Abstract Saponins are a diverse group of naturally occurring plant secondary metabolites present in a wide range of foods ranging from grains, pulses, green leaves to sea creatures. They consist of a hydrophilic sugar moiety linked to a lipophilic aglycone, resulting in an amphiphilic nature and unique functional properties. The amphiphilic structures enable saponins to exhibit surface-active properties, forming stable foams and complexes with various molecules. In the context of food applications, saponins are utilized as natural emulsifiers, foaming agents, and stabilizers. They contribute to texture and stability in food products and have potential health benefits, including cholesterol-lowering and anticancer effects. Saponins possess additional bioactivities that make them valuable in the pharmaceutical industry as anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, antiviral, and antiparasitic agents to name a few. Saponins can demonstrate cytotoxic activity against cancer cell lines and can also act as adjuvants, enhancing the immune response to vaccines. Their ability to form stable complexes with drugs further expands their potential in drug delivery systems. However, challenges such as bitterness, cytotoxicity, and instability under certain conditions need to be addressed for effective utilization of saponins in foods and related applications. In this paper, we have reviewed chemistry, functionality, and application aspects of saponins from various plant sources and have summarised the regulatory aspects of food application of Quillaja saponins. Further research to explore the full potential of saponins in improving food quality and human health has been suggested. It is expected that this article will be a useful resource for researchers in food, feed, pharmaceutical and material science.
1. Introduction
The name ‘saponin’ is derived from the Latin word ‘sapo’ meaning soap and associated with the ability to form a soapy foam when plant extract containing saponins is agitated in water (Kregiel et al., 2017). Saponins are a diverse group of compounds widely distributed in the plant kingdom, which are characterized by their structure comprising of a lipophilic triterpene or steroid aglycone linked to one or more hydrophilic sugar moieties (Mohan et al., 2016; Netala et al., 2015). Their structural diversity is reflected in their physicochemical and biological properties.
In recent years, consumer demand for natural products coupled with their physicochemical (surfactant) properties and mounting evidence on their biological activity (such as anticancer properties, and haemolytic and hypocholesterolemia activity) has led to the emergence of saponins as commercially significant compounds with expanding applications in food, cosmetics, and pharmaceutical industries (Güçlü-Üstündağ & Mazza, 2007; Mohan et al., 2016).
Although saponins are known for their health benefits and functional attributes, they also come with some limitations. One of them is associated with their ability to interact with other food components to form complexes with proteins, lipids, minerals such as iron, zinc, and calcium (insoluble saponin–mineral complexes) negatively influencing the absorption of such food components in the body (Milgate & Roberts, 1995). Some saponins have limited solubility in water, which can pose challenges in their incorporation and distribution within food matrices. This can affect their effectiveness as emulsifiers or stabilizers in certain food systems (Schreiner et al., 2022).
Saponins also find applications in pharmaceuticals and other allied industries. Saponins may help lower blood lipids, reduce cancer risks, and slower blood glucose response. A diet rich in saponins has been suggested to inhibit dental decays and aggregation of platelet. Saponin consumption has also shown promise in the treatment of hypercalciuria in humans and as an antidote against acute lead poisoning (Shi et al., 2004). Saponins are also used as expectorant and antitussive agents (Shibata, 1977). They are utilized in the cosmetic industry for their ability to act as natural emulsifiers, foaming agents, and cleansing agents. They are constituents of shampoos, soaps, facial cleansers, body washes and shaving creams, contributing to the lathering, cleansing and moisturizing properties of these products (Meshram et al., 2021).
As the functionality and subsequent applications of saponins are dictated by their composition, a thorough understanding of their chemical and structural features is essential. Methods of extraction and purification, their efficiency and extractability also play a vital role in their composition, functionality, and applications. Saponins are highly researched bioactives and there are several experimental studies and review articles that describe aspects of saponins. For example, a recent review article by El Aziz et al. (2019) focused on chemistry, isolation, and methods of quantification of saponins. Similarly, cytotoxic aspects of saponins are well reviewed in another article (Podolak et al., 2010). However, there is a scarcity of articles that cover a detailed overview of sources, methods of extraction, purification, quantification, and further application. In addition, regulatory requirements in the food and pharmaceutical application of saponins are also not clearly addressed in previous reviews. Therefore, this review paper is expected to fill the literature gaps in aspects of saponin chemistry, structure and application related to applications in foods, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals.
