1. Introduction
Human metapneumovirus (HMPV) causes respiratory infections in infants and young children (< 5 years old) [
1,
2]. These infections are like those caused by the human respiratory syncytial virus (HRSV), ranging from upper respiratory distress to bronchiolitis and pneumonia among infants, young children, older adults, and immunocompromised hosts [
3,
4,
5]. Individuals infected with HMPV do not acquire lifelong immunity to the virus, and reinfection occurs [
6,
7,
8].
HMPV is a non-segmented single-stranded RNA virus belonging to the family Paramyxoviridae. The HMPV genome is approximately 13 kb long and consists of eight genes that encode nine proteins (N, P, M, F, M2-1, M2-2, SH, G, and L) [
9,
10]. Depending on the genetic variation in membrane glycoproteins F and G, HMPV can be classified into five genotypes (A1, A2a, A2b, B1, and B2) [
9,
11]. HMPV genotypes co-circulate during the epidemic season; however, no specific dominant genotypes have been identified [
12,
13], and the association between the HMPV genotype and disease severity is unclear [
14].
Non-pharmaceutical interventions were implemented in response to the global COVID-19 pandemic, and these interventions may affect the circulation of other seasonal respiratory viruses [
15,
16]. The unusual occurrence of HMPV has been reported in many countries [
8,
17]. HMPV is generally prevalent during winter and spring in the Northern Hemisphere [
18]. Similarly, In South Korea, HMPV was prevalent from late winter to spring prior to the COVID-19 pandemic but was not detected during the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020 or 2021, and an out-of-season HMPV outbreak was observed in the fall of 2022.
Understanding the relationship between the irregular occurrence of HMPV and the virus’ characteristics is necessary to predict and develop preventive measures against future HMPV epidemic. Therefore, we conducted a comprehensive whole-genome analysis of HMPV before and after the COVID-19 pandemic.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Surveillance and sample collection
We participated in a national surveillance network called the Korea Influenza and Respiratory Virus Surveillance System (KINRESS) to monitor Acute Respiratory Infections (ARIs) in South Korea. Throat or nasal swabs were collected from outpatients with ARIs throughout the year from collaborating hospitals in the Gwangju area. These samples were analyzed using real-time RT-PCR to test for respiratory viruses, including HMPVs. A total of 427 HMPV-positive samples were collected from the Gwangju area during 2018–2022.
2.2. Whole genome sequencing
Among the HMPV-positive samples collected before and after the COVID-19 pandemic, 24 with a high viral load were randomly selected. Viral RNA was extracted using a QIAamp Viral RNA Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. A panel was developed using Ion AmpliSeq On-Demand Panel (ThermoFisher Scientific, Carlsbad, CA) technology for use on the Ion Torrent platform (ThermoFisher Scientific, Carlsbad, CA). The customized panel was designed to obtain coverage of the entire HMPV genome using combinations of 100 and 125 primers divided into two sets (pools) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. Reverse transcription was performed using a SuperScript VILO cDNA Synthesis Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Carlsbad, CA) following the manufacturer’s recommendations. For library preparation, an Ion Ampliseq Library 2.0 Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Carlsbad, CA) was used according to the manufacturer’s protocol. The automated Ion Chef (ThermoFisher Scientific, Carlsbad, CA) instrument prepared templates from the 25 μL sample pool using Ion 510/520/530 Chef Kits and Ion 530 Chips that were sequenced using the Ion S5 XL sequencer (ThermoFisher Scientific, Carlsbad, CA). The sequencing reads were mapped and aligned using the torrent-mapping alignment program. After the initial mapping, a variant call was performed using the Torrent Variant Caller.
2.3. Phylogenetic analyses
For the phylogenetic analyses, 53 reference strains were selected from GenBank (
Table 1). Multiple sequence alignment was performed using the MUSCLE algorithm in MEGA X software. Phylogenetic trees were constructed using the Maximum Likelihood (ML) method with the General Time Reversible model in MEGA X software. The reliability of the branching order was assessed by performing 1,000 bootstrap replicates.
