1. Introduction
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a heterogenous tumor with the majority of cases occur in the setting of underlying chronic liver disease (CLD) [
1]. Although chronic viral hepatitis has been the major risk factor of HCC, an increasing proportion of patients are now attributable to non-hepatitis B-, non-hepatitis C-related HCC (NBNC-HCC) as a result of the growing burden of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) [
1]. Currently, NAFLD is considered to be a leading cause of HCC in most Western countries. In Asian populations, the prevalence of NAFLD is also becoming an important public health concern that potentially leads to progressive liver disease including cirrhosis and HCC [
2]. Early detection of HCC enhances the likelihood of curative treatment by surgical resection, liver transplantation or local ablation. However, the overall prognosis of HCC remains unsatisfactory due to the biologic aggressiveness of the tumor and high rates of recurrence after therapies [
3]. Moreover, NBNC-HCC tends to be detected during late tumor stage, which could lead to worse prognosis in comparison to virus-related HCC [
4]. In this regard, a recent multicenter study demonstrated that there was no survival improvement among patients with NBNC-HCC over the past two decades while the survival rate of viral-related HCC considerably increased [
5]. Therefore, reliable circulating biomarkers for early diagnosis and prognostic prediction are highly required to improve clinical outcomes of patients with NBNC-HCC.
In recent years, ‘liquid biopsy’ has emerged as a novel method for the characterization of circulating cancer components, which provides a strong basis for precision oncology in terms of early diagnosis, therapeutic monitoring, and prognostication [
6]. Among various liquid-biopsy based techniques, extracellular vesicles (EVs) are promising circulating biomarkers for HCC [
6]. EVs are membrane-bound organelles produced by cells, which are classified based on size and biogenesis process. Exosomes (50-150 nm) originate from multivesicular bodies (MVBs), microvesicles (100-1000 nm) produce directly from membrane bubbling, and apoptotic bodies (500-2000 nm) generate from apoptotic process [
7]. EVs serve as cargoes to mediate intercellular communication and are involved in various biological functions and disease progress by active carrying proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids. Among them, microRNAs (miRNAs), small non-coding RNAs of 20–22 nucleotides, have attracted more attention due to their regulatory roles in a number of key pathophysiological processes [
8]. Additionally, circulating enriched EV-derived miRNAs (EV-miRNAs) appear to be more stable and homogeneous than free miRNAs in serum/plasma [
9]. Thus, EV-miRNAs, as opposed to free miRNAs, are considered to be more specific and better candidates for cancer biomarkers [
10]. Although several ‘free-circulating’ miRNAs have been shown to be useful for distinguishing HCC from non-HCC, available data regarding the role of EV-miRNAs are limited, particularly in NBNC-HCC.
In the present study, we aimed to explore the potential clinical significance of EV-miRNAs in patients with NBNC-HCC. First, we compared the profiles of plasma EV-miRNAs of the NBNC-HCC and non-cancerous groups, including patients with NAFLD and healthy controls using the NanoString technique. Additionally, the differentially expressed EV-miRNAs were validated in another set of plasma samples by qRT-PCR to identify novel biomarkers for NBNC-HCC. Finally, the diagnostic and prognostic roles of these potential biomarkers were analyzed.
2. Results
2.1. Characteristics of the participants
To construct miRNA profiling in the discovery set, 9 plasma samples per group of NBNC-HCC, NAFLD and heathy controls were analyzed by the NanoString miRNA assay. Moreover, the quantitative levels of candidate miRNAs were validated by qRT-PCR in the plasma samples of 35 healthy controls, 70 patients with NAFLD, and 70 patients with NBNC-HCC. Baseline characteristics of the participants in the validated cohort are shown in
Table 1.
2.2. Characterization of EVs
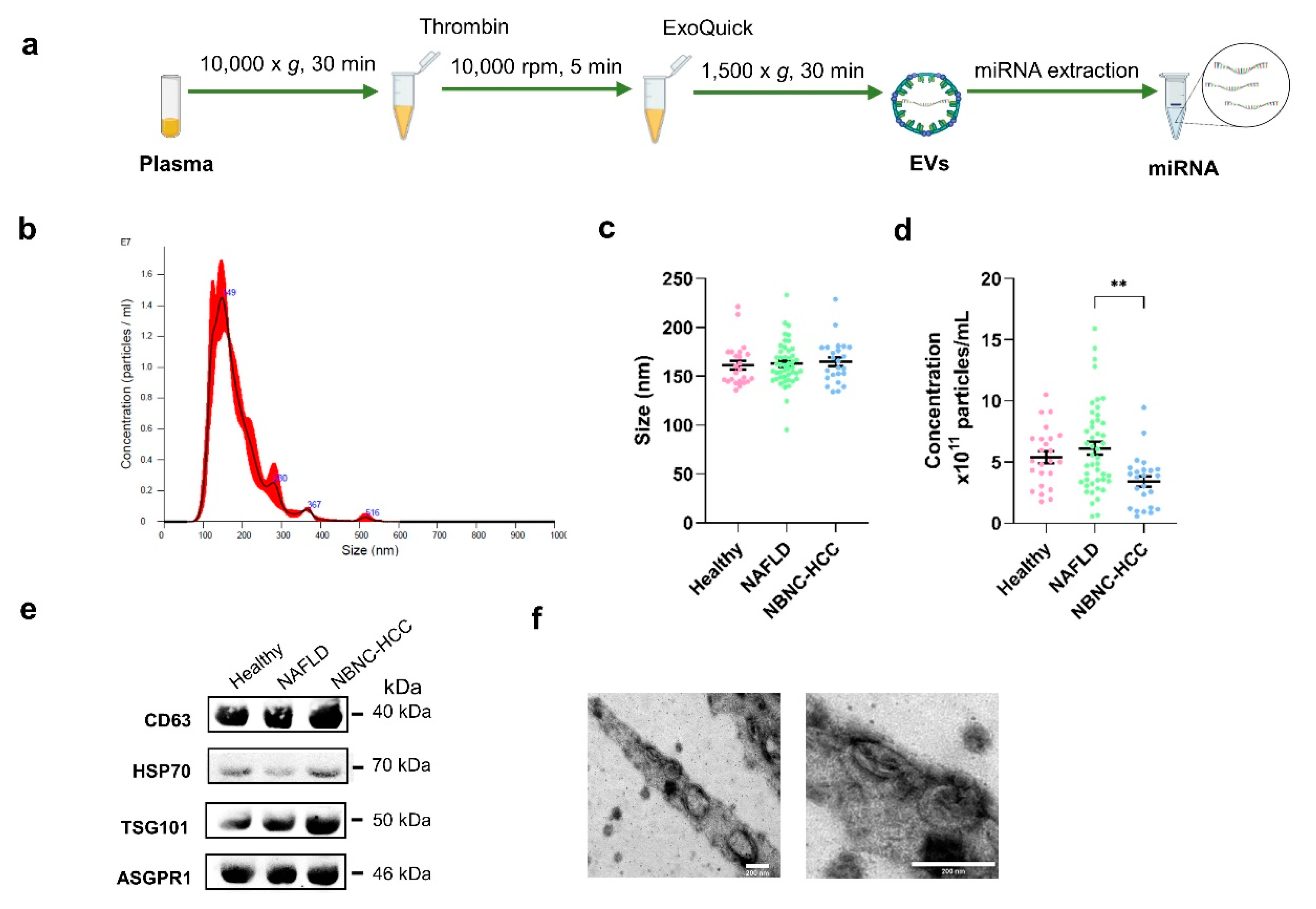
To characterize EVs isolated from plasma samples
(Figure 1a), the size and concentration of EVs were first determined by nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA). As expected, the average size of particles in overall samples was 162.9±22.1 nm in diameter (
Figure 1b-c). The concentrations of isolated EVs from healthy controls were similar to the NAFLD group (5.40 × 10
11 ± 2.39 × 10
11 and 6.12 × 10
11 ± 3.59 × 10
11 particles/mL, respectively;
Figure 1d), whereas the lowest concentration of EVs (3.41 × 10
11 ± 2.15 × 10
11 particles/mL) was found in samples from patients with NBNC-HCC. To verify the EV markers, Western blot analysis was then performed. Our results showed that the EV-enriched proteins, including CD63, HSP70, and TSG101 were expressed in isolated EV samples. Hepatocyte-specific receptor or asialoglycoprotein receptor 1 (ASGPR1) was also identified to verify that the isolated EVs were partially hepatocyte-derived EVs (
Figure 1e). In addition, the particle diameter and the morphology were confirmed and visualized by transmission electron microscopy (TEM). These vesicles were less than 200 nm in size, with a lipid bilayer, indicating that they were EVs as described previously [
11] (
Figure 1f). We next evaluated whether the isolated EVs provided intra-vesicular miRNAs. Our results were in line with previous data demonstrating that there was no statistically significant difference between
Ct values of miRNAs (such as miR-26a-5p, miR-223-3p, and let-7a-5p) in EVs treated with RNase and without RNase-A (
Figure S1a-c) [12, 13]. Together, these results indicated that our protocol could specifically identify EV-miRNAs, in accordance with previous data [
11], thus we did not perform RNase-A treatment for the subsequent experiments.