2. Sources of Saponins
Saponins are widely distributed in nature and are found in several plants, and some marine animals (e.g., sea stars, sea cucumbers and sponges) (Decroo et al., 2017). The major sources of dietary saponins are legumes. Soya saponins are one of the common types of legume-saponins (Mohan et al., 2016). Saponin content and their structure and composition may vary even among the same species of edible legumes, because of variations with cultivars as well as growing locations, irrigation conditions, soil types and climatic conditions (Shi et al., 2004). For example, soya saponins are classified into group A, B, and E based on the chemical structure of the aglycone. Some of the better-known botanicals rich in saponins are presented in
Table 1.
Among various botanicals listed in
Table 1, Liquorice, Yucca and Quillaja bark are among the plant sources containing the highest quantity of saponins; however, soapwort, milkwort, primula, and fenugreek also contain appreciable quantities of saponins. Sugar beet leaves, Chinese ginseng and horse chestnut also contain good quantity of saponins.
3. Chemistry of Saponins
Structurally, saponins are diverse class of compounds with vast functional diversity (Moses et al., 2014). As schematically presented in
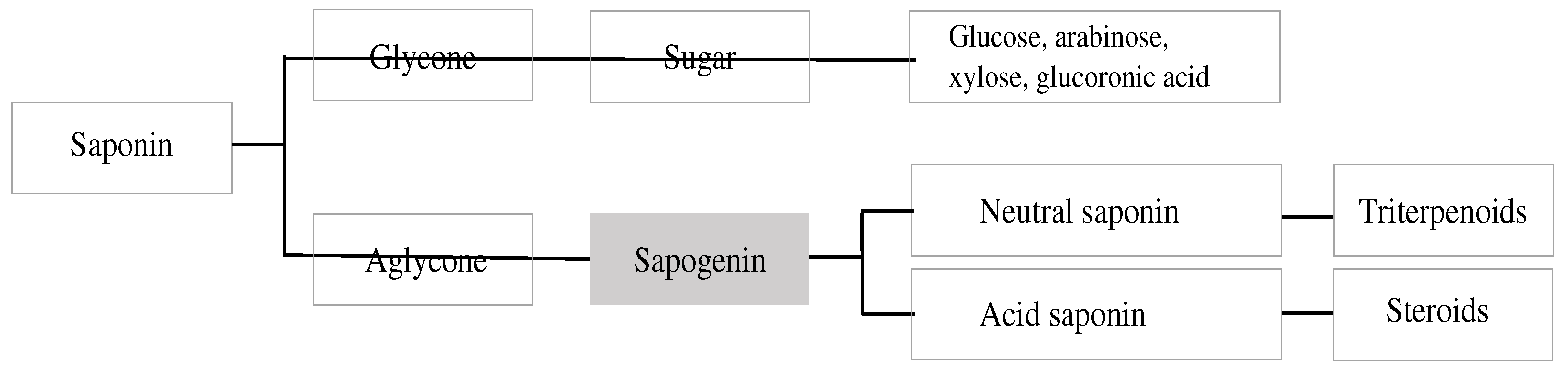
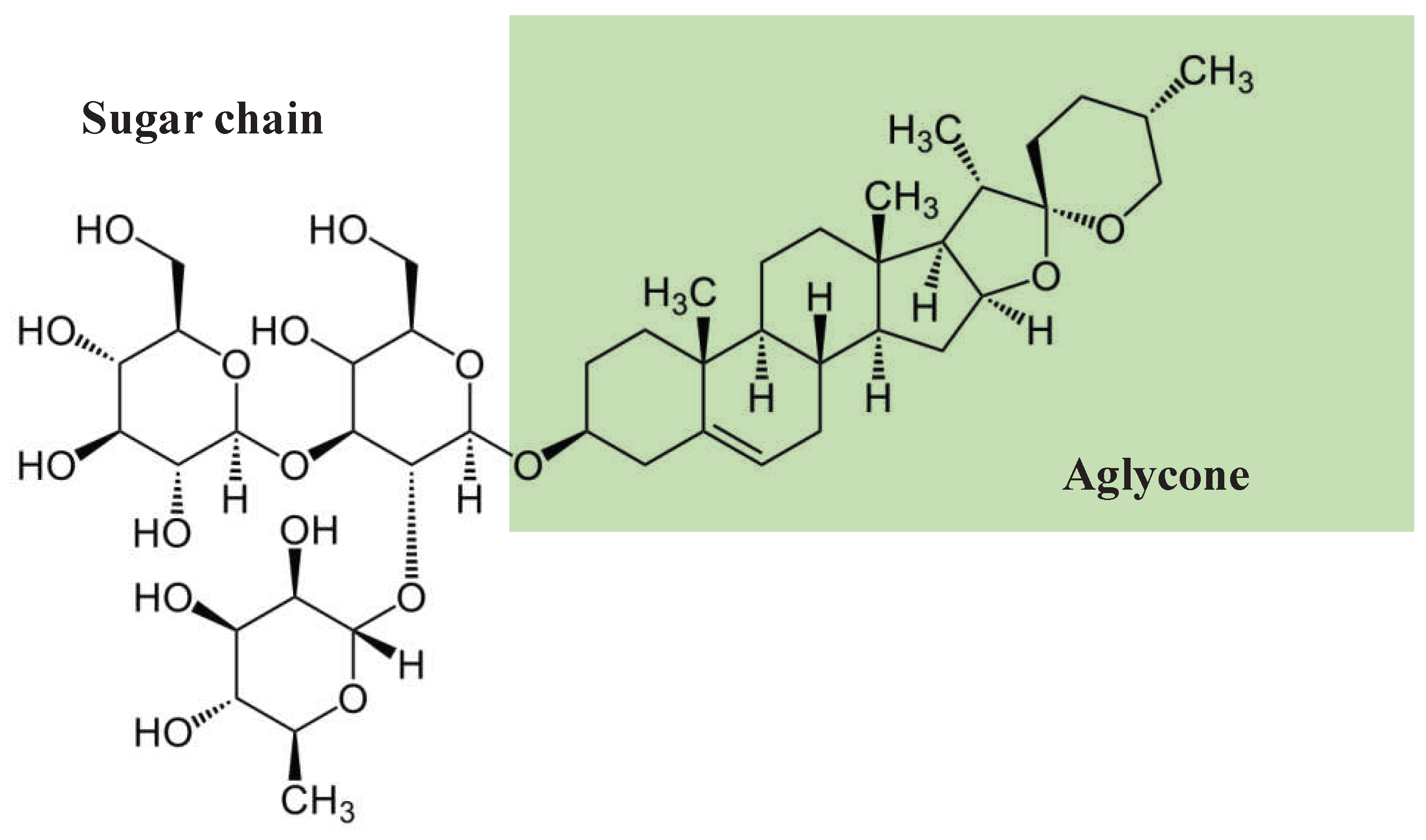
Figure 1 and
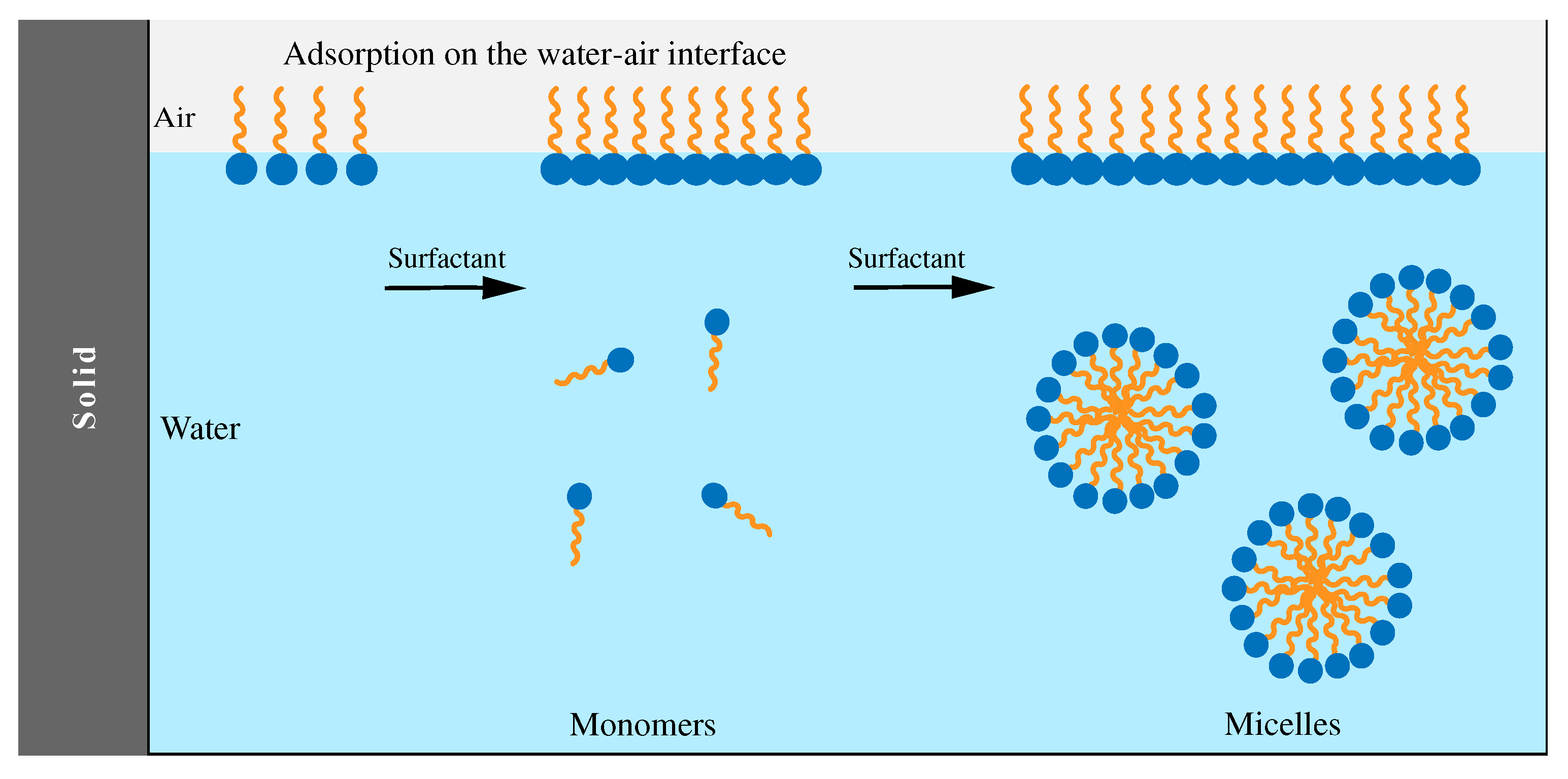
Figure 2, there are generally two functional groups in the saponin structure: an aglycone (30-carbon skeleton molecule) and a glycone (one or more sugar units) (El Aziz et al., 2019). Aglycone components are made up of a triterpenoid or steroid. In general, the glycone or sugar moiety consists of a monosaccharide, or an oligosaccharide covalently linked to the skeleton molecule at C3 position. In some cases, additional sugars are attached at C26 or C28 positions (Augustin et al., 2011; Roopashree et al., 2019). The presence of both lipophilic (aglycone) and hydrophilic (sugar) components into one molecule gives them soap-like properties. When saponins are mixed with water or aqueous alcohol and agitated for some time, a rich foam develops resulting from the diminished surface tension and aggregation into micelles (Roopashree & Naik, 2019).
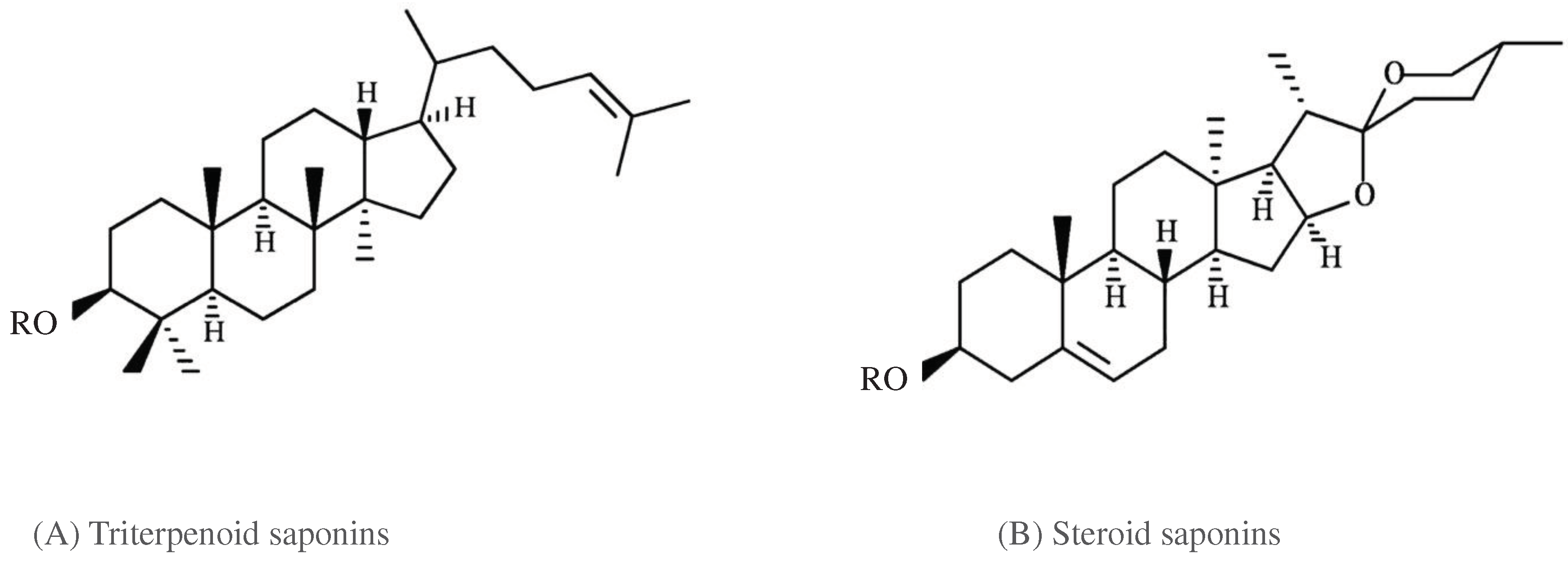
Broadly, saponins are classified into two main groups based on the structure of the aglycone. They are known as the triterpenoid saponins and the steroid saponins. Triterpenoid saponins consist of only 6-rings, with 30 C-atoms in total. Steroid saponins contains 5-rings and have only 27 C-atoms (
Figure 3). The steroid saponins have three methyl groups removed (Vincken et al., 2007). Some authors recognize a third group, that of the steroidal amines or alkaloid saponins; they have the same basic structure as the steroidal saponins but possess an NH-group instead of an O-atom (Roopashree et al., 2019; Vincken et al., 2007). The great complexity of saponin structure arises from the variability of the aglycone structure, the nature of the side chains and the position of attachment of these moieties on the aglycone (Francis et al., 2002).
4. Extraction and Isolation of Saponin
Saponins can be extracted from the source biomass by various techniques. Simple methods of extraction use either water or alcohol as extracting medium whereas Soxhlet extraction and the combination solvent extraction with intensification techniques such as ultrasound-assisted extraction, microwave-assisted extraction and accelerated solvent extraction methods have shown promising results but are still being explored. Reference?
In simple extraction methods, saponins can easily be extracted by immersion or soaking the powdered or macerated biomass in a suitable specific solvent for a specified time period. The polarity of the solvent, temperature, time, mixing speed, solubility of saponins and its effective diffusion in the liquid phase are the main operational variables affecting the efficiency of the extraction process (El Aziz et al., 2019). Longer extraction time, higher temperature, and higher mass of biomass generally result in increased extraction yields.
Water, ethanol, methanol, n-butanol, acetone, ethyl acetate, dichloro methane, or a mixture of solvents are commonly used for the extraction of saponins from plant materials; however, ethanol and n-butanol are most commonly used. The temperature of extraction varies from ambient to the boiling point of the chosen solvent. Le et al. (2018) has provided a detailed outline of a method to extract saponins using a mixture of ethanol-water (70% ethanol) at 50°C.
Soxhlet extraction process is considered a more efficient process in comparison to the simple extraction process because during Soxhlet extraction process a hot organic solvent directly contacts the plant tissue in the condenser, so the extraction process takes place via the direct contact between the plant tissue and the hot fumes of the solvent. After a considerable extraction time, the solvent is rich in the active ingredients.
In any solvent extraction process, after the completion of extraction cycle, the extract is further concentrated by evaporating the solvent.
