Submitted:
04 September 2023
Posted:
06 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Quality appraisal methods
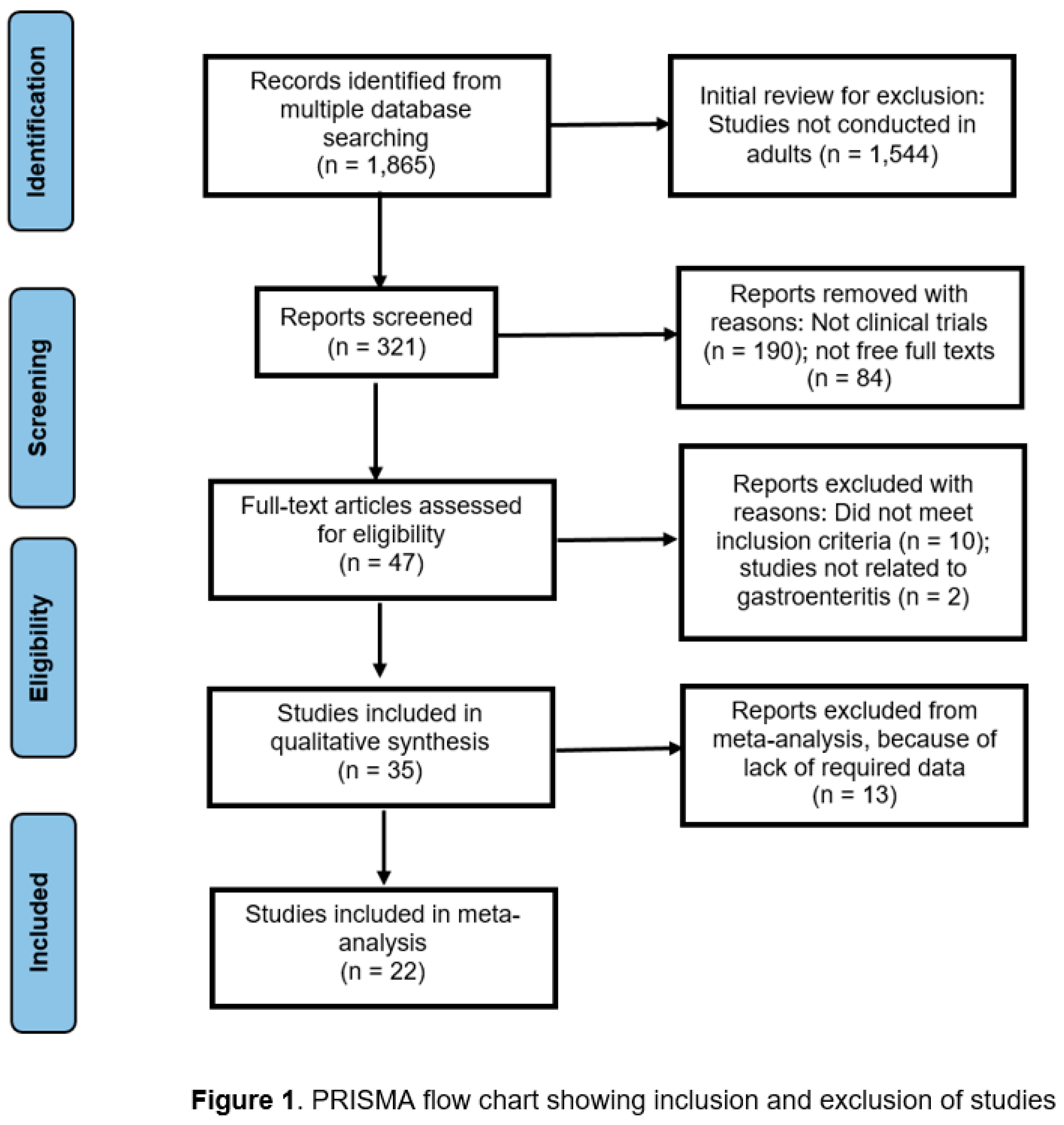
3. Results
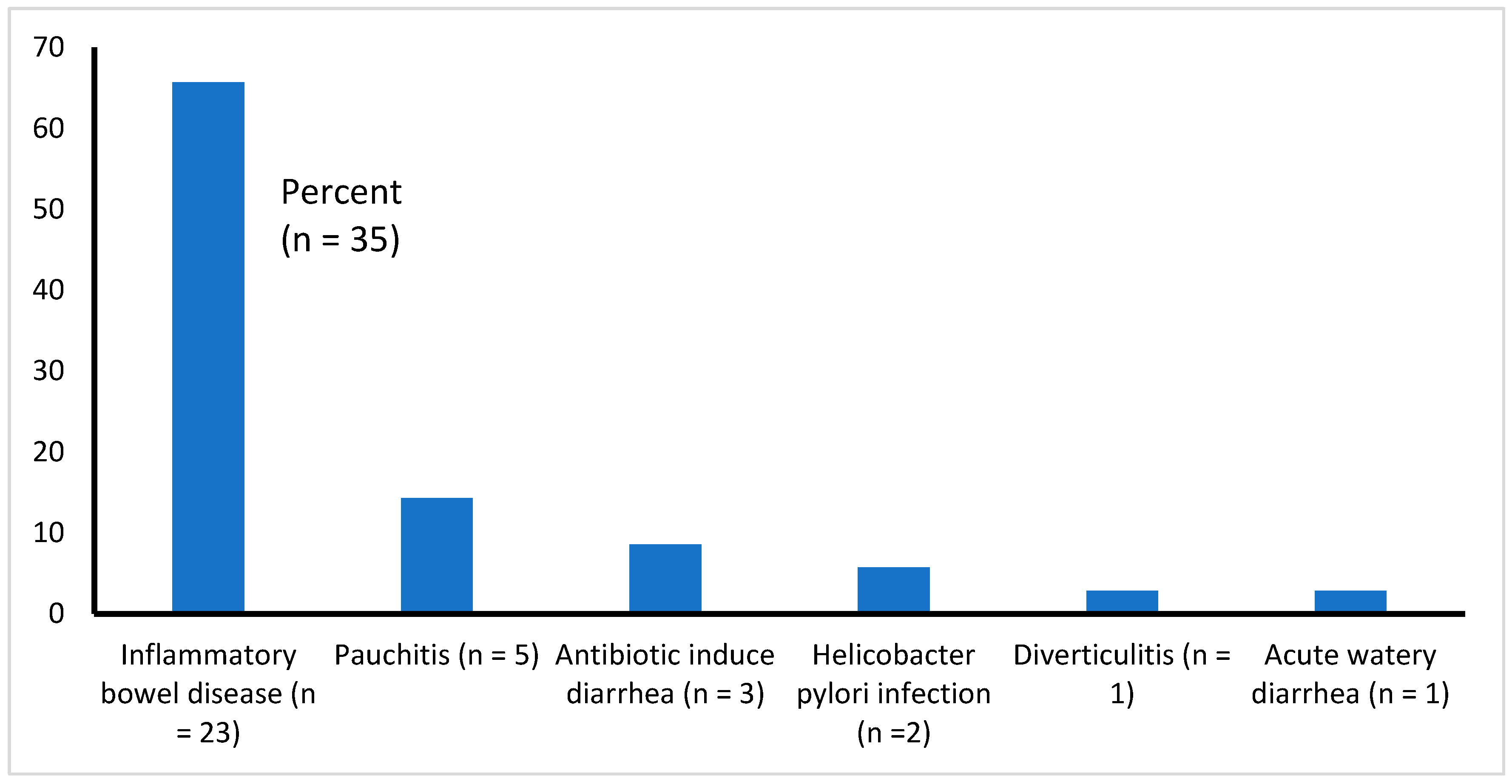
3.1. Type of Illnesses Associated with Diarrhea
3.2. Probiotic Strains Used and Follow-up
3.3. Quality Appraisal Findings
3.4. Efficacy and Safety of Probiotics
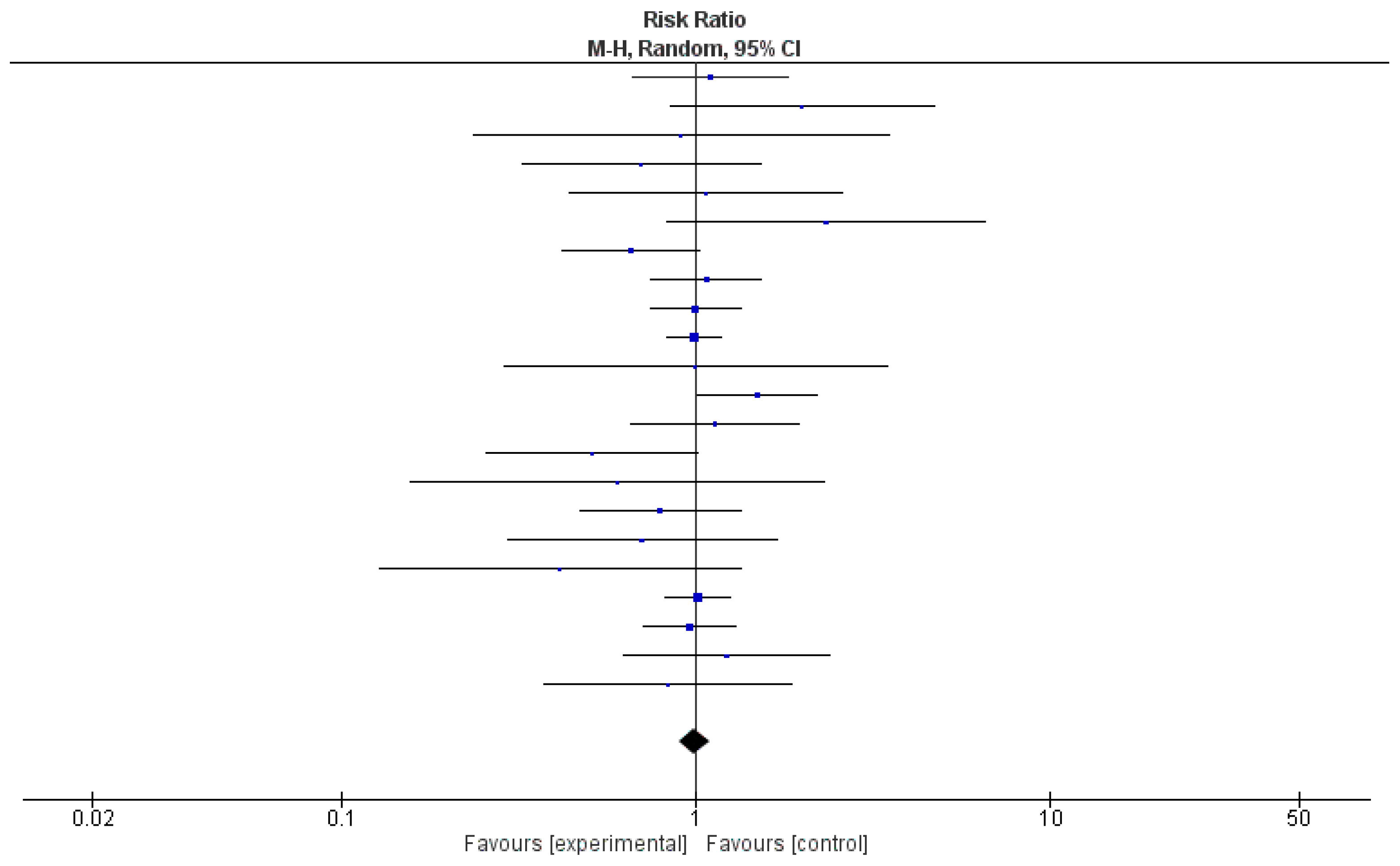
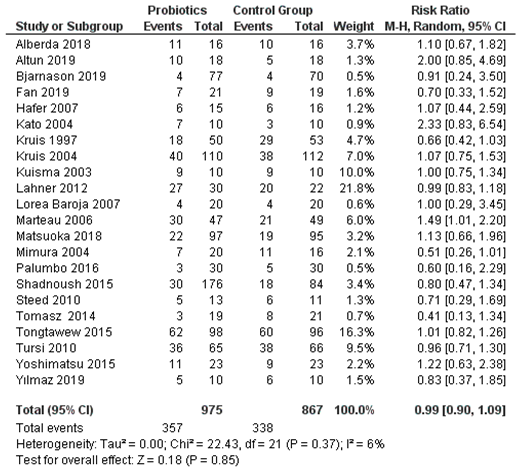
3.5. Effectiveness of Probiotics, as Evaluated by Meta-Analysis of 22 Clinical Trials
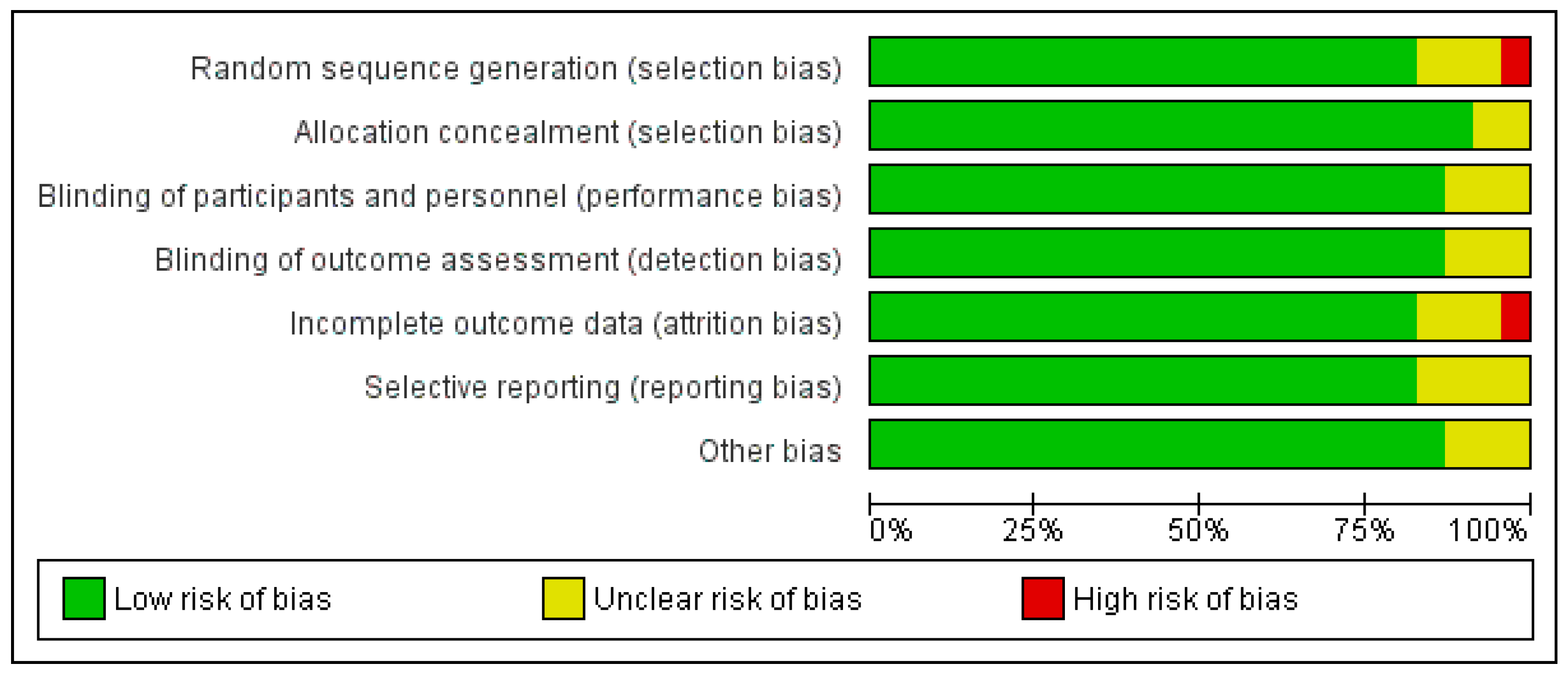
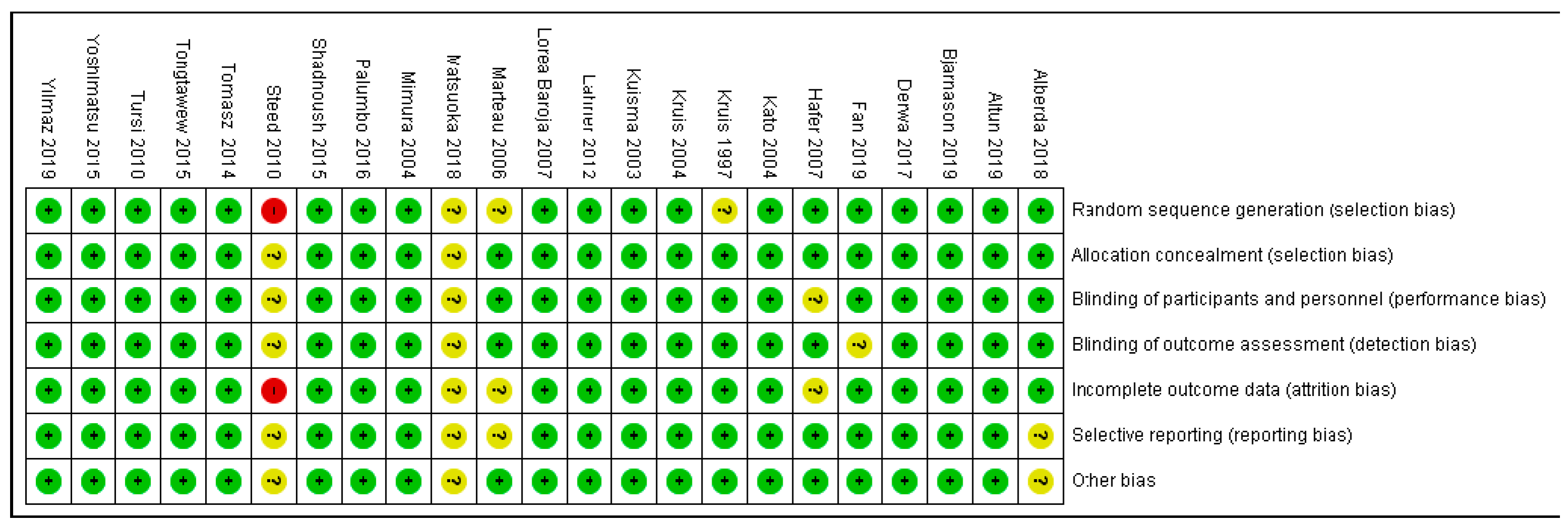
3.6. Overall Risk of Bias by Categories of Bias
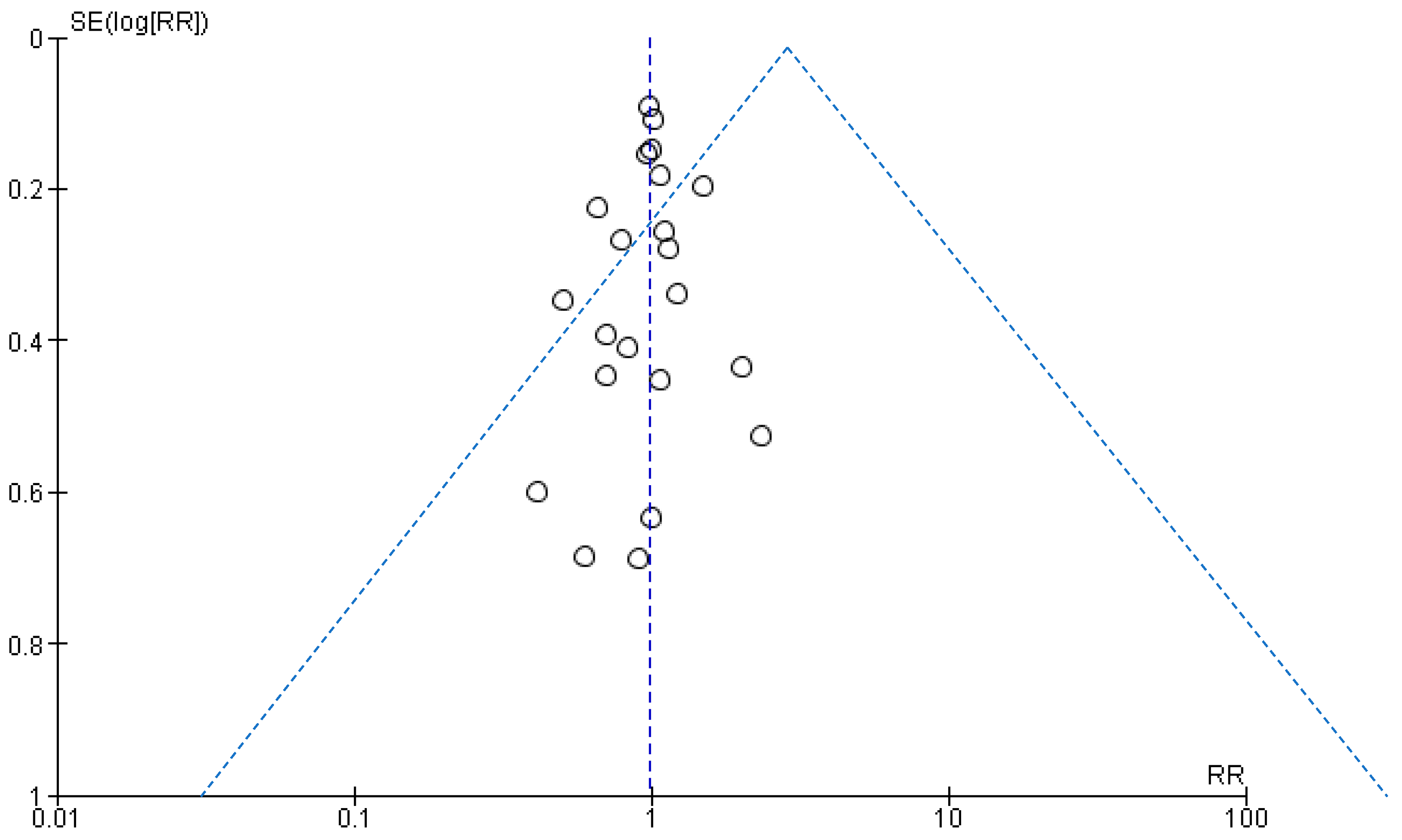
