Submitted:
27 July 2023
Posted:
28 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
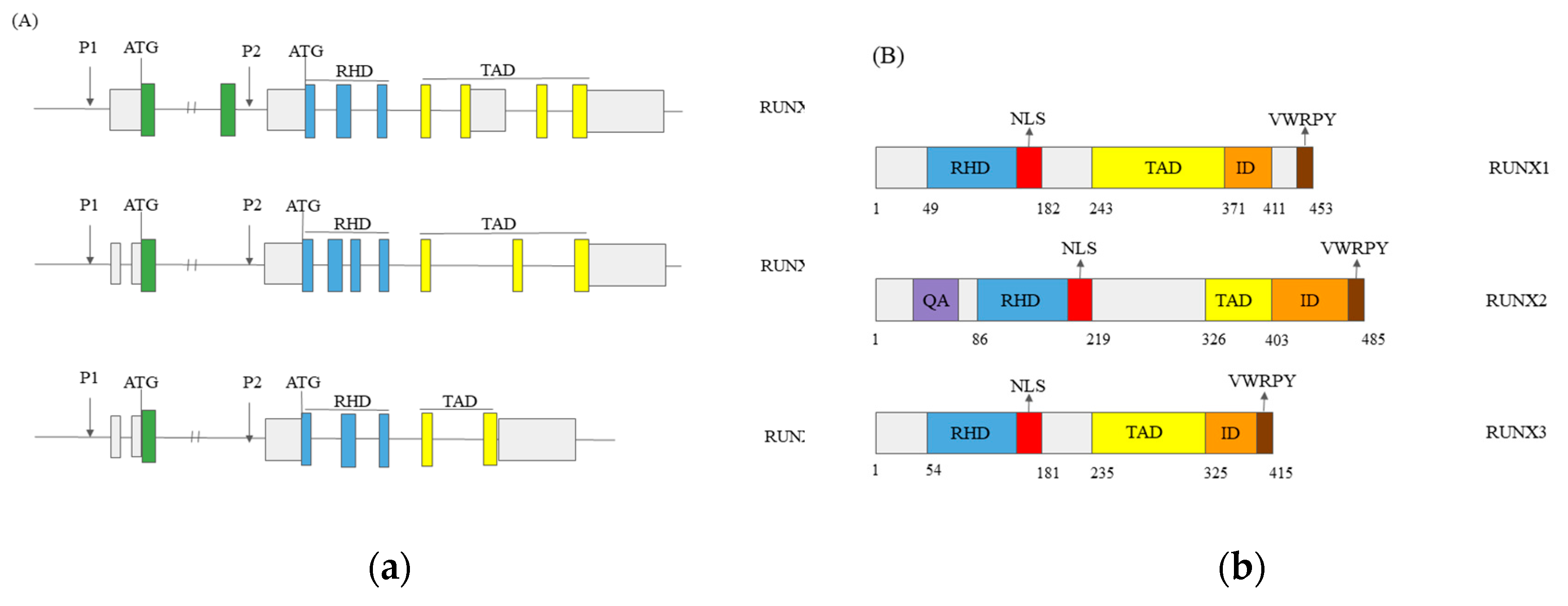
1.1. RUNX genes’ and proteins’ structure
1.2. The role of the RUNX genes in normal development
1.3. The role of RUNX genes in cancer
2. RUNX1 IN HCC
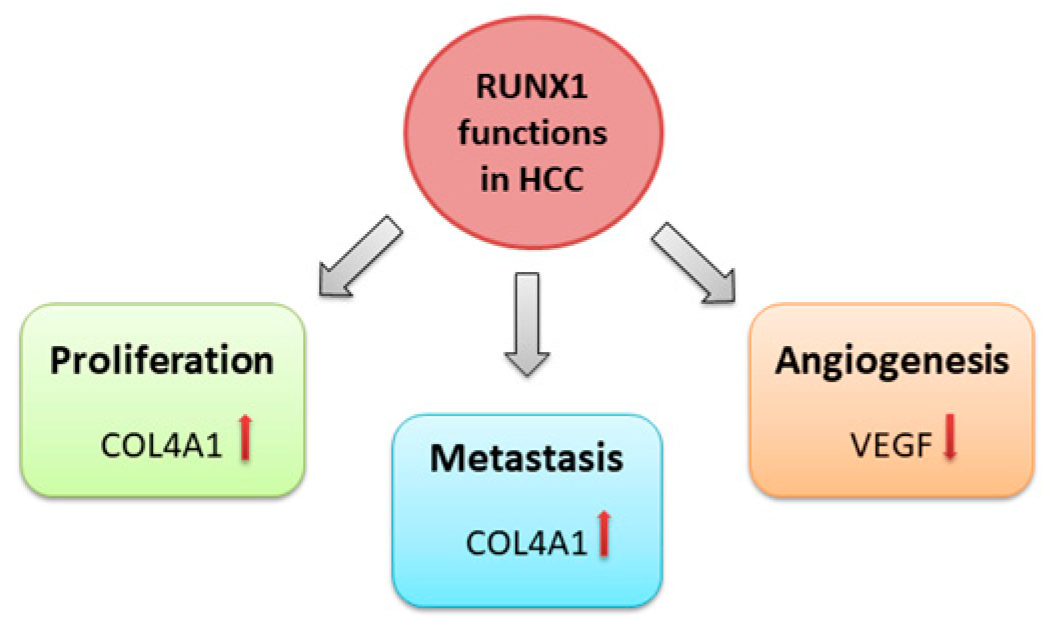
2.1. RUNX1 role in HCC
2.2. RUNX1 and miRNAs
3. RUNX2 IN HCC
3.1. General role of RUNX2 in HCC
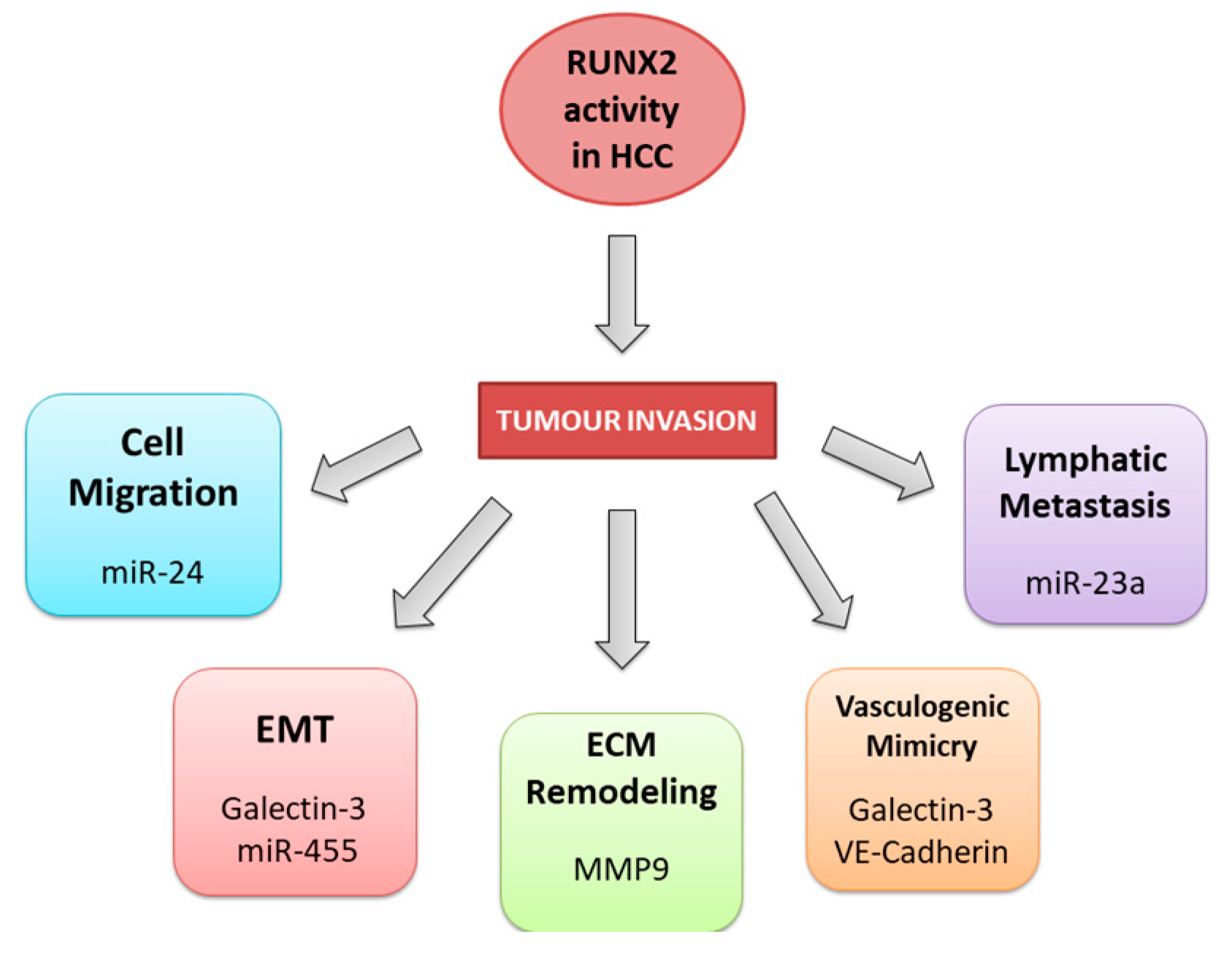
3.2. RUNX2 tumour invasion activity in HCC
3.3. RUNX2 and non-coding RNAs in HCC
4. RUNX3 IN HCC
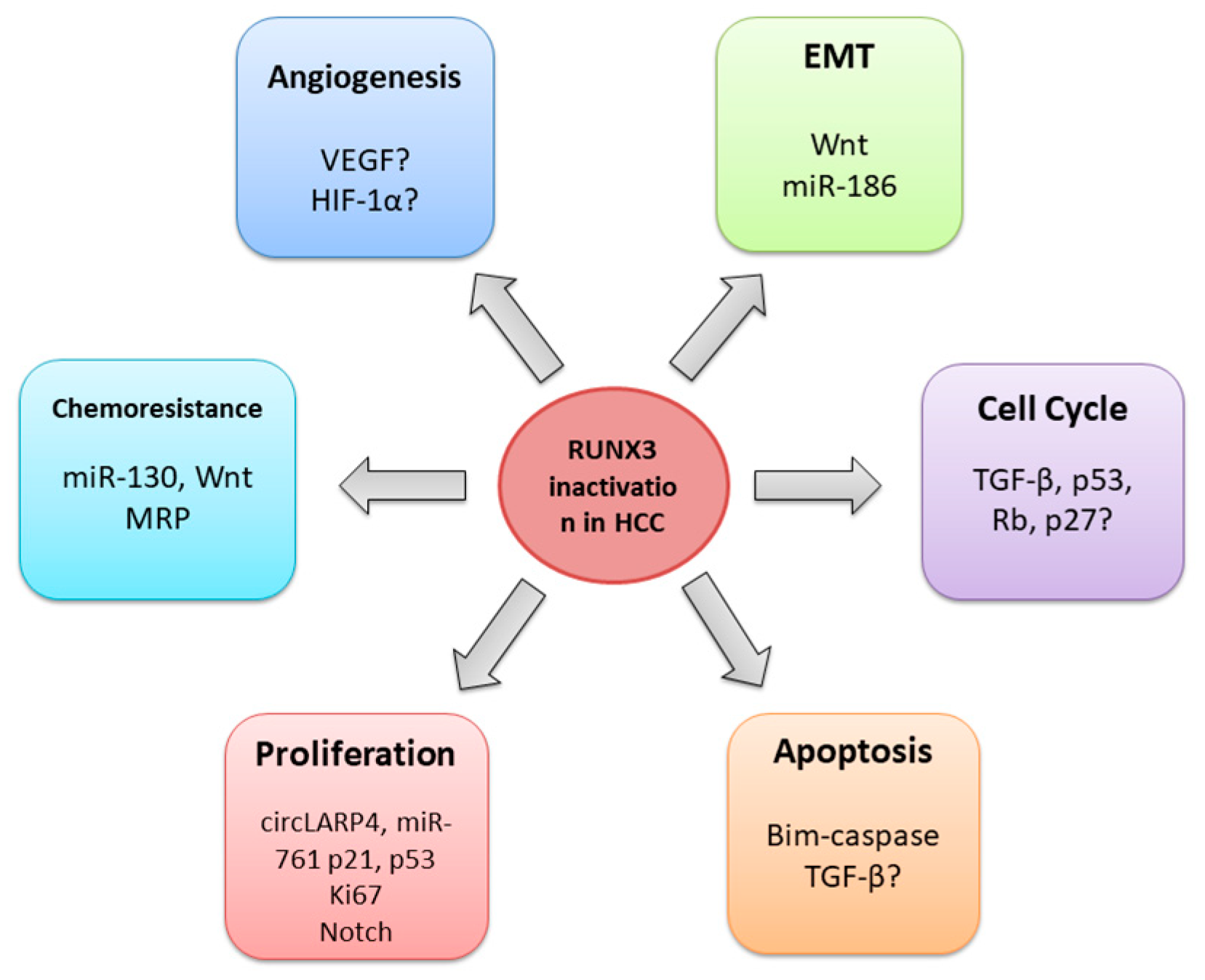
4.1. General role of RUNX3 in HCC
4.2. RUNX3 regulates cell cycle, proliferation, and apoptosis
4.3. RUNX3 in the angiogenesis regulation
4.4. RUNX3 and epithelial-mesenchymal transition
4.5. RUNX3 and chemoresistance
5. Conclusion and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HCC | Hepatocellular Carcinoma; |
| RUNX | Runt-related transcription factors;; |
| HBV | Hepatitis B Virus; |
| HCV | Hepatitis C Virus; |
| RHD | Runt homology domain; |
| miRNA | Micro ribonucleic acids; |
| lncRNAs | Long non-coding ribonucleic acids. |
References
- Asafo-Agyei, K.O.; Samant, H. Hepatocellular Carcinoma. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island (FL), 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Llovet, J.M.; Kelley, R.K.; Villanueva, A.; Singal, A.G.; Pikarsky, E.; Roayaie, S.; Lencioni, R.; Koike, K.; Zucman-Rossi, J.; Finn, R.S. Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2021, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balogh, J.; Victor, D.; Asham, E.H.; Burroughs, S.G.; Boktour, M.; Saharia, A.; Li, X.; Ghobrial, M.; Monsour, H. Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Review. JHC 2016, Volume 3, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, H.