5. Quantification of Saponins
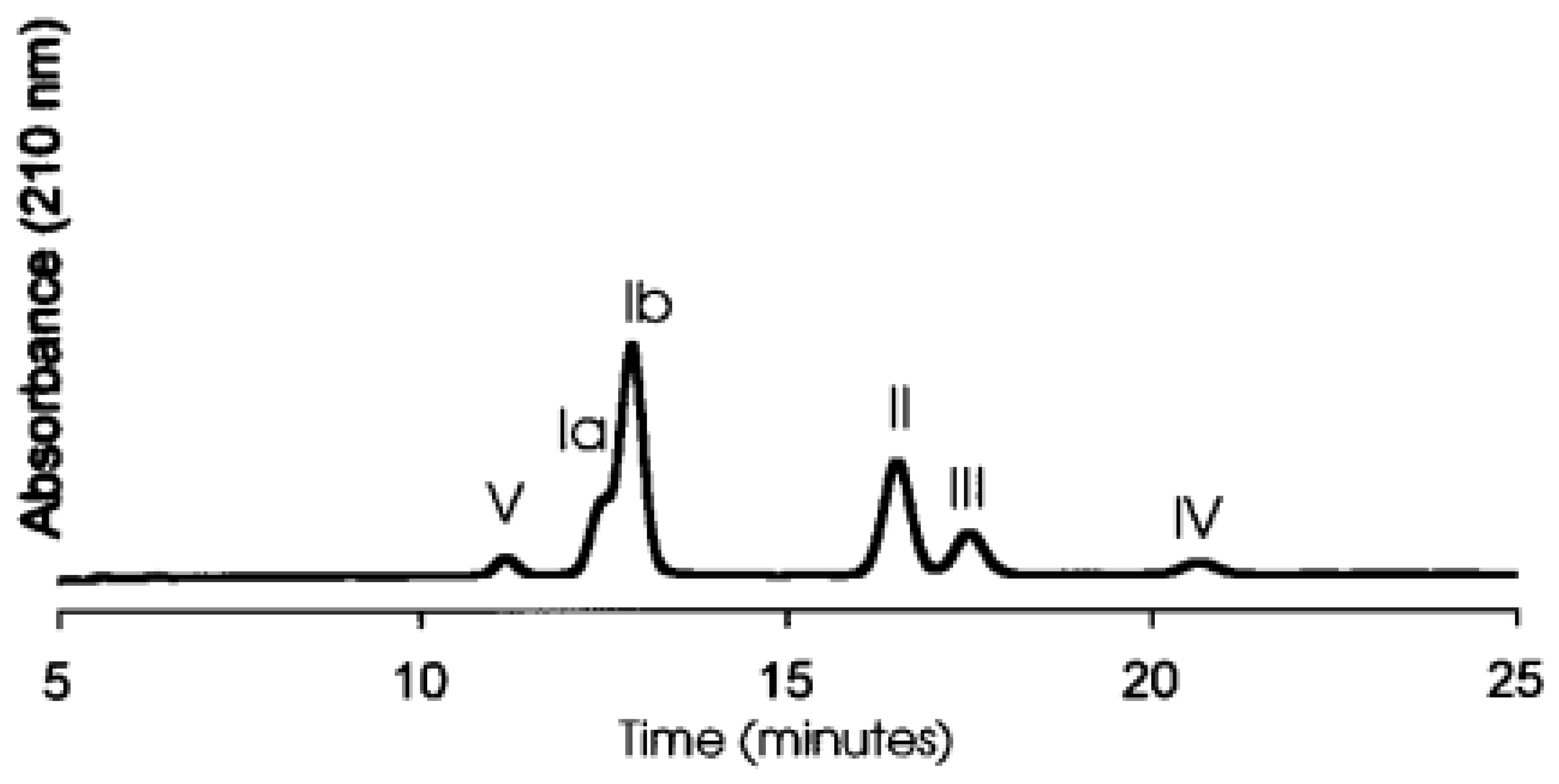
In general, extracted saponins are purified and characterised using variouschromatographic and spectroscopic methods. Among them, high performance thin layer chromatography (HPTLC) and high-performance liquid chromatographic (HPLC) have been widely used for separation and quantification of
Sapindus saponin (Saxena et al. 2004) and soya saponins (Berhow et al., 2002). Five different fractions of soya saponins were separated by HPLC using a C18 reversed-phase column (as shown in
Figure 4). The mobile phase was 40% aqueous acetonitrile with 0.025% trifluoroacetic acid (Berhow et al., 2002). In another study, six pairs of saponin diastereomers were isolated from Y. schidigera by using HPLC with a C30 column (Qu et al., 2018).
Mass spectrometry in combination with chromatography has been more widely used in the characterisation of saponins. Ultra-performance liquid chromatography- mass spectrometry (LC/MS) coupled to an exactive mass spectrometer was used for the characterization of the purified saponins from Chubak root extract (Acanthophyllum Glandulosum) (Dabestani et al., 2021). Kowalczyk et al. (2011) used LC-MS to characterised and quantified saponins from Y. schidigera. Similarly, Montoro et al. (2010) developed a method for the quantitative analysis of the steroidal saponins in Y. gloriosa flowers real samples using HPLC coupled to tandem mass spectrometry.
Gas–liquid chromatography has limited application for saponins are quite large molecules and are not volatile. Capillary electrophoresis has been applied for saponin determination only in a limited number of cases and this method is still being developed (Oleszek, 2002).
Among several spectroscopic methods, Vanillin-Sulphuric acid method is more commonly used to quantify saponins in a plant extracts (Le et al., 2018). Briefly, 25 µL of the appropriately diluted standard or experimental extract was added to a test tube with a cap and the tube was placed in a water bath at 65°C for 5 min to evaporate the solvent. A 500 µL aliquot of vanillin solution (4% w/v, in ethanol) and 2.5 mL of 72% H2SO4 (v/v) was added to each tube in a fume hood. The test tube was capped and vortexed for 30 s and incubated at 60°C for 15 min. The tubes were cooled to room temperature (25°C) in an iced-water bucket for 2 min and the absorbance was measured at 560 nm using a spectrophotometer. For the construction of the standard curve, 150 mg of aescin was weighed accurately and transferred to a 10 mL volumetric flask and dissolved in 10 mL of methanol. Total saponin contents were determined as mg aescin equivalents (AE) per gram dry weight of the botanical (mg AE/g). Another method for the determination of total saponin content has been reported by Kareru et al. (2008). In this method, dry aerial parts of the plant (5.0g) were defatted twice with petroleum ether (60-80°C) (2x50mL). Then alcoholic solution (75%, 150 mL) was added to the defatted product. The mixture was refluxed at 70°C for four hours, the extract solution filtered and evaporated at 40-50°C in a Rotavapor. The dry residue was dissolved by a suitable amount of distilled water and extracted thrice with n-butanol (3x40mL). The combined n-butanol solution was evaporated at 90°C using a Rotavapor to dryness, and the yield of saponin was calculated.
6. Functional Properties of Saponins
6.1. Technofunctional Characteristics of Saponins
Physical, chemical, and biological properties of saponins are the result of their structural complexity. These properties are not generic, only a few of them are common to all members of this diverse group of molecules. Almost all saponins are known to have a bitter, unpleasant taste and exist in colourless amorphous form (Alamgir et al., 2018). Each saponin has different solubility in different solvents. However, most saponins have good solubility in water, methanol, ethanol and n-butanol (Nguyen et al., 2020). Factors such as solvent temperature, composition and pH play a key role in the solubility and extractability of saponins.
Saponins have a high melting point (generally above 200oC) and maintain their biological activities even if they are thermally processed at high temperature. However, they are not very stable in acid or alkaline conditions as the glycosidic bond (bond between the sugar chain and the aglycone) can easily be hydrolysed in the presence of acids/alkali (Nguyen et al., 2020). The products of hydrolysis include aglycones, prosapogenins, sugar residues or monosaccharides depending on the extent and conditions of hydrolysis (Güçlü-Üstündağ et al., 2007).
It has been reported that the most important factor determining functional activity of saponins is the structure of aglycone part, in particular, the number and the location of functional groups. The activity level is strongly dependent on the number and the structure of the sugar chains. Generally, monodesmosides show much higher activities than bi- or tridesmosides. Sterol affinity is another important consideration that determine the application of saponins (Oleszek & Oleszek, 2020).
More details about the functional aspects of saponins will be presented in
Section 7 along with their application.
6.2. Bioactivities of Saponins
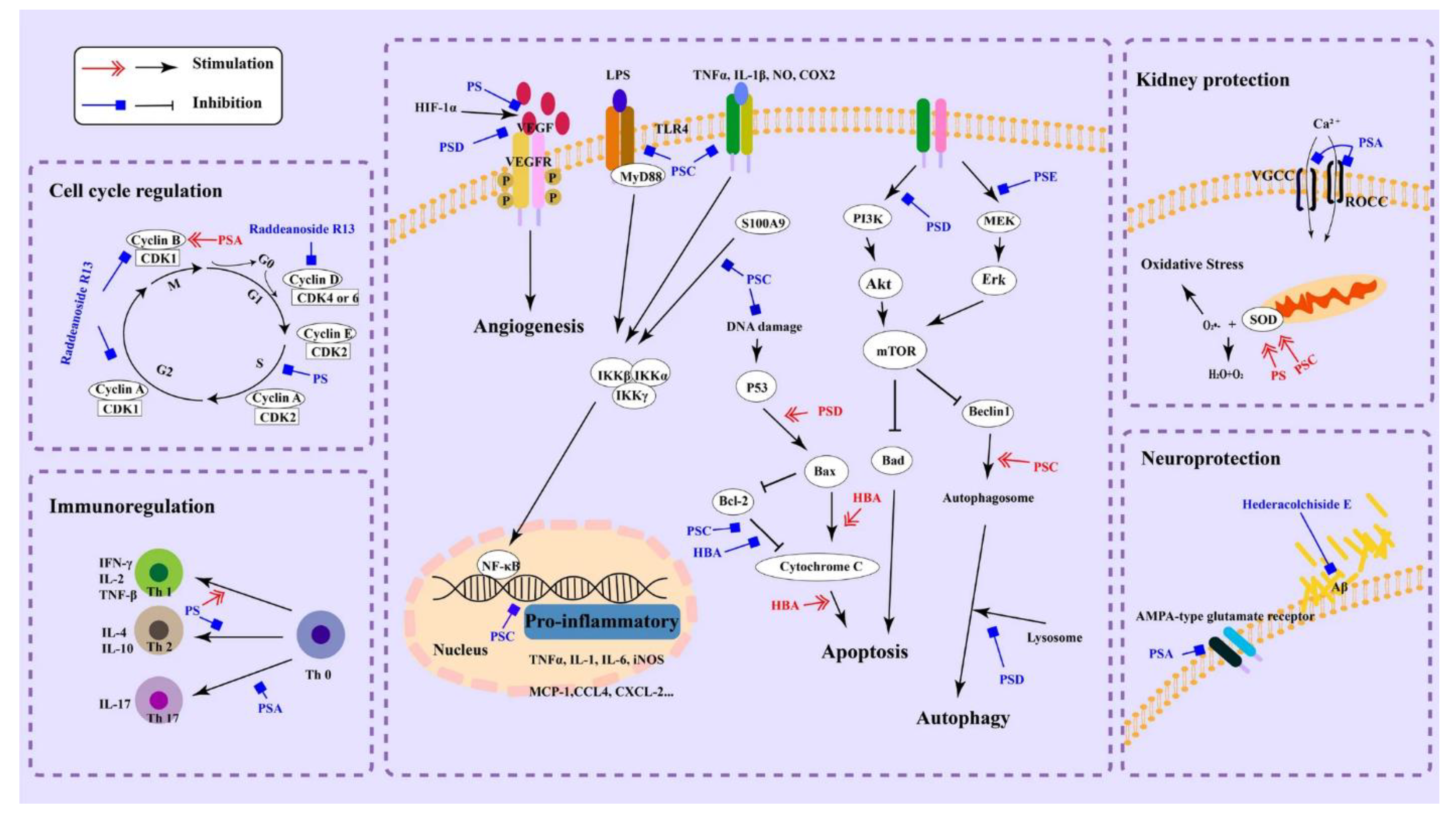
Saponins exhibit a variety of biological activities. They demonstrate efficacy in combating cancer and inflammation, as well as acting as potent antimicrobial agents. Saponins have shown promising anticancer effects in numerous studies. They can induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) in cancer cells, inhibit tumor cell proliferation, and suppress angiogenesis (the growth of new blood vessels that nourish tumors). Some saponins have been investigated for their potential to prevent or slow the progression of various types of cancer, including breast, lung, prostate and colon cancer (Zhong et al., 2022). They can inhibit the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and enzymes, thereby reducing inflammation and alleviating symptoms in conditions like arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and other inflammatory disorders (Dong et al., 2019). The anti-inflammatory effects of saponins primarily hinge on the mechanisms as shown in
Figure 5.
