Submitted:
21 July 2023
Posted:
24 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Preface
2. Objects and methods
2.1. Research object
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. General investigation
2.2.2. Management in hospital umbilical department
2.2.3. Follow-up
2.3. Observation Indicators
2.4. Statistical Methods
3. Results
3.1. Single factor analysis
3.2. Multiple Logistic regression analysis of factors affecting the time of premature infants' umbilical shedding
4. Discuss
5. Conclusion
References
- Carter, B.S. , How Do We Regard the Preemie at the Margins of Viability? J Pediatr, 2017, 188, 5–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reis, Z.S.N. , et al. , Prematurity detection evaluating interaction between the skin of the newborn and light: proto-col for the preemie-test multicentre clinical trial in Brazilian hospitals to validate a new medical device. BMJ Open, 2019, 9, e027442. [Google Scholar]
- Knorr, A.; Giambanco, D.; Staude, M.V.; Germain, M.; Porter, C.; Serino, E.; Gauvreau, K.; DeGrazia, M. Feasibility and Safety of the Preemie Orthotic Device to Manage Deformational Plagiocephaly in Extremely Low Birth Weight Infants. Adv. Neonatal Care 2019, 19, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perumal, N. , et al. , Implications for quantifying early life growth trajectories of term-born infants using INTER-GROWTH-21st newborn size standards at birth in conjunction with World Health Organization child growth standards in the postnatal period. Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol, 2022, 36, 839–850. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, E.; Schofield, D.; Owens, C.E.; Oei, J.-L. An economic analysis of the cost of survival of micro preemies: A systematic review. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2022, 27, 101336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, D.; Benitz, W. ; COMMITTEE ON FETUS AND NEWBORN Umbilical Cord Care in the Newborn Infant. Pediatrics 2016, 138, e20162149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leante Castellanos, J.L. , et al. , [Recommendations for the care of the umbilical cord in the newborn]. An Pediatr (Engl Ed), 2019, 90, 401.e1–401e5. [Google Scholar]
- Shang, Y. and Y. Sun, Comparison of the effectiveness of different umbilical cord care in infants: A protocol for systematic review and network meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore), 2019, 98, e14440. [Google Scholar]
- Painter, K., S. Anand, and K. Philip, Omphalitis, in StatPearls. 2022, StatPearls Publishing Copyright © 2022, StatPearls Publishing LLC.: Treasure Island (FL).