3.7. Assessment of Publication Bias
4. Discussion
4.1. Effective Treatment with Probiotics
4.2. Ineffectiveness of Probiotics
4.3. Safety Issues
4.4. Limitations of the Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bartsch, S.M.; Lopman, B.A.; Ozawa, S.; Hall, A.J.; Lee, B.Y. Global economic burden of norovirus gastroenteritis. PloS One 2016, 11, e0151219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, G.T.; Phan, K.; Teng, I.; Pu, J.; Watanabe, T. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the prevalence of norovirus in cases of gastroenteritis in developing countries. Medicine 2017, 96, e8139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graves, N.S. Acute gastroenteritis. Prim Care Clin Office Pract 2013, 40, 727–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagai, J.S.; Smith, G.S.; Schmid, J.E.; Wade, T.J. (2014). Trends in gastroenteritis-associated mortality in the United States, 1985–2005: Variations by ICD-9 and ICD-10 codes. BMC Gastroenterol 2014, 14, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, A.J.; Patel, M.M.; Lopman, B.A.; Armah, G.E. Part 2: Viral Diseases - Norovirus. In Hunter's Tropical Medicine and Emerging Infectious Disease, 9th ed.; Magill, A.J.; Ryan, E.T.; Hill, D.R.; Solomon, T. Eds.; Saunders Elsevier Inc., China, 2013; pp. 280-282.
- Williams, N.T. Probiotics. Am J Health Syst Pharm 2010, 67, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasik, P.; Tomasik, P. Probiotics, non-dairy prebiotics and postbiotics in nutrition. Appl Sci 2020, 10, 1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkins, T.; Sequoia, J. Probiotics for gastrointestinal conditions: A summary of the evidence. Am Fam Physician 2017, 96, 170–178. [Google Scholar]
- Liberati, A.; Altman, D.G.; Tetzlaff, J.; Mulrow, C.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Ioannidis, J.P.; et al. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate healthcare interventions: Explanation and elaboration. BMJ 2009, 339, b2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joanna Briggs Institute.JBI Critical Appraisal Tools. Available online: https://jbi.global/critical-appraisal-tools (accessed on 3 May 2023).
