Submitted:
31 July 2023
Posted:
02 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. General description of mee tree
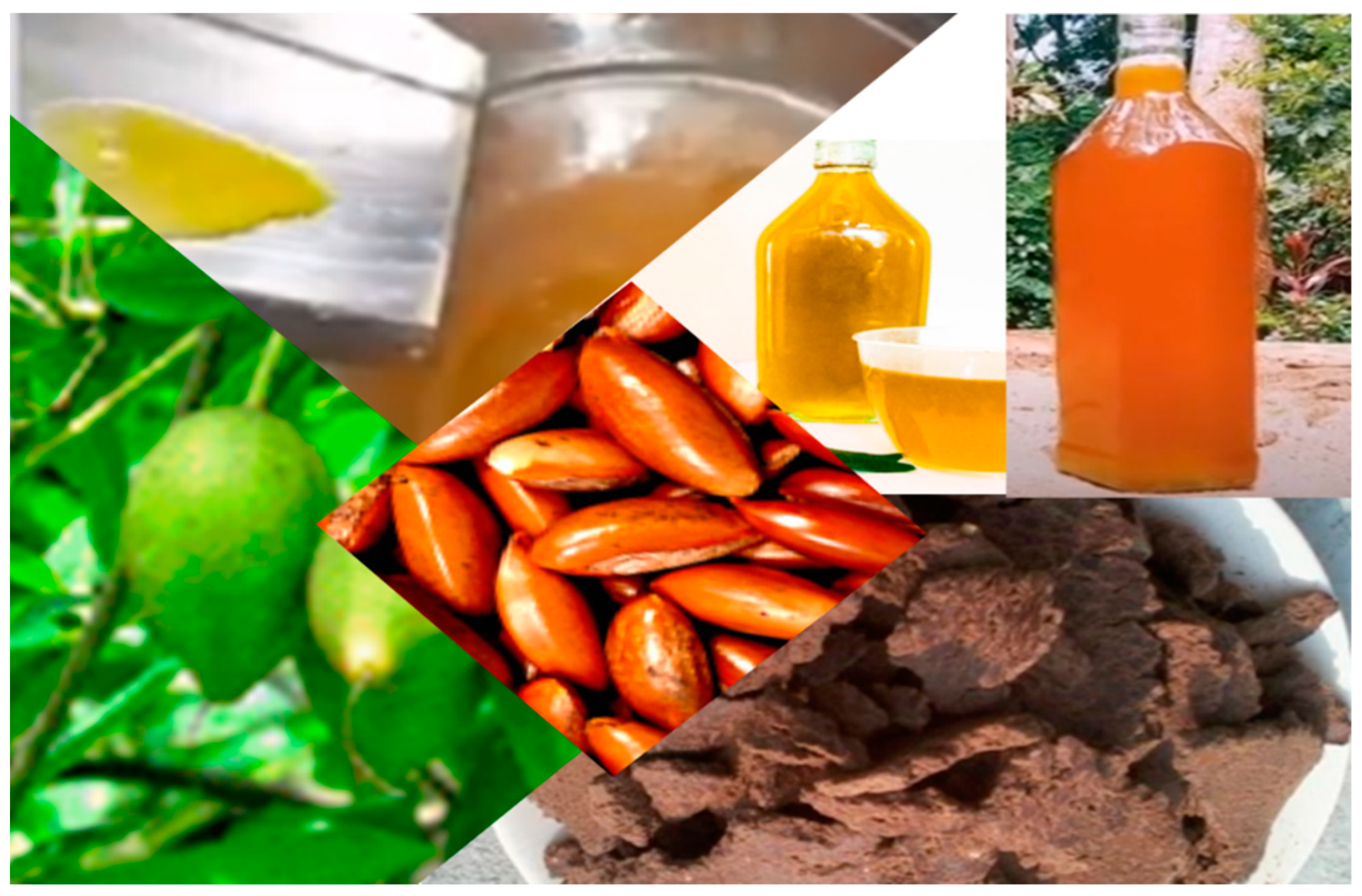
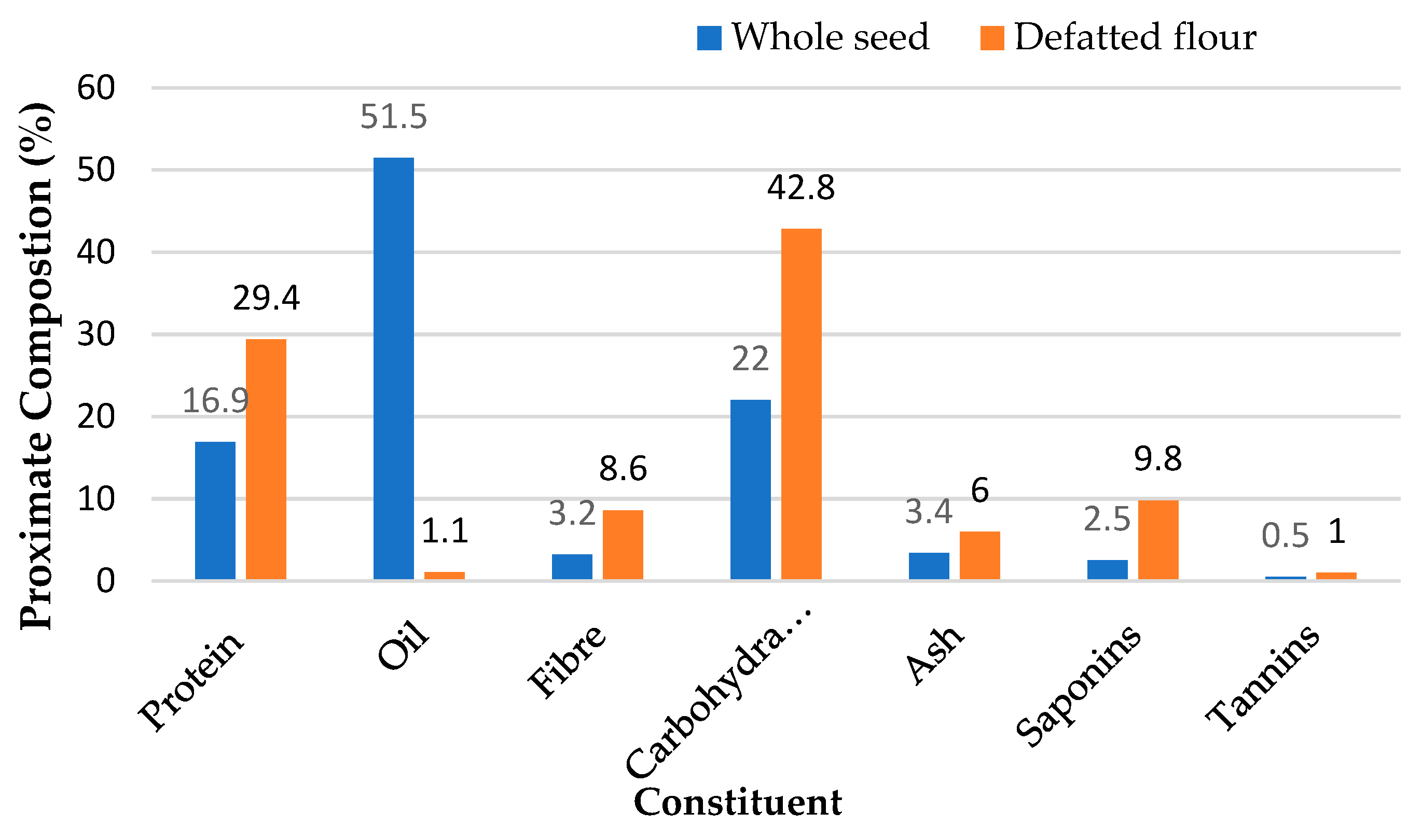
3. Value-added products from mee (Madhuca longifolia) fruits and seeds
3.1. Mee seed fat
3.2. Defatted Mee seed cake
4. Physical, biological, and chemical properties of mee seed fat
4.1. Physico-chemical properties of Mee seed fat
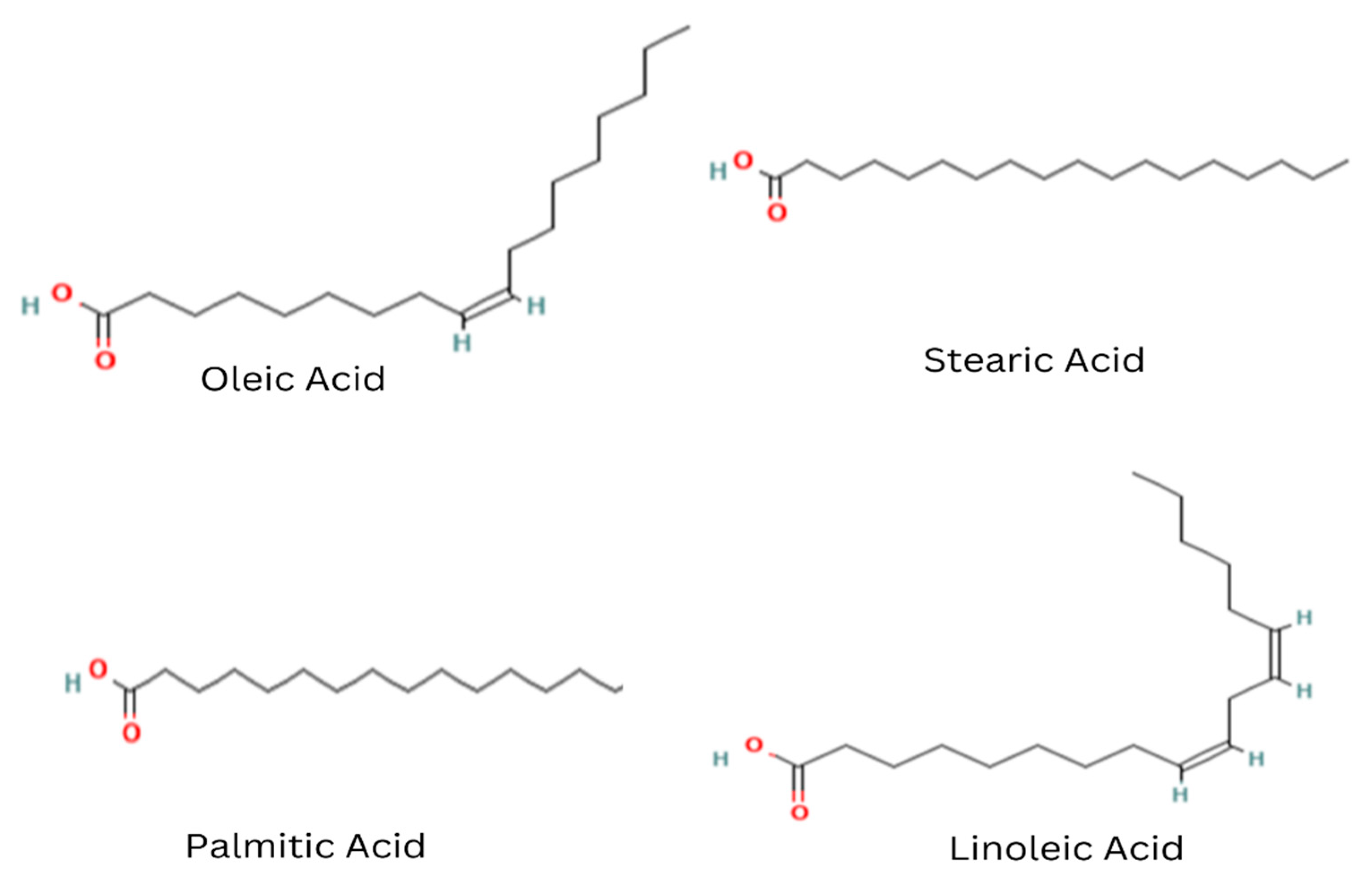
