Submitted:
14 September 2023
Posted:
15 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Quadrat Setting
2.2.2. Importance Value Calculation
| Trees and Shrub | IV = (RD + RH + RC) / 3, | (1) |
| Herbs | IV = (RH + RC) / 2. | (2) |
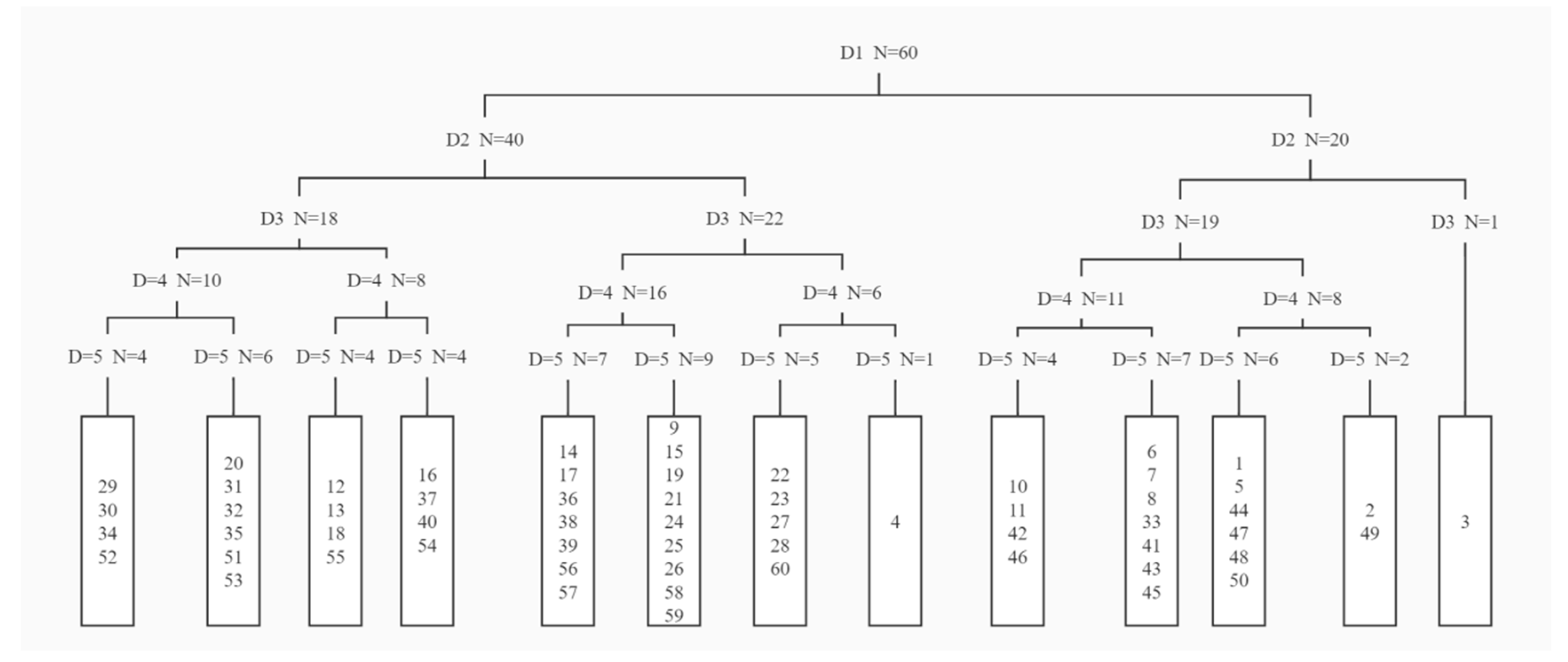
2.2.3. TWINSPAN Quantitative Classification
2.2.4. DCA and DCCA
3. Results
3.1. Classification of the Vegetation Community
