Submitted:
09 August 2023
Posted:
10 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Grooflab MGWS
2.2. Biotecture MGWS
2.3. Vertiss MGWS
2.4. Scotscape MGWS
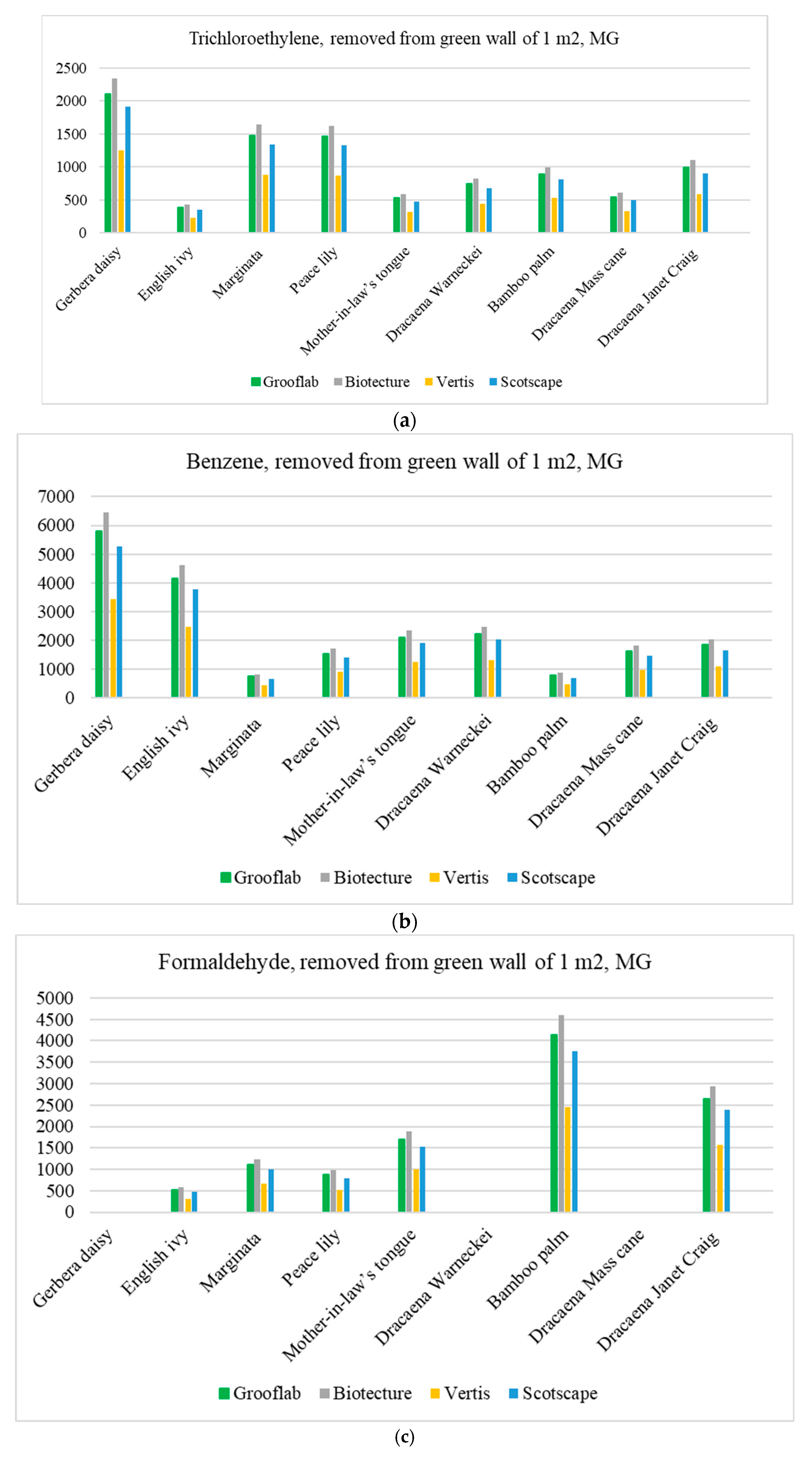
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhong, W., Schroeder, T., Bekkering, J. Designing with nature: Advancing three-dimensional green spaces in architecture through frameworks for biophilic design and sustainability. Frontiers of Architectural Research. 2023, 2095-2635. [CrossRef]
- Ruixue Zhang, Yuyan Tang, Yuanxin Zhang, Zeyu Wang, Collaborative relationship discovery in green building technology innovation: Evidence from patents in China’s construction industry, Journal of Cleaner Production, Volume 391,2023,136041. [CrossRef]
- Jianhua Yin, Changchun Li, Data governance and green technological innovation performance: A curvilinear relationship, Journal of Cleaner Production, Volume 379, Part 1,2022,134441, ISSN 0959-6526. [CrossRef]
- Du, Qiang, Lu, Xinran, Li, Yi, Wu, Min, Bai, Libiao, Yu, Ming. Carbon Emissions in China’s Construction Industry: Calculations, Factors and Regions, International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. Vol. 15. [CrossRef]
- Sang-Jin Ahn, Ho Young Yoon, ‘Green chasm’ in clean-tech for air pollution: Patent evidence of a long innovation cycle and a technological level gap, Journal of Cleaner Production, Volume 272,2020,122726. [CrossRef]
- Yang Han, Jechan Lee, Gu Haiping, Ki-Hyun Kim, Peng Wanxi, Neha Bhardwaj, Jong-Min Oh, Richard J.C. Brown. Plant-based remediation of air pollution: A review. Journal of Environmental Management, Volume 301, 2022, 113860. [CrossRef]
- Michael D. Flowers, Edwin L. Fiscus, Kent O. Burkey, Fitzgerald L. Booker, Jean-Jacques B. Dubois, Photosynthesis, chlorophyll fluorescence, and yield of snap bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) genotypes differing in sensitivity to ozone, Environmental and Experimental Botany, Volume 61, Issue 2, 2007, Pages 190-198. [CrossRef]
- Elisabetta Gravano, Valentina Giulietti, Rosanna Desotgiu, Filippo Bussotti, Paolo Grossoni, Giacomo Gerosa, Corrado Tani, Foliar response of an Ailanthus altissima clone in two sites with different levels of ozone-pollution, Environmental Pollution, Volume 121, Issue 1, 2003, Pages 137-146. [CrossRef]
