Introduction
The discussion of behavior management is covered in this article. Bibliometric analysis and speech comprehension are inseparable [
1,
2,
3,
4], referring to the use of different frameworks and techniques to examine citations in scientific publications. Such an effort results in the creation of several metrics to measure the intellectual influence of a specific field of study and to obtain insight into the intellectual structure of a broad academic discipline [
5,
6].
The purpose of this essay was to offer important information for comprehending global publication trends in behavior management. With the help of VOSviewer, this study analyzed the trends and bibliographic features of publications on behavior management that were produced by scholars from around the world and published in journals that were indexed by Scopus.
Material and methods
In this study, we followed the research methods successfully employed by several re-searchers who performed bibliometric/bibliographic and content analyses of article in in-ternational database. For example, in 2022 Prospero et.al published a paper Environmentally Friendly Technologies for Wastewater Treatment in Food Processing Plants : A Bibliometric Analysis. In 2009 Kim and Chung published a paper presenting a Bibliographic and content analysis of physics papers from North Korea indexed in the Scopus from 2005 to 2018. In 2020, Nguyen et.al published a paper presenting Bibliographic and content analysis of articles on education form Vietnam indexed in Scopus from 2009 to 2018. We believed that a similar research approach would be useful in this study.
Since there were no human participants in this study, neither informed consent nor institutional review board permission were required. Based on a literature database, this study was a descriptive and bibliometric analysis. Scopus was used to do the document search because of its vast collection of peer-reviewed literature, high level of accessibility, and advanced