Submitted:
18 September 2023
Posted:
19 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- To assess the characteristics of existing evidence on PLHP for pwCVDs globally.
- To identify the interventional approaches that have been used in PLHP strategies for pwCVDs
- To evaluate the type of population groups included in the PLHP research.
2. Methodology
2.1. Identifying the Research Question
2.2. Identifying Relevant Studies (Database and Search Strategy)
2.3. Eligibility Criteria
2.4. Study Selection (Screening)
2.5. Data Charting (Data Extraction)
2.6. Quality Appraisal
2.7. Collating, Summarising, and Reporting
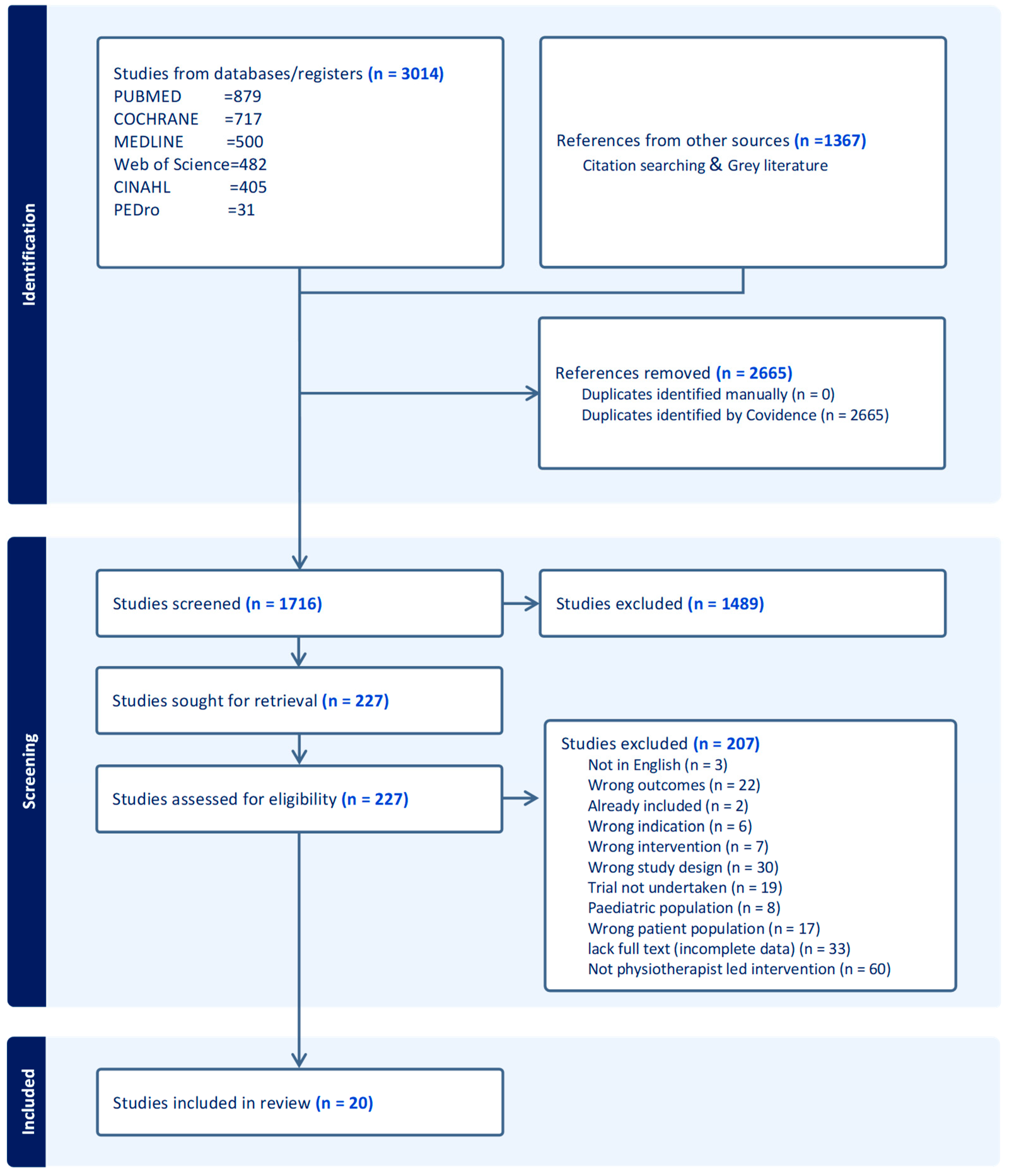
3. Results
3.1. Literature Search and Included Studies
3.2. Characteristics of Included Studies
3.3. Characteristics of the Included Interventions
4. Discussion
4.1. Implications for Clinical Practice
4.2. Research Implications
4.3. Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Medline Search Strings
References
- Piepoli, M.F.; Hoes, A.W.; Agewall, S.; Albus, C.; Brotons, C.; Catapano, A.L.; Cooney, M.-T.; Corrà, U.; Cosyns, B.; Deaton, C.; et al. 2016 European Guidelines on cardiovascular disease prevention in clinical practiceThe Sixth Joint Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology and Other Societies on Cardiovascular Disease Prevention in Clinical Practice (constituted by representatives of 10 societies and by invited experts)Developed with the special contribution of the European Association for Cardiovascular Prevention & Rehabilitation (EACPR). Eur Heart J 2016, 37, 2315–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Non communicable diseases Available online:. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/noncommunicable-diseases (accessed on 19 July 2021).
