Submitted:
16 August 2023
Posted:
21 August 2023
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
Keywords:
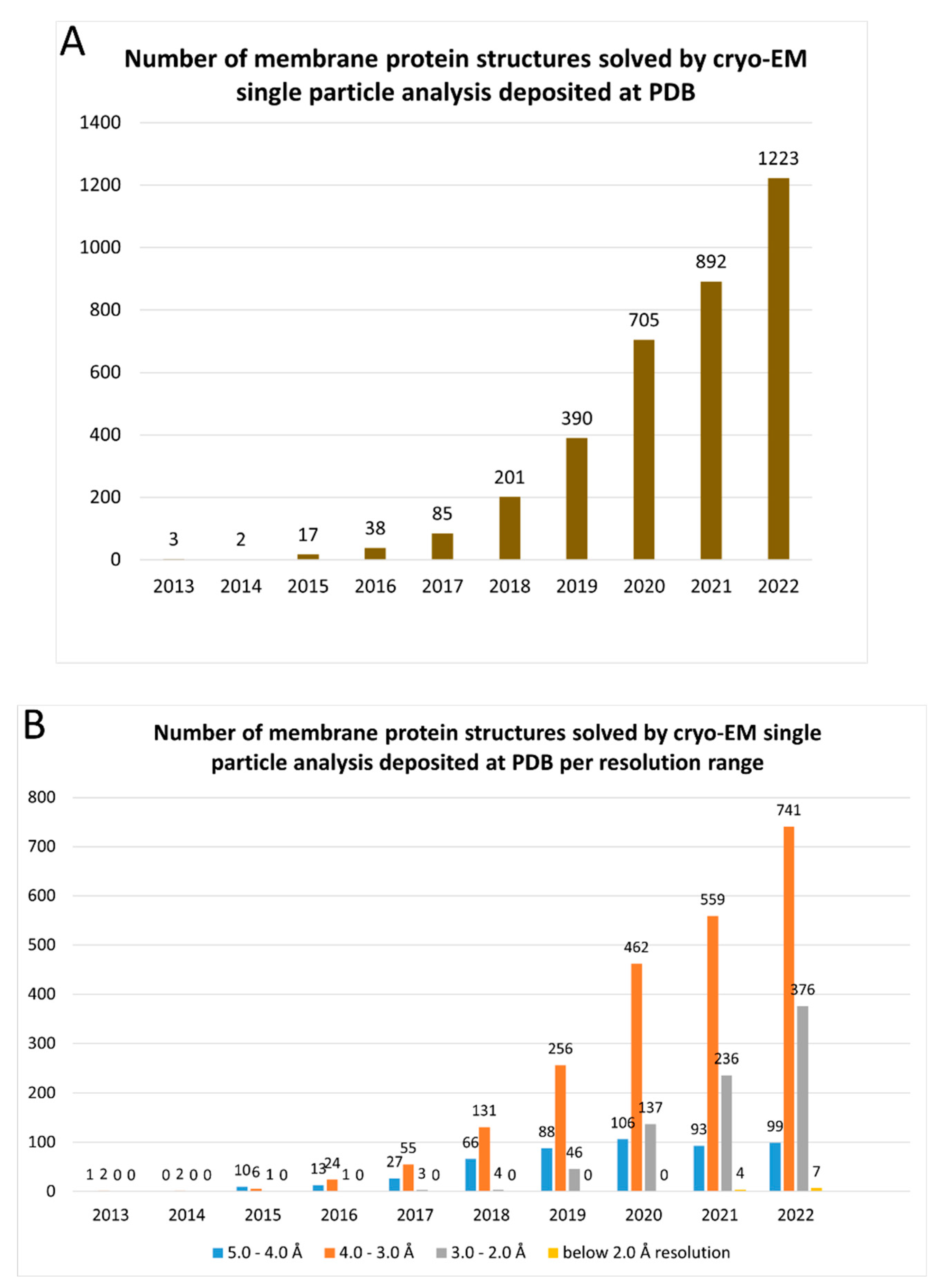
1. Introduction
2. Sample Preparation
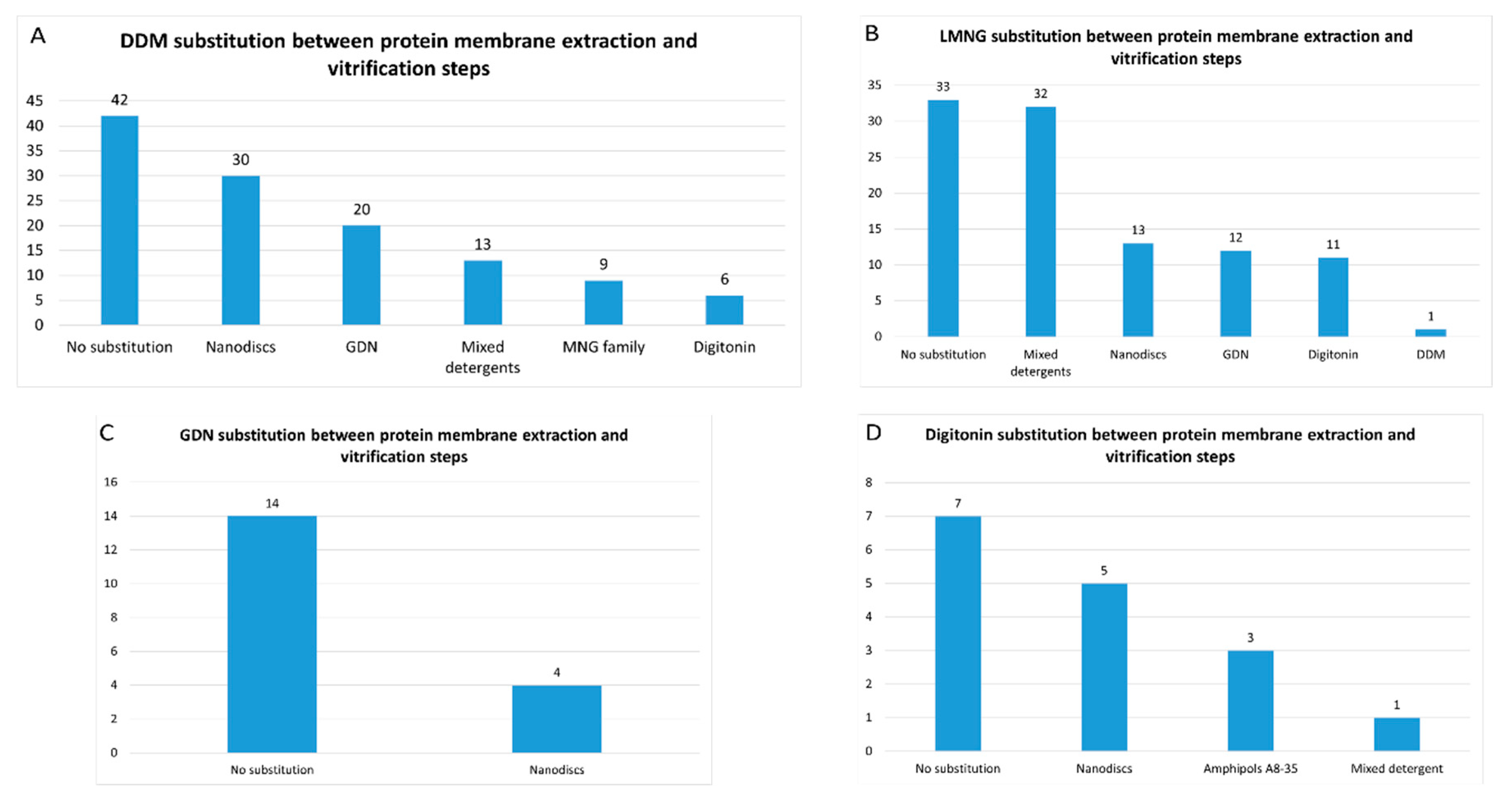
2.1. Amphiphiles Used for Membrane Protein Extraction
- 1)
- Detergents with a single maltose-based polar moiety and single alkyl chain (DDM, UDM, DM): 131 of 313 reports (41%). In this group, the most widely used detergent is DDM, which is present in 120 of 131 reports of this detergent class. DM is present in 10 of 131 reports and UDM in 1 of 131 reports;
- 2)
- Detergents belonging to the maltoside-neopentyl glycol (MNG) family (MNG, LMNG and DMNG): 107 of 313 reports (34%). In this group, the most widely used detergent is LMNG, which is present in 104 of 107 reports of this detergent class. MNG is present in 2 of 107 reports and DMNG is present in 1 of 107 reports;
- 3)
- Glyco-diosgenin (GDN): 18 of 313 reports (6%);
- 4)
- Digitonin: 16 of 313 reports (5%).
2.2. Amphiphiles and Other Molecules Used in the Vitrification Step
- 1)
- Mixed detergents: 64 of 316 reports (20%). In this group, the most widely used association of detergents was the combination of LMNG and GDN, which is present in 48 of 64 reports.
