Submitted:
15 September 2023
Posted:
18 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
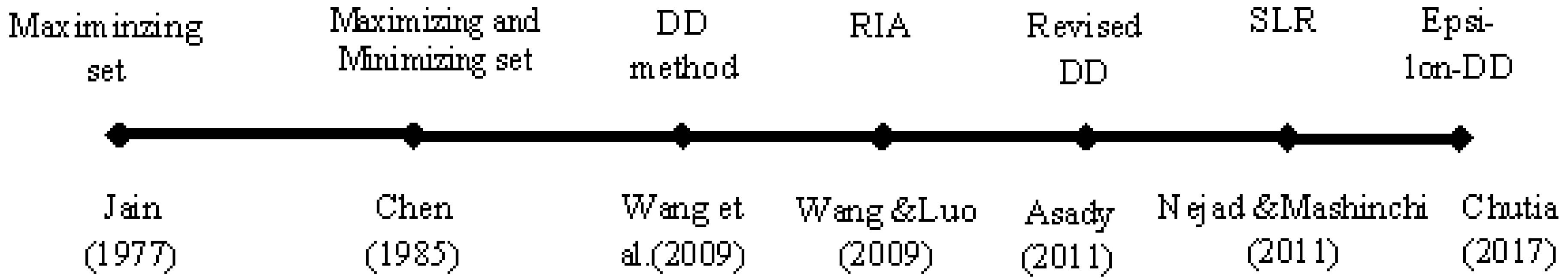
- (I)
- This research develops a new coefficient to calculate the impact of the height of fuzzy numbers on the final ranking score.
- (II)
- The new areas considered as benefit and cost are introduced to reflect the influence of vertical values on the final ranking score.
- (III)
- A new index is proposed to guarantee that both vertical and horizontal values of a fuzzy number are important parameters that impact the final ranking score.
