1. Introduction
Crohn’s disease (CD) is a chronic, relapsing disorder belonging to inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), with characteristic skip lesions and transmural inflammation that may affect the entire gastrointestinal tract from the mouth to the anus. It is manifested by relapsing transmural inflammation found in any segment of the gastrointestinal tract. The disease may appear at any age, with the median age of onset being 30 years. CD is manifested by numerous uncharacteristic symptoms, but several stand out and constitute a typical presentation: chronic diarrhea and abdominal pain, accompanied by weight loss, low-grade fevers and fatigue. Despite the effectiveness of treatments (e.g., corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, biological agents) for inducing long-term remission in adults with CD, secondary disorders such as arthritis, osteoporosis, ocular inflammation, and skin lesions, as well as other extraintestinal symptoms such as fatigue, depression, and anxiety still frequently occur, resulting in a reduced quality of life. As it becomes increasing clear that managing CD requires more than medical treatment alone, further research to identify second-line approaches for managing CD and its symptoms are necessary to address this public health concern.
Fatigue is a widely used term in both medical literature and everyday clinical practice. However, it is relatively poorly defined and often subjectively interpreted. Although multiple definitions of fatigue can be found in the literature, there is a general agreement that in most cases, fatigue can be identified as a feeling of weakness, sense of tiredness, lack of energy, feeling of exhaustion, reduced muscle strength, and cognitive impairment. In some patients, more atypical symptoms can be present [
1].
Acute fatigue is a physiological condition experienced in everyday life as a predictable response to a prolonged period of physical exertion or stress. This short-lasting, transient feeling is relieved by rest and thus does not cause long-term impairment of function. Contrarily, chronic fatigue, which lasts for at least 6 months, and which cannot be cured by sleep or adequate rest, can be a sign of a somatic or psychiatric disorder [
2,
3]. In fact, fatigue is one of the most reported symptoms in primary care, with some studies showing a prevalence of up to 25% in the patient population [
4], which is similar to the prevalence reported in the newly diagnosed IBD patients [
5]. However, in a 2012 online survey, more than 80% of 631 IBD patients who filled out the questionnaire (41% of which were in remission at that time) reported fatigue [
6]. In a prospective, population-based IBD cohort study, fatigue was a symptom reported in 72% patients with active disease and 30% patients with inactive disease [
7]. These findings suggest that although fatigue typically intensifies during periods of increased disease activity, it is also very prevalent in patients with clinical and endoscopic remission. What is also noticeable, fatigue is more common among patients with newly diagnosed CD, than in ulcerative colitis (48-62% for CD, 42-47% for UC) [