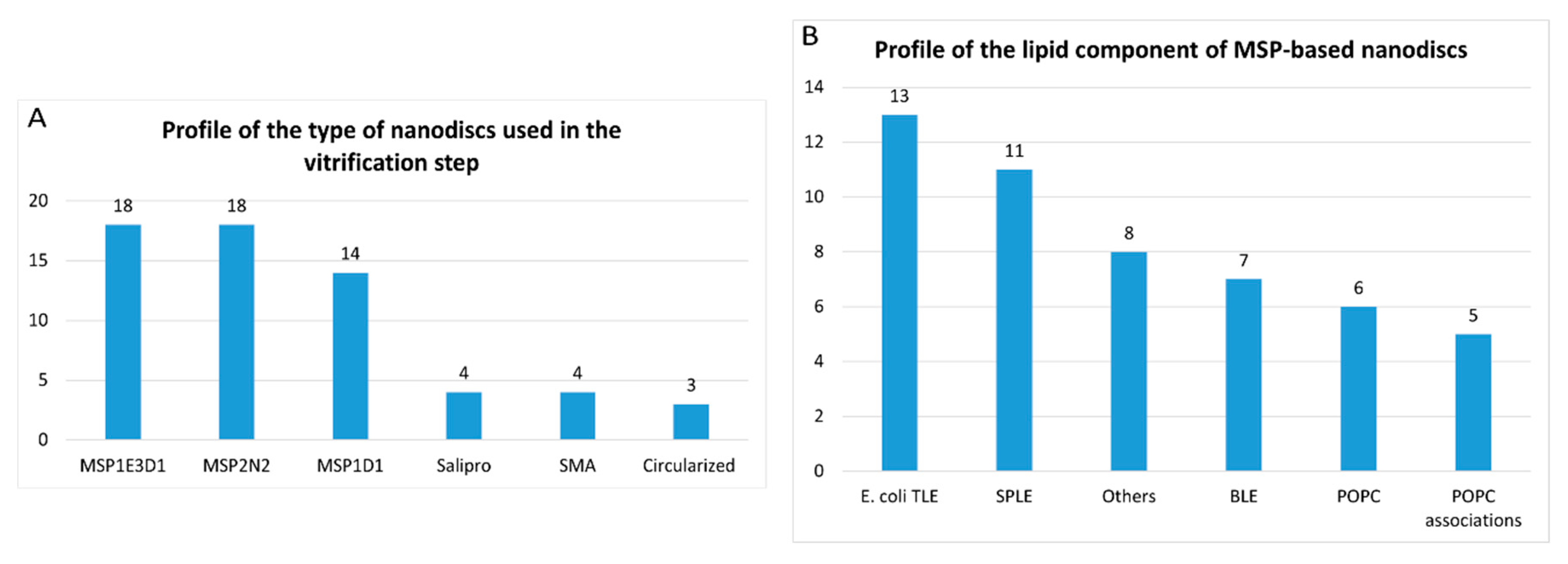
- 2)
- Nanodiscs: 61 of 316 reports (19%). In this group, the most widely used type is the membrane scaffold proteins (MSP)-based nanodiscs, which is present in 50 of 61 reports.
- 3)
- Detergents with a single maltose-based polar moiety and single alkyl chain (DDM, UDM, DM): 52 of 316 reports (16%). In this group, the most widely used detergent is DDM, which is present in 43 of the 53 reports of this detergent class. DM is responsible for the 9 remaining reports;
- 4)
- Glyco-diosgenin (GDN): 52 of 316 reports (16%).
- 5)
- Detergents belonging to the maltoside-neopentyl glycol (MNG) family (MNG and LMNG): 42 of 316 reports (13%). In this group, the most widely used detergent is LMNG, which is present in 40 of the 43 reports of this detergent class. MNG is responsible for the 3 remaining reports.
- 6)
- Digitonin: 29 of 316 reports (9%).