- Tulu, S.N.; Al Salmi, N.; Jones, J. Understanding cardiovascular disease in day-to-day living for African people: a qualitative metasynthesis. BMC Public Health 2021, 21, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) Available online:. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cardiovascular-diseases-(cvds) (accessed on 21 November 2021).
- Gaziano, T.A. Reducing The Growing Burden Of Cardiovascular Disease In The Developing World. Health Affairs 2007, 26, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donnell, M.J.; Chin, S.L.; Rangarajan, S.; Xavier, D.; Liu, L.; Zhang, H.; Rao-Melacini, P.; Zhang, X.; Pais, P.; Agapay, S.; et al. Global and regional effects of potentially modifiable risk factors associated with acute stroke in 32 countries (INTERSTROKE): a case-control study. The Lancet 2016, 388, 761–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feigin, V.L.; Roth, G.A.; Naghavi, M.; Parmar, P.; Krishnamurthi, R.; Chugh, S.; Mensah, G.A.; Norrving, B.; Shiue, I.; Ng, M.; et al. Global burden of stroke and risk factors in 188 countries, during 1990–2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. The Lancet Neurology 2016, 15, 913–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strong, K.; Mathers, C.; Bonita, R. Preventing stroke: saving lives around the world. The Lancet Neurology 2007, 6, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, K.M.; Wolfe, C.D.A.; Rudd, A.G.; Heuschmann, P.U.; Kolominsky-Rabas, P.L.; Grieve, A.P. Risk and Cumulative Risk of Stroke Recurrence: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Stroke 2011, 42, 1489–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhamoon, M.S.; Sciacca, R.R.; Rundek, T.; Sacco, R.L.; Elkind, M.S.V. Recurrent stroke and cardiac risks after first ischemic stroke: The Northern Manhattan Study. Neurology 2006, 66, 641–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, Y.; Guo, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Huang, Z.; Sun, S.; Kowal, P.; Shi, Y.; Wu, F. Cardiovascular disease (CVD) and associated risk factors among older adults in six low-and middle-income countries: results from SAGE Wave 1. BMC Public Health 2018, 18, 778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, S.; Hawken, S.; Ôunpuu, S.; Dans, T.; Avezum, A.; Lanas, F.; McQueen, M.; Budaj, A.; Pais, P.; Varigos, J.; et al. Effect of potentially modifiable risk factors associated with myocardial infarction in 52 countries (the INTERHEART study): case-control study. The Lancet 2004, 364, 937–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigna, J.J.; Noubiap, J.J. The rising burden of non-communicable diseases in sub-Saharan Africa. The Lancet Global Health 2019, 7, e1295–e1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowry, A.D.K.; Lewey, J.; Dugani, S.B.; Choudhry, N.K. The Burden of Cardiovascular Disease in Low- and Middle-Income Countries: Epidemiology and Management. Canadian Journal of Cardiology 2015, 31, 1151–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 2019 ACC/AHA Guideline on the Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease - American College of Cardiology Available online:. Available online: https://www.acc.org/latest-in-cardiology/ten-points-to-remember/2019/03/07/16/00/2019-acc-aha-guideline-on-primary-prevention-gl-prevention (accessed on 15 August 2020).
