Introduction:
Self-confidence is considered one of the positive personal characteristics, which plays a fundamental buffering tool in adjusting to the pressures of life. It plays a significant role in encouraging positive psychological growth, bringing the individual to the required level of self-esteem and psychological and social adaptation, and increases perseverance and effort to achieve goals and success, which in turn would contributes to building the concept of being self-Positive, so it makes the individual comfortable, liberated of fears, capable of organizing his boundaries in compatibility with his thoughts quickly and accurately with less help from others, which enables him to overcome difficulties and reach a high level of achievement.
Self-confidence, which is one of the strong predictors of academic success and defined Bozgun & Akin ,2023) , is one of the important determinants of an individual's feelings, thoughts, behaviors, and motivation for certain tasks Bandura (1997); it is defined by Toy (2023) as " Self-confidence is the belief that an action can be carried out successfully is the state of an individual to develop positive and optimistic feelings and thoughts towards himself/herself and to feel good about himself/herself (Yildrim, 2022).
The importance of self-confidence originates from the fact that it stems for achieving psychological compatibility among students in various educational stages, to love others, to acquire voluntary and involuntary experiences, as well as to form positive social bond-ships, self-acceptance, and success in interacting with others in various extracurricular sports and artistic activities (Yurtseven, 2011).
Music is considered one of the arts that has been known since ancient times because of its importance in social and human life. As the Greek civilization paid great attention to music, it had been viewed as one of the means of education and entertainment, before bestowing it with the classification of “ fine art”, and this is what made Plato urge the Greek State to incubate Music under its supervision, because of its great role in refining the human personality and developing morals, besides, its impact on the development of moral and psychological behaviors of individuals, and self-confidence as it is a sensual, psychological, and spiritual language, which has the great ability to express the culture of society. (Al-Amidi, & Abdel-Zahra, 2018).
Studying the self-confidence of individuals is of great importance, especially those who participate in artistic activities. On the other hand, bringing about the lineage between participation in those activities with self-confidence has a great role to identify the impact of participating in musical activities in refining the students' personality, and developing their self-concept. Given the importance of this subject and its nature, and the lack of previous studies on this subject, especially on the category of musically gifted/talented, except for some of the aforementioned studies that dealt with other subjects in extracurricular activities such as sports activities and drama. For the previously mentioned reasons, the researcher sought to study this specific subject; The self-confidence among Those with high musical abilities
The study/ Research quest:
Students' self-confidence plays a vital role in developing their persona and academia. Some specialists had indicated that self-confidence is compatible with the various educational aspects, and they tried to provide appropriate methods to develop students' self-confidence, as it is one of indispensable needs and necessities. The confidence factor creates Self-esteem, which is an important aspect that students need to continue developing through various activities. On the other hand, their lack of self-confidence is considered as one of the important factors, among others, leading to poor performance in practicing musical activities. The results by the Juhart & Kafol,.(2021). study revealed that individuals participating in musical activities were more able to Social- ties with others. Being involved in music give them a sense of achievement and pride. The results obtained by Bahar, 2019 study, showed that listening to music develops positive feelings, causes a sense of pleasure, regulates mood, relaxes, and increases affiliation. The results also showed a positive relationship between listening to music and the level of education and health, i.e. listening to music is directly proportional to the enhancement of health and education. Accordingly, the problem of the study is defined by the following questions:
Study/Research questions:
- -
The first question: What is the level of the self-confidence among Those with high musical abilities Student?
- -
The second question: Are there differences in the level of the self-confidence among Those with high musical abilities Student according to the level of gender and achievement academic?
The importance of the Study:
The theoretical aspect: The theoretical importance of this study lies in the following:
- -
The scarcity of recent Arab educational research that dealt with the self-confidence of musically gifted/talented students.
- -
The results of this study can be used to develop training programs to enhance students' self-confidence and skills, including stimulating the positive self-concept of musically gifted/talented students.
The practical aspect: The practical importance of this study lies in the following:
- -
The results of this study has a potential to be used through decision-makers in educational institutions.
- -
Enabling researchers in the field of positive psychology, gifted/talented Ness and excellence, and musical education to build/ design training programs, according to various musical programs and activities on which students are trained. With the aim of developing their self-confidence.
- -
The results of this study contribute effectively to raising the level of knowledge of the students.