3. Sample Vitrification
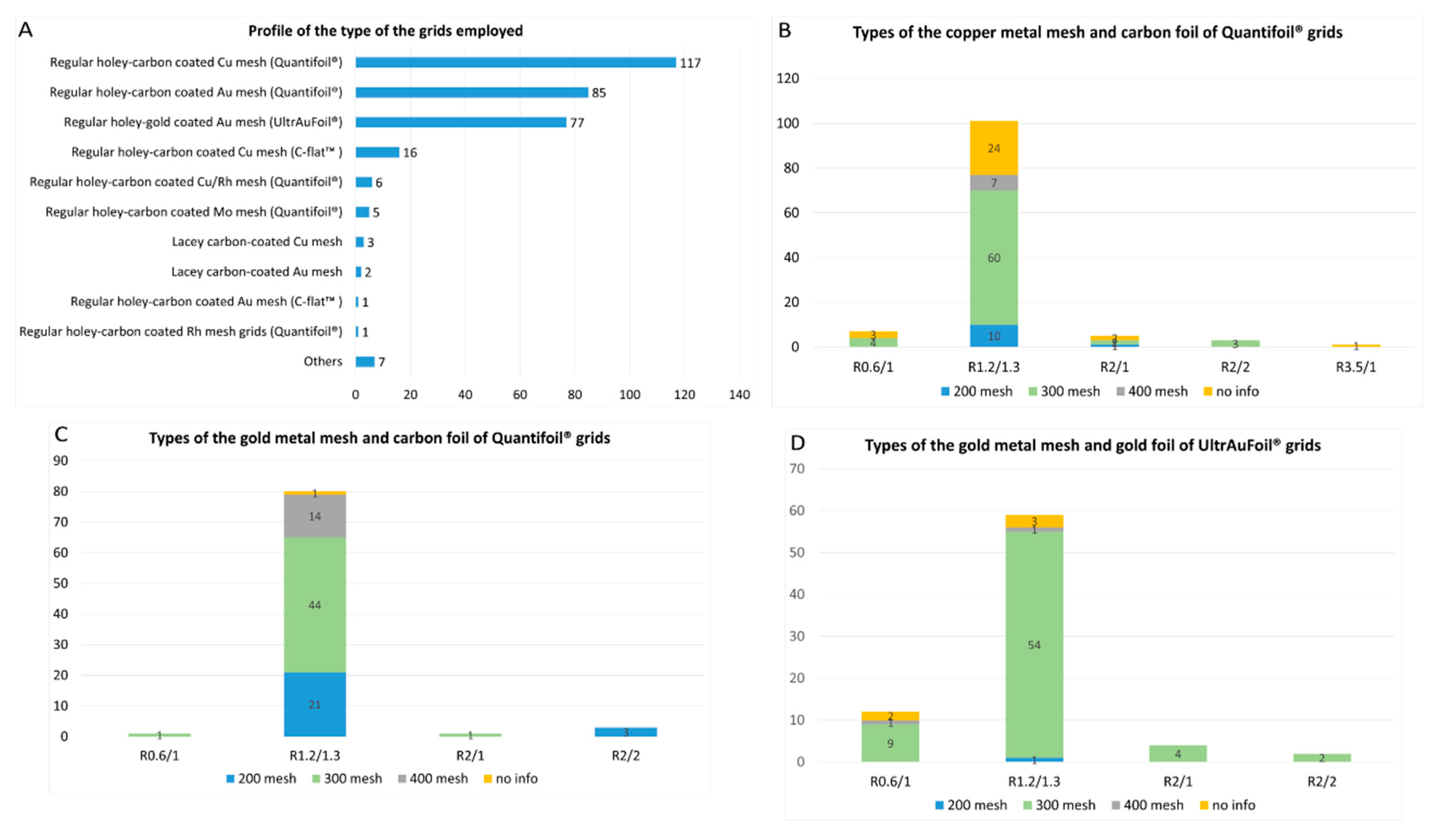
4. Type of the Grids
- 1)
- Regular holey-carbon coated copper mesh grids (Quantifoil®): 117 of 320 reports (36.5%);
- 2)
- Regular holey-carbon coated gold mesh grids (Quantifoil®): 85 of 320 reports (26.5%);
- 3)
- Regular holey-gold coated gold mesh grids (UltrAuFoil®): 77 of 320 reports (24%).
5. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ApoA1 | Apolipoprotein A1 |
| C12E9 | Nonaethylene glycol monododecyl ether |
| C12E8 | Octaethylene glycol monododecyl ether |
| CCD | Charged-coupled device |
| CHAPS | 3-[(3-cholamidopropyl)dimethylammonio]-1-propanesulfonate |
| CHS | Cholesteryl hemisuccinate |
| CMC | Critical micelle concentration |
| CMOS | Complementary metal-oxide semiconductor |
| Cryo-EM | Cryo-electron microscopy |
| Cymal-4 | 4-cyclohexyl-1-butyl-β-D-maltoside |
| Cymal-6 | 6-cyclohexyl-1-hexyl-β-D-maltoside |
| DDD | Direct detector device |
| DDM | n-Dodecyl-β-D-maltopyranoside |
| DM | Decyl-b-D-Maltopyranoside |
| DQE | Detective quantum efficiency |
| FOM | Fluorinated octyl maltoside |
| GDN | Glyco-diosgenin |
| LDAO | N,N-Dimethyl-n-dodecylamine N-oxide |
| LMNG | Lauryl Maltose Neopentyl Glycol |
| MNG | Maltose-Neopentyl Glycol |
| MP | Membrane Protein |
| MSP | Membrane Scaffold Protein |
| OGNG | Octyl glucose neopentyl glycol |
| t-PCCαM | 4-trans-(4-trans-Propylcyclohexyl)-cyclohexyl α-maltoside |
| PDB | Protein Data Bank |
| POPC | 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-glycero-3-phosphocholine (16:0-18:1PC) |
| POPE | 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine (16:0-18:1PE) |
| POPG | 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoglycerol (16:0-18:1PG) |
| Salipro | Saposin-lipid-protein complexes |
| SMA | Styrene maleic acid copolymer |
| SPA | Single-particle analysis |
| SPME | Soybean polar lipid extract |
| SNR | Signal-to-noise ratio |
| TEM | Transmission electron microscopy |
| TLE | Total lipid extract |
| UDM: | n-Undecyl-β-D-maltopyranoside |
References
- Pandey, A.; Shin, K.; Patterson, R.E.; Liu, X.-Q.; Rainey, J.K. Current Strategies for Protein Production and Purification Enabling Membrane Protein Structural Biology. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2016, 94, 507–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Chen, Y.; Pu, F.; Sun, P.; He, F.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Ma, Z.; Wang, H. Understanding Membrane Protein Drug Targets in Computational Perspective. CDT 2019, 20, 551–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arinaminpathy, Y.; Khurana, E.; Engelman, D.M.; Gerstein, M.B. Computational Analysis of Membrane Proteins: The Largest Class of Drug Targets. Drug Discovery Today 2009, 14, 1130–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vénien-Bryan, C.; Li, Z.; Vuillard, L.; Boutin, J.A. Cryo-Electron Microscopy and X-Ray Crystallography: Complementary Approaches to Structural Biology and Drug Discovery. Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun 2017, 73, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, E.P.; Beis, K.; Cameron, A.D.; Iwata, S. Overcoming the Challenges of Membrane Protein Crystallography. Current Opinion in Structural Biology 2008, 18, 581–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sgro, G.G.; Costa, T.R.D. Cryo-EM Grid Preparation of Membrane Protein Samples for Single Particle Analysis. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2018, 5, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Dang, S. Recent Technical Advances in Sample Preparation for Single-Particle Cryo-EM. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 892459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, M.; Cao, E.; Julius, D.; Cheng, Y. Structure of the TRPV1 Ion Channel Determined by Electron Cryo-Microscopy. Nature 2013, 504, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, E.; Liao, M.; Cheng, Y.; Julius, D. TRPV1 Structures in Distinct Conformations Reveal Activation Mechanisms. Nature 2013, 504, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Armache, J.