- Naomi J. Paull, Daniel Krix, Peter J. Irga, Fraser R. Torpy, Green wall plant tolerance to ambient urban air pollution, Urban Forestry & Urban Greening, Volume 63, 2021,127201. [CrossRef]
- Matteo De Lucia, Anna Treves, Elena Comino, Rice husk and thermal comfort: Design and evaluation of indoor modular green walls, Developments in the Built Environment, Volume 6, 2021, 100043. [CrossRef]
- Escolà-Gascón, Álex & Dagnall, Neil & Denovan, Andrew & Alsina-Pagès, Rosa & Freixes, Marc. (2023). Evidence of environmental urban design parameters that increase and reduce sense of place in Barcelona (Spain). Landscape and Urban Planning. 235. 104740. [CrossRef]
- K. Gunawardena, K. Steemers, Living walls in indoor environments, Build. Environ., 148 (2019), pp. 478-487. [CrossRef]
- L. Yi, R. Liangliang, Z. Chunyan. Application analysis on thermal insulation of building surface greening-based on U-wert simulation. Proc. - 2019 Int. Conf. Smart Grid Electr. Autom. ICSGEA (2019), pp. 2019 63-67. [CrossRef]
- Sathya Bandaranayake Tharika Kahandawa Arachchi Kumari Gamage, Comparative Study to Assess the Thermal Behaviour of Sandwich Roof Panels with Coconut Fibre as an Alternative Core Material to Polyurethane, Electronic Journal of Structural Engineering, Vol 23. [CrossRef]
- Bevilacqua, P. (2021). The effectiveness of green roofs in reducing building energy consumptions across different climates. A summary of literature results. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 151, 111523.
- Bevilacqua, P., Bruno, R., & Arcuri, N. (2020). Green roofs in a Mediterranean climate: Energy performances based on in-situ experimental data. Renewable Energy, 152, 1414-1430.
- Htet, Arkar & Liana, Sui & Aung, Theingi & Bhaumik, Amiya. (2023). Smart Buildings in the Age of Internet Technology: Civil Engineering’s Role in Shaping an Energy-Efficient Future. Journal of Technology Innovations and Energy. 2. 8-19. [CrossRef]
- Kasumu, Rebecca Oluwayimika & Oluwayimika. Senior secondary school students’ perception of smart classroom: attitude and challenges, International Journal of Trendy Research in Engineering and Technology, 2023, Volume 7, Issue 3, pp.1-15.
