Submitted:
04 August 2023
Posted:
07 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Literature review
2.1. Analysis of the demand structure in restaurants: consumer preferences
2.2. Impact of the COVID-19 crisis on the restaurant industry
3. Methodology
3.1. Method description
- 1.
- It allows the researcher and the expert to establish a comfortable relationship for more detailed answers on sensitive topics [41].
- 2.
- The researcher can independently select candidates for interviews, to receive the most accurate data obtained sample, and can also ask clarifying questions, obtain additional information, and return to key questions immediately in the dialogue to gain a better understanding of the expert’s attitude to the topic.
- 3.
- In-depth interviews are useful when a detailed portrait of customer opinions and behavior is needed. In addition, researchers analyze innovative ideas and contexts can provide a more accurate picture of market changes [9]. Berent [3] suggested two main reasons for this: first, the respondent’s ability to analyze motivation for a particular action, second, the use of active listening, together with anonymity, gives the respondent a sense of security and the chance to frankly express personal thoughts and feelings. Webb [46] noted researchers could track changes in a respondent's tone and choice of words to accurately interpret expert opinion. This makes it possible to establish a strong mutual understanding and a high degree of trust, thereby improving the data quality.
3.2. Research design
- The preparatory stage contains from sampling strategy development, selecting experts and developing an interview guide (script), which contains the questions, will be asked during the interview.
- A field study consists of recruiting experts, conducting the interview itself, and transcribing the interview, if an audio recording was made, or a text document is immediately recorded with answers to the questions posed during the interview.
- The analytical stage contains the interview results processing and the analytical report preparation. Using the text document data describing the answers and the expert's impressions, an analytical report and/or presentation on the study results is compiled.
3.3. Data collection
4. Findings and discussion
4.1. Analysis of respondent profiles
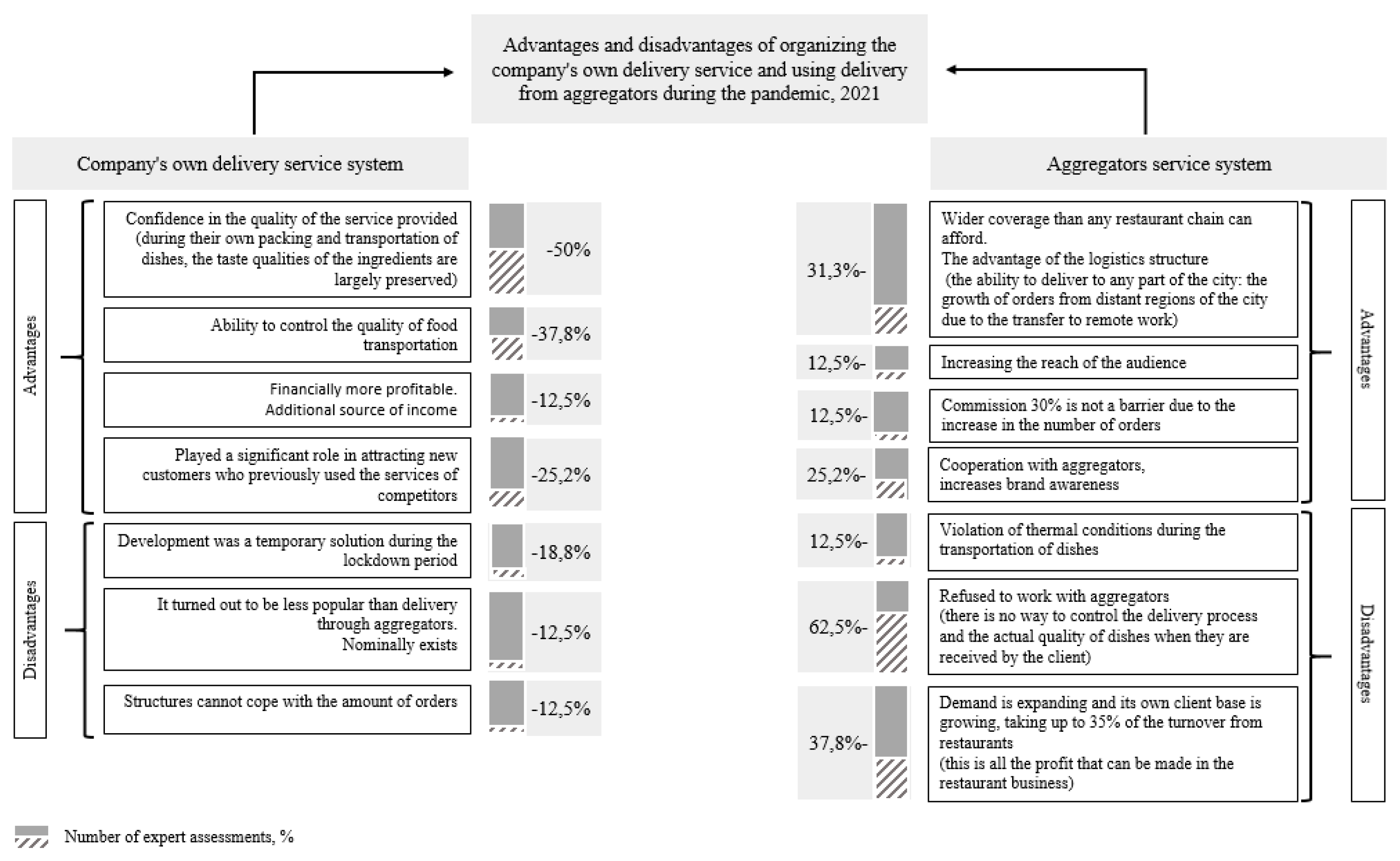
4.2. Restaurant business adaptability results and demand structure analysis
5. Conclusion and implications
- −
- Form a strategy for assessing the material and technical innovation potential, including: 1) material and technical resources availability, 2) production progressiveness and flexibility.
- −
- Analyze the investment innovation potential required, including: 1) financial stability, 2) liquidity and business activity, 3) profitability, 4) innovative financial strategy.
- −
- Assess the staff for innovation potential, including: 1) qualifications and production potential, 2) their motivation to carry out innovative activities, 3) training and retraining.