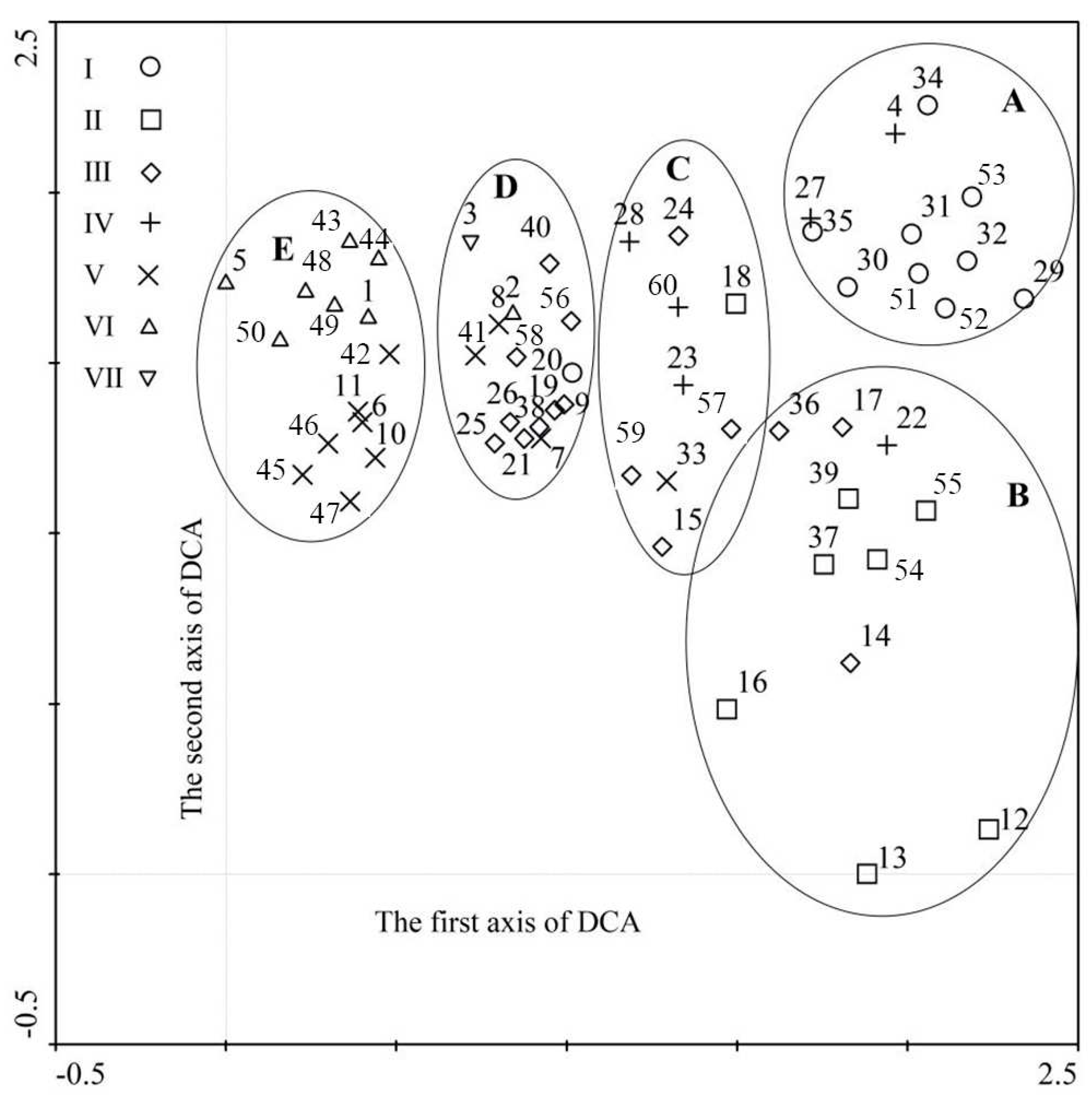
3.2. DCA Ordination of Vegetation Community Quadrats and Environmental Factors
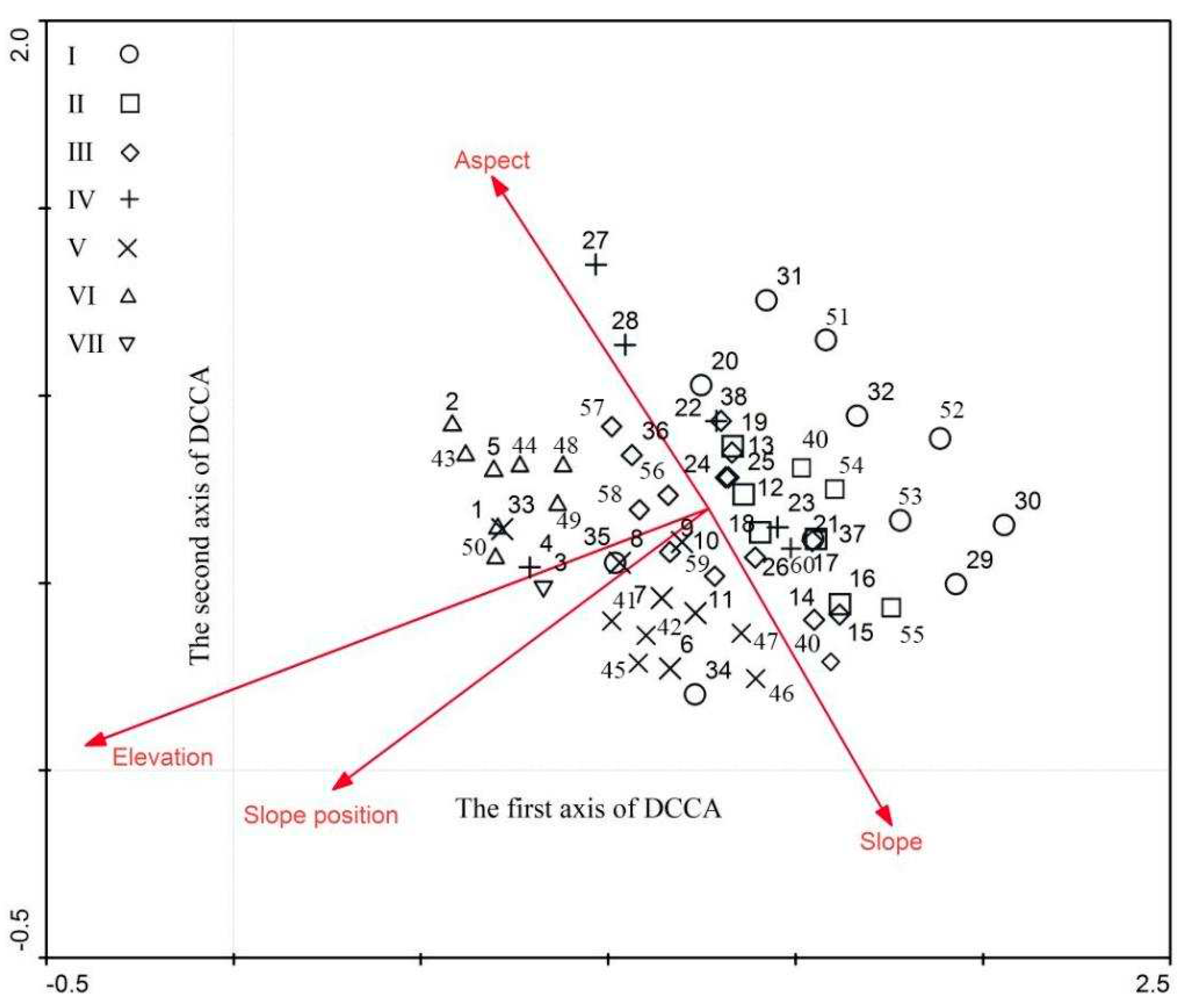
3.3. DCCA Ordination of Vegetation Community and Environmental Factors
4. Discussion
4.1. Vegetation Restoration Features of Burned Areas in the Dry Valleys
4.2. TWINSPAN Quantity Classification and DCA Ordination Features
4.3. DCA Ordination and DCCA Ordination Features
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- After forest fire disturbance in the Anning River Basin, the TWINSPAN classification method was used to classify the vegetation community in the early stage of vegetation regeneration and succession into seven community types. The community types were dominated by savanna communities. The Qg community was widely distributed in the region.