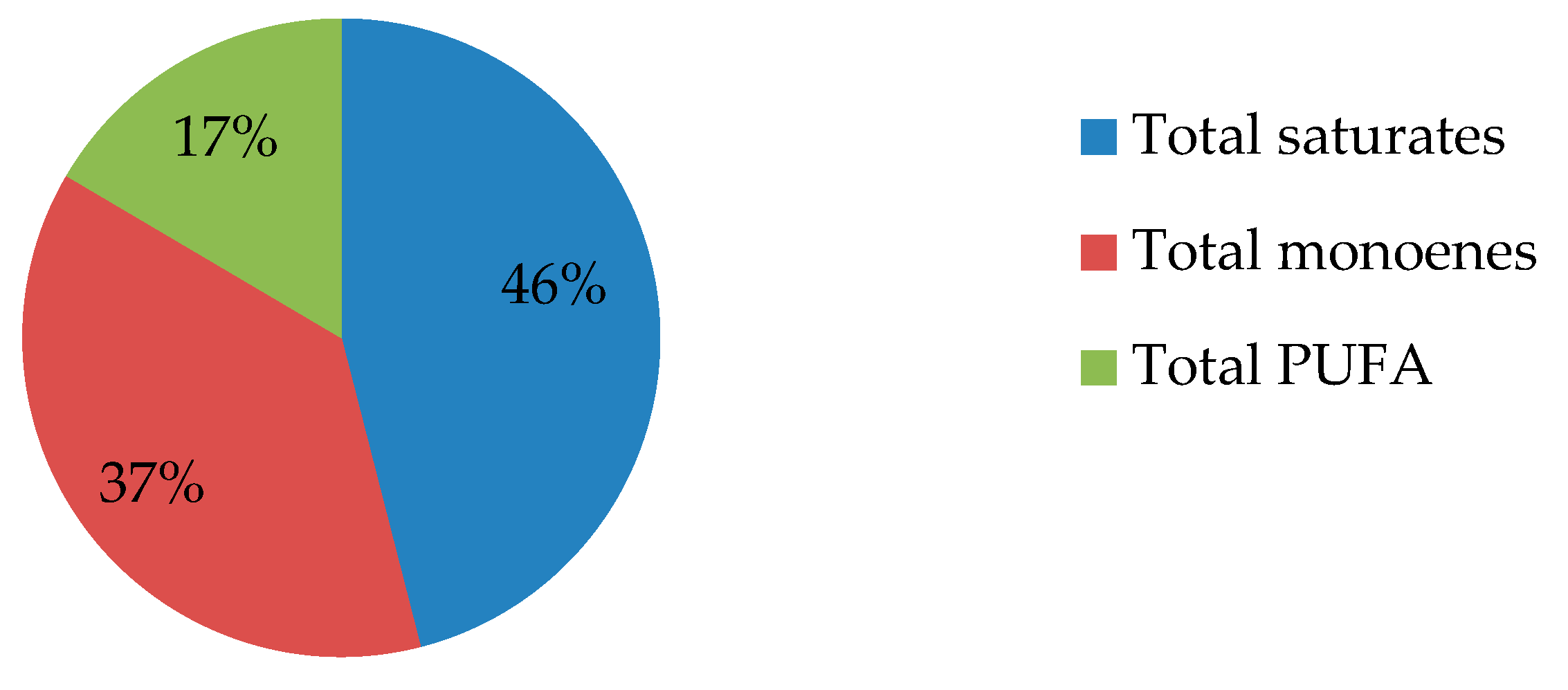
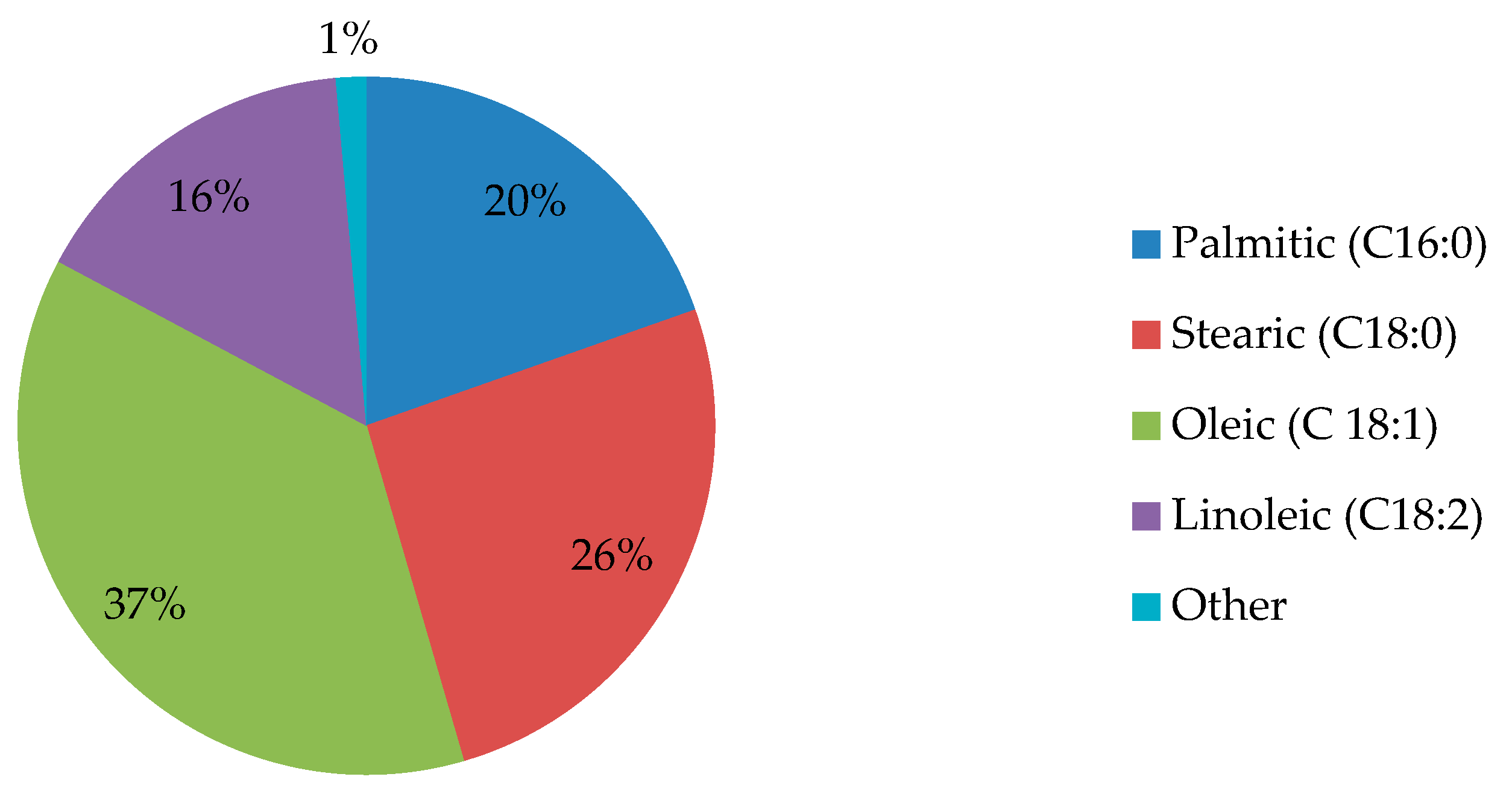
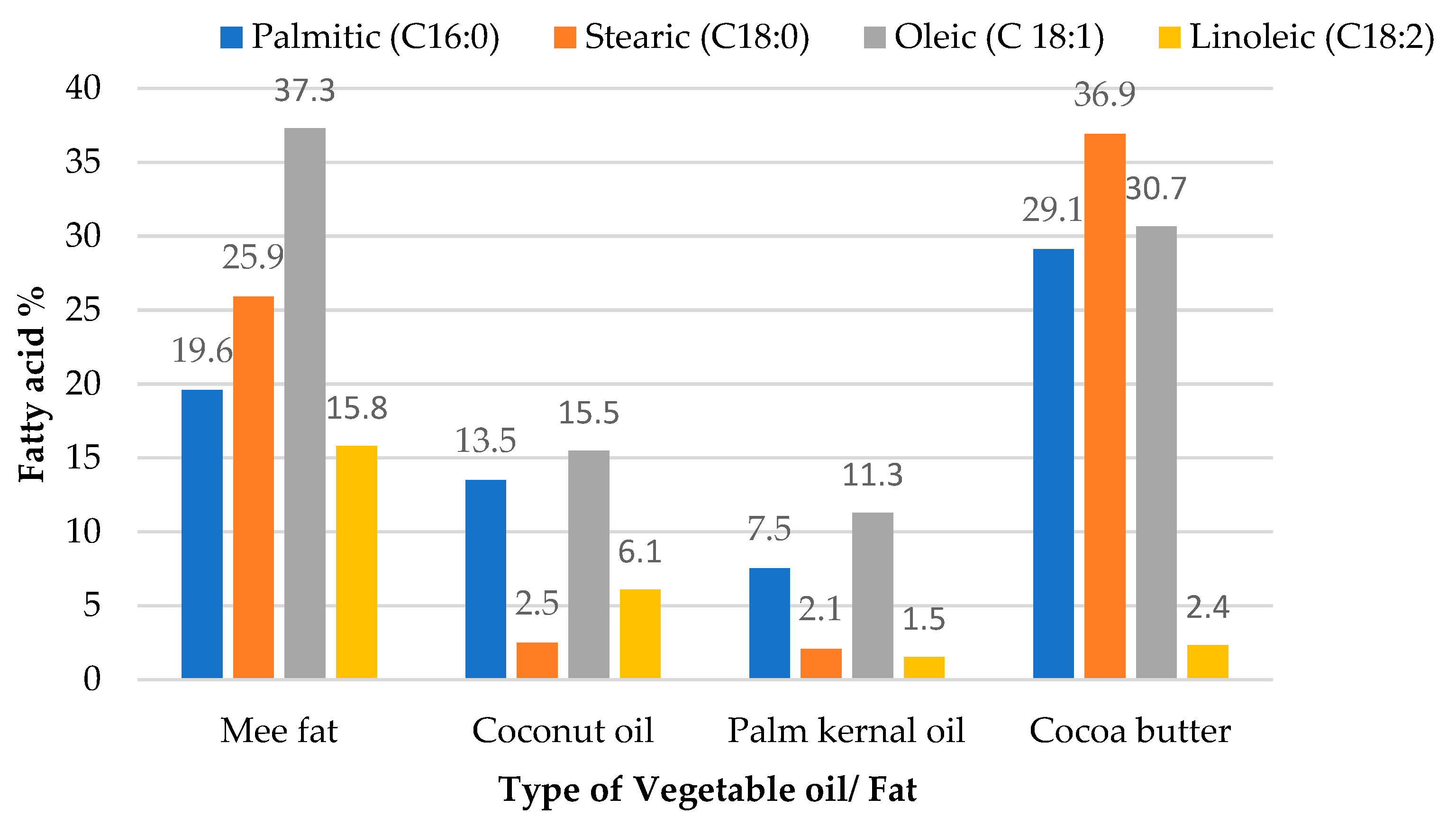
4.2. Fat Content and Fatty Acid Profile of Mee seed fat
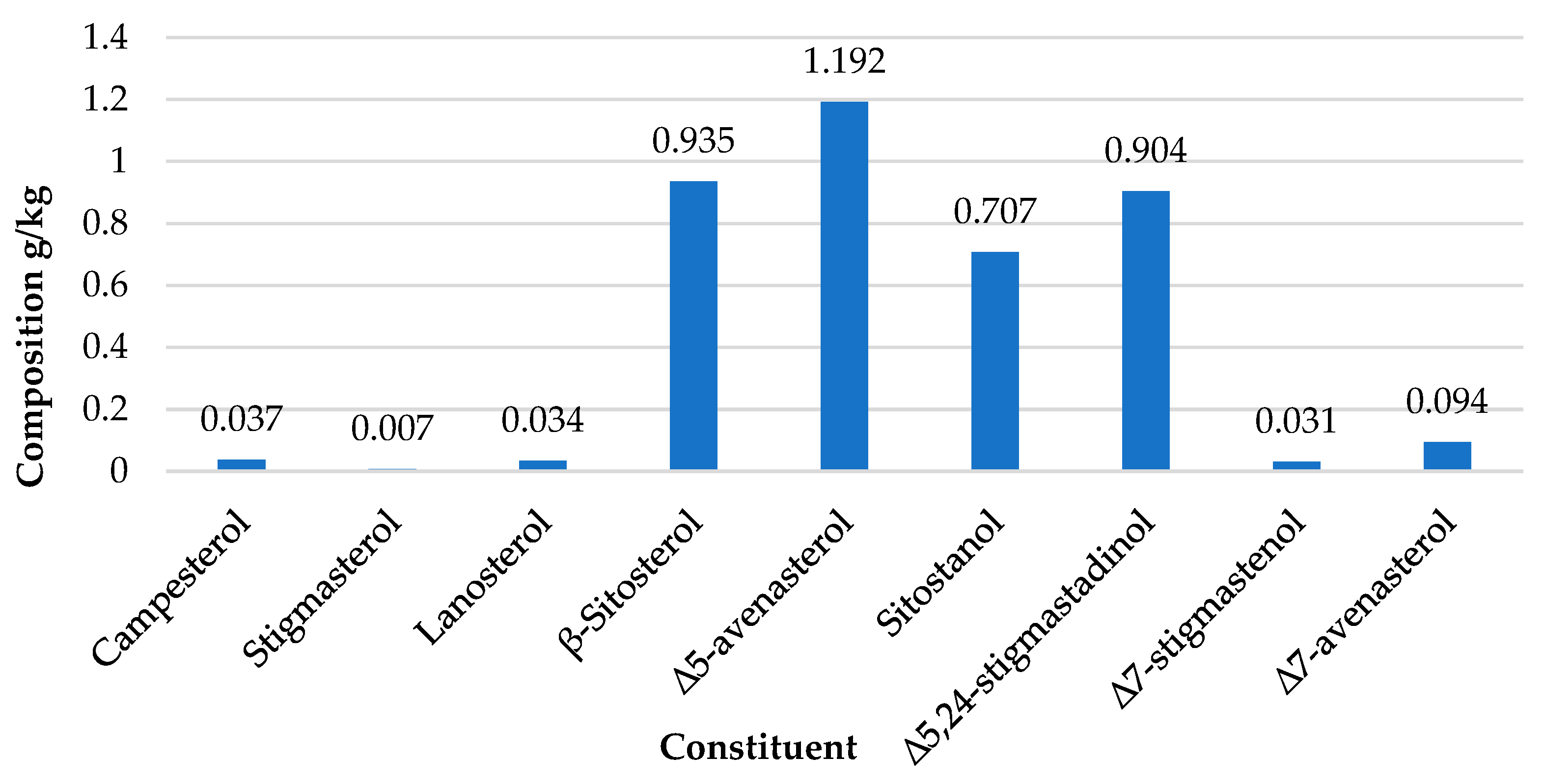
4.3. Unsaponifiable matters composition of Mee seed fat
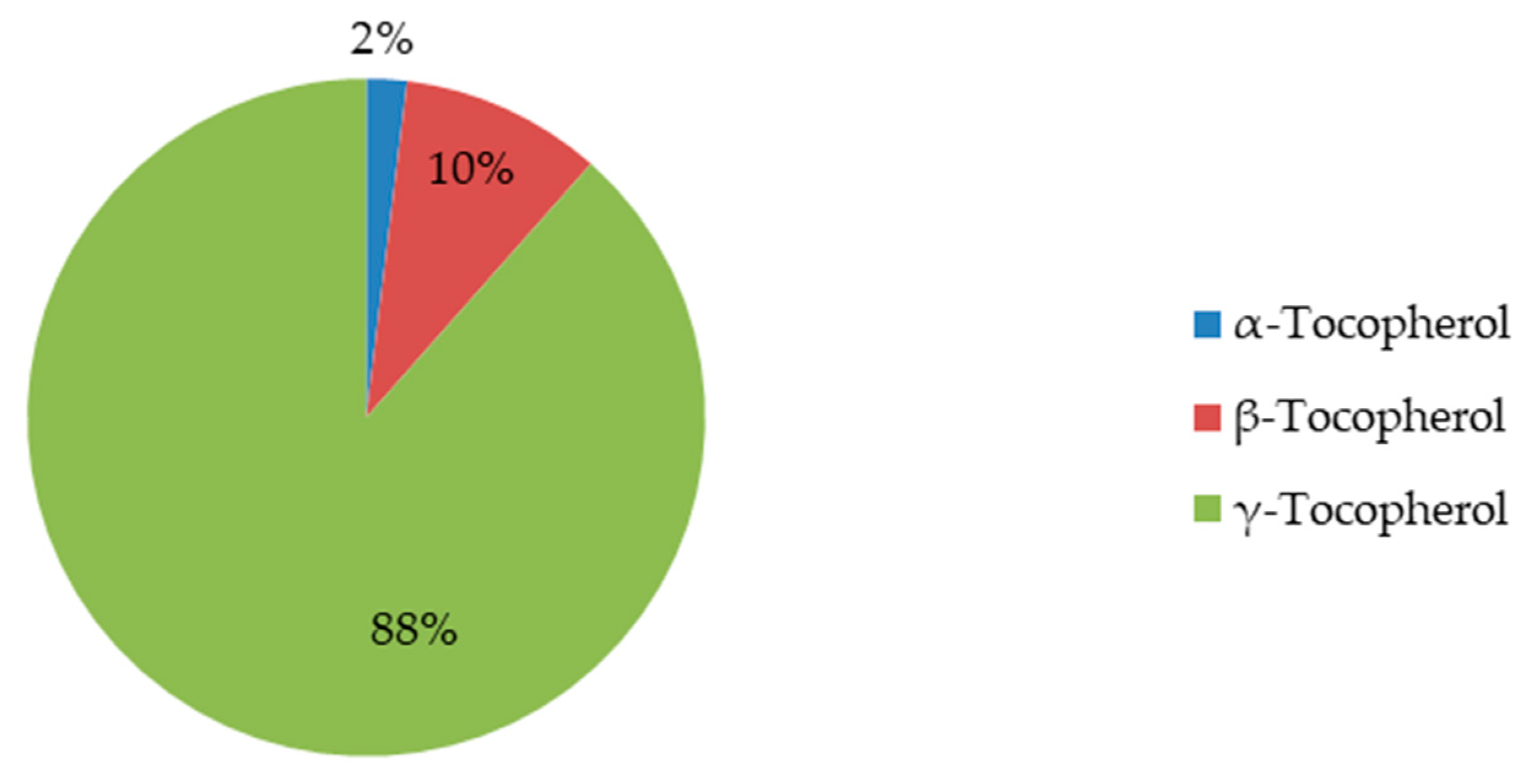
4.4. Antioxidant potential of mee seed fat
4.5. Mee seed oil content and quality upon storage
5. Processing of Mee (Madhuca longifolia) seed fat
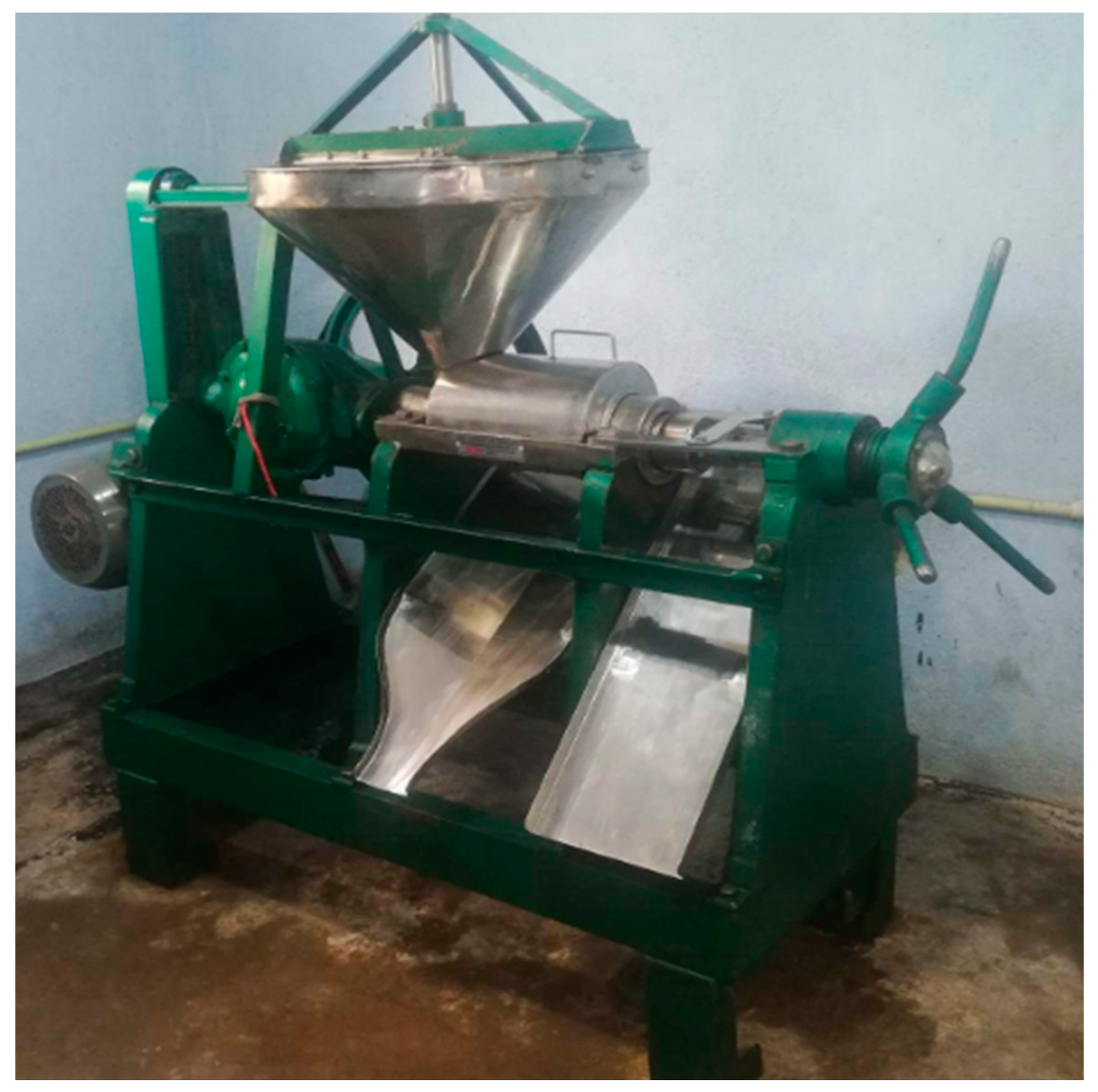