- Kaplan, R.L.; Cruz, A.T.; Freedman, S.B.; Smith, K.; Freeman, J.; Lane, R.D.; Michelson, K.A.; Marble, R.D.; Middelberg, L.K.; Bergmann, K.R.; et al. Omphalitis and Concurrent Serious Bacterial Infection. PEDIATRICS 2022, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Rooy, L. and A. Johns, Management of the vulnerable baby on the postnatal ward and transitional care unit. Early Hum Dev, 2010, 86, p. 281–5. [Google Scholar]
- Rabe, H.; Diaz-Rossello, J.L.; Duley, L.; Dowswell, T. Effect of timing of umbilical cord clamping and other strategies to influence placental transfusion at preterm birth on maternal and infant outcomes. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, CD003248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draiko, C.V.; McKague, K.; Maturu, J.D.; Joyce, S. The effect of umbilical cord cleansing with chlorhexidine gel on neonatal mortality among the community births in South Sudan: a quasi-experimental study. Pan Afr. Med J. 2021, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Naggar, W.; Afifi, J.; Dorling, J.; Bodani, J.; Cieslak, Z.; Canning, R.; Ye, X.Y.; Crane, J.; Lee, S.K.; Shah, P.S. A Comparison of Strategies for Managing the Umbilical Cord at Birth in Preterm Infants. J. Pediatr. 2020, 225, 58–64e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.; Kong, D.; Li, T.; Li, A.; Tan, Y.; Fang, J.; Zhuang, X.; Lai, C.; Xu, W.; Dong, H.; et al. Efficacy and safety of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of patients with COVID-19. Clinics 2021, 76, e2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidler, A.L.; Gyte, G.M.; Rabe, H.; Díaz-Rossello, J.L.; Duley, L.; Aziz, K.; Costa-Nobre, D.T.; Davis, P.G.; Schmölzer, G.M.; Ovelman, C.; et al. Umbilical Cord Management for Newborns <34 Weeks' Gestation: A Meta-analysis. PEDIATRICS 2021, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riskin, A. and D. Bader, [Premature infant's nutrition--feeding strategies]. Harefuah, 2004, 143, 60–6, 84, 83. [Google Scholar]
- Nosan, G. and D. Paro-Panjan, Umbilical cord care: national survey, literature review and recommendations. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med, 2017, 30, 1655–1658. [Google Scholar]
- Mlodawski, J.; Mlodawska, M.; Przybysz, N.; Bielak, A.; Detka, K.; Pasiarski, M.; Rokita, W. Collection of umbilical cord blood and the risk of complications in postpartum women after natural labour in the context of the possibility of umbilical cord stem cells usage in clinical practice. Ginekol. Polska 2021, 92, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashrafi, A.H.; Levy, V.Y. Management strategies for the preemie ductus. Curr. Opin. Cardiol. 