- (IV)
- The proposed method can rank both normal and nonnormal fuzzy numbers without normalization or height minimization, thereby avoiding information loss and incorrect final ranking results.
- (V)
- The proposed method can overcome the shortcomings of some existing methods and can be applied to many fuzzy MCDM model to support decision-makers to select the most suitable alternative in the decision-making process.
2. Preliminary
2.1. Definitions and notions
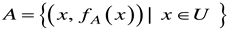 , where U is the universe of discourse, x is an element in U, A is a fuzzy set in U, fA (x) is the membership function of A at x (Kaufmann and Gupta, 1991). The larger, fA (x) the stronger the grade of membership for x in A.
, where U is the universe of discourse, x is an element in U, A is a fuzzy set in U, fA (x) is the membership function of A at x (Kaufmann and Gupta, 1991). The larger, fA (x) the stronger the grade of membership for x in A. 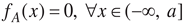 ;
;  ; (e) FA is strictly decreasing on [c,d];
; (e) FA is strictly decreasing on [c,d];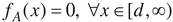 , where a ≤ b ≤ c ≤ d, A can be denoted as [a,b,c,d;w]. The membership function FA of the fuzzy number A can also be expressed as follows:
, where a ≤ b ≤ c ≤ d, A can be denoted as [a,b,c,d;w]. The membership function FA of the fuzzy number A can also be expressed as follows: 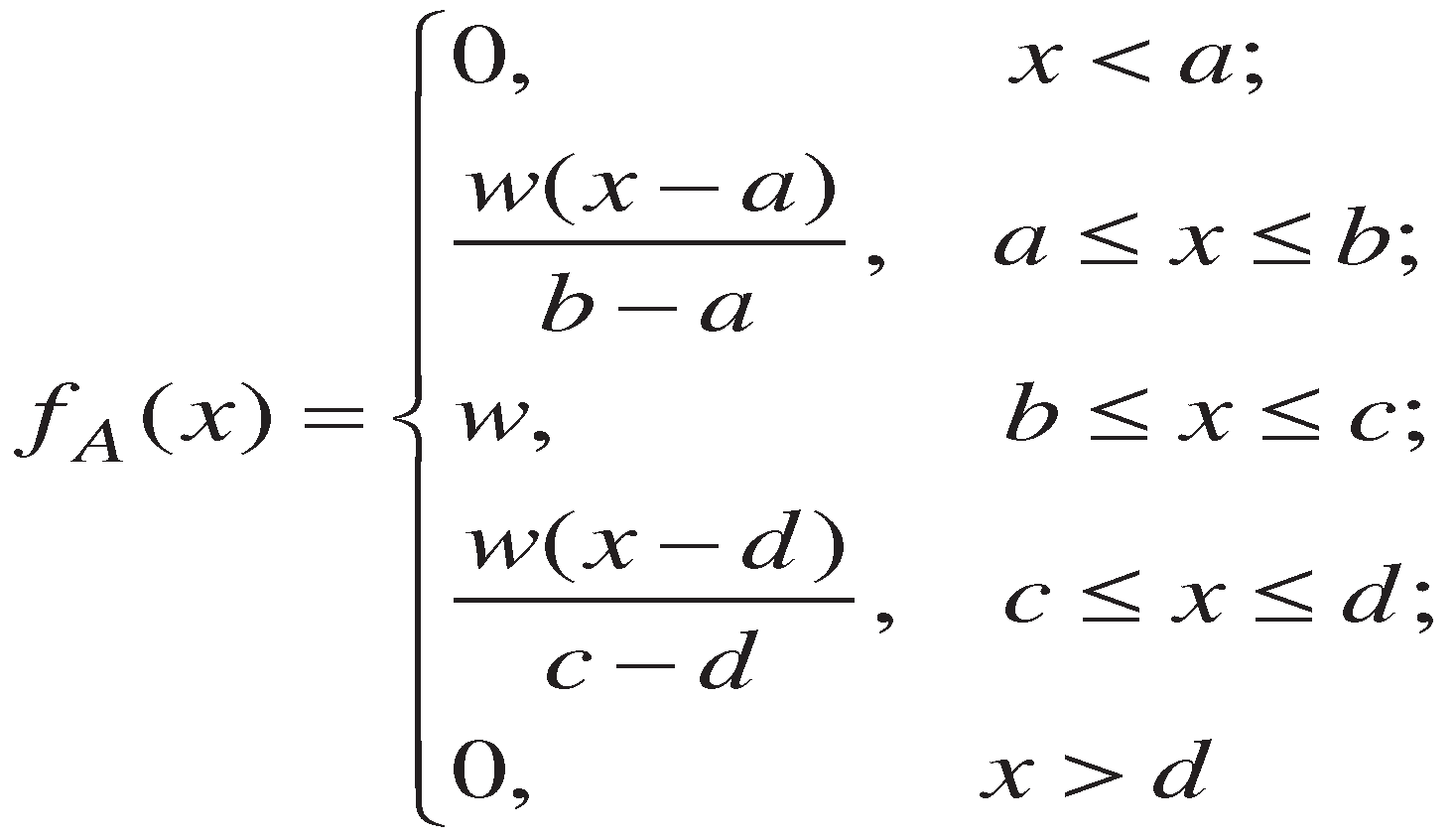
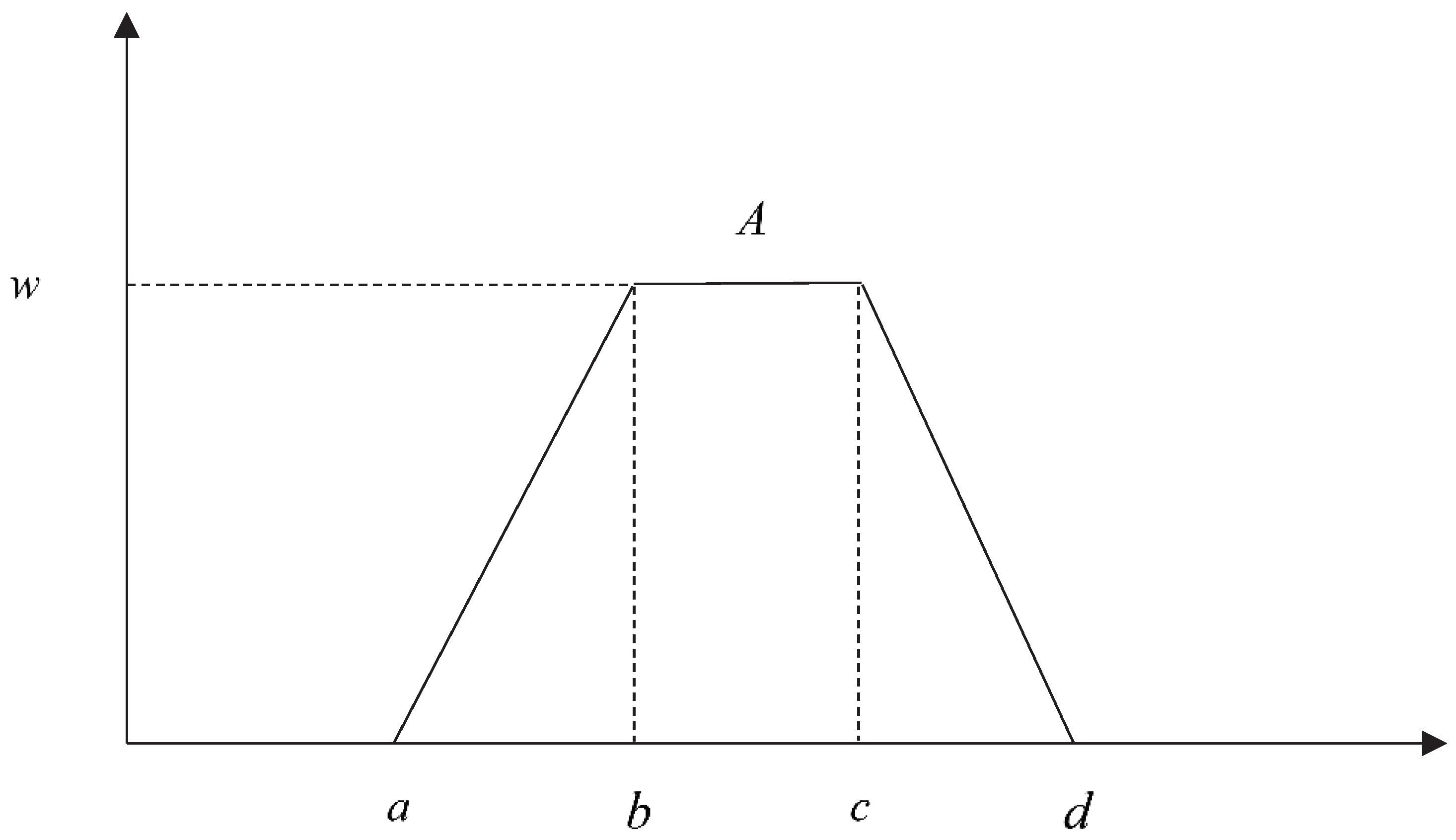

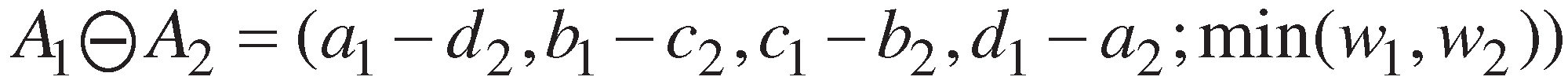
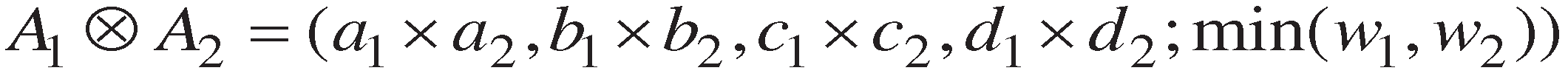
