues, by analyzing the digital transformation in Chinese traditional companies of sporting goods in tandem with the Covid-19 pandemic crisis and examining the role of digital transformation in coping with this problem, they found that the relevant businesses can increase their knowledge management capabilities and flexibility and experience a higher level of performance (Yang et al., 2023).
2.2. Digital maturity
Organizations are trying to successfully implement digital transformation in order to achieve sustainable success in their operations. This requires evaluating the organization's current digital maturity levels based on several dimensions and employing the best approach for this evaluation and creating a launching pad to implement digital transformation and use the digital maturity models (Aras &Büyüközkan, 2023). Digital maturity is closely related to digital transformation and is defined by Gökalp and Martinez as a state in which the digital technology of a unit has changed its activities, skills interaction and business frameworks (Gökalp& Martinez, 2021). Hägg and Sandhu call it a situation where a transformation has occurred in an organization that has succeeded in solving problems related to digital business prospects (Hägg& Sandhu, 2017). Schumacher and his colleagues define maturity as a complete provision or an ideal, which indicates the developing stages of a system (Schumacher et al., 2016). Teichert uses the term digital transformation maturity to specify that the relationship between digital transformation and digital maturity includes technological and managerial components (Teichert, 2019). Cargio and his colleagues have defined the maturity of digital transformation as the degree of organization's readiness and capacity to change strategy, business model, technology, products and services, internal and external processes, organizational structure and company culture using digital technologies (Carrijo et al., 2021). Based on these definitions, digital maturity can be summarized as a critical indicator that shows the adaptive performance of digital transformation (Aras &Büyüközkan, 2023).
In the field of sports, the digital maturity model can be used to evaluate the digital readiness of sports organizations such as clubs, leagues, and federations. This model can help them understand their strengths and weaknesses in terms of digital capabilities and create a road map for digital transformation (Wijnen, 2020). However, there is few empirical researches that emphasize the maturity of digital transformation in sports and sports industry and have determined what enablers the maturity of digital transformation need in terms of sports and what its achievements are for sports and sports businesses. In one of the few studies conducted in this field, Kitocompent and his colleagues showed in research entitled "Proposed framework of digital maturity dimension for sports media in Thailand: review and comparative analysis" that, there are eight characteristics that are used in the most common maturity models: culture, technology, organization, customer, strategy, operations, innovation, data analysis (Kittkumpanat et al., 2023). Wijnen also believes that strategy, culture, data, technology, processes and people are important pillars around which the maturity of digital transformation in sports revolves (Wijnen, 2020). In addition, Wylie and Palmer stated that the maturity of digital transformation in sports leads to increased digital capabilities, creating a digital advantage, increasing agility, innovation and greater participation, creating personalized products and services to improve sports experiences (Wylie & Palmer, 2016).).
2.3. Electronic businesses
E-business can be defined as the use of the Internet for networking and enabling business processes, e-commerce, organizational communication and collaboration within a company and with its customers, suppliers and other stakeholders. E-businesses use the Internet, intranets, extranets and other networks to support their business processes (Combe, 2012). Sports e-businesses are online retailers that specialize in sports-related goods and services. These retailers offer a wide range of products (including sports clothing, sports equipment, tickets to sports events) and sports services (including sports content production) (Tomanek et al., 2022). There are also businesses that provide sports-related products and services on the Internet or produce sports-related information and content (Tomanek et al., 2022). Therefore, e-sports businesses refer to online businesses that specialize in selling products and services related to digital sports and use digital technologies to reach a wider audience, improve customer experience, and simplify operations.
In general, though the existing literature has increased our understanding of the specific aspects of digital transformation in sports businesses, we lack a comprehensive picture of the nature and concepts of digital transformation and digital maturity in e-sports businesses. Perhaps the reason is that the studies conducted in sports management are mainly focused on the relationship between digital transformation and e-sports, and the comprehensive understanding of digital transformation in sports requires a broader approach (Vial, 2019). Therefore, in the present study, an attempt has been made to provide a framework for the maturity of digital transformation with an emphasis on electronic sports businesses.
3. Methodology
3.1. Research Methodology
In this study, the method of content analysis was used to identify, analyze, and report the patterns present in qualitative data. Content analysis encompasses a broad spectrum of methods and techniques, and suitable analytical methods can be employed based on the research goals and questions (Squires, 2023). Nevertheless, the most commonly accepted method for conducting content analysis involves six stages, all of which were carried out in this study: (1) Familiarization with the data, (2) Developing initial codes, (3) Searching for themes, (4) Reviewing themes, (5) Naming themes, and (6) Producing the report (Scharp& Sanders, 2019).
3.2. Sampling and Participants
The participants in this study were stakeholders of e-sports businesses operating in Iran, which is considered a developing country. The reason why this research focuses on developing countries and Iran is that García-Fernández and colleagues believe that digital transformation in developing countries is not comparable to that of developed countries in many aspects, including technology infrastructure, digital culture, and so on (García-Fernández et al., 2022). Therefore, a uniform digitalization pattern cannot be applied to them (Siani et al., 2022).
According to stakeholder theory, anyone who is in any way affected by an organization or its performance is considered a stakeholder (Freeman, 2010). However, in this study, stakeholders included employees, managers, producers, and suppliers of e-sports businesses who had a minimum of 5 years of experience in the field of technology and digitalization of e-sports businesses. The sampling method used was purposive sampling, and its strategy was snowball sampling. The reason why participants from different spectrums (employees, managers, producers, and suppliers) were selected for the interviews was to explore a range of perspectives on the research topic. After conducting 12 interviews, we reached data saturation, and to ensure data saturation, we conducted three more interviews (
Table 1).
3.3. Data Collection
The data was collected between August 2021 and January 2022. Participants were asked to participate in semi-structured interviews, the purpose of which was to identify the drivers of digital transformation, its achievements, and stages. Skype was used to collect the data because the time and location flexibility provided by the internet is beneficial for qualitative research, allowing researchers to access diverse and geographically dispersed populations that may not be easily accessible (Stewart & Williams, 2005).