processing capabilities. This study's title included the keyword "Behavior Management" in order to gather the essential information. We discovered 808 articles in this stage. The 808 articles that had been sorted by relevancy were then downloaded from the scopus database and evaluated. The Csv dataset formatted metadata and revised Scopus result values were obtained for this study. To address difficulties such a lack of consistency in country names and keywords, the consistency and reliability of the data were examined prior to the bibliometric analysis. To maintain uniformity with regard to key words that occasionally appeared in the singular or plural, abbreviations, or other forms, the data were also standardised. Microsoft Excel was used to construct simple statistics after VOSviewer software was used to evaluate the data taken from the Scopus database.
Results
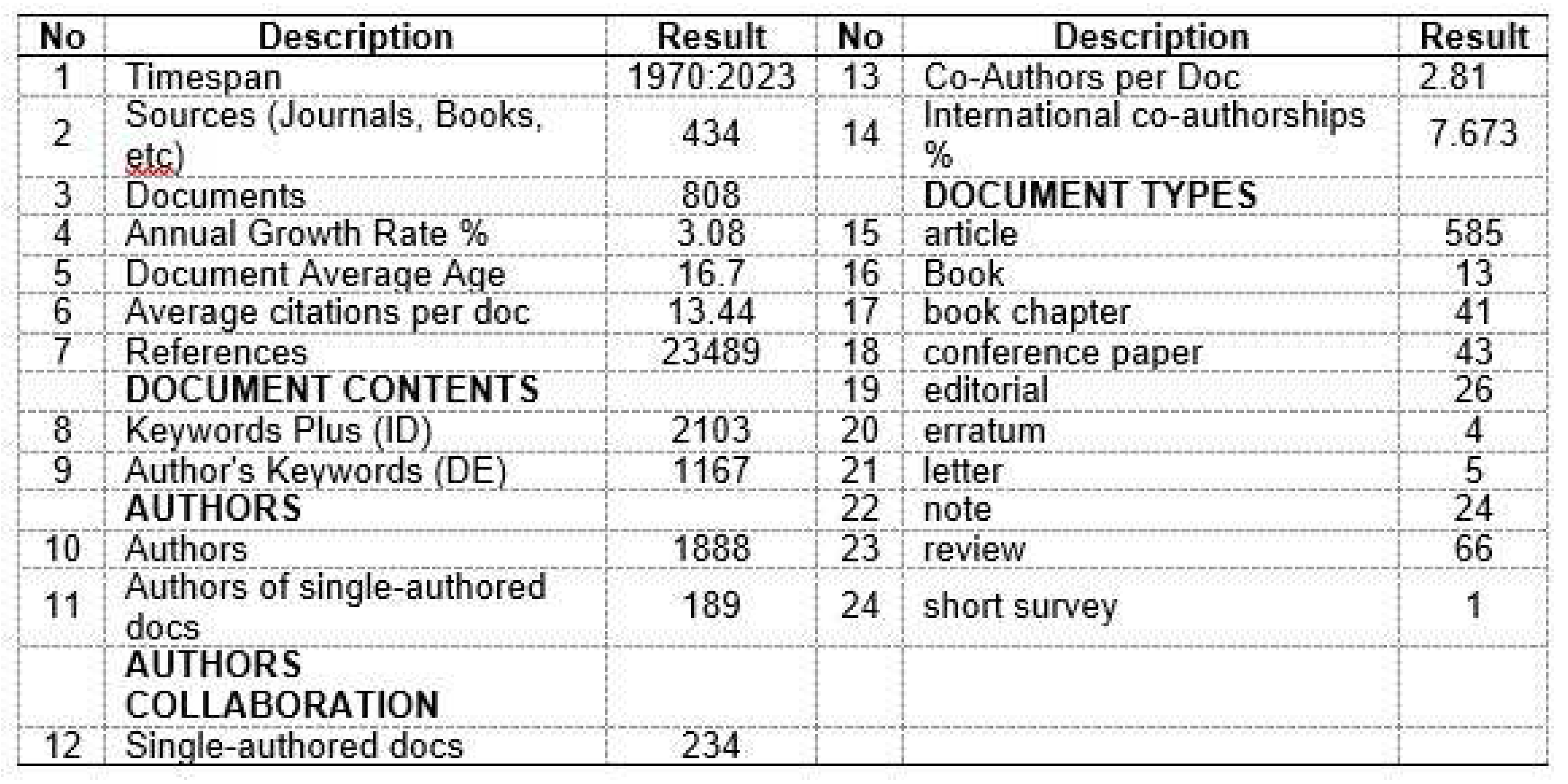
The study's Scopus data set included 808 unique publications from a total of 1888 authors. A wide analysis of the data set reveals that 2103 different keywords are used by 1888 authors to organize or categorize their works. Also, there are 13.44 citations for each article. This demonstrated the importance of the work and how frequently it is cited in these fields. There were 189 single writers when the distribution of authors in the data was evaluated. (
Table 1)
Annual Scientific Production: Classification by Subject Area and Document Type
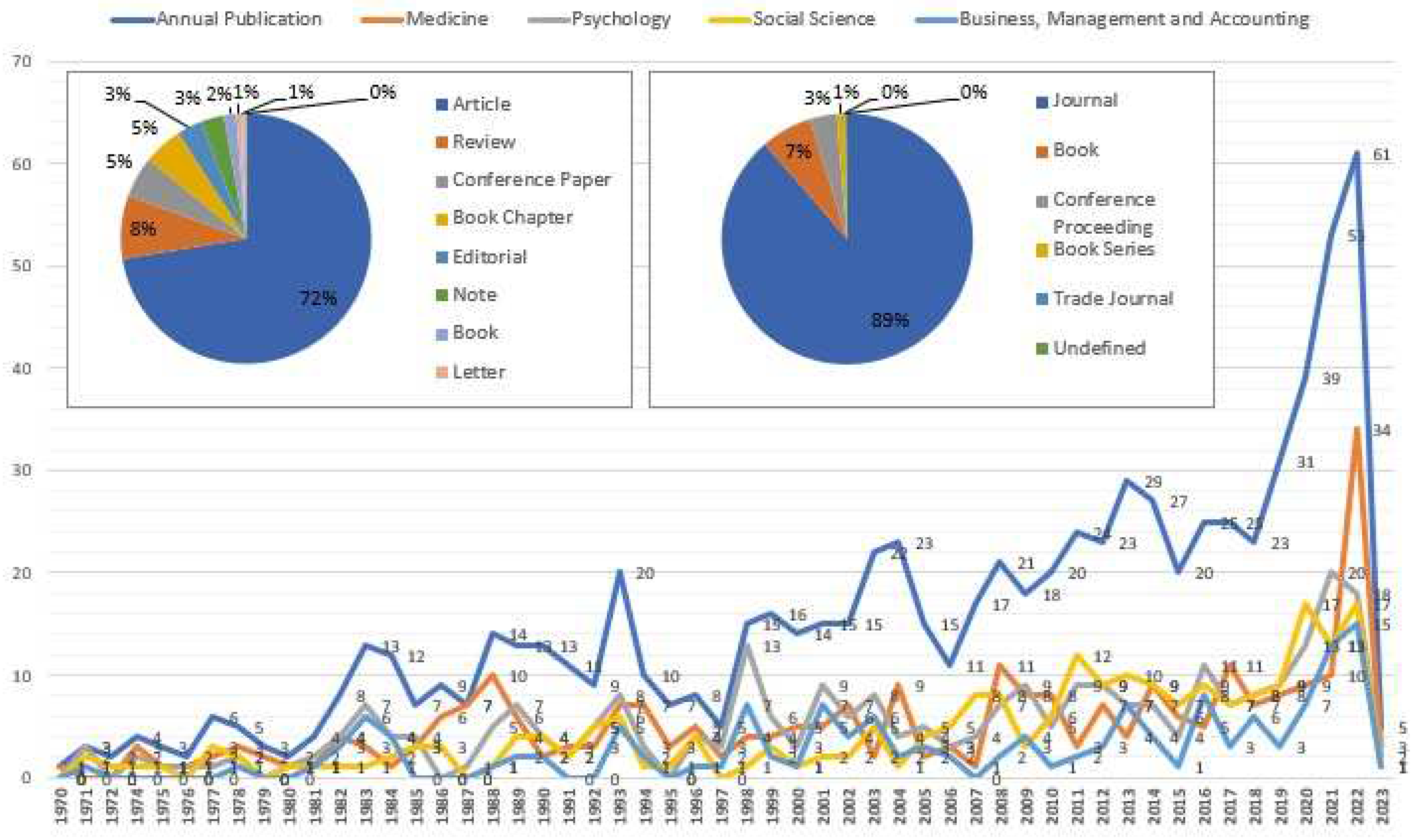
A rise in "Behavior Management" articles is predicted for the years 2020 and 2021. According to the trend analysis (see
Figure 1), there were no "Behavior Management" publications in the Scopus database prior to 1970. The number of studies during the first two decades was quite low (20 documents up to 1993). With 14 research, the threshold of 15 documents was broken in 1988. There has been consistent and strong growth since 2018. When 61 documents were published in 2022, a peak was reached.