-W.; Knox, J. Hepatocellular Carcinoma in the Era of Immunotherapy. Current Problems in Cancer 2018, 42, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suresh, D.; Srinivas, A.N.; Prashant, A.; Harikumar, K.B.; Kumar, D.P. Therapeutic Options in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Comprehensive Review. Clin Exp Med 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuang, L.S.H.; Ito, K.; Ito, Y. RUNX Family: Regulation and Diversification of Roles through Interacting Proteins. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 132, 1260–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otalora-Otalora, B.; Henriquez, B.; Lopez-Kleine, L.; Rojas, A. RUNX Family: Oncogenes or Tumor Suppressors (Review). Oncol Rep 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, Y.; Bae, S.-C.; Chuang, L.S.H. The RUNX Family: Developmental Regulators in Cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2015, 15, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levanon, D.; Groner, Y. Structure and Regulated Expression of Mammalian RUNX Genes. Oncogene 2004, 23, 4211–4219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.; He, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Fang, L. RUNX Proteins as Epigenetic Modulators in Cancer. Cells 2022, 11, 3687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mevel, R.; Draper, J.E.; Lie-a-Ling, M.; Kouskoff, V.; Lacaud, G. RUNX Transcription Factors: Orchestrators of Development. Development 2019, 146, dev148296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darnell, J.E. Transcription Factors as Targets for Cancer Therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 2002, 2, 740–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sood, R.; Kamikubo, Y.; Liu, P. Role