Submitted:
25 August 2023
Posted:
25 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
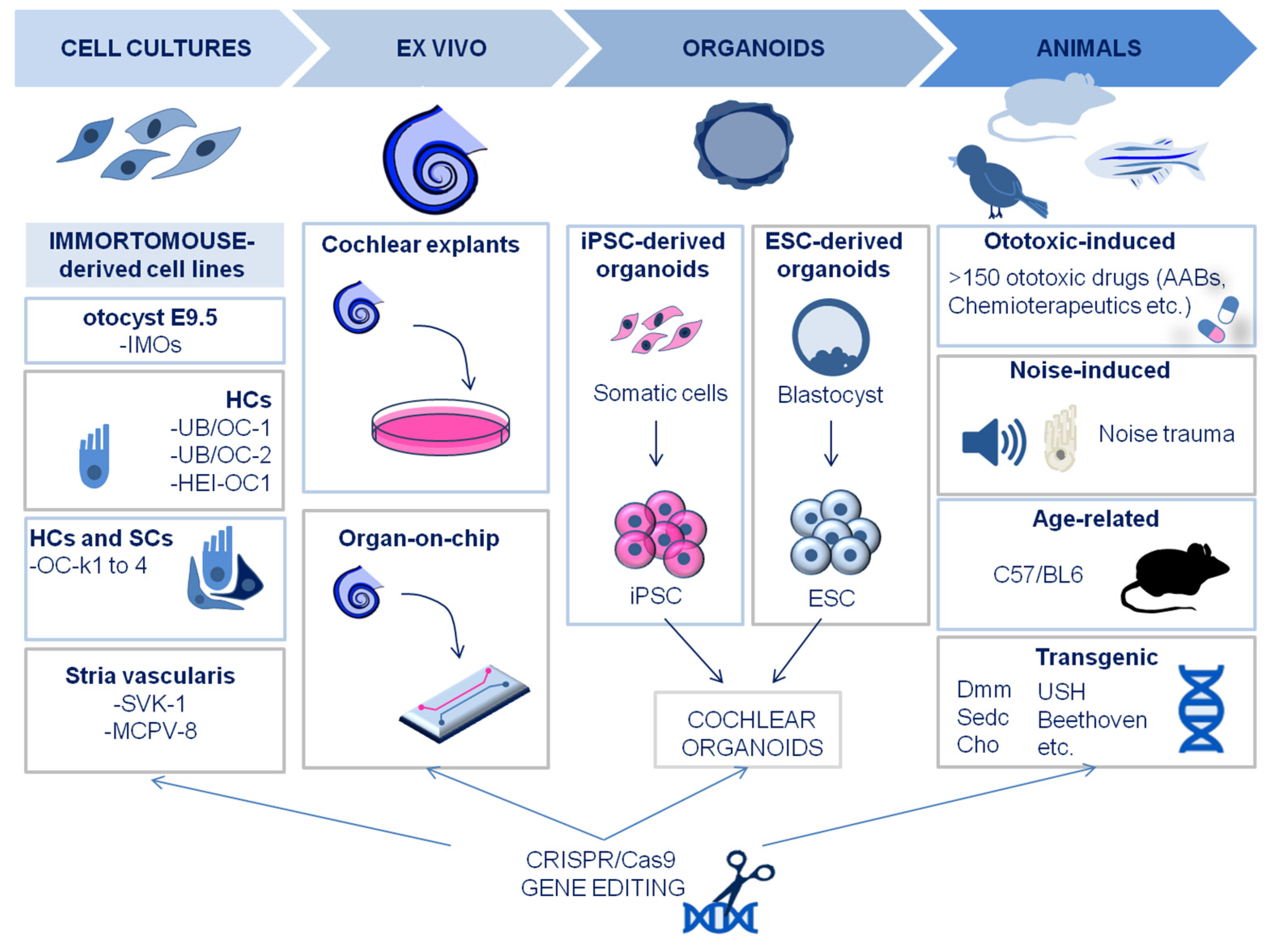
2. Experimental models in inner ear research
2.1. In vitro and ex vivo models: cochlear cell lines, organotypic cultures and organoids
2.2. In vivo models
2.3. New models created by CRISPR/Cas9 technology
3. Omics techniques
3.1. Introduction to omics: principles and advancements
3.2. Principles of single cell omics
3.3. Spatial omics
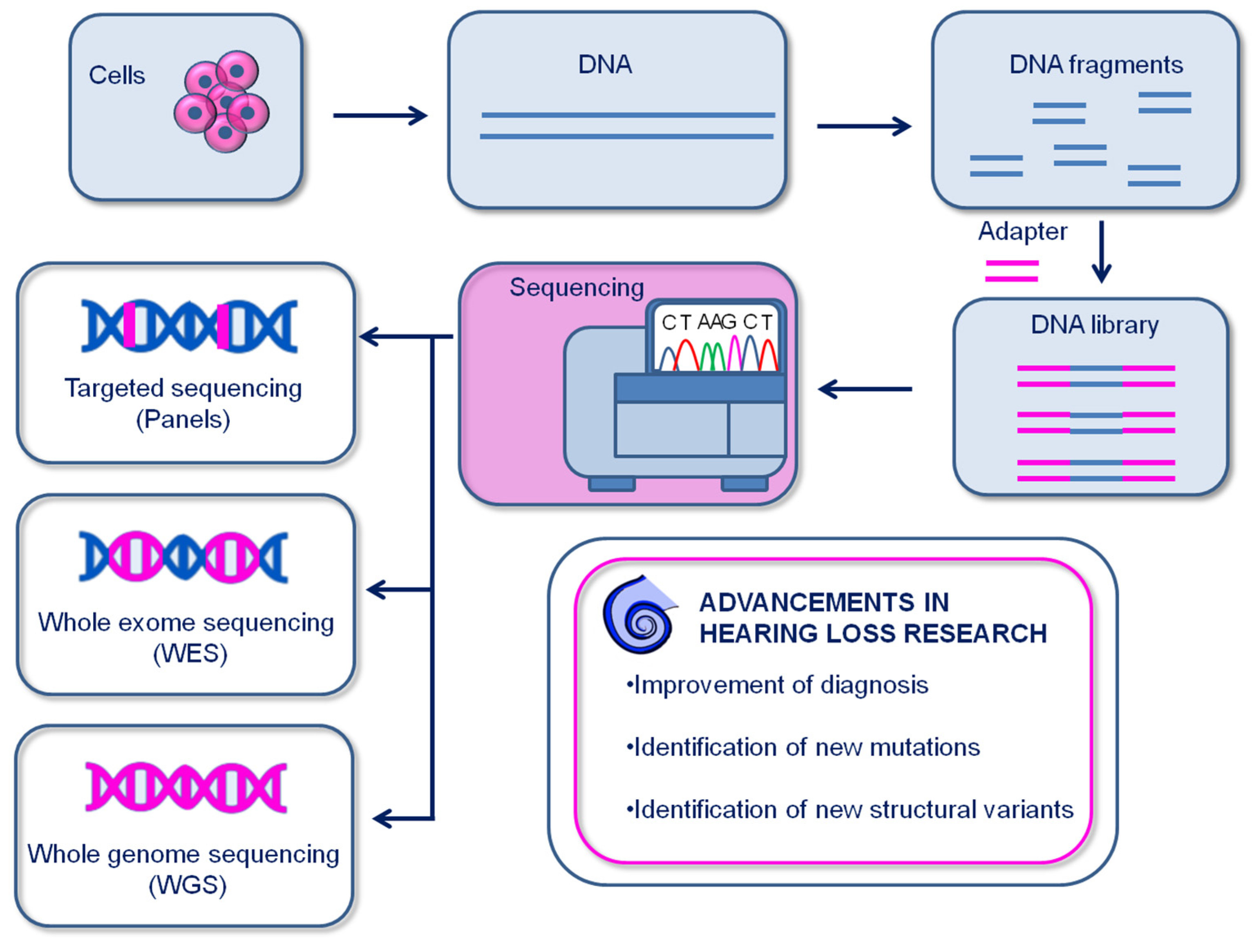
4. Genomics
4.1. Principles of sequencing
4.2. Single cell and spatial genomics
4.3. Genomic studies have delivered unprecedented knowledge on the genetic background and early diagnosis of inherited hearing loss
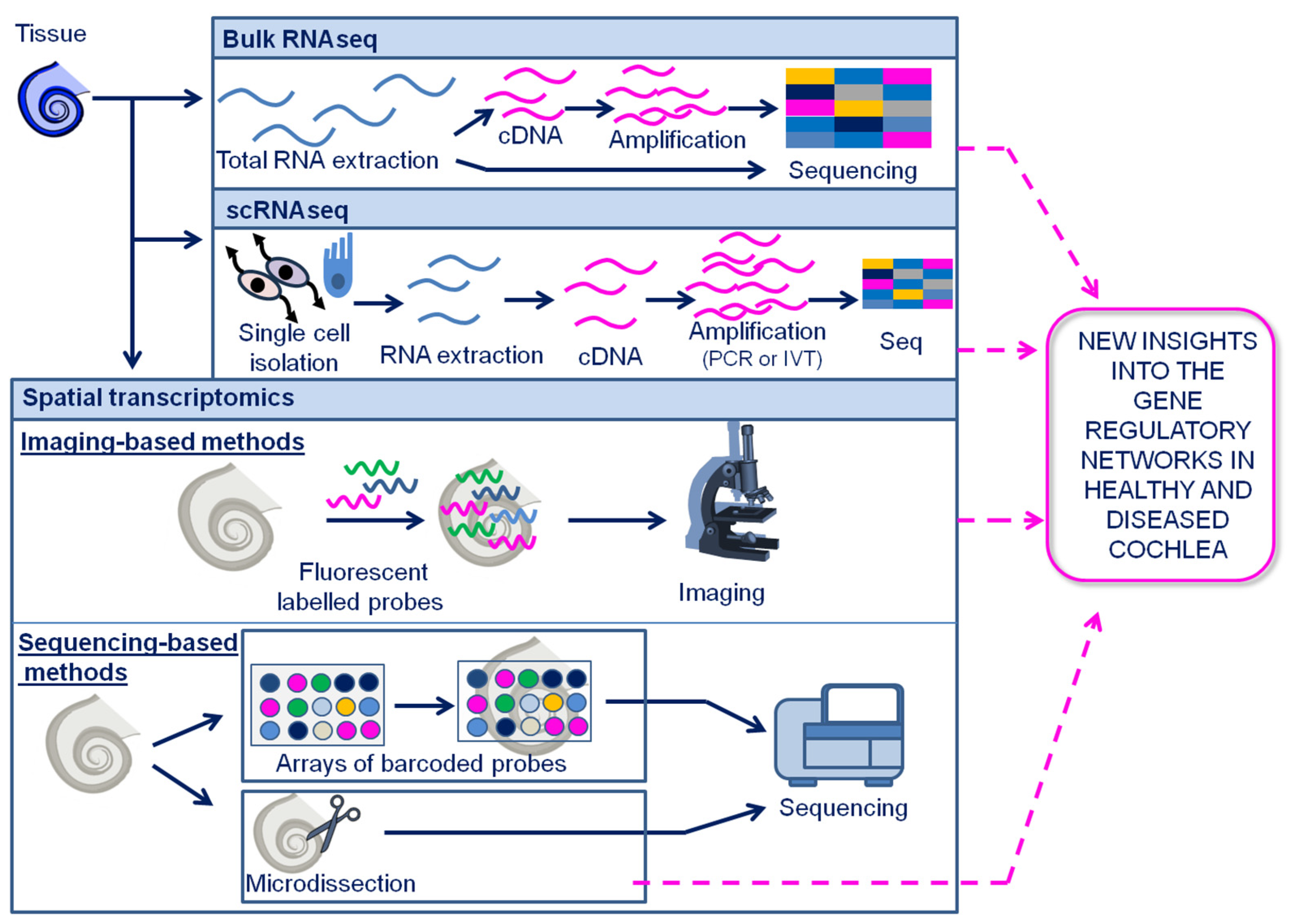
5. Transcriptomics
