4.1. Sample description
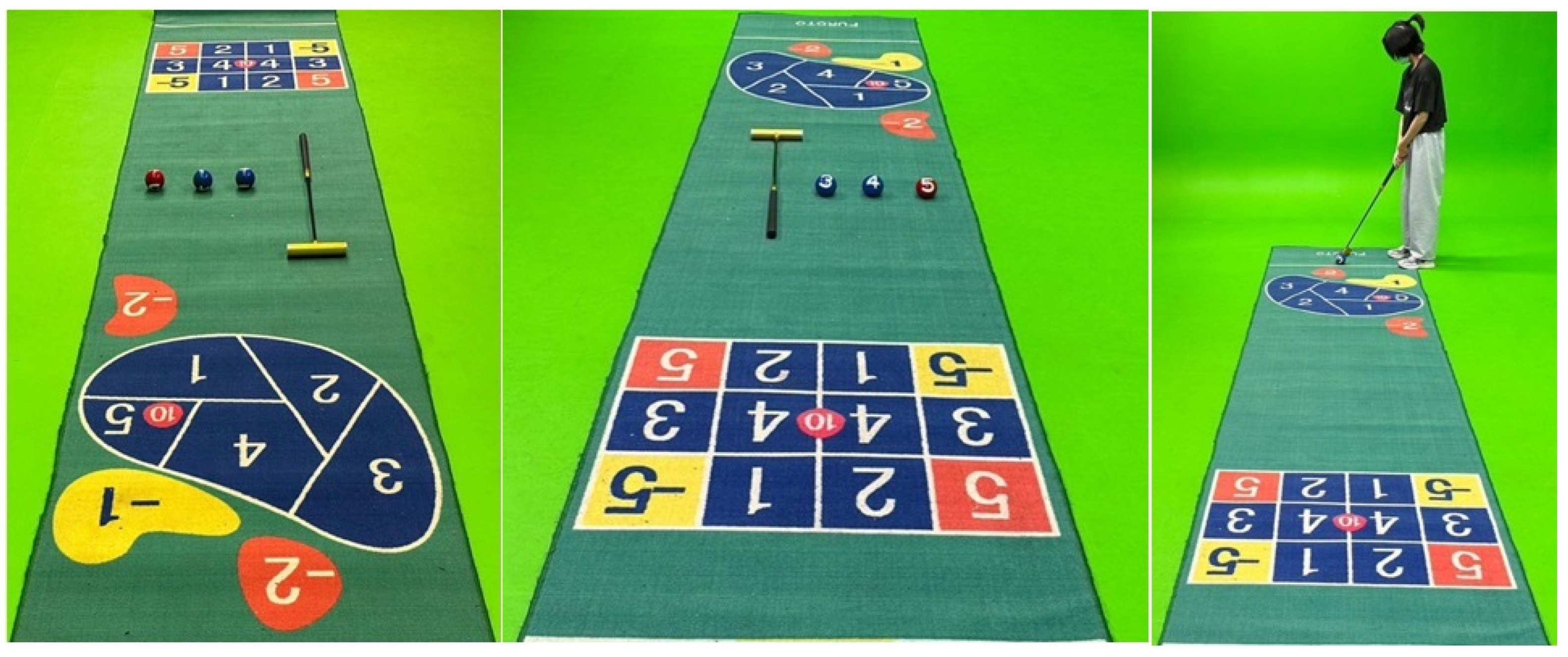
The subjects of this study are an elderly care center in northern Taiwan. The main subjects are seniors over 65 years old and their accompanying caregivers. A random sampling method is adopted. The number of questionnaires is 320. The questionnaires are completely recovered, and so the effective recovery rate is 100%. Our work adopts a physical questionnaire. Before filling out the questionnaire, the senior individual and their companion or caregivers will be gathered in a conference room and explained orally the rules and disadvantages of traditional golf croquet. Then, the improvement methods proposed in this study will be introduced. At the same time, recorded explanations and introduction videos will also be played to make the participants more aware of the overall testing procedure. After completing the explanation, move to a spacious indoor space to experience the golf croquet home-based intelligent exercise system. Finally, gradually fill out the questionnaire content based on the experience results. For those who do not understand the questionnaire content, we will provide assistance and explain the content of their questions.