Objectives of the study:
This study aims to achieve the following:
- -
Detection of the level of self-confidence of musically gifted/talented students
- -
- Identifying the differences in the level of self-confidence among musically gifted/talented students in light of the difference in gender and achievement levels
Procedural definitions:
Self-confidence: Guilford defined self-confidence as a factor that represents individual's attitude towards himself and his social surroundings, and is linked to the individual's tendency to engage or retreat from the surroundings. (Al-Sanabani, and Al-Tarek, (2020).
Musically Gifted/talented: Students' ability to accurately identify musical tones, understand their temporal rhythm, sense musical scales, and their ability to interact and react to the emotional effects of the elements of The Musical. (Al-Moumni, Al-Hamouri, Bani Younis, and Al-Qaraan, 2011)
Theoretical framework and previous studies:
First: self-confidence
Self-confidence is one of the important pivotal concepts in the field of studying the human personality. It is an important tool in constructing the individual's personality in view of psychological growth. It is one of the essential features of a normal personality, which is not limited specifically to the field of adaptation in individuals. “Adaptation, independence, achievement, and self-realization can only grow with the growth of self-confidence”. Qasim, Amna and Abd El-Ilah, (2018).
Self-confidence is the firm belief in an individual's capabilities through self-evaluation, which is a concept that has a physical aspect in addition to the mental state in the essence of self-confidence, and the difficulties that a person suffers from, that may arise in life, so that he can overcome them, based on his internal resources, ability, intelligence, and strength. (Ilhan; Bardakci, 2019).
Also, self-confidence is the self-formation that occurs as a result of self-esteem and self-satisfaction among individuals. Hince, it takes negative or positive values, resulting in High or Low confidence, it is not fixed and therefore varies according to circumstances and foundations, where each situation is evaluated within the context of basic theory of self-recognition, Which plays an important role in the formation of self-confidence, besides what is adopted by the self-esteem of the individual (Öntürk & Asma, 2020)
Bilgin defines self-confidence as an individual's belief in one's talents, judgment, power, and decisions. Therefore, It is an important feature of school life, personal, and social life. The concept of inner self-esteem; which includes self-awareness, self-esteem, and self-reflection, shows that the individual identifies himself in this context. The ability to express oneself, communicate, and control their emotions is related to external self-confidence, which is the image and impression that is given to the outside & perceived as self-confident and has a positive self-concept about oneself. (Tridinanti, 2018)
Bin Najma (2019) indicates that self-confidence is one of the required and important characters, as it helps the individual achieve success and adapt to their bounding society, whether at home, work, with friends, or school, but sometimes, it may happen that the individual is exposed to some problems that might hinders him from achieving many goals and ambitions, these circumstances in return may affect the individual's self-confidence.
While self-confidence, as indicated by Al-Sulaiman (2005), is the extent to which an individual is assured of himself- with complete conscious of himself and his abilities, according to the circumstances which he passes through, without excessive stubbornness, as well as without negligence of humiliation or unacceptable submission. Self-confidence is important for every person, regardless of his social rank. It is an indispensable need for every person to continuously monitoring his/her self-confidence in any matter. Many studies have shown that individuals who have high levels of self-confidence tend to succeed academically, among raising the level of students' achievement motivation, raising the level of performance within the school. They can efficiently access and acquire knowledge and experiences within the school. (Al-Ta'i, 2007 2016; Tridinanti, 2018 ; Nalbur, (2021).)
Music:
Art education occupies an important place from an early age so that people can come up with new ideas and products and learn to be creative, generating a pool of ideas, that can help them network. Creativity in music is usually based on the concepts of individual’s thinking orientation. In music education, which is an important part of art education, there are practices such as finding and writing rhythm patterns, words, poems, rhymes, and finding new melodies for these words, etc. All these activities play an important role in arts. (Aycan, 2017)
“Ucan” regards music as an aesthetic whole that expresses feelings, ideas, designs, and impressions with sounds combined with a purpose, unique method, and a precise understanding of aesthetics& beauty. To have a better understanding of this definition, which considers music as an aesthetic whole based on sounds; we must know that the origin of the word aesthetics here is developed as a branch of philosophy. It is rooted back to the Greek word Aisthanomai, which means perception through the senses, and the word Aistanomai which is based on the word perception and sensation (Engur, 2020).