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the study protocol and characterization of EVs derived from plasma. (a) Diagram of plasma EV isolation protocol. (b) Representative nanoparticle tracking plot for size distribution from a sample. (c) Quantification of particle size diameter (nm) and (d) concentration (particles/ml) of plasma EVs from the healthy controls, NAFLD, and NBNC-HCC groups. (e) Expression of EV markers, CD63, HSP70, and TSG101, and hepatocyte-specific receptor, ASGPR1 by Western blotting. (f) Transmission electron microscopy images of EVs from a sample. Scale bars, 200 μm. Data are presented as means ± S.E.M, **P < 0.01.
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the study protocol and characterization of EVs derived from plasma. (a) Diagram of plasma EV isolation protocol. (b) Representative nanoparticle tracking plot for size distribution from a sample. (c) Quantification of particle size diameter (nm) and (d) concentration (particles/ml) of plasma EVs from the healthy controls, NAFLD, and NBNC-HCC groups. (e) Expression of EV markers, CD63, HSP70, and TSG101, and hepatocyte-specific receptor, ASGPR1 by Western blotting. (f) Transmission electron microscopy images of EVs from a sample. Scale bars, 200 μm. Data are presented as means ± S.E.M, **P < 0.01.
2.3. Profiling of EV-derived microRNAs
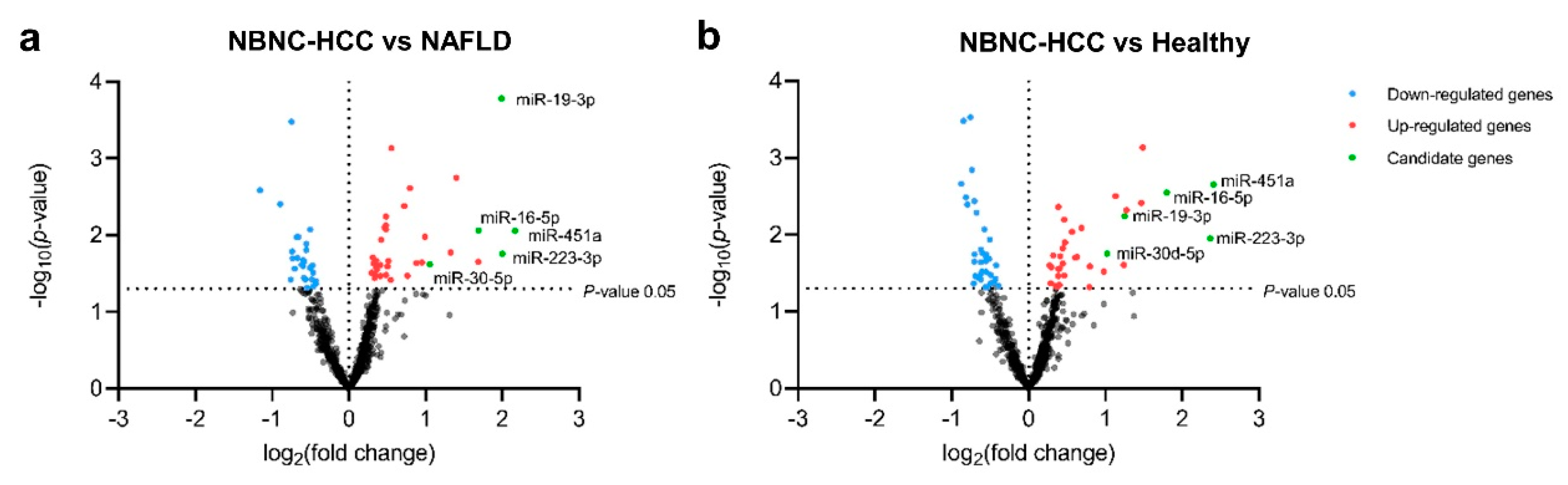
To explore the profiles of EV-miRNAs, we performed the expression of 800 miRNAs using NanoString platform (nCounter Human v3 miRNA expression assay) on the discovery set of patients with NBNC-HCC, NAFLD, and healthy controls. Raw data and normalized data outputs from nSolver 4.0 Software are available in Supplementary S1 File.
Based on differentially expressed miRNAs between groups (log2-fold change (FC) and P < 0.05), we found 66 significant differentially-expressed miRNAs (DEmiRNAs) in patients with NBNC-HCC vs. NAFLD, which included 39 up- and 27 downregulated miRNAs (Figure 2a), 73 DEmiRNAs between patients with NBNC-HCC vs. healthy controls, including 36 up- and 36 downregulated miRNAs (Figure 2b). Among the significantly upregulated miRNAs, Venn diagram showed that five miRNAs, including miR-19-3p, miR-16-5p, miR-223-3p, miR-30d-5p, and miR-451a overlapped between NBNC-HCC vs. NAFLD and NBNC-HCC vs. healthy controls (Figure S2). Accordingly, these five upregulated miRNAs were subsequently selected for further validation. The data of DEmiRNAs between patients with NAFLD and healthy controls are available in Figure S3.
Figure 2.
Transcriptome profiling of miRNAs from plasma EVs using NanoString microarray. (a) Volcano plot of all differentially expressed miRNAs in the NBNC-HCC samples compared with the NAFLD samples and (b) the NBNC-HCC samples compared with healthy controls. The significantly up-regulated and down-regulated miRNAs are marked in red and blue dots, respectively.
Figure 2.
Transcriptome profiling of miRNAs from plasma EVs using NanoString microarray. (a) Volcano plot of all differentially expressed miRNAs in the NBNC-HCC samples compared with the NAFLD samples and (b) the NBNC-HCC samples compared with healthy controls. The significantly up-regulated and down-regulated miRNAs are marked in red and blue dots, respectively.