The basic data of the collected questionnaire samples are as follows: 82.2% of the respondents are male, 78.4% of the respondents have a high school education, and 80.6% have more than five years of experience in using smartphones. Among the subjects, 31 had chronic diseases, with cardiovascular diseases accounting for the majority (52%), followed by diabetes (26%), and 61% had chronic diseases for more than five years. Those who participated in sports three times a week accounted for 49.7% of the sample, followed by more than five times at 26.3%. A duration of each exercise o less than 30 minutes, accounts for the majority (74.4%), followed by 1 hour (19.4%). The majority (37.2%) of them have continued to exercise for more than five years. The basic in-formation of the questionnaire is shown in
Table 2.
According to the statistical results in
Table 3, the average number of questions on perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, intention to use, social needs, self-esteem needs, cognitive needs, aesthetic needs, and self-actualization needs of the respondents ranged from 3.97 to 4.13. This represents the respondents’ positive attitude towards the home action system of golf croquet.
4.2. Factor analysis, reliability and validity analysis
In order to further understand the degree of consent of the subjects to each dimension, this study carried out factor analysis respectively for TAM’s perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, and intention to use and Maslow’s social needs, self-esteem needs, cognitive needs, aesthetic needs, and self-actualization needs. It extracted common factors with a characteristic value greater than 1 [
84], using principal component analysis and maximum variation pivot method. Questions with an absolute value of factor load greater than 0.5 are reserved and properly classified. In terms of scale reliability, according to Guilford [
85], Cronbach’s α greater than 0.7 means high reliability, and that less than 0.35 is of low reliability, which should be rejected [
86]. The construction validity of this study is based on the Item-Total Correlation method of Kerlinger [
87] - that is, assuming that the total score is valid, the size of the correlation coefficient between individual items and the total score is the measure of construct validity.
The results in
Table 4 show that the KMO value of each facet is between 0.500 and 0.851, Bartlett’s ball test is significantly in line with the requirements, and the values of each facet are quite good. The results of
Table 5 show that the factor load of each item is between 0.502 and 0.877, which is more than 0.5. The characteristic value of each facet is between 1.746 and 4.711, the cumulative explanatory variance is between 57.773 and 87.302, and the Item-Total Correlation value of each item is greater than 0.5, indicating considerable constructive validity and content validity. Cronbach’s α values are all greater than 0.6, indicating good internal reliability. There is thus real correlation between the measurement items, and the content of the questionnaire is highly consistent.