5.1. Single cell transcriptomics
5.2. Spatial transcriptomics
5.3. scRNAseq is a key tool for deciphering the complex cellular heterogeneity of the cochlea
5.4. Spatial transcriptomics have enabled to understand the cellular and molecular architecture of the cochlea
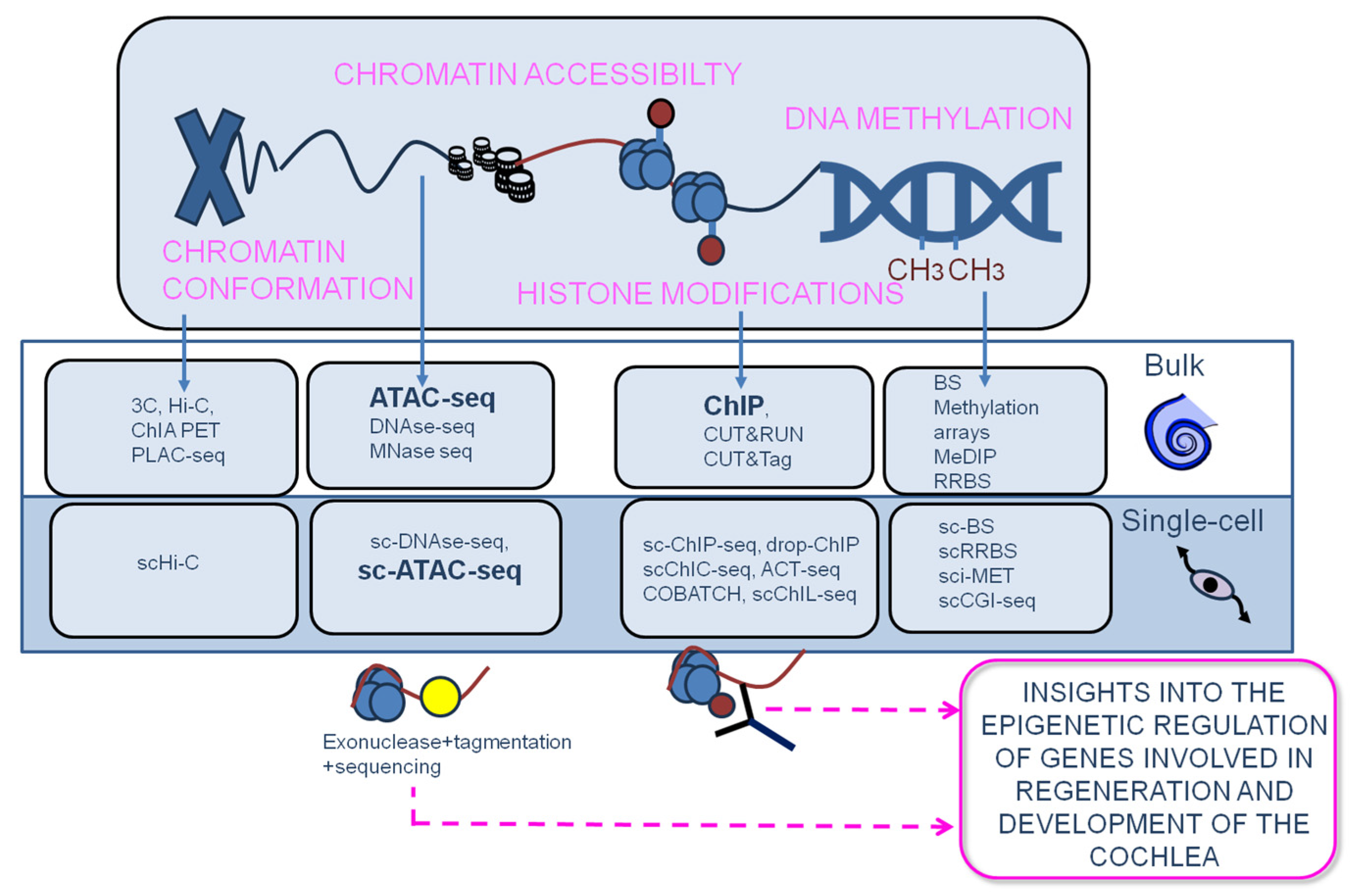
6. Epigenomics
6.1. Principles of epigenomics
6.2. Single-cell epigenomics
6.3. Spatial epigenomics
6.4. Epigenetic profiling of the cochlea has provided new insights into the mechanisms whereby genes responsible for auditory function are regulated
7. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Deafness and Hearing Loss Available online:. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/deafness-and-hearing-loss (accessed on 23 August 2023).