- Li, D.; Jia, Y.; Yu, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, F.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Q.; Liao, X.; Zeng, Z.; Wan, Z.; et al. Adherence to a Healthy Lifestyle and the Risk of All-Cause Mortality and Cardiovascular Events in Individuals With Diabetes: The ARIC Study. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 698608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuett, K.A.; Lehrke, M.; Marx, N.; Burgmaier, M. High-Risk Cardiovascular Patients: Clinical Features, Comorbidities, and Interconnecting Mechanisms. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellmann, B.; Lin, T.; Greissinger, K.; Rottner, L.; Rillig, A.; Zimmerling, S. The Beneficial Effects of Cardiac Rehabilitation. Cardiol Ther 2020, 9, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietary Restrictions and Nutrition in the Prevention and Treatment of Cardiovascular Disease | Circulation Research Available online:. Available online: https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.118.313352 (accessed on 1 August 2021).
- Darden, D.; Richardson, C.; Jackson, E.A. Physical Activity and Exercise for Secondary Prevention among Patients with Cardiovascular Disease. Curr Cardiovasc Risk Rep 2013, 7, 411–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyth, A.; Teo, K.K.; Rangarajan, S.; O’Donnell, M.; Zhang, X.; Rana, P.; Leong, D.P.; Dagenais, G.; Seron, P.; Rosengren, A.; et al. Alcohol consumption and cardiovascular disease, cancer, injury, admission to hospital, and mortality: a prospective cohort study. The Lancet 2015, 386, 1945–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobacco smoking and risk of 36 cardiovascular disease subtypes: fatal and non-fatal outcomes in a large prospective Australian study | BMC Medicine | Full Text Available online:. Available online: https://bmcmedicine.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12916-019-1351-4 (accessed on 1 August 2021).
- Nagai, M.; Hoshide, S.; Kario, K. Sleep Duration as a Risk Factor for Cardiovascular Disease- a Review of the Recent Literature. CCR 2010, 6, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, M.J.; Pagan, L.U.; Okoshi, M.P. Non-Pharmacological Treatment of Cardiovascular Disease | Importance of Physical Exercise. Arquivos Brasileiros de Cardiologia 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- How is Stress and Heart Disease Related? – Cleveland Clinic Available online:. Available online: https://health.clevelandclinic.org/how-is-stress-and-heart-disease-related/ (accessed on 1 August 2021).
- Kisling, L.A.; Das, J.M. Prevention Strategies. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island (FL), 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Arnett, D.K.; Blumenthal, R.S.; Albert, M.A.; Buroker, A.B.; Goldberger, Z.D.; Hahn, E.J.; Himmelfarb, C.D.; Khera, A.; Lloyd-Jones, D.; McEvoy, J.W.; et al. 2019 ACC/AHA Guideline on the Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease. Journal of the American College of Cardiology 2019, 74, e177–e232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, A.; Gee, M.; McLean, S.; Littlewood, C.; Lindsay, C.; Everett, S. Physical activity promotion in physiotherapy practice: a systematic scoping review of a decade of literature. Br J Sports Med 2018, 52, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korn, L.; Ben-Ami, N.; Azmon, M.; Einstein, O.; Lotan, M. Evaluating the Effectiveness of a Health Promotion Intervention Program Among Physiotherapy Undergraduate Students. Med Sci Monit 2017, 23, 3518–3527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maguire, A. Physiotherapy and Cardiovascular Disease: What Can It Do to Help? Available online: https://ballsbridgephysio.ie/news/physiotherapy-and-cardiovascular-disease-what-can-it-do-to-help/ (accessed on 10 August 2021).