3.4. Validity and Reliability
In this study, the following measures were taken to evaluate the validity and reliability of the results.
Table 2.
Validity and reliability of the results.
Table 2.
Validity and reliability of the results.
| Result |
Method |
Strategy |
Validit/Reliability |
| confirm |
Research process confirmation by 8 experts |
Credibility (reliability) |
Validity |
| confirm |
Using two coders for coding multiple interview samples |
Credibility (reliability) |
Validity |
| confirm |
Opinions of three experts who did not participate in the study |
Transferability |
Validity |
| confirm |
Recording and documenting all interviews |
Confirmability (verifiability) |
Validity |
| confirm |
Sharing information with 5 participants in the study |
process audit study |
Reliability |
| reliability between the two coders is 88% |
Analyzing three interviews by the researcher and a co-worker, and identifying similar and dissimilar codes |
Inter-coder agreement |
Reliability |
| |
|
|
|
3.5. Data Analysis
Data analysis began from the first day of data collection and was carried out using transcription, note-taking, coding, theoretical comparison, charting, and integration. All interviews were conducted in the local language (Persian) and transcribed as soon as they were completed. The primary author transcribed all recorded data in Microsoft Word. The transcripts were then checked and sent via email for review by the participants. This was done to ensure that the transcripts accurately reflected the participants' opinions. Each transcript was kept in its original form and was never translated into English because translating a significant portion of the data into another language carries the risk of losing its true meaning (Smith et al., 2008). However, themes or codes generated from the analysis were translated into English because they were shorter (in phrases or a few words) and were easier to translate with less chance of losing their meaning.
To facilitate the data analysis process, note-taking was carried out after each interview, during transcription, and throughout coding. They involved reflections on the environment, participants' expressions of emotions and responses, interview quality, lessons learned, and strategies for future interviews. Note-taking during transcription focused on key words, patterned questions, and gaps that needed to be filled. Note-taking during coding focused on the relationship between key ideas and themes that emerged during the analysis. Finally, the information was prepared for analysis using the reflexive thematic analysis method proposed by Braun and Clarke in 2006, which has since become one of the most common methods of conducting content analysis (Byrne, 2022).
4. Findings
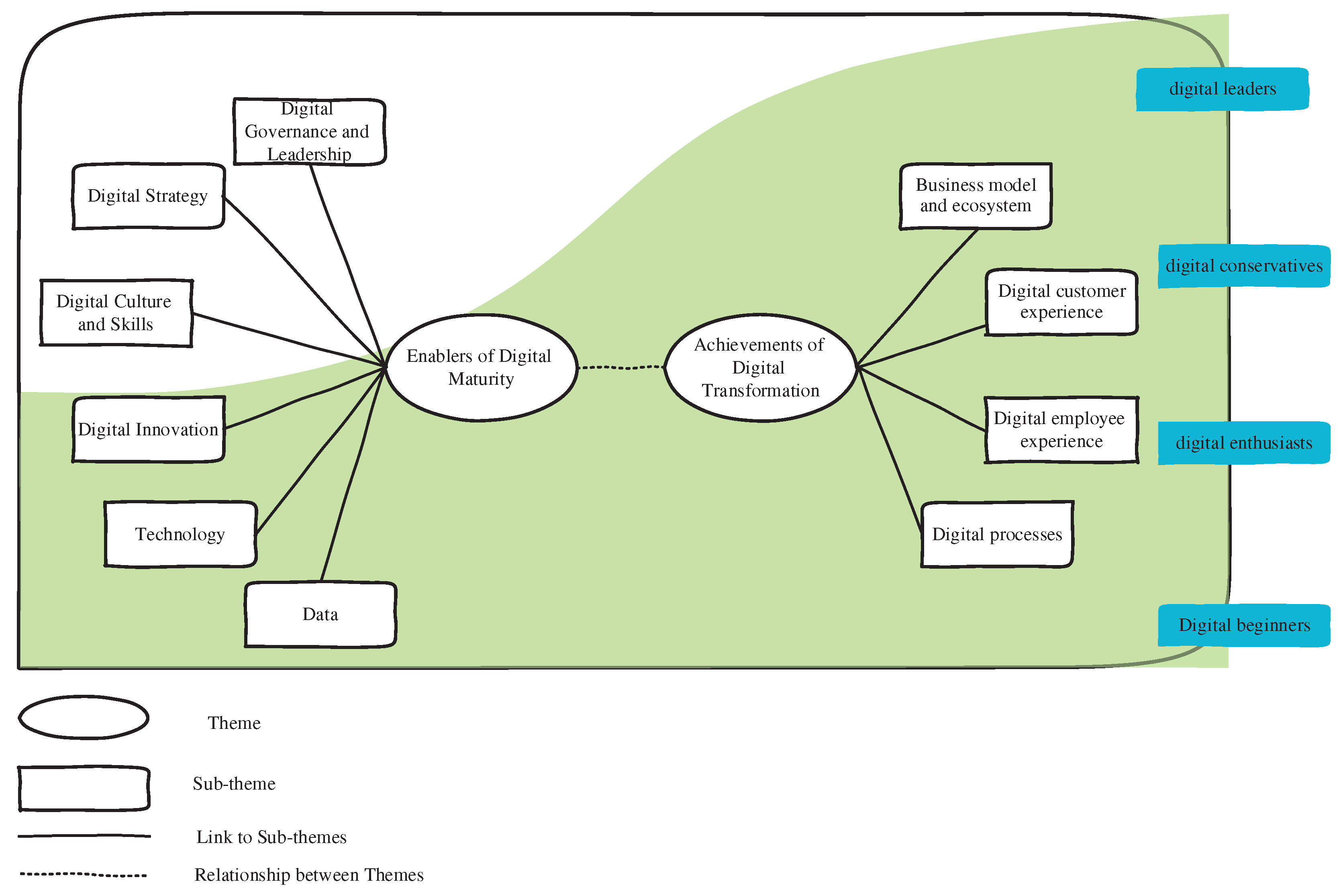
Our findings generally indicate that moving towards digital transformation and achieving digital maturity in e-sports businesses depends on six key capabilities. By equipping relevant businesses with these capabilities, it will be possible to move towards digital transformation and achieve the four outcomes of digital transformation. In addition, the maturity of digital transformation in e-sports businesses is divided into four levels. Now, we will discuss the enablers, achievements, and stages of digital transformation in e-sports businesses in more detail.