of RUNX1 in Hematological Malignancies. Blood 2017, 129, 2070–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, Y. Oncogenic Potential of the RUNX Gene Family: ‘Overview. ’ Oncogene 2004, 23, 4198–4208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.M. RUNX Family in Hypoxic Microenvironment and Angiogenesis in Cancers. Cells 2022, 11, 3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamagata, T.; Maki, K.; Mitani, K. Runx1/AML1 in Normal and Abnormal Hematopoiesis. International Journal of Hematology 2005, 82, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalle Carbonare, L.; Innamorati, G.; Valenti, M.T. Transcription Factor Runx2 and Its Application to Bone Tissue Engineering. Stem Cell Rev and Rep 2012, 8, 891–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-M.; Lee, D.-J.; Bae, S.-C.; Jung, H.-S. Abnormal Liver Differentiation and Excessive Angiogenesis in Mice Lacking Runx3. Histochem Cell Biol 2013, 139, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.W.; Stifani, S. Roles of Runx Genes in Nervous System Development. In RUNX Proteins in Development and Cancer; Groner, Y., Ito, Y., Liu, P., Neil, J.C., Speck, N.A., Van Wijnen, A., Eds.; Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Springer: Singapore, 2017; ISBN 978-981-10-3231-8. [Google Scholar]
- Guilliams, M.; Bonnardel, J.; Haest, B.; Vanderborght, B.; Wagner, C.; Remmerie, A.; Bujko, A.; Martens, L.; Thoné, T.; Browaeys, R.; et al. Spatial Proteogenomics Reveals Distinct and Evolutionarily Conserved Hepatic Macrophage Niches. Cell 2022, 185, 379–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Human All Liver Cells. Available online: https://www.livercellatlas.org/umap-humanAll.php (accessed on 3.11.22).