2.4. Functional gene annotation and pathway enrichment analysis
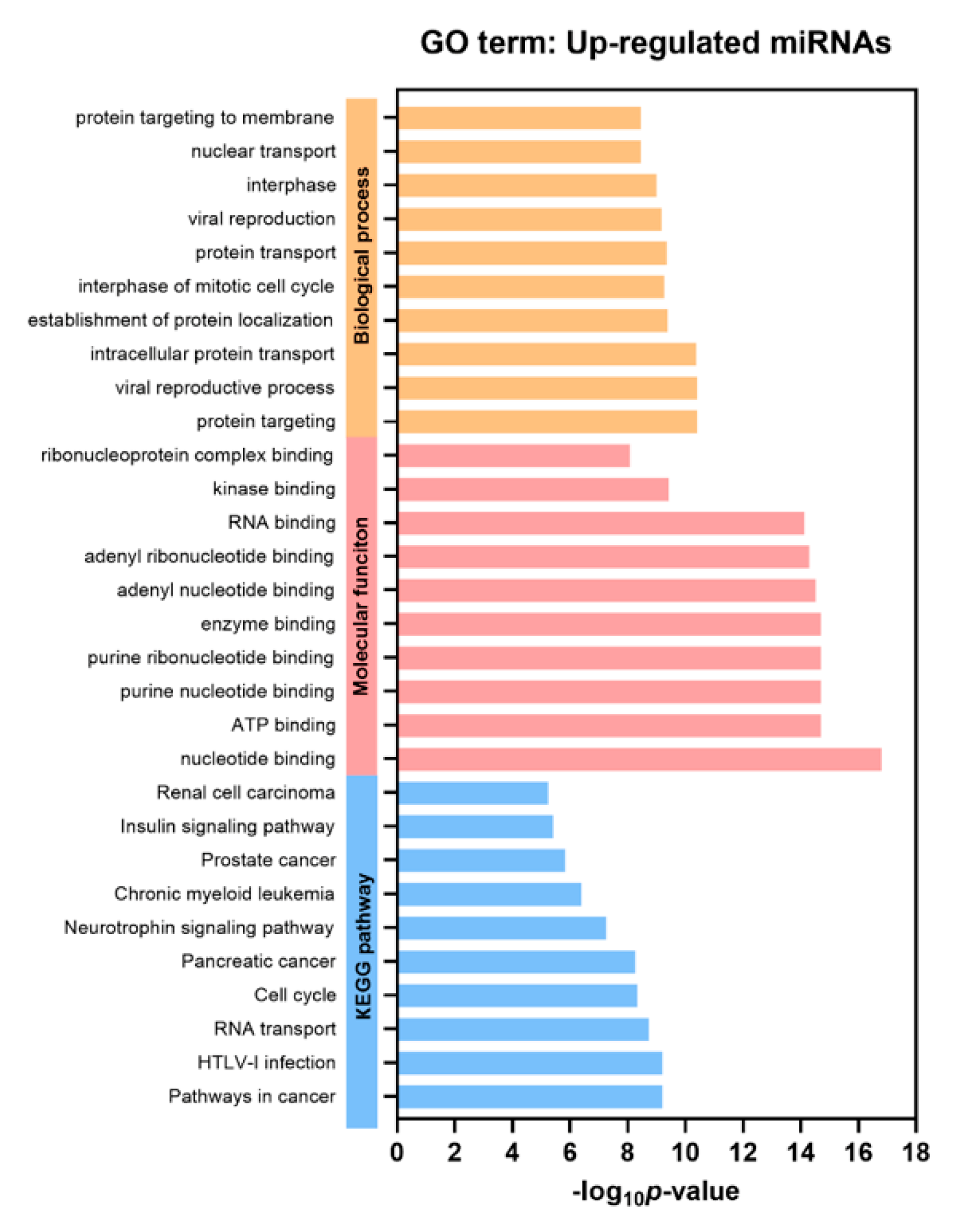
Gene Ontology (GO) and gProfiler analysis were performed to reveal enrichment of potential target genes of the significantly expressed miRNAs. The top 10 GO categories for the differentially upregulated miRNAs and downregulated miRNAs are demonstrated in Figure 3 and Figure S4 (P < 0.05), respectively. These significantly upregulated and downregulated miRNAs were involved in several biological processes, such as protein targeting and transport, nuclear transport, and cell cycle. Regarding molecular function analysis, these miRNAs were found to be enriched in nucleotide, ATP, and enzyme binding. Furthermore, Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathways indicated that the significantly upregulated miRNAs participated in pathways in cancer, similar to those with downregulated miRNAs.
Figure 3.
Gene Ontology (GO) analysis of the differentially upregulated EV miRNAs. Top 10 significantly enriched GO terms of biological process, molecular function, and KEGG pathways (P < 0.05).
Figure 3.
Gene Ontology (GO) analysis of the differentially upregulated EV miRNAs. Top 10 significantly enriched GO terms of biological process, molecular function, and KEGG pathways (P < 0.05).
2.5. Plasma EV-miRNA expression in the validation set
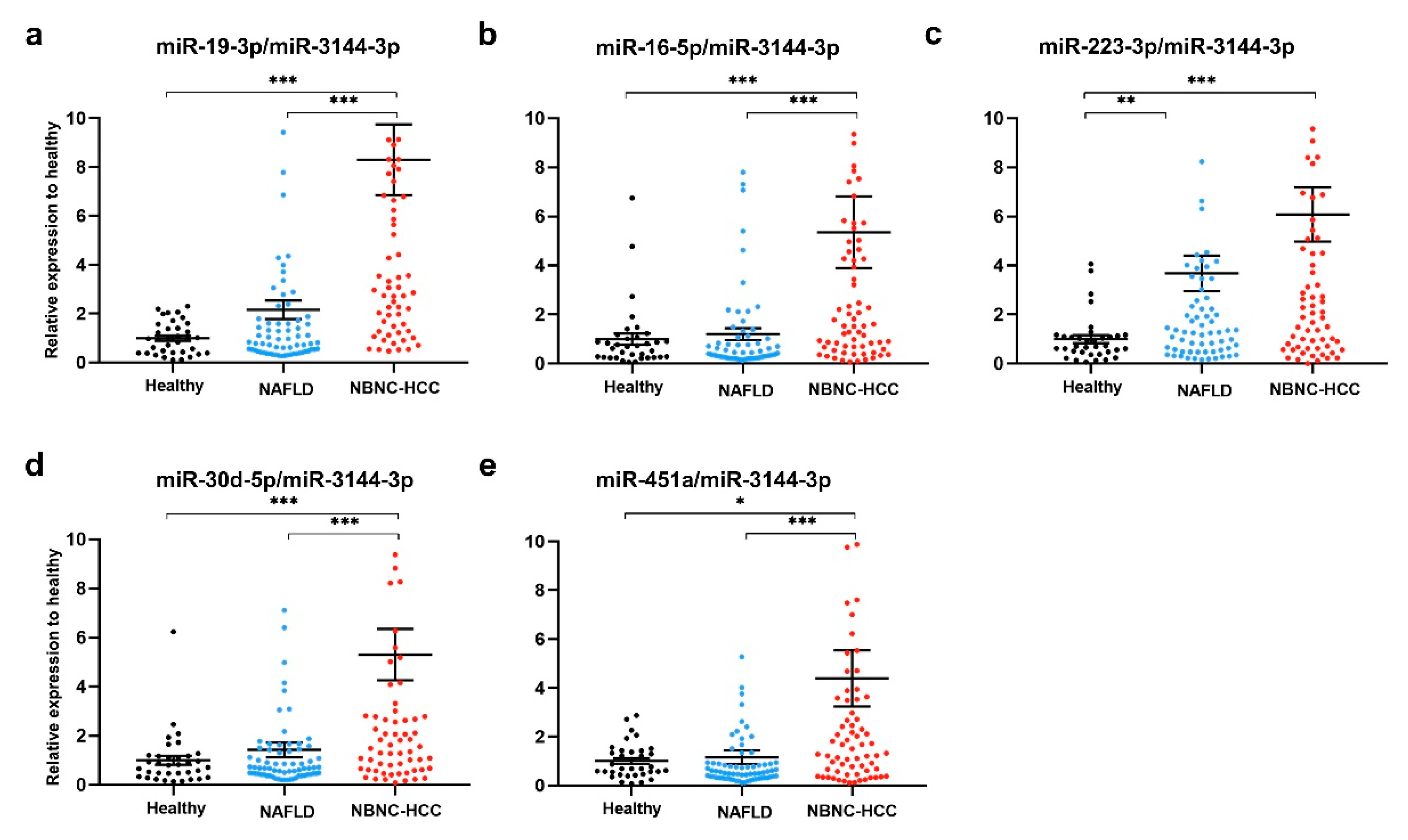
To validate the above-mentioned five upregulated candidate miRNAs, plasma EV- miRNAs from a total of 175 participants, including 35 healthy controls, 70 patients with NAFLD and 70 patients with NBNC-HCC were evaluated by qRT-PCR using miR-3144-
3p normalization. The results showed that all miR-19-3p, miR-16-5p, miR-223-3p, miR-30d-5p, and miR-451a expression levels were significantly higher in patients with NBNC-HCC compared with healthy controls (Figure 4a-e). When compared with the NAFLDgroup, the expression levels of miR-19-3p, miR-16-5p, miR-30d-5p, and miR-451a were significantly increased in the NBNC-HCC group (Figure 4a-e). Moreover, similar results of miRNA expression levels were found upon normalization with U6 (Figure S5a-e), suggesting the consistent results of the validated miRNAs across various internal controls. Overall, these findings indicated that plasma EV-miRNAs could effectively distinguish the NBNC-HCC from non-HCC groups.
Figure 4.
Validation of candidate miRNAs in plasma EV using qRT-PCR. The relative expressions of (a) miR-19-3p, (b) miR-16-5p, (c) miR-223-3p, (d) miR-30d-5p and (e) miR-451a in plasma EVs of healthy controls (n = 35), patients with NAFLD (n = 70), and patients with NBNC-HCC (n = 70). Data are presented as mean ±S.E.M., normalized with a reference miRNA, miR-3144-3p, and expressed relative to those of healthy controls. * P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 and *** P < 0.001.
Figure 4.
Validation of candidate miRNAs in plasma EV using qRT-PCR. The relative expressions of (a) miR-19-3p, (b) miR-16-5p, (c) miR-223-3p, (d) miR-30d-5p and (e) miR-451a in plasma EVs of healthy controls (n = 35), patients with NAFLD (n = 70), and patients with NBNC-HCC (n = 70). Data are presented as mean ±S.E.M., normalized with a reference miRNA, miR-3144-3p, and expressed relative to those of healthy controls. * P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 and *** P < 0.001.