-P.; Cheng, Y. Single-Particle Cryo-EM Data Acquisition by Using Direct Electron Detection Camera. Microscopy (Tokyo) 2016, 65, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissenberger, G.; Henderikx, R.J.M.; Peters, P.J. Understanding the Invisible Hands of Sample Preparation for Cryo-EM. Nat Methods 2021, 18, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Grigorieff, N.; Penczek, P.A.; Walz, T. A Primer to Single-Particle Cryo-Electron Microscopy. Cell 2015, 161, 438–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kühlbrandt, W. The Resolution Revolution. Science 2014, 343, 1443–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMullan, G.; Faruqi, A.R.; Henderson, R. Direct Electron Detectors. In Methods in Enzymology; Elsevier, 2016; Volume 579, pp. 1–17. ISBN 978-0-12-805382-9. [Google Scholar]
- Brilot, A.F.; Chen, J.Z.; Cheng, A.; Pan, J.; Harrison, S.C.; Potter, C.S.; Carragher, B.; Henderson, R.; Grigorieff, N. Beam-Induced Motion of Vitrified Specimen on Holey Carbon Film. Journal of Structural Biology 2012, 177, 630–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Mooney, P.; Zheng, S.; Booth, C.R.; Braunfeld, M.B.; Gubbens, S.; Agard, D.A.; Cheng, Y. Electron Counting and Beam-Induced Motion Correction Enable near-Atomic-Resolution Single-Particle Cryo-EM. Nat Methods 2013, 10, 584–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheres, S.H.W. RELION: Implementation of a Bayesian Approach to Cryo-EM Structure Determination. Journal of Structural Biology 2012, 180, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punjani, A.; Rubinstein, J.L.; Fleet, D.J.; Brubaker, M.A. CryoSPARC: Algorithms for Rapid Unsupervised Cryo-EM Structure Determination. Nat Methods 2017, 14, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Blanco, J.; De La Rosa-Trevín, J.M.; Marabini, R.; Del Cano, L.; Jiménez, A.; Martínez, M.; Melero, R.; Majtner, T.; Maluenda, D.; Mota, J.; et al. Using Scipion for Stream Image Processing at Cryo-EM Facilities. Journal of Structural Biology 2018, 204, 457–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakane, T.; Kotecha, A.; Sente, A.; McMullan, G.; Masiulis, S.; Brown, P.M.G.E.; Grigoras, I.T.; Malinauskaite, L.; Malinauskas, T.; Miehling, J.; et al. Single-Particle Cryo-EM at Atomic Resolution. Nature 2020, 587, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Franken, E.; Deng, Y.; Benlekbir, S.; Singla Lezcano, G.; Janssen, B.; Yu, L.; Ripstein, Z.A.; Tan, Y.Z.; Rubinstein, J.L. Electron-Event Representation Data Enable Efficient CryoEM File Storage with Full Preservation of Spatial and Temporal Resolution. IUCrJ 2020, 7, 860–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bon, C.; Michon, B.; Popot, J.-L.; Zoonens, M. Amphipathic Environments for Determining the Structure of Membrane Proteins by Single-Particle Electron Cryo-Microscopy. Quart. Rev. Biophys. 2021, 54, e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Wang, K.; Yan, N. The Recombinant Expression Systems for Structure Determination of Eukaryotic Membrane Proteins. Protein Cell 2014, 5, 658–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.J.; Lee, H.S.; Youn, T.; Byrne, B.; Chae, P.S. Impact of Novel Detergents on Membrane Protein Studies. Chem 2022, 8, 980–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stetsenko, A.; Guskov, A. An Overview of the Top Ten Detergents Used for Membrane Protein Crystallization. Crystals 2017, 7, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dörr, J.M.; Scheidelaar, S.; Koorengevel, M.C.; Dominguez, J.J.; Schäfer, M.; Van Walree, C.A.; Killian, J.A. The Styrene–Maleic Acid Copolymer: A Versatile Tool in Membrane Research. Eur Biophys J 2016, 45, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Ghosh, S.; Jana, S.; Robertson, N.; Tate, C.G.; Vaidehi, N. How Do Branched Detergents Stabilize GPCRs in Micelles? Biochemistry 2020, 59, 2125–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breyton, C.; Javed, W.; Vermot, A.; Arnaud, C.