- Pan, S.; Sun, S.; Liu, B.; Hou, Y. Pan-Cancer Landscape of the RUNX Protein Family Reveals Their Potential as Carcinogenic Biomarkers and the Mechanisms Underlying Their Action. Journal of Translational Internal Medicine 2022, 10, 156–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Library of Medicine. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/861 (accessed on 3.18.23).
- Miyoshi, H.; Shimizu, K.; Kozu, T.; Maseki, N.; Kaneko, Y.; Ohki, M. T(8;21) Breakpoints on Chromosome 21 in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Are Clustered within a Limited Region of a Single Gene, AML1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 1991, 88, 10431–10434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, M.; Hinojosa, M.; Trombly, D.; Morin, V.; Stein, J.; Stein, G.; Javed, A.; Gutierrez, S.E. Transcriptional Auto-Regulation of RUNX1 P1 Promoter. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0149119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.-C. RUNX1 and Cancer. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Reviews on Cancer 2022, 1877, 188715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- TIMER2.0. Available online: http://timer.cistrome.org/ (accessed on 4.3.23).
- GENT2. Available online: http://gent2.appex.kr/gent2/ (accessed on 4.3.23).
- Zhu, J.; Sanborn, J.Z.; Benz, S.; Szeto, C.; Hsu, F.; Kuhn, R.M.; Karolchik, D.; Archie, J.; Lenburg, M.E.; Esserman, L.J.; et al. The UCSC Cancer Genomics Browser. Nat Methods 2009, 6, 239–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- UCSC Xena. Available online: http://xena.ucsc.edu/welcome-to-ucsc-xena/ (accessed on 4.3.23).
- Miyagawa, K.; Sakakura, C.; Nakashima, S.; Yoshikawa, T.; Kin, S.; Nakase, Y.; Ito, K.; Yamagishi, H.; Ida, H.; Yazumi, S.; et al. Down-Regulation of RUNX1, RUNX3 and CBFbeta in Hepatocellular Carcinomas in an Early Stage of Hepatocarcinogenesis. Anticancer Res 2006, 26, 3633–3643. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Xu, D.; Xue, B.; Liu, B.; Li, J.; Huang, J. Upregulation of RUNX1 Suppresses Proliferation and Migration through Repressing VEGFA Expression in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2020, 26, 1301–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Jin, H.; Hu, J.; Li, X.; Ruan, H.; Xu, H.; Wei, L.; Dong, W.; Teng, F.; Gu, J.; et al. COL4A1 Promotes the Growth and Metastasis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells by Activating FAK-Src Signaling. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 2020, 39, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takakura, N.; Watanabe, T.; Suenobu, S.; Yamada, Y.; Noda, T.; Ito, Y.; Satake, M.; Suda, T. A Role for Hematopoietic Stem Cells in Promoting Angiogenesis. Cell 2000, 102, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwatsuki, K.; Tanaka, K.; Kaneko, T.; Kazama, R.; Okamoto, S.; Nakayama, Y.; Ito, Y.; Satake, M.; Takahashi, S.-I.; Miyajima, A.; et al. Runx1 Promotes Angiogenesis by Downregulation of Insulin-like Growth Factor-Binding Protein-3. Oncogene 2005, 24, 1129–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ter Elst, A.; Ma, B.; Scherpen, F.J.G.; De Jonge, H.J.M.; Douwes, J.; Wierenga, A.T.J.; Schuringa, J.J.; Kamps, W.A.; De Bont, E.S.J.M. Repression of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression by the Runt-Related Transcription Factor 1 in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Cancer Research 2011, 71, 2761–2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuo, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Dai, S.; Liu, K.; Xia, D.; Wang, J.; Bi, L. RUNX1 Is a Promising Prognostic Biomarker and Related to Immune Infiltrates of Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts in Human Cancers. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Library of Medicine. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene?Db=gene&Cmd=DetailsSearch&Term=80215 (accessed on 3.18.23).