- Turk-Adawi, K.; Supervia, M.; Lopez-Jimenez, F.; Pesah, E.; Ding, R.; Britto, R.R.; Bjarnason-Wehrens, B.; Derman, W.; Abreu, A.; Babu, A.S.; et al. Cardiac Rehabilitation Availability and Density around the Globe. EClinicalMedicine 2019, 13, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragupathi, L.; Stribling, J.; Yakunina, Y.; Fuster, V.; McLaughlin, M.A.; Vedanthan, R. Availability, Use, and Barriers to Cardiac Rehabilitation in LMIC. gh 2017, 12, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bäck, M.; Öberg, B.; Krevers, B. Important aspects in relation to patients’ attendance at exercise-based cardiac rehabilitation – facilitators, barriers and physiotherapist’s role: a qualitative study. BMC Cardiovasc Disord 2017, 17, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, J.; Bambury, E.; Mendoza, A.; Reynolds, J.; Veronneau, R.; Dean, E. Health education strategies used by physical therapists to promote behaviour change in people with lifestyle-related conditions: A systematic review. Hong Kong Physiotherapy Journal 2012, 30, 57–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunstler, B.E.; Cook, J.L.; Freene, N.; Finch, C.F.; Kemp, J.L.; O’Halloran, P.D.; Gaida, J.E. Physiotherapists use a small number of behaviour change techniques when promoting physical activity: A systematic review comparing experimental and observational studies. Journal of Science and Medicine in Sport 2018, 21, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, N.S.; Alison, J.A.; Holland, A.E. Interventions for promoting physical activity in people with cystic fibrosis. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockwood, C.; Dos Santos, K.B.; Pap, R. Practical Guidance for Knowledge Synthesis: Scoping Review Methods. Asian Nursing Research 2019, 13, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munn, Z.; Stern, C.; Aromataris, E.; Lockwood, C.; Jordan, Z. What kind of systematic review should I conduct? A proposed typology and guidance for systematic reviewers in the medical and health sciences. BMC Med Res Methodol 2018, 18, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arksey, H.; O’Malley, L. Scoping studies: towards a methodological framework. International Journal of Social Research Methodology 2005, 8, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levac, D.; Colquhoun, H.; O’Brien, K.K. Scoping studies: advancing the methodology. Implementation Sci 2010, 5, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tricco, A.C.; Lillie, E.; Zarin, W.; O’Brien, K.K.; Colquhoun, H.; Levac, D.; Moher, D.; Peters, M.D.J.; Horsley, T.; Weeks, L.; et al. PRISMA Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR): Checklist and Explanation. Ann Intern Med 2018, 169, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, M.D.J.; Marnie, C.; Tricco, A.C.; Pollock, D.; Munn, Z.; Alexander, L.; McInerney, P.; Godfrey, C.M.; Khalil, H. Updated methodological guidance for the conduct of scoping reviews. JBI Evidence Implementation 2021, 19, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, T.C.; Glasziou, P.P.; Boutron, I.; Milne, R.; Perera, R.; Moher, D.; et al. Better reporting of interventions: template for intervention description and replication (TIDieR) checklist and guide. BMJ 2014, 348, g1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, B.; Jamrozik, K.; Norman, P.; Allen, Y.; Wilkinson, E. Improving maximum walking distance in early peripheral arterial disease: randomised controlled trial. Australian Journal of Physiotherapy 2002, 48, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonet, J.; Coll, R.; Rocha, E.; Romero, R. Supervised versus recommended physical exercise in hypertensive women. Is its recommendation enough? Blood pressure 2003, 12, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, K.M.; Westborg, C.; Eliasson, M.C.E. A randomized trial of lifestyle intervention in primary healthcare for the modification of cardiovascular risk factors. Scandinavian Journal of Public Health 2006, 34, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisse, W.; Boer Rookhuizen, M.; de Kruif, M.D.; van Rossum, J.; Jordans, I.; ten Cate, H.; van Loon, L.J.C.; Meesters, E.W. Prescription of physical activity is not sufficient to change sedentary behavior and improve glycemic control in type 2 diabetes patients. Diabetes research and clinical practice 2010, 88, e10–e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molenaar, E.A.; van Ameijden, E.J.C.; Vergouwe, Y.; Grobbee, D.E.; Numans, M.E. Effect of nutritional counselling and nutritional plus exercise counselling in overweight adults: a randomized trial in multidisciplinary primary care practice. Family practice 2010, 27, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-T.; Hwang, C.