2019, 34, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couper, J. , Micro-preemie Parents' Perceptions of Trauma-Informed Developmental Neuroprotective Care and Nursing Support. Adv Neonatal Care, 2022, 22, 422–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraguela, A.; Matlalcuatzi, F.D.; Ramos. M. Mathematical modelling of thermoregulation processes for premature infants in closed convectively heated incubators. Comput. Biol. Med. 2015, 57, 159–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glass, L. and A. Valdez, Preterm Infant Incubator Humidity Levels: A Systematic Review. Adv Neonatal Care, 2021, 21, 297–307. [Google Scholar]
- Gowa, M.A.; Rakhia, A.; Bozdar, M.H.; Noonari, M.; Raza, S.J. A Quasi Experimental study to Compare Thermo-regulator blanket with conventional method (incubator) for temperature regulations in preterm, Low Birth weight neonates landing at Emergency department of a tertiary care pediatric facility. J. Pak. Med Assoc. 2022, 72, 1044–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, A.; Greenhalgh, M.; McGuire, W. Early planned removal of umbilical venous catheters to prevent infection in newborn infants. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobczak, A. , et al. , Umbilical catheters as vectors for generalized bacterial infection in premature infants regard-less of antibiotic use. J Med Microbiol, 2019, 68, 1306–1313. [Google Scholar]
| General Information | The number of cases(n) | Shedding time(d,n) | X2/H value | P value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <7d | 7~14d | >14d | ||||
| gender | 0.813 | 0.666 | ||||
| male | 72 | 2 | 33 | 37 | ||
| female | 79 | 2 | 42 | 35 | ||
| Preterm weight | 13.069 | 0.042 | ||||
| <1000g | 5 | 0 | 0 | 5 | ||
| <1500g | 31 | 0 | 11 | 20 | ||
| <2500g | 94 | 4 | 51 | 39 | ||
| ≥2500g | 21 | 0 | 13 | 8 | ||
| Gestational age | 15.993 | 0.014 | ||||
| <28w | 5 | 0 | 0 | 5 | ||
| 28~31+6w | 29 | 0 | 12 | 17 | ||
| 32~33+6w | 42 | 0 | 18 | 24 | ||
| 34~36+6w | 75 | 4 | 45 | 26 | ||
| Length of admission (age) | 9.040 | 0.011 | ||||
| <24h | 145 | 3 | 70 | 72 | ||
| ≥24h | 6 | 1 | 5 | 0 | ||
| Where the umbilical cord came off | 3.990 | 0.136 | ||||
| The court | 82 | 4 | 42 | 36 | ||
| Outside the court | 69 | 0 | 33 | 36 | ||
| Child time | 4.228 | 0.121 | ||||
| singletons | 73 | 2 | 30 | 41 | ||
| Twins and above | 78 | 2 | 45 | 31 | ||
| Whether you have NRDS | 14.651 | 0.001 | ||||
| There are | 45 | 0 | 13 | 32 | ||
| There is no | 106 | 4 | 62 | 40 | ||
| Whether it is in vitro baby | 0.062 | 0.969 | ||||
| There are | 75 | 2 | 38 | 35 | ||
| There is no | 76 | 2 | 37 | 37 | ||
| Oxygen absorption mode | 10.771 | 0.096 | ||||
| There is no | 62 | 4 | 36 | 22 | ||
| Oxygen in box | 47 | 0 | 20 | 27 | ||
| Non-invasive ventilator | 39 | 0 | 18 | 21 | ||
| Invasive ventilator | 3 | 0 | 1 | 2 | ||
| Whether to use antibiotics | 25.040 | 0.000 | ||||
| no | 82 | 4 | 52 | 26 | ||
| Usage time <7d | 31 | 0 | 15 | 16 | ||