8]. Reported by CD patients’ chronic fatigue not only has a significant influence on the quality of life of patients, but it can also negatively affect the overall outcome of treatment. Due to the subjective nature of fatigue, in order to improve the quality of treatment and individualize treatment, independent molecular factors that play a potential diagnostic role are sought. Current evidence on the efficacy of pharmacological CD therapy in the management of fatigue is limited, and some medications for the treatment of CD may even exacerbate fatigue [
9]. This review summarizes the current literature on fatigue in CD, considers its etiology, diagnosis, and treatment.
2. Methodology
2.1. Searching strategy
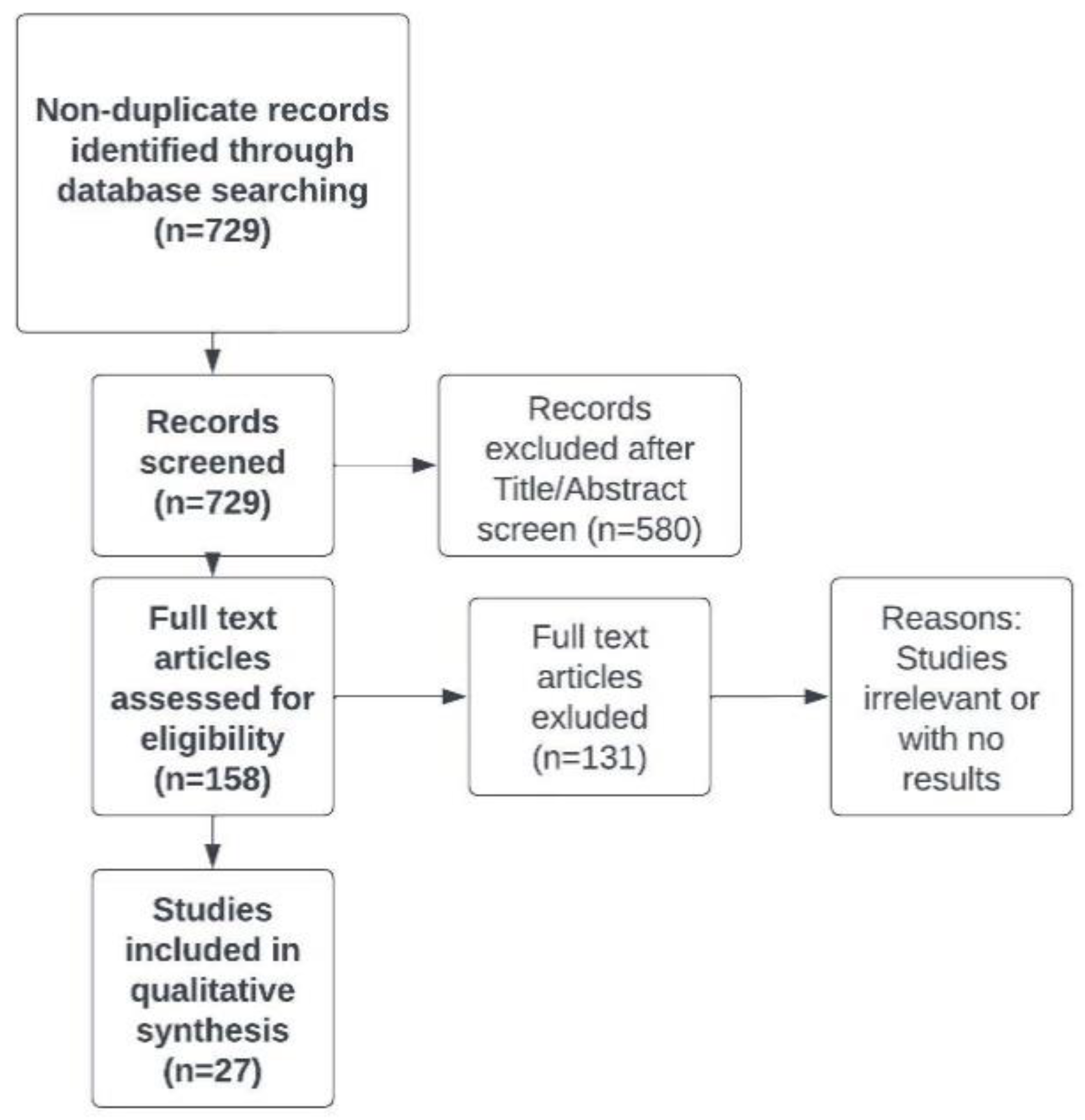
We carried out a systematic literature search to identify relevant original studies that enable to update the knowledge about chronic fatigue in CD patients and management in this disorder. The systematic literature search involved the following databases: OVID MEDLINE and EMBASE. The search query consisted of the combination of the following keywords: “Crohn’s disease”, “colitis”, ”gastrointestinal”, “chronic fatigue”, “myalgic encephalomyelitis”. Results were limited to papers relevant to the management of fatigue in CD patients, which were published in English in 2013-2022. The first search was performed on 2 June 2022, and the search was updated on 15 August 2022, with a final revision on 10 December 2022. The selection of eligible papers ais illustrated in
Figure 1.
2.2. Study selection and risk of bias
The references in all the included studies were reviewed for more eligible articles. Each article was reviewed independently by six researchers (MW, AM, MP, JW, KM, JF) for inclusion according to the inclusion and exclusion criteria, which follow. Disagreements regarding article selection were resolved through discussion until consensus was reached or resolved by discussion between authors MW and LD. Prospective and retrospective observational human studies on adult patients were included. Conference abstracts were excluded. Articles were also excluded if they were not in English, or the studies were preclinical research or commentaries. A standardized form was used to extract data from the included studies. Extracted details were study population and demographics, details of interventions and controls, study methodology, and information to assess bias. Data extraction was performed independently by seven authors, and discrepancies were resolved through discussion with the other co-authors.
3. Etiology of fatigue in CD patients
Fatigue among CD patients can partly be explained by chronicity, disease activity, and nutritional deficits. However, the cause of CD-related fatigue currently remains unexplained, in approximately half of the patients supporting that fatigue can be an independent, systemic extraintestinal disease manifestation in IBD. Association between fatigue and clinically active IBDs has been known for a long time and is well explored in the literature. Recent studies recognized serval factors that may be associated with fatigue in CD patients.