Education curricula are sought as Gok, 2023 points out. To maintain and support an ongoing musical commitment to professionally accepted elements and standards, these elements include the ability to hear, interpret, understand, and comprehend music. While, Practice, and ability to perform and/or compose music has been increasingly demanded by professional standards, types, and performance opportunities. Creativity, through composing and performing original musical works, by deploying the artistic expression of musical talent.
Music and education have a great relationship, as they depend on each other closely, so education depends directly on music, especially in nurturing the personality of students, so that they become balanced individuals within the social boundaries in which they live. While we find that music needs modern educational methods in refining students' personalities and providing them with the basics of musical education by implementing advanced musical theories. (Sahlawi, (2017).
The various educational programs seek to activate musical education and support its elements and vocabulary to be widely recognized and embraced, as these standards include the ability to listen, comprehend, understand, and practice, in addition to the ability to perform or compose music continuously according to various standards acquired by experience, adding to the previously mentioned requirements, we should consider the nature of the performance& innovation through composing and performing sophisticated musical compositions (Mitchell, 2018).
Sherman, on the other side, explains that music has a great effect on the physical aspect. An individual who listens to music, are subjected to increase in blood flow to the brain, activating multiple parts of the brain simultaneously. The researchers also discovered that during listening to/ and processing music, multiple parts of the brain are activated simultaneously, rather than activating one particular area of the brain regions, and this was achieved by processing music and sounds. The activation of multiple brain neurons during exposure to music occur at the same time. (Blackburn, 2017).
Many studies that dealt with the issue of self-confidence and the musically gifted/talented have been conducted, where the results of Malkoc & Mutlu, (2020) study indicated that there is a significant statistical relationship between self-confidence and psychological well-being.
While the results of the study by (Toktas & Bas, 2019) showed that there is a statistically significant relationship between demographic information and levels of self-confidence and motivation, while there was a significant difference in the level of self-confidence between the two sexes, and the differences were in favor of males. Other results were obtained by Bardakci & Ilhan (2019) study, which showed that university students who participated in physical activity had a higher level of self-confidence than those who did not attend. In addition, males participating in physical activity had higher levels of self-confidence than non-participants. The same applies to female students, and the results also indicated that there were no statistically significant differences due to gender.
While the results of Al-Sayed's study (2016) indicated that the levels of self-confidence among gifted/talented students were high, there was a significant difference in the level of self-confidence between the two sexes, and the differences were in favor of males.
Study Approach:
In the current study, the analytical descriptive approach was selected to detect the self-confidence of musically gifted/talented students, as it is the appropriate approach for the objectives of this study.
The study’s Sample:
The sample of the study consisted of students who were musically gifted/talented and who were representing the upper basic stages in terms of performances and instrumentation. Another condition of selection was that these selected sample of gifted/talented students were enrolled in all group and individual musical competitions, in one of the schools in the northern region of Jordan.
Honesty:
First-The validity of the content: To verify the validity of the content of the tool, it was distributed in its initial form, to a group of experts and specialists in the fields of: “Measurement & evaluation”, and “psychology”. The aim is to seek their opinions in the paragraphs of the questionnaire in terms of clarity of meaning and linguistic formulation and its suitability for the field to which it belongs. Notes were taken into account (85%) of the arbitrators are in line with the objectives of this study. Paragraphs that most of the arbitrators thought upon were deleted and modified, and their number reached (4) paragraphs. The scale in its final form consisted of (26) paragraphs.
Second-the validity of the construction: To extract the indications of the constructive validity of the scale, the correlation coefficients of the scale paragraphs were extracted with the total score in an exploratory sample outside the study sample (control). Between each paragraph and the total score on the one hand, and between each paragraph and its association with the domain to which it belongs.
On the other hand, the correlation coefficients of the paragraphs with the tool as a whole ranged between (0.32-0.78), and with the domain range of (0.84-0.40).
The reliability of the self-confidence scale:
To ensure the stability of the study tool, the (test-retest) was used through applying the scale, and re-applying it after two weeks on another standard group outside the study sample students, and then the
Pearson correlation coefficient was calculated between their estimates within the two times intervals. The
stability coefficient was also calculated using the
internal consistency method according to the
Cronbach alpha equation.