- May Tzuc, Oscar & Jiménez Torres, Mario & Cruz, Andrea & Canul Turriza, Román Alejandro & Andrade-Durán, Juan & Pat, Felipe. (2023). Feasibility of the adaptive thermal comfort model under warm sub-humid climate conditions: cooling energy savings in campeche, Mexico. 13. 120. [CrossRef]
- May Tzuc, Oscar & Hernández-Pérez, Iván & Castro, Karla Maria & Jiménez Torres, Mario & Castillo-Téllez, M & López, N. (2022). Modeling the effect of roof coatings materials on the building thermal temperature variations based on an artificial intelligence. Journal of Physics: Conference Series. 2180. 012014. [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.H.D., 2023. Green Walls as Mitigation of Urban Air Pollution: A Review of Their Effectiveness. Research in Ecology. 5(2): 1-13. DOI: https://doi.org/10.30564/re.v5i2.5710. [CrossRef]
- Kasim, Rezzan. (2017). Using of Potted Ornamental Plants to Clean up Volatile Organic Compount that Cause Air Pollution Indoor. I. International Congress on Medicinal and Aromatic Plants.
- Roy, Misha & Shamim, F & Das, A. (2018). Indoor air pollution: sources, health impacts and control. 13. 75-82.
- Wallace, L., E. Pellizzari, T. Hartwell, M. Rosenweig, M. Erickson, C. Sparacino, and H. Zelon. 1984. Personal exposureto volatile organic compounds: I. direct measurement in breathing-zone air, drinking water, food and exhaled breath. Env. Res. 35:193-211.
- Pellizzari, E., T. Hartwell, C. Sparacino, C. Shelson, R. Whitmore, C. Leininger, and H. Zelon. 1984. Total Exposure Assessment Methodology (TEAM) Study: First Season, Northern New Jersey--Interim Report. Contract No. 68-02-3679. Washington: U.S. EPA.
- Shushunova, N.; Korol, E.; Luzay, E.; Shafieva, D.; Bevilacqua, P. Ensuring the Safety of Buildings by Reducing the Noise Impact through the Use of Green Wall Systems. Energies 2022, 15, 8097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolverton, B. C., Johnson, A., & Bounds, K. (1989). Interior landscape plants for indoor air pollution abatement (No. NASA-TM-101766).
- Wolverton, B.C., and R.C. McDonald-McCaleb. 1986. Biotransformation of priority pollutants using biofilms and vascular plants. J. Miss. Acad. Sci., 31:79-89.
- Marc Ottelé, Katia Perini, A.L.A. Fraaij, E.M. Haas, R. Raiteri, Comparative life cycle analysis for green façades and living wall systems, Energy and Buildings, Volume 43, Issue 12, 2011, Pages 3419-3429, ISSN 0378-7788. [CrossRef]
- Ottelé, M. (2011). The green building envelope. Vertical Greening, Delft.
- Bruno, Roberto & Ferraro, Vittorio & Bevilacqua, Piero & Settino, Jessica & Rollo, Antonino. (2023). Experimental tests to assess the effects of Phase Change Materials in building envelopes. 168-172. [CrossRef]
- https://www.biotecture.uk.com/content/uploads/External_Cladding_Living_Walls_and_Fire_Safety_Best_Practice_Guide.pdf.
- https://www.vertiss.net/vertiss-plus-le-module-vegetalise?lang=en.
- https://www.scotscape.co.uk/thank-you-document-download.