- −
- Develop an organizational structure most closely matches the strategic choice of the value proposition and, in accordance with it, eliminate problems arise in communication between departments affect products and services quality.
- −
- Implement an adaptation strategy in accordance with the organizational culture, as part of the staff innovative potential assessment, and leave only those aspects the company can provide.
- −
- Carry out regular monitoring, as the information assessment and analytical block part of innovative potential, to consider provided opportunities and prospects, fix real difficulties, rules and restrictions the company will have to face in the near future.
- −
- Divide existing business processes into parts (separate characteristics of the value proposition) to form an understanding of the company's functioning logic and the division of responsibility areas for the products and services provided quality.
- −
- Identify and evaluate the client's attitude to each characteristic of the value proposition.
- −
- Develop or improve business processes considering the consumers interests.
6. Limitations and future research
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Al-kalouti, J., Kumar, V., Kumar, N., Garza-Reyes, J. A., Upadhyay, A., & Zwiegelaar, J. B. Investigating innovation capability and organizational performance in service firms. Strat. Change 2020, 29, 103-113. [CrossRef]
- Bae, S., Slevitch, L., & Tomas, S. The effects of restaurant attributes on satisfaction and return patronage intentions: Evidence from solo diners’ experiences in the United States. Cog. Bus. & Manag. 2018, 5, 1-24. [CrossRef]
- Berent, P. H. Depth Interview. J. of Adv. Res. 1996, 6, 32-39.
- Bilgihan A., Seo S., Choi J. Identifying restaurant satisfiers and dissatisfiers: Suggestions from online reviews. J. of Hospit. Mark. & Manag. 2018, 27, 601–625. [CrossRef]
- Bujisic, M., Bogicevic, V., & Parsa, H. G. The effect of weather factors on restaurant sales. J. of Foodservice Bus. Res. 2017, 20, 350-370. [CrossRef]
- Byrd, K., Fan, A., Her, E., Liu, Y., Leitch, S., & Almanza, B. Restaurant patronage during the COVID-19 pandemic and the protection motivation theory: influence of consumers’ socio-demographic, situational, and psychographic factors. J. of Foodservice Bus. Res. 2021, 1, 1-29. [CrossRef]
- Cacho, J. L., Marques, L., & Nascimento, Á. Customer-Oriented Global Supply Chains: Port Logistics in the Era of Globalization and Digitization. In V. Chkoniya, A. O. Madsen, & P. Bukhrashvili (Eds.), Anthropol. Appr. to Understanding Consumpt. Patterns and Cons. Behav. Hershey, PA, USA: IGI Global 2020, 1, 82–103. [CrossRef]
- Cao Q., Duan W., Gan Q. Exploring determinants of voting for the “helpfulness” of online user reviews: A text mining approach. Decis. Support Syst. 2011, 50, 511–521. [CrossRef]
- Cassell, C., & Symon, G. (Eds.). Essential guide to qualitative methods in organizational research. Sage 2004, 388.