A paper could fall under more than one type of subject (category). The primary topics related to the application of behavior management are shown in
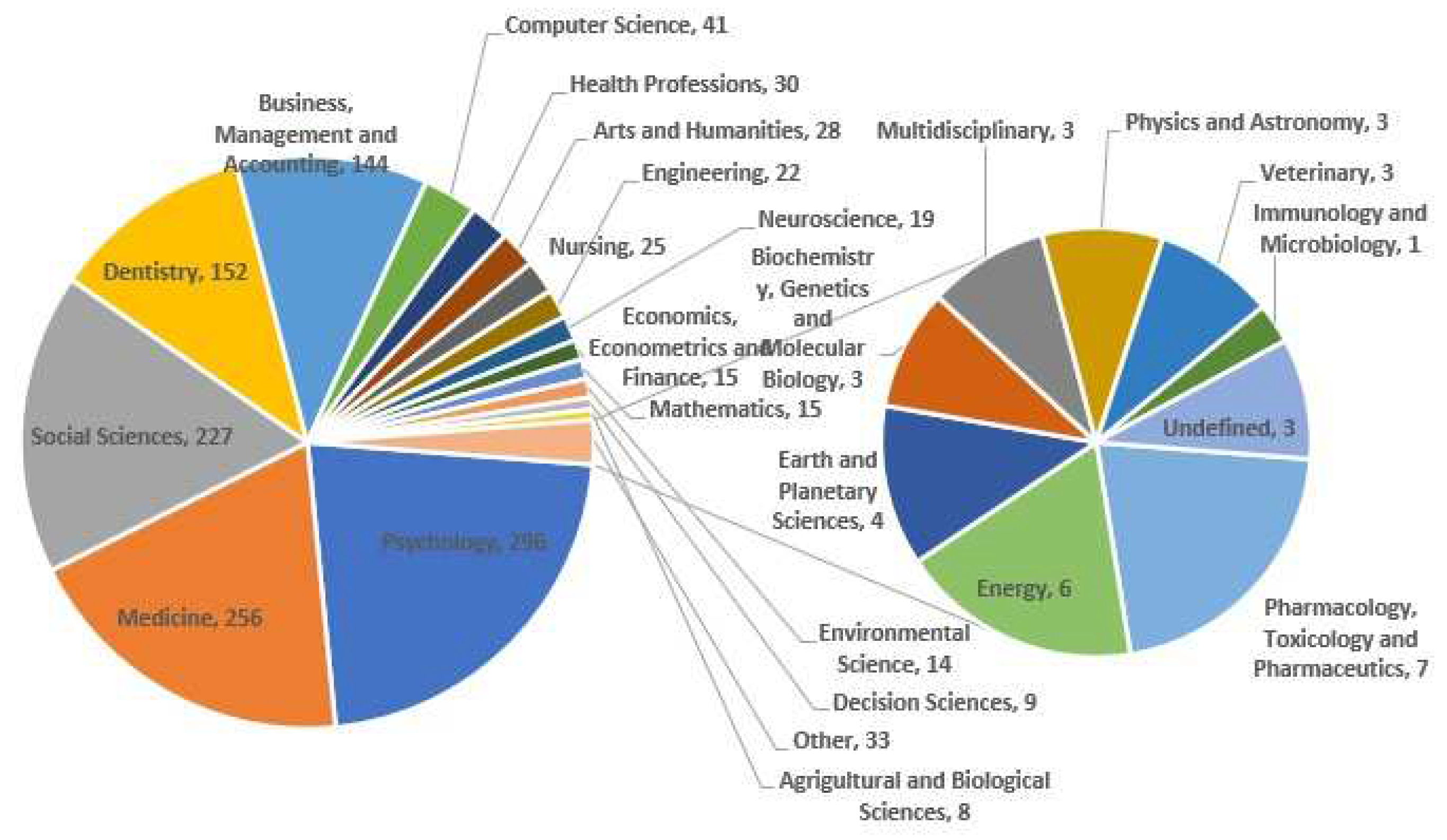
Figure 1. Early on, there were no clearly defined main subject areas. However, since 1988, particularly since 2008, psychology, social science, business, management, and accounting have overtaken medicine as the most popular field of study. The results of a search using the phrase "Behavior Management" revealed about 808 documents. Psychology (n=296), Medicine (n=256), Social Sciences (n=227), Dentistry (n=152), and Business, Management, and Accounting (n=144) were the subject categories with the highest number of publications.
Figure 2 displays the whole distribution of Behavior Management publications throughout different subject categories.
Main Authors
Table 2 lists the authors in order of their level of contribution to the subject. Despite the fact that there are no prolific authors in the field of research, Austin, J. has the most documents published (16). He is a writer now interested in the topic because the publications were created between 1999 and 2013. His most widely utilized paper examined organizational behavior management's journal objectively from 1987 to 1997. Wilson, S. is the primary author if the ranking is based on the ratio of citations to documents (about 286 citations). He published from 1991 to 2005, and his work is still relevant to the subject. Parental attitudes regarding behavior control approaches employed in pediatric dentistry is his most frequently referenced work.