2.2. A review of the deviation degree method
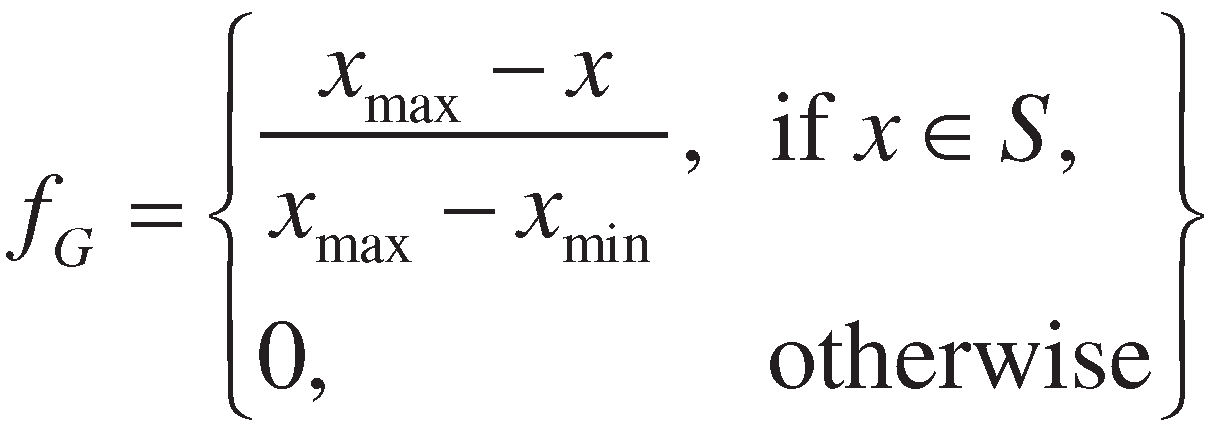
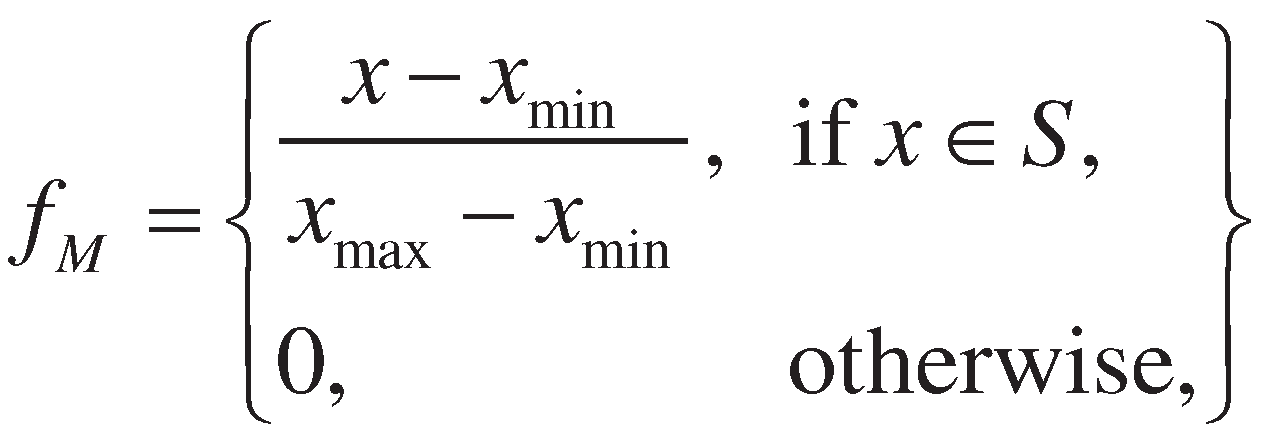
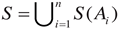
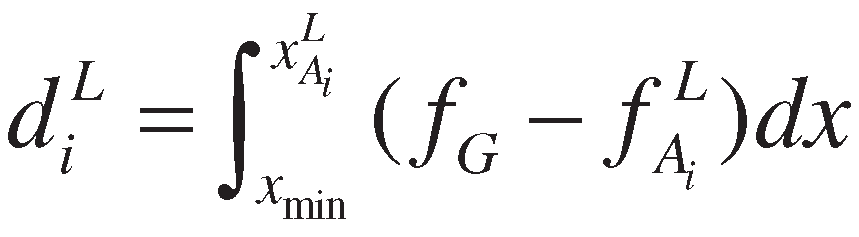
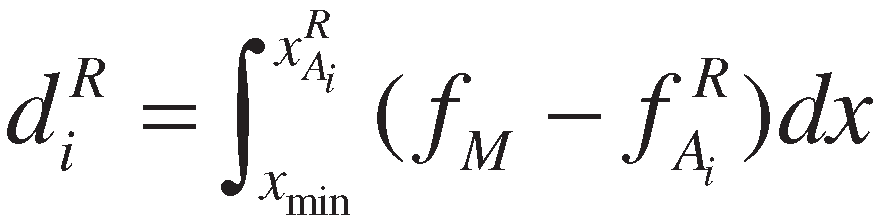
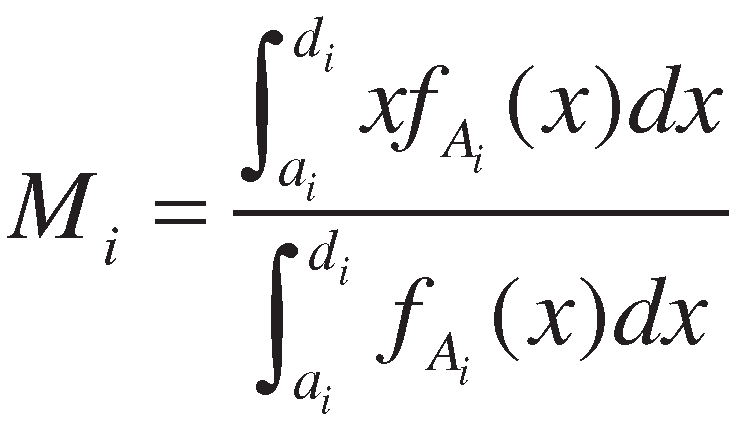
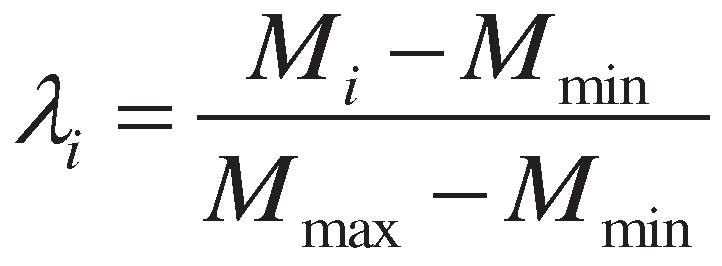
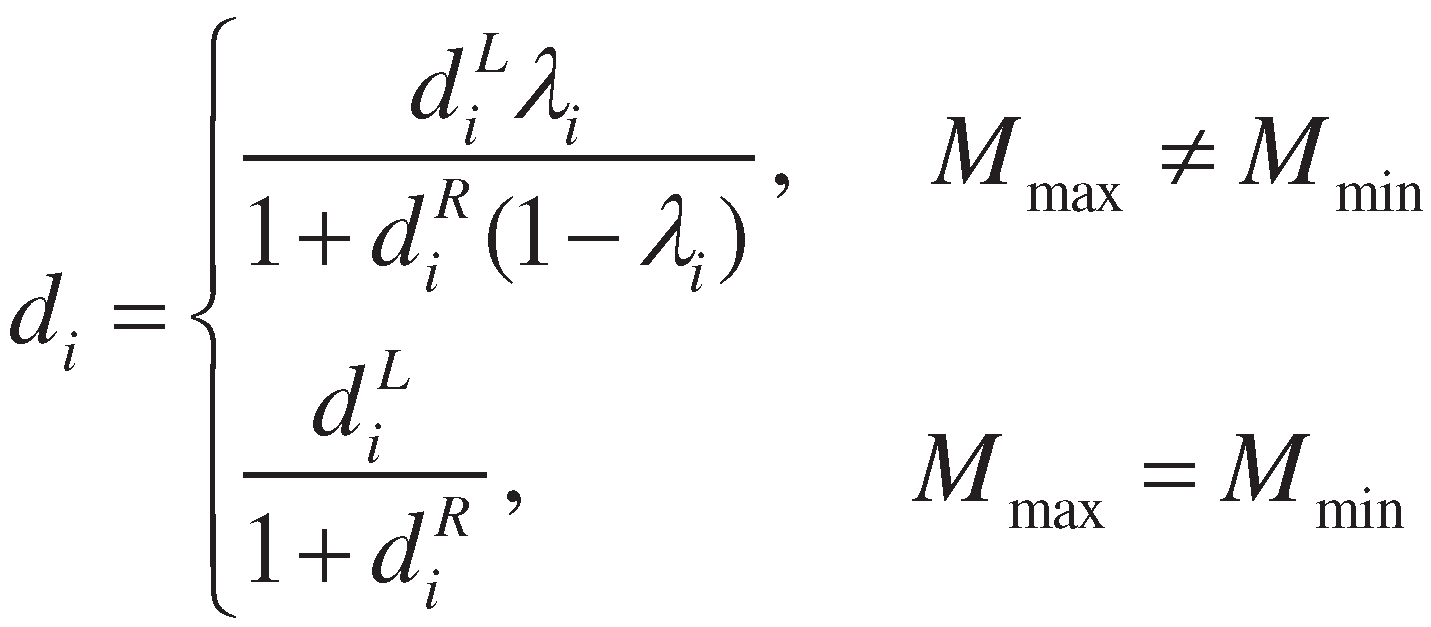
- (1)
- Ai ≻ Aj, if and only if di ≻ dj
- (2)
- Ai ≺ Aj, if and only if di ≺ dj
- (3)
- Ai ~ Aj, if and only if di = dj
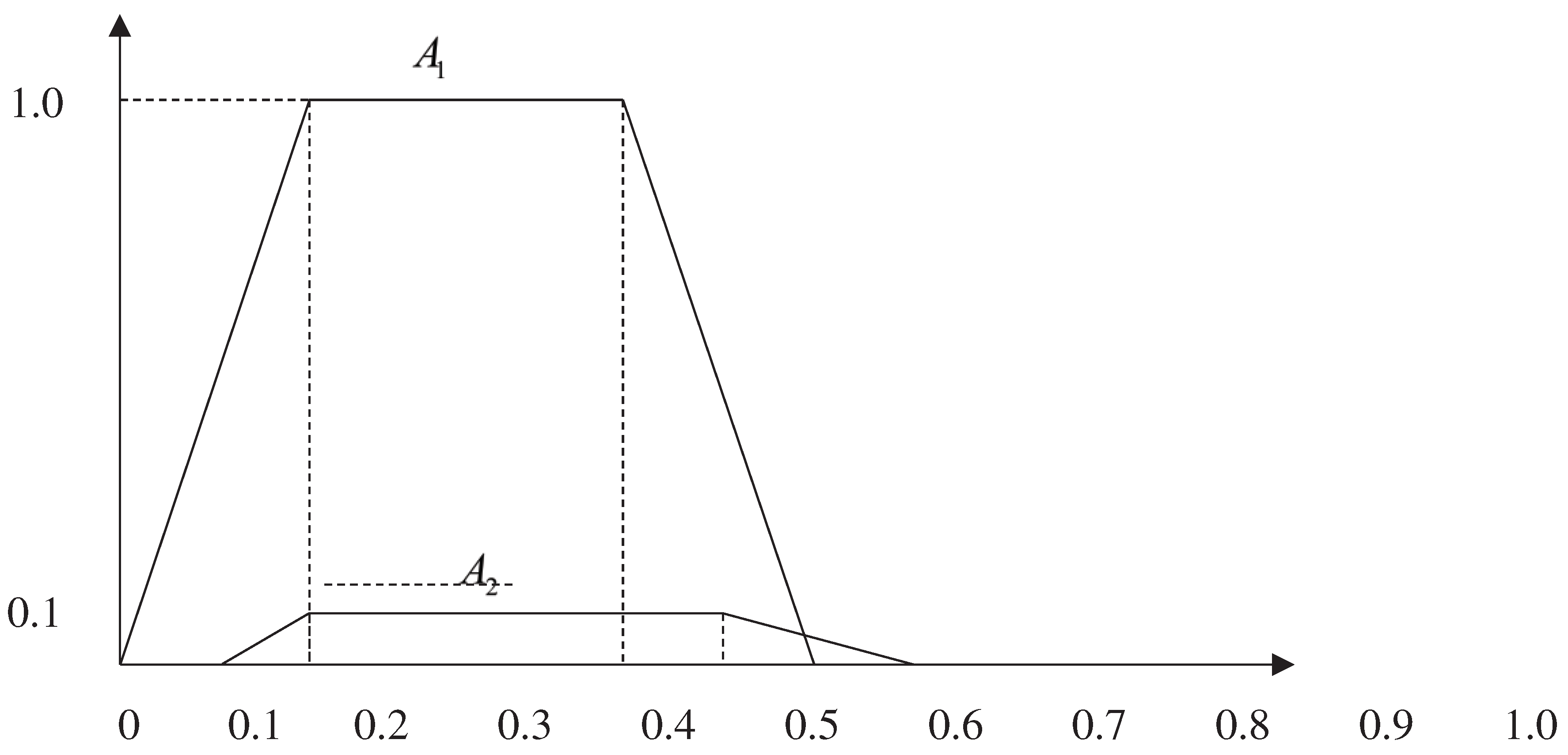
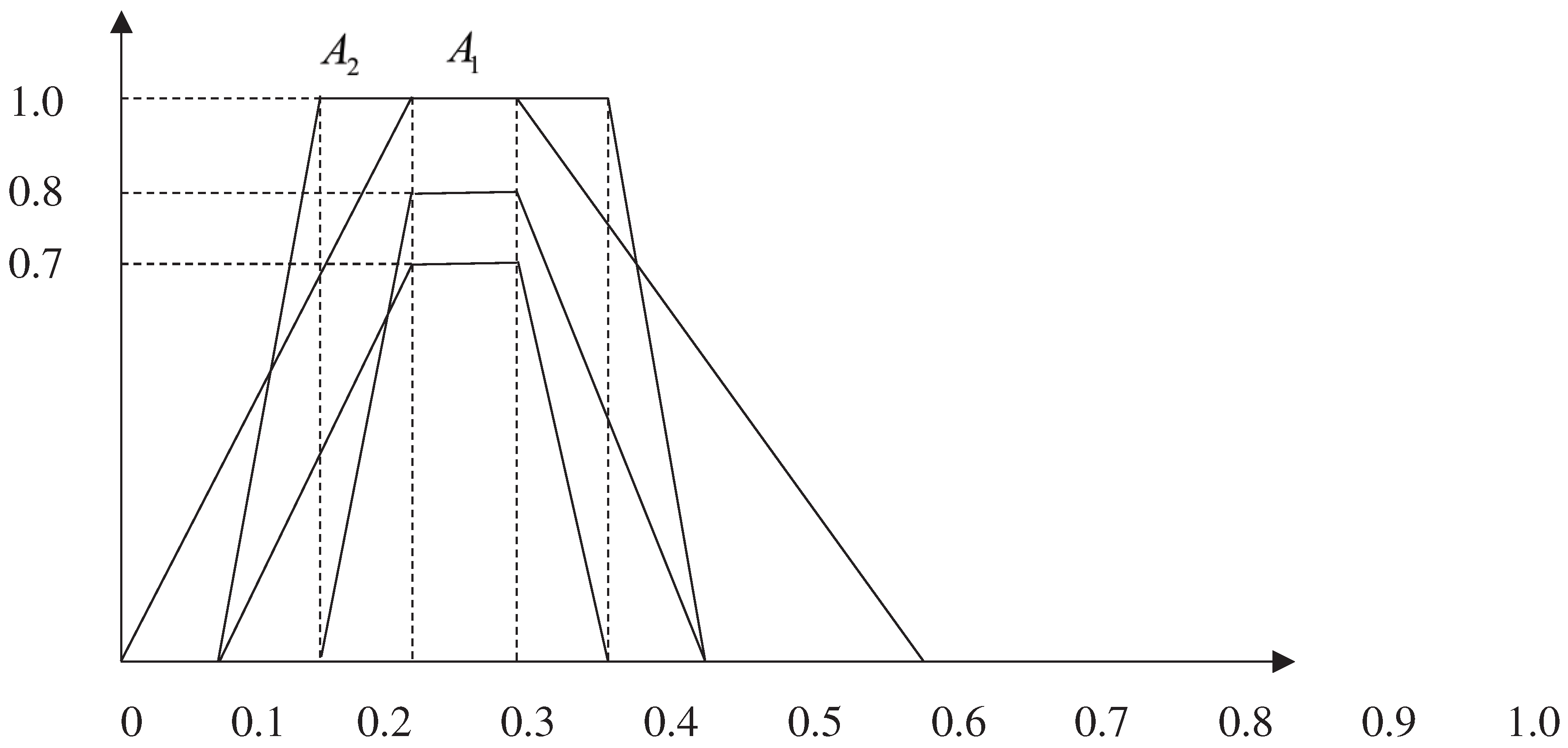