4. Inflammation of the gut
Multiple studies suggest a presence of communication system between the gastrointestinal tract and the nervous system, the brain-gut axis. Fatigue in active IBD is hypothesized to be mediated by inflammatory cytokines and increased activity of T lymphocytes, primarily through the brain–gut axis [
10]. High levels of experienced fatigue have been associated with higher levels of IL-10, IL-17A, IL-6, and interferon-γ (IFNγ) suggesting that inflammatory pathways play a role in fatigue pathogenesis [
11]. In another study the elevated levels of pro-inflammatory markers, such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF), IFNγ and calprotectin, correlated with the severity of fatigue during active IBD [
12]. On the other hand, one study showed that the levels of inflammatory cytokines do not differ between patients with or without fatigue during deep remission of IBD [
13]. Inflammation is also associated with increased resting energy expenditure, which may cause increased fatigue. At the same time, pro-inflammatory cytokines can lead to anorexia and a decrease in caloric intake, dysregulation of the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal (HPA) axis and promote anxiety and depressive symptoms by modulating the gut–brain axis [
14,
15]. Currently, the role of inflammation in the pathogenesis of fatigue in IBD is not fully understood and further studies are warranted.
The gut microbial dysbiosis may induce fatigue through the brain-gut axis. It is well known that gut microbial dysbiosis has a significant influence on the propagation of inflammation in IBD. It is characterized by a decrease of valuable bacterial populations, such as
Faecalibacterium prausnitzii,
Bacteroides fragilis and
Roseburia; and escalation of proinflammatory species, such as
Escherichia coli [
16]. Nagy-Szakal et al. supported this hypothesis with a study, which involved two groups, patients with chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS) and healthy control individuals. Patients with CFS had decreased stool bacterial diversity [
17]. Maes et al. reported that patients with CFS were characterized with increased levels of immunoglobulin (Ig) A and IgM. Higher levels of these Igs may be associated with increase of lipopolysaccharide from enterobacteria. The intestinal epithelium should be a barrier against translocation of lipopolysaccharide. This translocation may lead to activation of innate immune responses [
18]. Furthermore, in animal models, reduction of depressive behaviors and anxiety was noticed in groups, which received probiotics. Summarized overview of included studies are presented in
Table 1.[
19].
5. Anemia
Anemia is an abnormal state associated with fatigue in IBD patients. It occurs in up to 20% of ambulatory patients and up to 68% of hospitalized patients with IBD [
20]. Previous metanalysis, reported by Bartel et al., estimated, that prevalence of anemia among patients with CD is up 27% [
21]. Anemia may result from a wide spectrum of causes, which include malabsorption, impaired dietary intake, suppression of iron binding and erythropoiesis, chronic intestinal bleeding (visible or microscopic), inflammation and certain types of medications, such as sulfasalazine, 5-aminosalicylates and methotrexate [
22].
The most common anemia in IBD is a result of iron deficiency, which is often caused by chronic gastrointestinal bleeding and decreased nutritional intake. Vitamin B12 and folate deficiency can also be linked to weakness and fatigue [
23].
Due to prevalence of anemia, patients with CD, who complain about fatigue should be thoroughly investigated. Blood tests such as: level of red blood cells, hemoglobin, hematocrit, level of iron or vitamin B12 are basic, cheap tests, that may be a valuable clue for every clinician.
Patients with established anemia, regardless of the cause, should be treated accordingly to the cause of anemia - i.e., iron deficiency with parenteral or oral iron supplementation.
6. Psychological factors
Despite rapid advancements in medical science in the last decades, CD remains so far incurable, though it can be treated with both pharmacological and surgical approaches. The primary aim of treatment is an achievement and maintenance of clinical and endoscopic remission for as long as possible. Unfortunately, relapses are common, and as such many patients diagnosed with CD are presented with a prospect of a lifetime of recurrent absence from work and school due to sick leave and hospitalization, potential unemployment caused by the illness, health-related low quality of life and even potential disability [
24]. Such prospects along with the troublesome nature of CD symptoms may lead to increased prevalence of experienced fatigue in patients with CD in comparison to healthy individuals [
25]. It has even been hypothesized that the link between CD and chronic fatigue in patients during remission might be based mainly on an individual’s mental state, since a patient presented with a CD diagnosis is faced with challenges that for some might be too aggravating to endure on a daily basis. In recent study Radford et al. indicated the adults with IBD fatigue try to establish a sense of ‘new’ normality, through maintaining the same or similar, level of activities related to employment or education. However, this is often related to the expense of personal, social and leisure activities. Disease related fatigue led patients to perceptions of conservation of energy through planning and prioritizing tasks. Authors also indicates that high levels of social support were associated with better self-reported health related QoL in those patients with IBD, what indicates that underdiagnosed fatigue have significant impact on impaired QoL [
26].
Psychological factors such as a depressive mood, stress, anxiety and impaired QoL are strongly associated with fatigue, and all of them are more common in the CD patients than in the healthy population [
27]. All these factors have been associated with increased fatigue scores as well as deterioration of the inflammatory disease course. Therefore, it is possible that a positive feedback loop exists whereby active disease leads to psychological distress that in turn aggravates the inflammatory state, with both factors consequently leading to increased fatigue. Additionally, abdominal pain, one of the main symptoms of active CD, has been shown to be associated with psychological distress, which in turn may affect sensory processing and thus lead to increased perception of pain or occurrence of chronic pain and/or fatigue. Screening for psychiatric disorders should thus be considered as an essential part of holistic approach to fatigue in CD and justify a referral to an appropriate specialist.