2.6. Diagnostic role of plasma EV-miRNAs
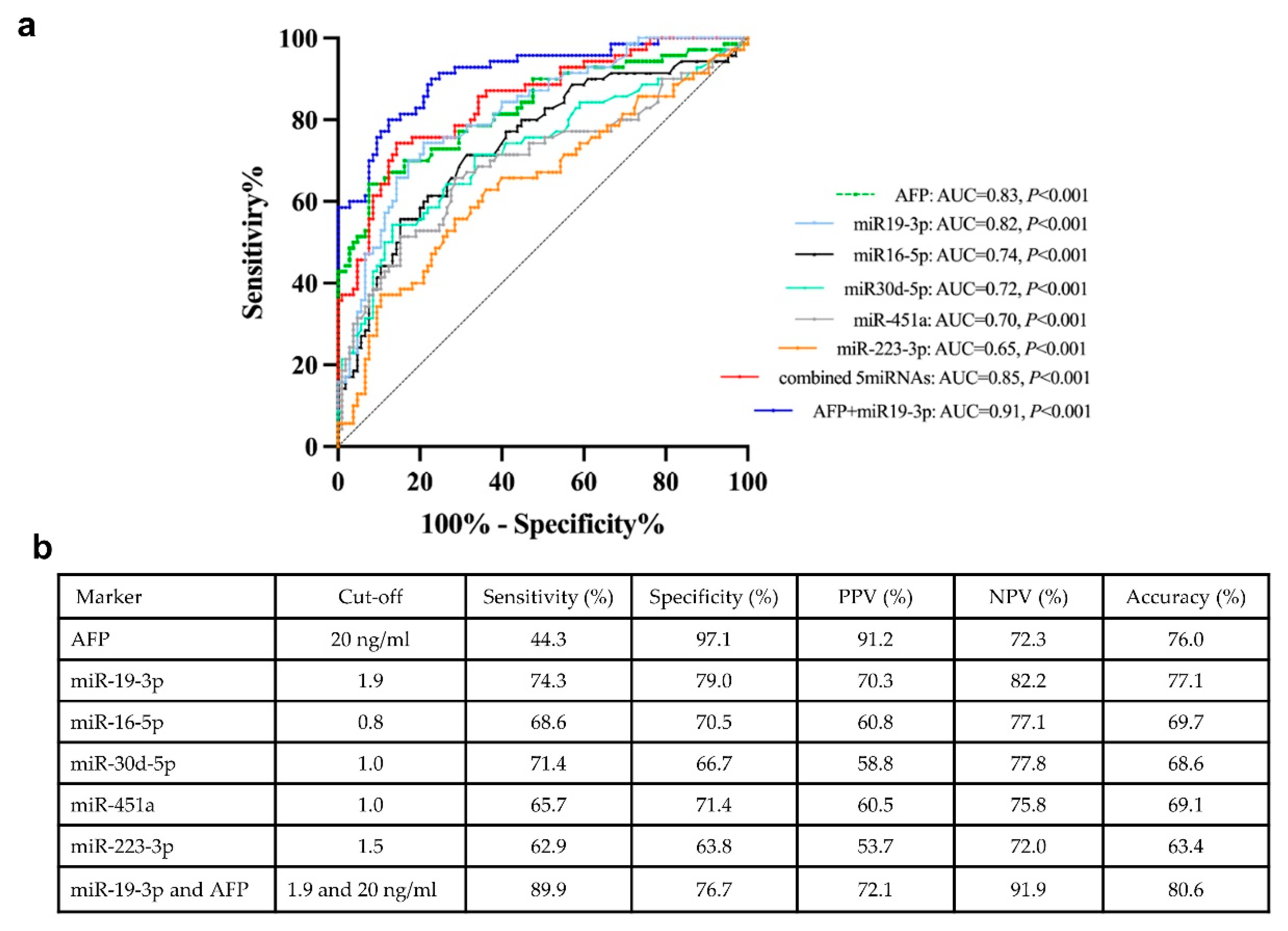
To evaluate the diagnostic performance of biomarkers in distinguishing between the NBNC-HCC and non-HCC groups, the ROC curves were analyzed (Figure 5a). The area under the curve (AUC) was 0.82 (95 % confidence interval (CI); 0.75-0.88, P < 0.001) for miR-19-3p, 0.74 (95 % CI; 0.67-0.82, P < 0.001) for miR-16-5p, 0.65 (95 % CI; 0.56-0.73, P = 0.001) for miR-223-3p, 0.72 (95 % CI; 0.64-0.80, P < 0.001) for miR-30d-5p, 0.70 (95 % CI; 0.61-0.78, P < 0.001) for miR451a and 0.83 (95 % CI; 0.76-0.89, P < 0.001) for AFP. In addition, the ROC curve for combination of all EV-miRNAs were also examined. Our results showed that multiple miRNAs did not provide a better AUC than miR-19-3p alone. However, combined miR-19-3p and AFP increased the performance for the diagnosis of HCC compared with miR-19-3p alone. The cut-off value and diagnostic performance of each EV-miRNAs, AFP, and the combination of miR-19-3p and AFP is shown in Figure 5b.
If categorized based on the normal upper limit of AFP (20 ng/mL), there were 39 (55.7%) and 31(44.3%) HCC patients with AFP-negative and AFP-positive, respectively. In the AFP-negative group, 76.9% (30/39) of HCC patients had elevated circulating miR-19-3p level (≥1.9), while the AFP-positive group, high expression of miR-19-3p was found in 71.0% (22/31). Among early HCC cases (BCLC stage 0 and A), we found that 36.0% (9/25) patients had elevated AFP level, while 80.0% (20/25) patients had high miR-19-3p expression. Together, these results might indicate that circulating EV-miR-19-3p was a promising biomarker for detecting AFP-negative HCC and early HCC, as well as a complementary to AFP in diagnosis of NBNC-HCC in our cohort.
Figure 5.
Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves of the candidate miRNAs for distinguishing between NBNC-HCC and non-HCC. (A) The area under the curve (AUC) and (B) the cut-off value and the discriminatory performance of each EV-miRNAs.
Figure 5.
Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves of the candidate miRNAs for distinguishing between NBNC-HCC and non-HCC. (A) The area under the curve (AUC) and (B) the cut-off value and the discriminatory performance of each EV-miRNAs.
2.7. Prognostic role of plasma EV-miRNAs regarding overall survival
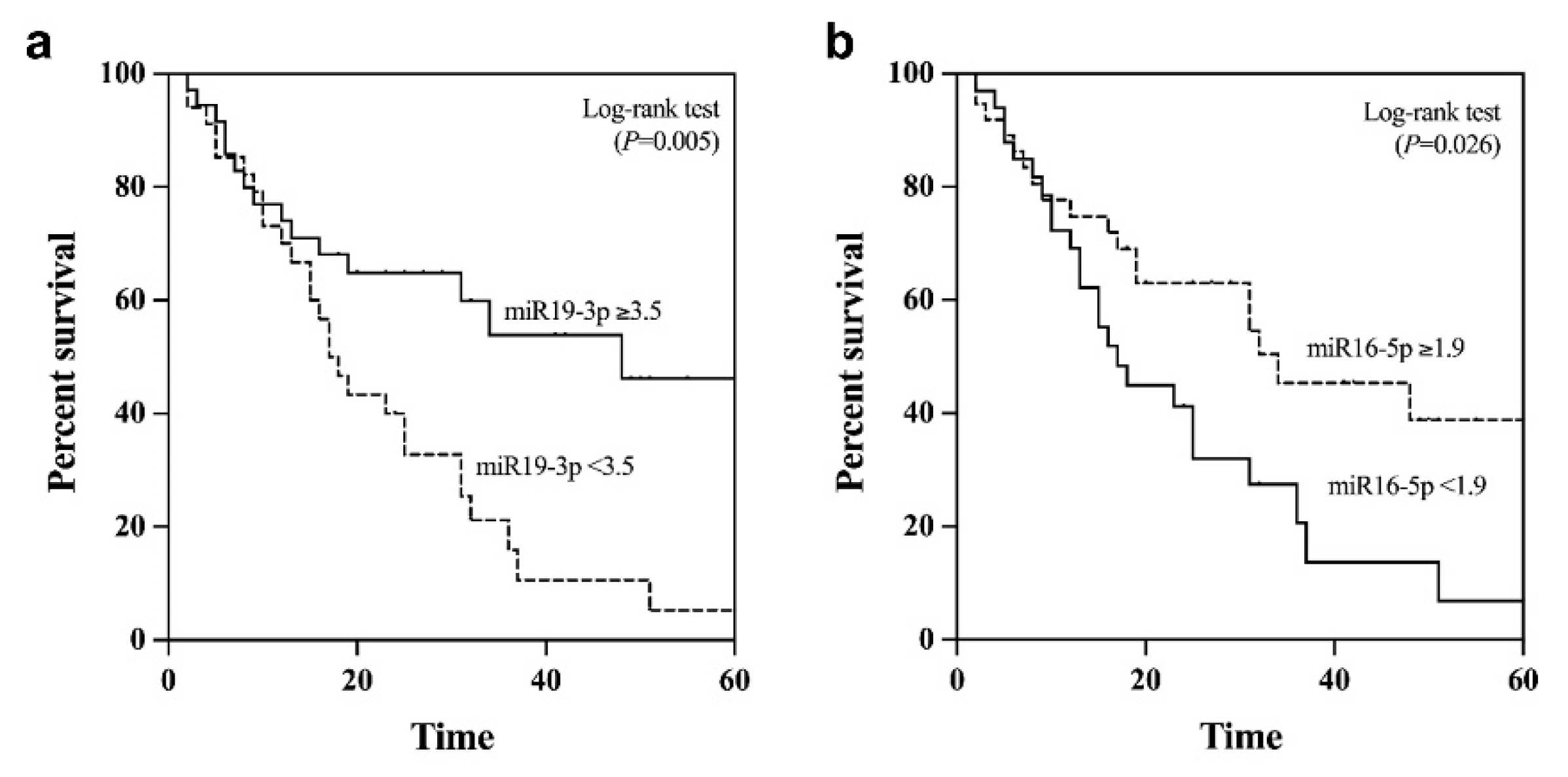
Apart from its diagnostic value, we further examined the potential prognostic role of plasma EV-miR-19-3p in patients with NBNC-HCC. Using the median value as the cut-off level (3.5), the median overall survival of patients with miR-19-3p <3.5 and ≥3.5 were 38.2 and 22.3 months, respectively (P = 0.05 by log rank test) (Figure 6a). For plasma EV-miR-16-5p, the median overall survival of HCC patients with low (<1.9) was significantly better than that of patients whose levels were elevated (35.7 vs. 23.1 months, P = 0.026) (Figure 6b). However, there was no significant difference in overall survival regarding the circulating levels of other EV-miRNAs, including miR-223-3p, miR-30d-5p, and miR-451a.