- Alberda, C.; Marcushamer, S.; Hewer, T.; Journault, N.; Kutsogiannis, D. Feasibility of a Lactobacillus casei drink in the intensive care unit for prevention of antibiotic associated diarrhea and Clostridium difficile. Nutrients 2018, 10, E539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altun, H.K.; Yildiz, E.A.; Akin, M. (2019). Effects of synbiotic therapy in mild-to-moderately active ulcerative colitis: A randomized placebo-controlled study. Turk J Gastroenterol 2019, 30, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjarnason, I.; Sission, G.; Hayee, B. A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of a multi-strain probiotic in patients with asymptomatic ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. Inflammopharmacol 2019, 27, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derwa, Y.; Gracie, D.J.; Hamlin, P.J.; Ford, A.C. Systematic review with meta-analysis: The efficacy of probiotics in inflammatory bowel disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2017, 46, 389–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, H.; Du, J.; Liu, X.; Zheng, W.W.; Zhuang, Z.H.; Wang, C.D.; et al. Effects of pentasa-combined probiotics on the microflora structure and prognosis of patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Turk J Gastroenterol 2019, 30, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groeger, D.; O’Mahony, L.; Murphy, E.F.; Bourke, J.F.; Dinan, T.G.; Kiely, B.; et al. Bifidobacterium infantis 35624 modulates host inflammatory processes beyond the gut. Gut Microbes 2013, 2013 4, 325–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafer, A.; Krämer, S.; Duncker, S.; Krüger, M.; Manns, M.P.; Bischoff, S.C. Effect of oral lactulose on clinical and immunohistochemical parameters in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: A pilot study. BMC Gastroenterol 2007, 7, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, K.; Mizuno, S.; Umesaki, Y.; Ishii, Y.; Sugitani, M.; Imaoka, A.; et al. Randomized placebo-controlled trial assessing the effect of bifidobacteria-fermented milk on active ulcerative colitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2004, 20, 1133–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krag, A.; Israelsen, H.; von Ryberg, B.; Andersen, K.K.; Bendtsen, F. Safety and efficacy of Profermin® to induce remission in ulcerative colitis. World J Gastroenterol 2012, 2012 18, 1773–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruis, W.; Schütz, E.; Fric, P.; Fixa, B.; Judmaier, G.; Stolte, M. Double-blind comparison of an oral Escherichia coli preparation and mesalazine in maintaining remission of ulcerative colitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 1997, 11, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruis, W.; Frič, P.; Pokrotnieks, J.; Lukáš, M.; Fixa, B.; Kaščák, M.; et al. Maintaining remission of ulcerative colitis with the probiotic Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 is as effective as with standard mesalazine. Gut 2004, 53, 1617–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuehbacher, T.; Ott, S.J.; Helwig, U.; Mimura, T.; Rizzello, F.; Kleessen, B.; et al. Bacterial and fungal microbiota in relation to probiotic therapy (VSL# 3) in pouchitis. Gut 2006, 55, 833–841. [Google Scholar]
- Kuisma, J.; Mentula, S.; Jarvinen, H.; Kahri, A.; Saxelin, M.; Farkkila, M. Effect of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG on ileal pouch inflammation and microbial flora. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2003, 17, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahner, E.; Esposito, G.; Zullo, A.; Hassan, C.; Cannaviello, C.; Di Paolo, M.C.; et al. (2012). High-fibre diet and Lactobacillus paracasei B21060 in symptomatic uncomplicated diverticular disease. World J Gastroenterol 2012, 18, 5918–5924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorea Baroja, M.; Kirjavainen, P.V.; Hekmat, S.; Reid, G. Anti-inflammatory effects of probiotic yogurt in inflammatory bowel disease patients. Clin Exp Immunol 2007, 149, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marteau, P.; Lémann, M.; Seksik, P.; Laharie, D.; Colombel, J.F.; Bouhnik, Y. Ineffectiveness of Lactobacillus johnsonii LA1 for prophylaxis of postoperative recurrence in Crohn’s disease: a randomised, double blind, placebo controlled GETAID trial. Gut 2006, 55, 842–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuoka, K.; Uemura, Y.; Kanai, T.; Kunisaki, R.; Suzuki, Y.; Yokoyama, K.; et al. Efficacy of Bifidobacterium breve fermented milk in maintaining remission of ulcerative colitis. Dig Dis Sci 2018, 63, 1910–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthes, H.; Krummenerl, T.; Giensch, M.; Wolff, C.; Schulze, J. Clinical trial: probiotic treatment of acute distal ulcerative colitis with rectally administered Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 (EcN). BMC Complement Altern Med 2010, 10, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mimura, T.; Rizzello, F.; Helwig, U.; Poggioli, G.; Schreiber, S.; Talbot, I.C.; et al. Once daily high dose probiotic therapy (VSL# 3) for maintaining remission in recurrent or refractory pouchitis. Gut 2004, 53, 108–114. [Google Scholar]
- Mitra, A.K.; Rabbani, G.H. A double-blind controlled trial of Bioflorin (Streptococcus faecium SF68) in adults with diarrhoea due to Vibrio cholerae and enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Gastroenterol 1990, 99, 1149–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montalto, M.; Gallo, A.; Curigliano, V.; D’Onofrio, F.; Santoro, L.; Covino, M.; et al. Clinical trial: The effects of a probiotic mixture on non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug enteropathy–a randomized, double-blind, cross-over, placebo-controlled study. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2010, 32, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palumbo, V.D.; Romeo, M.; Gammazza, A.M.; Carini, F.; Damiani, P.; Damiano, G.; et al. The long-term effects of probiotics in the therapy of ulcerative colitis: A clinical study. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub, 2016, 160, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persborn, M.; Gerritsen, J.; Wallon, C.; Carlsson, A.; Akkermans, L.M.A.; Söderholm, J.D. The effects of probiotics on barrier function and mucosal pouch microbiota during maintenance treatment for severe pouchitis in patients with ulcerative colitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2013, 38, 772–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shadnoush, M.; Hosseini, R.S.; Khalilnezhad, A.; Navai, L.; Goudarzi, H.; Vaezjalali, M. Effects of probiotics on gut microbiota in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: A double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Korean J Gastroenterol 2015, 65, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, B.; Brzezinski, A.; Fazio, V.W.; Remzi, F.H.; Achkar, J.P.; Bennett, A.E.; et al. Maintenance therapy with a probiotic in antibiotic-dependent pouchitis: Experience in clinical practice. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2005, 22, 721–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steed, H.; Macfarlane, G.T.; Blackett, K.L.; Bahrami, B.; Reynolds, N.; Walsh, S.V.; et al. Clinical trial: The microbiological and immunological effects of symbiotic consumption–a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled study in active Crohn’s disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2010, 32, 872–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasz, B.; Zoran, S.; Jarosław, W.; Ryszard, M.; Marcin, G.; Robert, B.; et al. Long-term use of probiotics Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium has a prophylactic effect on the occurrence and severity of pouchitis: A randomized prospective study. Biomed Res Int 2014, 2014, 208064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tongtawee, T.; Dechsukhum, C.; Leeanansaksiri, W.; Kaewpitoon, S.; Kaewpitoon, N.; Loyd, R.A.; et al. Effect of pretreatment with Lactobacillus delbrueckii and Streptococcus thermophillus on tailored triple therapy for Helicobacter pylori eradication: A prospective randomized controlled clinical trial. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 2015, 16, 4885–4890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tursi, A.; Brandimarte, G.; Papa, A.; Giglio, A.; Elisei, W.; Giorgetti, G.M.; et al. Treatment of relapsing mild-to-moderate ulcerative colitis with the probiotic VSL# 3 as adjunctive to a standard pharmaceutical treatment: A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study. Am J Gastroenterol 2010, 105, 2218–2227. [Google Scholar]
- Venturi, A.; Gionchetti, P.; Rizzello, F.; Johansson, R.; Zucconi, E.; Brigidi, P. Impact on the composition of the faecal flora by a new probiotic preparation: preliminary data on maintenance treatment of patients with ulcerative colitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 1999, 13, 1103–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yılmaz, İ.; Dolar, M.E.; Özpınar, H. Effect of administering kefir on the changes in fecal microbiota and symptoms of inflammatory bowel disease: A randomized controlled trial. Turk J Gastroenterol 2019, 30, 242–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimatsu, Y.; Yamada, A.; Furukawa, R.; Sono, K.; Osamura, A.; Nakamura, K.; et al. Effectiveness of probiotic therapy for the prevention of relapse in patients with inactive ulcerative colitis. World J Gastroenterol 2015, 21, 5985–5994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziemniak, W. Efficacy of Helicobacter pylori eradication taking into account its resistance to antibiotics. J Physiol Pharmacol 2006, 57, 123–141. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zocco, M.A.; Dal Verme, L.Z.; Cremonini, F.; Piscaglia, A.C.; Nista, E.C.; Candelli, M. Efficacy of Lactobacillus GG in maintaining remission of ulcerative colitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2006, 23, 1567–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwolinska-Wcislo, M.; Brzozowski, T.; Budak, A.; Kwiecien, S.; Sliwowski, Z.; Drozdowicz, D.; et al. Effect of Candida colonization on human ulcerative colitis and the healing of inflammatory changes of the colon in the experimental model of colitis ulcerosa. J Physiol Pharmacol 2009, 60, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Verna, E.C.; Lucak, S. Use of probiotics in gastrointestinal disorders: What to recommend? Ther Adv Gastroenterol 2010, 3, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, E.A.K.; Mitra, A.K.; Bisht, A.; Edet, P.P.; Iseguede, F.; Okoye, E. Probiotics in gastroenteritis in children: A systematic review. IMC J Med Sci 2023, 17, 010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, D.; Hock, Q.S.; Kadim, M.; Ryoo, E.; Sandhu, B.; Yamashiro, Y.; et al. Probiotics for gastrointestinal disorders: Proposed recommendations for children of the Asia-Pacific region. World J Gastroenterol 2017, 23, 7952–7964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doron, S.; Snydman, D.R. Risk and safety of probiotics. Clin Infect Dis 2015, 60 (Suppl 2), S129–S134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciernikova, S.; Mego, M.; Semanova, M.; Wachsmannova, L.; Adamcikova, Z.; Stevurkova, V.; et al. Probiotic survey in cancer patients treated in the outpatient department in a comprehensive cancer center. Integr Cancer Ther 2017, 16, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Nieuwboer, M.; Brummer, R.J.; Guarner, F.; Morelli, L.; Cabana, M.; Claassen, E. The administration of probiotics and synbiotics in immune compromised adults: is it safe? Beneficial Microbes 2015, 6, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Authors, year [ref.] | Disease condition and sample size | Type of probiotics used | Prevention / Treatment | Effective | Quality appraisal | Major findings / conclusions | Country |
| Alberda et al., 2018 [11] | Antibiotic-associated diarrhea (AAD) and Clostridium difficile-induced diarrhea; sample size = 32 | Lactobacillus casei | Prevention | Yes | Score 3 out of 4 (Moderate) | Probiotic drink can prevent AAD and Clostridium difficile infections. | Canada |
| Altun, et al., 2019 [12] | Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)1: ulcerative colitis (UC); sample size = 40 | Enterococcus faecium, Lactobacillus plantarum, Streptococcus thermophilus, Bifidobacterium lactis, Lactobacillus acidophilus, Bifidobacterium longum)-and fructooligosaccharide | Treatment | No | Score 4 out of 4 (High) | The use of synbiotic therapy2 had no statistically significant effect in the improvement of clinical and endoscopic parameters compared with controls. | Turkey |