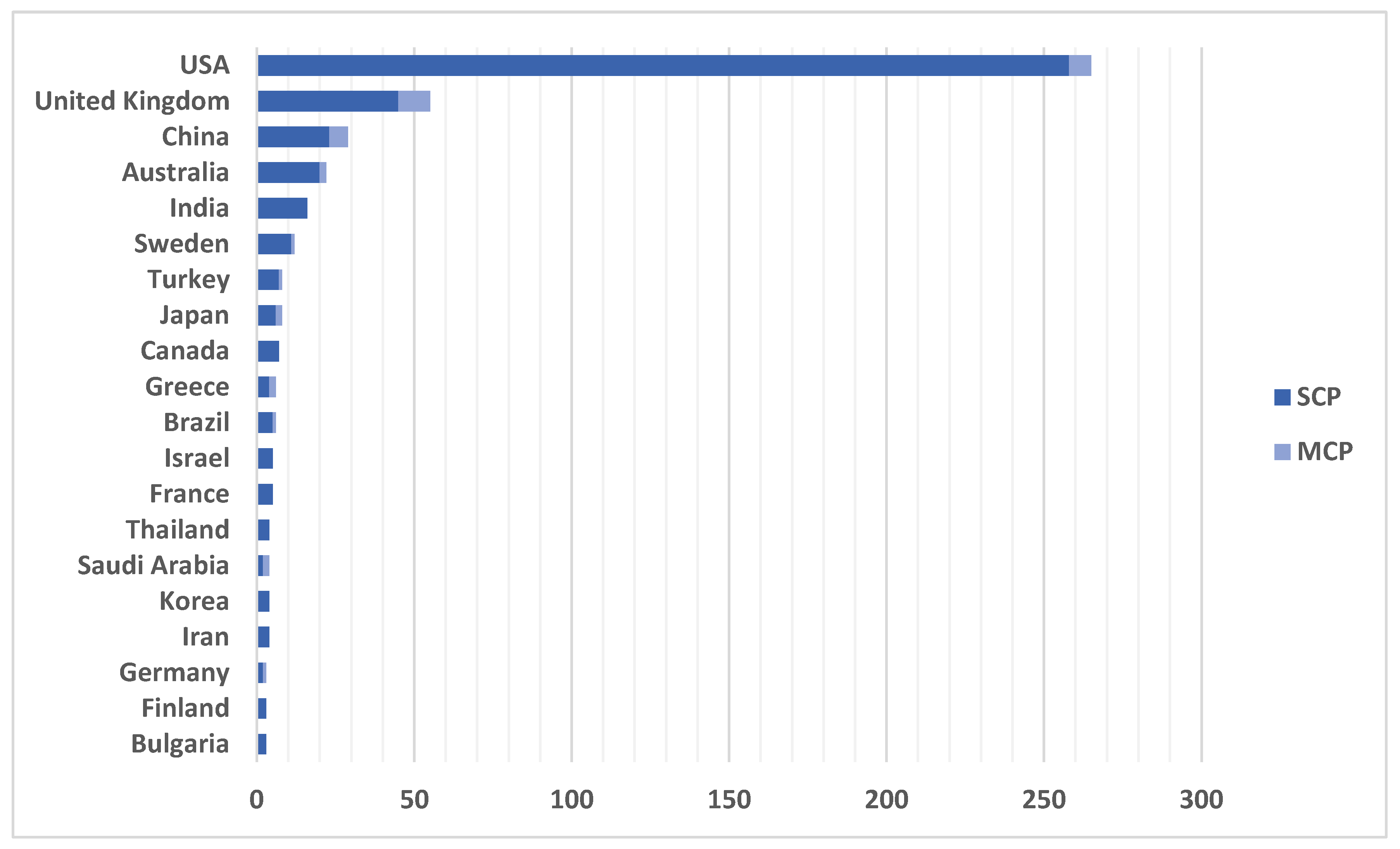
In addition, there are typically 0.009 authors each document. In conclusion, the field is seeing an increase in interest because research in it typically involves collaboration. Related Authors of Behavior Management are displayed in
Figure 3. United States produced the most articles, followed by the United Kingdom and China.
Main Countries
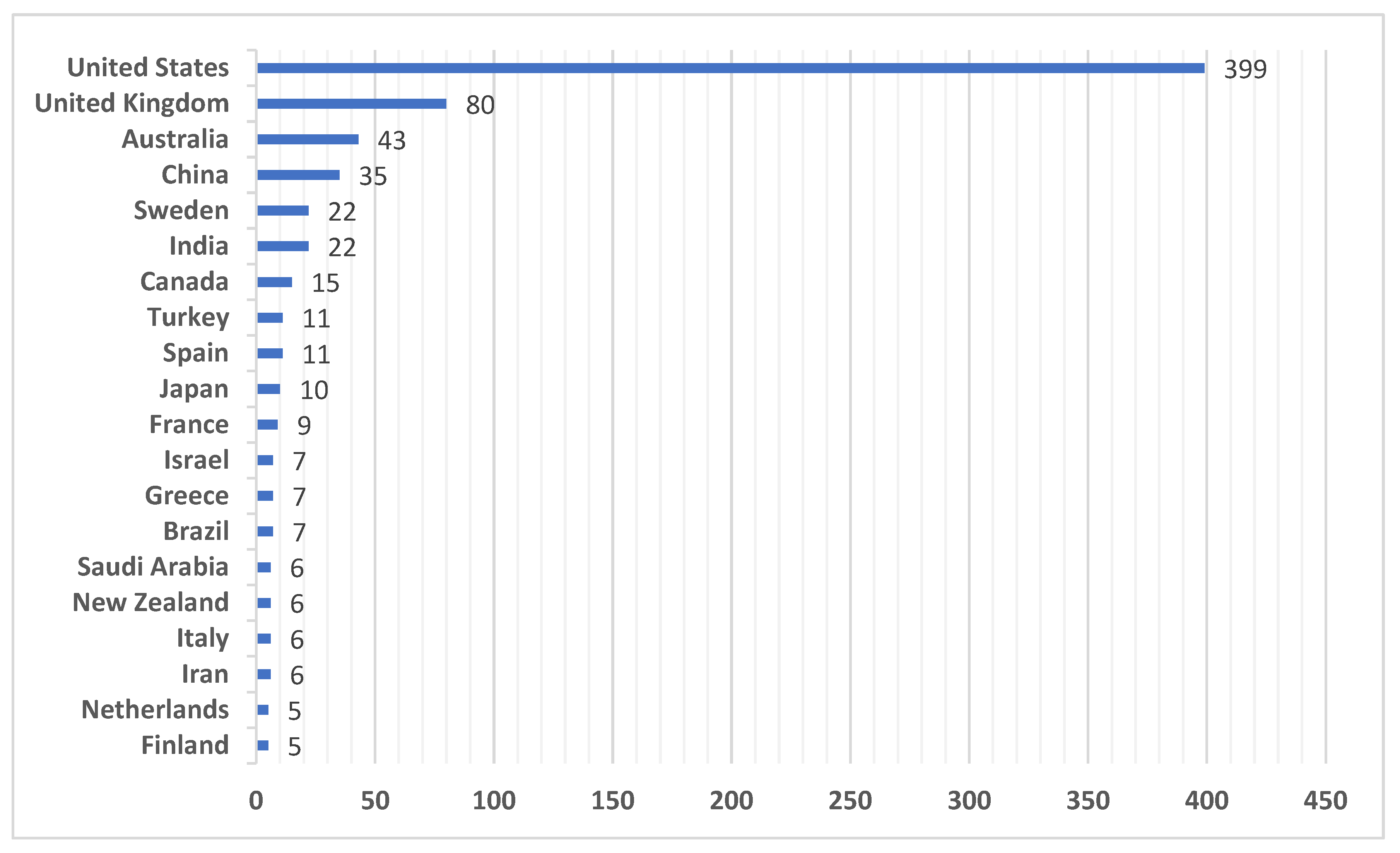
With 399 papers published between 1970 and 2023, the United States led the world in this category, followed by the United Kingdom with 80 pieces. The Asian nations with the highest percentage of Behavior Management publications were China, India, Japan, and Iran. These four Asian nations were rated 4, 5, 7, and 8 in the world. The top 20 nations are displayed in
Figure 4.