Various saponins serve as adjuvants and immunostimulants, while also displaying hypocholesterolemic and antioxidant properties. (Güçlü-Ustündağ and Mazza, 2007). They enhance the immune response to infections and diseases. They can activate immune cells, such as macrophages and natural killer cells, which play a crucial role in combating infections. Additionally, saponins are used as adjuvants in vaccines to boost the immune response and improve vaccine efficacy.
Saponins possess antioxidant activity, helping to neutralize free radicals and oxidative stress in the body. Free radicals are unstable molecules that can damage cells and contribute to aging and various diseases. By scavenging these free radicals, saponins help protect cells from damage and promote overall health. Saponins have the capability to create non-soluble compounds with cholesterol, as well as other sterols and bile acids. They possess the ability to trap total cholesterol, LDL, and bile salts in the intestines, inhibiting their absorption, while not affecting HDL levels (Kim et al., 2003). This leads to a reduction in blood cholesterol levels, specifically low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, which is considered "bad" cholesterol. By lowering LDL cholesterol, saponins contribute to cardiovascular health and reduce the risk of heart disease.
Saponins exhibit antimicrobial effects against a wide range of pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and protozoa. They disrupt microbial cell membranes and interfere with their replication, making them potential candidates for developing new antimicrobial agents and improving existing treatments. Oleanolic acid, derived from the root bark of Newbouldia laevis, exhibits wide-ranging antimicrobial properties when tested against 6 Gram-positive, 12 Gram-negative bacterial species, and three Candida species (Kuete et al. 2007). In animal nutrition, saponins are employed to decrease ammonia concentration and eliminate fecal odors (Cheeke, 2000). These compounds are known for their antiprotozoal effects, achieved by forming complexes with cholesterol present in protozoal cell membranes, leading to cell lysis and subsequent death. This antiprotozoal activity is particularly useful in reducing the populations of protozoa in the rumen of animals, contributing to improved animal health and nutrition (Francis et al., 2002).
6.3. Flavour Characteristics of Saponins and Their Effect on the Flavour of Food Ingredients and Foods
Saponins are generally associated with a bitter taste, and this bitterness can influence the overall flavor profile of foods containing these compounds. The bitterness of saponins may be more pronounced in certain types of foods and is correlated with the saponin concentration (Heng et al., 2006). Soya saponins are also found to have bitter, astringent, and metallic flavour. The presence of saponin in different air-classified pea flour fractions indicates that the protein-rich fraction could potentially contain enough saponin to cause undesirable flavors (Price et al., 1985; Aldin et al., 2006).
Due to their complex molecular structures, saponins may interact with other flavor compounds, potentially altering the perceived taste of the final product. In some instances, the true food flavour would be masked by saponins whereas in other instances foods may have unique interactions with saponins, leading to diverse flavor outcomes.
Although few studies have investigated the flavor attributes of saponins, research in this domain is not as extensive as other areas of saponin bioactivities. Furthermore, individual sensitivity to bitter tastes can differ, leading to subjective perceptions of saponin flavors among individuals.
7. Applications of Saponins
The plant extracts containing saponins have been widely used in food and other industrial applications mainly as surface active and foaming agents for centuries (San Martin & Briones, 1999). Recently they are regaining popularity especially in skincare and cosmetics applications (Karnwal et al., 2023).
Among various plants, Quillaja saponaria extracts have been used as foaming agents in carbonated beverages and cosmetics, as emulsifiers in preparations containing lipophilic colours or flavours, and as preservatives (Güçlü-Üstündağ et al., 2007; San Martin et al., 1999). Likewise, liquorice saponin extracts are used as flavour modifiers in baked foods, chewing gum, beverages, candies, herbs, seasonings, and dietary supplements (Güçlü-Üstündağ et al., 2007).
Saponins in foods have traditionally been considered as antinutritional factors (Thompson, 1993) and in some cases have limited their use due to their bitter taste (Ridout et al., 1991). Therefore, most of the earlier research on food processing targeted removal of saponins so that as low as quantities of saponins remain in the final products (Ridout et al., 1991). However, food and non-food sources of saponins have come into renewed focus in recent years due to increasing evidence of their health benefits including cholesterol lowering ability, anti-inflammatory, immunostimulant, hypoglycaemic, antifungal, cytotoxic and anticancer properties (Gurfinkel & Rao, 2003; Kim et al., 2003). Recent research has established saponins as the active components in many herbal medicines (Alice et al., 1991; Liu & Henkel, 2002) and highlighted their contributions to the health benefits of foods such as soybeans (Kerwin, 2004; Oakenfull, 2001) and garlic (Matsuura, 2001). The commercial potential of saponins has resulted in the development of new processes/processing strategies and re-evaluation of existing technologies (Muir et al., 2002) for their extraction/concentration (Rickert et al., 2004).
The ensuing section will elaborate some of the applications of saponins.
7.1. Saponins as Natural Surfactants and Emulsifiers
Saponins, due to the presence of a lipid-soluble aglycone and water-soluble sugar chain show amphiphilic characteristics. This structural make up attributes the saponins a surface-active property like that of a soap or detergent. With one hydrophilic component and one lipophilic component, when dissolved in water, saponins tend to align themselves with the lipophilic part away from water, which leads to the reduction of the surface tension and cause the foaming (Akbari et al., 2023). It is well reported that when the concentration of saponins is above the critical micelle concentration (CMC), they are able to form micelles (as shown in
Figure 6) in aqueous solution. Consequently, saponins can enhance the solubility of other substances. Compared to the synthetic surfactants, saponins are more effective in enhancing polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons solubilization (Zhou et al., 2011).
The size and structure of micelles are dependent on the type of saponin. For example, saponins from S. officinalis and soya bean form small micelles consisting of only two molecules, while the aggregates of Quillaya saponaria saponin consist of 50 molecules. It was documented that the properties and the aggregation number (number of monomers) of micelles forming by Quillaya saponins are affected by temperature, salt concentration, and pH level. Saponins from Quillaja saponaria has a CMC between 0.5 to 0.8 g/L at temperature 25°C and it decreases with increasing salt dose (Kjellin et al., 2010). The micelle shapes depend on the saponin molecule. For example, micelles formed by saponins from S. officinalis and Quillaya saponaria are elongated or even filamentous, while those formed by saponins of Glycine max are rather circular. Probably, the reason for these differences is the chemical structure of aglycone.
The presence of carboxylic acid in the saponin molecular structure may strongly influence its surface activity. The location of this acid in the molecule has a particular importance. For example, Soy saponins contains -COOH group in its hydrophilic part. The carboxylic group dissociates in aqueous phase and forms free carboxyl anions, responsible for increasing the solubility of saponins in water environments. In contrast, saponins of Indian soapberry/washnut/ritha (Sapindus mukorossi) also contain the carboxylic groups but they are attached to the hydrophobic aglycone. Consequently, the dissociation level of -COOH groups is very low. Saponins can also form mixed ‘sandwich-like’ or ‘pile of coins-like’ micelles with bile acids (Kjellin et al., 2010). These are much larger than the micelles of saponins alone, and they differ depending on the structure of the aglycone. In the presence of bile acids, saponins from Saponaria officinalis and Quillaja saponaria form filamentous structures, while Glycine max saponins have an open structure. The ability of saponins to form large stable micelles with bile acids gives important implications for dietary mechanisms. Saponins in food and feed increase faecal excretion of bile acids (Kjellin et al., 2010). Additionally, the incorporation of cholesterol into saponin micelles increases their size, critical micelle concentration (CMC), viscosity, and the aggregation level resulting in the solubility enhancement of cholesterol. The micelles formed are too large for the digestive tract to absorb. This mechanism leads to decreasing of the plasma cholesterol concentration. Saponin Quillaja saponaria was found to solubilize cholesterol significantly better than linear hydrocarbon chain surfactants (Mitra & Dungan, 2001).
Interaction between saponins and membrane-bound cholesterol leads to pore formation and increasing of membrane permeability. This specific effect of saponins depends on the combination of factors including the membrane composition, the type of saponin, and especially the nature of aglycone (Bachran et al., 2014). Saponins also form complexes with sterols in mucosal cell membranes resulting in the increase in the intestinal mucosal cells permeability. Thus, this facilitates the uptake of substances to which the gut would normally be impermeable, for example, α-lactoglobulin (Kjellin et al., 2010).
Emulsifiers play two key roles in the creation of successful emulsion-based products. They facilitate the initial formation of fine lipid droplets during homogenization and enhance the stability of the lipid droplets once they have been formed. Oil-in-water emulsions may be formed using either high- or low-energy approaches. High-energy approaches utilize mechanical devices such as homogenizers, microfluidizers, high shear mixers, colloid mills, and sonicators. Quillaja saponin is a natural effective emulsifier to form and stabilize oil/water emulsions with very small oil beads (d < 200 nm). They are stable in wide range of environmental parameters (pH, ionic strength, temperature). This fact makes Quillaja saponins suitable for wide application in food products (McClements & Gumus, 2016). Quillaja saponins currently find commercial applications as emulsifiers with milk and egg proteins such as β-lactoglobulin, β-casein or egg lysozyme by stabilisation through electrostatic and hydrophobic interactions as well as by specific sugar binding sites (Kezwon & Wojciechowski, 2014).