4.1. Enablers of Digital Maturity in E-Sports Businesses
Every e-sports business needs key enablers and capabilities to move towards digital transformation. Digital enablers refer to "governance and leadership," "digital strategy," "culture and skills," "innovation," "technology," and "data," and achieving digital transformation and digital maturity will be impossible without each of these enablers.
Table 3.
Enablers of Digital Maturity.
Table 3.
Enablers of Digital Maturity.
| Themes |
Subthemes |
Concepts |
| Enablers of Digital Maturity |
Digital Governance and Leadership |
Internal promotion of digital governance literacy
Efforts to increase digital governance literacy
Definition, approval, and management of digital transformation projects
Design of a digital governance system
Moving towards a digital-focused redesign of structures
Support for managers in digital transformation
The impact of managers on digital transformation
Attracting digital transformation managers from outside
Development of digital transformation managers at various levels
|
| Digital Strategy |
A strategic approach to digital transformation
Development of strategic pillars (vision and goals of the organization in the field of digitalization)
Expansion and coverage of strategic pillars
Alignment between digital transformation strategies and functional and competitive strategies
|
| Digital Culture and Skills |
Evaluation of digital culture
Evaluation of digital skills
Cultivation of digital culture
Development of digital skills and training
|
| Digital Innovation |
A strategic approach to digital innovation
Building a digital innovation governance system
Systematic research and development
Enhancement of business innovation literacy
Presence in innovation trends
|
| Technology |
Moving towards information technology governance
Thinking about information technology auditing
Thinking about information technology architecture
Entering the field of information technology management
Using transformative technologies in products and services
Having short-term and long-term development plans for the technology field
|
| Data |
Evaluation of data maturity
Data literacy
Use of data analysis platforms |
4.1.1. Digital Governance and Leadership
Digital governance is a system for guiding digital transformation in e-sports businesses that establishes policies, structures, processes, and mechanisms to ensure the acquisition of digital value and benefit. According to interviewee number 8, who is an employee of an e-sports business with 15 years of work experience, "digital governance pursues two main objectives: first, coordination for prioritizing, synchronizing, and aligning digital initiatives across the organization; second, sharing efficient resources to achieve digital transformation goals." Additionally, "digital leaders" are leaders who define and frame digital age issues well, offer technology-based solutions for them, and coordinate the elements of their organization to move towards digital transformation. In this regard, interviewee number 4 stated, "Digital leaders know that the digital transformation story is not just a technology story, but they consider strategy, culture, innovation, and employee skills as circles alongside technology that are essential to guide the organization on the path to digital transformation. Perhaps the most important role of digital leaders is to attract enthusiastic employee participation in the path of digital transformation."
4.1.2. Digital Strategy
Digital strategy is important in e-sports businesses because today, the role of technology in business has gone beyond a specific area such as information technology and encompasses the entire business. To take advantage of this, a business needs a more comprehensive strategy than an information technology strategy. In recent years, to address this problem, the convergence of information technology strategy and business strategy has been discussed in the form of "digital strategy." In this regard, interviewees 7 and 11 stated in a similar position, "Digital strategy seeks to create capabilities within a business using transformative technologies so that an organization can respond to changing market conditions. Therefore, e-sports businesses need to have a strategic outlook on digital transformation and at the same time formulate their vision and goals in the field of digitalization."
4.1.3. Digital Culture and Skills
Regarding the importance of "digital culture and skills," it can be said that to successfully implement digital transformation in e-sports businesses, digital culture must be nurtured. When we talk about digital culture, it does not mean an entity independent of the organizational culture. Digital culture is a set of systematic values and methods that each individual strengthens individually and empowers businesses to progress in a world that is advancing towards a digital economy. Therefore, digital culture is the same culture that organizations of this era must cultivate to embark on a digital journey. According to interviewee number 9, "E-sports businesses, according to my experience over the past 17 years, must have a technology-accepting culture for sustainable digital transformation." On the other hand, interviewee number 3 believes that "although culture may be an effective factor, we should not forget that without digital skills and talents, we cannot hope for digital transformation in business. Businesses should not necessarily focus on professional experts in technology such as data analysis and artificial intelligence; in fact, they should aim to attract, develop, and retain individuals with a set of cognitive, social, emotional, and technical skills."
4.1.4. Digital Innovation
"Digital innovation" refers to innovation in products, processes, or business models using digital technologies. "Digital innovation" refers to using digital technologies to solve problems and challenges in e-sports businesses. In this regard, interviewee number 3 stated, "Businesses have no choice but to innovate to take advantage of opportunities and overcome the implicit threats of transformative technologies." At the same time, interviewee number 5 stated, "Research, development, and innovation are an ongoing and dynamic process, not a one-time event, which requires both short-term and long-term results. Therefore, innovation must become a key capability in the organization."
4.1.5. Technology
"Technologies" are divided into two common and transformative types. Common technologies play a maintenance role in e-sports businesses and have become essential for survival. In contrast, transformative technologies aim to create fundamental changes in e-sports businesses. Common technologies are used only to perform routine and daily operations in organizations, and they cannot be expected to create transformation in business or industry. The internet, email, AR/VR ID, GPS, and smartphones are examples of such technologies. Although daily business operations become difficult without common technologies, their use does not create a competitive advantage for e-sports businesses and does not generate digital dividends. However, transformative technologies provide the possibility of fundamental changes for businesses. In this regard, interviewee number 12 stated: "Digital leaders equip themselves with innovative digital technologies more than their competitors and put themselves on the path of transformation through them. These technologies are a combination of information, communication, operations, and media technologies that facilitate the organization role through innovation in the business model, improving core processes of the organization and enhancing customer experience, leading to digital transformation in business. Data analytics, artificial intelligence, blockchain, the internet of things, cloud computing, 3D printing, virtual and augmented reality, robotics, phygital, and social media are among the most important digital technologies that play a key role in the digital transformation of businesses, and e-sports businesses are certainly not an exception."