-A.; Hajjar, C.; Dupuy, J.; Petit-Hartlein, I.; Le Roy, A.; Martel, A.; Thépaut, M.; et al. Assemblies of Lauryl Maltose Neopentyl Glycol (LMNG) and LMNG-Solubilized Membrane Proteins. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes 2019, 1861, 939–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnani, F.; Shibata, Y.; Serrano-Vega, M.J.; Tate, C.G. Co-Evolving Stability and Conformational Homogeneity of the Human Adenosine A 2a Receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2008, 105, 10744–10749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, A.A.; Liu, J.J.; Chun, E.; Wacker, D.; Wu, H.; Cherezov, V.; Stevens, R.C. GPCR Stabilization Using the Bicelle-like Architecture of Mixed Sterol-Detergent Micelles. Methods 2011, 55, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukunaga, K.; Szabo, L.; Fales, H.M.; Pitha, J. 2-Hydroxypropyldigitonin: Synthesis and Properties of Preparations Differing in Degree of Substitution. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 1988, 77, 640–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otzen, D.E. Protein Unfolding in Detergents: Effect of Micelle Structure, Ionic Strength, PH, and Temperature. Biophysical Journal 2002, 83, 2219–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sligar, S.G.; Denisov, I.G. Nanodiscs: A Toolkit for Membrane Protein Science. Protein Science 2021, 30, 297–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayburt, T.H.; Grinkova, Y.V.; Sligar, S.G. Self-Assembly of Discoidal Phospholipid Bilayer Nanoparticles with Membrane Scaffold Proteins. Nano Lett. 2002, 2, 853–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denisov, I.G.; Grinkova, Y.V.; Lazarides, A.A.; Sligar, S.G. Directed Self-Assembly of Monodisperse Phospholipid Bilayer Nanodiscs with Controlled Size. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 3477–3487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasr, M.L.; Baptista, D.; Strauss, M.; Sun, Z.-Y.J.; Grigoriu, S.; Huser, S.; Plückthun, A.; Hagn, F.; Walz, T.; Hogle, J.M.; et al. Covalently Circularized Nanodiscs for Studying Membrane Proteins and Viral Entry. Nat Methods 2017, 14, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasr, M.L.; Wagner, G. Covalently Circularized Nanodiscs; Challenges and Applications. Current Opinion in Structural Biology 2018, 51, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoonens, M.; Popot, J.-L. Amphipols for Each Season. J Membrane Biol 2014, 247, 759–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Maire, M.; Champeil, P.; Møller, J.V. Interaction of Membrane Proteins and Lipids with Solubilizing Detergents. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Biomembranes 2000, 1508, 86–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, M.L.; Young, J.W.; Zhao, Z.; Fabre, L.; Jun, D.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Dhupar, H.S.; Wason, I.; Mills, A.T.; et al. The Peptidisc, a Simple Method for Stabilizing Membrane Proteins in Detergent-Free Solution. eLife 2018, 7, e34085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampjut, D.; Steiner, J.; Sazanov, L.A. Cryo-EM Grid Optimization for Membrane Proteins. iScience 2021, 24, 102139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaeser, R.M. Preparing Better Samples for Cryo–Electron Microscopy: Biochemical Challenges Do Not End with Isolation and Purification. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2021, 90, 451–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naydenova, K.; Russo, C.J. Measuring the Effects of Particle Orientation to Improve the Efficiency of Electron Cryomicroscopy. Nat Commun 2017, 8, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorzano, C.O.S.; Semchonok, D.; Lin, S.-C.; Lo, Y.