- Cheng, C. C., Chang, Y. Y., Tsai, M. C., Chen, C. T., & Tseng, Y. C. An evaluation instrument and strategy implications of service attributes in LOHAS restaurants. Int. J. of Contemp. Hospit. Manag. 2018, 31, 194-216. [CrossRef]
- Christensen C. M., McDonald, R., Altman, E. J., & Palmer, J. E. Disruptive innovation: An intellectual history and directions for future research. J. of Manag. Stud. 2018, 55, 1043-1078. [CrossRef]
- De Vries, J., Roy, D., & De Koster, R. Worth the wait? How restaurant waiting time influences customer behavior and revenue. J. of Operat. Manag. 2018, 63, 59-78. [CrossRef]
- Durand, R., Grant, R. M., & Madsen, T. L. The expanding domain of strategic management research and the quest for integration. Strat. Manag. J. 2017, 38, 4-16. [CrossRef]
- Fainshtein, E., & Serova, E. Value Proposition of Network Companies Providing Restaurant Services in Russia: Analysis and Evaluation. In Anthropol. Appr. to Understanding Consumpt. Patterns and Cons. Behav. IGI Global 2020, 137-158. [CrossRef]
- Fainshtein, E., & Serova, E. Using Intelligent Text Analysis of Online Reviews to Determine the Main Factors of Restaurant Value Propositions. In Handbook of Res. on Applied Data Sci. and Artif. Intel. in Bus. and Ind. IGI Global 2021, 223-240. [CrossRef]
- Fainshtein E. Value Proposition Analysis of Network Business During Digital Adaptation in COVID-19 Conditions. Mark. and Smart Technol. Springer, Singapore 2021, 205, 145-153. [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, E., Moro, S., Cortez, P., Batista, F., & Ribeiro, R. A data-driven approach to measure restaurant performance by combining online reviews with historical sales data. Int. J. of Hospit. Manag. 2021, 94, 1-10. [CrossRef]
- Fleetwood, J. Scores on doors: Restaurant hygiene ratings and public health policy. J. of Public Health Pol. 2019, 40, 410-422. [CrossRef]
- Ghaharian, K., Abarbanel, B., Soligo, M., & Bernhard, B. Crisis management practices in the hospitality and gambling industry during COVID-19. Int. Hospit. Rev. 2021, 35, 171-194. [CrossRef]
- Gössling, S., Scott, D., & Hall, C. M. Pandemics, tourism and global change: a rapid assessment of COVID-19. J. of Sustainable Tourism 2020, 29, 1-20. [CrossRef]
- Golan, M. S., Jernegan, L. H., & Linkov, I. Trends and applications of resilience analytics in supply chain modeling: systematic literature review in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic. Env. Syst. and Dec. 2020, 40, 222–243. [CrossRef]
- Guo, H., Yang, Z., Huang, R., & Guo, A. The digitalization and public crisis responses of small and medium enterprises: Implications from a COVID-19 survey. Frontiers of Bus. Res. in China 2020, 14, 1-25. [CrossRef]
- Hajishirzi, R.; Costa, C.J.; Aparicio, M. Boosting Sustainability through Digital Transformation’s Domains and Resilience. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1822. [CrossRef]
- Jung, S. S., & Jang, S. S. Have restaurant firms been using right recession turnaround strategies?: Evaluating with propensity score measure. Int. J. of Hospit. Manag. 2020, 91, 242-250. [CrossRef]
- Kim, M. J., & Hall, C. M. Can sustainable restaurant practices enhance customer loyalty? The roles of value theory and environmental concerns. J. of Hospit. and Tourism Manag. 2020, 43, 127-138. [CrossRef]
- Kim, M., Kim, E. J., & Bai, B. Examining restaurant purchase intention during crises: the role of message appeal. Int. J. of Contemp. Hospit. Manag. 2021, 33, 4373-4390. [CrossRef]
- Koh, Y., Lee, S., & Choi, C. The income elasticity of demand and firm performance of US restaurant companies by restaurant type during recessions. Tourism Econ. 2013, 19, 855-881. [CrossRef]