| Bjarnason, et al., 2019 [13] | IBDs: ulcerative colitis (UC) (n = 81) and Crohn’s disease (n = 61); total samples more than 500. | Symprove contains multiple strains of probiotics such as Lactobacillus plantarum, Lactobacillus rhamnosus, Lactobacillus plantarum, Lactobacillus acidophilus, and E. faecium | Treatment | Yes | Score 4 out of 4 (High) | Multi-strain probiotics decreased intestinal inflammation in patients with ulcerative colitis, but not in patients with Crohn’s disease. | United Kingdom |
| Derwa, et al., 2017 [14] | IBDs; sample size = 777 | Probiotics vs.5-aminosalicylates (5-ASAs) (in one RCT); probiotics vs. placebo (in 7 RCTs). | Treatment | No | Score 4 out of 4 (High) | There was no benefit of probiotics over 5-ASAs4 or placebo in inducing remission in active inflammatory bowel diseases. For ulcerative colitis, relative risk of failure to achieve remission = 0.86; 95% CI = 0.68-1.08. | Multiple countries |
| Fan, et al., 2019 [15] | IBDs1; sample size = 40 | Bifico contains probiotic bacteria Bacillus Coagulans GBI-30, 6086. Bifico was given as an adjuvant treatment with Pentasa, which is an anti-inflammatory agent. | Treatment | Yes | Score 4 out of 4 (High) | Combination of probiotics and pentasa can improve microflora composition in patients with IBD and reduce the level of inflammatory cytokines. | China |
| Groeger, et al., 2013 [16] | IBDs1; chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS); Psoriasis. Sample sizes: UC = 22, CFS = 48, psoriasis = 26. | Bifidobacterium infantis 35624 | Treatment | Yes | Score 4 out of 4 (High) | Microbiota in humans have immuno-modulatory effects on both mucosal immune system and systemic immune system. | Ireland |
| Hafer, et al., 2007 [17] | IBDs1; sample sizes: UC = 14, Crohn’s disease = 17. | Standard treatment vs. standard treatment with oral lactulose. | Treatment | No | Score 3 out of 4 (Moderate) | Oral lactulose has no beneficial no clinical and immune-histological effects on IBD patients. | Germany |
| Kato, et al., 2004 [18] | IBD: ulcerative colitis (UC); sample size = 20 | Bifidobacteria-fermented milk (BFM) | Treatment | Yes | Score 3 out of 4 (Moderate) | Supplementation with BFM has beneficial effects in managing active ulcerative colitis and is more effective than the conventional treatment alone. | Japan |
| Krag, et al., 2012 [19] | IBD: ulcerative colitis (UC); sample size = 39 | Profermin, consisting of fermented oats, Lactobacillus plantarum 299v, barley malt, lecithin, and water | Treatment | Yes | Score 4 out of 4 (High) | Profermin is safe and may be effective in inducing remission of active ulcerative colitis. | Denmark |
| Kruis, et al., 1997 [20] | IBD: ulcerative colitis (UC); sample size = 120 | Escherichia coli Nissle (Serotype 06: K5: H1), as an adjuvant treatment with mesalazine (also known as 5-aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA)4 | Treatment | Yes | Score 4 out of 4 (High) | E. coli (Serotype 06: K5: H1) is effective in preventing remission of ulcerative colitis as a standard treatment with 5-ASA4. | Germany, Czech Republic, and Austria |
| Kruis, et al., 2004 [21] | IBD: ulcerative colitis (UC); sample size = 327 | Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 | Maintaining remission and prevention of relapses | Yes | Score 4 out of 4 (High) | Probiotic EcN has therapeutic effects and is safe for maintaining remission in ulcerative colitis. EcN can be used as an alternative of 5-ASA4. | Germany |
| Kuehbacher, et al., 2006 [22] | Pouchitis3; sample size = 15 | VSL #3 consists of Lactobacillus casei, L. plantarum, L. acidophilus, L. bulgaricus, Bifidobacterium longuum, B. breve, B. infantis, and Streptococcus salivarius sub-spp. Thermophillus | Treatment | Yes | Score 3 out of 4 (Moderate) | Probiotic therapy with VSL #3 increases the diversity, richness and total number of intestinal bacteria and bacterial microbiota. | Germany |
| Kuisma, et al., 2003 [23] | Pouchitis3; sample size = 20 | Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG | Treatment | No | Score 3 out of 4 (Moderate) | Lactobacillus GG can alter the microbial flora in ileo-anal pouches but was inefficient for clinically improving pouch inflammation. | Finland |
| Lahner, et al., 2012 [24] | Symptomatic uncomplicated diverticular disease; sample size = 45 | Lactobacillus paracasei B21060 (symbiotic sachet Flortec©) plus high fiber diet (Treatment Group) vs high fiber diet only (Controls) | Treatment | Yes | Score 3 out of 4 (Moderate) | The treatment group having symbiotic sachet Flortec© plus a high fiber diet improved of clinical symptoms (abdominal pain, bloating) significantly more than the control group. | Italy |
| Lorea Baroja, et al., 2007 [25] | IBD: Crohn’s disease (n = 15) and ulcerative colitis (n = 5), control, (n = 20); total sample size = 40 | Lactobacillus rhamnosus GR-1 and L. reuteri RC-14- supplemented yogurt vs. placebo | Prevention | Yes | Score 4 out of 4 (High) | Short-term consumption of probiotic yogurt with Lactobacillus rhamnosus GR-1 and RC-14 has beneficial immune modulatory effects. | Canada |
| Marteau, et al., 2006 [26] | IBD: Crohn’s disease; sample size = 98 | Lactobacillus johnsonii LA1 | Prevention of relapses | No | Score 4 out of 4 (High) | Lactobacillus johnsonii LA1 have no sufficient effect to prevent recurrence of Crohn’s disease. | France |
| Matsuoka, et al., 2018 [27] | IBD: ulcerative colitis (UC); sample size = 195 | Bifidobacterium breve fermented milk (BFM) | Prevention | No | Score 4 out of 4 (High) | BFM had no effect on time to relapse in UC patients, compared with placebo. | Japan |
| Matthes, et al., 2010 [28] | IBD: ulcerative colitis (UC); sample size = 90 (70 with UC and 20 controls) | Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 (EcN) | Treatment | Yes | Score 3 out of 4 (Moderate) | Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 (EcN) may be an alternative treatment for moderate distal ulcerative colitis. | Germany |
| Mimura, et al., 2004 [29] | Recurrent or refractory pouchitis3; sample size = 36 | VSL #3 contains Lactobacillus casei, L. plantarum, L. acidophilus, L. bulgaricus, Bifidobacterium. longuum, B. breve, B. infantis Streptococcus salivarius subsp. Thermophillus | Treatment of remission | Yes | Score 3 out of 4 (Moderate) | VSL#3 probiotic therapy is highly effective in maintaining treatment of recurrent pouchitis3 and improving quality of life. | United Kingdom and Italy |