- Ma, Y.; Wise, A.K.; Shepherd, R.K.; Richardson, R.T. New Molecular Therapies for the Treatment of Hearing Loss. Pharmacol Ther 2019, 200, 190–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberman, M.C.; Kujawa, S.G. Cochlear Synaptopathy in Acquired Sensorineural Hearing Loss: Manifestations and Mechanisms. Hear Res 2017, 349, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wise, A.K.; Pujol, R.; Landry, T.G.; Fallon, J.B.; Shepherd, R.K. Structural and Ultrastructural Changes to Type I Spiral Ganglion Neurons and Schwann Cells in the Deafened Guinea Pig Cochlea. JARO: Journal of the Association for Research in Otolaryngology 2017, 18, 751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith-Cortinez, N.; Tan, A.K.; Stokroos, R.J.; Versnel, H.; Straatman, L. V. Regeneration of Hair Cells from Endogenous Otic Progenitors in the Adult Mammalian Cochlea: Understanding Its Origins and Future Directions. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2023, Vol. 24, Page 7840 2023, 24, 7840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos-Cortez, R.L.P.; Yarza, T.K.L.; Bootpetch, T.C.; Tantoco, M.L.C.; Mohlke, K.L.; Cruz, T.L.G.; Perez, M.E.C.; Chan, A.L.; Lee, N.R.; Tobias-Grasso, C.A.M.; et al. Identification of Novel Candidate Genes and Variants for Hearing Loss and Temporal Bone Anomalies. Genes (Basel) 2021, 12, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelley, M.W. Cochlear Development; New Tools and Approaches. Front Cell Dev Biol 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Xia, M.; Li, W.; Li, H. Single-Cell Sequencing Applications in the Inner Ear. Front Cell Dev Biol 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bommakanti, K.; Iyer, J.S.; Stankovic, K.M. Cochlear Histopathology in Human Genetic Hearing Loss: State of the Science and Future Prospects. Hear Res 2019, 382, 107785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamakami, I.; Ito, S.; Higuchi, Y. Retrosigmoid Removal of Small Acoustic Neuroma: Curative Tumor Removal with Preservation of Function: Clinical Article. J Neurosurg 2014, 121, 554–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicoli, T.K.; Atula, T.; Sinkkonen, S.T.; Korpi, J.; Vnencak, M.; Tarkkanen, J.; Mäkitie, A.A.; Jero, J. Ear Canal and Middle-Ear Tumors: A Single-Institution Series of 87 Patients. 2022, 142, 132–139. [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.S.; Xia, A.; Applegate, B.E.; Shelton, R.L.; Yuan, T.; Raphael, P.D.; Oghalai, J.S. Quantitative Imaging of Cochlear Soft Tissues in Wild-Type and Hearing-Impaired Transgenic Mice by Spectral Domain Optical Coherence Tomography. Optics Express, Vol. 19, Issue 16, pp. 15415-15428 2011, 19, 15415–15428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivolta, M.N.; Holley, M.C. Cell Lines in Inner Ear Research. J Neurobiol 2002, 53, 306–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, D.J.; Moon, S.K. Establishment of Cell Lines from the Human Middle and Inner Ear Epithelial Cells. Adv Exp Med Biol 2011, 720, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haque, K.D.; Pandey, A.K.; Kelley, M.W.; Puligilla, C. Culture of Embryonic Mouse Cochlear Explants and Gene Transfer by Electroporation. JoVE (Journal of Visualized Experiments) 2015, e52260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzarda, F.; D’Elia, A.; Massari, R.; De Ninno, A.; Bertani, F.R.; Businaro, L.; Ziraldo, G.; Zorzi, V.; Nardin, C.; Peres, C.; et al. Organ-on-Chip Model Shows That ATP Release through Connexin Hemichannels Drives Spontaneous Ca2+ Signaling in Non-Sensory Cells of the Greater Epithelial Ridge in the Developing Cochlea. Lab Chip 2020, 20, 3011–3023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roccio, M.; Edge, A.S.B. Inner Ear Organoids: New Tools to Understand Neurosensory Cell Development, Degeneration and Regeneration. Development (Cambridge) 2019, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Luo, J.; Tan, J.; Yang, L.; Wang, M.; Li, P. Experimental Animal Models of Drug-Induced Sensorineural Hearing Loss: A Narrative Review. Ann Transl Med 2021, 9, 1393–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legan, P.K.; Rau, A.; Keen, J.N.; Richardson, G.P. The Mouse Tectorins. Modular Matrix Proteins of the Inner Ear Homologous to Components of the Sperm-Egg Adhesion System. J Biol Chem 1997, 272, 8791–8801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoeven, K.; Van Laer, L.; Kirschhofer, K.; Legan, P.K.; Hughes, D.C.; Schatteman, I.; Verstreken, M.; Van Hauwe, P.; Coucke, P.; Chen, A.; et al. Mutations in the Human Alpha-Tectorin Gene Cause Autosomal Dominant Non-Syndromic Hearing Impairment. Nat Genet 1998, 19, 60–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vreugde, S.; Erven, A.; Kros, C.J.; Marcotti, W.; Fuchs, H.; Kurima, K.; Wilcox, E.R.; Friedman, T.B.; Griffith, A.J.; Bailing, R.; et al. Beethoven, a Mouse Model for Dominant, Progressive Hearing Loss DFNA36. Nature Genetics 2002 30:3 2002, 30, 257–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, L.M.; Dror, A.A.; Avraham, K.B. Mouse Models to Study Inner Ear Development and Hereditary Hearing Loss. Int J Dev Biol 2007, 51, 609–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Prell, C.G.; Hammill, T.L.; Murphy, W.J. Noise-Induced Hearing Loss: Translating Risk from Animal Models to Real-World Environments. J Acoust Soc Am 2019, 146, 3646–3651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, F.A.; Hsu, P.D.; Wright, J.; Agarwala, V.; Scott, D.A.; Zhang, F. Genome Engineering Using the CRISPR-Cas9 System. Nature Protocols 2013 8:11 2013, 8, 2281–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Yang, Y.; Qi, H.; Cui, W.; Zhang, L.; Fu, X.; He, X.; Liu, M.; Li, P. feng; Yu, T. CRISPR/Cas9 Therapeutics: Progress and Prospects. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy 2023 8:1 2023, 8, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akram, F.; Sahreen, S.; Aamir, F.; Haq, I. ul; Malik, K.; Imtiaz, M.; Naseem, W.; Nasir, N.; Waheed, H.M. An Insight into Modern Targeted Genome-Editing Technologies with a Special Focus on CRISPR/Cas9 and Its Applications. Mol Biotechnol 2023, 65, 227–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, B.; Mittal, R.; Grati, M.; Lu, Z.; Shu, Y.; Tao, Y.; Feng, Y.; Xie, D.; Kong, W.; Yang, S.; et al. The Application of Genome Editing in Studying Hearing Loss. Hear Res 2015, 327, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Tao, Y.; Lamas, V.; Huang, M.; Yeh, W.H.; Pan, B.; Hu, Y.J.; Hu, J.H.; Thompson, D.B.; Shu, Y.; et al. Treatment of Autosomal Dominant Hearing Loss by in Vivo Delivery of Genome Editing Agents. Nature 2018 553:7687 2017, 553, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farooq, R.; Hussain, K.; Tariq, M.; Farooq, A.; Mustafa, M. CRISPR/Cas9: Targeted Genome Editing for the Treatment of Hereditary Hearing Loss. Journal of Applied Genetics 2020 61:1 2020, 61, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Tao, Y.; Deng, D.; Meng, Z.; Zhao, Y. The Applications of CRISPR/Cas-Mediated Genome Editing in Genetic Hearing Loss. Cell & Bioscience 2023 13:1 2023, 13, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathinam, R.; Rosati, R.; Jamesdaniel, S. CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated Knockout of Lim-Domain Only Four Retards Organ of Corti Cell Growth. J Cell Biochem 2018, 119, 3545–3553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Wang, D.; Xu, Z.; Wang, J.; Guo, L.; Chai, R.; Li, G.; Shu, Y.; Li, H. Prevention of Acquired Sensorineural Hearing Loss in Mice by in Vivo Htra2 Gene Editing. Genome Biol 2021, 22, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Duan, X.; Li, M.; Liu, D.; Bai, X. CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated Pou4f3 Knockout Induces Defects in the Development of the Zebrafish Inner Ear. J BioX Res 2021, 4, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Shen, L. Advances and Trends in Omics Technology Development. Front Med (Lausanne) 2022, 9, 911861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, S.; Li, R.