One of the investigations of the emulsifying properties of Quillaja saponins was carried out by Pekdemir et al. (2005), who screened for a natural surfactant to be used for the emulsification of Ekofisk crude oil from the North Sea. The researchers found that Quillaja bark saponin was able to emulsify the crude oil even at low concentrations of 0.1%, albeit only to a limited oil-to-surfactant ratio (Pekdemir et al., 2005). In recent years though, many studies have been performed to elucidate the formation of emulsions stabilized by various Quillaja saponin products and manufactured with different homogenization techniques (Chung etl., 2017). The observed emulsion-stabilizing properties were attributed to a strong electrostatic repulsion provided by Quillaja saponins because they have an unusually high negative ζ-potential of approximately −60 mV between pH 3 and 9 (Yang et al., 2013; Zhang et al., 2015). An additional contributor is their fast adsorption kinetics (Böttcher et al., 2017; Zhang et al., 2015). Lower mean droplet sizes of emulsions stabilized with Quillaja saponins can be achieved at higher saponin concentrations (Reichert et al., 2018; Yang et al., 2013), at high homogenization pressures (Yang et al., 2013), and after several homogenization passes (de Faria et al., 2017; Yang et al., 2013; Zhang et al., 2015).
7.2. Saponins as Natural Foaming Agents
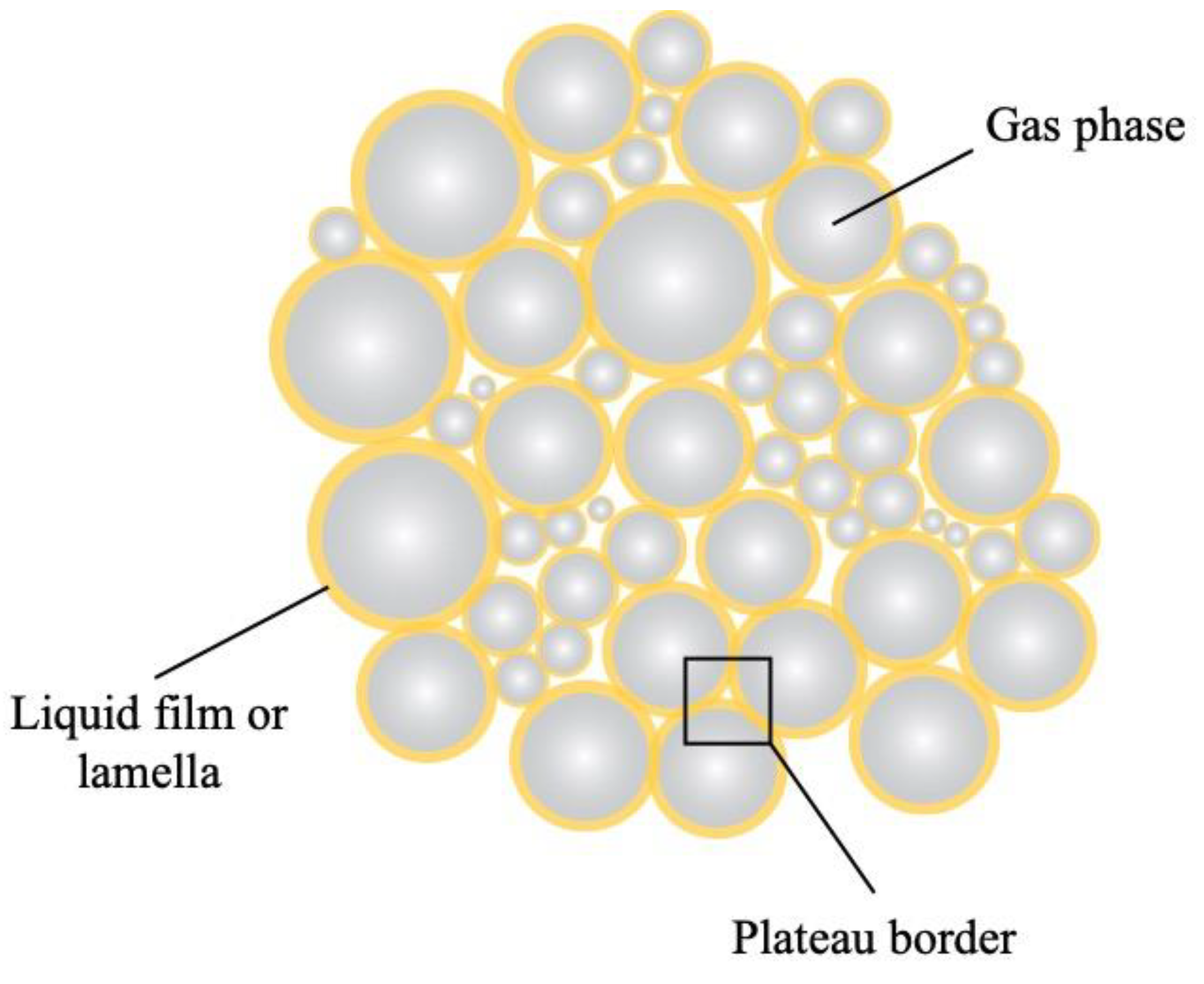
A foam consists of a gas dispersed in a liquid, solid, or gelled matrix in the form of bubbles (Drenckhan & Saint-Jalmes, 2015). Basically, the gas bubbles (often air) are surrounded by a continuous thin liquid film, the so-called lamella, and thin film intersections (Plateau borders) (
Figure 7), forming interstitial spaces between the bubbles, and thus creating a three-dimensional network (Reichert et al., 2019). The formation of foams requires energy and is facilitated by whipping, shaking, or sparging of a solution (Drenckhan et al., 2015). Depending on the chosen application, the continuous liquid phase can additionally be gelled or solidified after the foam has been generated (Rio et al., 2014). Foams are thermodynamically unstable and as such are prone to different instability mechanisms induced by gravitational and van der Waals forces, leading to drainage, coalescence, and coarsening (Hill & Eastoe, 2017). Therefore, their stabilization requires surface-active compounds such as surfactants and (bio)polymers and particles such as silica and polystyrene latex particles (Hill et al., 2017). These surface-active molecules adsorb to the gas–liquid interface and reduce the interfacial tension, thus enabling the formation and stabilization of foams. The stabilization mechanisms and kinetic stability of the foams depend on the characteristics of the surface-active compounds used (Hill et al., 2017).
Generally, saponins with one sugar chain have superior foaming characteristics compared to those containing more sugar chains (Kjellin & Johansson, 2010). Quillaja saponins are well known for their foaming ability. In fact, indigenous peoples of Chile used the aqueous solution of Quillaja saponaria bark to wash their hair and clothes as it produces a foam like soap lather (Güçlü-Üstündağ et al., 2007). The quality and quantity of foam produced in the extract is used to qualitatively measure the concentration of saponins in the extracts (San Martín & Briones, 2000). Quillaja extract exhibits a good foam-stabilizing ability, with 85% of the foam still intact after 1 h of storage (Böttcher & Drusch, 2016). Quillaja saponin–stabilized foams are found to be more stable at lower pH (pH 3) and higher ionic strength (500 mM NaCl). It is suggested that bidesmosidic nature of Quillaja saponins helps in reducing the destabilization of the membrane in foams (Böttcher et al., 2016).
A study involving foaming attributes of the saponins from Camellia oleifera showed that the crude saponin content in the defatted seed meal of C. oleifera was 8.34% and the total saponins content in the crude saponins extract was 39.5% (w/w) (Chen et al. 2010). The foaming power of the 0.5% crude saponins extract solution from defatted seed meal of C. oleifera was 37.1% compared to that of 0.5% sodium lauryl sulfate or Tween 80 solutions.
The green fruits of yerba mate (Ilex paraguariensis), a South American plant are a rich source of non-toxic and very low haemolytic saponins (Canto et al., 2010). A study conducted to compare the effectiveness of mate saponin fraction (MSF) with sodium dodecyl sulfate (ionic surfactant) and polysorbate 80 (non-ionic surfactant) showed that the foamability of MSF and both reference surfactants were equivalent. The addition of MgCl2 resulted in a negative effect on MSF foamability. The salts NaCl, KBr, and KNO3 exhibited a negative influence on MSF foam lifetime and film drainage.
7.3. Saponins as Natural Antioxidants
Saponins are well recognized for their antioxidant activities. A higher free radical scavenging capacity was found for Quillaja saponin extract compared to lecithin when using the oxygen radical absorbance capacity assay (Uluata et al., 2015). Quillaja saponin extract was also reported for its ability to make a significant reduction in hydroperoxide and propanal (propionaldehyde) formation in nanoemulsions stabilised by saponin-rich extract compared to lecithin, SDS and Tween 80-based systems (Uluata et al., 2015). Ivy leaf extract is a rich source of triterpenoid monodesmosidic saponins which exhibit a high antioxidant activity, DPPH radical and superoxide anion scavenging, hydrogen peroxide scavenging and metal chelating activities (Gülçin et al., 2004). These saponins demonstrate expectorant, mucolytic, spasmolytic, bronchodilatory, and antibacterial effects and are widely used the treatment of Bronchitis and pneumonia (Pizzorno et al., 2016). A study that investigated the possible antiradical and antioxidant activity of the monodesmosidic and crude extract of Leontice smirnowii showed a strong inhibition effect of peroxidation of linoleic acid emulsion (Gülçin et al., 2006). It has been reported that some saponins in legumes, such as soybeans, kidney beans, peanuts, chickpeas and clover, antioxidant properties are associated with the presence of DDMP (2,3-dihydro-2,5-dihydroxy-6-methyl-4H-pyran-4-one) linked to the C-22 of saponin aglycones (Takada et al., 2012; Yoshiki et al., 2001). In some saponin extracts including those from Quillaja, antioxidant properties are associated with the presence of phenolic compounds and their presence at the interface facilitated by saponin molecules (Tippel et al., 2017).
Han et al. (2019) investigated the contents of saponins and phenolic compounds in relation to their antioxidant activity and α-glucosidase inhibition activity of several coloured quinoa varieties. It was found that higher degree of milling through what mechanism? can reduce the contents of saponins, total phenolics and anti-nutritional factors and improve their sensory quality irrespective of the varietal differences. The saponins and phenolic compounds significantly contribute to the antioxidant activities of quinoa. In another study, quinoa sprouts showed better antioxidant activity than fully grown parts of the quinoa plant. Overall, root and sprout had a higher antioxidant capacity compared to other parts of the quinoa plant, suggesting the potential use of quinoa root and sprout as a nutraceutical ingredient in the health food industry (Lim et al., 2020).
Study of the antioxidant activities of Aralia taibaiensis, a natural medicinal and food plant that is rich in triterpenoid saponins, in D-galactose induced aging rats showed that it possesses a radical scavenging effect and can alleviate D-gal-induced aging damage in rats (Li et al., 2021). The saponins from Hedera helix, and Hedera colchica exhibited a strong total antioxidant activity. At the concentration of 75 pg/mL, these saponins showed 94, 86, 88 and 75% inhibition on lipid peroxidation of linoleic acid emulsion, respectively. These various antioxidant activities were compared with model antioxidants such as a-tocopherol, butylated hydroxyanisole (BHA) and butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT) (Gülçin et al., 2004).