A significant contributor to fatigue is a sleep disturbance, which is prevalent in patients with CD, both with active and non-active disease. Disrupted or restless sleep and multiple awakenings are reported to occur much more frequently in comparison to the general population [
28]. A prospective study has shown that sleep disturbance increases the risk of CD relapse and is a significant factor worsening patients’ life quality, on par with previously mentioned psychological disorders.
7. Nutrient deficiencies
Various nutrient deficiencies have been linked to fatigue in the general population [
29]. IBD patients are at higher risk of nutrient deficiencies in comparison to the general population due to chronic inflammation, impaired muscle strength and malabsorption that may be associated with the disease [
30]. Restrictive diets, which are sometimes included in the therapy regimen, also often carry the risk of nutritional deficiencies, unless properly fortified in lacking macro- or micronutrients. Patients with CD often harbor deficiencies of vitamins and minerals, such as vitamin B6 and B12, folate, ferritin, and zinc. It is observed mainly in patients with active disease and vitamin D deficiency in both active course and remission [
31]. List of vitamins and minerals linked with IBD are presented in
Table 2.
Chronic fatigue has been proven to correlate with vitamin D deficiency in cancer patients, but these findings does not apply to CD patients. Some studies showed that there is no direct association between fatigue in patients with IBD and vitamin D deficiency [
32]. Nonetheless, nutrient status (iron, copper, zinc, folate, phosphate, magnesium, vitamin B6 and B12, calcium, vitamin D) should be monitored, restored, and if necessary, with referral to a clinical dietician when appropriate.
8. Screening for fatigue in CD patients
When fatigue is a persistent or especially pronounced symptom, a patient will generally report it to the physician. However, in many cases it can be overlooked early and remain unrecognized. Routine screening for fatigue is an important initial step in clinical evaluation. This can be done by simply asking the patient if they feel or have recently felt fatigued.
There are also several screening tools which enable more thorough evaluation of fatigue. One of the quickest and easiest to use tools is the visual analogue scale (VAS) with a score from 0 to 10 covering the severity of fatigue, with 10 representing severe fatigue and 0 representing no fatigue [
33] (
Table 3).
This scale has been successfully applied in evaluation of cancer-related fatigue, enabling to distinguish patients with mild fatigue (score 0-3) from patients suffering from more severe fatigue (score 4-10) [
34].
Furthermore, there is the multidimensional fatigue inventory (MFI), a 20-item questionnaire, which measures fatigue in five dimensions – namely general, physical, motivation, activity, and mental. Similarly, the Multidimensional Assessment Fatigue (MAF) scale has 16 items to measure fatigue in four dimensions, i.e., severity, distress, degree of interference with activities of daily living, and timing of fatigue. The Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy-Fatigue (FACIT-F) is a 13-question sub-scale of the Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy (FACIT) Measurement System (
Table 4.). FACIT-F enables the assessment of general fatigue, but does not support the complex assessment of physical, mental, and activity – in contrast to MFI. The FACIT-F, however, has been validated to measure fatigue in chronic illnesses such as IBDs, with good internal consistency, reproducibility, and sensitivity [
35]. Unfortunately, there is a lack of consensus which scale is best to use to measure fatigue in the IBD population. Of the mentioned scales, IBD-F is the only scale tailored specifically to patients with IBD.
9. Treatment of fatigue in CD patients
Before proceeding to specifically targeted interventions, general anti-fatigue strategies should be employed. In particular, teaching patients how to plan their days seems to be the crucial approach in anti-fatigue strategies. Patients should be advised to distribute their energy throughout the whole day and to plan for necessary rests and breaks. Furthermore, relatives play an important role in the process of acceptance of fatigue, as their acceptance and support are crucial in managing disease-related symptoms, providing the better therapeutic outcomes.
Non-pharmacological interventions, such as physical activity and psychosocial interventions, have been shown to help patients with a range of other chronic conditions to manage fatigue. Consequently, several non-pharmacological interventions have been applied in IBD populations, mainly focused on mental health symptoms or overall QoL. It has also been proven that the appropriate use of stress-management techniques has a beneficial effect on fatigue. There is evidence suggesting that electroacupuncture effectively reduces fatigue and increases QoL [
36]. On the other hand, reduced activity and muscle strength is often reported in CD patients suffering from fatigue and there is increasing evidence showing that physical activity is beneficial by improving bone health, increasing muscle mass and function, increasing energy intake, and possibly improving nutritional status; additionally, QoL and fatigue are improved by exercise in CD patients. Moreover, studies in animal models have suggested that exercise may reduce the inflammatory response [
37,
38].