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Ou, Q.; Gao, P.; Li, K.; Zhang, Y. Single-Cell Omics: A New Direction for Functional Genetic Research in Human Diseases and Animal Models. Front Genet 2023, 13, 1100016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bingham, G.C.; Lee, F.; Naba, A.; Barker, T.H. Spatial-Omics: Novel Approaches to Probe Cell Heterogeneity and Extracellular Matrix Biology. Matrix Biology 2020, 91–92, 152–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Q.Y.; Rozanas, C.R.; Thalmann, I.; Chance, M.R.; Alagramam, K.N. Inner Ear Proteomics of Mouse Models for Deafness, a Discovery Strategy. Brain Res 2006, 1091, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navin, N.; Kendall, J.; Troge, J.; Andrews, P.; Rodgers, L.; McIndoo, J.; Cook, K.; Stepansky, A.; Levy, D.; Esposito, D.; et al. Tumour Evolution Inferred by Single-Cell Sequencing. Nature 2011, 472, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollen, A.A.; Nowakowski, T.J.; Shuga, J.; Wang, X.; Leyrat, A.A.; Lui, J.H.; Li, N.; Szpankowski, L.; Fowler, B.; Chen, P.; et al. Low-Coverage Single-Cell MRNA Sequencing Reveals Cellular Heterogeneity and Activated Signaling Pathways in Developing Cerebral Cortex. Nat Biotechnol 2014, 32, 1053–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ealy, M.; Ellwanger, D.C.; Kosaric, N.; Stapper, A.P.; Heller, S. Single-Cell Analysis Delineates a Trajectory toward the Human Early Otic Lineage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2016, 113, 8508–8513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasic, B. Single Cell Transcriptomics in Neuroscience: Cell Classification and Beyond. Curr Opin Neurobiol 2018, 50, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macaulay, I.C.; Ponting, C.P.; Voet, T. Single-Cell Multiomics: Multiple Measurements from Single Cells. Trends in Genetics 2017, 33, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, B.; Lee, J.H.; Bang, D. Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Technologies and Bioinformatics Pipelines. Experimental & Molecular Medicine 2018 50:8 2018, 50, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wang, J.; Wu, L.; Guo, J.; Song, Y.; Tian, T.; Wang, W.; Zhu, Z.; Yang, C. Microfluidic Single-Cell Omics Analysis. Small 2020, 16, 1903905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menze, L.; Duarte, P.A.; Haddon, L.; Chu, M.; Chen, J. Selective Single-Cell Sorting Using a Multisectorial Electroactive Nanowell Platform. ACS Nano 2022, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Navin, N.E. Advances and Applications of Single-Cell Sequencing Technologies. Mol Cell 2015, 58, 598–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mincarelli, L.; Lister, A.; Lipscombe, J.; Macaulay, I.C. Defining Cell Identity with Single-Cell Omics. Proteomics 2018, 18, 1700312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Y.; Guo, H.; Cao, C.; Li, X.; Hu, B.; Zhu, P.; Wu, X.; Wen, L.; Tang, F.; Huang, Y.; et al. Single-Cell Triple Omics Sequencing Reveals Genetic, Epigenetic, and Transcriptomic Heterogeneity in Hepatocellular Carcinomas. Cell Research 2016 26:3 2016, 26, 304–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raphael, Y.; Altschuler, R.A. Structure and Innervation of the Cochlea. Brain Res Bull 2003, 60, 397–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehman, A.U.; Morell, R.J.; Belyantseva, I.A.; Khan, S.Y.; Boger, E.T.; Shahzad, M.; Ahmed, Z.M.; Riazuddin, S.; Khan, S.N.; Riazuddin, S.; et al. Targeted Capture and Next-Generation Sequencing Identifies C9orf75, Encoding Taperin, as the Mutated Gene in Nonsyndromic Deafness DFNB79. Am J Hum Genet 2010, 86, 378–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Tekin, M.; Blanton, S.H.; Liu, X.Z. Next-Generation Sequencing in Genetic Hearing Loss. 2013, 17, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shearer, A.E.; Smith, R.J.H. Massively Parallel Sequencing for Genetic Diagnosis of Hearing Loss. Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery 2015, 153, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, P.; Albury, C.L.; Maksemous, N.; Benton, M.C.; Sutherland, H.G.; Smith, R.A.; Haupt, L.M.; Griffiths, L.R. Next Generation Sequencing Methods for Diagnosis of Epilepsy Syndromes. Front Genet 2018, 9, 314696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, M.; Santani, A.; Mao, R.; Ferreira-Gonzalez, A.; Weck, K.E.; Voelkerding, K. V. Development and Validation of Clinical Whole-Exome and Whole-Genome Sequencing for Detection of Germline Variants in Inherited Disease. Arch Pathol Lab Med 2017, 141, 798–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ascari, G.; Rendtorff, N.D.; De Bruyne, M.; De Zaeytijd, J.; Van Lint, M.; Bauwens, M.; Van Heetvelde, M.; Arno, G.; Jacob, J.; Creytens, D.; et al. Long-Read Sequencing to Unravel Complex Structural Variants of CEP78 Leading to Cone-Rod Dystrophy and Hearing Loss. Front Cell Dev Biol 2021, 9, 664317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanger, F.; Nicklen, S.; Coulson, A.R. DNA Sequencing with Chain-Terminating Inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1977, 74, 5463–5467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shendure, J.; Porreca, G.J.; Reppas, N.B.; Lin, X.; McCutcheon, J.P.; Rosenbaum, A.M.; Wang, M.D.; Zhang, K.; Mitra, R.D.; Church, G.M. Accurate Multiplex Polony Sequencing of an Evolved Bacterial Genome. Science 2005, 309, 1728–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drmanac, R.; Drmanac, S.; Chui, G.; Diaz, R.; Hou, A.; Jin, H.; Jin, P.; Kwon, S.; Lacy, S.; Moeur, B.; et al. Sequencing by Hybridization (SBH): Advantages, Achievements, and Opportunities. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 2002, 77, 75–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blazej, R.G.; Kumaresan, P.; Mathies, R.A. Microfabricated Bioprocessor for Integrated Nanoliter-Scale Sanger DNA Sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2006, 103, 7240–7245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quail, M.A.; Smith, M.; Coupland, P.; Otto, T.D.; Harris, S.R.; Connor, T.R.; Bertoni, A.; Swerdlow, H.P.; Gu, Y. A Tale of Three next Generation Sequencing Platforms: Comparison of Ion Torrent, Pacific Biosciences and Illumina MiSeq Sequencers. BMC Genomics 2012, 13, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, M.; Fiddes, I.T.; Miga, K.H.; Olsen, H.E.; Paten, B.; Akeson, M. Improved Data Analysis for the MinION Nanopore Sequencer. Nature Methods 2015 12:4 2015, 12, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evrony, G.D.; Hinch, A.G.; Luo, C. Applications of Single-Cell DNA Sequencing. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet 2021, 22, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gawad, C.; Koh, W.; Quake, S.R. Single-Cell Genome Sequencing: Current State of the Science. Nature Reviews Genetics 2016 17:3 2016, 17, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Yang, C.; Li, W.; Bai, X.; Zhou, X.; Xie, H.; Wen, L.; Tang, F. SMOOTH-Seq: Single-Cell Genome Sequencing of Human Cells on a Third-Generation Sequencing Platform. Genome Biol 2021, 22, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L. Spatially Resolved DNA Sequencing. Nature Methods 2022 19:2 2022, 19, 139–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.X.; Kun, S.; Jing, Q.; Jing, C.; Denise, Y. Non-Syndromic Hearing Loss and High-Throughput Strategies to Decipher Its Genetic Heterogeneity. J Otol 2013, 8, 6–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldè, M.; Cantarella, G.; Zanetti, D.; Pignataro, L.; Mantia, I. La; Maiolino, L.; Ferlito, S.; Mauro, P. Di; Cocuzza, S.; Lechien, J.R.; et al. Autosomal Dominant Non-Syndromic Hearing Loss (DFNA): A Comprehensive Narrative Review. Biomedicines 2023, Vol. 11, Page 1616 2023, 11, 1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koffler, T.; Ushakov, K.; Avraham, K.B. Genetics of Hearing Loss – Syndromic. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 2015, 48, 1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, X.; Nian, S.; Feng, L.; Ruan, Q.; Luo, X.; Wu, M.; Yan, Z. Identification of Novel Variants in MYO15A, OTOF, and RDX with Hearing Loss by next-Generation Sequencing. Mol Genet Genomic Med 2019, 7, e808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.; Capponi, S.; Wakeling, E.; Marchi, E.; Li, Q.; Zhao, M.; Weng, C.; Stefan, P.G.; Ahlfors, H.; Kleyner, R.; et al. Missense Variants in TAF1 and Developmental Phenotypes: Challenges of Determining Pathogenicity. Hum Mutat 2020, 41, 449–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brownstein, Z.; Gulsuner, S.; Walsh, T.; Martins, F.T.A.; Taiber, S.; Isakov, O.; Lee, M.K.; Bordeynik-Cohen, M.; Birkan, M.; Chang, W.; et al. Spectrum of Genes for Inherited Hearing Loss in the Israeli Jewish Population, Including the Novel Human Deafness Gene ATOH1. Clin Genet 2020, 98, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costales, M.; Diñeiro, M.; Cifuentes, G.A.; Capín, R.; Otero, A.; Viejo-Díaz, M.; Plasencia, A.; Núñez, F.; Gómez, J.R.; Llorente, J.L.; et al. Utilidad Clínica de La Secuenciación de Nueva Generación En El Diagnóstico Etiológico de La Hipoacusia Neurosensorial En Una Unidad de Hipoacusia Infantil. Acta Otorrinolaringol Esp 2020, 71, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Heurck, R.; Carminho-rodrigues, M.T.; Ranza, E.; Stafuzza, C.; Quteineh, L.; Gehrig, C.; Hammar, E.; Guipponi, M.; Abramowicz, M.; Senn, P.; et al. Benefits of Exome Sequencing in Children with Suspected Isolated Hearing Loss. Genes (Basel) 2021, 12, 1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tropitzsch, A.; Schade-Mann, T.; Gamerdinger, P.; Dofek, S.; Schulte, B.; Schulze, M.; Battke, F.; Fehr, S.; Biskup, S.; Heyd, A.; et al. Diagnostic Yield of Targeted Hearing Loss Gene Panel Sequencing in a Large German Cohort With a Balanced Age Distribution from a Single Diagnostic Center: An Eight-Year Study. Ear Hear 2022, 43, 1049–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Hu, L.; Yang, L.; Wang, L.; Lu, Y.; Dong, X.; Xiao, T.; Xu, Z.; Wu, B.; Zhou, W. Association Between Expanded Genomic Sequencing Combined With Hearing Screening and Detection of Hearing Loss Among Newborns in a Neonatal Intensive Care Unit. JAMA Netw Open 2022, 5, e2220986–e2220986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Z.C.; Chen, Y. Transcriptomics: Advances and Approaches. Sci China Life Sci 2013, 56, 960–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wongsurawat, T.; Jenjaroenpun, P.; Wanchai, V.; Nookaew, I. Native RNA or CDNA Sequencing for Transcriptomic Analysis: A Case Study on Saccharomyces Cerevisiae. Front Bioeng Biotechnol 2022, 10, 842299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jovic, D.; Liang, X.; Zeng, H.; Lin, L.; Xu, F.; Luo, Y.; Correspondence, Y.; Luo, D.; Jovic, L. Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Technologies and Applications: A Brief Overview. Clin Transl Med 2022, 12, e694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, T.K.; Baryawno, N. Introduction to Single-Cell RNA Sequencing. Curr Protoc Mol Biol 2018, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macosko, E.Z.; Basu, A.; Satija, R.; Nemesh, J.; Shekhar, K.; Goldman, M.; Tirosh, I.; Bialas, A.R.; Kamitaki, N.; Martersteck, E.M.; et al. Highly Parallel Genome-Wide Expression Profiling of Individual Cells Using Nanoliter Droplets. Cell 2015, 161, 1202–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilionis, R.; Nainys, J.; Veres, A.; Savova, V.; Zemmour, D.; Klein, A.M.; Mazutis, L. Single-Cell Barcoding and Sequencing Using Droplet Microfluidics. Nature Protocols 2016 12:1 2016, 12, 44–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gierahn, T.M.; Wadsworth, M.H.; Hughes, T.K.; Bryson, B.D.; Butler, A.; Satija, R.; Fortune, S.; Christopher Love, J.; Shalek, A.K. Seq-Well: Portable, Low-Cost RNA Sequencing of Single Cells at High Throughput. Nat Methods 2017, 14, 395–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grindberg, R. V.; Yee-Greenbaum, J.L.; McConnell, M.J.; Novotny, M.; O’Shaughnessy, A.L.; Lambert, G.M.; Araúzo-Bravo, M.J.; Lee, J.; Fishman, M.; Robbins, G.E.; et al. RNA-Sequencing from Single Nuclei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2013, 110, 19802–19807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slyper, M.; Porter, C.B.M.; Ashenberg, O.; Waldman, J.; Drokhlyansky, E.; Wakiro, I.; Smillie, C.; Smith-Rosario, G.; Wu, J.; Dionne, D.; et al. A Single-Cell and Single-Nucleus RNA-Seq Toolbox for Fresh and Frozen Human Tumors. Nature Medicine 2020 26:5 2020, 26, 792–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fangma, Y.; Liu, M.; Liao, J.; Chen, Z.; Zheng, Y. Dissecting the Brain with Spatially Resolved Multi-Omics. J Pharm Anal 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, A.C.; Chiang, Z.D.; Reginato, P.L.; Mangiameli, S.M.; Murray, E.M.; Yao, C.C.; Markoulaki, S.; Earl, A.S.; Labade, A.S.; Jaenisch, R.; et al. In Situ Genome Sequencing Resolves DNA Sequence and Structure in Intact Biological Samples. Science (1979) 2021, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, C.G.; Lee, H.J.; Asatsuma, T.; Vento-Tormo, R.; Haque, A. An Introduction to Spatial Transcriptomics for Biomedical Research. Genome Med 2022, 14, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lubeck, E.; Coskun, A.F.; Zhiyentayev, T.; Ahmad, M.; Cai, L. Single-Cell in Situ RNA Profiling by Sequential Hybridization. Nature Methods 2014 11:4 2014, 11, 360–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.H.; Boettiger, A.N.; Moffitt, J.R.; Wang, S.; Zhuang, X. Spatially Resolved, Highly Multiplexed RNA Profiling in Single Cells. Science (1979) 2015, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borm, L.E.; Mossi Albiach, A.; Mannens, C.C.A.; Janusauskas, J.; Özgün, C.; Fernández-García, D.; Hodge, R.; Castillo, F.; Hedin, C.R.H.; Villablanca, E.J.; et al. Scalable in Situ Single-Cell Profiling by Electrophoretic Capture of MRNA Using EEL FISH. Nature Biotechnology 2022 41:2 2022, 41, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Eddison, M.; Fleishman, G.; Weigert, M.; Xu, S.; Wang, T.; Rokicki, K.; Goina, C.; Henry, F.E.; Lemire, A.L.; et al. EASI-FISH for Thick Tissue Defines Lateral Hypothalamus Spatio-Molecular Organization. Cell 2021, 184, 6361–6377.e24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, R.; Mignardi, M.; Pacureanu, A.; Svedlund, J.; Botling, J.; Wählby, C.; Nilsson, M. In Situ Sequencing for RNA Analysis in Preserved Tissue and Cells. Nat Methods 2013, 10, 857–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishio, S. ya; Takumi, Y.; Usami, S. ichi Laser-Capture Micro Dissection Combined with next-Generation Sequencing Analysis of Cell Type-Specific Deafness Gene Expression in the Mouse Cochlea. Hear Res 2017, 348, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruse, F.; Junker, J.P.; van Oudenaarden, A.; Bakkers, J. Tomo-Seq: A Method to Obtain Genome-Wide Expression Data with Spatial Resolution. Methods Cell Biol 2016, 135, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Suo, S.; Tam, P.P.; Han, J.D.J.; Peng, G.; Jing, N. Spatial Transcriptomic Analysis of Cryosectioned Tissue Samples with Geo-Seq. Nature Protocols 2017 12:3 2017, 12, 566–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, S.; Lazcano, R.; Serrano, A.; Powell, S.; Kostousov, L.; Mehta, J.; Khan, K.; Lu, W.; Solis, L.M. Challenges and Opportunities for Immunoprofiling Using a Spatial High-Plex Technology: The NanoString GeoMx® Digital Spatial Profiler. Front Oncol 2022, 12, 890410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merritt, C.R.; Ong, G.T.; Church, S.E.; Barker, K.; Danaher, P.; Geiss, G.; Hoang, M.; Jung, J.; Liang, Y.; McKay-Fleisch, J.; et al. Multiplex Digital Spatial Profiling of Proteins and RNA in Fixed Tissue. Nature Biotechnology 2020 38:5 2020, 38, 586–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schede, H.H.; Schneider, C.G.; Stergiadou, J.; Borm, L.E.; Ranjak, A.; Yamawaki, T.M.; David, F.P.A.; Lönnerberg, P.; Tosches, M.A.; Codeluppi, S.; et al. Spatial Tissue Profiling by