4.1.6. Data
Another empowering element of digital transformation maturity is "data," which helps e-sports businesses move away from guesswork and towards inspiring predictions and continuous testing of hypotheses. Today, data provides the necessary insight for decision-making, and the era of decision-making based solely on intuition and emotions is over. In this regard, interviewee number 4 stated: "Today's businesses have become data-driven businesses. They need data analysis and information to gain a better understanding of customers, competitors, target markets, and even products and services to be offered. These analyses help managers define new business lines." Also, interviewee number 15 stated: "Digital e-sports business managers must make all their decisions data-driven, from formulating business strategies to determining employee salaries and rewards, to succeed in the digital age."
4.2. Achievements of Digital Transformation Maturity
The findings indicate that by equipping e-sports businesses with the aforementioned capabilities and tools, they can move towards digital transformation and achieve four digital transformation achievements: "business model and ecosystem," "digital customer experience," "digital employee experience," and "digital processes."
Table 4.
Achievements of Digital Transformation.
Table 4.
Achievements of Digital Transformation.
| Themes |
Subthemes |
Concepts |
| Achievements of Digital Transformation |
Business model and ecosystem |
Reviewing the ways and methods of creating value in the digital age
Adaptation of actions to the capabilities and opportunities of the digital age
Sustainability of the digital business model
A digital ecosystem approach
Developing a digital ecosystem
|
| Digital customer experience |
Evaluation of digital customer experience
Design and analysis of customer journey maps
Program and process for enhancing the digital customer experience before, during, and after purchase
Upgrading management and knowledge of digital customer experience
Co-creation of digital product and service development with customers
|
| Digital employee experience |
A strategic approach to digital employee experience management
Evaluation of the work environment and digital employee experience
Development of a digital work system
Design and analysis of employee journey maps
Upgrading digital employee experience before, during, and after employment
|
| Digital processes |
Documenting digital processes
Modeling and architecture of digital processes
Ensuring the maturity of digital processes
Using digital technologies and innovation in business processes
Redesigning digital business processes |
4.2.1. Business Model and Ecosystem
"Business models" are business models that create value for e-sports businesses with a focus on digital technologies. The transformation that digital technologies create in business models can be partial or fundamental. Sometimes, a review of the business model is carried out by creating innovation, limitations, and non-structural changes in the current model. These changes do not bring a completely new business model for e-sports businesses, but rather focus on innovation and improvement in the current model's performance. On the other hand, the transformation of the business model through digital technologies can go beyond limited innovations in the current model and lead to creating new products and services or fundamental changes in sales approaches or revenue generation methods. This fundamental re-creation sometimes not only affects the business itself but also affects related industries and creates new structures in the industry or new behaviors in customers.
Furthermore, the concept of the "business ecosystem" is a new concept that emphasizes the cooperation and synergy among various players in the business space, where the business space is considered as an ecosystem and a network of actors plays a role in creating value for the customer. Interviewee number 14 stated in this regard, "The participation of each of the main and ancillary players with each other in the ecosystem of the product or service offered in related businesses creates a dependency that ultimately brings more value to the customer."
4.2.2. Customer Digital Experience
Digital technologies are impacting the "customer experience" more than ever before. Although "customer experience" is not a new concept in the field of e-sports businesses, due to the amazing impact that digital technologies have had on customer experience in various industries, it has received more attention than ever before, and a new concept called "customer digital experience" has been introduced. Interviewee number 13 believes: "Digital technologies are able to significantly improve the customer experience by creating an attractive, interactive and completely different environment and meeting their expectations in the best possible way." Interviewee number 10 also stated: "To create an attractive digital experience, coherence must be created between the physical and technological experience of customers to create the highest value for them."
4.2.3. Employee Digital Experience
Entering the era of "employee experience" is a major revolution in the field of e-sports businesses. In this era, organizations no longer treat individuals as "assets and resources of the organization," but rather as "humans." The result of this new approach is a greater effort to understand employees and provide solutions tailored to their needs. In fact, when employees have a positive experience in the business, they have a high level of attachment, are well integrated with the organization, participate, are sensitive to what they do, and have higher productivity. In this regard, participant number 6 stated: "The employee experience includes all factors that affect the perception and feelings of employees about their work environment and job, and e-sports businesses must always have a strategic approach to managing the digital experience of employees and design and analyze employee travel plans."
4.2.4. Digital Processes
Advances in information technology and the emergence of digital technologies have provided better conditions for improving "organizational processes." Digital technologies can help improve the work processes in e-sports businesses. Based on this approach, processes are eliminated, simplified, and automated. Businesses have been trying for years to automate manual tasks, but today, with the use of technologies, these tasks can be easily done, and many good and low-cost solutions have been provided through technologies.