3. Results
3.1. Epidemiology of HMPV
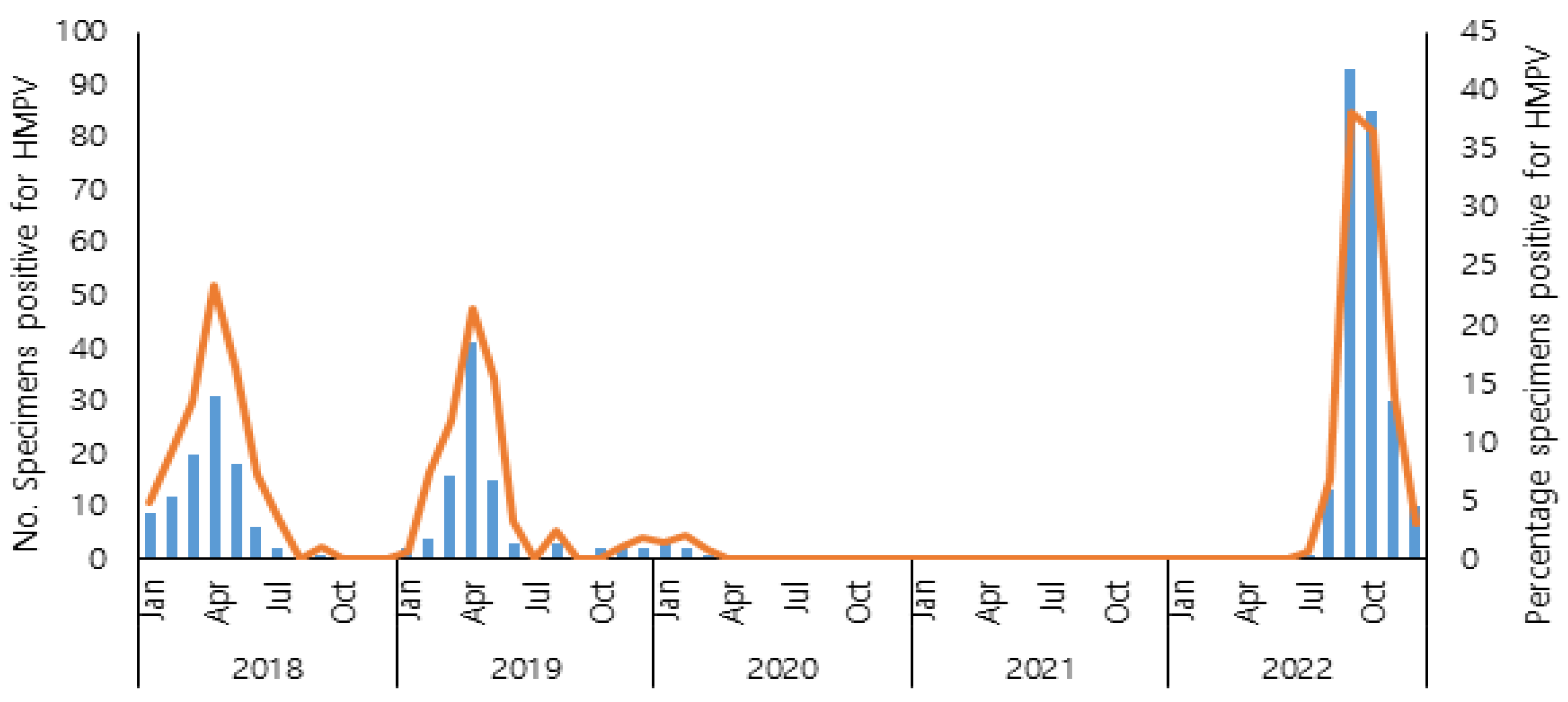
Before the COVID-19 pandemic, human metapneumovirus exhibited a progressive increase from January, reaching its peak in April, followed by a subsequent decline during the summer months. During the COVID-19 pandemic, HMPV infections rarely occurred in 2020, and HMPV was not detected in 2021, coinciding with the implementation of non-pharmacological interventions against COVID-19. In 2022, according to the results of the KINRESS in the Gwangju area, HMPV reappeared in July, and the number of HMPV-positive cases increased in September and October. The HMPV positive rate was significantly higher than that before the COVID-19 pandemic. The seasonal distribution of HMPV infections from 2018 to 2022 is shown in
Figure 1. There was a higher detection rate of HMPV in children aged 6 to 10 years old in 2022 than before the COVID-19 pandemic (
Table 2).