-C.; Vilas, J.L.; Jiménez-Moreno, A.; Gragera, M.; Vacca, S.; Maluenda, D.; Martínez, M.; et al. Algorithmic Robustness to Preferred Orientations in Single Particle Analysis by CryoEM. Journal of Structural Biology 2021, 213, 107695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchański, T.; Masiulis, S.; Fischer, B.; Kalichuk, V.; López-Sánchez, U.; Zarkadas, E.; Weckener, M.; Sente, A.; Ward, P.; Wohlkönig, A.; et al. Megabodies Expand the Nanobody Toolkit for Protein Structure Determination by Single-Particle Cryo-EM. Nat Methods 2021, 18, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, M.; Han, B.-G.; Gomez, S.; Turner, J.; Fletcher, D.A.; Glaeser, R.M. Microscale Fluid Behavior during Cryo-EM Sample Blotting. Biophysical Journal 2020, 118, 708–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noble, A.J.; Wei, H.; Dandey, V.P.; Zhang, Z.; Tan, Y.Z.; Potter, C.S.; Carragher, B. Reducing Effects of Particle Adsorption to the Air–Water Interface in Cryo-EM. Nat Methods 2018, 15, 793–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razinkov, I.; Dandey, V.P.; Wei, H.; Zhang, Z.; Melnekoff, D.; Rice, W.J.; Wigge, C.; Potter, C.S.; Carragher, B. A New Method for Vitrifying Samples for CryoEM. Journal of Structural Biology 2016, 195, 190–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaledhonkar, S.; Fu, Z.; White, H.; Frank, J. Time-Resolved Cryo-Electron Microscopy Using a Microfluidic Chip. In Protein Complex Assembly; Marsh, J.A., Ed.; Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer New York: New York, NY, 2018; ISBN 978-1-4939-7758-1. [Google Scholar]
- Kontziampasis, D.; Klebl, D.P.; Iadanza, M.G.; Scarff, C.A.; Kopf, F.; Sobott, F.; Monteiro, D.C.F.; Trebbin, M.; Muench, S.P.; White, H.D. A Cryo-EM Grid Preparation Device for Time-Resolved Structural Studies. IUCrJ 2019, 6, 1024–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinstein, J.L.; Guo, H.; Ripstein, Z.A.; Haydaroglu, A.; Au, A.; Yip, C.M.; Di Trani, J.M.; Benlekbir, S.; Kwok, T. Shake-It-off: A Simple Ultrasonic Cryo-EM Specimen-Preparation Device. Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol 2019, 75, 1063–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.Z.; Rubinstein, J.L. Through-Grid Wicking Enables High-Speed CryoEM Specimen Preparation. Acta Crystallogr D Struct Biol 2020, 76, 1092–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashtiani, D.; De Marco, A.; Neild, A. Tailoring Surface Acoustic Wave Atomisation for Cryo-Electron Microscopy Sample Preparation. Lab Chip 2019, 19, 1378–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, H.D.; Thirumurugan, K.; Walker, M.L.; Trinick, J. A Second Generation Apparatus for Time-Resolved Electron Cryo-Microscopy Using Stepper Motors and Electrospray. Journal of Structural Biology 2003, 144, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravelli, R.B.G.; Nijpels, F.J.T.; Henderikx, R.J.M.; Weissenberger, G.; Thewessem, S.; Gijsbers, A.; Beulen, B.W.A.M.M.; López-Iglesias, C.; Peters, P.J. Cryo-EM Structures from Sub-Nl Volumes Using Pin-Printing and Jet Vitrification. Nat Commun 2020, 11, 2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rima, L.; Zimmermann, M.; Fränkl, A.; Clairfeuille, T.; Lauer, M.; Engel, A.; Engel, H.-A.; Braun, T. CryoWriter: A Blotting Free Cryo-EM Preparation System with a Climate Jet and Cover-Slip Injector. Faraday Discuss. 2022, 240, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darrow, M.C.; Moore, J.P.; Walker, R.J.; Doering, K.; King, R.S. Chameleon: Next Generation Sample Preparation for CryoEM Based on Spotiton. Microsc Microanal 2019, 25, 994–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandey, V.P.; Wei, H.; Zhang, Z.; Tan, Y.Z.; Acharya, P.; Eng, E.T.; Rice, W.J.; Kahn, P.A.; Potter, C.S.; Carragher, B. Spotiton: New Features and Applications. Journal of Structural Biology 2018, 202, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Dandey, V.P.; Zhang, Z.; Raczkowski, A.; Rice, W.J.; Carragher, B.; Potter, C.S. Optimizing “Self-Wicking” Nanowire Grids. Journal of Structural Biology 2018, 202, 170–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levitz, T.S.; Weckener, M.; Fong, I.; Naismith, J.H.; Drennan, C.L.; Brignole, E.J.; Clare, D.K.; Darrow, M.C. Approaches to Using the Chameleon: Robust, Automated, Fast-Plunge CryoEM Specimen Preparation. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 903148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilella, P. Étude Des Mécanismes Moléculaires Régulant l’activité Des Complexes Formés Par Le Récepteur Nucléaire ERRa; University of Strasbourg, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Russo, C.J.; Passmore, L.A. Progress towards an Optimal Specimen Support for Electron Cryomicroscopy. Current Opinion in Structural Biology 2016, 37, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, C.J.; Passmore, L.A. Ultrastable Gold Substrates for Electron Cryomicroscopy. Science 2014, 346, 1377–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, C.J.; Passmore, L.A. Ultrastable Gold Substrates: Properties of a Support for High-Resolution Electron Cryomicroscopy of Biological Specimens. Journal of Structural Biology 2016, 193, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quispe, J.; Damiano, J.; Mick, S.E.; Nackashi, D.P.; Fellmann, D.; Ajero, T.G.; Carragher, B.; Potter, C.S. An Improved Holey Carbon Film for Cryo-Electron Microscopy. Microsc Microanal 2007, 13, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.-J.; Hyun, J.-K.; Kim, J.-G.; Jeong, H.S.; Park, H.N.; You, D.-J.; Jung, H.S. Measurement of Ice Thickness on Vitreous Ice Embedded Cryo-EM Grids: Investigation of Optimizing Condition for Visualizing Macromolecules. J Anal Sci Technol 2013, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Park, J.; Lee, S.; Roh, S.-H. Grid Selection Strategy for High-Resolution Cryo-EM. Korean Soc Struct Biol 2020, 8, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naydenova, K.; Jia, P.; Russo, C.J. Cryo-EM with Sub–1 Å Specimen Movement. Science 2020, 370, 223–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naydenova, K.; Peet, M.J.; Russo, C.J. Multifunctional Graphene Supports for Electron Cryomicroscopy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2019, 116, 11718–11724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Jiang, W. Single Particle Cryo-Electron Microscopy and 3-D Reconstruction of Viruses. In Electron Microscopy; Kuo, J., Ed.; Methods in Molecular Biology; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, 2014; ISBN 978-1-62703-775-4. [Google Scholar]
- Mahler, F.; Meister, A.; Vargas, C.; Durand, G.; Keller, S. Self-Assembly of Protein-Containing Lipid-Bilayer Nanodiscs from Small-Molecule Amphiphiles. Small 2021, 17, 2103603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, D.F.; Abeyrathne, P.D.; Dukovski, D.; Walz, T. The Affinity Grid: A Pre-Fabricated EM Grid for Monolayer Purification. Journal of Molecular Biology 2008, 382, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llaguno, M.C.; Xu, H.; Shi, L.; Huang, N.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, Q.-X. Chemically Functionalized Carbon Films for Single Molecule Imaging. Journal of Structural Biology 2014, 185, 405–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.-G.; Watson, Z.; Kang, H.; Pulk, A.; Downing, K.H.; Cate, J.; Glaeser, R.M. Long Shelf-Life Streptavidin Support-Films Suitable for Electron Microscopy of Biological Macromolecules. Journal of Structural Biology 2016, 195, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyerson, J.R.; Rao, P.; Kumar, J.; Chittori, S.; Banerjee, S.; Pierson, J.; Mayer, M.L.; Subramaniam, S. Self-Assembled Monolayers Improve Protein Distribution on Holey Carbon Cryo-EM Supports. Sci Rep 2014, 4, 7084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Shigematsu, H.; Shimizu, T.; Ohto, U. Improving Particle Quality in Cryo-EM Analysis Using a PEGylation Method. Structure 2021, 29, 1192–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).