- (2)
- In the DCA ordination diagram, the burned areas were divided into five ecotopes based on the distribution of quadrats. Elevation was significantly correlated with the classification and distribution pattern of community types in this area. With the decrease of elevation, the dominance of the main dominant species of Qg decreased continuously, and the community type changed from a shrub-grass community to a savanna community.
- (3)
- In the DCCA ordination diagram, the first ordination axis mainly reflected the changes in elevation and slope position. The elevation and slope position gradually decreased along the first ordination axis. The second ordination axis mainly reflected the changes of slope and aspect. The slope direction decreased along the second ordination axis direction, and the aspect transitioned from shady slopes to sunny slopes.
Acknowledgments
Disclosure statemen
Abbreviations
References
- Bai, Y.; Wang, B. ; Y.D. Wu, Liu, B.; 2020. Fire Environment of Forest Fire Formation in Liangshan Prefecture. Forest Resources Management. (5), 116-122+130.
- Cai, W.H.; Yang, J.; Liu, Z.H.; Hu, Y.M.; Liu, S.J.; Jing, G.Z.; Zhao, Z.F. ; 2012. Controls of post-fire tree recruitment in Great Xing'an Mountains in Heilongjiang Province. Acta Ecologica Sinica. 32, 3303-3312.
- Calvo, L.; Tárrega, R.; Luis, E.; Valbuena, L.; Marcos, E. ; 2005. Recovery after experimental cutting and burning in three shrub communities with different dominant species. Plant Ecology. 180, 175-185.
- Chian, Y.S.; Yeh, C.L.; Wang, C.C. ; 2016. Variation in Mountain Vegetation Composition between the East and the West Sides of Southern Taiwan. Forests. 7, 179.
- Cho, K.T.; Jang, R.H.; You, Y.H. ; 2015. Analysis for the relationship of environmental factors and vegetation structure at natural streamside valley and riparian forest in South Korea. Journal of Ecology and Environment. 38, 405-413.
- Di, L.Y.; Sun, R.Y. ; 2007. Summarization of Research on Forest Fire in China. Journal Of Catastrophology. 22, 118-123.
- Dalel, T.; Bruce, M. K. ; 1979. Fire history of a sequoia-mixed conifer forest. Ecology. 60, 129-142.
- Gholamhosein, M.; Harald, V. ; 2018. Relationship between vegetation types, soil and topography in southern forests of Iran. Journal of Forestry Research. 29, 1635-1644.
- Guo, X.L.; Shangguan, T.L.; Zhang, J. ; 2010. Quantitative classification and ordination of wetland vegetation from the mouth of Fen River to the Yellow River. Journal of Wuhan Botanical Research. 28, 431-436.
- Hideo, K.; Shiro, T. ; 2011. Fire severity affects vegetation and seed bank in a wetland. Applied Vegetation Science. 14, 350-357.
- Jan, R.; Lubomír, T.; David, Z.; Milan, C. ; 2009. Modified TWINSPAN Classification in Which the Hierarchy Respects Cluster Heterogeneity. Journal of Vegetation Science. 20, 596-602.
- Jens, T.S.; Jesse, E.D.M.; Paula, J. F. ; 2019. Fire severity and changing composition of forest understory plant communities. Journal of Vegetation Science. 30, 1099-1109.