-L.; Chen, C.-N.; Chuang, L.-M. Home-based exercise improves exercise behavior and metabolic risk factors in middle-aged adults at diabetic risk. 2011, 97, eS523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, R.D.; Morrin, L.I.; Higginson, L.A.J.; Wielgosz, A.; Blanchard, C.; Beaton, L.J.; Nelson, C.; McDonnell, L.; Oldridge, N.; Wells, G.A.; et al. Motivational counselling for physical activity in patients with coronary artery disease not participating in cardiac rehabilitation. European journal of preventive cardiology 2012, 19, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oerkild, B.; Frederiksen, M.; Hansen, J.F.; Prescott, E. Home-based cardiac rehabilitation is an attractive alternative to no cardiac rehabilitation for elderly patients with coronary heart disease: results from a randomised clinical trial. BMJ Open 2012, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takatori, K.; Matsumoto, D.; Okada, Y.; Nakamura, J.; Shomoto, K. Effect of intensive rehabilitation on physical function and arterial function in community-dwelling chronic stroke survivors. Topics in stroke rehabilitation 2012, 19, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Wu, X.; Tsang, R.C.; Yun, R.; Lu, Y.; Dean, E.; Jones, A.Y. A Randomised Controlled Trial to Evaluate the Administration of the Health Improvement Card as a Health Promotion Tool: A Physiotherapist-Led Community-Based Initiative. International journal of environmental research and public health 2020, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerage, A.M.; Benedetti, T.R.B.; Cavalcante, B.R.; Farah, B.Q.; Ritti-Dias, R.M. Efficacy of a behavior change program on cardiovascular parameters in patients with hypertension: a randomized controlled trial. Einstein (Sao Paulo) 2020, 18, eAO5227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bearne, L.M.; Volkmer, B.; Peacock, J.; Sekhon, M.; Fisher, G.; Galea Holmes, M.N.; Douiri, A.; Amirova, A.; Farran, D.; Quirke-McFarlane, S.; et al. Effect of a Home-Based, Walking Exercise Behavior Change Intervention vs Usual Care on Walking in Adults With Peripheral Artery Disease: The MOSAIC Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2022, 327, 1344–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preston, E.; Dean, C.M.; Ada, L.; Stanton, R.; Brauer, S.; Kuys, S.; Waddington, G. Promoting physical activity after stroke via self-management: a feasibility study. Topics in Stroke Rehabilitation 2017, 24, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunnes, M.; Langhammer, B.; Aamot, I.-L.; Lydersen, S.; Ihle-Hansen, H.; Indredavik, B.; Reneflot, K.H.; Schroeter, W.; Askim, T.; group, L.C. Adherence to a Long-Term Physical Activity and Exercise Program After Stroke Applied in a Randomized Controlled Trial. Physical Therapy 2019, 99, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgs, C.; Skinner, M.; Hale, L. Outcomes of a community-based lifestyle programme for adults with diabetes or pre-diabetes. J Prim Health Care 2016, 8, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pariser, G.; Ann Demeuro, M.; Gillette, P.; Stephen, W. Outcomes of an Education and Exercise Program for Adults with Type 2 Diabetes, and Comorbidities that Limit their Mobility: A Preliminary Project Report. Cardiopulmonary physical therapy journal 2010, 21, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinn, A.; Doody, C.; O’Shea, D.; Quinn, A.; Doody, C.; O’Shea, D. The effect of a physical activity education programme on physical activity, fitness, quality of life and attitudes to exercise in obese females. Journal of Science & Medicine in Sport 2008, 11, 469–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batsis, J.A.; Petersen, C.L.; Clark, M.M.; Cook, S.B.; Lopez-Jimenez, F.; Al-Nimr, R.I.; Pidgeon, D.; Kotz, D.; Mackenzie, T.A.; Bartels, S.J. A Weight Loss Intervention Augmented by a Wearable Device in Rural Older Adults With Obesity: A Feasibility Study. The journals of gerontology. Series A, Biological sciences and medical sciences 2021, 76, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deka, P.; Blesa, J.; Pathak, D.; Sempere-Rubio, N.; Iglesias, P.; Micó, L.; Soriano, J.M.; Klompstra, L.; Marques-Sule, E. Combined Dietary Education and High-Intensity Interval Resistance Training Improve Health Outcomes in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease. International journal of environmental research and public health 2022, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunnes, M.; Indredavik, B.; Langhammer, B.; Lydersen, S.; Ihle-Hansen, H.; Dahl, A.E.; Askim, T. Associations Between Adherence to the Physical A ctivity and Exercise Program Applied in the LAST Study and Functional Recovery After Stroke. Archives