4.3. Levels of Digital Maturity
Findings show that after evaluation and auditing, e-sports businesses are placed in one of the levels of digital maturity according to their score. "Digital beginners" are at the lowest level, followed by "digital enthusiasts," "digital conservatives," and at the highest level of maturity, "digital leaders." Participant number 3 states, "Beginners are at the starting point of their digital journey. Many of them are trying to ensure success before taking action, which is why they have adopted the 'let's see what happens' strategy." Interviewee number 5 also believes that "some beginners think that technological opportunities are suitable for other industries, not theirs. Others lack the necessary leadership to create change. As a result, beginners only have basic technological capabilities and are placed lower than their competitors in many financial performance criteria." On the other hand, enthusiasts do not wait (interviewee number 12). They buy every new digital tool. They follow technological trends and fashions and are proud of this feature, but do not change the nature of their affairs (interviewee number 9). However, due to the lack of strong digital governance and leadership, many of their expenses are wasted. Or they find that they need to review everything they have done so far in order to integrate and upgrade their capabilities (interviewee number 3). Interviewee number 10 believes that "none of these enthusiasts have a mechanism for coordinating activities or creating synergy between their investments. Creating a wide range of non-adaptive processes and systems may seem like progress, but in reality, it will limit the exploitation of larger opportunities. This inflexibility prevents the creation of a coordinated approach to customer interaction and a unified approach to operations." Furthermore, conservatives are at the opposite end of enthusiasts in terms of capability. Interviewee number 9 believes that "although conservatives have useful digital leadership capabilities, excessive caution prevents these businesses from creating powerful technological capabilities. These businesses focus on the fact that each technological investment should be carefully selected and fully coordinated with each other. Leaders in these businesses avoid making mistakes because they know it will waste scarce resources like time, effort, and money." Finally, unlike most businesses, digital leaders excel in both empowering and achieving superior results. This is while some businesses may only appear strong in technological capabilities and be weak in leadership capabilities, and vice versa.
Figure 1.
Concept Map of Digital Maturity in Developing Countries' E-Sports Businesses
Figure 1.
Concept Map of Digital Maturity in Developing Countries' E-Sports Businesses
5. Conclusions
In simple terms, in any change or transformation, we need a benchmark model to compare and measure our progress. Digital transformation is no exception, and using a benchmark model is crucial for achieving the best results. Moreover, a crucial element that different businesses should consider before embarking on the digital transformation journey is determining an appropriate model for assessing digital maturity in their industry. This is because in different time intervals, the basis for measuring progress and desired indicators must be determined to obtain a proper comparison and analysis of progress, strengths, and weaknesses. In this study, based on interviews with stakeholders in developing countries' e-sports businesses, a framework has been developed for digital maturity in these businesses.
This framework emphasizes digital enablers and digital achievements in the path of digital transformation of e-sports businesses in developing countries. Digital governance and leadership are one of the digital enablers, as they ensure that e-sports businesses have a clear strategy, structure, and accountability for their digital initiatives. Without effective governance and leadership, digital transformation efforts may lack direction, compatibility, and harmony with business objectives, resulting in wasted resources and missed opportunities. Digital governance includes creating policies, procedures, and standards for managing digital assets, data, and processes. It also involves defining roles, responsibilities, and decision-making processes for digital initiatives. Effective digital governance ensures that businesses can manage risks, comply with regulations, and optimize their digital investment value. On the other hand, digital leadership includes creating a vision, culture, and mindset that enhances innovation, collaboration, and agility in the digital age. Digital leaders must be able to inspire and motivate their teams to embrace change, experiment with new ideas, and continuously learn and improve. They also need to be able to communicate the value of digital transformation to stakeholders and align it with business strategy.
Strategy is another enabler of digital transformation maturity in e-sports businesses, which has been highlighted in past research, unlike governance and leadership (Kittkumpanat et al., 2023; Wijnen, 2020). This is because strategy provides a roadmap for how digital technologies and processes can be used to achieve business objectives. A well-defined digital strategy ensures alignment between digital initiatives and the overall business strategy, and resources are effectively allocated to achieve maximum impact. A digital strategy also helps e-sports businesses identify opportunities for innovation and growth and stay ahead of competitors in a digital landscape, while enabling businesses to prioritize investment in technologies and digital processes based on their potential to deliver value and improve customer experiences. Furthermore, a digital strategy provides a framework for measuring the success of digital transformation initiatives and continuous improvement and optimization over time, helping e-sports businesses stay agile and respond to changing market conditions and customer needs.
Another enabler identified for digital maturity in e-sports businesses is culture and skills, which have been previously mentioned in studies (Kittkumpanat et al., 2023; Wijnen, 2020). The reason culture and skills were recognized as an enabler for digital transformation maturity in e-sports businesses is that both are vital factors that determine the success or failure of digital initiatives. A culture that is open to change, innovation, and experimentation is essential for accepting new technologies and processes and fostering a mindset of continuous improvement. In addition, having the appropriate skills and expertise for effective implementation of digital initiatives is crucial. This includes technical skills such as data analysis, artificial intelligence, and cybersecurity, as well as soft skills such as communication, collaboration, and adaptability. Without a culture that supports digital transformation and the necessary skills to implement it effectively, businesses may struggle to fully leverage the potential of digital technologies and processes. They may face resistance to change, encounter obstacles in implementation, or fail to achieve desired results. Therefore, businesses must invest in developing a culture that encompasses digital transformation and creating the necessary skills and capabilities for effective implementation. This requires a commitment to continuous learning and development, as well as a willingness to experiment and take risks in pursuit of innovation and growth.
The fourth enabler identified through the combination of themes in the study (Kittkumpanat et al., 2023) is innovation, which plays a role in the maturity of digital transformation in e-sports businesses as it fosters growth, competition, and customer satisfaction. Digital technologies are constantly evolving, and businesses that fail to innovate are at risk of falling behind their competitors and losing market share. Innovation can also help businesses identify new opportunities, create new products and services, improve processes, and enhance customer experiences. By embracing innovation, businesses can stay ahead of the curve and remain relevant in a rapidly changing marketplace. Furthermore, innovation can reinforce a culture of continuous experimentation and improvement, which is essential for successful digital transformation. It encourages employees to think creatively and remain open to new ideas, technologies, and approaches. Finally, innovation helps e-sports businesses overcome challenges and obstacles that may arise during the digital transformation process, enabling them to find solutions for complex problems, adapt to changing conditions, and take advantage of new opportunities.