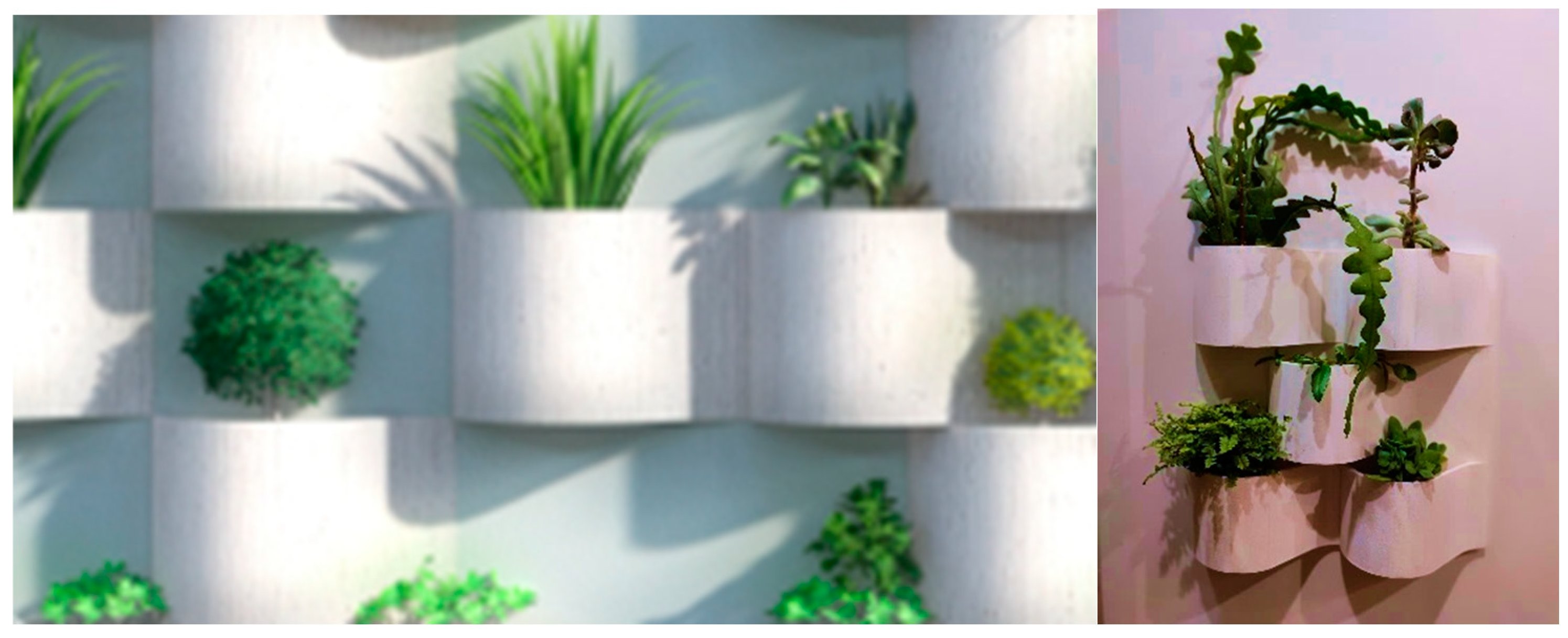
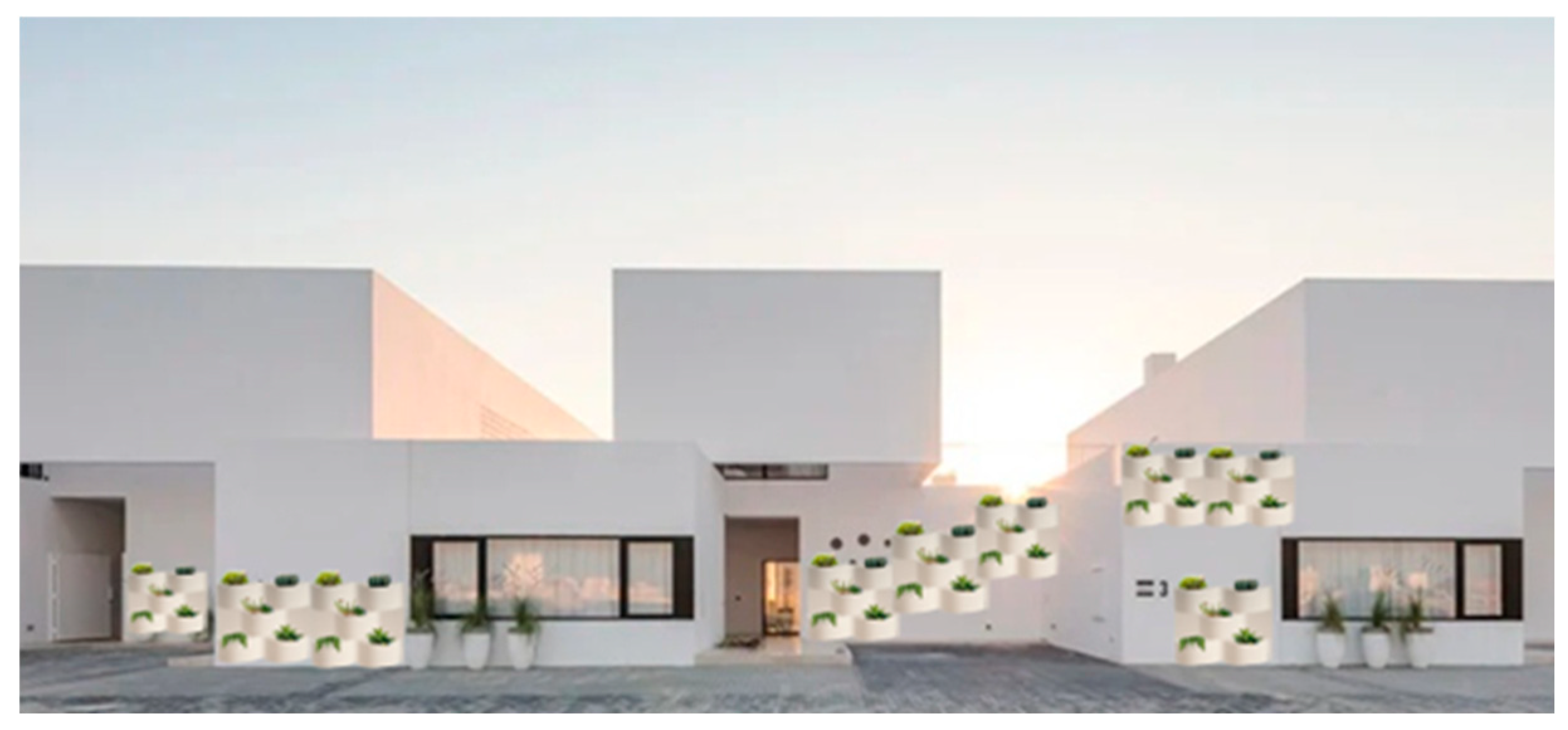

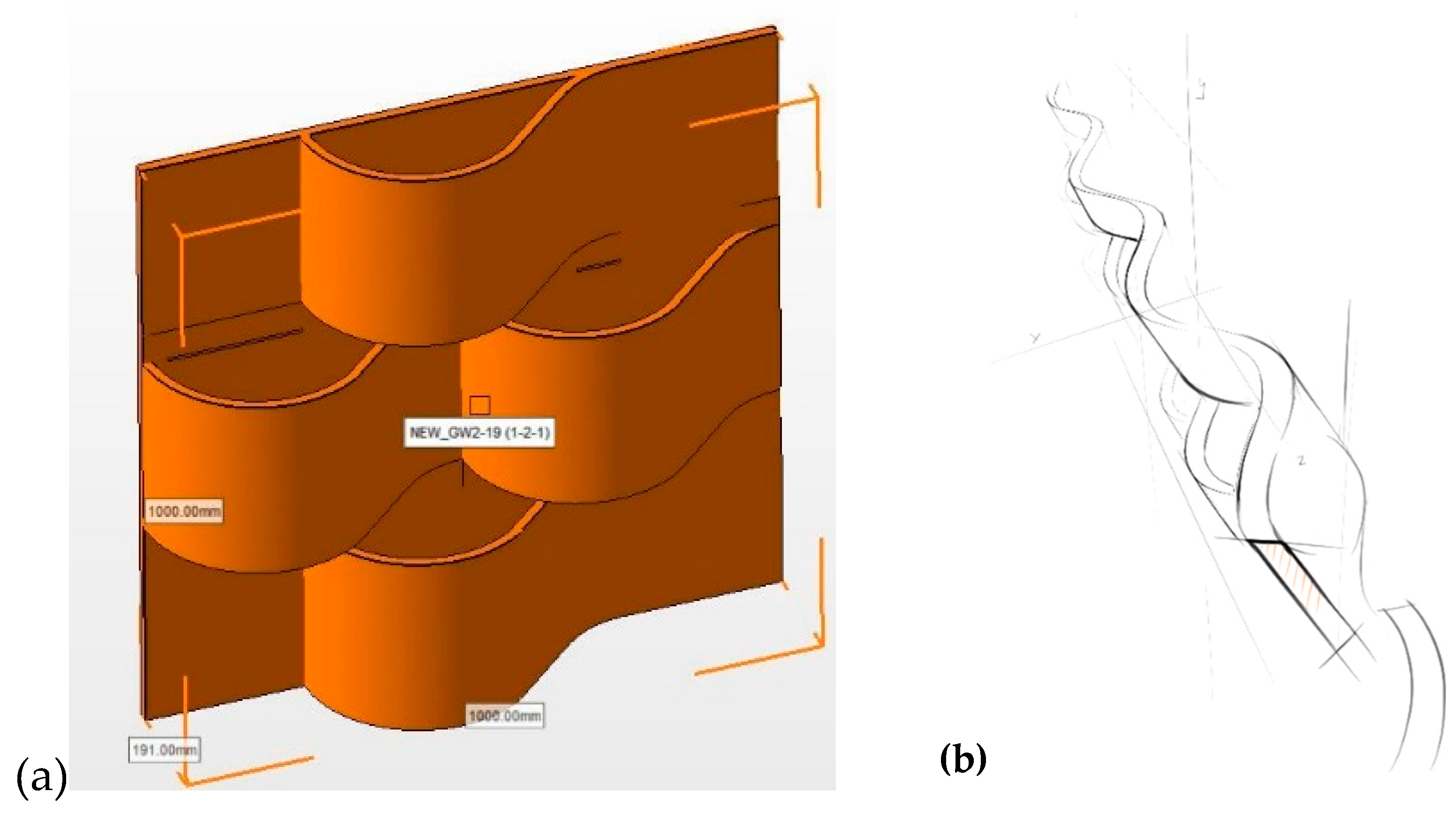
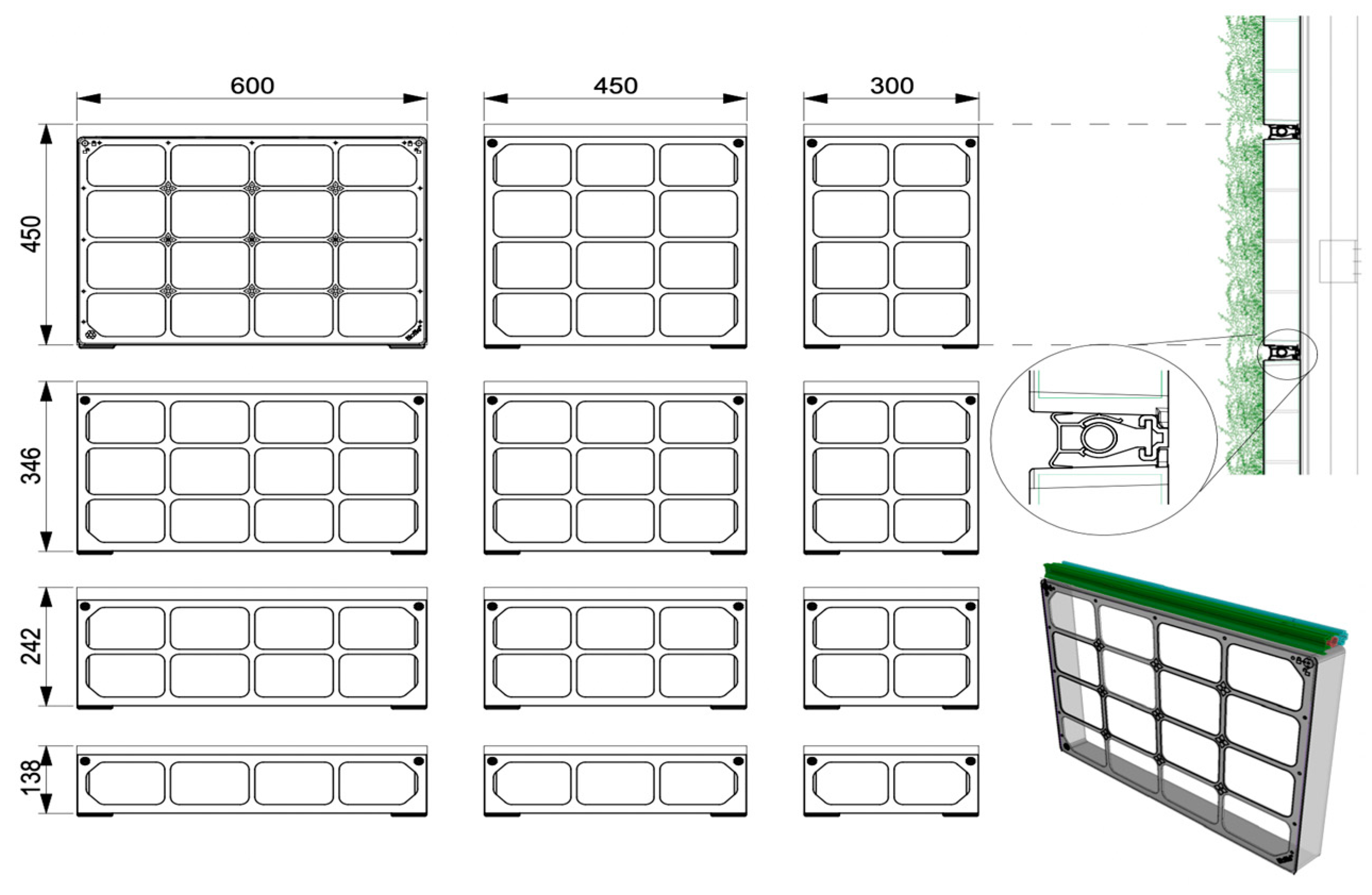
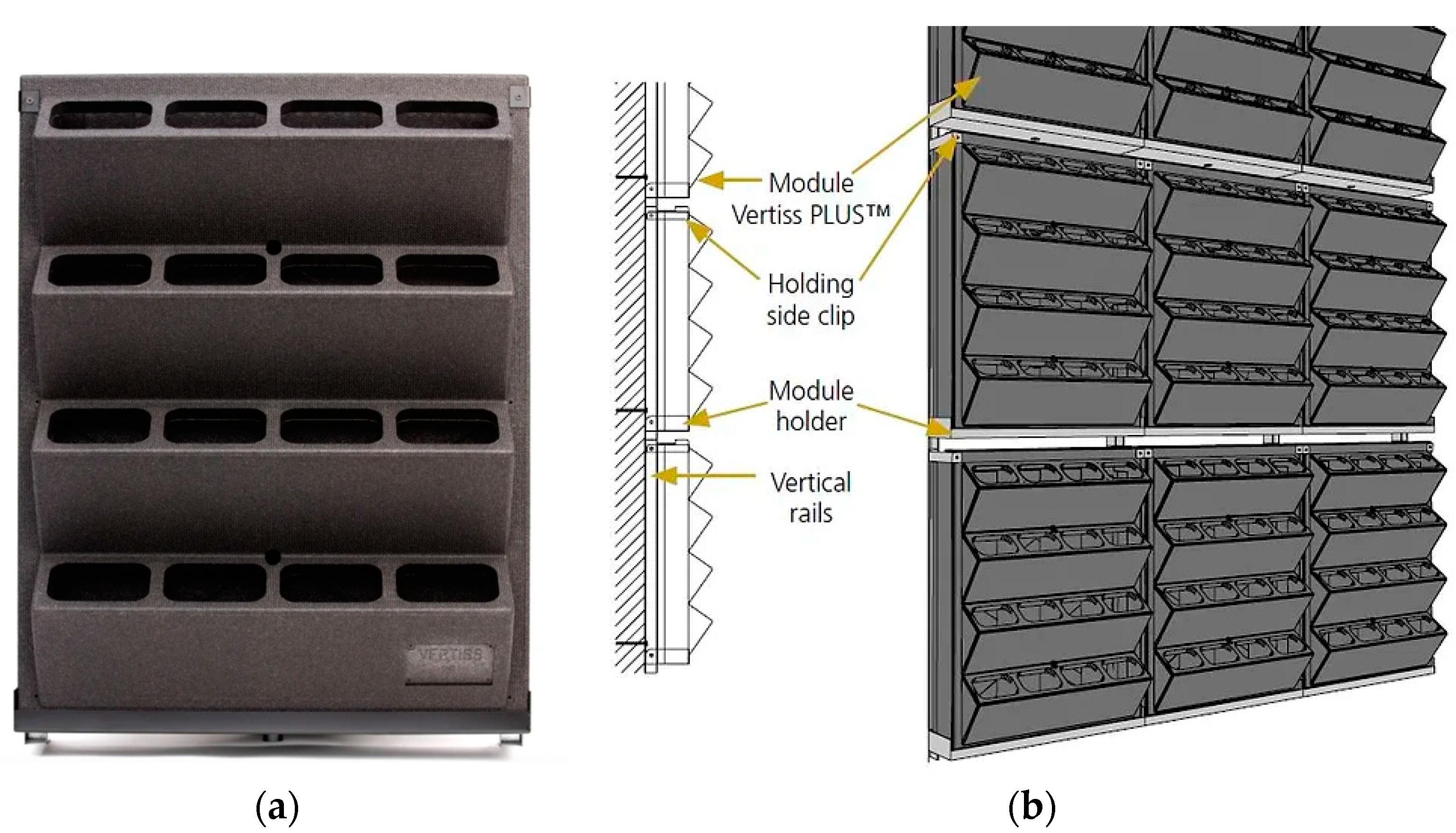
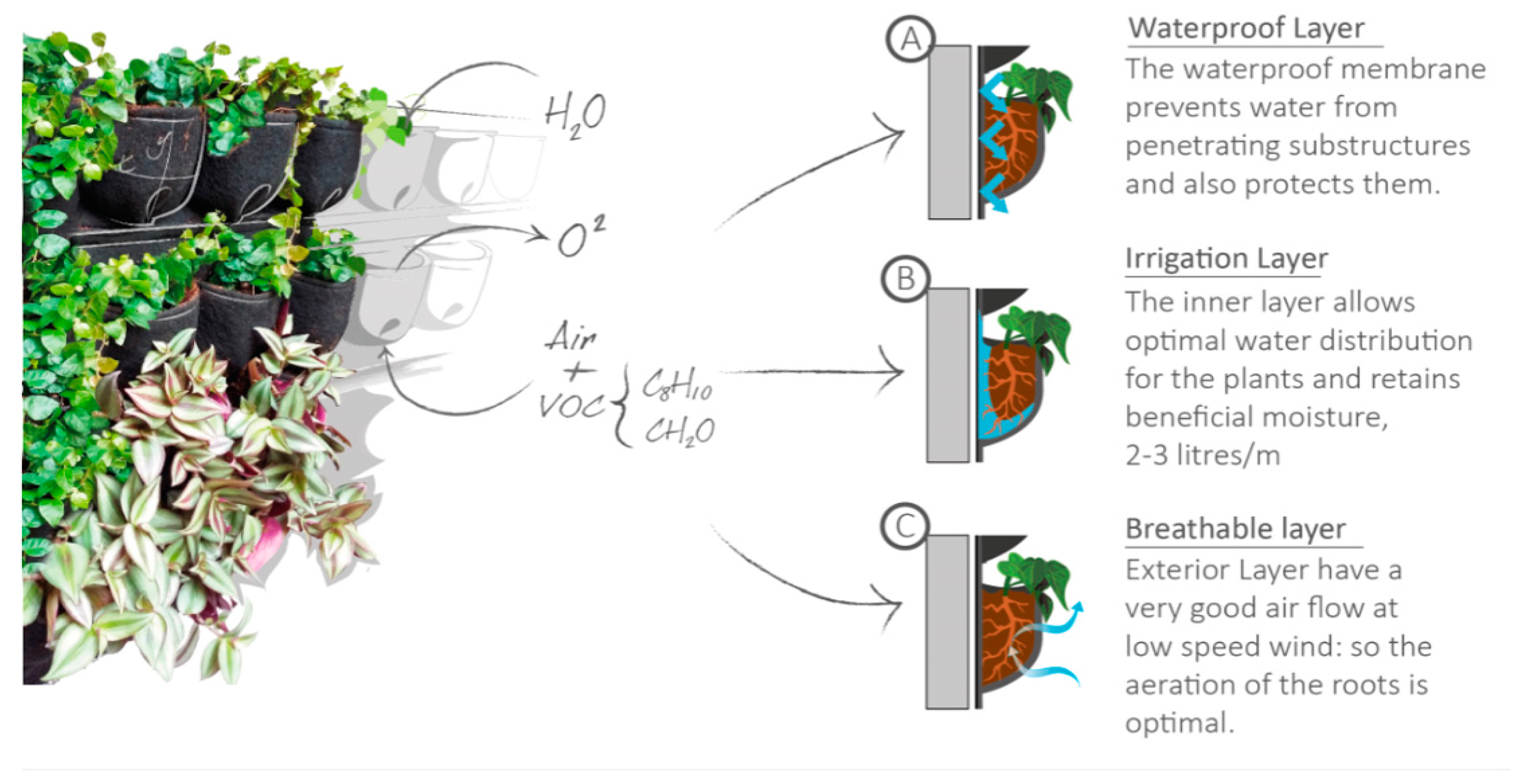

| MGWS / parameters | Grooflab | Biotecture | Vertis | Scotscape |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Module dimensions, mm2 | 300 х 300 | 600 x 450 | 760 x 590 | 1000 x 1000 |
| Quantity of plants in standart module | 5 | 16 | 14 | 49 |
| Quantity of plants, per 1 m2 | 45 | 60 | 32 | 49 |
| Modular green wall system / criterion for comparison | Grooflab | Biotecture | Vertis | Scotscape |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Growing medium | Soil | Mineral wool | Pozzolan, crushed clay balls, peat | Fytotextile |
| Watering system | Manually or automatically, by pipework | Automatic | Automatic | Manually or automatically, by pipework |
| Changing the design | Rearranging modules | Rearranging modules | Rearranging modules | No, only dismantle |
| Square | 1 m2 | 1 m2 | 1 m2 | 1 m2 |
| Number of plants per 1 m2 | 45 | 60 | 32 | 49 |
| System weight | 30 kg/ m2 | 70 kg/ m2 | 93,3 kg/ m2 | 40 kg/ m2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