of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation 2019, 100, 2251–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oerkild, B.; Frederiksen, M.; Hansen, J.F.; Prescott, E. Home-based cardiac rehabilitation is an attractive alternative to no cardiac rehabilitation for elderly patients with coronary heart disease: results from a randomised clinical trial. BMJ open 2012, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgs, C.; Skinner, M.; Hale, L. Outcomes of a community-based lifestyle programme for adults with diabetes or pre-diabetes. Journal of primary health care 2016, 8, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.; Wu, X.; Tsang, R.C.; Yun, R.; Lu, Y.; Dean, E.; Jones, A.Y. A Randomised Controlled Trial to Evaluate the Administration of the Health Improvement Card as a Health Promotion Tool: A Physiotherapist-Led Community-Based Initiative. International journal of environmental research and public health 2020, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerage, A.M.; Benedetti, T.R.B.; Cavalcante, B.R.; Farah, B.Q.; Ritti-Dias, R.M. Efficacy of a behavior change program on cardiovascular parameters in patients with hypertension: a randomized controlled trial. Einstein (Sao Paulo, Brazil) 2020, 18, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batsis, J.A.; Petersen, C.L.; Clark, M.M.; Cook, S.B.; Lopez-Jimenez, F.; Al-Nimr, R.I.; Pidgeon, D.; Kotz, D.; Mackenzie, T.A.; Bartels, S.J. A Weight Loss Intervention Augmented by a Wearable Device in Rural Older Adults With Obesity: A Feasibility Study. Journals of Gerontology Series A: Biological Sciences & Medical Sciences 2021, 76, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molenaar, E.A.; van Ameijden, E.J.; Vergouwe, Y.; Grobbee, D.E.; Numans, M.E. Effect of nutritional counselling and nutritional plus exercise counselling in overweight adults: a randomized trial in multidisciplinary primary care practice. Fam Pract 2010, 27, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pariser, G.; Ann Demeuro, M.; Gillette, P.; Stephen, W. Outcomes of an Education and Exercise Program for Adults with Type 2 Diabetes, and Comorbidities that Limit their Mobility: A Preliminary Project Report. Cardiopulmonary physical therapy journal 2010, 21, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dean, E. Physical therapy in the 21st century (Part I): toward practice informed by epidemiology and the crisis of lifestyle conditions. Physiotherapy theory and practice 2009, 25, 330–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dean, E.; Skinner, M.; Myezwa, H.; Mkumbuzi, V.; Mostert, K.; Parra, D.C.; Shirley, D.; Söderlund, A.; de Andrade, A.D.; Abaraogu, U.O.; et al. Health Competency Standards in Physical Therapist Practice. Physical Therapy 2019, 99, 1242–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dean, E.; Creig, A.; Murphy, S.; Roots, R.; Nembhard, N.; Rankin, A.; Bainbridge, L.; Anthony, J.; Hoens, A.M.; Garland, S.J. Raising the Priority of Lifestyle-Related Noncommunicable Diseases in Physical Therapy Curricula. Physical Therapy 2016, 96, 940–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzudie, A.; Rayner, B.; Ojji, D.; Schutte, A.E.; Twagirumukiza, M.; Damasceno, A.; Ba, S.A.; Kane, A.; Kramoh, E.; Kacou, J.B.A.; et al. Roadmap to achieve 25% hypertension control in Africa by 2025. CVJA 2017, 28, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngeh, E.N. Research among undergraduate biomedical students in Cameroon: contextual barriers, room for improvement. Pan Afr Med J 2019, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngeh Ngeh, E.; Chigbo, N.N.; Whitehouse, Z.; Anekwu, E.M.; Mukaruzima, L.M.; Mtsetfwa, L.; Kitur, R.; Agoriwo, M.W.; Ondogah, P.; Douryang, M.; et al. A report on the development of COVID-19 guidelines for rehabilitation professionals in African settings. Pan Afr Med J 2021, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, P.; Dieppe, P.; Macintyre, S.; Michie, S.; Nazareth, I.; Petticrew, M. Developing and evaluating complex interventions: the new Medical Research Council guidance. BMJ 2008, a1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennell, K.L.; Lawford, B.J.; Keating, C.; Brown, C.; Kasza, J.; Mackenzie, D.; Metcalf, B.; Kimp, A.J.; Egerton, T.; Spiers, L.; et al. Comparing Video-Based, Telehealth-Delivered Exercise and Weight Loss Programs With Online Education on Outcomes of Knee Osteoarthritis : A Randomized Trial. Ann Intern Med 2022, 175, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batsis, J.A.; Petersen, C.L.; Clark, M.M.; Cook, S.B.; Kotz, D.; Gooding, T.L.; Roderka, M.N.; Al-Nimr, R.I.; Pidgeon, D.; Haedrich, A.; et al. Feasibility and acceptability of a technology-based, rural weight management intervention in older adults with obesity. BMC geriatrics 2021, 21, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Participants/population | Cardiovascular disease and risk factors block keywords, cardiovascular diseases, heart diseases, coronary artery disease, coronary heart disease, myocardial infarction, heart failure, angina, cerebrovascular disease, stroke patients, and aortic atherosclerosis patients—overweight, obesity, diabetes, blood pressure, hypertension, dyslipidaemia. |