In this study, technology was also identified as an enabler of digital maturity in e-sports businesses, previously mentioned in studies (Kittkumpanat et al., 2023; Wijnen, 2020). The reason technology explains digital transformation maturity is that it is the foundation upon which digital transformation is built. Digital technologies enable businesses to automate processes, collect and analyze data, engage with customers, and create new products and services. Technology also guides innovation by providing new tools and platforms for experimentation and development. For example, cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and blockchain are all technologies that drive innovation in various industries. Additionally, technology is essential for businesses to remain competitive in a rapidly evolving market. Finally, by using technology, e-sports businesses can improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance customer experiences.
The latest enabler identified through the combination of themes in this study is the sub-theme of data, which has also been emphasized in the studies by Kittkumpanat et al. (2023) and Wijnen (2020). Data provides valuable insights that can be used to improve decision-making, optimize processes, and enhance customer experiences. As the volume of data generated by businesses increases, the use of data analysis tools and techniques to extract meaningful insights from this data has become essential. Through data analysis, e-sports businesses can identify patterns, trends, and correlations that can help them understand customer behavior, market trends, and business performance. This information can then be used for informed decision-making about product development, marketing strategies, and resource allocation. Data is also important for improving operational efficiency. By collecting and analyzing data about processes and workflows, e-sports businesses can identify inefficiencies and areas for improvement, leading to cost savings, improved productivity, and better resource utilization. Finally, data is vital for enhancing customer experiences. By collecting and analyzing customer data, businesses can gain insights into their preferences, needs, and behaviors. This information can then be used to personalize products and services, improve customer service, and create more engaging marketing campaigns.
By equipping organizations with these capabilities, it is possible to move towards digital maturity. "Business model and ecosystem," "digital customer experience," "digital employee experience," and "digital processes" are the four achievements of digital transformation that, when combined, will create a digital-savvy organization. The reason why the business model ecosystem contributes to the digital maturity of e-sports businesses is that this model provides a framework for how businesses operate and interact with other businesses and stakeholders in the digital economy. On the other hand, it defines the value proposition, revenue streams, and cost structure of the business, showing how the business creates value for customers, shareholders, and other stakeholders. A well-designed business model can help businesses identify new opportunities, optimize operations, and achieve sustainable growth. Additionally, the ecosystem can provide access to new technologies and resources that can accelerate digital transformation. For example, partnering with technology providers or startups can help e-sports businesses gain access to technologies and expertise that can assist in innovation and staying ahead of competitors.
One of the sub-themes of achieving digital maturity is the digital customer experience, which has been mentioned in the study by Kittkumpanat et al. (2023) as one of the indicators of digital transformation maturity. The reason why the digital customer experience explains digital maturity is that customer experience directly affects satisfaction, loyalty, and retention. In today's digital age, customers expect holistic and personalized experiences at all touchpoints, including websites, mobile applications, social media, and other digital channels. As a result, e-sports businesses that prioritize the customer experience can gain a competitive advantage by providing exceptional experiences that meet or exceed customer expectations, leading to increased customer loyalty, positive word-of-mouth referrals, and higher revenue growth. In addition, the digital customer experience can also provide valuable insights into customer behavior and preferences that businesses can use to inform their digital transformation strategies. By collecting and analyzing customer data, businesses can identify pain points, opportunities for improvement, and new areas for innovation.
Furthermore, it has been found that in addition to the digital customer experience, e-sports businesses must also focus on the digital employee experience to achieve digital maturity. A positive digital experience for employees can lead to increased productivity and efficiency. When employees have access to the right tools and technology, they can work more efficiently and complete tasks more quickly. When employees gain the necessary experience, they can provide better services and support to customers, and they are more likely to offer innovative ideas that can contribute to business growth.
Finally, it has been determined that digital processes are the foundation of digital maturity in e-sports businesses, as previously mentioned in the study by Wijnen (2020). They enable e-sports businesses to streamline their operations, increase efficiency, and improve customer experiences. Digital processes also allow businesses to collect and analyze data more effectively, which can help them make informed decisions and identify areas for improvement. By implementing digital processes, e-sports businesses can automate repetitive tasks, reduce errors, and free up employees to focus on higher-value activities, which can lead to increased productivity, faster response times, and improved customer satisfaction. Digital processes also enable e-sports businesses to leverage emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and the internet of things. These technologies can help businesses gain insights into customer behavior, optimize operations, and create new products and services.
6. Limitations
Despite the benefits of the digital transformation maturity framework for e-sports businesses in developing countries, there are limitations that must be considered. The first limitation is that this framework is relatively new and there is limited empirical research on its effectiveness in the e-sports industry. The second limitation is that this framework may not be applicable to all e-sports businesses, as different businesses may have different goals, resources, and levels of digital maturity. Finally, this framework may not take into account the rapidly evolving nature of e-sports businesses and the continuous emergence of new technologies and business models.
7. Recommendations for future research
To address these limitations, there are various areas for future research that can be explored. Firstly, empirical research can be conducted to evaluate the effectiveness of the digital transformation maturity framework in the e-sports industry. Secondly, future research can examine the applicability of the maturity framework for different types of e-sports businesses. For example, this framework may be necessary for small and medium-sized businesses or start-ups that have limited resources. This research can also investigate the factors that impact the level of digital maturity in e-sports businesses and how to address them. Lastly, future research can investigate the impact of emerging technologies and business models on the digital transformation maturity framework for e-sports businesses. For instance, the emergence of blockchain technology and non-fungible tokens (NFTs) in the e-sports industry may require a different approach to digital transformation. This research can also examine the challenges that e-sports businesses may face in adopting these new technologies and how to overcome them.
References
- Aras, A.; Büyüközkan, G. Digital Transformation Journey Guidance: A Holistic Digital Maturity Model Based on a Systematic Literature Review. Systems 2023, 11, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannikov, V.; Lobunets, T.; Buriak, I.; Maslyhan, O.; Shevchuk, L. On the question of the role of project management in the digital transformation of small and medium-sized businesses: essence and innovative potential. Amazonia Investiga 2022, 11, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boorstin, J. (2019). NBA and NFL commissioners tell how they’re turning to technology to draw in fans. CNBC. https://www.cnbc.com/.