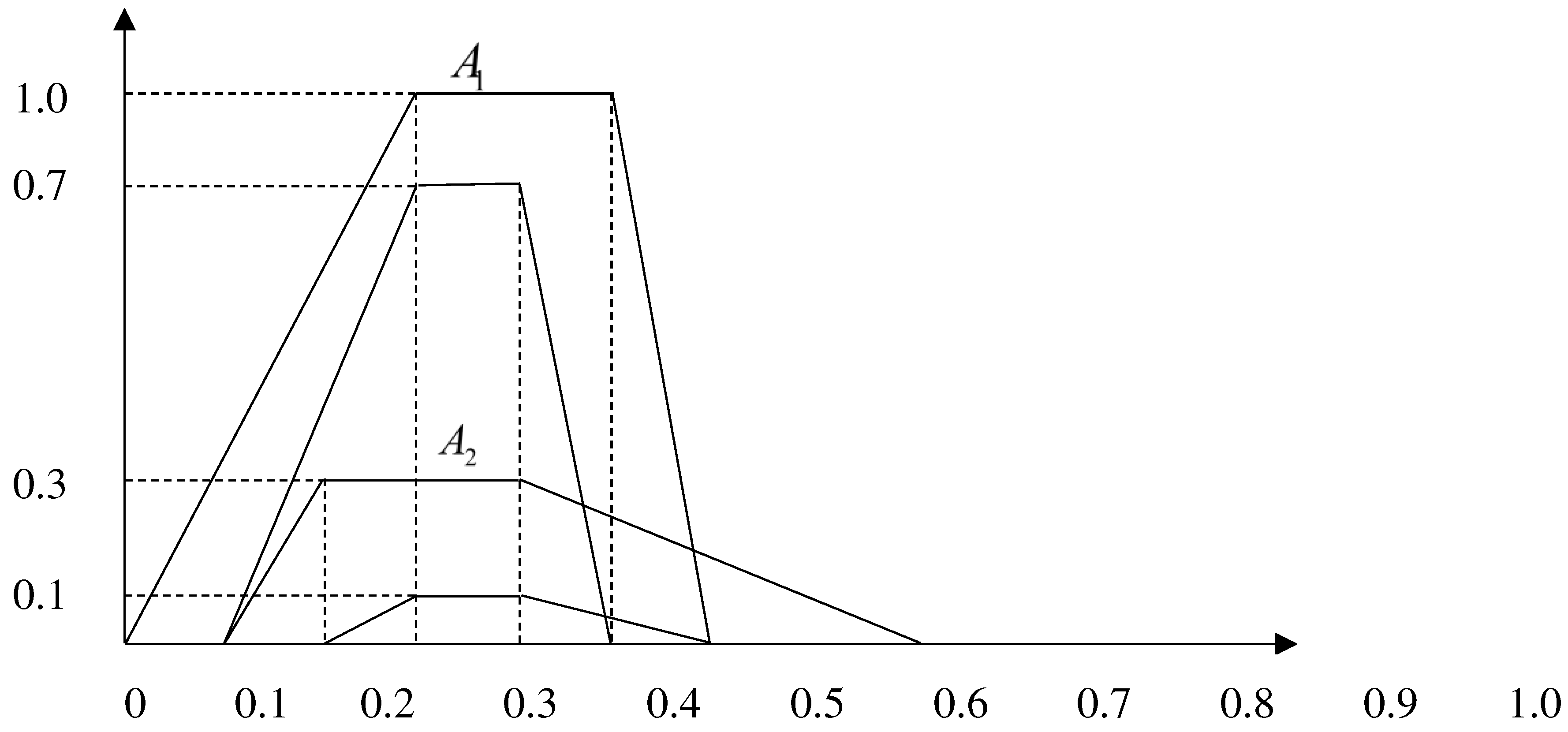
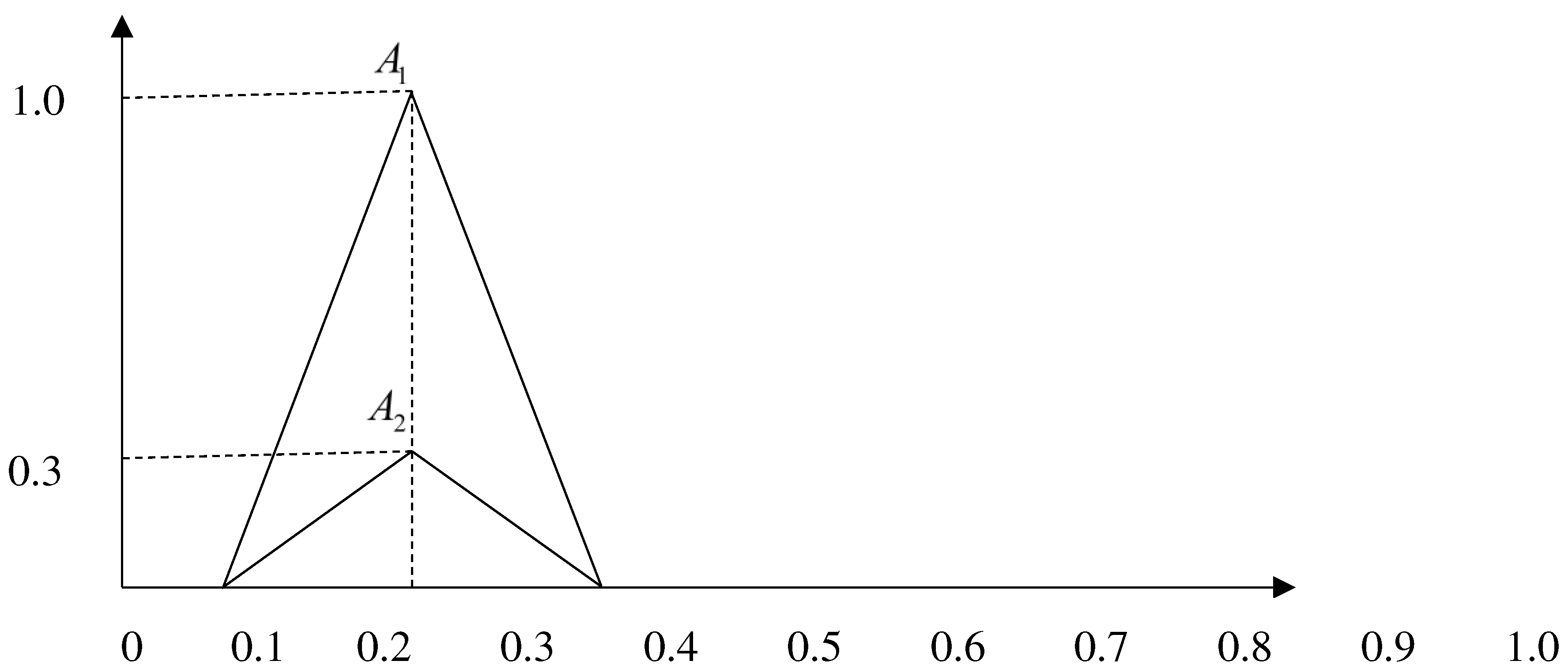
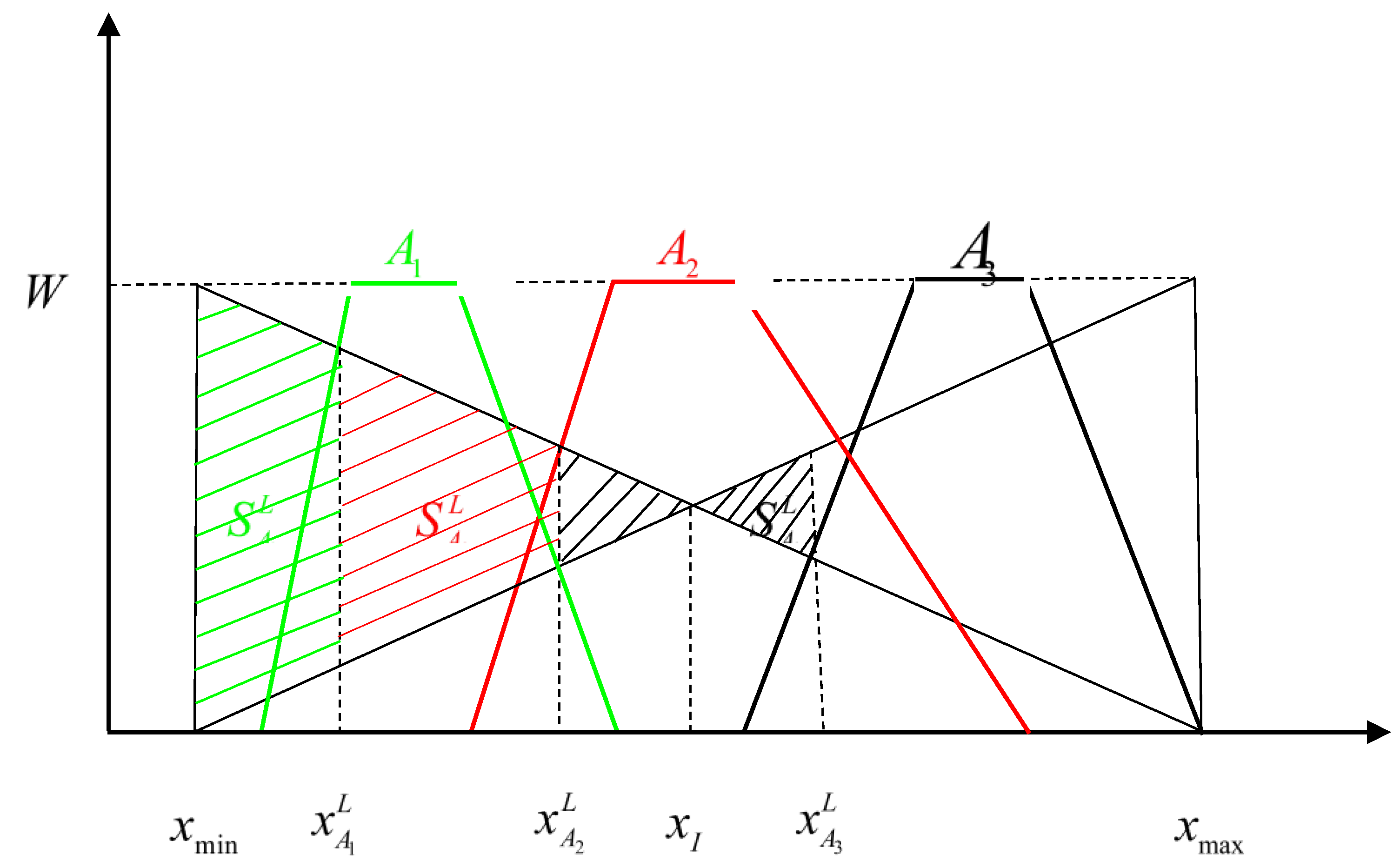
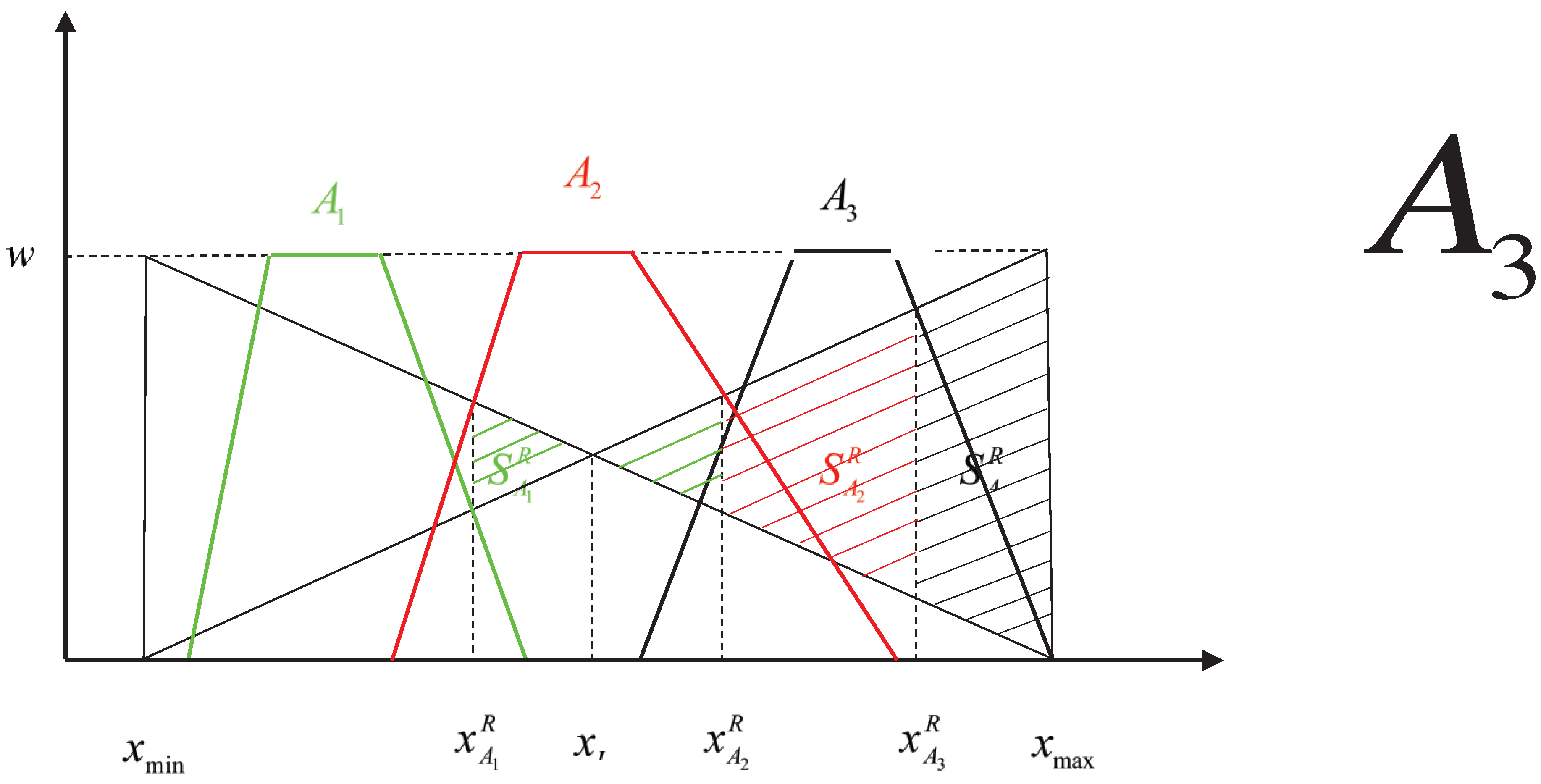
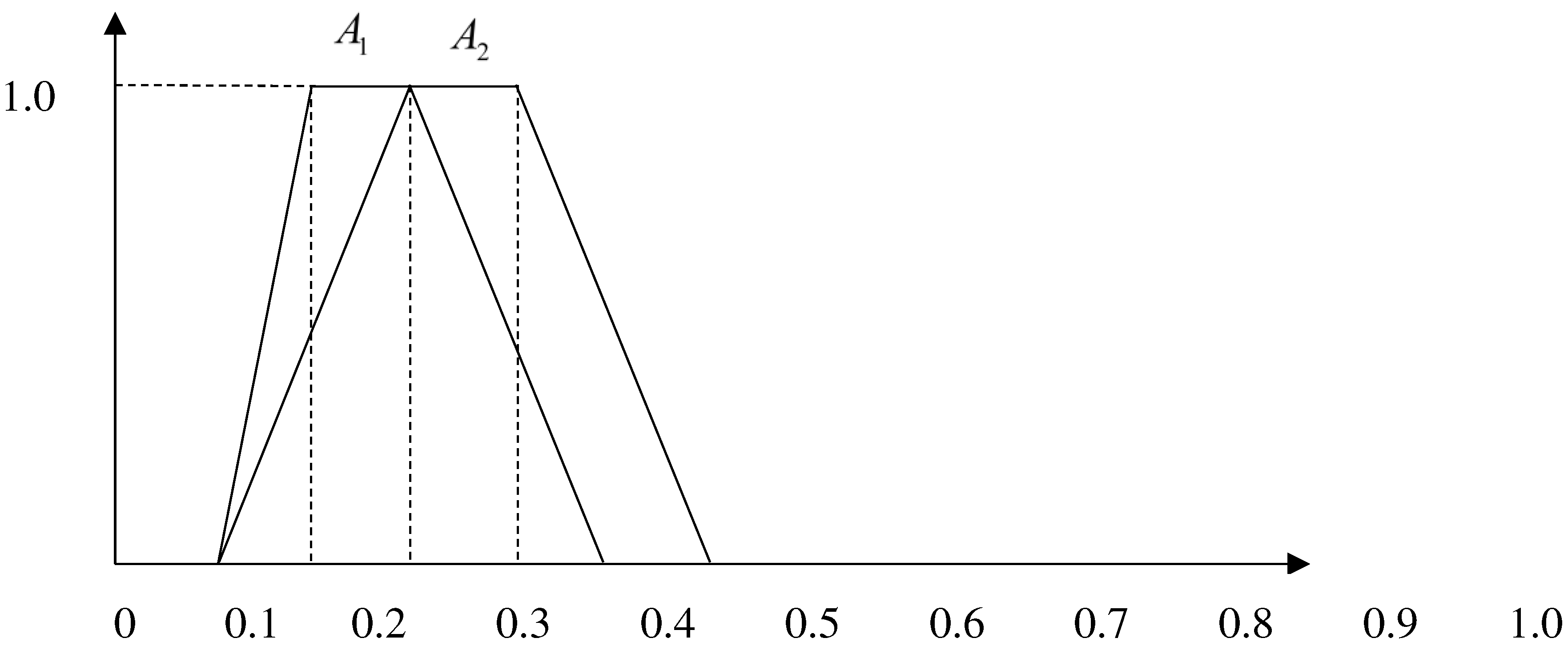
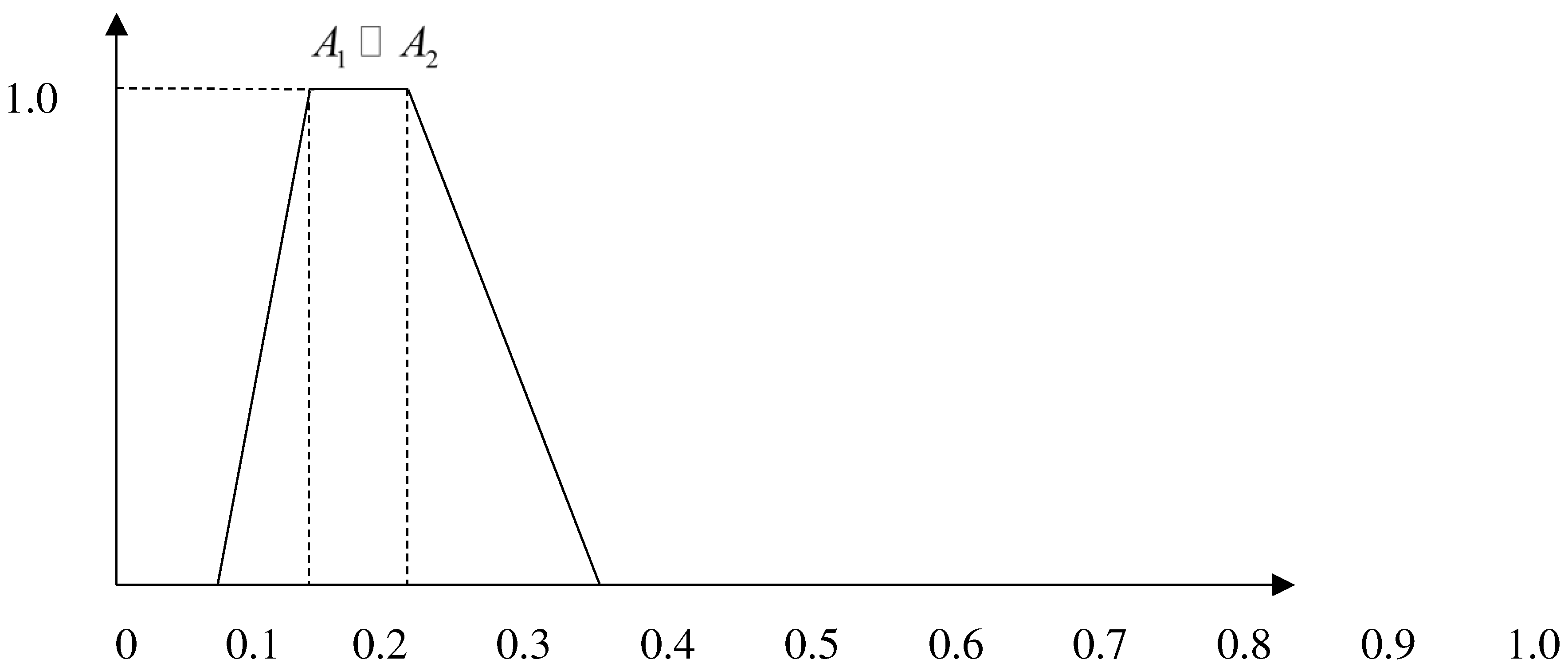
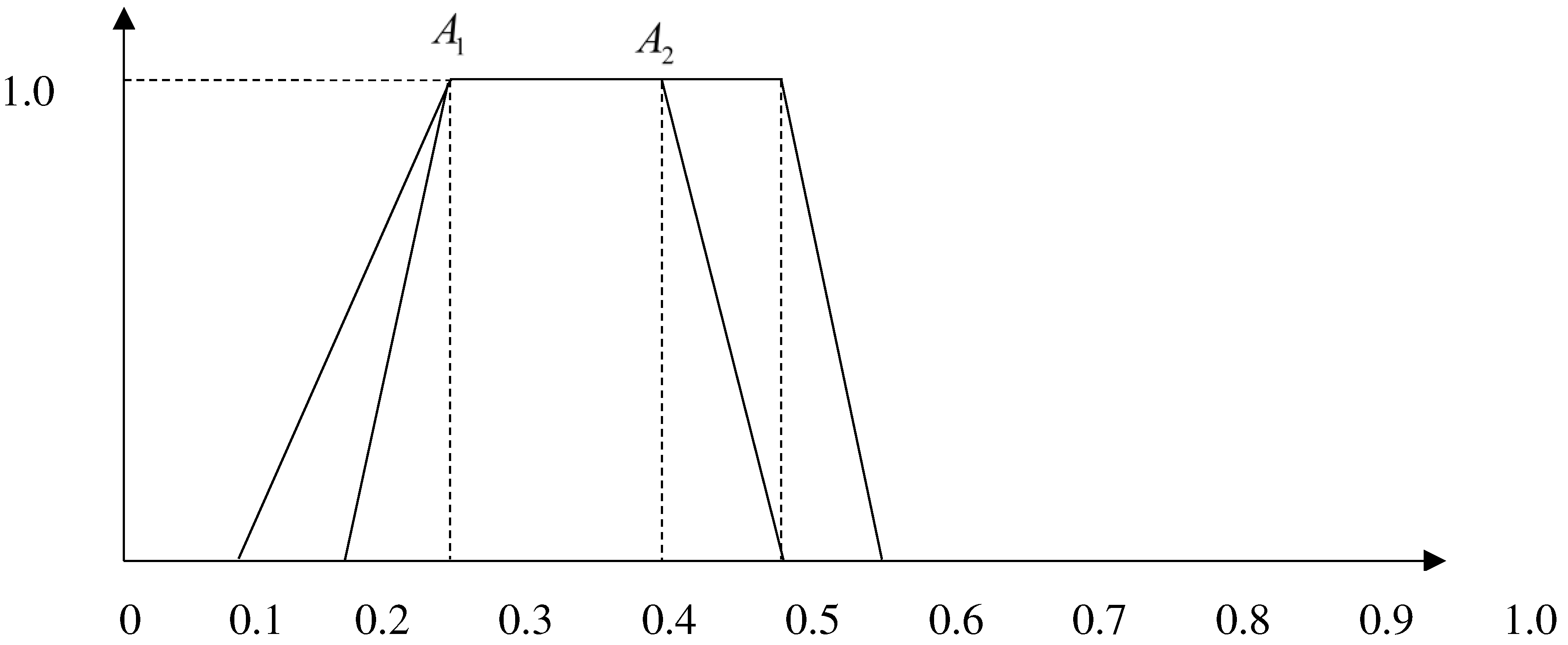
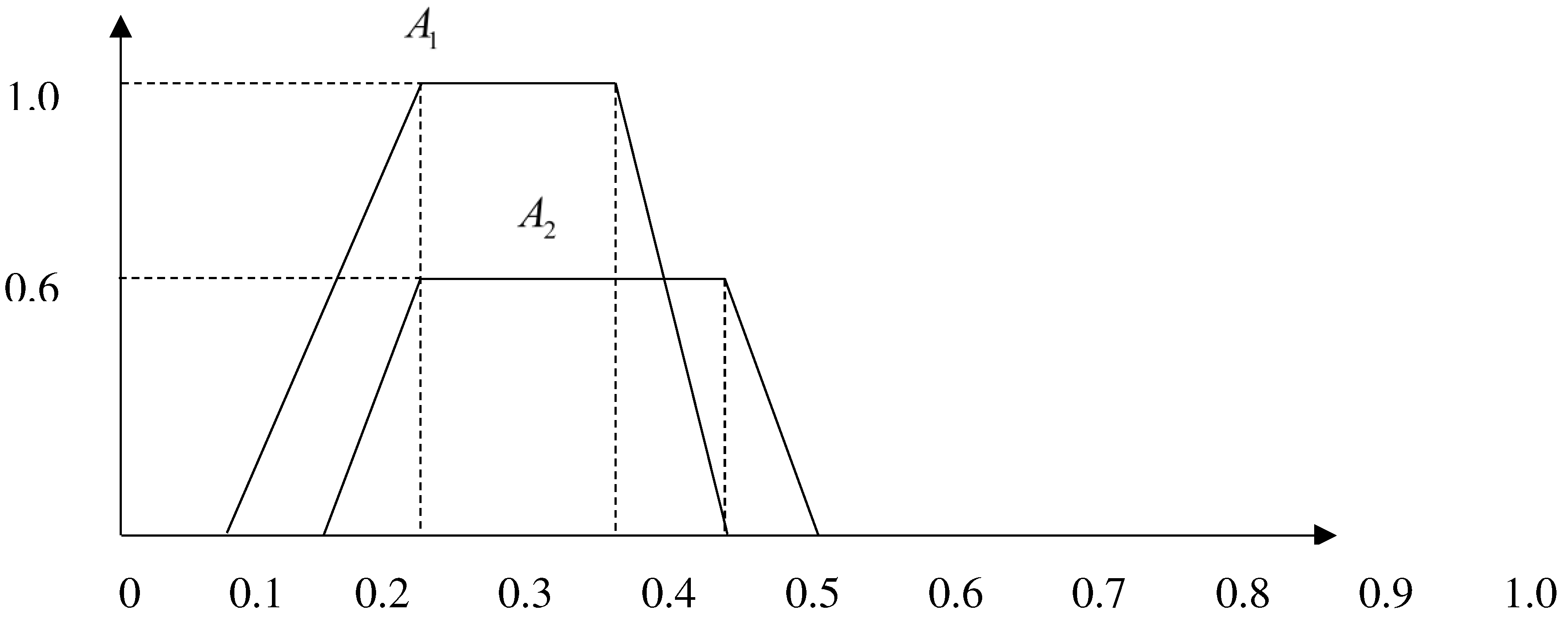
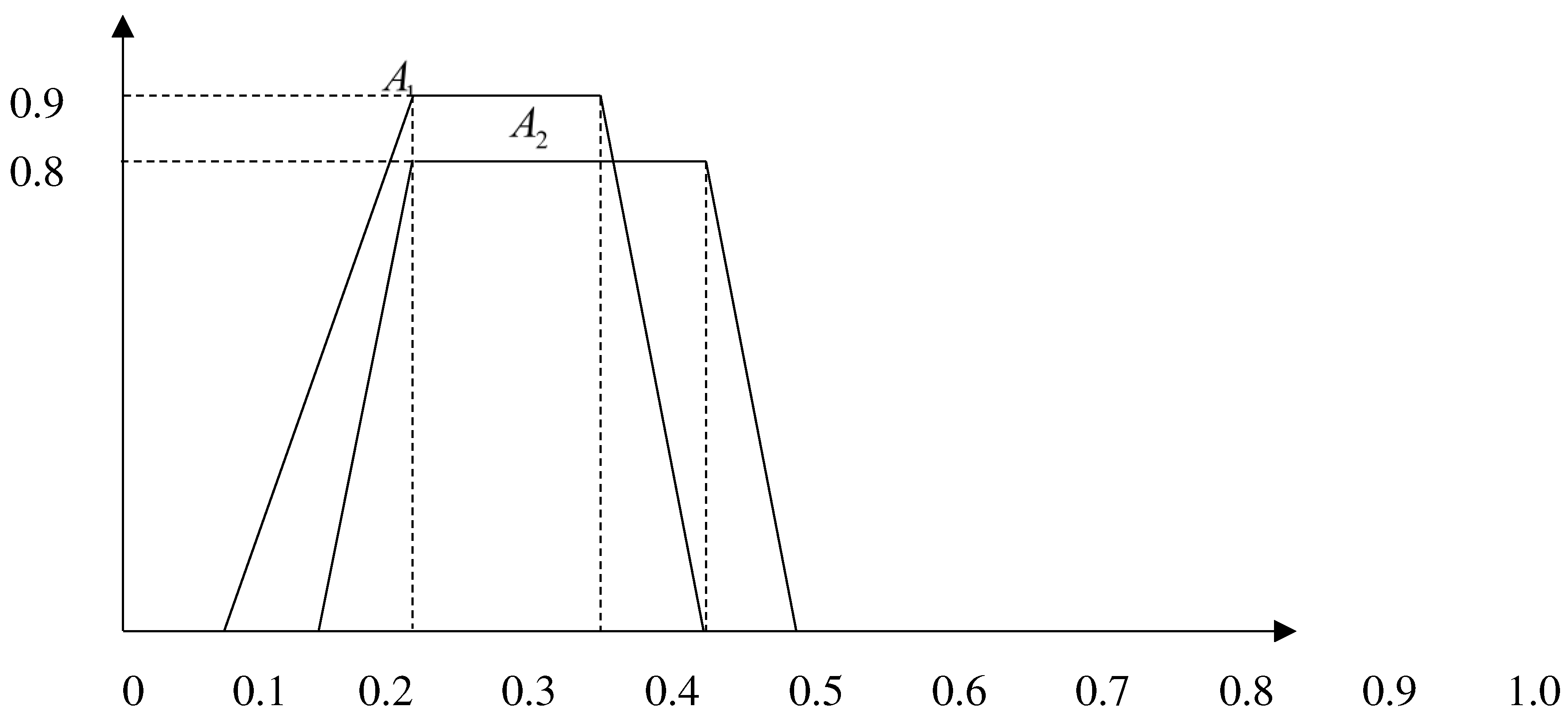
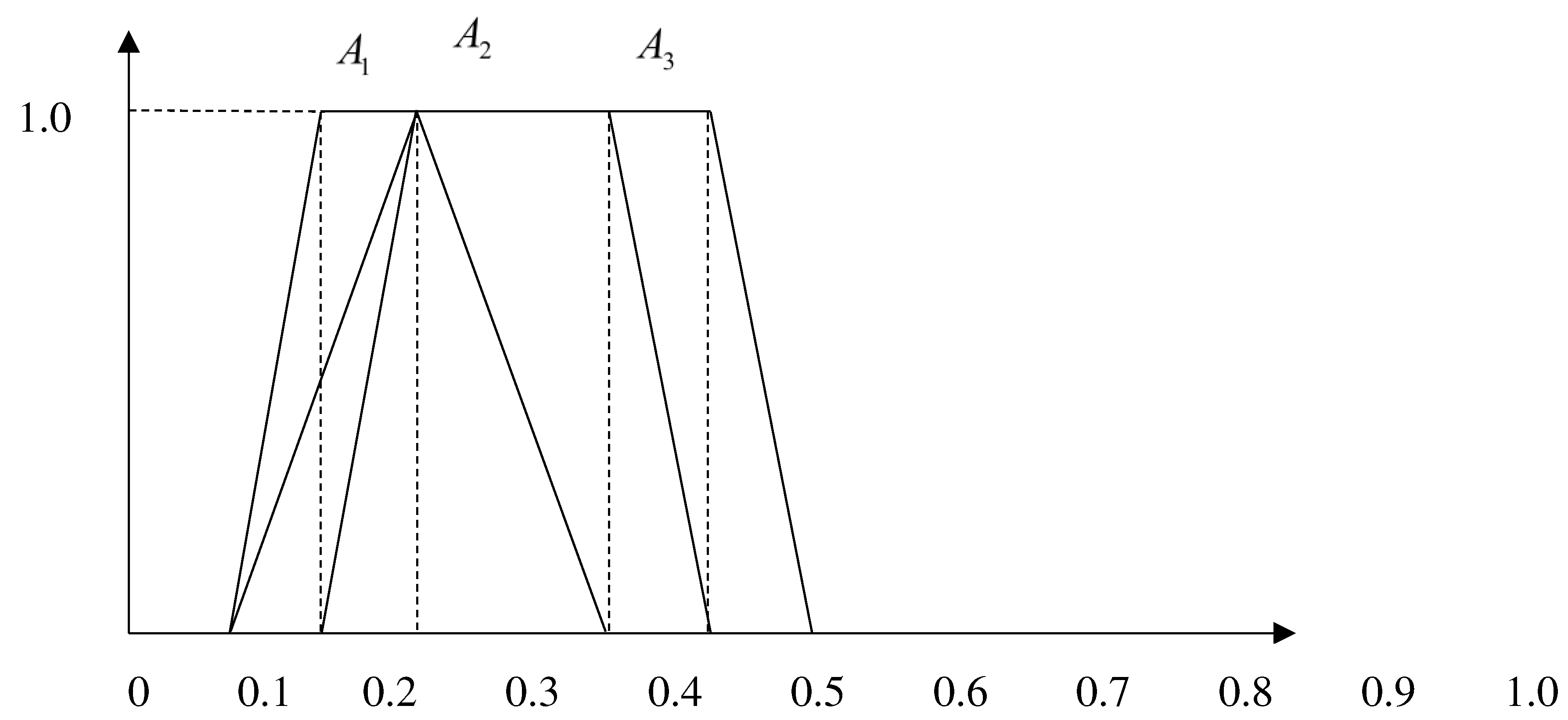
2.3. Limitations and shortcomings of existing methods
- Figure 2. Fuzzy number A1 and A2 of set 1 in example 2.