- Kohtamäki, M., Parida, V., Oghazi, P., Gebauer, H., & Baines, T. Digital servitization business models in ecosystems: A theory of the firm. J. of Bus. Res. 2019, 104, 380-392. [CrossRef]
- Konuk F. A. The influence of perceived food quality, price fairness, perceived value and satisfaction on customers’ revisit and word-of-mouth intentions towards organic food restaurants. J. of Retailing and Cons. Serv. 2019, 50, 103-110. [CrossRef]
- Lasek A., Cercone N., Saunders J. Restaurant sales and customer demand forecasting: Literature survey and categorization of methods. In: Leon-Garcia A. et al. (eds). Smart City 360°. Cham: Springer 2016, 166, 479–491. [CrossRef]
- Larue, B. COVID-19 and labor issues: An assessment. Canadian J. of Agricult. Econ. 2021, 69, 269–279. [CrossRef]
- Leiblein, M. J., & Reuer, J. J. Foundations and futures of strategic management. Strat. Manag. Rev. 2020, 1, 1-33. [CrossRef]
- Li H., Meng F., Jeong M., Zhang Z. To follow others or be yourself? Social influence in online restaurant reviews. Int. J. of Contemp. Hospit. Manag. 2020, 32, 1067–1087. [CrossRef]
- Li H., Xie K. L., Zhang Z. The effects of consumer experience and disconfirmation on the timing of online review: Field evidence from the restaurant business. Int. J. of Hospit. Manag. 2020, 84, 1–11. [CrossRef]
- Liu, P., & Tse, E. C. Y. Exploring factors on customers’ restaurant choice: an analysis of restaurant attributes. British Food J. 2018, 120, 2289-2303.
- Liu, W., Choi, T., Niu, X., Zhang, M., & Fan, W. Determinants of Business Resilience in the Restaurant Industry During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Textual Analytics Study on an O2O Platform Case. IEEE Transactions on Engineering Manag. 2022, 99, 1–14. [CrossRef]
- McTeigue, C., Sanchez, C., Santos, E., Walter, C. E., & Au-Yong-Oliveira, M. A Strategy for Tourism Growth, Rebound, and Revival: Promoting Portugal as a Destination Post-COVID-19. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12588. [CrossRef]
- Nemeschansky, B., von der Heidt, T., & Kim, P. B. Customer-driven menu analysis (CDMA): Capturing customer voice in menu management. Int. J. of Hospit. Manag. 2020, 91, 1-14. [CrossRef]
- Paužuolienė, J., Šimanskienė, L., & Fiore, M. What about Responsible Consumption? A Survey Focused on Food Waste and Consumer Habits. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1-13. [CrossRef]
- Ritala, P., Baiyere, A., Hughes, M., & Kraus, S. Digital strategy implementation: The role of individual entrepreneurial orientation and relational capital. Tech. Forecasting and Soc. Change 2021, 171, 1-15. [CrossRef]
- Robson, S., & Foster, A. Qualitative research in action. Edward Arnold 1989.
- Singh, S., Kumar, R., Panchal, R., & Tiwari, M. K. Impact of COVID-19 on logistics systems and disruptions in food supply chain. Int. J. of Prod. Res. 2021, 59, 1993–2008. [CrossRef]
- Vu, H. Q., Li, G., Law, R., & Zhang, Y. Exploring tourist dining preferences based on restaurant reviews. J. of Travel Res. 2019, 58, 149-167. [CrossRef]
- Yi, S., Zhao, J., & Joung, H. W. Influence of price and brand image on restaurant customers’ restaurant selection attribute. J. of Foodservice Bus. Res. 2018, 21, 200-217. [CrossRef]
- Yost, E., Kizildag, M., & Ridderstaat, J. Financial recovery strategies for restaurants during COVID-19: Evidence from the US restaurant industry. J. of Hospit. and Tourism Manag. 2021, 47, 408-412. [CrossRef]
- Webb, J. R. Understanding and Designing Marketing Research (2e: uppl.) 2001, 390.