4.3. Hypothesis testing
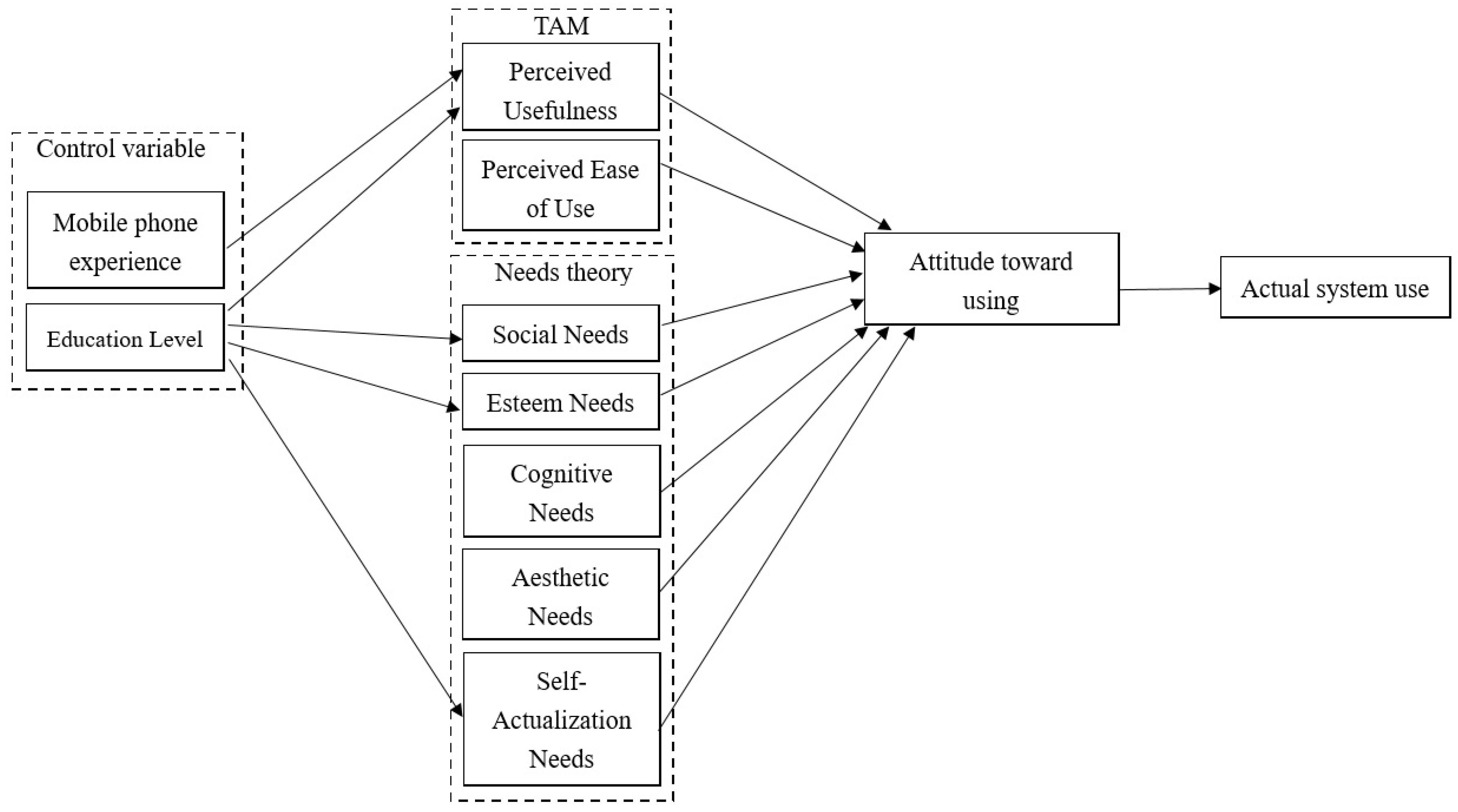
Table 6 shows that, for the prediction of the intention of use, each dimension uses SPSS software to carry out regression analysis. According to the research framework (
Figure 5), it is assumed that the variable of path direction is the dependent variable, and the variable of path starting is the independent variable or predictive variable. According to analysis of the relationship between perceived usefulness and intention to use, the empirical results show that hypothesis H6 is supporting, indicating that perceived usefulness has a positive and significant impact (
P < 0.001) on intention to use. According to analysis of the relationship between perceived usefulness and intention to use, the empirical results show that hypothesis H7 is supported. This indicates that perceived usefulness has a positive and significant impact (
P < 0.001) on intention to use. According to analysis of the relationship between social needs and intention to use, the empirical results show that hypothesis H8 is supported. This indicates that social needs have a positive and significant impact (
P < 0.001) on intention to use. According to analysis of the relationship between esteem needs and intention to use, the empirical results show that hypothesis H9 is supported. It indicates that esteem needs have a positive and significant impact (
P < 0.001) on intention to use. According to analysis of the relationship between cognitive needs and intention to use, the empirical results show that hypothesis H10 is supported. This indicates that cognitive needs have a positive and significant impact (
P < 0.001) on intention to use. According to analysis of the relationship between aesthetic needs and intention to use, the empirical results show that hypothesis H11 is supported. This indicates that aesthetic needs have a positive and significant impact (
P < 0.001) on intention to use. According to analysis of the relationship between the need for self-actualization and the intention to use, the empirical results show that hypothesis H12 is supported. This indicates that the need for self-actualization has a positive and significant impact (
P < 0.001) on the intention to use.
Table 7 shows the difference between education level and mobile phone experience in terms of perceived usefulness, social needs, esteem needs, and self-actualization needs when analyzed using SPSS software. According to the research framework (
Figure 5), the variable of path direction is assumed to be the dependent variable, and the variable of path starting is assumed to be a factor.