| Mitra & Rabbani, 1990 [30] | Acute watery diarrhea due to Vibrio cholerae and E. coli infection; sample size = 183 | Bioflorin (Streptococcus faecium SF68), given orally along with intravenous rehydration, and followed by oral rehydration solution | Treatment | No | Score 4 out of 4 (High) | Bioflorin was not effective in treating acute diarrhea due to V. cholerae and enterotoxigenic E. coli infections. | Bangladesh |
| Montalto, et al., 2010 [31] | Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug-induced enteropathy; sample size = 20 | VSL #3 contains Lactobacillus casei, L. plantarum, L. acidophilus, L. bulgaricus, Bifidobacterium. longuum, B. breve, B. infantis Streptococcus salivarius subsp. Thermophillus | Treatment | Yes | Score 2 out of 4 (Poor) | Probiotics mixture could be useful in decreasing indomethacin-induced intestinal inflammation. | Italy |
| Palumbo, et al., 2016 [32] | IBD: ulcerative colitis (UC); sample size = 60 | A probiotic blend, which consists of Lactobacillus salivarius, Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium bifidus strain BGN4, given as an adjuvant therapy with Mesalazine | Treatment | Yes | Score 3 out of 4 (Moderate) | Long-term treatment modality of anti-inflammatory drugs and probiotics is viable and could be an alternative treatment for mild-to moderate ulcerative colitis. | Italy |
| Persborn, et al., 2013 [33] | Pouchitis3; sample size = 16 patients with pouchitis and 13 controls with a healthy ileoanal pouch | Bifidobacterium bifidum (W23), B. lactis (W51), B. lactis (W52), Lactobacillus acidophilus (W22), L. casei (W56), L. paracasei (W20), L. plantarum (W62), L. salivarius (W24), L. lactis (W19) | Treatment | Yes | Score 3 out of 4 (Moderate) | Probiotics restored the mucosal barrier to E. coli in patients with pouchitis3. This can prevent recurrence during maintenance therapy. | Sweden |
| Shadnoush, et al., 2015 [34] | IBDs1; sample size = 305, of which 105 IBD patients received probiotic yogurt, 105 IBD patients received placebo, and 95 healthy controls received probiotic yogurt | Probiotic yogurt containing Lactobacillus acidophilus La-5 and Bifidobacterium BB-12 | Treatment | Inconclusive | Score 3 out of 4 (Moderate) | Fiber and energy intake in the treatment group did not increase when compared with those of controls. However, consumption of probiotic yogurt by patients with IBD may help to increase the number of probiotic bacteria in the intestine, thus improving intestinal function. | Iran |
| Shen, et al., 2005 [35] | Antibiotic-dependent pouchitis3; sample size = 31 | VSL #3 contains four strains of Lactobacillus, three Bifidobacterium species, Streptococcus salivarius subsp. thermophillus | Treatment | Yes | Score 3 out of 4 (Moderate) | The use of probiotics is useful, and the authors suggested it in routine clinical care. | United States |
| Steed, et al., 2010 [36] | IBD: Crohn’s disease; sample size = 35 | Bifidobacterium longum and Synergy 1 which contains Orafti, Tienen, Belgium | Treatment | Yes | Score 4 out of 4 (High) | Effective in improving clinical symptoms in patients with active Crohn's disease. | Scotland |
| Tomasz, et al., 2014 [37] | Pouchitis3; sample size = 43 | Lactobacillus acidophillus, L. delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus, and Bifidobacterium bifidus | Prevention | Yes | Score 4 out of 4 (High) | Long-term use of probiotics is safe and can be an effective method of preventing pouchitis3. | Poland |
| Tongtawee, et al., 2015 [38] | Helicobacter pylori; sample size = 200 | Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophillus | Treatment | Yes | Score 4 out of 4 (High) | Pretreatment with probiotic containing yogurt can potentiate the effects of triple therapy for Helicobacter pylori. | Italy |
| Tursi, et al., 2010 [39] | IBD: ulcerative colitis (UC); sample size = 144 | VSL #3 consists of Lactobacillus casei, L. plantarum, L. acidophilus, L. bulgaricus, Bifidobacterium longuum, B. breve, B. infantis, and Streptococcus salivarius sub-spp. Thermophillus | Treatment | Yes | Score 4 out of 4 (High) | High potency probiotic mixture supplementation is safe and improves rectal bleeding and reduce remission in relapsing ulcerative colitis patients after 8 weeks of treatment. | Thailand |
| Venturi, et al., 1999 [40] | IBD: ulcerative colitis (UC); sample size = 20 | VSL #3 consists of Lactobacillus casei, L. plantarum, L. acidophilus, L. bulgaricus, Bifidobacterium longuum, B. breve, B. infantis, and Streptococcus salivarius sub-spp. Thermophillus | Treatment | Yes | Score 3 out of 4 (Moderate) | Intake of VSL #3 preparation enhances the concentrations of some strains of protective bacteria in the intestinal microflora. | Italy |
| Yilmaz, et al., 2019 [41] | IBDs1; sample size = 45 | Kefir, a cultured, fermented beverage, which contains Lactobacillus bacteria | Treatment | Yes | Score 3 out of 4 (Moderate) | Consumptions of kefir has short term effects on improving the quality of life of patients. | Turkey |
| Yoshimatsu, et al., 2015 [42] | IBD: ulcerative colitis (UC); sample size = 46 | Streptococcus faecalis (lactomin), Clostridium butyricum, and Bacillusmesentericus | Prevention of relapse | Yes | Score 3 out of 4 (Moderate) | Probiotics may be effective for maintaining clinical remission in patients with quiescent ulcerative colitis. | Japan |
| Ziemniak, 2006 [43] | Chronic gastritis, or duodenal ulcer caused by Helicobacter pylori; sample size = 641 | Lacidofil containing Lactobacillus acidophilus and Lactobacillus rhamnosus, as an adjuvant therapy with antibiotics and proton pump inhibitor (PPI) | Treatment | Yes | Score 4 out of 4 (High) | Lacidofil increases the efficacy of clarithromycin and amoxicillin and also reduces complications of antibiotic therapy. | Poland |
| Zocco, et al., 2006 [44] | IBD: ulcerative colitis (UC); sample size = 187 | Lactobacillus GG | Treatment and prevention of remissions | Yes | Score 4 out of 4 (High) | Lactobacillus GG is effective and safe for maintaining ulcerative colitis remission and could be a good therapeutic alternative. | Italy |
| Zwolinsk, et al., 2009 [45] | IBD: ulcerative colitis (UC); sample size = 101, of which 56 had active phase of UC, 33 non-active phase of UC, and 12 IBS controls | Lacidofil, containing two well-characterized strains of Lactobacillus: L. helveticus R-52 and L. rhamnosus R-11. | Treatment | Yes | Score 4 out of 4 (High) | Probiotic therapy is beneficial in counteracting the effects of delayed healing of trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid induced colitis caused by Candida. | Poland |
 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