3. Proposed method
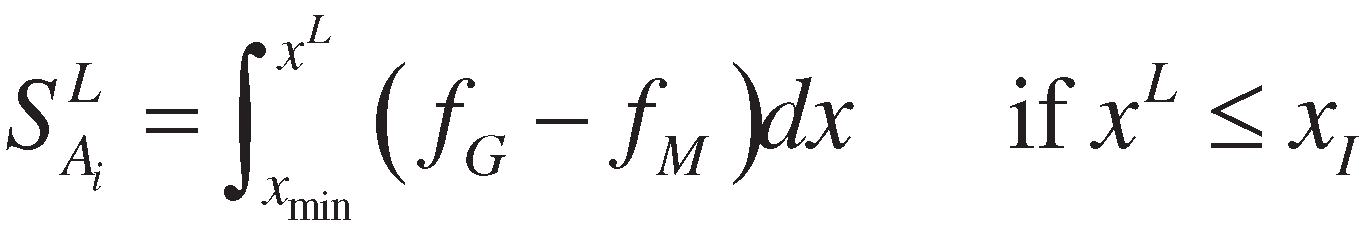
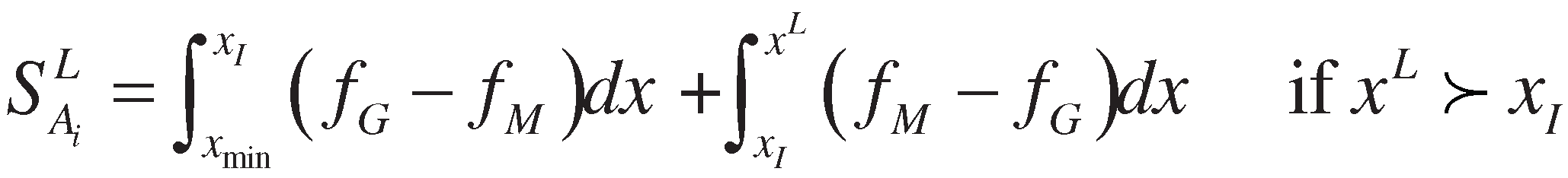
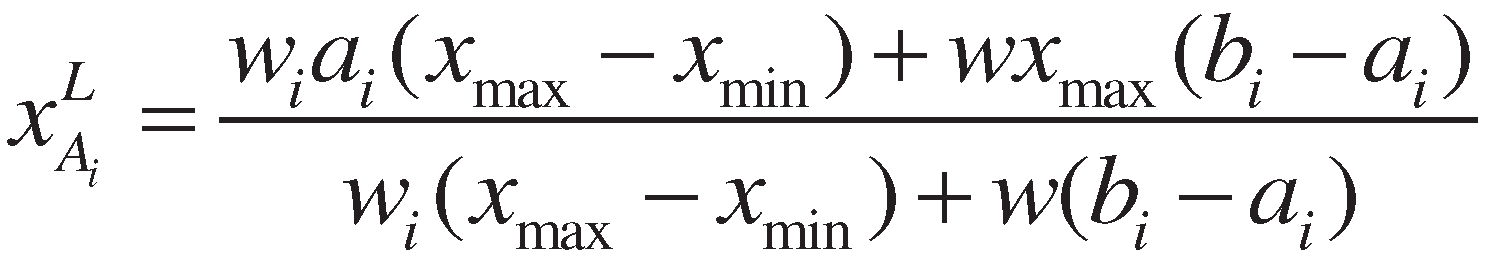
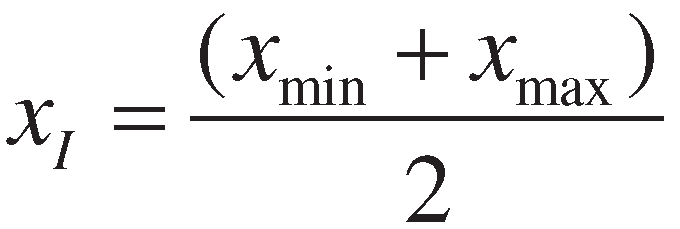
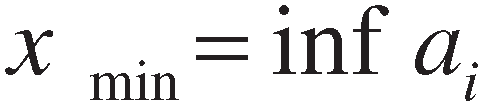
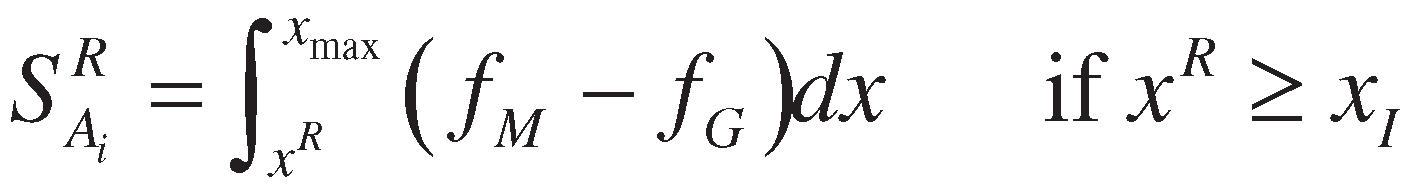
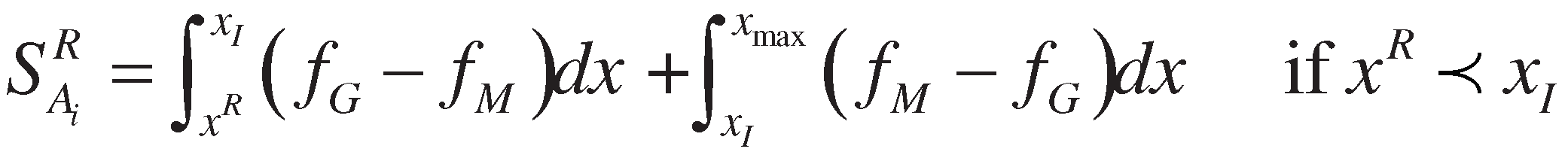
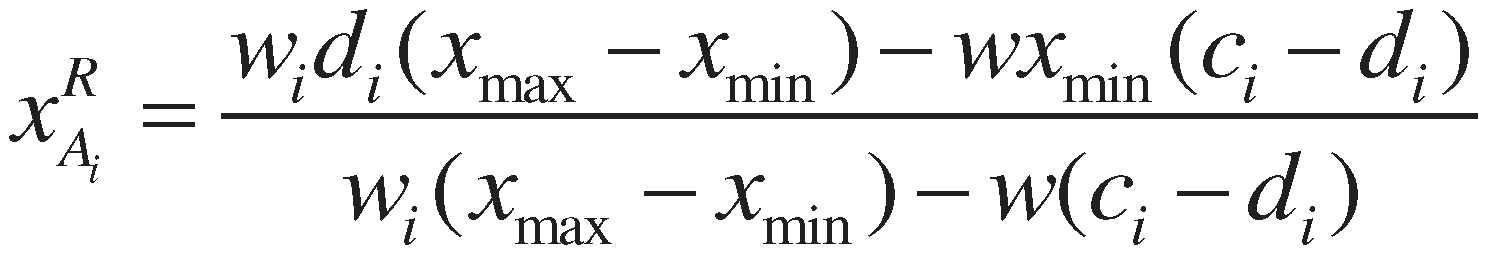
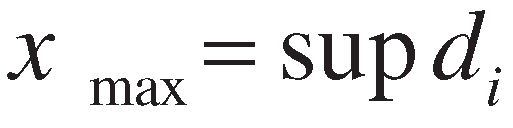
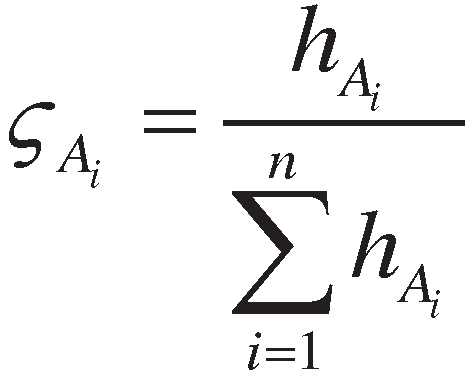
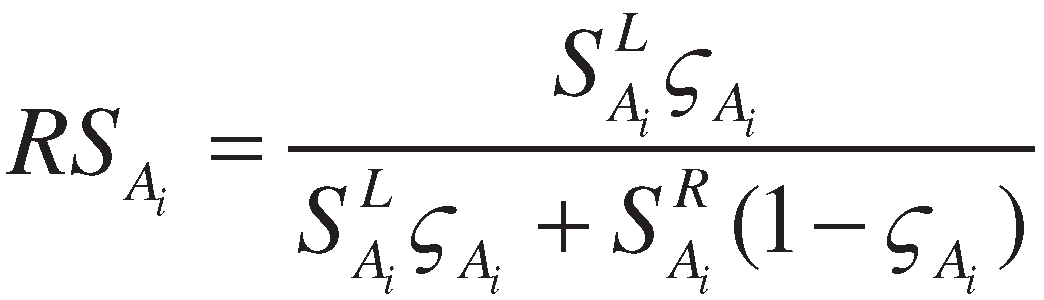
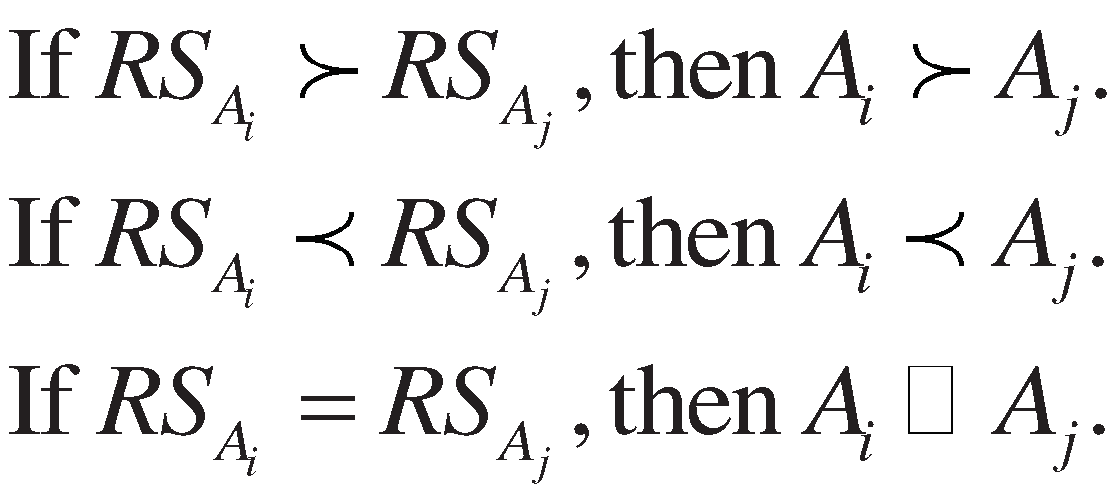
4. Numerical example and comparative study
4.1. Examples
4.2. Comparison
5. Conclusion
Funding
References
- Asady B (2010) The revised method of ranking LR fuzzy number based on deviation degree. Expert Systems with Applications, 37(7), 5056–5060. [CrossRef]
- Bortolan G, Degani R (1985) A review of some methods for ranking fuzzy subsets. Fuzzy Sets and Systems, 15(1), 1–19. [CrossRef]
- Brunelli M, Mezei J (2013) How different are ranking methods for fuzzy numbers ? A numerical study. International Journal of Approximate Reasoning, 54(5), 627–639. [CrossRef]
- Chen SH (1985) Ranking fuzzy numbers with maximizing set and minimizing set. Fuzzy Sets and Systems, 17(2), 113–129. [CrossRef]
- Chen SJ, Chen SM (2007) Fuzzy risk analysis based on the ranking of generalized trapezoidal fuzzy numbers. Applied Intelligence, 26(1), 1–11.
- Chen SM, Chen JH (2009) Fuzzy risk analysis based on ranking generalized fuzzy numbers with different heights and different spreads. Expert Systems with Applications, 36, 6833–6842. [CrossRef]
- Chen SM, Sanguansat K (2011) Analyzing fuzzy risk based on a new fuzzy ranking method between generalized fuzzy numbers. Expert Systems with Applications, 38, 2163–2171. [CrossRef]
- Chi HTX, Yu VF (2018) Ranking generalized fuzzy numbers based on centroid and rank index. Applied Soft Computing Journal, 68, 283–292. 68. [CrossRef]
- Chou SY, Dat LQ, Yu VF (2011) A revised method for ranking fuzzy numbers using maximizing set and minimizing set. Computers and Industrial Engineering, 61(4), 1342–1348. 1342. [CrossRef]
- Chu TC, Kysely M (2021) Ranking objectives of advertisements on Facebook by a fuzzy TOPSIS method. Electronic Commerce Research. 21(4), 881-916. [CrossRef]
- Chutia R (2017) Ranking of fuzzy numbers by using value and angle in the epsilon-deviation degree method. Applied Soft Computing Journal, 60, 706–721. [CrossRef]
- De A, Kundu P, Das S, Kar S (2020) A ranking method based on interval type-2 fuzzy sets for multiple attribute group decision making. Soft Computing, 24(1), 131–154. [CrossRef]
- Dubois D, Prade H (1978) Operations on fuzzy numbers. International Journal of Systems Science 9(6):613-626. 6: International Journal of Systems Science 9(6).