- Jennifer, S.L.; Heather, A.V.; Neil, C.; Catherine, C. ; 2006. The influence of multi-scale environmental variables on the distribution of terricolous lichens in a fog desert. Journal of Vegetation Science. 17, 831-838.
- Jiang, Y.B.; Liu, X.H.; Song, S.S.; Yu, Z.; Shao, X.M. ; 2015. Diversity and distribution of ground bryophytes in broadleaved forests in Mabian Dafengding National Nature Reserve, Sichuan, China. Acta Ecologica Sinica. 35, 13-19.
- Jiang, R.F.; Yang, B.; Song, L.; Pan, T.Y.; Deng, X.H. ; 2022. Forest Fire Monitoring and Vegetation Evaluation Based on Sentinel-2 Satellite in Muli County, Liangshan Prefecture. GEOSPATIAL INFORMATION. 20, 38-44.
- Jin, S.; Wu, S.K. ; 2021. The plant community structure of burned Pinus tabuliformis forest in Taiyue mountain in the early ecological restoration stage. Acta Ecologica Sinica. 41, 4182-4193.
- Li, Y.Y. ; 2002. The multivariate analysis methods applying in the domain of ecology. Journal of Guizhou University (Agricultural and Biological Science). 21, 215-218+223.
- Liu, L.G.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Chen, X.; Liu, S.J. ; 2022. Ecological Niche and Interspecific Association of Dominant Species in the Initial Stage of Vegetation restoration in Zhongba Village of Xide County. Journal of West China Forestry Science. 51, 110-117.
- Lourens, P.; Masha, T.V.D.S.; Eric, J.M.M.A.; Nataly, A. ; 2017. Biodiversity and climate determine the functioning of Neotropical forests. Global Ecology and Biogeography. 26, 1423-1434.
- Lasaponara, R.; Lanorte, A.; Telesca, L. ; 2009. On the evaluation of vegetation resilience after two successive fires in southern Italy by using SPOT-VGT NDVI time series. IOS Press. 10, 511-516.
- Michal, S.; Richard, H.; Karol, U.; Mariana, U.; František, M.; Anna, P. ; 2016. Syntaxonomy and ecology of acidophilous beech forest vegetation in Slovakia. Phytocoenologia. 46, 69-87.
- Michel, L.; Claire, d.M. ; 2013. Biodiversity and ecosystem stability: a synthesis of underlying mechanisms. Ecology Letters. 16, 106-115.
- Qiu, Y.; Zhang, J.T. ; 2000. The ordination axes clustering based on detrended canonical correspondence analysis ordination and its application to the analysis of the ecological gradients of plant communities. Acta Ecologica Sinica 20, 199-206.
- Rahman, I.U.; Khan, N.; Ali, K. ; 2017. Classification and ordination of understory vegetation using multivariate techniques in the Pinus wallichiana forests of Swat Valley, northern Pakistan. Die Naturwissenschaften. 104(3-4), 24.
- Schoennagel, T.; Waller, D.M.; Turner, M.G.; Romme, W.H. ; 2004. The effect of fire interval on post-fire understorey communities in Yellowstone National Park. Journal of Vegetation Science. 15, 797-806.
- Sun, J.B.; Hu, H.Q. ; 2010. Community successional of burned forestland of larix gmelinii in greatxing′ an Mountains. JOURNAL OF NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY. 38, 30-33.
- Ted, L.H. ; 1971. Succession after fire in the Chaparral of southern California. Ecological Monographs. 41, 389-389.
- Virginia, F.T.; Diane, L.M.; Justin, K.R.; Clifford, N.D. ; 2018. The effects of a catastrophic forest fire on the biomass of submerged stream macrophytes. Aquatic Botany. 152, 36-42.
- Wang, X.G.; Li, X.Z.; He, H.S.; Leng, W.F.; Wen, Q.C. ; 2004. Postfire succession of larch forest in the northern slope of Daxinganling. Chinese Journal of Ecology. 23, 35-41.