Main Institutions
14.48% of the total number of documents were published by the top 10 institutions in the field of study (
Table 3). American institutions predominate; Western Michigan University shares the top spot in the ranking with 31 published documents.
Main Journals
According to VOSViewer, Pediatric Dentistry (n=34), European Archives Of Paediatric Dentistry (n=9), Journal Of Indian Society Of Pedodontics And Preventive Dentistry (9), and Australian Journal Of Teacher Education (n=8) published the next highest number of articles, with 120, in the Journal of Organizational Behavior Management.
Table 4 lists the additional most active journals by number of publications.
The influential sources (i.e. journals) are shown in
Table 5 based on citations. Journal of Head Trauma Rehabilitation (n=191), Pediatric Dentistry (n=967), International Journal of Paediatric Dentistry (n=752), European Archives of Paediatric Dentistry (n=213), and Journal of Organizational Behavior Management (n=1598) were the next most influential journals, with a total readership of 1698. There were five American journals, two British journals, one journal each from Australia, Germany, and Denmark. The majority of "Behavior Management" articles are published in journals with Scopus quartiles Q1 (up to 60% or 4 journals). This shows that the essay "Behavior Management" is an engaging topic that has been published in reputable journals (Q1).
Main Documents and Keywords
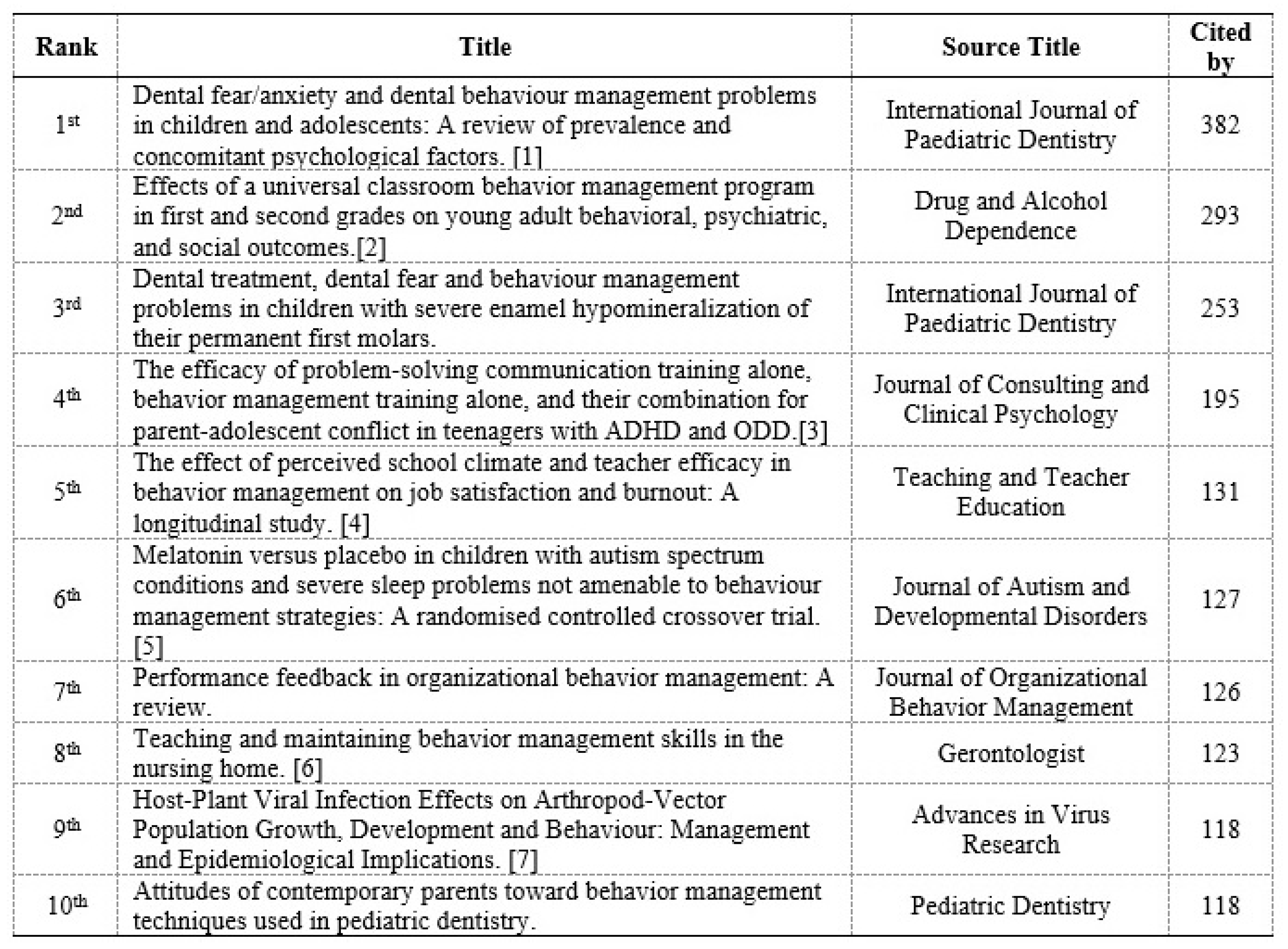
Table 6 lists the most influential document based on citations recorded by the Scopus database. The most influential documents was Dental fear/anxiety and dental Behavior management problems in children and adolescents : A review of prevalence and concomitant psychological factors, with 382 cititations, followed Effects of a universal classroom behavior management program in first and second grades on young adult behavioral, psychiatric, and social outcomes (n=293), and Dental treatment, dental fear and Behavior management problems in children with severe enamel hypomineralization of their permanent first molars. (n=253).