Considering pharmacological interventions, there is no specific drug aimed at reducing feeling of fatigue alone. Various studies considered commonly used drugs in CD and its influence on fatigue. Infliximab is an antibody against TNF. Patients, after administration of infliximab, often reported improvement in terms of fatigue [
39]. Minderhoud et al. compared CD patients who received Infliximab with a placebo group. The placebo group initially reported a decrease in fatigue score, and at the conclusion of study reported a recurrence of this condition. Whereas the group, which was administered Infliximab, reported a decrease in fatigue, which continued to the end of the study. Despite the fact that the study was conducted on a small number of patients, it seems to be a possible treatment in CD and severe fatigue [
40]. Another drug, which is administered in patients suffering from CD, is Adalimumab. In a study reported in 2008, patients were divided into three groups: patients who received the drug only as induction, patients who received Adalimumab every week, and patients who received the drug every other week for 56 weeks. All groups reported a significant decrease in fatigue, however the group which received the drug only once, reported a recurrence of their symptoms after a few weeks [
41]. Psychostimulants such as methylphenidate and dexamethasone have shown promising results in severe cancer-related fatigue [
42]. However, these agents have not been investigated in IBD-related fatigue yet. Additionally, in a pilot study in 12 IBD patients with no preexisting thiamine deficiency, high-dose thiamine decreased overall fatigue score [
43]. In the study by Regev S et al, the short-term cognitive-behavioral and mindfulness intervention has the capacity to reduce chronic fatigue as well as improve functioning in patients with mild-to-moderate CD [
44]. Nevertheless, randomized trials that have been performed in fatigued cancer patients have shown a significant placebo response. Consequently, there is no specific medical intervention which can reduce fatigue during remission, while at the time of relapse underlying disease treatment according to the current guidelines should be initiated.
As mentioned before, multiple aspects should be taken into consideration during development of fatigue therapy, i.e., anemia, nutritional deficiencies, mood disorders, sleep disorders and some comorbidities [
10]. Most of these are treatable, thus they should be recognized, and appropriate treatment initiated, in line with guidelines for the specific disorder.
10. Chronic fatigue syndrome and CD
In some cases, chronic fatigue can constitute a part of a larger cluster of symptoms called chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS) or myalgic encephalomyelitis (ME). CFS/ME is a severe multimodal disease with a high degree of physical disability, which leads to a high need for patient care. The disease is characterized by debilitating fatigue with unrefreshing sleep, neurocognitive impairments, and flu-like symptoms such as muscle weakness and pain, headaches, sore throat, and tender lymph nodes. The malaise and the accompanying symptoms are worsening dramatically after minimal physical, orthostatic, and cognitive activity. There is growing evidence that gastrointestinal tract may play a role in the pathogenesis of CFS, but the exact link between these two disorders is yet to be determined.
A retrospective cohort study from 2019, which evaluated the risk of CFS in patients with IBD showed that the incidence of CFS in women and men with IBD were 5.14 and 7.09 per 1000 person-years, respectively [
45]. In the group of women and men without IBD it was 2.83 and 1.90 per 1000 person-years. Moreover, the incidence rates of CFS rose with age in both groups. Additionally, male sex was identified as increasing the risk of CFS. No difference in incidence rates were observed between patients with CD and other types of IBD. According to another study on IBD and CSF from 2018, higher scores of chronic fatigues were linked to clinically active disease in UC patients. However, this observation did not correlate with increased inflammatory markers [
13].
Intestinal microbiota alterations and dysbiosis was detected in several CFS studies, but a specific consistent microbial signature was not found. There is inconsistency of results and thus an exact link between alterations in the intestinal bacteria and the disease mechanisms cannot be made. Newberry et al. [
46] reported in their systematic literature review that there were eight agreeing and seven conflicting results between CFS microbiome studies, while there was overall evidence for dysbiosis.
Some researchers proposed that bacterial translocation through inflamed colon wall may be involved in pathogenesis of CSF. This process is thought to be one of the main causes of CD as well, therefore suggesting that these two diseases may have a common pathogenesis. This idea is supported by the fact that serum IgA levels against the lipopolysaccharide (LPS) of enterobacteria is increased in patients suffering from CFS and is correlated with the severity of the disease. The elevated levels of bacterial components in plasma of CFS patients is a result of increased gut permeability. According to Giloteaux and co-workers [
47,
48] it might be possible that increased bacterial proliferation in the gut results in high endotoxin levels and further damage of epithelial barrier. Resulting infiltration of LPS into the bloodstream provokes the immune response and systemic inflammation. LPS also induces localized inflammation by binding to the toll-like receptor-4 complex. A mutation of Nucleotide binding oligomerization domain 2 (NOD2) leads to the binding of protein to the peptidoglycan of bacteria, which results in NF-kB activation and inflammatory response; this may also play a role in the development of CD. Clinically, activation of NF-kB has been related to a feeling of tiredness [
49].