- Brodie, R.J.; Benson-Rea, M.; Medlin, C.J. Branding as a dynamic capability: Strategic advantage from integrating meanings with identification. Marketing Theory 2017, 17, 183–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, N.; Brown, I. From digital business strategy to digital transformation-How: A systematic literature review. Proceedings of the South African Institute of Computer Scientists and Information Technologists 2019, 2019, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Byrne, D. A worked example of Braun and Clarke’s approach to reflexive thematic analysis. Quality & quantity 2022, 56, 1391–1412. [Google Scholar]
- Carrijo, P.; Alturas, B.; Pedrosa, I. (2021). Análise de modelos de maturidade de transformação digital Conference on Information Systems andTechnologies (CISTI).
- Combe, C. (2012). Introduction to E-business. Routledge.
- Egodawele, M.; Sedera, D.; Bui, V. (2022). A Systematic Review of Digital Transformation Literature (2013-2021) and the development of an overarching apriori model to guide future research. arXiv preprint arXiv:2212.03867.
- Fitzgerald, M.; Kruschwitz, N.; Bonnet, D.; Welch, M. Embracing digital technology: A new strategic imperative. MIT Sloan Management Review 2014, 55, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Freeman, R.E. (2010). Strategic management: A stakeholder approach. Cambridge university press.
- García-Fernández, J.; Valcarce-Torrente, M.; Gálvez-Ruiz, P.; Mohammadi, S. (2022). The Challenges of Digital Transformation in the Fitness Industry in the World. In The Digital Transformation of the Fitness Sector: A Global Perspective (pp. 1-3). Emerald Publishing Limited.
- Gökalp, E.; Martinez, V. Digital transformation capability maturity model enabling the assessment of industrial manufacturers. Computers in Industry 2021, 132, 103522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorokhova, T. The transformation of business processes in conditions of digitalization of economic systems. Economic journal of LesyaUkrainka Volyn National University 2021, 3, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hägg, J.; Sandhu, S. (2017). Do or Die: How large organizations can reach a higher level of digital maturity. In.
- Hicks, J. (2021). Environmental Challenges of Digital Transformation in Developing Countries.
- Hinings, B.; Gegenhuber, T.; Greenwood, R. Digital innovation and transformation: An institutional perspective. Information and Organization 2018, 28, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horbel, C.; Buck, C.; Diel, S.; Reith, R.; Walter, Y. Stadium visitors' smartphone usage and digital resource integration. Sport, Business and Management: An International Journal 2021, 11, 10–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jewapatarakul, D.; Ueasangkomsate, P. (2022). Digital Transformation: The Challenges for Manufacturing and Service Sectors. 2022 Joint International Conference on Digital Arts, Media and Technology with ECTI Northern Section Conferenceon Electrical, Electronics, Computer and Telecommunications Engineering (ECTI DAMT & NCON),.
- Ji, X.; Li, W. Digital Transformation: A Review and Research Framework. Frontiers in Business, Economics and Management 2022, 5, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kane, G.C.; Palmer, D.; Phillips, A.N. (2017). Achieving digital maturity.
- Kane, G.C.; Palmer, D.; Phillips, A.N.; Kiron, D.; Buckley, N. Strategy, not technology, drives digital transformation. MIT Sloan Management Review 2015, 56, 18–26. [Google Scholar]
- Kittkumpanat, M.; Chankuna, D.; Sriboon, N. (2023). A Suggested Framework of Digital Maturity Dimension for Sport Media in Thailand : Review and Comparative Analysis. 15. https://so01.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/bahcuojs/index.
- Korachi, Z.; Bounabat, B. Integrated methodological framework for digital transformation strategy building (IMFDS). International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legner, C.; Eymann, T.; Hess, T.; Matt, C.; Böhmann, T.; Drews, P.; Mädche, A.; Urbach, N.; Ahlemann, F. Digitalization: opportunity and challenge for the business and information systems engineering community. Business & Information Systems Engineering 2017, 59, 301–308. [Google Scholar]
- Merten, S.; Schmidt, S.L.; Winand, M. (2022). Organisational capabilities for successful digital transformation: a global analysis of national football associations in the digital age. Journal of Strategy and Management(ahead-of-print).
- Mertens, P.; Wiener, M. Riding the Digitalization Wave: Toward a Sustainable Nomenclature in Wirtschaftsinformatik: A Comment on Riedlet al.(2017). Business & Information Systems Engineering 2018, 60, 367–372. [Google Scholar]
- Osterrieder, P.; Budde, L.; Friedli, T. The smart factory as a key construct of industry 4.0: A systematic literature review. International Journal of Production Economics 2020, 221, 107476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parviainen, P.; Tihinen, M.; Kääriäinen, J.; Teppola, S. Tackling the digitalization challenge: how to benefit from digitalization in practice. International journal of information systems and project management 2017, 5, 63–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, C.S.; Durão, N.; Moreira, F.; Veloso, B. The Importance of Digital Transformation in International Business. Sustainability 2022, 14, 834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phuong, N.M. Opportunities and Challenges of Digital Transformation in Vietnam's Tourism Industry. International Journal of Economics, Business and Management Research 2022, 6, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratten, V. (2020). Digital transformation in sport and social media. In Sport startups: new advances inentrepreneurship (pp. 89-104). Emerald Publishing Limited.