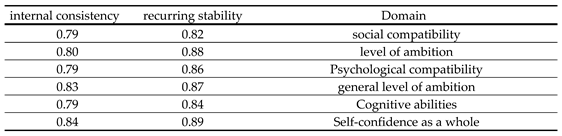
Table 2 Shows the internal consistency coefficient according to the Cronbach alpha equation and the repetition stability of the domains and the tool as a whole. These values were considered appropriate for this study.
Statistical processing: In this study, the arithmetic means, standard deviations, and the "T-test" were used, as well as multiple pair analysis of variance.
Results related to the first question, which states: What is the level of the self-confidence among Those with high musical abilities Student? To answer this question, the arithmetic means and standard deviations of the level of self-confidence of gifted/talented students were extracted, and the following table shows this.
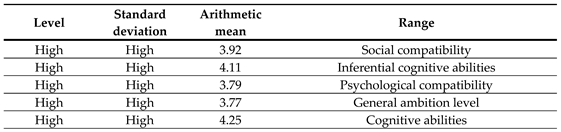
Table 3 shows that the arithmetic means ranged between (3.71-4.15), where the domain which reads (cognitive abilities) came in the first place with the highest arithmetic mean of (4.15) for each of them, while the domain which reads (psychological compatibility) came in the rank The latter, with an arithmetic mean of (3.71), and the arithmetic mean of self-confidence as a whole was (3.93).
The second question: Are there differences in the level of self-confidence among Those with high musical abilities Student according to the level of gender and achievement academic?
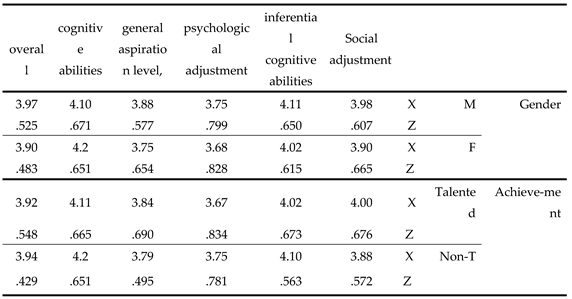
Table 4 shows an apparent variation in the arithmetic means and standard deviations of the level of self-confidence of the musically gifted/talented, due to the different categories of the variables of gender and academic achievement.
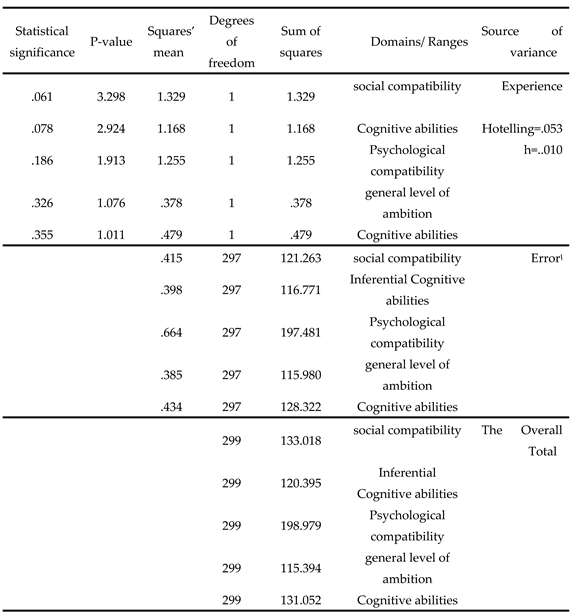
To show the significance of the statistical differences between the arithmetic means, multiple binary analysis of variance was used on the domains,
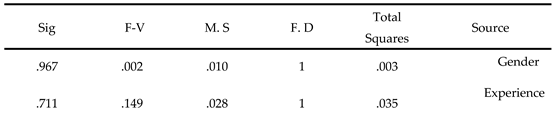
Table 5, and the binary analysis of variance for the tool as a whole,
Table 6.
The following can be seen from
Table 5:
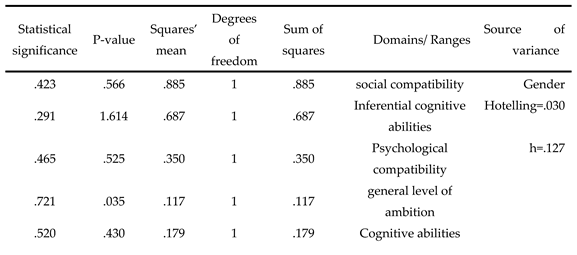
There were no statistically significant differences (α ≥ 0.05) attributable to the effect of gender in all domains.