| Concept/intervention |
Physiotherapy block keywords: Physiotherapist(s), Physiotherapy, kinesiotherapy, physical therapist(s), physiotherapy assistant. Health promotion block keywords: Patient education, health promotion, health education, health behaviour, educational technology, diet therapy, educational health promotion, group-based, individual, home and hospital-based approaches, lifestyle modification, lifestyle change recommendations, physical activity and exercise promotion, brief counselling, face to face, group sessions, skill training, visual presentation, handouts, brochures and diaries, motivational prompts, individualised plan, goal setting, nutrition and weight management, smoking cessation, sleep, stress management. |
| Participants/Population | Concept/Intervention | Context | Study Types and Design |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inclusion criteria | |||
|
|
|
|
| Exclusion criteria | |||
| Studies on pwCVD with relevant outcomes were initiated and implemented by clinicians other than physiotherapists. |
|
|
|
| [44] | [45] | [46] | [60] | [59] | [47] | [48] | [49] | [50] | [64] | [51] | [52] | [58] | [56] | [57] | [53] | [54] | [68] | [55] | [62] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Education on lifestyle | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||||||||||||||
| Dietary education and physiotherapy | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||||||||||
| Exercise and or physical activity | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| Self-management and home programs | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||||||||||||
| Behaviour change programs on physical activity uptake | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||||||||
| Individualised coaching on physical activity and exercise | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||||||||||
| Health improvement card (HIC) | ✓ | |||||||||||||||||||
| Provision of educational materials/resources such as brochures on healthy lifestyle practices and lifestyle behaviour change | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||||||||||||||
| Workbook | ✓ | |||||||||||||||||||
| Written instructions and recommendations | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||||||||||||||
| Handouts following each session | ✓ | |||||||||||||||||||
| Technology based | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||||||||||||
| Theory-based intervention | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||||||||||||||
| Supplemented by telephone calls | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Author Year |
Country | N | Study Design | Population | Nature of the Intervention | Intervention Duration | Theory Use | Mode of, and Delivered by | Setting(s) | Educational Component | Delivery Format | Number of Sessions | Technology | Tailoring | Fidelity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fowler et al. 2002 [44] |
Australia | 882 | RCT | Males aged 65 to 79 years with peripheral arterial disease | Individual and community intervention for people with PAD advised participants to walk >30 minutes daily | Short (12 months) | No | Educational materials and f-t-f by PT | Combined | Yes | Combined | high | no | Yes | No |
| Bone et al. 2003 [45] |
Spain | 18 | RCT | Overweight women of 30-50 years with grade 1 hypertension | Supervised physical exercise | Short (6 months) | No | f-t-f/ supplemented by educational materials by PT | Combined | No | group | high | no | Yes | No |
| Eriksson et al. 2006 [46] |
Sweden | 151 | Randomised controlled parallel group trial | Patients diagnosed with hypertension, dyslipidaemia, type 2 diabetes, obesity, or any combination thereof are aged 18-65. | Lifestyle intervention in primary healthcare | Short (3 months) | No | f-t-f by PT and assistants, dietician and a physician | Clinical setting | Yes | group | High | no | Yes | No |
| Quinn et al. 2007[60] |
Ireland | 18 | Pre-post-test design | Obese females | Physical activity education for obese females | Short (4 months) | No | f-t-f by PT | Clinical setting | Yes | Individual | low | No | No | No |
| Pariser et al. 2010[59] |