- Riedl, R.; Benlian, A.; Hess, T.; Stelzer, D.; Sikora, H. On the relationship between information management and digitalization. Business & Information Systems Engineering 2017, 59, 475–482. [Google Scholar]
- Romanova, A.N.; Shvalev, N.S. Digital transformation of professional sports organizations’ business model: The case of the US National Football League. Vestnik of Saint Petersburg University. Management 2023, 84–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupeika-Apoga, R.; Petrovska, K.; Bule, L. The effect of digital orientation and digital capability on digital transformation of SMEs during the COVID-19 pandemic. Journal of Theoretical and Applied Electronic Commerce Research 2022, 17, 669–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safonov, Y.; Borshch, V.; Shulzhenko, I.; Zahrebelna, I.; Bolshakova, I. Digital transformation in developing economies under the COVID-19 pandemic. IEEE Engineering Management Review 2022, 50, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharp, K.M.; Sanders, M.L. What is a theme? Teaching thematic analysis in qualitative communication research methods. Communication Teacher 2019, 33, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumacher, A.; Erol, S.; Sihn, W. A maturity model for assessing Industry 4.0 readiness and maturity of manufacturing enterprises. Procedia Cirp 2016, 52, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siani, M.G.; Mohammadi, S.; Veisi, K. (2022). Digital Transformation in Iranian Fitness Centres. In The Digital Transformation of the Fitness Sector: A Global Perspective (pp. 159-164). Emerald Publishing Limited.
- Skog, D.A.; Wimelius, H.; Sandberg, J. Digital disruption. Business & Information Systems Engineering 2018, 60, 431–437. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, H.J.; Chen, J.; Liu, X. Language and rigour in qualitative research: problems and principles in analyzing data collected in Mandarin. BMC medical research methodology 2008, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squires, V. (2023). Thematic Analysis. In Varieties of Qualitative Research Methods: Selected Contextual Perspectives (pp. 463-468). Springer.
- Stegmann, P.; Nagel, S.; Ströbel, T. The digitaltransformation of value co-creation: a scoping review towards an agenda for sport marketing research. European Sport management quarterly 2021, 1–28. [Google Scholar]
- Stewart, K.; Williams, M. Researching online populations: the use of online focus groups for social research. Qualitative Research 2005, 5, 395–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ströbel, T.; Stieler, M.; Stegmann, P. Guest editorial. Digital transformation in sport: the disruptive potential of digitalization for sport management research. Sport, Business and Management: An International Journal 2021, 11, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, R.; Bandara, W. (2019). Controlling corruption in developing country public sector: A process ecosystems perspective.
- Teichert, R. Digital transformation maturity: A systematic review of literature. Acta universitatis agriculturae et silviculturaemendelianaebrunensis 2019, 67, 1673–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teker, S.; Teker, D.; Orendil, E. (2022). Digital transformation in businesses: The process and its outcomes 8th global business research vongress, Istanbul, Turkey.
- Tilson, D.; Lyytinen, K.; Sørensen, C. Research commentary—Digital infrastructures: The missing IS research agenda. Information systems research 2010, 21, 748–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toanca, L. Empirical research regarding the importance of digital transformation for Romanian SMEs. Management and Economics Review 2016, 1, 92–108. [Google Scholar]
- Tomanek, M.; Cieslinski, W.; Polasik, M. (2022). Digital Business Models in Sport. Taylor & Francis.
- Vandenhouweele, J. (2020). Digital transformation in sports. MySueño Sport & Health Marketing. https://mysueno.com/digital-transformation-in-sports/.
- Verhoef, P.C.; Broekhuizen, T.; Bart, Y.; Bhattacharya, A.; Dong, J.Q.; Fabian, N.; Haenlein, M. Digital transformation: A multidisciplinary reflection and research agenda. Journal of business research 2021, 122, 889–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vial, G. Understanding digital transformation: A review and a research agenda. The journal of strategic information systems 2019, 28, 118–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijnen, M.V. (2020). What’s your sports organisation’s digital maturity level? https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/whats-your-sports-organisations-digital-maturity-level-van-wijnen/.
- Wylie, J.; Palmer, K. (2016). Connecting Digital and Technology with Australia’s Competitive Sport Obsession to achieve world-leading physical activity and high performance objectives. Australian sports commission. https://www.clearinghouseforsport.gov.au/__data/assets/pdf_file/0007/876661/34871_Connecting_Digital_with_Sport_Final.pdf.
- Yang, J.; Zhang, X.; Pei, Y. (2023). Digitaltransformation of the business models of Chinese sporting goods enterprises in the post-COVID-19 era: a knowledge-management perspective. Journal of Knowledge Management.
- Zhai, H.; Yang, M.; Chan, K.C. Does digital transformation enhance a firm's performance? Evidence from China. Technology in Society 2022, 68, 101841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Table 1.
Characteristics of Participants in the Study
Table 1.
Characteristics of Participants in the Study
| Business Activity Description |
Business List |
Education |
Experience |
Age |
SEX |
Row |
| Video-based fitness and bodybuilding movement educational database |
FitB |
PhD |
11 |
40 |
Male |
1 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Home workout application |
Energym |
MA |
13 |
47 |
Male |
2 |
| Football news, statistics, and data reference website |
Free Foot |
PhD |
7 |
38 |
Female |
3 |
| Specialized online sales platform for sports equipment |
Pilates Shop |
MA |
9 |
51 |
Male |
4 |
| Science of bodybuilding educational system |
Arnold Show |
PhD |
12 |
39 |
Male |
5 |
| Social network for sports with the ability to compare sports clubs |
Gym Center |
BA |
9 |
43 |
Male |
6 |
| Online store for sports clothing and equipment |
Gisha Sport |
BA |
13 |
45 |
Female |
7 |
| Comprehensive sports directory for Iran |
Varzin |
BA |
15 |
47 |
Female |
8 |
| Online store for sports clothing and equipment |
Anik |
PhD |
17 |
36 |
Male |
9 |
| Sports social network and information platform |
Tarrfdari (Supporter) |
MA |
8 |
46 |
Male |
10 |
| Online platform for introducing and booking sports facilities |
Bashgam |
MA |
11 |
52 |
Female |
11 |
| Platform for providing diet and exercise plans |
Health Land |
BA |
9 |
31 |
Male |
12 |
| Online store for sports clothing and equipment |
Online Sport |
PhD |
8 |
29 |
Male |
13 |
| Sports industry platform |
Hamyar-e-Varzesh (Sports Companion) |
MA |
16 |
37 |
Male |
14 |
| Specialized store for yoga and meditation equipment |
Zibazin |
BA |
17 |
38 |
Female |
15 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).