There were no statistically significant differences (α ≥ 0.05) attributed to the effect of academic achievement in all domains.
- -
There were no statistically significant differences (α ≥ 0.05) due to the effect of gender, as the p-value was 0.002 and the statistical significance was 0.967.
- -
There were no statistically significant differences (α ≥ 0.05) due to the effect of achievement, as the p-value was 0.149 and the statistical significance was 0.711.
Discussing the results and recommendations:
The results of the first question indicated that the level of self-confidence of the musically gifted/talented students was high, and this result can be interpreted in terms of the ability mastered by the musically gifted/talented students to interact and manage social relations in a balanced manner, as well as their ability to adapt to different turns of life, through the method of solving problems, and dealing with events realistically. Where we find that musically gifted/talented students have many pillars that they seek to achieve, and it is highlighted through perseverance and diligence in mastering playing various musical instruments, participating in competitions & various musical activities. Due to the great motivation in achieving excellence and creativity in various musical activities, the explanation for the field of cognitive abilities being ranked first, given that musically gifted/talented students have great self-confidence in the field of knowledge, through their excellence in playing musical instruments, as well as participating in individual and group competitions, which leads to the development of their cognitive abilities The results can also be interpreted in terms of the mental and cognitive abilities of the musically gifted/talented, as mental abilities and cognitive development are closely related to musical abilities, this is also since musically gifted/talented students have great motivation, to reach achievements and excellence, in a way that increases their ability to make their decisions, in Many of the endowments that are taken, and therefore they are distinguished in achieving those achievements efficiently.
The findings of these results are consistent with the results of the study by Bardakci & Lhan (2019), which showed that university students who participated in physical activity had a higher level of self-confidence than those who did not attend. As well as the results of the study Malkoc & Mutlu, (2020), where the results showed that there is a statistically significant relationship between self-confidence and psychological well-being. As well as, the study by Edgar & Scott (2019), whose results showed that music has a deep connection to these challenges, either as a catalyst or as relief, which increases self-confidence, as well as the study of Al-Khalayleh, (2017), whose results indicated that there is an impact of musical activities on the development of social behavior affirmative. Yöndem, et al, (2017) aimed for self-concept factors to be significantly higher than those of art students.
As for the results related to the second question, about differences in the level of self-confidence among musically gifted/talented students according to gender and achievement levels? The results showed that, there are no statistically significant differences due to the effect of gender, as well as the absence of statistically significant differences due to the effect of academic achievement on the level of self-confidence among musically gifted/talented students.
The researcher attributes this result as an explanation to the great similarity between male and female students in terms of musical talent, as they were chosen based on the high level of performance in playing and chanting, and thus the degree of pleading musical abilities. In addition, these students belong to the same educational habitat, where the educational programs provided to them are applied, which helped the study to focus on their entirety on extracurricular activities and programs for developing musical skills, as well as their subjection to a specific educational and training philosophy. In addition to convergence in Cultural and social boundaries. From here, we find that these variables lead, naturally & to a large extent, to the absence of fundamental differences between students of the male and female sexes, in the level of self-confidence. These results are consistent with the outcome of the study
The study aimed at Ilhan, (2019) Bardakci together with the obtained results also indicated that there were no statistically significant differences due to gender. While this result differs from the result of the study by (Toktas & Bas, 2019), which stated that, there was a significant difference in the level of self-confidence due to gender, and the differences were in favor of males. Mawang et al, (2019), stated that the level of musical creativity where males scored higher than females, yet, there was no significant difference in the participants' musical creativity based on age.
The results also showed that there were no statistically significant differences due to the effect of academic achievement on the level of self-confidence of the musically gifted/talented students in all fields illustrated in the calculated total degree. This can be explained in terms of the great homogeneity between students who excel in achievement versus ordinary students, through participation in musical activities. Since mental and cognitive abilities are directly related to growth through musical abilities, among musically gifted/talented students, as they were diagnosed based on the level of outstanding performance and musical abilities, and thus, the impact of their academic achievement did not have any meaning because they belong to one educational culture, and a closeness in their social environment as independent individuals. As they practice extracurricular activities, where most of their interest is in the practice of musical activities, we find that all of these variables lead, of course, to the absence of significant differences between students who excel in achievement and ordinary students, because of the positive effects it has on them. In the level of self-confidence, whereas, musical activities and playing in groups, assisted their ability to achieve more advanced level of social interaction with each other, and they had positive perceptions of life skills, as well.