- Yan, P.-H.; Wang, L.; Chen, H.; Yu, F.-Q.; Guo, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, W.-J.; Bai, Y.-L. LncRNA RUNX1-IT1 Inhibits Proliferation and Promotes Apoptosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Regulating MAPK Pathways. European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2019, 23, 8287–8294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Wang, L.; Chen, T.; Shi, Y.; Yao, B.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, Q.; Liu, R.; Niu, Y.; et al. LncRNA RUNX1-IT1 Which Is Downregulated by Hypoxia-Driven Histone Deacetylase 3 Represses Proliferation and Cancer Stem-like Properties in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Cell Death Dis 2020, 11, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivacqua, A.; De Marco, P.; Santolla, M.F.; Cirillo, F.; Pellegrino, M.; Panno, M.L.; Abonante, S.; Maggiolini, M. Estrogenic Gper Signaling Regulates Mir144 Expression in Cancer Cells and Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts (Cafs). Oncotarget 2015, 6, 16573–16587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Li, F.; Xu, L.; Liu, X.; Zhu, X.; Gao, W.; Shen, X. TLR2 Agonist Promotes Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cell Polarization via Runx1 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. International Immunopharmacology 2022, 111, 109168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, T.P.; Später, D.; Taketo, M.M.; Birchmeier, W.; Hartmann, C. Canonical Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Prevents Osteoblasts from Differentiating into Chondrocytes. Developmental Cell 2005, 8, 727–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-W.; Yasui, N.; Ito, K.; Huang, G.; Fujii, M.; Hanai, J.; Nogami, H.; Ochi, T.; Miyazono, K.; Ito, Y. A RUNX2/PEBP2 AA/ CBFA1 Mutation Displaying Impaired Transactivation and Smad Interaction in Cleidocranial Dysplasia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2000, 97, 10549–10554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Yang, H.; Chai, J.; Xing, L. RUNX2 as a Promising Therapeutic Target for Malignant Tumors. CMAR 2021, Volume 13, 2539–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, G.; Zheng, X.; Ji, X. LncRNA HAND2-AS1 Overexpression Inhibits Cancer Cell Proliferation in Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Downregulating RUNX2 Expression. J Clin Lab Anal 2021, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yu, W.; Huang, T.; Zhu, Y.; Huang, C. RUNX2 Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell Migration and Invasion by Upregulating MMP9 Expression. Oncology Reports 2016, 36, 2777–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Sun, B.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, Q.; Liang, X.; Dong, X.; Zhao, N. Correction: Cao, Z., et al. The Expression and Functional Significance of Runx2 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Its Role in Vasculogenic Mimicry and Epithelial—Mesenchymal Transition. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 500. IJMS 2020, 22, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emma, M.R.; Iovanna, J.L.; Bachvarov, D.; Puleio, R.; Loria, G.R.; Augello, G.; Candido, S.; Libra, M.; Gulino, A.; Cancila, V.; et al. NUPR1, a New Target in Liver Cancer: Implication in Controlling Cell Growth, Migration, Invasion and Sorafenib Resistance. Cell Death Dis 2016, 7, e2269–e2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Li, L.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, M.; Liao, D.; Wang, G.; Qin, G.; Xu, R.; Kang, T. CBX4 Suppresses Metastasis via Recruitment of HDAC3 to the Runx2 Promoter in Colorectal Carcinoma. Cancer Research 2016, 76, 7277–7289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sase, T.; Suzuki, T.; Miura, K.; Shiiba, K.; Sato, I.; Nakamura, Y.; Takagi, K.; Onodera, Y.; Miki, Y.; Watanabe, M.; et al. Runt-Related Transcription Factor 2 in Human Colon Carcinoma: A Potent Prognostic Factor Associated with Estrogen Receptor. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 131, 2284–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komori, T. Runx2, A Multifunctional Transcription Factor in Skeletal Development. J. Cell. Biochem. 2002, 87, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratap, J.; Javed, A.; Languino, L.R.; Van Wijnen, A.J.; Stein, J.L.; Stein, G.S.; Lian, J.B. The Runx2 Osteogenic Transcription Factor Regulates Matrix Metalloproteinase 9 in Bone Metastatic Cancer Cells and Controls Cell Invasion. Molecular and Cellular Biology 2005, 25, 8581–8591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boregowda, R.K.; Olabisi, O.O.; Abushahba, W.; Jeong, B.-S.; Haenssen, K.K.; Chen, W.; Chekmareva, M.; Lasfar, A.; Foran, D.J.; Goydos, J.S.; et al. RUNX2 Is Overexpressed in Melanoma Cells and Mediates Their Migration and Invasion. Cancer Letters 2014, 348, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-Q.; Du, X.; Li, D.-M.; Kong, P.-Z.; Sun, Y.; Liu, P.-F.; Wang, Q.-S.; Feng, Y.-M. ITGBL1 Is a Runx2 Transcriptional Target and Promotes Breast Cancer Bone Metastasis by Activating the TGFβ Signaling Pathway. Cancer Research 2015, 75, 3302–3313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Gendi, S.M.; Mostafa, M.F. Runx2 Expression as a Potential Prognostic Marker in Invasive Ductal Breast Carcinoma. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2016, 22, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baniwal, S.K.; Khalid, O.; Gabet, Y.; Shah, R.R.; Purcell, D.J.; Mav, D.; Kohn-Gabet, A.E.; Shi, Y.; Coetzee, G.A.; Frenkel, B. Runx2 Transcriptome of Prostate Cancer Cells: Insights into Invasiveness and Bone Metastasis. Mol Cancer 2010, 9, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Sun, B.