3.2. Phylogenetic analysis of HMPV Whole genome sequences
We analyzed 24 whole-genome sequences and 53 reference sequences obtained from GenBank to determine their subtypes. Of the 24 whole-genome sequences, 16 were obtained from strains isolated before the COVID-19 pandemic, and the remaining eight were obtained from strains isolated during the pandemic. Before the pandemic, 15 strains were identified as A2b2 and one as B2. Among the eight strains identified during the pandemic, five were A2b1, and three were B2. A1, A2a, and B1 were not detected in any of the samples analyzed in this study.
Before the COVID-19 pandemic, A2b2 was the predominant circulating strain. However, the HMPV strains that reappeared during the pandemic were identified as A2b1 and B2. The 2022 A2b1 sequences were observed in a monophyletic clade, with one sequence that circulated in the USA in 2016. However, the 2022 B2 sequences were distributed between two closely related strains, one from Australia in 2020 and the other from the USA in 2019, without clade formation.
Figure 2. The phylogenetic tree was constructed based on 77 whole HMPV genome sequences. The tree was created using the maximum likelihood method with a GTR+G+I substitution model and tested with 1000 bootstrap replicates. In the tree, HMPV samples before the pandemic were depicted as triangles. Among them, samples containing a 111-nt duplication in the G gene were indicated with an orange triangles. HMPV samples after the pandemic were represented by green circles. All sequences from this study have been registered in the SRA (Sequence Read Archive) database(accession number: PRJNA987724). Biosample accession numbers of all strains are indicated in parentheses.
4. Discussion
The non-pharmaceutical interventions implemented to prevent COVID-19, such as mandatory mask-wearing, social distancing, and travel restrictions, have affected the prevalence of respiratory viruses [
15,
16]. Social distancing measures were implemented in South Korea following the first COVID-19 outbreak in January 2020 and relaxed by April 2022. Changes in the prevalence of respiratory viruses were also observed during this period. According to the KIRNESS results, PIV3, which did not occur in 2020, re-emerged in the fall of 2021 [
19]. In 2022, HMPV reappeared in the fall, which is typically a non-epidemic season, and the magnitude of the epidemic was larger than that before the COVID-19 pandemic.
This study conducted a whole-genome analysis to investigate the molecular genetic characteristics of HMPV before and after the COVID-19 pandemic. Most HMPV strains that re-emerged in 2022 were of the A2b subtype. Recent studies have suggested classifying A2b into A2b1 and A2b2 based on the presence of 111-nt or 180-nt duplications in the G gene [
10]. In 2022, the predominant circulating A2b subtype did not have a G gene duplication, whereas, before the COVID-19 pandemic, the A2b subtype had a 111-nt duplication in the G gene. According to Nao et al., A2b2 was predominant before COVID-19, and A2b1 was responsible for HMPV’s re-emergence during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Although some researchers have suggested that the A2b2 subtype is the most virulent, the variation in virulence among HMPV subtypes remains unclear [
20,
21]. In this study, the A2b1 subtype was responsible for the re-emergence in 2022, and the scale of occurrence was larger than that before the COVID-19 pandemic when the A2b2 subtype was prevalent. This could be due to lower herd immunity to the HMPV virus resulting from reduced exposure during social distancing measures rather than differences in virulence between the subtypes. The clustering of A2b during the pre-COVID-19 and COVID-19 pandemic periods suggests that the re-emergence of HMPV during the pandemic period may not have been a local outbreak.
Additionally, HMPV mainly affects children under five years of age [
1,
17]. However, during the COVID-19 pandemic, there was a significant increase in the age group of 6–10 years affected by HMPV. An atypical age distribution of acute respiratory viruses during the COVID-19 pandemic has also been observed in RSV [
22,
23]. This atypical age distribution might be associated with reduced immunity owing to the lack of exposure to HMPV during the COVID-19 pandemic.
In this study, no significant differences were observed in the prevalence of Subtype B2 between before and after the COVID-19 pandemic. However, securing a larger sample size is recommended for future studies. Additionally, it would be beneficial to analyze the clinical symptoms of HMPV in the future. Since its discovery in 2001, research on HMPV has primarily focused on genetic variations in the F and G genes [
9,
10]. Partial analysis of the F and G genes may limit our understanding of overall virus evolution by overlooking variations in other regions [
24]. Whole-genome analysis can overcome these limitations. Therefore, the results of this study, which conducted a whole-genome analysis to investigate the epidemiological trends of HMPV before and after the COVID-19 pandemic, are significant for obtaining genetic information on HMPV in South Korea.