Imaging-Free Molecular Tomography. Nature Biotechnology 2021 39:8 2021, 39, 968–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ståhl, P.L.; Salmén, F.; Vickovic, S.; Lundmark, A.; Navarro, J.F.; Magnusson, J.; Giacomello, S.; Asp, M.; Westholm, J.O.; Huss, M.; et al. Visualization and Analysis of Gene Expression in Tissue Sections by Spatial Transcriptomics. Science (1979) 2016, 353, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maynard, K.R.; Collado-Torres, L.; Weber, L.M.; Uytingco, C.; Barry, B.K.; Williams, S.R.; Catallini, J.L.; Tran, M.N.; Besich, Z.; Tippani, M.; et al. Transcriptome-Scale Spatial Gene Expression in the Human Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex. Nat Neurosci 2021, 24, 425–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Liao, S.; Cheng, M.; Ma, K.; Wu, L.; Lai, Y.; Qiu, X.; Yang, J.; Xu, J.; Hao, S.; et al. Spatiotemporal Transcriptomic Atlas of Mouse Organogenesis Using DNA Nanoball-Patterned Arrays. Cell 2022, 185, 1777–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriques, S.G.; Stickels, R.R.; Goeva, A.; Martin, C.A.; Murray, E.; Vanderburg, C.R.; Welch, J.; Chen, L.M.; Chen, F.; Macosko, E.Z. Slide-Seq: A Scalable Technology for Measuring Genome-Wide Expression at High Spatial Resolution. Science 2019, 363, 1463–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stickels, R.R.; Murray, E.; Kumar, P.; Li, J.; Marshall, J.L.; Di Bella, D.J.; Arlotta, P.; Macosko, E.Z.; Chen, F. Highly Sensitive Spatial Transcriptomics at Near-Cellular Resolution with Slide-SeqV2. Nature Biotechnology 2020 39:3 2020, 39, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, M.; Deng, Y.; Su, G.; Enninful, A.; Guo, C.C.; Tebaldi, T.; Zhang, D.; Kim, D.; Bai, Z.; et al. High-Spatial-Resolution Multi-Omics Sequencing via Deterministic Barcoding in Tissue. Cell 2020, 183, 1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schimmang, T.; Maconochie, M. Gene Expression Profiling of the Inner Ear. J Anat 2016, 228, 255–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Gordillo, D.; Powers, T.R.; Van Velkinburgh, J.C.; Trujillo-Provencio, C.; Schilkey, F.; Serrano, E.E. RNA-Seq and Microarray Analysis of the Xenopus Inner Ear Transcriptome Discloses Orthologous OMIM® Genes for Hereditary Disorders of Hearing and Balance. BMC Res Notes 2015, 8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrauwen, I.; Hasin-Brumshtein, Y.; Corneveaux, J.J.; Ohmen, J.; White, C.; Allen, A.N.; Lusis, A.J.; Van Camp, G.; Huentelman, M.J.; Friedman, R.A. A Comprehensive Catalogue of the Coding and Non-Coding Transcripts of the Human Inner Ear. Hear Res 2016, 333, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.; Takechi, M.; Wang, X.; Furutera, T.; Nojiri, T.; Koyabu, D.; Li, J. Temporal and Regulatory Dynamics of the Inner Ear Transcriptome during Development in Mice. Scientific Reports 2022 12:1 2022, 12, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Giffen, K.P.; Chen, L.; Henderson, H.J.; Cao, T.A.; Kozeny, G.A.; Beisel, K.W.; Li, Y.; He, D.Z. Molecular and Cytological Profiling of Biological Aging of Mouse Cochlear Inner and Outer Hair Cells. Cell Rep 2022, 39, 110665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cederroth, C.R.; Park, J. sub; Basinou, V.; Weger, B.D.; Tserga, E.; Sarlus, H.; Magnusson, A.K.; Kadri, N.; Gachon, F.; Canlon, B. Circadian Regulation of Cochlear Sensitivity to Noise by Circulating Glucocorticoids. Current Biology 2019, 29, 2477–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lush, M.E.; Diaz, D.C.; Koenecke, N.; Baek, S.; Boldt, H.; St Peter, M.K.; Gaitan-Escudero, T.; Romero-Carvajal, A.; Busch-Nentwich, E.M.; Perera, A.G.; et al. Scrna-Seq Reveals Distinct Stem Cell Populations That Drive Hair Cell Regeneration after Loss of Fgf and Notch Signaling. Elife 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janesick, A.; Scheibinger, M.; Benkafadar, N.; Kirti, S.; Ellwanger, D.C.; Heller, S. Cell-Type Identity of the Avian Cochlea. Cell Rep 2021, 34, 108900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, R.; Noda, T.; Mulvaney, J.F.; Lin, V.Y.W.; Edge, A.S.B.; Dabdoub, A. Comprehensive Expression of Wnt Signaling Pathway Genes during Development and Maturation of the Mouse Cochlea. PLoS One 2016, 11, e0148339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagarde, M.M.M.; Wan, G.; Zhang, L.L.; Gigliello, A.R.; McInnis, J.J.; Zhang, Y.; Bergles, D.; Zuo, J.; Corfas, G. Spontaneous Regeneration of Cochlear Supporting Cells after Neonatal Ablation Ensures Hearing in the Adult Mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2014, 111, 16919–16924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranum, P.T.; Goodwin, A.T.; Yoshimura, H.; Kolbe, D.L.; Walls, W.D.; Koh, J.Y.; He, D.Z.Z.; Smith, R.J.H. Insights into the Biology of Hearing and Deafness Revealed by Single-Cell RNA Sequencing. Cell Rep 2019, 26, 3160–3171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, P.C.; Alex, A.L.; Nie, J.; Lee, J.; Roth, A.A.; Booth, K.T.; Koehler, K.R.; Hashino, E.; Nelson, R.F. Defective Tmprss3-Associated Hair Cell Degeneration in Inner Ear Organoids. Stem Cell Reports 2019, 13, 147–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milon, B.; Shulman, E.D.; So, K.S.; Cederroth, C.R.; Lipford, E.L.; Sperber, M.; Sellon, J.B.; Sarlus, H.; Pregernig, G.; Shuster, B.; et al. A Cell-Type-Specific Atlas of the Inner Ear Transcriptional Response to Acoustic Trauma. Cell Rep 2021, 36, 109758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.M.; Cheah, K.S.E.; Huh, S.H.; Ornitz, D.M. Sox2 and FGF20 Interact to Regulate Organ of Corti Hair Cell and Supporting Cell Development in a Spatially-Graded Manner. PLoS Genet 2019, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, G.; Eckrich, S. Quantitative Fluorescent in Situ Hybridization Reveals Differential Transcription Profile Sharpening of Endocytic Proteins in Cochlear Hair Cells Upon Maturation. Front Cell Neurosci 2021, 15, 643517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoa, M.; Olszewski, R.; Li, X.; Taukulis, I.; Gu, S.; DeTorres, A.; Lopez, I.A.; Linthicum, F.H.; Ishiyama, A.; Martin, D.; et al. Characterizing Adult Cochlear Supporting Cell Transcriptional Diversity Using Single-Cell RNA-Seq: Validation in the Adult Mouse and Translational Implications for the Adult Human Cochlea. Front Mol Neurosci 2020, 13, 491389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munnamalai, V.; Fekete, D.M. Notch-Wnt-Bmp Crosstalk Regulates Radial Patterning in the Mouse Cochlea in a Spatiotemporal Manner. Development (Cambridge) 2016, 143, 4003–4015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrmohamadi, M.; Sepehri, M.H.; Nazer, N.; Norouzi, M.R. A Comparative Overview of Epigenomic Profiling Methods. Front Cell Dev Biol 2021, 9, 714687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oakes, C.C.; La Salle, S.; Robaire, B.; Trasler, J.M. Evaluation of a Quantitative DNA Methylation Analysis Technique Using Methylation-Sensitive/Dependent Restriction Enzymes and Real-Time PCR. 2007, 1, 146–152. [CrossRef]