- Whyte, William Foote. “The Social Structure of the Restaurant.” American Journal of Sociology, vol. 54, no. 4, 1949, pp. 302–10. JSTOR, http://www.jstor.org/stable/2770650. Accessed 31 July 2023.
- Zhang, C., Zhang, H., & Wang, J. Personalized restaurant recommendation method combining group correlations and customer preferences. Inf. Sci. 2018, 454, 128-143. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S. N., Li, Y. Q., Liu, C. H., & Ruan, W. Q. Reconstruction of the relationship between traditional and emerging restaurant brand and customer WOM. Int. J. of Hospit. Manag. 2021, 94, 1-12. [CrossRef]
- Zott, C., Amit, R., & Massa, L. The business model: recent developments and future research. J. of Manag. 2011, 37, 1019-1042. [CrossRef]
| Criterion | Description | Number of answers | % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Restaurant format (classes of restaurants by service characteristics [14]) | 1.Luxury dining (upscale) | 2 | 12,5 |
| 2. Fine dining (midscale) | 6 | 37,5 | |
| 3. Casual and business dining (low-scale) | 4 | 25 | |
| 4.Quick service dining | 4 | 25 | |
| Foundation date | Restaurants working before 2019, before the pandemic | 16 | 100 |
| Company size (number of employees) | Small: 15-100 | 6 | 37,5 |
| Average: 101-250 | 3 | 18,8 | |
| Large: > 251 | 7 | 43,8 | |
| Directions of activity (establishments of new sales channels) | Online & offline business formats | 10 | 62,5 |
| Mostly offline operations | 5 | 31,2 | |
| Mostly delivery and takeaway orders | 1 | 6,3 | |
| Delivery form | Own delivery system | 12 | 75,6 |
| Own delivery system & aggregators | 4 | 25,4 | |
| Key innovations, helped businesses during the pandemic | New products and services | 6 | 37,5 |
| Marketing campaign | 8 | 50 | |
| Online services and applications | 16 | 100 | |
| Loyalty program | 12 | 75 |
| The level of adaptability of restaurants to the challenges have arisen during the pandemic by experts’ evaluation from "1" to "7" | Number of answers | % |
|---|---|---|
| “1” - No, the restaurant has not adapted to the pandemic problems | 1 | 6,3 |
| “2” - Poorly adapted, there are serious problems (customer demand/ margins continue to fall, while costs rise, etc.) | 1 | 6,3 |
| “3” - Quite poorly adapted, there are minor problems with optimizing the format of the proposed dishes and service (purchasing ingredients, optimizing menu, developing delivery, etc.) | 2 | 12,5 |
| “4” - Difficult to answer, forced to emergency problem adaptation caused by the repeated lockdown | 1 | 6,3 |
| “5” - Some adaptation, but there are serious problems with increased safety requirements (redevelopment, purchasing personal protective equipment, monitoring the workers well-being, etc.) | 0 | 0 |
| “6” - Adapted, but there are minor management problems (staff turnover, technological development, etc.) | 6 | 37,5 |
| “7” - Yes, the restaurant has fully adapted to the pandemic problems, customers come back not only for the food, but for the atmosphere | 5 | 31,3 |
| Key elements of restaurants adaptability | Characteristics of consumer demand | Estimates of characteristics by adaptability level types, % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | ||
| 1.a Structure of demand | Increased for cheaper meals | 6,3 | 12,5 | 18,8 |
| Increased stratification of expensive & cheap meals | 6,3 | 0,0 | 6,3 | |
| The structure of demand has not changed compared to the pre-pandemic demand | 18,8 | 25,1 | 6,3 | |
| Increased demand for higher quality food ingredients | 12,5 | 0,0 | 0,0 | |
| 1.b Consumer preferences in the range of dishes | Narrowed range of popular dishes | 12,5 | 25,1 | 12,5 |
| Increased demand for exotic, unusual dishes | 6,3 | 0,0 | 0,0 | |
| Increased demand for the most popular dishes | 12,5 | 0,0 | 6,3 | |
| Preferences haven’t changed compared to pre-pandemic period | 12,5 | 25,1 | 12,5 | |
| Bias in favor of delivery orders | 6,3 | 25,2 | 18,8 | |
| Increased demand for speed of service | 0,0 | 0,0 | 12,5 | |
| Bulk purchase of semi-finished products | 0,0 | 0,0 | 12,5 | |
| 1.c Changes in average bill per restaurant visit | Dropped significantly | 6,3 | 0,0 | 0,0 |
| Decreased slightly | 12,5 | 18,8 | 0,0 | |