- Wang, Y.J.; Tao, J.P.; Zhang, W.Y.; Zang, R.G.; Ding, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, W. ; 2006. Vegetation restoration patterns and their relationships with disturbance on the Giant Panda Corridor of Tudiling, Southwest China. Acta Ecologica Sinica. 26, 3525-3532.
- Xu, X.N. ; 2004. Eco-environmental Geological Issues and Effects in Anning RiverUpper Yangtze. JOURNAL OF MOUNTAIN SCIENCE. 22, 572-577.
- Xofis, P.; Buckley, P.G.; Takos, I.; Mitchley, J. ; 2021. Long Term Post-Fire Vegetation Dynamics in North-East Mediterranean Ecosystems. The Case of Mount Athos Greece. Fire. 4, 92-92.
- Yu, X.H.; Li, X.W.; Bai, J.L. ; 2005. Research progress and development trend on numerical analysis of vegetation in China. Chinese Journal of Ecology. 24, 448-451.
- Zhang, F.; Zhang, J.T. ; 2000. Research Progress of Numerical Classification and Ordination of Vegetation in China. Journal of Shanxi University (Nat. Sci. Ed.). 23, 278-282.
- Zhang, J.T. ; 1994. Ordination Axis Paritioning and Its Application. Chinese Journal of Ecology. 13, 73-75.
- Zhang, J.T. ; 2004. Quantitative ecology. Beijing, Chnia: Science Press.
- Zhao, P.; Qu, J.J.; Xu, X.Y.; Yu, Q.S.; Jiang, S.X.; Zhao, H.R. ; 2019. Desert vegetation distribution and species-environment relationships in an oasis-desert ecotone of northwestern China. Journal of Arid Land. 11, 461-476.
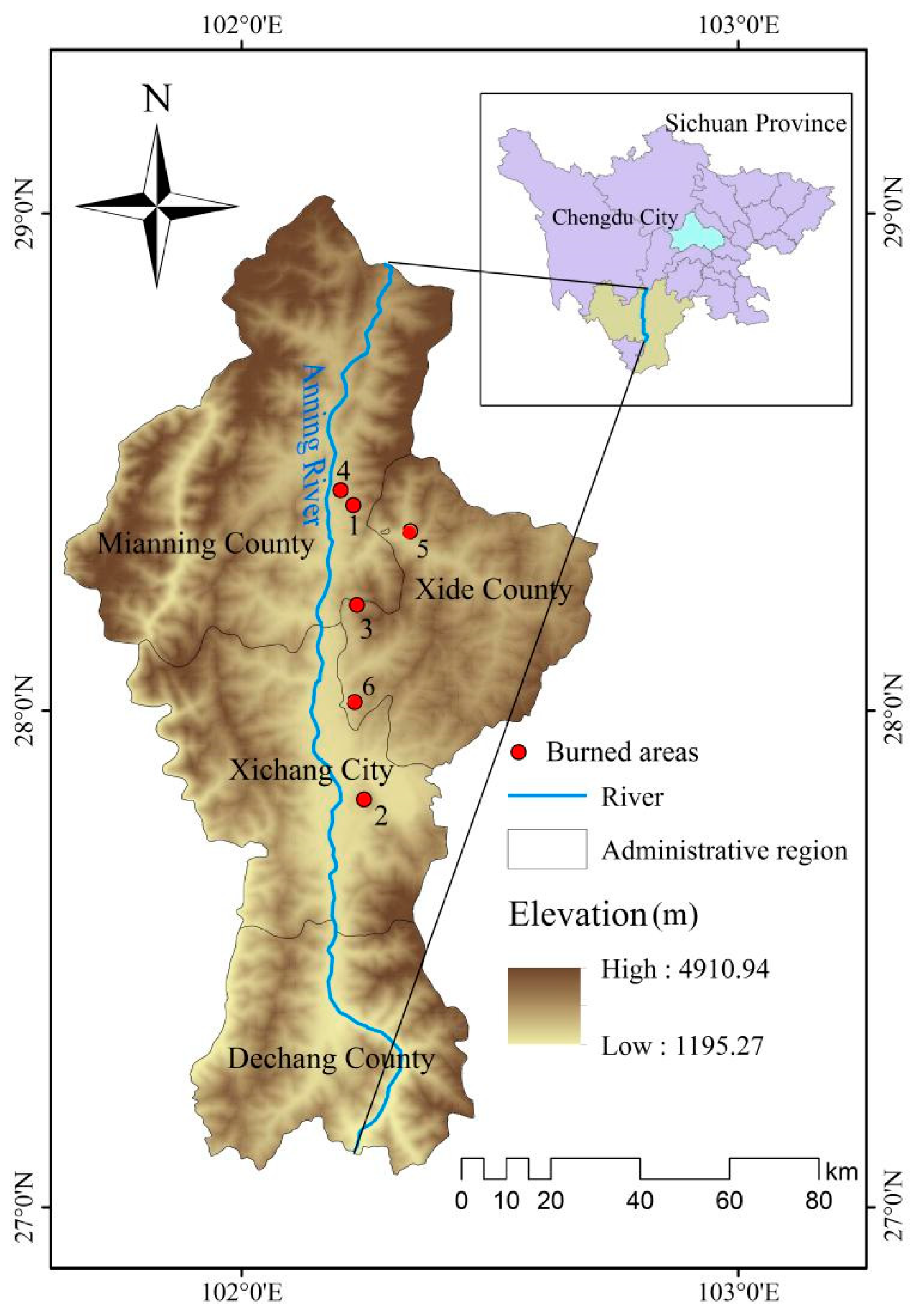