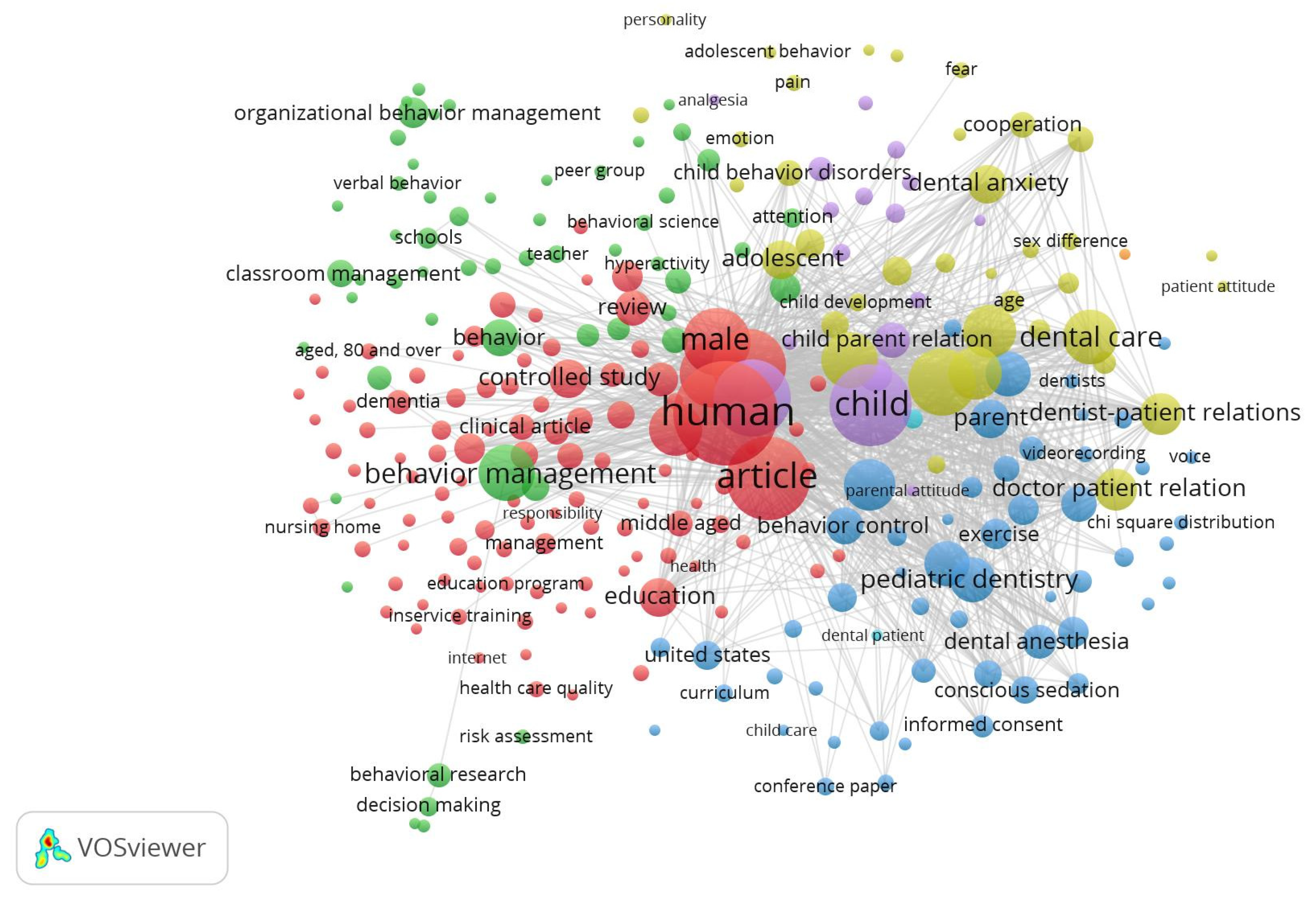
The 808 publications were organized by relevancy, and their contents were examined. Then, we used VOSviewer's "all keyword" analysis unit and "full counting" method to do a co-occurrence study. Out of 3007 keywords, VOSviewer detected 273 that met the threshold when we set the keyword frequency restriction to 5 times. In
Figure 5, the findings of this investigation are displayed.