USA | 22 | Pre-post-test design | Type 2 Diabetes patients with impaired mobility issues | Active Steps for Diabetes (Exercise and educational intervention) | Short (2months) | No | f-t-f by PT (assisted by PT student or nurse/diabetes educator) | Combined | No | Combined | High | Yes | Yes | No |
| Wisse et al. 2010 [47] |
Netherlands | 74 | RCT | Sedentary, insulin-treated type 2 diabetes | regular, structured, and personalised exercise prescription | Long (24 months) | No | f-t-f by PT supplemented with telephone calls | Combined | Yes | Individual | low | Yes | yes | No |
| Molenaar et al. 2010 [48] |
Netherlands | 203 |
RCT | Men and non-pregnant women aged 18 -65 years with a BMI of 28-35 kg/m2. | Nutritional counselling and nutritional plus exercise counselling in overweight adults. | long (13.7 months) | No | f-t-f by Dietician and PT | Clinic | Yes | Individual | low | No | yes | yes |
| Wu et al. 2011 [49] |
Taiwan | 135 | RCT | People 45 to 64 years old are at risk of developing diabetes. | Home-based exercise | Short (6 months) | Yes | f-t-f supplemented with telephone calls by PT. | Community | Yes | Individual | High | Yes | yes | Yes |
| Reid et al. 2011[50] |
Canada | 141 | RCT | Patients with acute coronary syndromes | motivational counselling intervention |
Short (12 months) | Yes | f-t-f supplemented by telephone calls. | Combined | Yes | Individual | Low | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Oerkild et al. 2012 [64] |
Denmark | 40 | RCT | Elderly coronary heart disease above 65 years | Cardiac home program for the elderly | Short (12 months) | No | home visits in person, follow-up with telephone calls by PT | Community | Yes | Individual | Low | Yes | Yes | No |
| Takatori et al. 2012 [52] |
Japan | 44 | RCT | Chronic stroke survivors 57-89 years | Exercise therapy for post-stroke patients | Short (3monhs) | No | f-t-f by PT | Clinic | No | Individual | High | No | Yes | No |
| Higgs et al. 2016 [58] |
New Zealand | 36 | Prospective observational | Diabetic or at a high risk of developing diabetes. | Education and exercise | Short (3months) | No | f-t-f by PT, PT students and a nurse. | Clinic | Yes | Individual | High | No | Yes | Yes |
| Preston et al. 2017 [56] |
Australia | 20 | pre-post-test intervention | Patients with mild to moderate acute stroke | Self-management | Short (3months) | No | f-t-f by PT | Community | Yes | Individual | Low | No | Yes | Yes |
| Gunnes et al. 2018 [57] |
Norway | 186 | Prospective longitudinal | Adult stroke patients | Physical activity and exercise program | Long (18 months) | Yes (MI) | f-t-f and over the phone by PT | Community | Yes | Individual | High | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Gunnes et al. 2019 [63] |
Norway | 186 | Secondary analyses of multisite RCT | Stroke patients | Individualised coaching on physical activity and exercise | Long (18 months) | Yes (MI) | F-t-f supplemented by telephone calls by PT | Clinic | Yes | Individualised | High | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Bai et al. 2020 [53] |
China | 200 | RCT | 50-90 years | Health education based on the HIC, individualised exercise programme. Standard brochure on healthy lifestyle practices | Short (3months) | Yes (HIC) | f-t-f by PT students supervised by PT. | Community | Yes | Individualised | Low | No | Yes | No |
| Gerage et al. 2020 [67] | Brazil | 90 | RCT | Patients with primary hypertension | Behavioural change program supplemented with educational materials. | Short (3months) | Yes (VAMOS) | f-t-f by PT | Clinic | Yes | Group | Low | No | No | No |
| Batsis et al. 2021 [61] |
USA | 54 | single-arm trial | Older (65+) adults with obesity (BMI > 30 kg/m2) residing in rural New Hampshire and Vermont. | Technology-based weight management intervention | Short (6 months) | Yes (social cognitive theory, MI) | f-t-f and telemedicine (videoconferencing, remote use of Fitbit) and periodic face-to-face interaction onsite. By Dietitian and PT | Community | Yes | Combined | High | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Bearne et al. 2022 [55] |
England | 190 | RCT | Adults with peripheral arterial disease and intermittent claudication | Walking Exercise Behaviour Change Intervention | Short (6 months) | Yes (Theory of Planned Behaviour and The Common Sense Model of Illness Representation) | face-to-face and supplemented by telephone calls by PT. | Clinic | Yes | Individualised | Low | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Deka et al.2022 [62] | Spain | 22 | Single-arm trial | Patients with Coronary Artery Diseases | Dietary education and a high-intensity interval resistance training program (DE–HIIRT) | Short (3months) | Yes (Bandura’Self-Efficacy Theory) | f-t-f by Dietician and PT | Clinic | Yes | Combined | 22 | No | Yes | Yes |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