- Hajjari T, Abbasbandy S (2011) A note on “the revised method of ranking LR fuzzy number based on deviation degree.” Expert Systems with Applications, 38(10), 13491–13492. [CrossRef]
- He W, Rodríguez RM, Takáč Z, Martínez L (2023) Ranking of Fuzzy Numbers on the Basis of New Fuzzy Distance. International Journal of Fuzzy Systems. [CrossRef]
- Jain R (1977) A procedure for multiple-aspect decision making using fuzzy sets. International Journal of Systems Science, 8(1), 1–7. [CrossRef]
- Kaufmann A, Gupta MM (1985, 1991) Introduction to fuzzy arithmetic: theory and application. Van Nostrand Reinhold, New York. [CrossRef]
- Kumar A, Singh P, Kaur P, Kaur A (2011) RM approach for ranking of L-R type generalized fuzzy numbers. Soft Computing, 15(7), 1373–1381. 1373. [CrossRef]
- Liou TS, Wang MJJ (1992) Ranking fuzzy numbers with integral value. Fuzzy Sets and Systems, 50(3), 247–255. [CrossRef]
- Nejad AM, Mashinchi M (2011) Ranking fuzzy numbers based on the areas on the left and the right sides of fuzzy number. Computers and Mathematics with Applications, 61(2), 431–442. [CrossRef]
- Nguyen HT, Chu TC (2023) Ranking startups using DEMATEL-ANP-Based fuzzy PROMETHEE II, Axioms, 12(6), 1-34. [CrossRef]
- Revathi M, Valliathal M (2021) Non-normal fuzzy number analysis in various levels using centroid method for fuzzy optimization. Soft Computing, 25(14), 8957–8969. [CrossRef]
- Seghir F (2021) FDMOABC: Fuzzy discrete multi-objective artificial bee colony approach for solving the non-deterministic QoS-driven web service composition problem. Expert Systems with Applications, 167(2021), 114413. [CrossRef]
- Wang X, Kerre EE (2001) Reasonable properties for the ordering of fuzzy quantities ( I ). Fuzzy Sets and Systems 118(2001), 375–385. [CrossRef]
- Wang YM, Luo Y (2009) Area ranking of fuzzy numbers based on positive and negative ideal points. Computers and Mathematics with Applications, 58(9), 1769–1779. [CrossRef]
- Wang ZX, Liu YJ, Fan ZP, Feng B (2009) Ranking L-R fuzzy number based on deviation degree. Information Sciences, 179(13), 2070–2077. [CrossRef]
- Xu P, Su X, Wu J, Sun X, Zhang Y, Deng Y (2012). A note on ranking generalized fuzzy numbers. Expert Systems with Applications, 39(7), 6454–6457. [CrossRef]
- Yu VF, Chi HTX, Dat LQ, Phuc PNK, Shen CW (2013) Ranking generalized fuzzy numbers in fuzzy decision making based on the left and right transfer coefficients and areas. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 37(16–17), 8106–8117. [CrossRef]
- Yu VF, Chi HTX, Shen CW (2013) Ranking fuzzy numbers based on epsilon-deviation degree. Applied Soft Computing Journal, 13(8), 3621–3627. [CrossRef]


| Fuzzy numbers | SL | SR | ȝ | RS | Rank | |
| Ex.6 | A1 (0.1,0.2,0.3,0.5;1) | 0.069 | 0.122 | 0.500 | 0.362 | 2 |
| A2(0.1,0.3,0.4,0.6;1) | 0.102 | 0.102 | 0.500 | 0.500 | 1 | |
| Ex.7 | A1(0.1,0.2,0.3,0.5;1) | 0.064 | 0.089 | 0.500 | 0.419 | 1 |
| A2(0.1,0.2,0.3,0.5;1) | 0.064 | 0.089 | 0.500 | 0.419 | 1 | |
| Ex.8 | A1 (0.1,0.2,0.3,0.5;1) | 0.044 | 0.065 | 0.556 | 0.460 | 1 |
| A2(0.1,0.2,0.3,0.5;0.8) | 0.051 | 0.071 | 0.444 | 0.365 | 2 | |
| Ex.9 | A1(0.1,0.3,0.5,0.6;1) | 0.113 | 0.122 | 0.500 | 0.479 | 2 |
| A2(0.2,0.3,0.6,0.7;1) | 0.122 | 0.073 | 0.500 | 0.625 | 1 | |
| Ex.10 | A1(0.1,0.3,0.5,0.6;1) | 0.050 | 0.066 | 0.625 | 0.558 | 1 |
| A2(0.2,0.3,0.6,0.7;0.6) | 0.073 | 0.044 | 0.375 | 0.500 | 2 | |
| Ex.11 | A1(0.1,0.3,0.5,0.6;0.9) | 0.085 | 0.096 | 0.529 | 0.499 | 2 |
| A2(0.2,0.3,0.6,0.7;0.8) | 0.098 | 0.059 | 0.471 | 0.597 | 1 | |
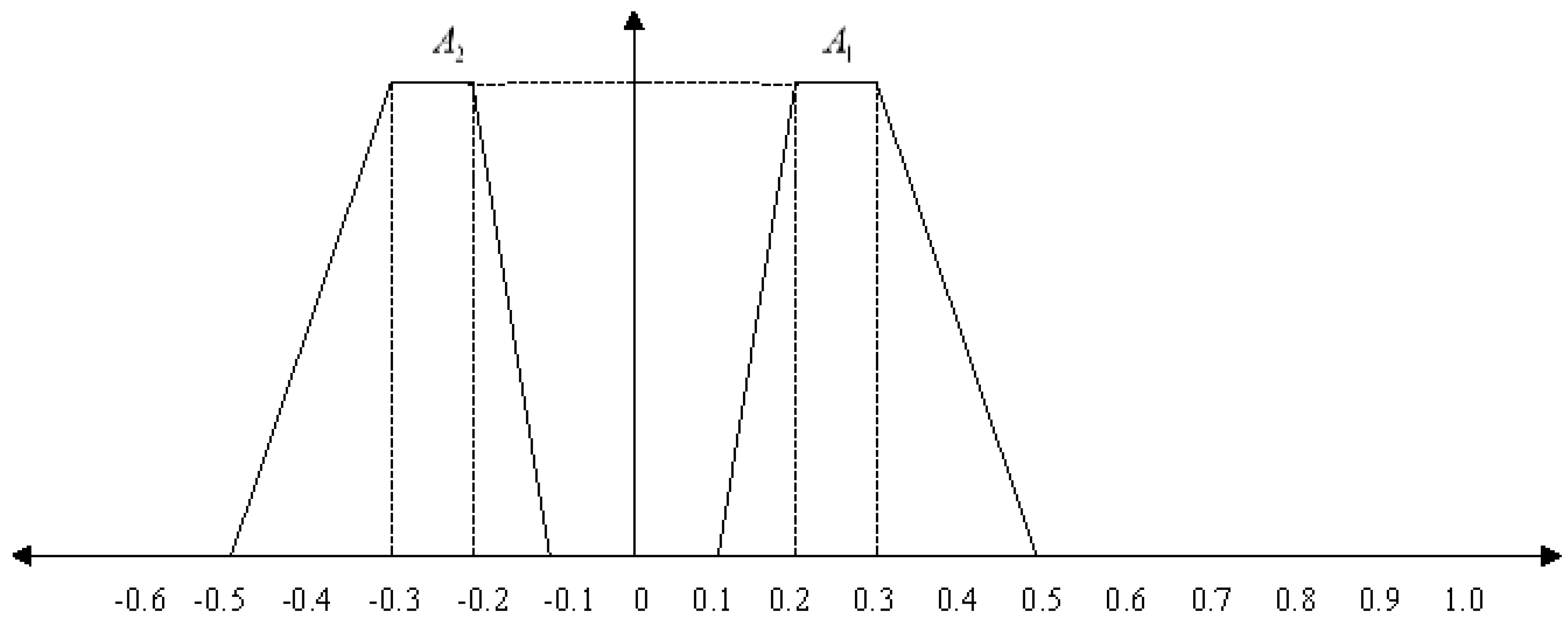
| Ex.12 | A1(0.1,0.2,0.3,0.5;1) | 0.231 | 0.139 | 0.500 | 0.625 | 1 |
| A2(-0.5,-0.3,-0.2,-0.1;1) | 0.139 | 0.231 | 0.500 | 0.375 | 2 | |
| Ex.13 | A1(0.1,0.2,0.3,0.5;1) | 0.073 | 0.150 | 0.333 | 0.197 | 3 |
| A2(0.1,0.3,0.5,0.6;1) | 0.113 | 0.122 | 0.333 | 0.315 | 2 | |
| A3(0.2,0.3,0.6,0.7;1) | 0.122 | 0.073 | 0.333 | 0.455 | 1 |
| Set | FNs | Ut | R | DD | R | RIA | R | RDD | R | SLR | R | MEDD | R | RS | R |
| Set 5 | A1(0.1,0.3,0.3,0.5;1) | 0.375 | 2 | 0.000 | 2 | 0.250 | 2 | 0.222 | 2 | 0.075 | 2 | 0.041 | 2 | 0.429 | 2 |
| A2(0.3,0.5,0.5,0.7;1) | 0.625 | 1 | 0.300 | 1 | 0.750 | 1 | 0.571 | 1 | 0.303 | 1 | 24.462 | 1 | 0.571 | 1 | |
| Set 6 | A1(0.1,0.3,0.3,0.5;1) | 0.500 | 1 | 0.063 | 1 | 0.500 | 1 | 0.286 | 1 | 0.130 | 1 | 1.000 | 1 | 0.500 | 1 |
| A2(0.1,0.3,0.3,0.5;1) | 0.500 | 1 | 0.063 | 1 | 0.500 | 1 | 0.286 | 1 | 0.130 | 1 | 1.000 | 1 | 0.500 | 1 | |
| Set 7 | A1(0.1,0.3,0.3,0.5;0.8) | 0.400 | 1 | 0.063 | 1 | 0.500 | 1 | 0.242 | 2 | 0.242 | 2 | 0.126 | 2 | 0.444 | 2 |
| A2(0.1,0.3,0.3,0.5;1) | 0.400 | 1 | 0.061 | 2 | 0.500 | 1 | 0.286 | 1 | 0.286 | 1 | 9.488 | 1 | 0.556 | 1 | |
| Set 8 | A1(-0.5,-0.3,-0.3,-0.1;1) | 0.250 | 2 | 0.000 | 2 | 0.125 | 2 | 0.154 | 2 | 0.035 | 2 | 0.015 | 2 | 0.333 | 2 |
| A2(0.1,0.3,0.3,0.5;1) | 0.750 | 1 | 1.333 | 1 | 0.875 | 1 | 1.143 | 1 | 0.679 | 1 | 65.091 | 1 | 0.667 | 1 | |
| Set 9 | A1(0.3,0.5,0.5,1.0;1) | 0.503 | 1 | 0.327 | 1 | 0.545 | 1 | 0.514 | 1 | 0.285 | 1 | 1.185 | 1 | 0.502 | 1 |
| A2(0.1,0.6,0.6,0.8;1) | 0.497 | 2 | 0.000 | 2 | 0.455 | 2 | 0.436 | 2 | 0.196 | 2 | 0.844 | 2 | 0.498 | 2 | |
| Set 10 | A1(0.0,0.4,0.6,0.8;1) | 0.517 | 3 | 0.000 | 3 | 0.500 | 3 | 0.474 | 3 | 0.229 | 3 | 0.087 | 3 | 0.349 | 3 |
| A2(0.2,0.5,0.5,0.9;1) | 0.554 | 2 | 0.313 | 1 | 0.636 | 2 | 0.600 | 2 | 0.363 | 1 | 0.498 | 2 | 0.363 | 2 | |
| A3(0.1,0.6,0.7,0.8;1) | 0.614 | 1 | 0.207 | 2 | 0.700 | 1 | 0.647 | 1 | 0.362 | 2 | 2.176 | 1 | 0.434 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