| Use time ≧7d | 38 | 0 | 8 | 30 | ||
| Time in the warm tank | 151 | 4 | 75 | 72 | 55.752 | 0.000 |
| Inlet temperature | 151 | 4 | 70 | 72 | 14.138 | 0.001 |
| Final temperature | 151 | 4 | 70 | 72 | 2.691 | 0.260 |
| Phototherapy duration | 151 | 4 | 75 | 72 | 11.162 | 0.004 |
| Admitted leukocyte | 151 | 4 | 75 | 72 | 1.703 | 0.427 |
| Hospitalized CRP | 151 | 4 | 75 | 72 | 2.131 | 0.345 |
| Apgar1 minute degree | 16.421 | 0.003 | ||||
| normal | 116 | 4 | 67 | 45 | ||
| Mild asphyxia | 29 | 0 | 6 | 23 | ||
| Severe asphyxia | 6 | 0 | 2 | 4 | ||
| Apgar5 minutes degree | 2.648 | 0.618 | ||||
| normal | 141 | 4 | 72 | 65 | ||
| Mild asphyxia | 9 | 0 | 3 | 6 | ||
| Severe asphyxia | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | ||
| Maternal age | 6.414 | 0.378 | ||||
| 20~30 | 52 | 1 | 21 | 30 | ||
| 30~40 | 94 | 3 | 53 | 38 | ||
| 40~50 | 4 | 0 | 1 | 3 | ||
| ≥50 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | ||
| Maternal BMI rating | 4.439 | 0.350 | ||||
| Normal weight | 26 | 0 | 12 | 14 | ||
| overweight | 88 | 4 | 41 | 43 | ||
| obesity | 37 | 0 | 22 | 15 | ||
| Level of education | 10.336 | 0.035 | ||||
| Junior high school and below | 60 | 2 | 26 | 32 | ||
| High school and technical secondary school | 37 | 0 | 14 | 23 | ||
| College degree or above | 54 | 2 | 35 | 17 | ||
| Family residence | 0.619 | 0.734 | ||||
| Cities and towns | 121 | 3 | 62 | 56 | ||
| rural | 30 | 1 | 13 | 16 | ||
| Nature of Work | 6.127 | 0.190 | ||||
| brain-based | 59 | 2 | 35 | 22 | ||
| Physical strength is dominant | 21 | 0 | 7 | 14 | ||
| unemployed | 71 | 2 | 33 | 36 | ||
| Mode of delivery | 2.357 | 0.308 | ||||
| Cesarean section | 121 | 2 | 61 | 58 | ||
| Natural birth | 30 | 2 | 14 | 14 | ||
| Whether gestational diabetes is present | 4.473 | 0.107 | ||||
| There are | 52 | 1 | 32 | 19 | ||
| There is no | 99 | 3 | 43 | 53 | ||
| The presence of gestational hypertension | 4.035 | 0.133 | ||||
| There are | 41 | 1 | 15 | 25 | ||
| There is no | 110 | 3 | 60 | 47 | ||
| Whether placenta previa is present | 1.491 | 0.474 | ||||
| There are | 9 | 0 | 3 | 6 | ||
| There is no | 142 | 4 | 72 | 66 | ||
| Whether there is premature rupture of membranes | 1.233 | 0.540 | ||||
| There are | 28 | 0 | 13 | 15 | ||
| There is no | 123 | 4 | 62 | 57 | ||
| Whether there is pregnancy infection | 0.431 | 0.806 | ||||
| There are | 9 | 0 | 4 | 5 | ||
| There is no | 142 | 4 | 71 | 67 | ||
| Whether other diseases are present | 0.296 | 0.862 | ||||
| There are | 10 | 0 | 5 | 5 | ||
| There is no | 141 | 4 | 70 | 67 | ||
| Whether there is pregnancy with arrhythmia | 2.186 | 0.335 | ||||
| There are | 5 | 0 | 1 | 4 | ||
| There is no | 146 | 4 | 74 | 68 | ||
| Whether you have hypothyroidism | 2.052 | 0.358 | ||||
| There are | 17 | 1 | 6 | 10 | ||