Pro-inflammatory cytokines produced in the gut can then be transferred to the brain by the autonomic nervous system, causing an increase in cytokine levels in the brain and exacerbating neuroinflammatory processes, which are linked to the feeling of fatigue. For example, an increased level of IFNy is associated with fatigue and hyperalgesia [
50].
11. Conclusions
Chronic fatigue is a common and underrecognized symptom of CD, which prevalence is much higher in the population of CD patients as compared to healthy population. It stems from an intricate web of interactions between various risk factors, and its pathophysiology is still not fully understood. However, despite the wide range of available treatments, management of chronic fatigue remains a significant challenge for both CD patients and medical practitioners. Implementation of routine screening and holistic, multidisciplinary approach involving psychological support may be crucial in the management of CD patients with chronic fatigue. There is currently no single intervention aimed at decreasing fatigue alone, and its treatment is especially difficult in patients with fatigue persisting despite clinical and endoscopic remission. The fatigue in CD is driven by various factors and that a multidisciplinary approach is crucial to manage fatigue. Further extensive research is still needed in order to be able to predict, prevent, identify and ultimately treat fatigue associated with CD. It would be beneficial for future studies to examine different types of fatigue (physical, emotional, or mental fatigue). Finally, research is needed to develop effective fatigue interventions which can be easily translated into clinical practice.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.W., J.W. and Ł.D.; methodology, A.M. and M.P.; software, J.W. and K.M.; validation, M.W., J.W. and J.F.; formal analysis, M.W. and A.M.; investigation, M.P., J.W. and K.M.; resources, M.W. and Ł.D.; data curation, M.P. and J.W.; writing—original draft preparation, M.W., A.M.; writing—review and editing, M.W., J.W. and J.F.; visualization, J.W. and Ł.D.; supervision, J.F. and Ł.D.; project administration, M.W.; funding acquisition, M.W. and Ł.D. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by statutory funds from the Medical University of Lodz, Poland.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical review and approval were waived for this study due to the retrospective analysis of data collected during the routine daily clinical work.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and / or analyzed withing the framework of this study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Barsevick AM, Cleeland CS, Manning DC, et al. ASCPRO recommendations for the assessment of fatigue as an outcome in clinical trials. J Pain Sympt Manag 2010, 39, 1086–1099. [CrossRef]
- Finsterer, J.; Mahjoub, S.Z. Fatigue in healthy and diseased individuals. Am. J. Hosp. Palliat. Care 2014, 31, 562–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, M.P.; Walsh, D. Mechanisms of fatigue. J. Support. Oncol. 2010, 8, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cullen, W.; Kearney, Y.; Bury, G. Prevalence of fatigue in general practice. Ir. J. Med. Sci. 2002, 171, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, B.L.; Zoëga, H.; Shah, S.A.; Leleiko, N.; Lidofsky, S.; Bright, R.; Flowers, N.; Law, M.; Moniz, H.; Merrick, M.; et al. Fatigue is highly associated with poor health-related quality of life, disability and depression in newly-diagnosed patients with inflammatory bowel disease, independent of disease activity. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 39, 811–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danese, S.; Hoffman, C.; Vel, S.; Greco, M.; Szabo, H.; Wilson, B.; Avedano, L. Anaemia from a patient perspective in inflammatory bowel disease: results from the European Federation of Crohn’s and Ulcerative Colitis Association’s online survey. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 26, 1385–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graff, L.A.; Vincent, N.; Walker, J.R.; Clara, I.; Carr, R.; Ediger, J.; Miller, N.; Rogala, L.; Rawsthorne, P.; Lix, L.; et al. A population-based study of fatigue and sleep difficulties in inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2011, 17, 1882–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimstad T, Norheim KB, Isaksen K, et al. Fatigue in newly diagnosed inflammatory bowel disease. J Crohns Colitis 2015;9(9):725–730. [CrossRef]
- Borren NZ, van der Woude CJ, Ananthakrishnan AN. Fatigue in IBD: epidemiology, pathophysiology and management. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;16:247-59. [CrossRef]