| Plot name | Fire time / year | Fire area / hm2 | Elevation / m | Slope / ° | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Maan Village, Mianning County | 2021 | 100 | 1991–2110 | 12–20 |
| 2 | Lushan, Xichang City | 2020 | 1000 | 1825–1984 | 10–30 |
| 3 | Zhongba Village, Xide County | 2020 | 200 | 2063–2390 | 20–60 |
| 4 | Shanzha Village, Mianning County | 2019 | 100 | 2064–2127 | 25–50 |
| 5 | Gantuo Village, Xide County | 2019 | 80 | 2070–2212 | 20–42 |
| 6 | Lizi Village, Mianning County | 2020 | 30 | 1985–2105 | 10–25 |
| Serial number | Community name | Eigenvalue | Elevation/ m | Slope/ ° | Aspect | Vegetation coverage/ % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | Vf-Ic | 0.524 | 1825–2115 | 10–25 | 2–5 | 40–85 |
| II | Dc-Lc | 0.652 | 2110–2140 | 30–50 | 1–3 | 20–60 |
| III | Mp-Mt | 0.522 | 2090–2245 | 25–45 | 3–5 | 20–85 |
| IV | Qg-Pl | 0.322 | 2120–2380 | 25–35 | 2–4 | 35–40 |
| V | Qg-Pp | 0.552 | 2240–2385 | 30–45 | 1–4 | 40–65 |
| VI | Qg-Ms | 0.454 | 2360–2390 | 10–20 | 2–4 | 55–80 |
| VII | Qg-Ll | 0.492 | 2380 | 5 | 4 | 90 |
| Note:Aspect 2(slope position)-5(slope direction). | ||||||
| Correlation coefficient | Eigenvalue | Correlation coefficient between species and environmental factors | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DCCA | DCA | DCCA | DCA | |
| First axis | 0.244 | 0.618 | 0.712 | 0.505 |
| Second axis | 0.146 | 0.406 | 0.776 | 0.325 |
| Third axis | 0.038 | 0.304 | 0.581 | 0.402 |
| Fourth axis | 0.016 | 0.186 | 0.514 | 0.275 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