Among crude and total saponin fractions of Chlorophytum borivilianum, the crude extract showed higher free radical scavenging activity (ascorbic acid equivalents 2578 ± 111 mg AA/100 g) and bleaching activity (IC50 = 0.7 mg mL−1), whist the total purified??? saponin fraction displayed higher ferrous ion chelating (EC50 = 1 mg mL−1) (Ashraf et al., 2013).
7.4. Medicinal Applications of Saponins
Saponins are considered pro-drugs as they are converted to pharmacologically active substances after metabolization in the body (Waheed et al., 2012). Various in vivo studies have established their haemolytic (Hassan et al., 2010), anti-inflammatory (Just et al., 1998), antibacterial (Sparg et al., 2004), antifungal (Sindambiwe et al., 1998), antiviral (Simões et al., 1999), insecticidal (Ellen et al., 2007), anticancer (Cheng et al., 2011), cytotoxic (Mbaveng et al., 2018), hepatoprotective and molluscicidal (Abdel-Gawad et al., 1999) properties. In addition, saponins are reported to exhibit cholesterol-lowering action in animals and human (Moghimipour & Handali, 2015; Oboh & Omofoma, 2008) and are found effective in decreasing blood glucose level in diabetic patients (El Barky et al., 2017). Several mechanisms have been proposed to explain the hypocholesterolemic activity of saponins. Possible mechanisms may involve the capacity of saponins to form insoluble complexes with cholesterol, interfere with bile acid metabolism, and inhibit lipase activity, or regulate cholesterol homeostasis via monitoring the expression of the key regulatory genes of proteins or enzymes related to cholesterol metabolism (Marrelli et al., 2016; Zhao, 2016). Cholesterol-lowering activity of saponins has been demonstrated in both animal and human trials. Animal diets containing purified saponins or concentrated saponin extracts containing digitonin (saponin from Digitalis purpurea), saikosaponin (saponin from Bupleurumfalcatum and related plants) as well as saponins from Saponaria, soya, chickpea, Yucca, alfalfa, fenugreek, Quillaja, Gypsohila, and garlic resulted in reductions of cholesterol concentrations (Güçlü-Üstündağ et al., 2007).
Saponins can also be beneficial for hyperlipidaemia and are capable of reducing the risk of heart disease in humans (Mohan et al., 2016). Saponin may play a major role in protection from cancer. Research on colon cancer cells suggests that it is the lipophilic saponin cores that may be responsible for the biological activity (Mohan et al., 2016). The study of the relationship between chemical structure of aglycones and colon anticancer activity of saponins revealed that the sapogenols were more bioactive than the glycosidic saponins. Other aglycones with anticancer activity include dammarane sapogenins from ginseng, betulinic acid, and oleanolic acid. These compounds were also reported to possess anti-viral, anti-inflammatory, hepatoprotective, anti-ulcer, antibacterial, hypoglycaemic, anti-fertility, and anticariogenic activities. However, the conversion of saponins to their aglycones may result in the loss of activity. For example, the hydrolysis of saponins by ruminal bacteria results in the loss of antiprotozoal activity. Similarly, the deacylation of Quillaja saponins decreases their adjuvant activity (Marciani et al., 2002).
Due to the structural complexity and toxicity of plant saponins, their use in human vaccines is limited, but the progress in new processing and purification techniques with maintaining of immunological adjuvant activity is important to create saponins as new generation vaccines (Netala et al., 2015).
A steroidal saponin glycoside isolated from Fagonia indica was found to induce cell-selective apoptosis or necrosis in cancer cells. The clinical significance of triterpenoid saponins in the prevention and treatment of metabolic and vascular disease is noteworthy.
Saponins from various sources are important constituents of traditional folk medicines. Ginsenosides are saponins produced by Panax species which are known for their antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-cancer activities (Qi et al., 2011). It has been reported that most saponins form insoluble complexes with 3-β-hydroxysteroids and are known to interact with bile acids and cholesterol forming large mixed micelles. These functionalities are thought to result in the cholesterol-lowering capacities of saponins in some animal species; however, their hypocholesterolemic effects in humans are more speculative (Mohan et al., 2016).
Although saponins are considered beneficial in several medical conditions and are being used as alternative medical substances, a detailed understanding of the relationship between the chemistry of saponins and their interactions with signalling and other biological pathways and systems is necessary to confirm action and safety for human or animal use. Multidisciplinary approaches involving chemists, physicians, toxicologists, molecular biologists and others will be essential to shed more light on this space (Sheng & Sun, 2011).
8. Bioavailability of Saponins
Saponins are generally regarded as having low bioavailability. The absorption of saponins in the human diet is highly variable and is affected by several factors, including the amount of saponins consumed in a meal, interaction of saponins with bile acids and other micronutrients, food processing methods, and metabolic adaptation of individuals to dietary saponins (Zhao, 2016). Saponins imparts bitter taste in dietary plants at high concentrations which ultimately reduces the consumption of saponins by animals and humans (Liener, 1994). It was also reported that acetyl-soya saponins taste more bitter than nonacetylated constituents (Shimoyamada et al., 1990).
Studies involving physiological digestion and absorption of saponins in the human body revealed that they have longer residence time in the gastrointestinal tract and are poorly absorbed in the body. This is mainly attributed to their large molecular mass (> 500 Da), high hydrogen-bonding capacity (> 12), and high molecular flexibility (> 10), resulting in poor membrane permeability (Yu et al., 2012). If saponins are not absorbed through the small intestine, they pass to the large intestine where the gut microbiota converts them to the sapogenin. Various in vivo studies with rats, mice, and rabbits demonstrated that saponins are not absorbed in the alimentary canal and passes to the large intestine where they get hydrolysed enzymatically to sapogenins (Güçlü-Üstündağ et al., 2007). These sapogenins usually have better lipid solubility and are more readily absorbed in the body (Bone et al., 2012).
Interaction of saponins with minerals such as zinc and iron forms insoluble phytate-mineral complexes resulting in the reduction in the bioavailability of both saponin and the minerals (Shi et al., 2004). Saponins from alfalfa and soybean were reported to decrease iron and zinc absorption in rats and pigs (Shi et al., 2004).
9. Food Regulations on Saponin Products
It's important to note that the use of saponins in food applications requires careful consideration of their concentration, interactions with other food components, and potential effects on taste and texture. Additionally, specific regulations and safety guidelines regarding the use of saponins in food products may vary across different countries or regions.
Food Standards Australia and New Zealand approved the use of saponin-rich Quillaia/ Quillaja extract as a Food Additive (Emulsifier) in 2013. Quillaia extracts type 1 (INS 999i), and type 2 (INS 999ii) are listed in the Codex Alimentarius General Standard for Food Additives. The permissions are for addition to specific types of water-based flavoured drinks, including “sport”, “energy”, or “electrolyte” drinks and particulate drinks. The maximum level of addition is 50 mg/kg expressed on a saponins basis, but only for Quillaia extract type 1. The functional class is listed as emulsifier and foaming agent. Both extracts differ in their purity and the concentrations of the active ingredients, i.e., saponin. Similarly, the European Food Safety Authority has also permitted Quillaia extract (E999) for use in non-alcoholic flavoured beverages and cider (excluding cidre bouché) to a maximum level of 200 mg/L as an anhydrous extract.
Quillaia extract has the generally recognized as safe (GRAS) status in the USA, for its use as an emulsifier or encapsulating agent in beverage products, to deliver fats, nutrients, vitamins, colours, and clouding agents to a similar range of beverages and a foaming agent for semi-frozen carbonated and non-carbonated beverages. It is also permitted as a flavouring adjuvant, with technological function as emulsifier, stabiliser, or foam stabiliser for both natural and synthetic flavours. Similarly, Quillaia extract is approved in Canada as a miscellaneous food additive in beverage bases, beverage mixes and soft drinks as a foaming agent. Saponin-rich quillaia extract is permitted in several other countries (China, Japan, India, Singapore, Thailand, Taiwan, and Vietnam) in food and pharmaceutical applications. The permissions are for its use with flavours, as an emulsifier or stabiliser, or as a foaming agent for a range of beverages at a wide range of levels from 50 mg/kg saponins to 1,500 mg/kg. As such, regulatory advice will need to be sought prior to introduction of any saponin containing extracts or ingredients to the Australian foods & beverages or supplements sector, as indeed is the case for introductions to markets in other jurisdictions.
10. Concluding Remarks and Future Perspectives
In conclusion, saponins are a diverse group of compounds with unique chemistry and occurrences in the plant kingdom. Their structural diversity, characterized by a hydrophilic sugar moieties attached to lipophilic aglycones, contributes to their wide-ranging functional and biological properties. Saponins have shown great potential in various applications, particularly in the food, cosmetics and pharmaceutical industries. In food applications, saponins serve as natural emulsifiers, foaming agents and stabilizers resulting in enhanced texture and stability in food products. They also exhibit potential health benefits, including cholesterol-lowering and anticancer effects, making them attractive functional food ingredients. Saponins derived from certain plants have shown promising health benefits, such as cholesterol-lowering or immune system modulatory effects. Similarly, saponins' antimicrobial properties could be explored for their potential as natural preservatives in food products as they may help to inhibit the growth of spoilage-causing microorganisms and extend the shelf life of perishable goods. They may also be incorporated into (edible) packaging as antimicrobial agents and help address the challenge of shelf-life extension of foods. However, barriers such as bitterness and cytotoxicity need to be addressed to fully exploit saponins’ potential in the food industry. Due to increased consumer focus towards natural ingredients, saponins application in food, cosmetic and pharmaceutical sector could witness a substantial growth in the coming decade is structure function relationships can be further understood and tailored to end-use.
In the pharmaceutical field, saponins possess diverse bioactivities, including anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, antiviral and antiparasitic properties. Their cytotoxic activity against cancer cell lines has also generated interest in their potential as anticancer agents. Furthermore, saponins can act as adjuvants, improving immune response in vaccines, and as drug delivery agents, enhancing solubility and bioavailability. In the future, they may be employed as excipients or carriers in pharmaceutical formulations to improve drug delivery and increase the efficacy of therapeutic compounds. Some saponins have exhibited cytotoxic properties against cancer cells. Further research may focus on the development of saponin-based drugs or formulations for targeted cancer therapies, potentially complementing existing treatment modalities.
Saponins have cleansing and foaming properties, making them potential alternatives to synthetic surfactants in personal care products such as shampoos, soaps, and body washes. Their natural origin and mildness may appeal to consumers seeking sustainable and skin-friendly options. Due to their reported antioxidant and skin-soothing properties, saponins may find applications in cosmetics and skincare products. They could be explored as natural ingredients in formulations for anti-aging, skin hydration, or soothing sensitive skin.
Future research on saponins might focus on addressing the challenges associated with their utilization, such as bitterness and cytotoxicity. Further investigations into their mechanisms of action, bioavailability, and interactions with other compounds including the human body are needed to fully understand their potential in food, cosmetics and pharmaceutical applications. Additionally, exploring novel sources of saponins and developing sustainable extraction methods can broaden their availability and enhance their commercial viability. In summary, saponins offer exciting prospects for the food and associated industries due to their unique chemistry, diverse functionalities, and potential health benefits. Continued research and innovation will pave the way for their successful integration into various applications, contributing to improved human health and well-being.