These results are consistent with the result of the study by Edgar & Scott (2019) , that music has a deep connection to these challenges either as a catalyst or as a relief. The most common challenge was difficulty with time management and over-commitment. These results are consistent with the outcome of the Bahar (2019) study, the results of which, showed that the level of social skills among students who mastered playing musical instruments was much higher than those who did not, regardless of achievement. The study (Al-Khalayleh, (2017), which indicated that there is an impact of musical activities on the development of positive social behavior.
Recommendations:
In light of the objectives and results of the study, the researcher recommends investing in a high level of self-confidence among musically gifted/talented students, to help them succeed in scientific and practical life. This study also recommends conducting more studies in this regard on variable age groups of musically gifted/talented students. Among other variables, and studying its relationship with other variables such as; spiritual intelligence, emotional intelligence, and quality of life.
References
- Al Amidi, H & Hamza, A. (2018). The educational function of music in school operetta performances: operetta (read) as a model. Journal of the College of Basic Education for Educational and Human Sciences. 39, 1108-1120.
- Al Khalayleh, B. (2017). The effect of using musical activities on developing positive social behavior among sixth grade students in Jordan. Unpublished master's thesis, College of Graduate Studies, Hashemite University, Jordan, Zarqa.
- Al-Moumni,M; Al-Hamouri,K; Bani Younis, N; and Al-Qaraan, J. (2011). the between Relation The Academic and Abilities Musical of Achievement among Talented Students, Jordan Journal of Arts, 4(1),29-34.
- Al Sanabani, E; Al-Tarek, A. (2020). Self-confidence and its relationship Teacher's gender among preparatory stage students in the capital Sana'a. Journal of Arts for Psychological and Educational Studies, 3, 8-46.
- Al Sayed’s, W (2016). Self-confidence among gifted students and its relationship to some demographic variables. Graduate Studies, Al-Neelain University Journal, 6 ((23, 177-202).
- Al-Sulaiman, H (2005), Self-confidence. Amman, Dar Al-Isra for publication and distribution.
- Aycan, K. (2017). Kodaly metodundan uyarlanan desifre sarkı soyleme uygulamaları. Abant Izzet Baysal Universitesi Egitim Fakultesi Dergisi, 17(4), 1683–1701.
- Bahar, A. (2019). An examination of high school students’ social skill levels according to participation in musical activities. Cypriot Journal of Educational Sciences, 14, (4), 618-629.
- Bandura, A. (1977). Self-efficacy: Toward a unifying theory of behavioral change. Psychological Review, 84, 191-215.
- Bin Najma, N (2019) The impact of a proposed counseling program during the physical education and sport seance to raise the level of self-confidence for middle school students. Sports Creativity Journal, 10(1), 211-230.
- Blackburn, H. (2017). Music in the Classroom. International Journal of the Whole Child, 2 (1), 26-33.
- Bozgun, K; Akin-K, M. (2023). Self-Confidence as the Predictor of Metacognitive Awareness in High School Students. Participatory Educational Research, 10 (1), 375-388. [CrossRef]
- Edgar, S, N. (2019). Music and the Social and Emotional Challenges of Undergraduate Instrumental Music Students. Update: Applications of Research in Music Education, 37 (3), 46-56. [CrossRef]
- Ilhan, A; Bardakci, U. S.(2019). Analysis on the Self-Confidence of University Students According to Physical Activity Participation. African Educational Research Journal, 8 (1), 111-114.