| There is no | 134 | 3 | 69 | 62 | ||
| History of cesarean section | 1.005 | 0.605 | ||||
| There are | 15 | 0 | 9 | 6 | ||
| There is no | 136 | 4 | 66 | 66 | ||
| Independent variable | Assignment mode |
|---|---|
| Gestational age | <28w=1;28~31+6w=2;32~33+6w=3;34~36+6w=4 |
| Time of admission | <24h=1;≥24h=2 |
| Whether you have NRDS | Yes=1;no=2 |
| Preterm weight | <1000g=1;<1500g=2;<2500g=3;≥2500g=4 |
| Antibiotic use | There is no=1;<7d=2;≥7d=2 |
| Apgar score in 1 minute | normal=1;Mild asphyxia=2;Severe asphyxia=3 |
| Maternal education level | Junior high school and below=1;High school and technical secondary school=2;College degree or above=3 |
| Umbilical cord shedding time | <7d =1,7~14d =2,>14d=3 |
| Time in box | Original value entry |
| Inlet temperature | Original value entry |
| Phototherapy duration | Original value entry |
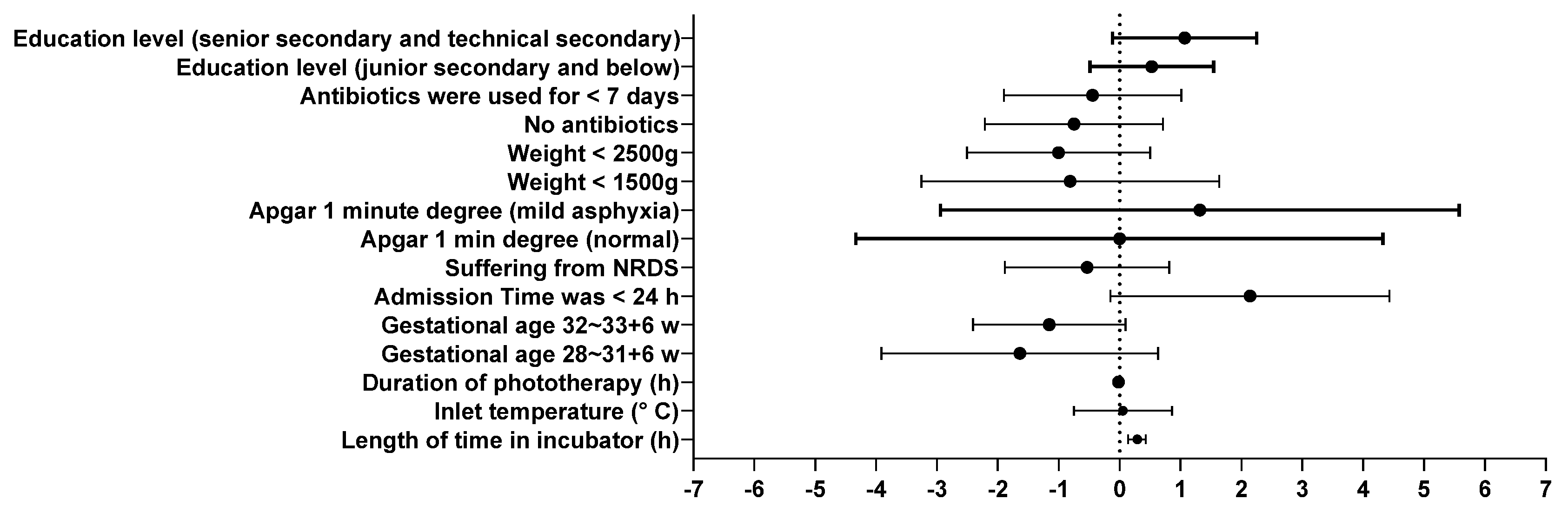
| variable | β | S.E | Wald | df | P | 95% CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| The lower limit ceiling | |||||||
| Time in the warm tank(h) | 0.018 | 0.004 | 23.581 | 1 | 0.000 | 0.138 | 0.427 |
| Inlet temperature(℃) | 0.054 | 0.411 | 0.017 | 1 | 0.895 | -0.751 | 0.859 |
| Phototherapy duration(h) | -0.017 | 0.013 | 1.746 | 1 | 0.186 | -0.043 | 0.008 |
| Gestational age | |||||||
| <28w | 13.504 | 0.000 | . | 1 | . | 13.504 | 13.504 |
| 28~31+6w | -1.638 | 1.159 | 1.997 | 1 | 0.158 | -3.911 | 0.634 |
| 32~33+6w | -1.156 | 0.638 | 3.286 | 1 | 0.070 | -2.406 | 0.094 |
| 34~36+6w | Reference class | ||||||
| Time of admission | |||||||
| <24h | 2.142 | 1.168 | 3.361 | 1 | 0.067 | -0.148 | 4.432 |
| ≥24h | Reference class | ||||||
| Whether you have NRDS | |||||||
| Yes | -0.535 | 0.689 | 0.603 | 1 | 0.438 | -1.885 | 0.815 |
| No | Reference class | ||||||
| Apgar1 minute degree | |||||||
| normal | -0.003 | 2.207 | 0.000 | 1 | 0.999 | -4.330 | 4.323 |
| Mild asphyxia | 1.317 | 2.174 | 0.367 | 1 | 0.545 | -2.944 | 5.579 |
| Severe asphyxia | Reference class | ||||||
| weight | |||||||
| <1000g | 17.251 | 0.000 | . | 1 | . | 17.251 | 17.251 |
| <1500g | -.812 | 1.247 | 0.424 | 1 | 0.515 | -3.257 | 1.632 |
| <2500g | -1.005 | 0.768 | 1.712 | 1 | 0.191 | -2.510 | 0.500 |
| ≥2500g | Reference class | ||||||
| Whether to use antibiotics | |||||||
| No | -0.749 | 0.746 | 1.007 | 1 | 0.316 | -2.212 | 0.714 |
| Service time<7d | -0.444 | 0.743 | 0.358 | 1 | 0.550 | -1.900 | 1.011 |
| Service time≥7d | Reference class | ||||||
| Level of education | |||||||
| Junior high school and below | 0.527 | 0.518 | 1.036 | 1 | 0.309 | -0.488 | 1.543 |
| High school and technical secondary school | 1.068 | 0.604 | 3.123 | 1 | 0.077 | -0.116 | 2.252 |
| College degree or above | Reference class | ||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