| Grew slightly | 0,0 | 12,5 | 12,5 | |
| Grew significantly | 0,0 | 12,5 | 18,8 | |
| 1.d Changes in format preferences of restaurants food consumption | Visiting by two persons/small groups | 6,3 | 12,5 | 6,3 |
| Decreased number of corporations | 6,3 | 18,8 | 6,3 | |
| Increased takeaway orders | 18,8 | 31,5 | 12,5 | |
| Increased delivery orders to home | 0,0 | 18,8 | 18,8 | |
| Increased delivery orders to work | 6,3 | 18,8 | 6,3 | |
| Menu assortment matrix has not changed, changes in dishes (size, visual) | 0,0 | 12,5 | 6,3 | |
| “Breakfast” format is developing | 0,0 | 0,0 | 6,3 | |
| 1.e Changes in the visitors composition | Decreased number of older visitors | 12,5 | 6,3 | 12,5 |
| Increased share of romantic couples | 6,3 | 0,0 | 6,3 | |
| Number of tourists has fallen sharply | 12,5 | 25,1 | 25,1 | |
| Composition of visitors hasn’t changed | 6,3 | 18,8 | 0,0 | |
| Culture of consumption has changed | 6,3 | 0,0 | 0,0 | |
| Fewer impulsive restaurant visits | 6,3 | 6,3 | 0,0 | |
| Number of tourists has increased | 0,0 | 0,0 | 12,5 | |
| Increased influx of new guests from competing restaurants | 0,0 | 0,0 | 12,5 | |
| 1.f Other new consumer requirements | Tendency to buy cheaper meals but larger portions | 6,3 | 0,0 | 0,0 |
| Demand for the bonus system, service quality. Active feedback in reviews | 0,0 | 12,5 | 0,0 | |
| Demand for takeaway and delivery orders doubled | 6,3 | 25,2 | 12,5 | |
| Increased demand for stock diversity | 12,5 | 0,0 | 0,0 | |
| Increased demand for menu variety | 0,0 | 0,0 | 12,5 | |
| No additional requirements due to COVID-19 | 6,3 | 12,5 | 12,5 | |
| The main innovations implemented in the restaurant during the 2020 lockdown | % | Developments that were used during the 2021 lockdown | % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cost reduction: menu, service types, events, and staff amount. | 37 | Full use of ensuring sanitary standards developments, services provision introduction new rules in accordance with the additional requirements of 2021. | 40 |
| Compliance with sanitary standards for customers and staff. | 32 | Optimization of the concept and well-functioning management mechanism improvement, in accordance with the restaurant development new directions. Service developments integration in 2020 in the process of providing restaurant services. | 30 |
| Development of a food delivery service (own and through aggregators). | 26 | Analysis of the company's strategy in accordance with the target audience change connected with the tourism migrations. | 15 |
| Optimization of all management processes. A radical change in the concept from “fine dining” to “quick service”. | 5 | Use this period to carry out renovations to improve the atmosphere in restaurants. | 15 |
| Innovations that were fixed in the work after the lockdown | % | Innovations that will be used on an ongoing basis in the post-pandemic period | % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Improvement of service quality in accordance with sanitary standards. | 23 | Compliance with sanitary standards. | 50 |
| Development of the meals delivery system, semi-finished products and groceries. | 17 | Development of delivery service forms. | 14 |
| Compliance with government regulations. | 14 | Development of catering service. | 11 |
| Development of employees multitasking due to the staff reduction. | 14 | Development of website and social networks, business digitalization. | 7 |
| Reduction of working hours in line with the restaurants opening hour’s reduction. | 10 | Analysis of positioning, strategic development, loyalty programs. | 7 |
| Analysis and change of strategy to attract additional customer audiences. | 8 | Coordinate concept change does not allow making accurate forecast now. | 4 |
| Development of food delivery through aggregators. | 6 | Development of loyalty programme. | 4 |
| Development of loyalty programs (carrying out new promotions, advertising campaigns, providing gifts). | 4 | Changing the economic model of doing business when the crisis worsens. | 3 |
| Usual work process without innovations. | 4 | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