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, X.; Gu, Q.; Dong, X.; Zhao, N.; Liu, P.; Liu, Y. Doxycycline as an Inhibitor of the Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition and Vasculogenic Mimicry in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Molecular Cancer Therapeutics 2014, 13, 3107–3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Zhao, N.; Zhao, X.; Gu, Q.; Zhang, S.; Che, N.; Wang, X.; Du, J.; Liu, Y.; Sun, B. Expression and Functional Significance of Twist1 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Its Role in Vasculogenic Mimicry. Hepatology 2010, 51, 545–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funasaka, T.; Raz, A.; Nangia-Makker, P. Galectin-3 in Angiogenesis and Metastasis. Glycobiology 2014, 24, 886–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vestweber, D. VE-Cadherin: The Major Endothelial Adhesion Molecule Controlling Cellular Junctions and Blood Vessel Formation. ATVB 2008, 28, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Wang, L.; Chen, T.; Liu, R.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, L. ZNF521 Which Is Downregulated by MiR-802 Suppresses Malignant Progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma through Regulating Runx2 Expression. J. Cancer 2020, 11, 5831–5839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, J.; Shentu, Y.; Xie, X. MicroRNA-455 Regulates Migration and Invasion of Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Targeting Runx2. Oncology Reports 2016, 36, 3325–3332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.-J.; Ping, C.; Tang, J.; Zhang, W. MicroRNA-455 Suppresses Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer through Targeting ZEB1: The Role of MiRNA-455 in NSCLC. Cell Biol Int 2016, 40, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, J.; Wang, S.; Han, D.; Dong, W.; Xie, C.; Guo, H. MicroRNA-455 Inhibits Proliferation and Invasion of Colorectal Cancer by Targeting RAF Proto-Oncogene Serine/Threonine-Protein Kinase. Tumor Biol. 2015, 36, 1313–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, C.-H.; Shrestha, S.; Yang, C.-D.; Chang, N.-W.; Lin, Y.-L.; Liao, K.-W.; Huang, W.-C.; Sun, T.-H.; Tu, S.-J.; Lee, W.-H.; et al. MiRTarBase Update 2018: A Resource for Experimentally Validated MicroRNA-Target Interactions. Nucleic Acids Research 2018, 46, D296–D302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Zhang, S.; Wang, B.; Huang, J.; Lu, W.W.; Chen, D. Runx2 and MicroRNA Regulation in Bone and Cartilage Diseases: Runx2 and MiRNAs in Bone and Cartilage. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 2016, 1383, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-Y.; Chen, C.-L.; Hu, Y.-C.; Chi, Y.; Huang, Y.-H.; Su, C.-W.; Jeng, W.-J.; Liang, Y.-J.; Wu, J.-C. High Expression of MicroRNA-196a Is Associated with Progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Younger Patients. Cancers 2019, 11, 1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wai, P.Y.; Kuo, P.C. The Role of Osteopontin in Tumor Metastasis. Journal of Surgical Research 2004, 121, 228–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, C.; Chen, X.; Huang, H.; Li, W.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Y. Upregulation of OGT by Caveolin-1 Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell Migration and Invasion. Cell Biology International 2021, 45, 2251–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Liu, Y.; Yu, P.; Qu, J.; Guo, Y.; Li, W.; Wang, S.; Zhang, J. MiR-23a Transcriptional Activated by Runx2 Increases Metastatic Potential of Mouse Hepatoma Cell via Directly Targeting Mgat3. Sci Rep 2018, 8, 7366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, W.; Qiao, Y.; Tang, X.; Ma, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Weng, W.; Pan, Q.; Yu, Y.; Sun, F.; et al. Tumor Suppressor Long Non-Coding RNA, MT1DP Is Negatively Regulated by YAP and Runx2 to Inhibit FoxA1 in Liver Cancer Cells. Cellular Signalling 2014, 26, 2961–2968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lund, A.H.; Van Lohuizen, M. RUNX: A Trilogy of Cancer Genes. Cancer Cell 2002, 1, 213–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.-L.; Ito, K.; Sakakura, C.; Fukamachi, H.; Inoue, K.; Chi, X.-Z.; Lee, K.-Y.; Nomura, S.; Lee, C.-W.; Han, S.-B.; et al. Causal Relationship between the Loss of RUNX3 Expression and Gastric Cancer. Cell 2002, 109, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, A.; Arnold, C.N.; Tassone, P.; Chang, D.K.; Niedzwiecki, D.; Dowell, J.M.; Wasserman, L.; Compton, C.; Mayer, R.J.; Bertagnolli, M.M.; et al. Epigenetic Inactivation OfRUNX3 in Microsatellite Unstable Sporadic Colon Cancers. Int. J. Cancer 2004, 112, 754–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, G.H.; Lee, S.; Lee, H.J.; Hwang, K.S. Aberrant CpG Island Hypermethylation of Multiple Genes in Prostate Cancer and Prostatic Intraepithelial Neoplasia: CpG Island Methylation in Prostate Cancer and PIN. J. Pathol. 2004, 202, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, Q.C.; Raja, E.; Salto-Tellez, M.; Liu, Q.; Ito, K.; Inoue, M.; Putti, T.C.; Loh, M.; Ko, T.K.; Huang, C.; et al. RUNX3 Is Frequently Inactivated by Dual Mechanisms of Protein Mislocalization and Promoter Hypermethylation in Breast Cancer. Cancer Research 2006, 66, 6512–6520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-S.; Lee, J.-W.; Jang, J.-W.; Chi, X.-Z.; Kim, J.-H.; Li, Y.-H.; Kim, M.-K.; Kim, D.-M.; Choi, B.-S.; Kim, E.-G.; et al. Runx3 Inactivation Is a Crucial Early Event in the Development of Lung Adenocarcinoma. Cancer Cell 2013, 24, 603–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, G.; Cheng, Y.; Martinka, M.; Li, G. Prognostic Significance of RUNX3 Expression in Human Melanoma: RUNX3 in Melanoma Prognosis. Cancer 2011, 117, 2719–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nevadunsky, N.S.; Barbieri, J.S.; Kwong, J.; Merritt, M.A.; Welch, W.R.; Berkowitz, R.S.; Mok, S.C. RUNX3 Protein Is Overexpressed in Human Epithelial Ovarian Cancer. Gynecologic Oncology 2009, 112, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsunematsu, T.; Kudo, Y.; Iizuka, S.; Ogawa, I.; Fujita, T.; Kurihara, H.; Abiko, Y.; Takata, T. RUNX3 Has an Oncogenic Role in Head and Neck Cancer. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whittle, M.C.; Izeradjene, K.; Rani, P.G.; Feng, L.; Carlson, M.A.; DelGiorno, K.E.; Wood, L.D.; Goggins, M.; Hruban, R.H.; Chang, A.E.; et al. RUNX3 Controls a Metastatic Switch in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Cell 2015, 161, 1345–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Sundaram, S.; Rayala, S.K.; Venkatraman, G. UnPAKing RUNX3 Functions–Both Sides of the Coin. Small GTPases 2017, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, Y.; Shiraha, H.; Nishina, S.; Tanaka, S.; Matsubara, M.; Horiguchi, S.; Iwamuro, M.; Takaoka, N.; Uemura, M.; Kuwaki, K.; et al. Loss of Runt-Related Transcription Factor 3 Expression Leads Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells to Escape Apoptosis. BMC Cancer 2011, 11, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, T.; Nomoto, S.; Koshikawa, K.; Fujii, T.; Sakai, M.; Nishikawa, Y.; Inoue, S.; Takeda, S.; Kaneko, T.; Nakao, A. Decreased Expression and Frequent Allelic Inactivation of the RUNX3 Gene at 1p36 in Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Liver Int 2005, 25, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.-H.; Liu, W.-W. Hemizygous Deletion and Hypermethylation of RUNX3 Gene in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. WJG 2004, 10, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; He, H.; Zhang, X.; Guo, W.; Wang, Y. RUNX3 Promoter Methylation Is Associated with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Risk: A Meta-Analysis. Cancer Investigation 2015, 33, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Ye, Z.; Zou, Z.; Xiao, G.; Luo, G.; Yang, H. Clinicopathological Significance of RUNX3 Gene Hypermethylation in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Tumor Biol. 2014, 35, 10333–10340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-shaarawy, F.; Abo ElAzm, M.M.; Mohamed, R.H.; Radwan, M.I.; Abo-Elmatty, D.M.; Mehanna, E.T. Relation of the Methylation State of RUNX3 and P16 Gene Promoters with Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Egyptian Patients. Egypt J Med Hum Genet 2022, 23, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, Y.; Zhai, F.; Zhang, L.; Cui, L. RUNX3 Regulates Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell Metastasis via Targeting MiR-186/E-Cadherin/EMT Pathway. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 61475–61486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, G.; Zhang, C.; Feng, M.; Liu, W.; Xie, H.; Qin, Q.; Zhao, E.; Wan, L. Methylation Analysis of P16, SLIT2, SCARA5, and Runx3 Genes in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Medicine 2017, 96, e8279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Bendary, M.; Nour, D.; Arafa, M.; Neamatallah, M. Methylation of Tumour Suppressor Genes RUNX3, RASSF1A and E-Cadherin in HCV-Related Liver Cirrhosis and Hepatocellular Carcinoma. British Journal of Biomedical Science 2020, 77, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Liu, X.; Bai, J.; Pei, D.; Zheng, J. The Emerging Role of RUNX3 in Cancer Metastasis (Review). Oncology Reports 2016, 35, 1227–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Chen, Y.; Wu, K.-C.; Liu, J.; Zhao, Y.-Q.; Pan, Y.-L.; Du, R.; Zheng, G.-R.; Xiong, Y.-M.; Xu, H.-L.; et al. RUNX3 Directly Interacts with Intracellular Domain of Notch1 and Suppresses Notch Signaling in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Experimental Cell Research 2010, 316, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, X.-Z.; Lee, J.-W.; Lee, Y.-S.; Park, I.Y.; Ito, Y.; Bae, S.-C. Runx3 Plays a Critical Role in Restriction-Point and Defense against Cellular Transformation. Oncogene 2017, 36, 6884–6894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiraha, H.; Nishina, S.; Yamamoto, K. Loss of Runt-Related Transcription Factor 3 Causes Development and Progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Cell. Biochem. 2011, 112, 745–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, S.; Shiraha, H.; Nakanishi, Y.; Nishina, S.-I.; Matsubara, M.; Horiguchi, S.; Takaoka, N.; Iwamuro, M.; Kataoka, J.; Kuwaki, K.; et al. Runt-Related Transcription Factor 3 Reverses Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 131, 2537–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataoka, J.; Shiraha, H.; Horiguchi, S.; Sawahara, H.; Uchida, D.; Nagahara, T.; Iwamuro, M.; Morimoto, H.; Takeuchi, Y.; Kuwaki, K.; et al. Loss of Runt-Related Transcription Factor 3 Induces Resistance to 5-Fluorouracil and Cisplatin in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Oncology Reports 2016, 35, 2576–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Shen, C.; Luo, Y.; Xia, L.; Xue, F.; Xia, Q.; Zhang, J. Upregulated MiR-130a Increases Drug Resistance by Regulating RUNX3 and Wnt Signaling in Cisplatin-Treated HCC Cell. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 2012, 425, 468–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Gao, N.; Shen, Y.; Cen, J. Hypermethylation Downregulates Runx3 Gene Expression and Its Restoration Suppresses Gastric Epithelial Cell Growth by Inducing P27 and Caspase3 in Human Gastric Cancer. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2010, 25, 823–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, D.; Gong, W.; Oh, S.C.; Li, Q.; Kim, W.D.; Wang, L.; Le, X.; Yao, J.; Wu, T.T.; Huang, S.; et al. Loss of RUNX3 Expression Significantly Affects the Clinical Outcome of Gastric Cancer Patients and Its Restoration Causes Drastic Suppression of Tumor Growth and Metastasis. Cancer Research 2005, 65, 4809–4816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, X.-Z.; Yang, J.-O.; Lee, K.-Y.; Ito, K.; Sakakura, C.; Li, Q.-L.; Kim, H.-R.; Cha, E.-J.; Lee, Y.-H.; Kaneda, A.; et al. RUNX3 Suppresses Gastric Epithelial Cell Growth by Inducing P21 WAF1 / Cip1 Expression in Cooperation with Transforming Growth Factor β-Activated SMAD. Molecular and Cellular Biology 2005, 25, 8097–8107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-W.; Kim, D.-M.; Jang, J.-W.; Park, T.-G.; Song, S.-H.; Lee, Y.-S.; Chi, X.-Z.; Park, I.Y.; Hyun, J.