The top three terms that appeared the most frequently were Human (338), Article (224), and Child (209). Seven clusters were also discovered in this research, in total. These keywords are grouped into seven clusters in
Figure 5, each of which has a distinct amount of keywords and is represented by a different color.
Human, Article, Behavior Therapy, Male, and Adult were the main topics in the first cluster (red, 107 keywords). The second cluster, which was green and contained 55 keywords, was focused on decision-making, organizational behavior management, behavior management, and behavioral research. The third cluster (blue, 53 terms) included topics such as methodology, behavior modification, parental involvement, pediatric dental care, and dentists.
The fourth cluster (yellow, 38 terms) included topics including adolescent development, dental care, patient relations, and child behavior. Child, Epidemiology, Humans, Parental Attitude, and Prevalence were the main topics in the five cluster (purple, 17 keywords). The sixth cluster, which featured the terms "dental patient" and "infant," was light blue. The nonparametric test was the topic of the seventh cluster (orange, 1 keyword).
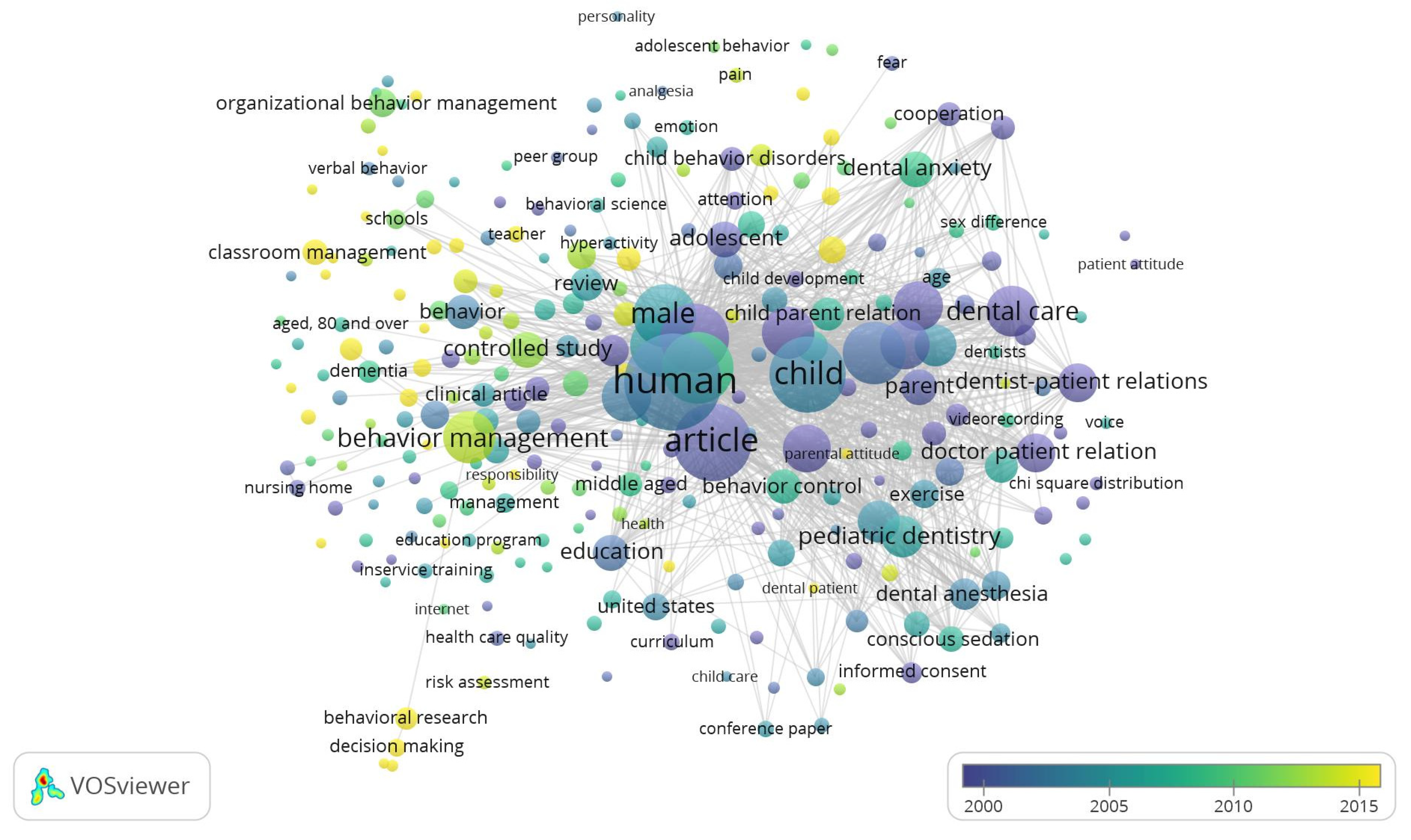
A depiction of the Behavior Management literature overlayed with the typical number of publications from 2000 to 2015 is shown in
Figure 6. The focus of the literature on behavior management changed; before to 2005, the phrases "Pediatric Dentistry," "Behavior Control," and "Human" were extensively studied. In the next three years, "Behavior Management," "Behavioral Research," and "Decision Making" were discussed.