Figure 6.
Kaplan–Meier survival curves for overall survival analysis of patients with NBNC-HCC (a) plasma EV-miR-19-3p and (b) plasma EV-miR-16-5p.
Figure 6.
Kaplan–Meier survival curves for overall survival analysis of patients with NBNC-HCC (a) plasma EV-miR-19-3p and (b) plasma EV-miR-16-5p.
All 5 plasma EV-miRNAs were entered into the multivariate analysis together with other parameters that could influence overall survival of patients with NBNC-HCC. These variables included age, gender, serum TB, albumin, AST, ALT, platelet counts, AFP level, tumor size and BCLC stage. The multivariate analysis based on the Cox regression analysis demonstrated that miR-19-3p, AFP and BCLC stage were independent predictive factors for overall survival. However, miR-16-5p was not selected as a parameter associated with overall survival (Table 2).
Table 2.
Variables associated with overall survival in patients with HCC.
Table 2.
Variables associated with overall survival in patients with HCC.
| Variables |
Category |
Overall survival |
| Univariate analysis |
Multivariate analysis |
| OR (95%CI) |
P |
OR (95%CI) |
P |
| Age (years) |
< 60 vs. ≥ 60 |
0.62 (0.28-1.41) |
0.254 |
|
|
| Gender |
Male vs. Female |
0.67 (0.32-1.42) |
0.295 |
| Total bilirubin (mg/dL) |
< 1.2 vs. ≥ 1.2 |
0.77 (0.49-1.27) |
0.303 |
|
|
| Serum albumin (g/dL) |
< 3.5 vs. ≥ 3.5 |
0.97 (0.46-2.04) |
0.931 |
|
|
| Aspartate aminotransferase (IU/L) |
< 55 vs. ≥ 55 |
1.64 (1.83-3.23) |
0.153 |
|
|
| Alanine aminotransferase (IU/L) |
< 50 vs. ≥ 50 |
1.00 (0.42-2.39) |
0.998 |
|
|
| Platelet count (109/L) |
≥ 100 vs. <100 |
1.05 (0.37-2.97) |
0.927 |
|
|
| Alpha fetoprotein (ng/mL) |
< 100 vs. ≥ 100 |
2.09 (1.08-4.08) |
0.029* |
2.04 (1.01-4.13) |
0.048* |
| Tumor size (cm.) |
< 5.0 vs. ≥ 5.0 |
1.63 (0.88-3.04) |
0.123 |
|
|
| BCLC stage |
0-A vs. B vs. C |
2.15 (1.38-3.36) |
0.001* |
2.07 (1.29-3.32) |
0.002* |
| EV-miR-19-3p |
< 3.5 vs. ≥ 3.5 |
2.39 (1.26-4.52) |
0.008* |
2.71 (1.19-6.19) |
0.018* |
| EV-miR-16-5p |
< 1.9 vs. ≥ 1.9 |
1.98 (1.07-3.69) |
0.030* |
0.97 (0.44-2.13) |
0.944 |
| EV-miR-30d-5p |
< 2.0 vs. ≥ 2.0 |
1.56 (0.83-2.93) |
0.171 |
|
|
| EV-miR-451a |
< 1.7 vs. ≥ 1.7 |
1.74 (0.94-3.23) |
0.078 |
|
|
| EV-miR-223-3p |
< 2.5 vs. ≥ 2.5 |
1.71 (0.92-3.19) |
0.091 |
|
|
3. Discussion
The detection of HCC at early-stage cancer is an unmet clinical need because only 20-30% of patients are eligible for curative therapy mainly due to the lack of early-detection biomarkers. At present, serum AFP remains the most commonly used serum biomarker despite its insufficient performance in early detection for HCC. Overall, the sensitivity and specificity of AFP are approximately 60% and 80%, respectively, and its sensitivity decreases significantly in patients with early HCC [
14]. Moreover, AFP levels remain normal (AFP level <20 ng/ml) in up to 30% of advanced cancer stage but are elevated in some individuals without HCC, leading to high negative and false-positive rates. In this report, our data demonstrated that only 36% of early NBNC-HCC were AFP-positive (AFP level ≥20 ng/ml). Thus, additional novel biomarkers that could be used individually or in complementary with AFP for better accurate detection of HCC are required.
In recent years, the potential role of EV-based liquid biopsy in the management of liver disease is of great interest. Emerging evidence highlights the significance of EV-miRNAs in various chronic liver diseases, including viral hepatitis, NAFLD, alcohol-related liver disease and HCC [
15]. For instance, circulating EV-miRNA profiles could be non-invasive biomarkers for the assessment of severity in patients with NAFLD [16, 17]. Regarding HCC, previous studies demonstrated that either single or panels of EV-miRNAs are potentially specific and sensitive biomarkers for the diagnosis of viral-related HCC [18, 19]. However, data regarding the role of EV-miRNAs as novel biomarkers of NBNC-HCC are still missing. In this study, we initially characterized microtranscriptome to examine circulating EV-miRNA profiles in patients with NBNC-HCC by comparison with those of patients with NAFLD and healthy controls. In this discovery set, several differential expression profiles of EV-miRNAs between the HCC and control groups were revealed. In the validation set by qRT-PCR, plasma-derived EV-miRNAs, including miR-19-3p, miR-16-5p, miR-223-3p, miR-30d-5p, and miR-451a were significantly elevated in NBNC-HCC compared with the control groups. Also, the data based on bioinformatics identified up- and downregulated miRNAs associated with various biological processes, including protein targeting and transport, nuclear transport, and cell cycle. Moreover, the enriched KEGG pathways of DEGs were found to participate in several cancer-related signaling pathways.
In our report, we demonstrate for the first time that EV-miR-19-3p could be used as a promising biomarker for NBNC-HCC. We showed that EV-miR-19-3p had a high diagnostic ability for detecting AFP-negative cases. Additionally, the combined use of EV-miR-19-3p and AFP increased the diagnostic accuracy of NBNC-HCC. These findings suggest the potential use of EV-miR-19-3p as a sensitive biomarker for early HCC and a complementary biomarker with AFP-negative HCC. Of note, it was recently shown that circulating EV-miR-19a-3p was identified as a novel biomarker among other miRNAs for early and non-invasive diagnosis of pancreatic cancer [
20]. Moreover, a recent study showed that EV-miR-19a-3p was highly upregulated in the advanced stage of prostate cancer tissue specimens, particularly after androgen stimulation [
21]. Regarding its predictive role, Kaplan-Meier analysis also showed that high circulating EV-miR-19-3p was positively correlated with poor overall survival in patients with NBNC-HCC. Moreover, multivariate analysis verified that an increased EV-miR-19-3p level was an independently unfavorable predictor of overall survival. Collectively, our results provide evidence supporting a novel role of EV-miR-19-3p in early detection and prognostic value of NBNC-HCC.