5.1. Mechanical press oil extraction
5.2. Solvent oil extraction (chemical extraction)
5.3. Ultrasonic-assisted bio-oil extraction
6. Potential industrial applications of mee seed fat
6.1. Stir frying application
6.2. An alternative ingredient for halal fats
6.3. A cocoa butter substitute
6.4. Development of food packaging material
6.5. Pharmaceutical product manufacturing
6.6. Formulation of coating binders
6.7. Biodiesel production
7. Limitations and gaps in processing and applications of Mee fat
8. Health-promoting potential and nutritional properties of mee (Madhuca longifolia) seed fat
9. Future perspectives of edible mee (Madhuca longifolia) seed fat
10. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ramadan, M. F.; Mörsel, J.T. Madhuca longifolia Butter. Fruit Oils: Chem Funct 2019, 291–300. [CrossRef]
- Thangamani, D; Rajan, S.P.; Karunamoorthi, J; Lalitha, S. Spiritually significant natural resource of Madhuca longifolia (J. Koenig ex L.) J.F. Macbr. Conservation and its value added products management. Pharma Innov J 2022, 11(8), 792-796.
- Ramadan, M.F.; Abdel-Hamed, E.M.W. Health-promoting Potential and Nutritional Value of Madhuca longifolia Seeds. Nuts and Seeds in Health Dis Prev 2020, Second Edition. [CrossRef]
- Saif, M; Varma, R; Kant, R; Gupta, R. Madhuca longifolia (Mahua): A comprehensive ethno pharmacological review. Intern J Chem Stud 2020, 8,172-175. [CrossRef]
- Khare, P; Kishore, K; Sharma, D.K. Medicinal uses, Phytochemistry and Pharmacological profile of Madhuca longifolia. Asian J Pharm Pharm 2018, 4(5), 570-581. [CrossRef]
- Kendre, N.; Wakte, P. A review on Phytochemicals and biological attributes of Madhuca longifolia. Asian Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology 2021, 7(2),74-84. [CrossRef]
- Shrirao, A.V; Koch, N.I; Chandewar, A.V. Madhuca longifolia (Sapotaceae): A Review of its Traditional Uses and Phyto-Pharmacological Profile. Res Chron Health Sci 2017,3(4), 45-50.