-W.; Ito, Y.; et al. RUNX3 Regulates Cell Cycle-Dependent Chromatin Dynamics by Functioning as a Pioneer Factor of the Restriction-Point. Nat Commun 2019, 10, 1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, Y.; Miyazono, K. RUNX Transcription Factors as Key Targets of TGF-β Superfamily Signaling. Current Opinion in Genetics & Development 2003, 13, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yano, T.; Ito, K.; Fukamachi, H.; Chi, X.-Z.; Wee, H.-J.; Inoue, K.; Ida, H.; Bouillet, P.; Strasser, A.; Bae, S.-C.; et al. The RUNX3 Tumor Suppressor Upregulates Bim in Gastric Epithelial Cells Undergoing Transforming Growth Factorβ-Induced Apoptosis. Molecular and Cellular Biology 2006, 26, 4474–4488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, S.-C.; Choi, J.-K. Tumor Suppressor Activity of RUNX3. Oncogene 2004, 23, 4336–4340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, S.K.; Sullivan, A.J.; Van Wijnen, A.J.; Stein, J.L.; Stein, G.S.; Lian, J.B. Integration of Runx and Smad Regulatory Signals at Transcriptionally Active Subnuclear Sites. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2002, 99, 8048–8053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, S.; Shen, W.; Liu, L. Senescence and Cancer. Cancer Transl Med 2018, 4, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zuo, X.; Pu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Han, G.; Zhang, L.; Wu, J.; Wang, X. Circ LARP 4 Induces Cellular Senescence through Regulating MiR-761/ RUNX 3/P53/P21 Signaling in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Sci 2019, 110, 568–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sweeney, K.; Cameron, E.R.; Blyth, K. Complex Interplay between the RUNX Transcription Factors and Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway in Cancer: A Tango in the Night. Mol Cells 2020, 43, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wei, W.; Cheng, N.; Wang, K.; Li, B.; Jiang, X.; Sun, S. Hepatitis C Virus-Induced up-Regulation of MicroRNA-155 Promotes Hepatocarcinogenesis by Activating Wnt Signaling. Hepatology 2012, 56, 1631–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinhart, Z.; Angers, S. Wnt Signaling in Development and Tissue Homeostasis. Development 2018, 145, dev146589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, K.; Chuang, L.S.H.; Ito, T.; Chang, T.L.; Fukamachi, H.; Salto–Tellez, M.; Ito, Y. Loss of Runx3 Is a Key Event in Inducing Precancerous State of the Stomach. Gastroenterology 2011, 140, 1536–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, K.; Lim, A.C.-B.; Salto-Tellez, M.; Motoda, L.; Osato, M.; Chuang, L.S.H.; Lee, C.W.L.; Voon, D.C.-C.; Koo, J.K.W.; Wang, H.; et al. RUNX3 Attenuates β-Catenin/T Cell Factors in Intestinal Tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell 2008, 14, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovannini, C.; Fornari, F.; Piscaglia, F.; Gramantieri, L. Notch Signaling Regulation in HCC: From Hepatitis Virus to Non-Coding RNAs. Cells 2021, 10, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.; Hyeon, J.; Park, C.-K. Notchl and Notch4 Are Markers for Poor Prognosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Hepatobiliary & Pancreatic Diseases International 2013, 12, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishina, S.-I. Restored Expression of the Tumor Suppressor Gene RUNX3 Reduces Cancer Stem Cells in Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Suppressing Jagged1-Notch Signaling. Oncol Rep 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, M.Y.; Kou, B.X.; Fu, Z.; Wei, F.L.; Dou, S.S.; Chen, D.X.; Liu, X.N. [Sorafenib regulates vascular endothelial growth factor by runt-related transcription factor-3 to inhibit angiogenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma]. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi 2022, 30, 770–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Bae, S.C.; Kim, K.W.; Lee, Y.M. RUNX3 Inhibits Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1α Protein Stability by Interacting with Prolyl Hydroxylases in Gastric Cancer Cells. Oncogene 2014, 33, 1458–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galle, P.R.; Forner, A.; Llovet, J.M.; Mazzaferro, V.; Piscaglia, F.; Raoul, J.-L.; Schirmacher, P.; Vilgrain, V. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Journal of Hepatology 2018, 69, 182–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamouille, S.; Xu, J.; Derynck, R. Molecular Mechanisms of Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2014, 15, 178–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voon, D.C.-C.; Wang, H.; Koo, J.K.W.; Nguyen, T.A.P.; Hor, Y.T.; Chu, Y.-S.; Ito, K.; Fukamachi, H.; Chan, S.L.; Thiery, J.P.; et al. Runx3 Protects Gastric Epithelial Cells Against Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition-Induced Cellular Plasticity and Tumorigenicity. Stem Cells 2012, 30, 2088–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loh, C.-Y.; Chai, J.; Tang, T.; Wong, W.; Sethi, G.; Shanmugam, M.; Chong, P.; Looi, C. The E-Cadherin and N-Cadherin Switch in Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition: Signaling, Therapeutic Implications, and Challenges. Cells 2019, 8, 1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Jung, Y.D.; Choi, Y.S.; Lee, Y.M. Targeting of RUNX3 by MiR-130a and MiR-495 Cooperatively Increases Cell Proliferation and Tumor Angiogenesis in Gastric Cancer Cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 33269–33278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wang, X.; Liu, W. MicroRNA-130a-3p Promotes the Proliferation and Inhibits the Apoptosis of Cervical Cancer Cells via Negative Regulation of RUNX3. Mol Med Rep 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Gene | miRNA(s) or lncRNA(s) | References |
| RUNX1 | miR-632 | Sun et al., 2020 |
| miR-144 | Vivacqua et al., 2015 | |
| RUNX2 | miR-455 | Qin et al., 2016 |
| miR-196 | Wang et al., 2019 | |
| miR-24 | Wang et al., 2021 | |
| miR-23a | Huang et al., 2018 | |
| lncRNA HAND2 antisense RNA 1 (HAND2-AS1) | Jing et al., 2021 | |
| lncRNAmetallothionein 1D, pseudogene (MT1DP) | Yu et al., 2014 | |
| RUNX3 | miR-186 | Chen et al., 2019 |
| miR-130 | Gou et al., 2017 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