- Patarca, R. Cytokines and chronic fatigue syndrome. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2001, 933, 185–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucia Casadonte, C.J.; Brown, J.; Strople, J.; Neighbors, K.; Fei, L.; Alonso, E.M. Low Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 Influences Fatigue and Quality of Life in Children With Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2018, 67, 616–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogelaar, L.; de Haar, C.; Aerts, B.R.; Peppelenbosch, M.P.; Timman, R.; Hanssen, B.E.; van der Woude, C.J. Fatigue in patients with inflammatory bowel disease is associated with distinct differences in immune parameters. Clin. Exp. Gastroenterol. 2017, 10, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonefjäll, B.; Simrén, M.; Lasson, A.; Öhman, L.; Strid, H. Psychological distress, iron deficiency, active disease and female gender are independent risk factors for fatigue in patients with ulcerative colitis. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2018, 6, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsherif, Y.; Alexakis, C.; Mendall, M. Determinants of Weight Loss prior to Diagnosis in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Retrospective Observational Study. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2014, 2014, 762191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantzer, R.; O’Connor, J.C.; Freund, G.G.; Johnson, R.W.; Kelley, K.W. From inflammation to sickness and depression: when the immune system subjugates the brain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2008, 9, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Missaghi, B.; et al. Perturbation of the human microbiome as a contributor to inflammatory bowel disease. Pathogens 2014, 3, 510–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagy-Szakal, D.; et al. Fecal metagenomic profiles in subgroups of patients with myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome. Microbiome 2017, 5, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maes, M., Mihaylova, I. & Leunis, J. C. Increased serum IgA and IgM against LPS of enterobacteria in chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS): indication for the involvement of gram-negative enterobacteria in the etiology of CFS and for the presence of an increased gut-intestinal permeability. J Affect Disord. 2007, 99, 237–240. [CrossRef]
- Smith, C. J.; et al. Probiotics normalize the gut-brain-microbiota axis in immunodeficient mice. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2014, 307, G793–G802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bager, P.; Befrits, R.; Wikman, O.; Lindgren, S.; Moum, B.; Hjortswang, H.; Dahlerup, J.F. The prevalence of anemia and iron deficiency in IBD outpatients in Scandinavia. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 46, 304–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartels U., Pedersen N.S., Jarnum S. Iron absorption and serum ferritin in chronic inflammatory bowel disease. Scand J Gastroenterol 1978;13:649–656. [CrossRef]
- Guagnozzi, D.; Lucendo, A.J. Anemia in inflammatory bowel disease: a neglected issue with relevant effects. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 3542–3551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasche, C.; Lomer, M.C.E.; Cavill, I.; Weiss, G. Iron, anaemia, and inflammatory bowel diseases. Gut 2004, 53, 1190–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelsness-Jørgensen, L.-P.; Bernklev, T.; Henriksen, M.; Torp, R.; Moum, B.A. Chronic fatigue is associated with impaired health-related quality of life in inflammatory bowel disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 33, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelsness-Jørgensen, L.-P.; Bernklev, T.; Henriksen, M.; Torp, R.; Moum, B.A. Chronic fatigue is more prevalent in patients with inflammatory bowel disease than in healthy controls. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2011, 17, 1564–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radford SJ, Moran GW, Czuber-Dochan W. The impact of Inflammatory Bowel Disease related fatigue on Health-Related Quality of Life: a qualitative semi-structured interview study. J Res Nurs. 2022 Dec;27(8):685-702. [CrossRef]
- Kurina, L.M.; Goldacre, M.J.; Yeates, D.; Gill, L.E. Depression and anxiety in people with inflammatory bowel disease. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2001, 55, 716–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashash JG, Knisely MR, Germain A, McAuliff K, Strassburger M, Vachon A, Binion DG, Regueiro M, Wallace M, Szigethy E. Brief Behavioral Therapy and Bupropion for Sleep and Fatigue in Young Adults With Crohn’s Disease: An Exploratory Open Trial Study. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 Jan;20(1):96-104. [CrossRef]
- Russell, D.M.; Leiter, L.A.; Whitwell, J.; Marliss, E.B.; Jeejeebhoy, K.N. Skeletal muscle function during hypocaloric diets and fasting: a comparison with standard nutritional assessment parameters. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1983, 37, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mijac, D.D.; Janković, G.L.J.; Jorga, J.; Krstić, M.N. Nutritional status in patients with active inflammatory bowel disease: prevalence of malnutrition and methods for routine nutritional assessment. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2010, 21, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vagianos, K.; Bector, S.; McConnell, J.; Bernstein, C.N. Nutrition assessment of patients with inflammatory bowel disease. JPEN. J. Parenter. Enteral Nutr. 2007, 31, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frigstad, S.O.; Høivik, M.L.; Jahnsen, J.; Cvancarova, M.; Grimstad, T.; Berset, I.P.; Huppertz-Hauss, G.; Hovde, Ø.; Bernklev, T.; Moum, B.; et al. Fatigue is not associated with vitamin D deficiency in inflammatory bowel disease patients. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 3293–3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyidova-Khoshknabi, D.; Davis, M.P.; Walsh, D. Review article: a systematic review of cancer-related fatigue measurement questionnaires. Am. J. Hosp. Palliat. Care 2011, 28, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Belle, S.; Paridaens, R.; Evers, G.; Kerger, J.; Bron, D.; Foubert, J.; Ponnet, G.; Vander Steichel, D.; Heremans, C.; Rosillon, D. Comparison of proposed diagnostic criteria with FACT-F and VAS for cancer-related fatigue: proposal for use as a screening tool. Support. care cancer Off. J. Multinatl. Assoc. Support. Care Cancer 2005, 13, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinsley, A.; Macklin, E.A.; Korzenik, J.R.; Sands, B.E. Validation of the functional assessment of chronic illness therapy-fatigue (FACIT-F) in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 34, 1328–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, D.; Artom, M.; Czuber-Dochan, W.; Jelsness-Jørgensen, L.P.; Norton, C.; Savage, E. Interventions for fatigue in inflammatory bowel disease. Cochrane database Syst. Rev. 2020, 4, CD012005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxena, A.; Fletcher, E.; Larsen, B.; Baliga, M.S.; Durstine, J.L.; Fayad, R. Effect of exercise on chemically-induced colitis in adiponectin deficient mice. J. Inflamm. (Lond). 2012, 9, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazur-Bialy, A.I.; Bilski, J.; Wojcik, D.; Brzozowski, B.; Surmiak, M.; Hubalewska-Mazgaj, M.; Chmura, A.; Magierowski, M.; Magierowska, K.; Mach, T.; et al. Beneficial Effect of Voluntary Exercise on Experimental Colitis in Mice Fed a High-Fat Diet: The Role of Irisin, Adiponectin and Proinflammatory Biomarkers. Nutrients 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtenstein GR, Bala M, Han C, DeWoody K, Schaible T. Infliximab improves quality of life in patients with Crohn’s disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2002 Jul;8(4):237-43. [CrossRef]
- Minderhoud IM, Samsom M, Oldenburg B. Crohn’s disease, fatigue, and infliximab: is there a role for cytokines in the pathogenesis of fatigue? World J Gastroenterol. 2007 Apr 14;13(14):2089-93. [CrossRef]
- Loftus EV, Feagan BG, Colombel JF, Rubin DT, Wu EQ, Yu AP, Pollack PF, Chao J, Mulani P. Effects of adalimumab maintenance therapy on health-related quality of life of patients with Crohn’s disease: patient-reported outcomes of the CHARM trial. Am J Gastroenterol. 2008 Dec;103(12):3132-41. [CrossRef]
- Yennurajalingam, S.; Bruera, E. Cancer-related fatigue, the role of adrenal suppression and steroids: reply to the comments of Eren et al. Support. care cancer Off. J. Multinatl. Assoc. Support. Care Cancer 2014, 22, 2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantini, A.; Pala, M.I.; Catalano, M.L.; Notarangelo, C.; Careddu, P. High-dose thiamine improves fatigue after stroke: a report of three cases. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2014, 20, 683–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regev S, Schwartz D, Sarid O, Goren G, Slonim-Nevo V, Friger M, Sergienko R, Greenberg D, Monsonego A, Nemirovsky A, Odes S. Randomised clinical trial: Psychological intervention improves work productivity and daily activity by reducing abdominal pain and fatigue in Crohn’s disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2023 Feb 2. [CrossRef]
- Tsai, S.-Y.; Chen, H.-J.; Lio, C.-F.; Kuo, C.-F.; Kao, A.-C.; Wang, W.-S.; Yao, W.-C.; Chen, C.; Yang, T.-Y. Increased risk of chronic fatigue syndrome in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: a population-based retrospective cohort study. J. Transl. Med. 2019, 17, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newberry, F.; Hsieh, S.-Y.; Wileman, T.; Carding, S.R. Does the microbiome and virome contribute to myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome? Clin. Sci. (Lond). 2018, 132, 523–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- König, R.S.; Albrich, W.C.; Kahlert, C.R.; Bahr, L.S.; Löber, U.; Vernazza, P.; Scheibenbogen, C.; Forslund, S.K. The Gut Microbiome in Myalgic Encephalomyelitis (ME)/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (CFS). Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 628741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giloteaux, L.; Goodrich, J.K.; Walters, W.A.; Levine, S.M.; Ley, R.E.; Hanson, M.R. Reduced diversity and altered composition of the gut microbiome in individuals with myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome. Microbiome 2016, 4, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varesi, A.; Deumer, U.-S.; Ananth, S.; Ricevuti, G. The Emerging Role of Gut Microbiota in Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (ME/CFS): Current Evidence and Potential Therapeutic Applications. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Yang, Y.; Wang, D.; Li, C.; Qu, Y.; Guo, J.; Shi, T.; Bo, W.; Sun, Z.; Asakawa, T. The clinical value of cytokines in chronic fatigue syndrome. J. Transl. Med. 2019, 17, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).