According to analysis of the relationship between mobile phone experience and perceived usefulness, the actual results of the study show that hypothesis H1 is not supported. This indicates that the positive impact of mobile phone experience on perceived usefulness is not significant. According to analysis of the relationship between education level and perceived usefulness, the actual results of the study show that hypothesis H2 is not supported. It means that the positive impact of education level on perceived usefulness is not significant. According to analysis of the relation-ship between education level and social needs, the actual results of the study show that hypothesis H3 is not supported. It indicates that the positive impact of education level on social needs is not significant.
According to analysis of the relationship be-tween education level and esteem needs, the actual results of the study show that hypothesis H4 is supported. This indicates that education level has a positive and significant impact (P < 0.01) on esteem needs. According to analysis of the relation-ship between education level and self-actualization needs, the actual results of the study show that hypothesis H5 is supported. This means that education level has a positive and significant impact on (P < 0.01) self-actualization needs.
4.4. Discussion
Based on the TAM and HNT model, this study constructs a demand model to confirm the needs of senior for a healthy home-based intelligent exercise system. After analyzing the empirical data of 320 senior using regression and difference analysis methods, this study finds that perceived usefulness (PU), perceived ease of use (PE), social needs (SN), esteem needs (EN), cognitive needs (CN), aesthetic needs (AN), and self-actualization needs (SA) positively affect the willingness of the subjects to use the home-based intelligent exercise system of golf croquet. Based on the comprehensive analysis results, the following important findings are summarized.
The subjects mostly agree with the ease of use of the home-based intelligent exercise system of golf croquet.
This study presents that the subjects are highly receptive to the home-based intelligent exercise system of golf croquet, especially in terms of perceived ease of use. The average number of each item was the highest, indicating that they believed that the system is convenient to use, and that they could operate the system skillfully without the help of others.
Aspects that affect intention to use
Perceived usefulness (PU): This study notes that when a user believes that a system can increase his work performance or be of practical benefit to him, the higher his willingness to use the system will be. On the contrary, the lower the system helps him, the lower is his willingness to use. The subjects recognize that the home-based intelligent exercise system of golf croquet is helpful to improve their quality of life. This will make the sub-jects more likely to use this system. In other words, this method has a positive effect on the limbs and waist, can strengthen muscles, and achieve exercise effects. The research findings are of great significance to the acceptance of the initial subjects. Some previous studies have put forward a relatively pessimistic view of the ability to predict user behavior based on subjective measurement [
88,
89]. The results of this study show that the subjects can have a good impression of cognition when they actually communicate with each other in a group interactive way. Therefore, it is more critical to ensure that the prototype of the design is fully implemented, because at the initial stage the testers expect to provide valuable insights on the acceptability of the subsequently revised software/hardware products [
90].
Perceived ease of use (PE): This study finds that when a user believes that a system is easy to learn, easy to use, and can operate skillfully, the user’s willingness to use the system will be higher. On the contrary, the more complex and difficult the operation process of the system is to learn, the lower is the willingness to use it. The subjects think that the home-based intelligent exercise sys-tem of golf croquet is very convenient to use, without any assistance from others, and can be easily used skillfully, which will make the sub-jects likely to use the system. In other words, this study combines robot and IoT devices, which tends to be easier to use. From the perspective of knowledge and learning [
91], cognitive ease of use is based on procedural knowledge. Anderson [
92] suggested that procedural learning only occurs when per-forming skills, such as learning while doing. This is one of the reasons why procedural learning is more gradual than declarative learning. Therefore, it reflects the ease of use related to the use of technology, which requires personal experience.
Social needs (SN): This study presents that when a user believes that a system can increase interaction with others, his willingness to use the system will be higher; otherwise, the willingness to use the system will be lower. The subjects believe that the home-based intelligent exercise sys-tem of golf croquet can increase the interaction between them and their families, interact with each other, and accept others, which will make the subjects likely to use the system. In other words, in the mode of multi-person interaction, social relations can be enhanced. Fang [
93] explored the role of interaction strategies in consumer decision-making. That study pointed out that among the diverse online communication mechanisms, some customers are hesitant to do online shopping given that IoT cannot provide the opportunity to inspect products before purchasing, thus increasing online interactivity of the website and the addition of product information to supplement online decision-making, which increase purchase and usage intentions. Yim et al. [
94] stated that AR positively affects media and purchase intentions by generating greater novelty, immersion, interactivity, and usefulness compared to web-based product presentations.