Dysregulated expression of miR-19 has been shown to be involved in several types of solid tumors and represents one of the most investigated miRNAs in human cancer [
22]. Many studies have demonstrated that miR-19 plays a significant role in regulating and maintaining homeostasis of tissue function and immune regulation. Additionally, its dysregulation has been implicated in the pathogenesis and progression of tissue inflammation and fibrosis, as well as tumorigenesis [
23]. For example, previous data reported that serum miR-19a, could be a biomarker for early detection of colorectal cancer [
24] and breast cancer [
25]. Among studies related to HCC, most previous reports examined the expression of miR-19 in HCC cell lines or liver tissue specimens [26-31], with limited available data on blood-based samples [
32]. For instance, miR-19 was shown to be upregulated in tissue specimens and cell lines through the PTEN/Akt pathway in promoting HCC metastasis and chemoresistance [29, 32]. In contrast, the expression level of miR-19a in human cancer specimens was significantly lower than that found in adjacent non-cancerous tissue, which might play an inhibitory role for HCC progression by targeting Cyclin D1 [
28]. This discrepancy might be due to several factors such as the etiologies and the heterogeneity of HCC, as well as different studied HCC cell lines. Although miR-19 expression levels in HCC were rather inconsistent, a recent systematic review and meta-analysis revealed that upregulated miR-19 expression was detected in HCC compared with non-malignant controls in most reports, indicative of its crucial role in the diagnosis and prognosis of HCC [
33]. Further studies are therefore required to elucidate the mechanism by which EV-miR-19-3p plays a crucial role in the development and progression of NBNC-HCC.
Our work had some limitations as the sample size was relatively small, and thus additional studies from multi-centers are required to confirm our findings. Secondly, although there are several potential etiologies for NBNC-HCC, the majority of our cases could likely be related to NAFLD as other major causes of HCC including significant alcohol consumption were already excluded at the initial enrollment. Moreover, most cases of NBNC-HCC in our cohort had coexisting metabolic syndrome that was linked to NAFLD as reported in most studies [
34]. Thirdly, liver biopsy was not performed in patients with NAFLD. Although liver biopsy is currently the gold standard for diagnosis of NAFLD, this invasive method has limitations including sampling error, risk of complications and being not feasible to perform in all patients. Instead, we used transient elastography, which is considered to be an accurate non-invasive tool to determine the severity of fibrosis and steatosis. Despite these limitations, our results demonstrated that circulating EV-miR-19-3p was a reliable biomarker to differentiate between the NBNC-HCC and non-HCC groups. Apart from its diagnostic role, plasma EV-miR-19-3p also displayed a good prognostic indicator for NBNC-HCC. Together, this novel circulating biomarker might serve as a promising tool for the diagnosis and prognosis prediction of NBNC-HCC.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Research subjects and participant consent
Blood samples for the assessment of EV-miRNAs were obtained from patients with NBNC-HCC who were followed-up at King Chulalongkorn Memorial Hospital (Bangkok, Thailand). All patients enrolled in this study were seronegative for HBsAg and anti-HCV, had no significant alcohol consumption (defined as > 20 g ethanol/day in males and >10 g ethanol/day in females) and no coexisting causes of other chronic liver disease such as autoimmune hepatitis, primary biliary cholangitis and Wilson’s disease. HCC was diagnosed on the basis of typical findings on imaging studies and/or histopathology according to the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD) guideline [
35]. Briefly, diagnostic criteria with dynamic imaging were established by findings of focal lesions with hyper-attenuation at the arterial phase and hypo-attenuation at the portal phase. Liver biopsy or fine needle aspiration was performed in case of uncertain diagnosis by the imaging studies. Baseline clinical parameters were recorded, including tumor staging classified by the Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer staging system (BCLC) [
36]. Blood samples were collected from patients prior to any HCC therapy, including liver resection, radiofrequency ablation (RFA) and transarterial chemoembolization (TACE). Moreover, the overall survival (OS) of patients with NBNC-HCC defined by the interval between initial assessment and death or the last follow-up visit was documented.
Patients with NAFLD, who had no evidence of HCC, as well as other liver disease, and seronegative for both HBsAg and anti-HCV, were included as a control group. The diagnosis of NAFLD was according to the American Association for the Study of Liver (AASLD) criteria as determined by controlled attenuation parameter (CAP) using FibroScan device (Echosens, Paris, France), with the cut-off >248 dB/m [37, 38]. Among this group of patients, current and past daily alcohol intake was less than 20 g/week and none of the patients received any steatogenic medication. Additionally, individuals who had no underlying disorders and had normal vibration-controlled transient elastography (VCTE) and CAP values were served as healthy controls. The study was conducted according to the Declaration of Helsinki. The protocol was approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of Faculty of Medicine, Chulalongkorn University and all participants signed informed consent before collecting the samples.
4.2. Blood collection and plasma processing
Blood samples obtained from each subject were processed by centrifugation at 12,000 x g for 30 min at 4°C and then stored at -80°C until analysis for miRNA profile in the discovery cohort by NanoString® nCounter miRNA Expression Assay (NanoString Technologies, WA, USA) and the validation of miRNAs by quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR, Applied Biosystems, MA, USA) technique.
4.3. EV isolation
EVs were extracted from plasma samples using the ExoQuick™ Exosome Isolation Kit (SBI, System Biosciences, CA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. Briefly, for collecting the clear supernatant of plasma, 1 mL of the samples were incubated for 5 min with 8 µL of thrombin (final concentration of 5U/mL) before centrifugation at 10,000 rpm for 5 min at 4°C. Next, 250 µL of ExoQuick™ was added and incubated at 4°C for 30 min. The mixture of ExoQuick™-plasma samples were centrifuged to precipitate EVs at 1,500 x g for 30 min. The pellet was then resuspended in 0.22 µm-filtered 1x PBS and stored at −80°C until further use. For the validation, 200 µL of plasma samples were used.
4.4. EV characterization
4.4.1. Nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA)
To characterize EVs from plasma, the quantity and size distribution of EVs in plasma samples were carried out using the NTA (NanoSight NS300, ATA Scientific, Taren Point NSW 2229, Australia). EVs were diluted 1000-fold for detecting between 50 and 100 particles per frame. Three 40-s videos were recorded with screen gain 3 and camera level 9 followed by an analysis of the data using NanoSight software (NTA 3.4 Build 3.4.003) with screen gain 9 and detection threshold 3.
4.4.2. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM)
To characterize the morphology and size of EVs, 5 µL drop of the suspension was loaded onto a 400 mesh formvar/carbon-coated grid (Electron Microscopy Sciences, USA). To enhance the contrast between EVs and background, grids were negatively stained with 2.5% uranyl acetate for 5 min. The excessive stain was blotted, and the grid was dried. Images were visualized under a transmission electron microscope using JEM-1400plus TEM (JEOL, Tokyo, Japan) at 80 kV.
4.4.3. Western blotting
To detect EV protein markers by immunoblotting, EV samples were lysed using RIPA buffer with Proteinase and Phosphatase Inhibitor Cocktail (Merck, NJ, USA). The lysates were sonicated with 7 sets of 3-s pulses using Sonics Vibra-Cell™ (Sonics & Materials, CT, USA). EV proteins (10 µg) were measured using Pierce™ BCA Protein Assay Kit (ThermoFisher Scientific, MA, USA.) and loaded onto sodium dodecyl polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE). The proteins were then transferred to nitrocellulose membranes, blocked for 1 hour with 5% BSA, and incubated at 4ºC overnight with primary antibodies against TSG101 (1:1,000) (Ab83, 4A10) (Abcam, MA, USA), HSP70 (1:1,000) (4876, D69, Cell signaling), CD63 (1:2,000) (Ab193349, MX-49.129.5, Abcam). To identify hepatocyte-specific marker, ASGPR1 (1:1,000) (SC-52623, 8D7, Santa Cruz) was used [39, 40]. Following this process, the membrane was stained with HRP-conjugated secondary antibodies for 1 hour. Antigen-antibody reactions were visualized with an enhanced chemiluminescence detection reagent and images were acquired using a ChemiDoc Imaging System (Bio-Rad Laboratories, CA, USA).