- Munasinghe, M.; Wansapala, J. Study on variation in seed morphology, oil content and fatty acid profile of Madhuca longifolia grown in different Agro-climatic zones in Sri Lanka. Sci Res 2015, 3 (3). P 105-109. [CrossRef]
- Ramadan, M.F; Mohdaly, A.A.A; Assiri, M.A.A.; Tadros, M; Niemeyer, B. Functional characteristics, nutritional value and industrial applications of Madhuca longifolia seeds: an overview. J Food Sci Technol 2016, 53,2149–2157. [CrossRef]
- Saral, S.K; Indumathi, M.P.; Rajarajeswari, G.R. Mahua oil based polyurethane/chitosan/ nano ZnO composite films for biodegradable food packaging applications. Internat J Biol Macromol 2019, 124,163-174 . [CrossRef]
- Singh,A; Singh, I S. Chemical evaluation of mahua (Madhuca indica) seeds. Food Chem. 1991, 40,221-228. [CrossRef]
- Munasinghe, M; Wansapala, J. Oil extraction from Madhuca longifolia (J.Konig) J.F. Macbr seeds and evaluation of physico- chemical properties, fatty acid profile, antioxidant potential and sensory characteristics. Trop. Agric (Trinidad) 2016, 9 (1),29-35.
- Seneviratne, K.; Jayathilaka, N. Coconut Oil: Chemistry and Nutrition, Lakva Publishers: Battaramulla, Sri Lanka, 2016; pp 18-34.
- Bandara, D.M.S.P; Dissanayake, C.A.K.; Rathnayaka, H.M.A.P.; Senanayake, D.P. Performance evaluation of the screw type oil expeller for extracting Mee (Madhuca longifolia) oil. J. Biol systems Eng. 2016, 41(3), 177-183. [CrossRef]
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (2023). PubChem Compound Summary for CID 445639, Oleic Acid. Retrieved February 10, 2023 from https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Oleic-Acid.
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (2023). PubChem Compound Summary for CID 985, Palmitic Acid. Retrieved February 10, 2023 from https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Palmitic-Acid.
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (2023). PubChem Compound Summary for CID 5281, Stearic Acid. Retrieved February 10, 2023 from https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Stearic-Acid.
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (2023). PubChem Compound Summary for CID 5280450, Linoleic Acid. Retrieved February 12, 2023 from https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Linoleic-Acid.
- Nayak S.,Sahoo U.K., Thangjam U., Garnayak L.M. Provenance Variations of Morphometric Traits and oil contents of Madhuca latifolia Macbride in Odisha: Implication for tree improvement. J Exp Biol Agri Sci 2020, 8(3), 224 – 232. [CrossRef]
- Suryawanshi, Y.C; Mokat, D.N. GCMS and Elemental Analysis of Madhuca longifolia var. latifolia Seeds. IJPSR 2019, 10(2): 786-789. [CrossRef]
- Thilakarathna, R.C.N.; Lee Fong Siow; Teck-Kim Tang; Eng-Seng Chan; Yee-Ying Lee. Physicochemical and antioxidative properties of ultrasound-assisted extraction of mahua (Madhuca longifolia) seed oil in comparison with conventional Soxhlet and mechanical extractions. Ultras Sonochem 2023, Vol. 92, 106280. [CrossRef]
- Bopitiya, D; Madhujith, T. Antioxidant activity and total phenolic content of mee (Madhuca sp.) oil, Book of Abstracts of the Peradeniya, University Research Sessions, Sri Lanka. 2012, Vol. 17.
- Munasinghe, M.; Wansapala, J. β – Carotene content of Madhuca longifolia seed oil in different Agro-climatic zones in Sri Lanka. The Effect of heat on its stability and the composition of seed cake. Postravinarstvo 2015, 9 (1), 474-479. [CrossRef]
- Madhujith, T; Bopitiya, D; Sivakanthan, S; Jayawardana, N.W.I.A; Walallawita, W.K.U.S. Comparison of oxidative stability of sesame (Sesamum indicum), soybean (Glycine max) and mahua (mee) (Madhuca longifolia) oils against photo-oxidation and autoxidation. Proced Food Sci 2016, 6, 204 – 207. [CrossRef]
- Issaoui M., Delgado A.M. 2019.Grading, labeling and standardization of edible oils. In: Ramadan M, eds Fruit oils: chemistry and functionality. Springer, Cham. [CrossRef]
- Nayak, S.; Sahoo, U.K. Changes in Madhuca latifolia Macbride seed oil content and quality upon storage at different duration and condition. Vegetos 2021, 34(2), 422–431. [CrossRef]
- Behera, S.; Swain, M.R. A survey of post-harvest spoilage of mahua (Madhuca latifolia L.) flowers. J Agric Technol 2013, 9(1), 227–235.
- Varghese, B.; Naithani, R.; Dulbo, M.S.; Naithani, S.C. Seed storage behavior of MadhucaindicaJ.P.Gmel. Seed Sci Technol 2002, 30,107–117.
- Baskar, G.; Naveenkumar, R; Mohanapriya, N.; Roselin, S.; Nivetha; Aiswarya R. Optimization and kinetics of ultrasonic assisted bio oil extraction from Madhuca indica seeds. Ind Crop Prod 2018,124,954–959. [CrossRef]
- Keneni, Y.G.; Marchetti, J.M. Oil extraction from plant seeds for biodiesel production. AIMS Energy 2017, 5(2), 316-340, . [CrossRef]
- Shashikumar, C.; Pradhan, R.C.; Mishra, S. Characterisation of Madhuca longifolia seed in relation to processing and design of equipment. Qual Assur Saf Crop Food 2018, 10 (3), 215-221. [CrossRef]
- Keneni, Y. G.; Bahiru, L. A.; Marchetti, J. M. Effects of Different Extraction Solvents on Oil Extracted from Jatropha Seeds and the Potential of Seed Residues as a Heat Provider. Bio Energy Res 2020, 14, 1207–1222 . [CrossRef]
- Marikkar, J.M.N; Yanty, N.A.M. Seed fat from Madhuca longifolia as raw material for Halal alternative fats. Borneo Sci 2012, 31,97-106.