References
- Abdel-Gawad, M.; El-Sayed, M.; Abdel-Hameed, E. Molluscicidal steroidal saponins and lipid content of Agave decipiens. Fitoterapia 1999, 70, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, S.; Abdurahman, N.H.; Kudrashou, V. Surface Activity and Emulsification Properties of Saponins as Biosurfactants. 2023, 137–153. [CrossRef]
- Alamgir, A.N.M.; Alamgir, A.N.M. Secondary metabolites: Secondary metabolic products consisting of C and H; C, H, and O; N, S, and P elements; and O/N heterocycles. In Therapeutic Use of Medicinal Plants and their Extracts: Phytochemistry and Bioactive Compounds; 2018; Volume 2, pp. 165–309.
- Aldin, E.; Reitmeier, H.A.; Murphy, P. Bitterness of Soy Extracts Containing Isoflavones and Saponins. J. Food Sci. 2006, 71, S211–S215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alice, C.; Vargas, V.; Silva, G.; de Siqueira, N.; Schapoval, E.; Gleye, J.; Henriques, J.; Henriques, A. Screening of plants used in south Brazilian folk medicine. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1991, 35, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashraf, M.F.; Aziz, M.A.; Stanslas, J.; Ismail, I.; Kadir, M.A. Assessment of Antioxidant and Cytotoxicity Activities of Saponin and Crude Extracts ofChlorophytum borivilianum. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustin, J.M.; Kuzina, V.; Andersen, S.B.; Bak, S. Molecular activities, biosynthesis and evolution of triterpenoid saponins. Phytochemistry 2011, 72, 435–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachran, C.; Bachran, S.; Sutherland, M.; Bachran, D.; Fuchs, H. Preclinical Studies of Saponins for Tumor Therapy. 2014, 272–302. [CrossRef]
- Berhow, M.A.; Cantrell, C.L.; Duval, S.M.; Dobbins, T.A.; Maynes, J.; Vaughn, S.F. Analysis and quantitative determination of group B saponins in processed soybean products. Phytochem. Anal. Int. J. Plant Chem. Biochem. Tech. 2002, 13, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bissinger, R.; Modicano, P.; Alzoubi, K.; Honisch, S.; Faggio, C.; Abed, M.; Lang, F. Effect of saponin on erythrocytes. Int. J. Hematol. 2014, 100, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bone, K.; Simon Mills MC, P.P.; Fnimh, M.A. Principles and practice of phytotherapy: modern herbal medicine. Elsevier Health Sciences. 2012.
- Böttcher, S.; Drusch, S. Interfacial Properties of Saponin Extracts and Their Impact on Foam Characteristics. Food Biophys. 2015, 11, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böttcher, S.; Keppler, J.K.; Drusch, S. Mixtures of Quillaja saponin and beta-lactoglobulin at the oil/water-interface: Adsorption, interfacial rheology and emulsion properties. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 518, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canto, G.S.D.; Treter, J.; Yang, S.; Borré, G.L.; Peixoto, M.P.G.; Ortega, G.G. Evaluation of foam properties of saponin from Ilex paraguariensis A. St. Hil. (Aquifoliaceae) fruits. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 46, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheeke, P.R. Actual and potential applications ofYuccaschidigeraandQuillaja saponariasaponins in human andanimal nutrition. Proc. Phytochem. Soc. Eur. 2000, 45, 241–254. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Miao, Y.; Huang, L.; Li, J.; Sun, H.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhou, W. Antioxidant activities of saponins extracted from Radix Trichosanthis: an in vivo and in vitro evaluation. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 14, 86–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-F.; Yang, C.-H.; Chang, M.-S.; Ciou, Y.-P.; Huang, Y.-C. Foam Properties and Detergent Abilities of the Saponins from Camellia oleifera. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2010, 11, 4417–4425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.-C.; Lu, J.-F.; Wang, J.-S.; Lin, L.-J.; Kuo, H.-I.; Chen, B.-H. Antiproliferation Effect and Apoptosis Mechanism of Prostate Cancer Cell PC-3 by Flavonoids and Saponins Prepared from Gynostemma pentaphyllum. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 11319–11329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, C.; Sher, A.; Rousset, P.; Decker, E.A.; McClements, D.J. Formulation of food emulsions using natural emulsifiers: Utilization of quillaja saponin and soy lecithin to fabricate liquid coffee whiteners. J. Food Eng. 2017, 209, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabestani, M.; Yeganehzad, S.; Miller, R. A natural source of saponin: Comprehensive study on interfacial properties of Chubak (Acanthophyllum Glandulosum) root extract and related saponins. Colloids Surfaces A: Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 630, 127594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Faria, J.T.; de Oliveira, E.B.; Minim, V.P.R.; Minim, L.A. Emulsifying properties of β-lactoglobulin and Quillaja bark saponin mixtures: Effects of number of homogenization passes, pH, and NaCl concentration. Int. J. Food Prop. 2017, 20, 1643–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decroo, C.; Colson, E.; Demeyer, M.; Lemaur, V.; Caulier, G.; Eeckhaut, I.; Cornil, J.; Flammang, P.; Gerbaux, P. Tackling saponin diversity in marine animals by mass spectrometry: data acquisition and integration. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 3115–3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Liang, W.; Wang, T.; Sui, J.; Wang, J.; Deng, Z.; Chen, D. Saponins regulate intestinal inflammation in colon cancer and IBD. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 144, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drenckhan, W.; Saint-Jalmes, A. The science of foaming. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 222, 228–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashour, A.S.; El Aziz, M.M.A.; Melad, A.S.G. A review on saponins from medicinal plants: chemistry, isolation, and determination. J. Nanomed. Res. 2019, 7, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elekofehinti, O.O. Saponins: Anti-diabetic principles from medicinal plants – A review. Pathophysiology 2015, 22, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellen, D.; Ellen, L.; Danny, G.; Guy, S. Novel advances with plant saponins as natural insecticides to control pest insects. Pest Technology, 2007, 96–105.
- Francis, G.; Kerem, Z.; Makkar, H.P.S.; Becker, K. The biological action of saponins in animal systems: a review. Br. J. Nutr. 2002, 88, 587–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Güçlü-Üstündağ, Ö.; Mazza, G. Saponins: properties, applications and processing. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2007, 47, 231–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gülçin, İ.; Mshvildadze, V.; Gepdiremen, A.; Elias, R. Antioxidant activity of saponins isolated from ivy: α-hederin, hederasaponin-C, hederacolchiside-E and hederacolchiside-F. Planta Medica 2004, 70, 561–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gülçin, I.; Mshvildadze, V.; Gepdiremen, A.; Elias, R. Screening of antiradical and antioxidant activity of monodesmosides and crude extract from Leontice smirnowii tuber. Phytomedicine 2006, 13, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurfinkel, D.M.; Rao, A.V. Soyasaponins: The Relationship Between Chemical Structure and Colon Anticarcinogenic Activity. Nutr. Cancer 2003, 47, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Chi, J.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, R.; Fan, S.; Huang, F.; Xue, K.; Liu, L. Characterization of saponins and phenolic compounds: antioxidant activity and inhibitory effects on α-glucosidase in different varieties of colored quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd). Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2019, 83, 2128–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, S.; Haq, A.; Byrd, J.; Berhow, M.; Cartwright, A.; Bailey, C. Haemolytic and antimicrobial activities of saponin-rich extracts from guar meal. Food Chem. 2010, 119, 600–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heng, L.; Vincken, J.-P.; van Koningsveld, G.; Legger, A.; Gruppen, H.; van Boekel, T.; Roozen, J.; Voragen, F. Bitterness of saponins and their content in dry peas. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2006, 86, 1225–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, C.; Eastoe, J. Foams: From nature to industry. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 247, 496–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Just, M.J.; Recio, M.C.; Giner, R.M.; Cuéllar, M.J.; Máñez, S.; Bilia, A.R.; Ríos, J.-L. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Unusual Lupane Saponins fromBupleurum fruticescens. Planta Medica 1998, 64, 404–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kareru, P.; Keriko, J.; Gachanja, A.; Kenji, G. Direct Detection Of Triterpenoid Saponins In Medicinal Plants. Afr. J. Tradit. Complement. Altern. Med. 2008, 5, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karnwal, A.; Shrivastava, S.; Al-Tawaha, A.R.M.S.; Kumar, G.; Singh, R.; Kumar, A.; Mohan, A.; Yogita; Malik, T. Microbial Biosurfactant as an Alternate to Chemical Surfactants for Application in Cosmetics Industries in Personal and Skin Care Products: A Critical Review. BioMed Res. Int. 2023, 2023, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerwin, S.M. Soy saponins and the anticancer effects of soybeans and soy-based foods. Curr. Med. Chem. Agents 2004, 4, 263–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kezwon, A.; Wojciechowski, K. Interaction of Quillaja bark saponins with food-relevant proteins. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 209, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-W.; Park, S.-K.; Kang, S.-L.; Kang, H.-C.; Oh, H.-J.; Bae, C.-Y.; Bae, D.-H. Hypocholesterolemic property ofYucca schidigera andQuillaja saponaria extracts in human body. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2003, 26, 1042–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjellin, M.; Johansson, I. Surfactants from Renewable Resources; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kowalczyk, M.; Pecio, Ł.; Stochmal, A.; Oleszek, W. Qualitative and quantitative analysis of steroidal saponins in crude extract and bark powder of Yucca schidigera Roezl. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 8058–8064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kregiel, D.; Berlowska, J.; Witonska, I.; Antolak, H.; Proestos, C.; Babic, M.; Zhang, B. Saponin-based, biological-active surfactants from plants. Appl. Charact. Surfactants 2017, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhai, B.; Sun, J.; Fan, Y.; Zou, J.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, X.; Shi, Y.; Guo, D. Antioxidant, Anti-Aging and Organ Protective Effects of Total Saponins from Aralia taibaiensis. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2021, 15, 4025–4042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liener, I.E. Implications of antinutritional components in soybean foods. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 1994, 34, 31–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, J.G.; Park, H.; Yoon, K.S. Analysis of saponin composition and comparison of the antioxidant activity of various parts of the quinoa plant ( Chenopodium quinoa Willd.). Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 8, 694–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Henkel, T. Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM): are polyphenols and saponins the key ingredients triggering biological activities? Curr. Med. Chem. 2002, 9, 1483–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marciani, D.J.; Ptak, R.G.; Voss, T.G.; Reynolds, R.C.; Pathak, A.K.; Chamblin, T.L.; Scholl, D.R.; May, R.D. Degradation of Quillaja saponaria Molina saponins: loss of the protective effects of a herpes simplex virus 1 subunit vaccine. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2002, 2, 1703–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrelli, M.; Conforti, F.; Araniti, F.; Statti, G.A. Effects of Saponins on Lipid Metabolism: A Review of Potential Health Benefits in the Treatment of Obesity. Molecules 2016, 21, 1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuura, H. Saponins in Garlic as Modifiers of the Risk of Cardiovascular Disease. J. Nutr. 2001, 131, 1000S–1005S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbaveng, A.T.; Ndontsa, B.L.; Kuete, V.; Nguekeu, Y.M.; Çelik, I.; Mbouangouere, R.; Tane, P.; Efferth, T. A naturally occuring triterpene saponin ardisiacrispin B displayed cytotoxic effects in multi-factorial drug resistant cancer cells via ferroptotic and apoptotic cell death. Phytomedicine 2018, 43, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J.; Gumus, C.E. Natural emulsifiers — Biosurfactants, phospholipids, biopolymers, and colloidal particles: Molecular and physicochemical basis of functional performance. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 234, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milgate, J.; Roberts, D. The nutritional & biological significance of saponins. Nutr. Res. 1995, 15, 1223–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, S.; Dungan, S.R. Cholesterol Solubilization in Aqueous Micellar Solutions of Quillaja Saponin, Bile Salts, or Nonionic Surfactants. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 49, 384–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghimipour, E.; Handali, S. Saponin: properties, methods of evaluation and applications. Annu. Res. Rev. Biol. 2015, 207–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, V.; Tresina, P.; Daffodil, E. Antinutritional factors in legume seeds: characteristics and determination. In Encyclopedia of Food and Health, Benjamin Caballero; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 211–220. [Google Scholar]
- Montoro, P.; Skhirtladze, A.; Perrone, A.; Benidze, M.; Kemertelidze, E.; Piacente, S. Determination of steroidal glycosides in Yucca gloriosa flowers by LC/MS/MS. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2010, 52, 791–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moses, T.; Papadopoulou, K.K.; Osbourn, A. Metabolic and functional diversity of saponins, biosynthetic intermediates and semi-synthetic derivatives. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 49, 439–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muir, A.; Paton, D.; Ballantyne, K.; Aubin, A. Process for recovery and purification of saponins and sapogenins from quinoa. Chenopodium quinoa. 2002.