Overall, due to the social distancing measures implemented to prevent the spread of COVID-19, there was a lack of exposure to HMPV, resulting in lower natural immunity to HMPV. With the relaxation of social distancing measures in 2022, HMPV exposure during this period led to an irregular HMPV epidemic in South Korea. This indicates that the COVID-19 pandemic may have impacted the age and subtype distribution of HMPV, emphasizing the importance of social distancing measures. Strengthening herd immunity is thought to help prevent future epidemics. Therefore, continuous monitoring of HMPV is required for vaccine development and distribution.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.J.C., S.-H.K. and Y.-S.C.; Methodology, S.J.C., Formal Analysis, S.J.C. and J.P.; Investigation, H.L.,Y.-U.L.,J.M., S.P., J.-S.P. and C.L., Writing- original draft, S.J.C.; Project administration, S.-H.K.; Writing-review& editing, S.-H.K. and Y.-S.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The dataset generated for this study can be found online. All sequences from this study have been registered in the SRA (Sequence Read Archive) database (accession number: PRJNA987724).
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our gratitude to the cooperative hospitals in Gwangju who assisted us in monitoring respiratory viral pathogens.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Van den Hoogen, B.G.; de Jong, J.C.; Groen, J.; Kuiken, T.; de Groot, R.; Fouchier, R.A.; Osterhaus, A.D. A newly discovered human pneumovirus isolated from young children with respiratory tract disease. Nature medicine 2001, 7, 719–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebihara, T.; Endo, R.; Kikuta, H.; Ishiguro, N.; Ishiko, H.; Hara, M.; Takahashi, Y.; Kobayashi, K. Human metapneumovirus infection in Japanese children. Journal of clinical microbiology 2004, 42, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, G.; Gonzalez, R.; Guo, L.; Wu, C.; Wu, J.; Vernet, G.; Paranhos-Baccalà, G.; Wang, J.; Hung, T. Large-scale seroprevalence analysis of human metapneumovirus and human respiratory syncytial virus infections in Beijing, China. Virol J 2011, 8, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuster, J.E.; Williams, J.V. Human Metapneumovirus. Microbiol Spectr 2014, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, W.; Liu, D.; Chen, D.; Tan, W.; Qiu, S.; Xu, D.; Li, X.; Liu, T.; Zhou, R. Epidemiological and clinical features of human metapneumovirus in hospitalised paediatric patients with acute respiratory illness: a cross-sectional study in Southern China, from 2013 to 2016. BMJ Open 2018, 8, e019308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Hoogen, B.G.; van Doornum, G.J.; Fockens, J.C.; Cornelissen, J.J.; Beyer, W.E.; Groot, R.d.; Osterhaus, A.D.; Fouchier, R.A. Prevalence and clinical symptoms of human metapneumovirus infection in hospitalized patients. The Journal of infectious diseases 2003, 188, 1571–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falsey, A.R.; Erdman, D.; Anderson, L.J.; Walsh, E.E. Human metapneumovirus infections in young and elderly adults. J Infect Dis 2003, 187, 785–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, D.A.; Sikazwe, C.T.; Minney-Smith, C.A.; Ernst, T.; Moore, H.C.; Nicol, M.P.; Smith, D.W.; Levy, A.; Blyth, C.C. An Unusual Resurgence of Human Metapneumovirus in Western Australia Following the Reduction of Non-Pharmaceutical Interventions to Prevent SARS-CoV-2 Transmission. Viruses 2022, 14, 2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Hoogen, B.G.; Herfst, S.; Sprong, L.; Cane, P.A.; Forleo-Neto, E.; de Swart, R.L.; Osterhaus, A.D.; Fouchier, R.A. Antigenic and genetic variability of human metapneumoviruses. Emerg Infect Dis 2004, 10, 658–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nao, N.; Saikusa, M.; Sato, K.; Sekizuka, T.; Usuku, S.; Tanaka, N.; Nishimura, H.; Takeda, M. Recent Molecular Evolution of Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV): Subdivision of HMPV A2b Strains. Microorganisms 