- Yanty, N.A.M.; Dollah, S.; Marikkar, J. M. N.; Miskandar, M.S.; Desa, M. N. M.;Nusantoro, B.P. Physicochemical Properties and Thermal Behavior of Binary Blends of Madhuca longifolia Seed Fat and Palm Oil as a Lard Substitute.J. Adv. Agric. Technol. 2018, 5(3), 202-208. [CrossRef]
- Bisht, V; Neeraj; Solanki, V.K.; Dalal, N. Mahua an important Indian species: A review. J Pharm Phytochem 2018, 7(2), 3414-3418.
- Dalvi, T.S.; Kumbhar, U.J.; Shah, N. Madhuca longifolia: Ethanobotanical, phytochemical studies, pharmacological aspects with future prospects. Interdis J Appl Basic Subj 2022, 2(7), 1-9.
- Naik, B.; Kumar, V. Cocoa Butter and Its Alternatives: A Review. J Biores Engin Technol, 2014, 1, 7-17.
- Tambun, R.; Ferani, D. G.; Afrina, A.; Tambun, J. A. A.; Tarigan, I. A. A. Fatty Acid Direct Production from Palm Kernel Oil In the proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Industrial and Manufacturing Engineering. Medan City North Sumatera, Indonesia, 16 October 2018 . [CrossRef]
- Medeiros de Azevedo W.; Ferreira Ribeiro de Oliveira L.; Alves Alcântara M.; Tribuzy de Magalhães Cordeiro, A.M.; Florentino da Silva; Chaves Damasceno, K.S.; Kelly de Araújo, N. Physicochemical characterization, fatty acid profile, antioxidant activity and antibacterial potential of cacay oil, coconut oil and cacay butter 2020. Plos One 15(4), e0232224. [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, U. N.; Mahapatra, D.K.; Mahajan, N.M.; Kazi, F.S.; Baghel, N. Exploring the role of Mahua oil as potent emulsifier in cream formulations, Int. J. Herb. Med. 2017, 5 (3), 93-97.
- Pawar, M.S.; Kadam, A.S; Omprakash, S.; Yemul. Development of polyether amide-based corrosion protective polyurethane coating from mahua oil. Prog Organ Coat 2015, 89,143-149. [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, S.S.; Gogate, P.R. Process intensification of fatty acid ester production using esterification followed by transesterification of high acid value mahua (lluppai ennai) oil: Comparison of the ultrasonic reactors. Fuel 2021, 294, 120560. [CrossRef]
- Marchetti, J.M.; Keneni, Y.G. Review Oil extraction from plant seeds for biodiesel production. AIMSEnergy 2017, 5(2), 316-340. [CrossRef]
- Kayode, B.; Hart, A. An overview of transesterification methods for producing biodiesel from waste vegetable oils. Biofuels 2017.10(3), 1-19. [CrossRef]
- Yadav, M.; Singh, V.; Sharma, Y. C. Methyl transesterification of waste cooking oil using a laboratory synthesized reusable heterogeneous base catalyst: Process optimization and homogeneity study of catalyst. Energy Conv Manag 2017, 148,1438–1452. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.V; Babu, A.V; Kumar, P. R. Experimental investigation on mee methyl ester blended with diesel fuel in a compression ignition diesel engine, Intern J Amb Energy 2017,40 (3), 304-316 . [CrossRef]
- Manjunath, H.; Omprakash, H. B; Hemachandra, R.K. Process optimization for biodiesel production from simarouba, mahua, and waste cooking oils, Int J Green Energy, 2015, 12, 424–430. [CrossRef]
- Hegde, H.T.; Gunaga, R.P.; Thakur, N.S. Current trends and future prospects for utilization of mahua resources, Trop Forest Res Inst 2019, 6(2).
- Reddy, I. S. Madhuca indica: An untapped forest tree for its medicinal uses. The Pharma Innovation Journal 2022, 11(3), 1747-1751.
- Janghel, V.; Chandel, S.S.; Sahu, J.; Patel, P. K. Madhuca indica (Mahua) - Pharmaceutical, Nutraceutical and Economical Importance for Tribal People of Chhattisgarh State, Intern J Pharm Phytopharm Res 2019, 9(3), 16-28.
- Ramchandra, D; Gaikwad, M.D; Liyaqat, A.M.D; Swamy S.K.P. Anti-inflammatory activity of Madhuca longifolia seeds saponin mixture. Pharmaceut Biol.2009. 47, 592-597. [CrossRef]
- Bhaumik, A; Kumar, M.U.; Khan, K.A.; Srinivas, C.H. The Bioactive Compounds Obtained from the Fruit Seeds of Madhuca longifolia (L.) act as potential anticancer agents. Sch J App Med Sci. 2014. 2, 1235-1238.
- Withana, W.V.E; Hapuarachchi, N.S.; Cooray, R.; Dissanayake, Y.; Warnakula, L. Importance of Genetic Diversity and Phytochemical Assessment of Madhuca spp. in Sri Lanka: A Review. In the Proceeding of the International Research Conference, Uva Wellassa University, Badulla 90000, Sri Lanka, 7-9 February 2019.




| Type of oil | Saponification value(mg KOH/g) | Iodine value (gI2/100g) |
Acid value (mg KOH/g) | Peroxide value (meq/kg) | Melting point ºC | Smoke point ºC | Specific gravity (at 25ºC) |
Refractive index (at 40ºC) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mee | 181-184 | 56-57 | 4 | 3 | 33-34 | 168-171 | 0.9272 | 1.4672 |
| Coconut | 250 – 268 | 6-11 | 0.2 | 3 | 24 | 177 | 0.918 | 1.4486 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).