- Girgin, D. (2020). Motivation, Self-Efficacy and Attitude as Predictors of Burnout in Musical Instrument Education in Fine Arts High Schools. Eurasian Journal of Educational Research,85,93-108. [CrossRef]
- Gok, M. (2023). Evaluation of Students' Cognitive and Conceptual Learning Levels in Middle School Music Lessons. International Journal of Education and Literacy Studies, 11 (1), 194-206. [CrossRef]
- Joseph, D., & Southcott, J. E. (2015). Singing and companionship in the Hawthorn University of the Third Age Choir, Australia. International Journal of Lifelong Education, 34(3), 334–347. [CrossRef]
- Juhart, P, B; Kafol, B, S.(2021). Music Teachers' Perception of Music Teaching at the Stage of Early Adolescence. Center for Educational Policy Studies Journal, 11 (3), 97-118. [CrossRef]
- Laukka, Petri. (2007). Uses of music and psychological well-being among the elderly. Journal of happiness studies, 8(2), 215. [CrossRef]
- Malkoc, A ; Mutlu, A,.(2019). Mediating the Effect of Cognitive Flexibility in the Relationship between Psychological Well-Being and Self-Confidence: A Study on Turkish University Students. International Journal of Higher Education, 8 (6), 278-87. [CrossRef]
- Mawang, L.; Kigen, E.; Mutweleli, S. (2019). The relationship between musical self-concept and musical creativity among secondary school music students. International Journal of Music Education, 37(1), 78- 90. [CrossRef]
- Nalbur, V., (2021). Interdisciplinary art education and primary teaching students' self-confidence Cypriot Journal of Educational Science. 16(4), 2010-2024. [CrossRef]
- Onturk, U., and Asma, M. B. (2020). The effect of 12-week service training on self-confidence in racket sport. African Educational Research Journal, 8(2): 410-416. [CrossRef]
- Qasim, A; Abd El-Ilah, S (2018). Psychological happiness in its relationship to cognitive flexibility and self-confidence among a sample of postgraduate students, Suhag University. Educational Journal, Suhag University, 53, 81-145.
- Sahlawi,M (2017). The role of music education in addressing aggressive behavior in the school environment - the middle school stage. Educator Journal, 20,.80-99.
- Tridinanti, G. (2018). The Correlation between Speaking Anxiety, Self-Confidence, and Speaking Achievement of Undergraduate EFL Students of Private University in Palembang. International Journal of Education and Literacy Studies, 6 (4), 35-39. [CrossRef]
- Toktas, S ; Bas, M.(2019). Investigation of the Relationship between the Self-Confidence and Motivation of High School Students Participating School Sport Contests. Universal Journal of Educational Research, 7 (2), 472-479. [CrossRef]
- Toy, A. (2023). Relationship Between Sportsmanlike Behaviors and Self-confidence of Physical Education and Sports Students within the Scope of Sports Literacy. International Journal of Education & Literacy Studies, 11(1), 170-174. [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, I. (2013). Let there be music: Making a case for using music in schools to enhance relationships and readiness for learning. Canadian Music Educator, 55(1), 28-31.
- Yildrim, A. (2022). Investigation of the Effect of 8-Week Life Kinetic Training on Self-Confidence, Attention and Psychological Skill Levels in Sedentary Men Students. Education Quarterly Reviews, 5(3), 152-158. [CrossRef]
- Yondem, S ; Yondem, Z. D; Per, M. (2017).Personality Traits and Psychological Symptoms of Music and Art Students. Journal of Education and Training Studies, 5 (7), 53-59. [CrossRef]
Table 2.
the index of internal consistency to Cronbach alpha with recurring stability of domains and total degree.
Table 2.
the index of internal consistency to Cronbach alpha with recurring stability of domains and total degree.
Table 3.
the arithmetic means and standard deviations of the level of self-confidence arranged in descending order with reference to the arithmetic means.
Table 3.
the arithmetic means and standard deviations of the level of self-confidence arranged in descending order with reference to the arithmetic means.
Table 4.
Arithmetic means and standard deviations of the level of self-confidence among Those with high musical abilities Student according to the level of gender and achievement academic according to the variables of gender and achievement.
Table 4.
Arithmetic means and standard deviations of the level of self-confidence among Those with high musical abilities Student according to the level of gender and achievement academic according to the variables of gender and achievement.
Table 5.
Bivariate multiple analysis of the effect of gender and achievement on domains.
Table 5.
Bivariate multiple analysis of the effect of gender and achievement on domains.
Table 6.
Two-way analysis of variance of the effect of gender and experience on the total score.
Table 6.
Two-way analysis of variance of the effect of gender and experience on the total score.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).