Esteem needs (EN): This study finds that if a system allows the user to gain confidence and self-affirmation in the process of using the system, then his willingness to use the system will be higher; otherwise, the willingness to use the system will be lower. The subjects believe that using the golf croquet home-based intelligent exercise system can make them feel proud, positive, confident, and respected, which will make the subjects likely to use the system. The scoring system of golf croquet designed in this study, its ranking function can boost morale and make people feel honored. Liao et al. [
95] took the self-affirmation theory in order to examine the influence of real-world need satisfaction on online players’ loyalty. Their research results showed that users’ achievements and relationships in the real world can enhance their satisfaction with real-world needs, thereby enhancing the self-worth and loyalty of game players and further maintaining or enhancing the willingness to use.
Cognitive needs (CN): This study notes that when users think that a system can arouse their curiosity, satisfy their thirst for knowledge during use, or want to enhance their use skills, then their perception of the system will increase, and the higher the willingness to use will be. On the contrary, if the system cannot arouse the user’s curiosity, the lower the willingness to use will be. The subjects think that the home-based intelligent exercise system of golf croquet can make people feel curious and want to try to use it and that learning the use skills of this system is suffice for cognitive needs. They will want to hone and enhance their proficiency, and so it will make the subject likely to use this system. In other words, with the application of emerging technologies such as AIoT and App, it can stimulate users' cognitive curiosity. The concept of curiosity is derived from flow theory. When people are in a state of immersion, they may be willing to interact with their environment [
96]. Yoon et al. [
97] investigated the influence of hedonic and utilitarian shopping values on continuous aspects that affect the intention to use online cross-border shopping. Their research results showed that hedonic value affects the continuous intention to use online shopping through the mediation of curiosity and self-efficacy.
Aesthetic needs (AN): This study presents that when the user thinks that a system is more recognizable in appearance, screen, and function, the higher his willingness to use the system will be. The subject believes that the golf croquet home-based intelligent exercise system can be clearly identified and easy to use on the font display, and the functional design is not too complex, which will make the subject likely to use this system. The scoring system of golf croquet designed in this study has an elegant user interface design, which can increase the overall aesthetic feeling and thus increase the willingness to use it. Tsai et al. [
98] investigated how user interface design affects the intention and attitude of the elderly to use social networking sites. Their results showed that user interface design and perceived ease of use are positively related to perceived usefulness, and an appropriate interface design will further affect adoption intention.
Self-actualization needs (SA): This study finds that if a system can make users feel a sense of achievement, excitement, and happiness in the process, then the more willing they will be to use the system. Each time the subject uses the golf croquet home-based intelligent exercise system, it is like a new challenge, which makes people want to obtain higher scores. The user process can fully exert a user’s potential, gain a sense of achievement, and feel excited and happy, which makes the subject likely to use this system. In other words, learning to use mobile phone applications can achieve self-growth for users, and they are never too old to learn. Zhang and Dang [
99] found in a survey of the basic factors of students’ perceived sense of achievement, pleasure, and willingness to learn web development that the characteristics of teachers and teaching methods can significantly affect their perceived sense of achievement, pleasure, and then their intention to learn web development.
Dimensions affected by different levels of education
This study finds that people with different levels of education will have different views on esteem needs and self-actualization needs. The subjects with different education levels have significantly different views on the use of the home-based intelligent exercise system of golf croquet to gain pride, affirmation, confidence, and respect. And the subjects with different education levels have significantly different views on using the home-based intelligent exercise system of golf croquet to make people want to achieve higher scores and can fully exert their potential, have a sense of achievement, and feel excited and happy during the use process. Maslow [
29] referred to so-called self-actualized people, who are satisfied with life, can play their potential and have creativity, and can have a loving and accepting attitude towards themselves and others. So-called esteem needs refer to all the needs to acquire and maintain personal esteem, including the respect of others and self-respect. Solomon et al. [
100] pointed out in a study on the level of education and job satisfaction that it is theoretically inferred that education level involves a significant trade-off relationship. Because of the need for self-actualization, well-educated people will enjoy more resources from the job (including income, job autonomy, and diversity). Yu and Chang [
101] explored the needs of the elderly according to the type of community. They found that senior with high education levels have better self-confidence and value of themselves, and their level of respect and self-actualization needs