- Weber, M.; Davies, J.J.; Wittig, D.; Oakeley, E.J.; Haase, M.; Lam, W.L.; Schübeler, D. Chromosome-Wide and Promoter-Specific Analyses Identify Sites of Differential DNA Methylation in Normal and Transformed Human Cells. Nature Genetics 2005 37:8 2005, 37, 853–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skene, P.J.; Henikoff, S. An Efficient Targeted Nuclease Strategy for High-Resolution Mapping of DNA Binding Sites. Elife 2017, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaya-Okur, H.S.; Wu, S.J.; Codomo, C.A.; Pledger, E.S.; Bryson, T.D.; Henikoff, J.G.; Ahmad, K.; Henikoff, S. CUT&Tag for Efficient Epigenomic Profiling of Small Samples and Single Cells. Nature Communications 2019 10:1 2019, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buenrostro, J.D.; Wu, B.; Chang, H.Y.; Greenleaf, W.J. ATAC-Seq: A Method for Assaying Chromatin Accessibility Genome-Wide. Curr Protoc Mol Biol 2015, 109, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Crawford, G.E. DNase-Seq: A High-Resolution Technique for Mapping Active Gene Regulatory Elements across the Genome from Mammalian Cells. Cold Spring Harb Protoc 2010, 2010, pdb–prot5384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajoro, A.; Muiño, J.M.; Angenent, G.C.; Kaufmann, K. Profiling Nucleosome Occupancy by MNase-Seq: Experimental Protocol and Computational Analysis. Methods Mol Biol 2018, 1675, 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davie, K.; Jacobs, J.; Atkins, M.; Potier, D.; Christiaens, V.; Halder, G.; Aerts, S. Discovery of Transcription Factors and Regulatory Regions Driving In Vivo Tumor Development by ATAC-Seq and FAIRE-Seq Open Chromatin Profiling. PLoS Genet 2015, 11, e1004994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y. Modern Epigenetics Methods in Biological Research. Methods 2021, 187, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartzman, O.; Tanay, A. Single-Cell Epigenomics: Techniques and Emerging Applications. Nature Reviews Genetics 2015 16:12 2015, 16, 716–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, L.; Wu, H.J.; Zhu, H.; Kim, K.Y.; Marjani, S.L.; Riester, M.; Euskirchen, G.; Zi, X.; Yang, J.; Han, J.; et al. Bisulfite-Independent Analysis of CpG Island Methylation Enables Genome-Scale Stratification of Single Cells. Nucleic Acids Res 2017, 45, e77–e77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulqueen, R.M.; Pokholok, D.; Norberg, S.J.; Torkenczy, K.A.; Fields, A.J.; Sun, D.; Sinnamon, J.R.; Shendure, J.; Trapnell, C.; O’Roak, B.J.; et al. Highly Scalable Generation of DNA Methylation Profiles in Single Cells. Nat Biotechnol 2018, 36, 428–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, S.J.; Lee, H.J.; Smallwood, S.A.; Kelsey, G.; Reik, W. Single-Cell Epigenomics: Powerful New Methods for Understanding Gene Regulation and Cell Identity. Genome Biology 2016 17:1 2016, 17, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, J.H.; Zheng, P.; Kinrot, S.S.; Bintu, B.; Zhuang, X. Genome-Scale Imaging of the 3D Organization and Transcriptional Activity of Chromatin. Cell 2020, 182, 1641–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takei, Y.; Yun, J.; Zheng, S.; Ollikainen, N.; Pierson, N.; White, J.; Shah, S.; Thomassie, J.; Suo, S.; Eng, C.H.L.; et al. Integrated Spatial Genomics Reveals Global Architecture of Single Nuclei. Nature 2021 590:7845 2021, 590, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Bartosovic, M.; Kukanja, P.; Zhang, D.; Liu, Y.; Su, G.; Enninful, A.; Bai, Z.; Castelo-Branco, G.; Fan, R. Spatial-CUT&Tag: Spatially Resolved Chromatin Modification Profiling at the Cellular Level. Science (1979) 2022, 375, 681–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Bartosovic, M.; Ma, S.; Zhang, D.; Kukanja, P.; Xiao, Y.; Su, G.; Liu, Y.; Qin, X.; Rosoklija, G.B.; et al. Spatial Profiling of Chromatin Accessibility in Mouse and Human Tissues. Nature 2022, 609, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Ang, C.E.; Zhuang, X. Spatially Resolved Epigenomic Profiling of Single Cells in Complex Tissues. Cell 2022, 185, 4448–4464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhamidipati, T.; Sinha, M.; Sen, C.K.; Singh, K. Laser Capture Microdissection in the Spatial Analysis of Epigenetic Modifications in Skin: A Comprehensive Review. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2022, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeming, X.; Fengying, R.; Yaning, L.; Meng, L.; Chen, Z.; Zhichao, C.; Zhe, X.; Zhe, W.; Weitian, C.; Wenfang, C.; et al. Spatial Chromatin Accessibility Sequencing Resolves High-Order Spatial Interactions of Epigenomic Markers. Elife 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, C.J.; Bird, T.; Ertekin-Taner, N.; Lincoln, S.; Hjorth, R.; Wu, Y.; Kwok, J.; Mer, G.; Dyck, P.J.; Nicholson, G.A. DNMT1 Mutation Hot Spot Causes Varied Phenotypes of HSAN1 with Dementia and Hearing Loss. Neurology 2013, 80, 824–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balendran, V.; Ritter, K.E.; Martin, D.M. Epigenetic Mechanisms of Inner Ear Development. Hear Res 2022, 426, 108440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyama, R.; Tsuchida, N.; Okada, Y.; Sakata, S.; Hamada, K.; Azuma, Y.; Hamanaka, K.; Fujita, A.; Koshimizu, E.; Miyatake, S.; et al. Two Families with TET3-Related Disorder Showing Neurodevelopmental Delay with Craniofacial Dysmorphisms. J Hum Genet 2022, 67, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, M.; Streit, A. Lsd1 Interacts with CMyb to Demethylate Repressive Histone Marks and Maintain Inner Ear Progenitor Identity. Development (Cambridge) 2018, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.O.; Lee, J.J.; Kim, M.; Chung, Y.W.; Min, H.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, H.P.; Bok, J. CTCF Regulates Otic Neurogenesis via Histone Modification in the Neurog1 Locus. Moleucles and Cells 2018, 41, 695–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, L.; Yu, H. V.; Llamas, J.; Trecek, T.; Wang, X.; Stojanova, Z.; Groves, A.K.; Segil, N. Enhancer Decommissioning Imposes an Epigenetic Barrier to Sensory Hair Cell Regeneration. Dev Cell 2021, 56, 2471–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vissers, L.E.L.M.; Van Ravenswaaij, C.M.A.; Admiraal, R.; Hurst, J.A.; De Vries, B.B.A.; Janssen, I.M.; Van Der Vliet, W.A.; Huys, E.H.L.P.G.; De Jong, P.J.; Hamel, B.C.J.; et al. Mutations in a New Member of the Chromodomain Gene Family Cause CHARGE Syndrome. Nature Genetics 2004 36:9 2004, 36, 955–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawe, C.E.; Kooistra, M.K.; Fairbridge, N.A.; Pisio, A.C.; McDermid, H.E. Role of Chromatin Remodeling Gene Cecr2 in Neurulation and Inner Ear Development. Developmental Dynamics 2011, 240, 372–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, A.A.; Hosamani, I.; Nguyen, J.D.; Cai, T.; Singh, S.; McGovern, M.M.; Beyer, L.; Zhang, H.; Jen, H.I.; Yousaf, R.; et al. Cellular Reprogramming with ATOH1, GFI1, and POU4F3 Implicate Epigenetic Changes and Cell-Cell Signaling as Obstacles to Hair Cell Regeneration in Mature Mammals. Elife 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez, E.; Slevin, C.C.; Song, W.; Chen, Z.; Frederickson, S.C.; Gildea, D.; Wu, W.; Elkahloun, A.G.; Ovcharenko, I.; Burgess, S.M. A Regulatory Network of Sox and Six Transcription Factors Initiate a Cell Fate Transformation during Hearing Regeneration in Adult Zebrafish. Cell Genomics 2022, 2, 100170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Jadali, A.; Fritzsch, B.; Kwan, K.Y. NEUROG1 Regulates CDK2 to Promote Proliferation in Otic Progenitors. Stem Cell Reports 2017, 9, 1516–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Yuan, S.S.; Zhang, L.J.; Ji, Z.L.; Quan, X.J. Atonal BHLH Transcription Factor 1 Is an Important Factor for Maintaining the Balance of Cell Proliferation and Differentiation in Tumorigenesis (Review). Oncol Lett 2020, 20, 2595–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalra, G.; Lenz, D.; Abdul-Aziz, D.; Hanna, C.; Herb, B.R.; Colantuoni, C.; Milon, B.; Saxena, M.; Shetty, A.C.; Hertzano, R.P.; et al. Cochlear Organoids Reveal Epigenetic and Transcriptional Programs of Postnatal Hair Cell Differentiation from Supporting Cells. bioRxiv 2021, 2021.09.19.460948. [CrossRef]