4.5. NanoString miRNA expression analysis
To extract miRNA from EVs, isolated EVs from the above-mentioned method was extracted using miRNeasy Serum/Plasma Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany). Before applying to NanoString analysis, miRNA was concentrated and minimized contamination using an Amicon Ultra YM-3 filter (Merck Millipore, NJ, USA). Briefly, 320 µL of RNase-free water was added to the isolated miRNA, loaded onto the filter, and centrifuged at 14,000 x g at 25 ºC for 90 min. Three µL of the concentrated miRNAs were subjected to human NanoString nCounter miRNA expression assay (NanoString Technologies, WA, USA) using the nCounter Human miRNA Panel v3 that evaluated 800 miRNAs according to the manufacturer’s instructions. In brief, miRNAs were hybridized to capture and reporter probes at 65°C for 18 hours, followed by purification and quantification on the nCounter Prep Station and Digital Analyzer. The resulting data were analyzed by the nSolver 4.0 software to obtain the count of individual miRNA. The miRNA data were calculated by normalization to the top 100 miRNA counts in each sample.
4.6. Real-Time Quantitative Reverse Transcription PCR (qRT-PCR)
The miRNAs were reverse transcribed to complementary DNA (cDNA) by SL-poly (A) sequence: GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATACGACAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAVN using RevertAid First Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit (ThermoFisher Scientific). qRT-PCR were performed in duplicate using the QPCR Green Master Mix HRox 4x (Biotechrabbit, Hennigsdorf, Germany). The reactions were detected by a QuantStudio 5 Real-Time PCR System (Applied Biosystems, MA, USA). Reaction with no cDNA template was run as a negative control on every plate for each assay. Thermal cycling parameters were started with activation step at 95°C for 10 min, followed by 40 cycles of denaturation at 95°C for 15 s, and extension at 72°C for 20 s with optimal annealing temperatures of each gene for 15 s. Primer sequences are listed in Table S1.
Four internal control miRNAs including U6, miR-26a-5p, miR-3144-3p and miR-302d-3p from NanoString data were used to normalize the miRNA expressions. The results indicated that in the validation set of samples (n=10 for healthy controls, n=10 for NAFLD, and n =9 for NBNC-HCC), all four miRNAs showed a similar Ct value, 29.92±1.10, 28.06±1.21, 31.987±1.03, and 29.46±1.17 for U6, miR-26a-5p, miR-3144-3p, and miR-302d-3p, respectively (Figure S6a-d). However, miR-3144-3p and U6 exhibited the lowest % cv of 3.23 and 3.69 compared to miR-26a-5p, and miR-302d-3p (4.30 and 3.98, respectively). In this respect, it was suggested that the expression of miR-3144-3p and U6 were the most constant in our sample set. Thus, these miRNAs were suitable for normalization in the validated samples and data were calculated by the 2-ΔΔCT method.
4.7. Statistical analysis
Data were analyzed by SPSS statistics version 22 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL) and graph visualizations were constructed using GraphPad Prism 8.0 (GraphPad Software, CA, USA). To compare between groups, Chi’s square or Fisher’s exact test were applied for categorical variables and Student’s t-test or one-way ANOVA were used for quantitative variables. The diagnostic performance was evaluated using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve and the area under the curve (AUC) with sensitivity and specificity analysis. The Kaplan-Meier analysis and log-rank test were calculated for the survival analysis. In addition, the Cox regression was applied for identifying independent factors associated with overall survival of patients with NBNC-HCC. A P-value<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org. Figure S1: qRT-PCR analysis of EV miRNAs, (a) miR-26a-5p, (b) miR-223-3p, and (c) let-7a-5p upon RNase A treatment of lysed EVs and intact EVs with or without RNase A. Data are presented as means ±S.E.M of 5 independent samples; ns = not significant, **P < 0.01, and *** P < 0.001; Figure S2: Venn diagram of intersect genes with fold change values more than 2 0 and showed a significant increase (P < 0.05) when pairwise comparison between NBNC HCC and NAFLD, and NBNC HCC and healthy controls; Figure S3: Volcano plot of all differentially expressed miRNAs in NAFLD samples compared with healthy control samples. The significantly up-regulated and down-regulated miRNAs are marked in red and blue dots, respectively; Figure S4: Gene Ontology (GO) analysis of the differentially downregulated EV miRNAs Top10 significantly enriched GO terms of biological process, molecular function, and KEGG pathways (P < 0.05); Figure S5: Validation of candidate miRNAs in plasma EV using qRT-PCR. The relative expressions of (a) miR-19-3p, (b) miR-16-5p, (c) miR-223-3p, (d) miR-30d-5p and (e) miR-451a in plasma EVs of healthy controls (n = 35), patients with NAFLD (n = 70), and patients with NBNC-HCC (n = 70). Data are presented as mean ± S.E.M., normalized with a reference gene, U6, and expressed relative to those of healthy controls. * P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 and *** P < 0.001; Figure S6: qRT-PCR analysis of candidate internal controls in the study cohort from plasma EVs of healthy controls (n = 10), NAFLD (n = 10), and NBNC-HCC (n = 9). Data are presented as means ± S.D.; ns =not significant; Table S1: Sequences of primers used for qRT-PCR analysis.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.B., N.C. and P.T.; Methodology, B.B., N.S. and N.C.; Software, B.B. and N.C.; Validation, B.B. and N.C.; Formal analysis, B.B. and N.C.; Investigation, B.B.; Resources, P.T. and N.P.; Data curation, P.T. and N.C.; Writing—original draft preparation, B.B.; Writing—review and editing, N.C. and P.T.; Visualization, B.B. and N.C.; Supervision, N.C. and P.T.; Project administration, P.T.; Funding acquisition, N.C. and P.T. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by National Research Council of Thailand (NRCT) (N41A640187) and the Second Century Fund (C2F), Chulalongkorn University. The study was also supported by Fundamental Fund 2022, Thailand Science Research and Innovation (TSRI) via Chulalongkorn University [CUFRB65_hea(14)_021_30_02], Program Management Unit for Human Resources & Institutional Development, Research and Innovation (PMU-B) and Center of Excellence in Hepatitis and Liver Cancer, Faculty of Medicine, Chulalongkorn University. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of Faculty of Medicine, Chulalongkorn University (IRB No. 909/64, COA No. 0042/2022).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
This published article and the
Supplementary Materials contain all of the established data or analyzed data throughout this study. Raw data for quantitative analysis could be requested from corresponding authors upon reasonable inquiry.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank all of members in Center of Excellence in Hepatitis and Liver Cancer, Faculty of Medicine, Chulalongkorn University for their efforts in conducting the experiments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
References
- Singal, A.G.; Lampertico, P.; Nahon, P. Epidemiology and surveillance for hepatocellular carcinoma: New trends. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zou, B.; Yeo, Y.H.; Feng, Y.; Xie, X.; Lee, D.H.; Fujii, H.; Wu, Y.; Kam, L.Y.; Ji, F.; et al. Prevalence, incidence, and outcome of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in Asia, 1999–2019: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 4, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulik, L.; El-Serag, H.B. Epidemiology and Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 477–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, P.-Y.; Hsu, C.-T.; Yeh, M.-L.; Huang, C.-F.; Huang, C.-I.; Liang, P.-C.; Lin, Y.-H.; Hsieh, M.-Y.; Wei, Y.-J.; Hsieh, M.-H.; et al. Early Fibrosis but Late Tumor Stage and Worse Outcomes in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients Without Hepatitis B or Hepatitis C. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2020, 65, 2120–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyoda, H.; Kariyama, K.; Hiraoka, A.; Tsuji, K.; Ishikawa, T.; Hatanaka, T.; Naganuma, A.; Yasuda, S.; Nouso, K.; Kakizaki, S.; et al. Improved survival of viral hepatocellular carcinoma but not non-viral hepatocellular carcinoma from 2000 to 2020: A multi-centre cohort study of 6007 patients from high-volume academic centres in Japan. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 56, 694–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Felden, J.; Garcia-Lezana, T.; Schulze, K.; Losic, B.; Villanueva, A. Liquid biopsy in the clinical management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gut 2020, 69, 2025–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocucci, E.; Meldolesi, J. Ectosomes and exosomes: shedding the confusion between extracellular vesicles. Trends Cell Biol. 2015, 25, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, M.; Hu, R.; Runtsch, M.C.; Kagele, D.A.; Mosbruger, T.L.; Tolmachova, T.; Seabra, M.C.; Round, J.L.; Ward, D.M.; O’connell, R.M. Exosome-delivered microRNAs modulate the inflammatory response to endotoxin. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Zhang, T.; Zheng, M.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Z. Exosomal proteins as potential markers of tumor diagnosis. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2017, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thind, A.; Wilson, C. Exosomal miRNAs as cancer biomarkers and therapeutic targets. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2016, 5, 31292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amorim, M.G.; Valieris, R.; Drummond, R.D.; Pizzi, M.P.; Freitas, V.M.; Sinigaglia-Coimbra, R.; Calin, G.A.; Pasqualini, R.; Arap, W.; Silva, I.T.; et al. A total transcriptome profiling method for plasma-derived extracellular vesicles: applications for liquid biopsies. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Xiang, G.-M.; Liu, L.-L.; Liu, C.; Liu, F.; Jiang, D.-N.; Pu, X.-Y. Assessment of endogenous reference gene suitability for serum exosomal microRNA expression analysis in liver carcinoma resection studies. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 4683–4691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, F.; Xiang, G.; Jiang, D.; Pu, X. Identification of Endogenous Controls for Analyzing Serum Exosomal miRNA in Patients with Hepatitis B or Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Dis. Markers 2015, 2015, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forner, A.; Reig, M.; Bruix, J. α-Fetoprotein for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Diagnosis: The Demise of a Brilliant Star. Gastroenterology 2009, 137, 26–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szabo, G.; Momen-Heravi, F. Extracellular vesicles in liver disease and potential as biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 455–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vulf, M.; Shunkina, D.; Komar, A.; Bograya, M.; Zatolokin, P.; Kirienkova, E.; Gazatova, N.; Kozlov, I.; Litvinova, L. Analysis of miRNAs Profiles in Serum of Patients With Steatosis and Steatohepatitis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, L.A.; Useckaite, Z.; Johnson, J.; Sorich, M.J.; Hopkins, A.M.; Rowland, A. Selective Isolation of Liver-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Redefines Performance of miRNA Biomarkers for Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorop, A.; Iacob, R.; Iacob, S.; Constantinescu, D.; Chitoiu, L.; Fertig, T.E.; Dinischiotu, A.; Chivu-Economescu, M.; Bacalbasa, N.; Savu, L.; et al. Plasma Small Extracellular Vesicles Derived miR-21-5p and miR-92a-3p as Potential Biomarkers for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Screening. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin J, Lin W, Bai Y, Liao Y, Lin Q, Chen L, et al. Identification of exosomal hsa-miR-483-5p as a potential biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma via microRNA expression profiling of tumor-derived exosomes. Experimental Cell Research. 2022;417(2):113232.
- Zou, X.; Wei, J.; Huang, Z.; Zhou, X.; Lu, Z.; Zhu, W.; Miao, Y. Identification of a six-miRNA panel in serum benefiting pancreatic cancer diagnosis. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 2810–2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martens-Uzunova, E.S.; Kusuma, G.D.; Crucitta, S.; Lim, H.K.; Cooper, C.; Riches, J.E.; Azad, A.; Ochiya, T.; Boyle, G.M.; Southey, M.C.; et al. Androgens alter the heterogeneity of small extracellular vesicles and the small RNA cargo in prostate cancer. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2021, 10, e12136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ardizzone, A.; Calabrese, G.; Campolo, M.; Filippone, A.; Giuffrida, D.; Esposito, F.; Colarossi, C.; Cuzzocrea, S.; Esposito, E.; Paterniti, I. Role of miRNA-19a in Cancer Diagnosis and Poor Prognosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Teng, C.; Ma, J.; Fu, N.; Wang, L.; Wen, J.; Wang, T.-Y. miR-19 family: A promising biomarker and therapeutic target in heart, vessels and neurons. Life Sci. 2019, 232, 116651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, G.; Du, L.; Yang, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Yang, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, C. Serum microRNA panel as biomarkers for early diagnosis of colorectal adenocarcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 111, 1985–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sochor, M.; Basova, P.; Pesta, M.; Dusilkova, N.; Bartos, J.; Burda, P.; Pospisil, V.; Stopka, T. Oncogenic MicroRNAs: miR-155, miR-19a, miR-181b, and miR-24 enable monitoring of early breast cancer in serum. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 448–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.-B.; Zhong, L.; Teng, M.-J.; Fan, J.-W.; Tang, H.-M.; Wu, J.-Y.; Chen, H.-Y.; Wang, Z.-W.; Qiu, G.-Q.; Peng, Z.-H. Identification of recurrence-related microRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma following liver transplantation. Mol. Oncol. 2012, 6, 445–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, C.-L.; Yen, C.-S.; Tsai, H.-W.; Su, Y.-C. Upregulation of MicroRNA-19b predicts good prognosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma presenting with vascular invasion or multifocal disease. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Guo, X.; Li, Z.; Li, B.; Li, Z.; Li, R.; Guo, Q.; Xiong, L.; Yu, L.; Zhao, J.; et al. A systematic investigation based on microRNA-mediated gene regulatory network reveals that dysregulation of microRNA-19a/Cyclin D1 axis confers an oncogenic potential and a worse prognosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma. RNA Biol. 2015, 12, 643–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.-M.; Yu, X.-N.; Liu, T.-T.; Zhu, H.-R.; Shi, X.; Bilegsaikhan, E.; Guo, H.-Y.; Song, G.-Q.; Weng, S.-Q.; Huang, X.-X.; et al. microRNA-19a-3p promotes tumor metastasis and chemoresistance through the PTEN/Akt pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. BioMedicine Pharmacother. 2018, 105, 1147–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.; Tang, W.; Fan, J.; Xu, Y.; Sun, H. Differentially expressed miRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma cells under hypoxic conditions are associated with transcription and phosphorylation. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.-X.; Yang, Z.-F.; Tang, W.-G.; Ke, A.-W.; Liu, W.-R.; Li, Y.; Gao, C.; Hu, B.; Fu, P.-Y.; Yu, M.-C.; et al. MicroRNA-19a-3p regulates cell growth through modulation of the PIK3IP1-AKT pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Cancer 2020, 11, 2476–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, G.; Chen, X.; Chen, S.; Ye, W.; Hou, K.; Liang, M. MiR-19a, miR-122 and miR-223 are differentially regulated by hepatitis B virus X protein and involve in cell proliferation in hepatoma cells. J. Transl. Med. 2016, 14, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Li, W.; Shen, P.; Bai, B.; Cao, L.-L. miR-19 Is a Potential Clinical Biomarker for Gastrointestinal Malignancy: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.Q.; El-Serag, H.B.; Loomba, R. Global epidemiology of NAFLD-related HCC: trends, predictions, risk factors and prevention. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 223–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruix, J.; Sherman, M. Management of hepatocellular carcinoma: An update. Hepatology 2011, 53, 1020–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llovet, J.M.; Di Bisceglie, A.M.; Bruix, J.; Kramer, B.S.; Lencioni, R.; Zhu, A.X.; Sherman, M.; Schwartz, M.; Lotze, M.; Talwalkar, J.; et al. Design and Endpoints of Clinical Trials in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. PEDIATRICS 2008, 100, 698–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlas, T.; Petroff, D.; Sasso, M.; Fan, J.G.; Mi, Y.Q.; de Lédinghen, V.; Kumar, M.; Lupsor-Platon, M.; Han, K.H.; Cardoso, A.C.; et al. Individual patient data meta-analysis of controlled attenuation parameter (CAP) technology for assessing steatosis. J. Hepatol. 2017, 66, 1022–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalasani, N.; Younossi, Z.; LaVine, J.E.; Charlton, M.; Cusi, K.; Rinella, M.; Harrison, S.A.; Brunt, E.M.; Sanyal, A.J. The diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Practice guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology 2018, 67, 328–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conde-Vancells, J.; Rodriguez-Suarez, E.; Embade, N.; Gil, D.; Matthiesen, R.; Valle, M.; Elortza, F.; Lu, S.C.; Mato, J.M.; Falcon-Perez, J.M. Characterization and Comprehensive Proteome Profiling of Exosomes Secreted by Hepatocytes. J. Proteome Res. 2008, 7, 5157–5166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Povero, D.; Yamashita, H.; Ren, W.; Subramanian, M.G.; Myers, R.P.; Eguchi, A.; Simonetto, D.A.; Goodman, Z.D.; Harrison, S.A.; Sanyal, A.J.; et al. Characterization and Proteome of Circulating Extracellular Vesicles as Potential Biomarkers for NASH. Hepatol. Commun. 2020, 4, 1263–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).