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huck, B.; Scharf, G.; Neumann-Haefelin, D.; Puppe, W.; Weigl, J.; Falcone, V. Novel human metapneumovirus sublineage. Emerg Infect Dis 2006, 12, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiche, J.; Jacobsen, S.; Neubauer, K.; Hafemann, S.; Nitsche, A.; Milde, J.; Wolff, T.; Schweiger, B. Human metapneumovirus: insights from a ten-year molecular and epidemiological analysis in Germany. PLoS One 2014, 9, e88342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oketch, J.W.; Kamau, E.; Otieno, G.P.; Otieno, J.R.; Agoti, C.N.; Nokes, D.J. Human metapneumovirus prevalence and patterns of subgroup persistence identified through surveillance of pediatric pneumonia hospital admissions in coastal Kenya, 2007–2016. BMC infectious diseases 2019, 19, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cong, S.; Wang, C.; Wei, T.; Xie, Z.; Huang, Y.; Tan, J.; Chen, A.; Ma, F.; Zheng, L. Human metapneumovirus in hospitalized children with acute respiratory tract infections in Beijing, China. Infection, Genetics and Evolution 2022, 106, 105386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agca, H.; Akalin, H.; Saglik, I.; Hacimustafaoglu, M.; Celebi, S.; Ener, B. Changing epidemiology of influenza and other respiratory viruses in the first year of COVID-19 pandemic. J Infect Public Health 2021, 14, 1186–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, S.J.; Winn, A.K.; Budd, A.P.; Prill, M.M.; Steel, J.; Midgley, C.M.; Kniss, K.; Burns, E.; Rowe, T.; Foust, A.; et al. Changes in Influenza and Other Respiratory Virus Activity During the COVID-19 Pandemic - United States, 2020-2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 2021, 70, 1013–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, M.; Cohen, H.; Nemet, I.; Atari, N.; Kliker, L.; Fratty, I.S.; Bucris, E.; Geva, M.; Mendelson, E.; Zuckerman, N. Human metapneumovirus prevalence during 2019-2021 in Israel is influenced by the COVID-19 pandemic. International Journal of Infectious Diseases 2022, 120, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, S.; Mohakud, N.K.; Pena, L.; Kumar, S. Human metapneumovirus: review of an important respiratory pathogen. International journal of infectious diseases 2014, 25, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Kim, S.H.; Cho, S.J.; Lee, Y.U.; Lee, K.; Lee, Y.P.; Seo, J.; Chung, Y.S. Genetic Analysis of HPIV3 That Emerged during the SARS-CoV-2 Pandemic in Gwangju, South Korea. Viruses 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saikusa, M.; Nao, N.; Kawakami, C.; Usuku, S.; Sasao, T.; Toyozawa, T.; Takeda, M.; Okubo, I. A novel 111-nucleotide duplication in the G gene of human metapneumovirus. Microbiol Immunol 2017, 61, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wei, T.; Ma, F.; Wang, H.; Guo, J.; Chen, A.; Huang, Y.; Xie, Z.; Zheng, L. Epidemiology and genotypic diversity of human metapneumovirus in paediatric patients with acute respiratory infection in Beijing, China. Virol J 2021, 18, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casalegno, J.S.; Ploin, D.; Cantais, A.; Masson, E.; Bard, E.; Valette, M.; Fanget, R.; Targe, S.C.; Myar-Dury, A.F.; Doret-Dion, M.; et al. Characteristics of the delayed respiratory syncytial virus epidemic, 2020/2021, Rhône Loire, France. Euro Surveill 2021, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.Y.; Wu, T.H.; Fang, Y.P.; Chang, J.C.; Wang, H.C.; Lin, S.J.; Mai, C.H.; Chang, Y.C.; Chou, T.Y. Delayed respiratory syncytial virus outbreak in 2020 in Taiwan was correlated with two novel RSV-A genotype ON1 variants. Influenza Other Respir Viruses 2022, 16, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groen, K.; van Nieuwkoop, S.; Meijer, A.; van der Veer, B.; van Kampen, J.J.; Fraaij, P.L.; Fouchier, R.A.; van den Hoogen, B.G. Emergence and Potential Extinction of Genetic Lineages of Human Metapneumovirus between 2005 and 2021. Mbio 2022, e02280–02222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions, or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).