Discussion
For research on behavior management challenges globally, Scopus data were used to analyze publishing trends, journal performance, content analysis, and bibliographic coupling of nations and sources. The current analysis concentrated on Behavior Management journal articles. The purpose of this study was to report on the current state of publications in these areas. The scopus database listed 808 published research in total. The statistics demonstrated the speed at which articles were published and the eagerness with which researchers worldwide examined behavior management. Unfortunately, little study on behavior management from a global viewpoint has been done in the last three years.
Journal of Organizational Behavior Management (n=120), which produced the most articles, was the most productive publication venue. United States (n=399) was the most productive nation, followed by the United Kingdom. China, India, Japan, and Iran were the Asian nations placed in the top 20 countries in terms of the most publications on behavior management, despite the fact that European nations led the top 20 countries with the most publications by affiliated researchers. According to citations, (Wilson, S.) (n=286) and Journal of Organizational Behavior Management (n=1598) had the most significant authors and journals. Seven clusters were established by the behavior management study terms (e.g Human, Article, and Child). Behavior Management research has grown dramatically during the past 50 years, seen from a worldwide viewpoint. These were publications in European-published journals.
The current study has several limitations because Web of Science, Crossref, and PubMed Central were not used; instead, we solely retrieved studies from Scopus. Last but not least, we didn't employ any of the additional VOSviewer analyses, including co-citation or co-authorship. Hence, in order to present a more comprehensive picture of the problem, we anticipate that bibliometric research on this subject will grow in terms of the databases used, the subject areas, and the analyses performed.
Conclusion
Global research on behavior management has grown dramatically during the past 50 years. The majority of documents are published in prestigious journals, which is further sign of the caliber of the research. Discussions in the future could find the topic of behavior management research in relation to local government fascinating. Also, there are chances to promote conversation on behavior management in social science publications that are relevant to public administration. Lastly, Europe led this sector in terms of publications, whereas Asia's research on this subject is still scarce, necessitating additional study.
Disclosure
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Acknowledgments
Author delivered many thanks to Prof. Dr. Rina Indiastuti, S.E., M.SIE as Rector of Universitas Padjadjaran, Indonesia and the Directorat Riset Pengabdian Masyarakat (DRPM) for funding the APC.
References
- D. Lee, “Bibliometric Analysis of Korean Journals in Arts and Kinesiology – from the Perspective of Authorship,” J. Inf. Sci. Theory Pract., vol. 8, no. 3, pp. 15–29, Sep. 2020. [CrossRef]
- S. Mifrah, “Toward a Semantic Graph of Scientific Publications: A Bibliometric Study,” Int. J. Adv. Trends Comput. Sci. Eng., vol. 9, no. 3, pp. 3323–3330, Jun. 2020. [CrossRef]
- O. Omoregbe, A. N. Mustapha, R. Steinberger-Wilckens, A. El-Kharouf, and H. Onyeaka, “Carbon capture technologies for climate change mitigation: A bibliometric analysis of the scientific discourse during 1998–2018,” Energy Reports, vol. 6, pp. 1200–1212, Nov. 2020. [CrossRef]
- G. Saravanan and J. Dominic, “A Ten-year Bibliometric Analysis of Research Trends in Three Leading Ecology Journals during 2003-2012,” J. Inf. Sci. Theory Pract., vol. 2, no. 3, pp. 40–54, Sep. 2014. [CrossRef]
- P. Akhavan, N. A. Ebrahim, M. A. Fetrati, and A. Pezeshkan, “Major trends in knowledge management research: a bibliometric study,” Scientometrics, vol. 107, no. 3, pp. 1249–1264, Jun. 2016. [CrossRef]
- P. B. Putera, S. Suryanto, S. Ningrum, I. Widianingsih, and Y. Rianto, “Increased Number of Scopus Articles from Indonesia from 1945 To 2020, an Analysis of International Collaboration, and a Comparison with other Asean Countries from 2016 to 2020,” Sci. Ed., vol. 9, no. 1, pp. 62–68, 2022. [CrossRef]
- G. Klingberg and A. G. Broberg, “Dental fear/anxiety and dental Behavior management problems in children and adolescents: A review of prevalence and concomitant psychological factors,” Int. J. Paediatr. Dent., vol. 17, no. 6, pp. 391–406, 2007. [CrossRef]
- S. G. Kellam et al., “Effects of a universal classroom behavior management program in first and second grades on young adult behavioral, psychiatric, and social outcomes,” Drug Alcohol Depend., vol. 95, no. SUPPL. 1, 2008. [CrossRef]
- R. A. Barkley, G. Edwards, M. Laneri, K. Fletcher, and L. Metevia, “The efficacy of problem-solving communication training alone, behavior management training alone, and their combination for parent-adolescent conflict in teenagers with ADHD and ODD,” J. Consult. Clin. Psychol., vol. 69, no. 6, pp. 926–941, 2001. [CrossRef]
- O. P. Malinen and H. Savolainen, “The effect of perceived school climate and teacher efficacy in behavior management on job satisfaction and burnout: A longitudinal study,” Teach. Teach. Educ., vol. 60, pp. 144–152, 2016. [CrossRef]
- B. Wright et al., “Melatonin versus placebo in children with autism spectrum conditions and severe sleep problems not amenable to Behavior management strategies: A randomised controlled crossover trial,” J. Autism Dev. Disord., vol. 41, no. 2, pp. 175–184, 2011. [CrossRef]
- A. B. Stevens et al., “Teaching and maintaining behavior management skills with nursing assistants in a nursing home,” Gerontologist, vol. 38, no. 3, pp. 379–384, 1998. [CrossRef]
- J. Colvin et al., “Host-Plant Viral Infection Effects on Arthropod-Vector Population Growth, Development and Behavior: Management and Epidemiological Implications,” Adv. Virus Res., vol. 67, no. 06, pp. 419–452, 2006. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).