- Nasri, H.; Baradaran, A.; Shirzad, H.; Rafieian-Kopaei, M. New Concepts in Nutraceuticals as Alternative for Pharmaceuticals. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2014, 5, 1487–1499. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Netala, V.R.; Ghosh, S.B.; Bobbu, P.; Anitha, D.; Tartte, V. Triterpenoid saponins: a review on biosynthesis, applications and mechanism of their action. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 7, 24–28. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, L.; Farcas, A.; Socaci, S.A.; Tofana, M.; Diaconeasa, Z.M.; Pop, O.L.; Salanta, L. An Overview of Saponins–A Bioactive Group. Bull. UASVM Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 77, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oakenfull, D. Soy Protein, Saponins and Plasma Cholesterol. J. Nutr. 2001, 131, 2971–2971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oboh, H.; Omofoma, C. The Effects of Heat Treated Lima Beans (Phaseolus lunatus) on Plasma Lipids in Hypercholesterolemic Rats. Pak. J. Nutr. 2008, 7, 636–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oda, K.; Matsuda, H.; Murakami, T.; Katayama, S.; Ohgitani, T.; Yoshikawa, M. Adjuvant and Haemolytic Activities of 47 Saponins Derived from Medicinal and Food Plants. Biol. Chem. 2000, 381, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oleszek, W. Chromatographic determination of plant saponins. J. Chromatogr. A 2001, 967, 147–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oleszek, M.; Oleszek, W. Saponins in food. In Handbook of Dietary Phytochemicals; 2020; pp. 1–40.
- Pekdemir, T.; Çopur, M.; Urum, K. Emulsification of Crude Oil–Water Systems Using Biosurfactants. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2005, 83, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzorno, J.E.; Murray, M.T.; Joiner-Bey, H. pneumonia. In The Clinician's handbook of natural medicine; Churchill Livingstone: London, UK, 2016; pp. 147–157. [Google Scholar]
- Podolak, I.; Galanty, A.; Sobolewska, D. Saponins as cytotoxic agents: A review. Phytochem. Rev. 2010, 9, 425–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, L.-W.; Wang, C.-Z.; Yuan, C.-S. Ginsenosides from American ginseng: Chemical and pharmacological diversity. Phytochemistry 2011, 72, 689–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, L.; Ruan, J.; Wu, S.; Huang, P.; Yan, J.; Yu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, T. Separation and Bioactive Assay of 25R/S-Spirostanol Saponin Diastereomers from Yucca schidigera Roezl (Mojave) Stems. Molecules 2018, 23, 2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichert, C.L.; Salminen, H.; Weiss, J. Quillaja Saponin Characteristics and Functional Properties. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 10, 43–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichert, C.L.; Salminen, H.; Bönisch, G.B.; Schäfer, C.; Weiss, J. Concentration effect of Quillaja saponin – Co-surfactant mixtures on emulsifying properties. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 519, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rickert, D.; Meyer, M.; Hu, J.; Murphy, P. Effect of Extraction pH and Temperature on Isoflavone and Saponin Partitioning and Profile During Soy Protein Isolate Production. J. Food Sci. 2004, 69, C623–C631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridout, C.L.; Price, K.R.; Dupont, M.S.; Parker, M.L.; Fenwick, G.R. Quinoa saponins—analysis and preliminary investigations into the effects of reduction by processing. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1991, 54, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rio, E.; Drenckhan, W.; Salonen, A.; Langevin, D. Unusually stable liquid foams. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 205, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roopashree, K.; Naik, D. Saponins: properties, applications and as insecticides: a review. Biosci. Trends 2019, 8, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- San Martin, R.; Briones, R. Industrial uses and sustainable supply of Quillaja saponaria (Rosaceae) saponins. Econ. Bot. 1999, 53, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San Martín, R.; Briones, R. Quality control of commercial quillaja (Quillaja saponaria Molina) extracts by reverse phase HPLC. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2000, 80, 2063–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, D.; Pal, R.; Dwivedi, A.K.; Singh, S. Characterisation of sapindosides in Sapindus mukorosii saponin (reetha saponin) and quantitative determination of sapindoside B. 2004.
- Schreiner, T.B.; Dias, M.M.; Barreiro, M.F.; Pinho, S.P. Saponins as Natural Emulsifiers for Nanoemulsions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 6573–6590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, H.; Sun, H. Synthesis, biology and clinical significance of pentacyclic triterpenes: a multi-target approach to prevention and treatment of metabolic and vascular diseases. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2011, 28, 543–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Arunasalam, K.; Yeung, D.; Kakuda, Y.; Mittal, G.; Jiang, Y.; Ercan, P.; El, S.N.; Kim, J.E.; Go, J.; et al. Saponins from Edible Legumes: Chemistry, Processing, and Health Benefits. J. Med. Food 2004, 7, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibata, S. activity. In New Natural Products and Plant Drugs with Pharmacological, Biological or Therapeutical Activity: Proceedings of the First International Congress on Medicinal Plant Research, Section A, held at the University of Munich, Germany, September 6–10; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1976; pp. 177–196. [Google Scholar]
- Shimoyamada, M.; Kudo, S.; Okubo, K.; Yamauchi, F.; Harada, K. Distributions of saponin constituents in some varieties of soybean plant. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1990, 54, 77–81. [Google Scholar]
- Simões, C.; Amoros, M.; Girre, L. Mechanism of antiviral activity of triterpenoid saponins. Phytother. Res. Int. J. Devoted Pharmacol. Toxicol. Eval. Nat. Prod. Deriv. 1999, 13, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sindambiwe, J.B.; Calomme, M.; Geerts, S.; Pieters, L.; Vlietinck, A.J.; Berghe, D.A.V. Evaluation of Biological Activities of Triterpenoid Saponins from Maesa lanceolata. J. Nat. Prod. 1998, 61, 585–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparg, S.G.; Light, M.E.; Van Staden, J. Biological activities and distribution of plant saponins. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2004, 94, 219–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takada, Y.; Tayama, I.; Sayama, T.; Sasama, H.; Saruta, M.; Kikuchi, A.; Ishimoto, M.; Tsukamoto, C. Genetic analysis of variations in the sugar chain composition at the C-3 position of soybean seed saponins. Breed. Sci. 2012, 61, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, L.U. Potential health benefits and problems associated with antinutrients in foods. Food Res. Int. 1993, 26, 131–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tippel, J.; Gies, K.; Harbaum-Piayda, B.; Steffen-Heins, A.; Drusch, S. Composition of Quillaja saponin extract affects lipid oxidation in oil-in-water emulsions. Food Chem. 2017, 221, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uluata, S.; McClements, D.J.; Decker, E.A. Physical stability, autoxidation, and photosensitized oxidation of ω-3 oils in nanoemulsions prepared with natural and synthetic surfactants. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 9333–9340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinay, T.-N.; Park, C.-S.; Kim, H.-Y.; Jung, S.-J. Toxicity and dose determination of quillaja saponin, aluminum hydroxide and squalene in olive flounder (Paralichthys olivaceus). Veter- Immunol. Immunopathol. 2014, 158, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincken, J.-P.; Heng, L.; de Groot, A.; Gruppen, H. Saponins, classification and occurrence in the plant kingdom. Phytochemistry 2007, 68, 275–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waheed, A.; Barker, J.; Barton, S.J.; Owen, C.P.; Ahmed, S.; Carew, M.A. A novel steroidal saponin glycoside from Fagonia indica induces cell-selective apoptosis or necrosis in cancer cells. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 47, 464–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Leser, M.E.; Sher, A.A.; McClements, D.J. Formation and stability of emulsions using a natural small molecule surfactant: Quillaja saponin (Q-Naturale®). Food Hydrocoll. 2012, 30, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshiki, Y.; Kahara, T.; Okubo, K.; Sakabe, T.; Yamasaki, T. Superoxide-and 1, 1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl radical-scavenging activities of soyasaponin β g related to gallic acid. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2001, 65, 2162–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Chen, F.; Li, C. Absorption, Disposition, and Pharmacokinetics of Saponins from Chinese Medicinal Herbs: What Do We Know and What Do We Need to Know More? Curr. Drug Metab. 2012, 13, 577–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zana, R. Dynamics of Surfactant Self-Assemblies: Micelles, Microemulsions, Vesicles and Lyotropic Phases; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Bing, L.; Reineccius, G.A. Formation, optical property and stability of orange oil nanoemulsions stabilized by Quallija saponins. LWT 2015, 64, 1063–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D. Challenges associated with elucidating the mechanisms of the hypocholesterolaemic activity of saponins. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 23, 52–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Tan, L.; Chen, M.; He, C. Pharmacological activities and molecular mechanisms of Pulsatilla saponins. Chin. Med. 2022, 17, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Yang, J.; Lou, L.; Zhu, L. Solubilization properties of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons by saponin, a plant-derived biosurfactant. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 1198–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).