- Webster, M.; Webster, D.B. Spiral Ganglion Neuron Loss Following Organ of Corti Loss: A Quantitative Study. Brain Res 1981, 212, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shepherd, R.K.; Hardie, N.A. Deafness-Induced Changes in the Auditory Pathway: Implications for Cochlear Implants. Audiology and Neurotology 2002, 6, 305–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Versnel, H.; Agterberg, M.J.H.; de Groot, J.C.M.J.; Smoorenburg, G.F.; Klis, S.F.L. Time Course of Cochlear Electrophysiology and Morphology after Combined Administration of Kanamycin and Furosemide. Hear Res 2007, 231, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Maheshwari, S.; Kirtane, M.; Shrivastav, N. Pictorial Review of MRI/CT Scan in Congenital Temporal Bone Anomalies, in Patients for Cochlear Implant. Indian J Radiol Imaging 2009, 19, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burwood, G.W.S.; Fridberger, A.; Wang, R.K.; Nuttall, A.L. Revealing the Morphology and Function of the Cochlea and Middle Ear with Optical Coherence Tomography. Quant Imaging Med Surg 2019, 9, 85881–85881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rask-Andersen, H.; Liu, W.; Erixon, E.; Kinnefors, A.; Pfaller, K.; Schrott-Fischer, A.; Glueckert, R. Human Cochlea: Anatomical Characteristics and Their Relevance for Cochlear Implantation. The Anatomical Record: Advances in Integrative Anatomy and Evolutionary Biology 2012, 295, 1791–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tisi, A.; Ramekers, D.; Flati, V.; Versnel, H.; Maccarone, R. MTOR Signaling in BDNF-Treated Guinea Pigs after Ototoxic Deafening. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tisi, A.; Rovers, J.; Vink, H.A.; Ramekers, D.; Maccarone, R.; Versnel, H. No Protective Effects of Hair Cells or Supporting Cells in Ototoxically Deafened Guinea Pigs upon Administration of BDNF. Brain Sci 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pujol, R.; Lavigne-rebillard, M.; Uziel, A. Development of the Human Cochlea. 2009, 111, 7–13. 13. [CrossRef]
- Jean, P.; Tai, F.W.J.; Singh-Estivalet, A.; Lelli, A.; Scandola, C.; Megharba, S.; Schmutz, S.; Roux, S.; Mechaussier, S.; Sudres, M.; et al. Single-Cell Transcriptomic Profiling of the Mouse Cochlea: An Atlas for Targeted Therapies. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2023, 120, e2221744120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldhaus, J.; Durruthy-Durruthy, R.; Heller, S. Quantitative High-Resolution Cellular Map of the Organ of Corti. Cell Rep 2015, 11, 1385–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.G.; Huang, M.; Obholzer, N.D.; Sun, S.; Li, W.; Petrillo, M.; Dai, P.; Zhou, Y.; Cotanche, D.A.; Megason, S.G.; et al. Myc and Fgf Are Required for Zebrafish Neuromast Hair Cell Regeneration. PLoS One 2016, 11, e0157768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Jin, R.; Xu, J.; Ji, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Han, Z.; Zeng, S. Hair Cell Regeneration or the Expression of Related Factors That Regulate the Fate Specification of Supporting Cells in the Cochlear Ducts of Embryonic and Posthatch Chickens. Hear Res 2016, 332, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Romero-Carvajal, A.; Haug, J.S.; Seidel, C.W.; Piotrowski, T. Gene-Expression Analysis of Hair Cell Regeneration in the Zebrafish Lateral Line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2014, 111, E1383–E1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Li, X.; Bi, Z.; Sugino, K.; Wang, G.; Zhu, T.; Liu, Z. Comprehensive Transcriptome Analysis of Cochlear Spiral Ganglion Neurons at Multiple Ages. Elife 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Gao, D.; Chen, J.; Hou, S.; He, B.; Li, Y.; Li, S.; Zhang, F.; Sun, X.; Jin, Y.; et al. Pseudo-Temporal Analysis of Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Reveals Trans-Differentiation Potential of Greater Epithelial Ridge Cells Into Hair Cells During Postnatal Development of Cochlea in Rats. Front Mol Neurosci 2022, 15, 832813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sequencing technology | Category | Principle | Reads length | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NGS | Cyclic-array sequencing (Illumina and Ion Torrent) | Repeated cycles of enzymatic catalytic reactions | Short | [57] |
| NGS | Hybridization-based sequencing | Multiple oligonucleotides are hybridized with complementary sequences of the target genome/transcriptome. | Short | [58] |
| NGS | microelectrophoretic-based | Lab-on-a-chip-level which combines all the Sanger sequencing steps together for a more efficient sequencing. | Short | [59] |
| TGS | Pacific Biosciences (PacBio) | Laser-induced fluorescence signals that are activated during the incorporation of dNTPs into DNA, alongside recording the color and duration of the signals in real time. | Long | [60] |
| TGS | Oxford Nanopore technology (ONT) | Nanopore-based technology in which sequencing is allowed by determination of current change induced by nucleotides passing through the nanopore. | Long | [61] |
| Omics Categories | Techniques | Applications in hearing research | Models utilized | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genomics | WGS, WES | Identification of novel structural variants and rare mutations in genes associated with deafness | Humans (Affected individuals with the CRDHL) | [55] |
| WES | Early detection of hearing loss for diagnostic purposes | Humans (individuals with diagnosis of hearing loss) | [73] | |
| Target exome panel | Improvement in the clinical diagnostic yield and thereby routine genetic screening | Humans (deaf patients suspected with underlying genetic causes of deafness) | [74] | |
| Humans (patients diagnosed with SNHL) | [72] | |||
| Transcriptomics | TruSeq | Identification of differential and preferential gene expression patterns and characterization of novel molecular pathways of the cochlea | Humans (patients with tumors of the skull base with normal hearing) | [107] |
| Engineered mouse models of genes related to circadian rhythm with noise damage | [110] | |||
| Comprehension of mechanisms involved in hair cell regeneration. | Ototoxic (neomycin) treated zebrafish | [169] | ||
| SMART-Seq v4 | Insights into the transcriptional changes of HCs during the process of ageing and damage | CBA/J mice 1,9, 18, 22 and 26 months-old | [109] | |
| RNA-Seq V2 | Unraveling the genes specific to SGNs and their dynamicity in developmental processes. | Mouse at different stages: E15.5, P1, P8, P14 and P30 | [170] | |
| Single-cell transcriptomics | SMART-Seq2 | Identification of novel subtypes of cochlear cells | Chicken | [112] |
| Identification of new markers of HCs | Mouse (C3HeB/FeJ) | [115] | ||
| 10x Genomics | Identification of gene regulatory networks involved in HCs regeneration. | Zebrafish (transgenic model for HCs ablation) | [152] | |
| Identification of genes associated with Tmprss3-related hearing loss | Mouse (Tmprss3-KO organoids) | [116] | ||
| Delineation of key regulatory mechanisms in HCs regeneration | Rats | [171] | ||
| Spatial transcriptomics | Single molecule FISH (smFISH) | Annotating distinct transcriptome of SCs populations in specific anatomic locations of the cochlea | Mouse | [120] |
| Whole mount ISH | Spatio-temporal cadence of key signalling pathways in the context of developmental processes of the cochlea | Mouse organotypic cultures | [121] | |
| Genetically engineered mouse models of genes related to developmental processes | [118] | |||
| Fluor | Uncovering quantitative differential transcriptional profile in pre-mature and mature HCs, revealing novel role of genes in the differentiation process | Mice (P4 and 3 weeks old) | [119] | |
| LCM-NGS | Discovery of quantitative information of transcripts relevant in deafness in the organ of Corti, spiral ganglion, lateral wall, and spiral limbus | Mice (C57BL/6J) | [93] | |
| Epigenomics | ChIP-seq and ChIP-qPCR | Epigenetic modifications in the promoters of genes involved in SGNs differentiation | In vitro immortalized multipotent otic progenitors (iMOP cells) | [153] |
| ATAC-seq | Identification of dynamics in chromatin accessibility of key transcriptional factors during the reprogramming of SCs into HCs | Mouse (Atoh1-nGFP, Sox2-GFP or Lgr5-GFP) and cochlear organoids | [155] | |
| Single-cell epigenomics | scATAC seq | Regulation of chromatin accessibility during the process of regeneration and identification of genetically conserved regenerative response elements necessary for injury/regenerative responses | Zebrafish (transgenic model for HCs ablation) | [152] |
| Identification of the epigenetic mechanisms responsible for the inability of SCs to trans-differentiation in HCs in the adult mammalian cochlea | Transgenic mouse models expressing transcription factors | [151] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





