Submitted:
04 October 2023
Posted:
04 October 2023
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
1.1. Endometriosis and the Endocannabinoid System
1.1.1. Endocannabinoid Deficiency in Endometriosis
1.1.2. Potential Interplay of the ECS and Endometriosis
1.1.3. Exogenous cannabinoids
1.2. The Endocannabinoid System and the Gut Microbiota
1.2.1. Interactions between gut microbial communities and endocannabinoids
1.2.2. The ECS-gut-brain axis
1.2.3. The ECS in IBD
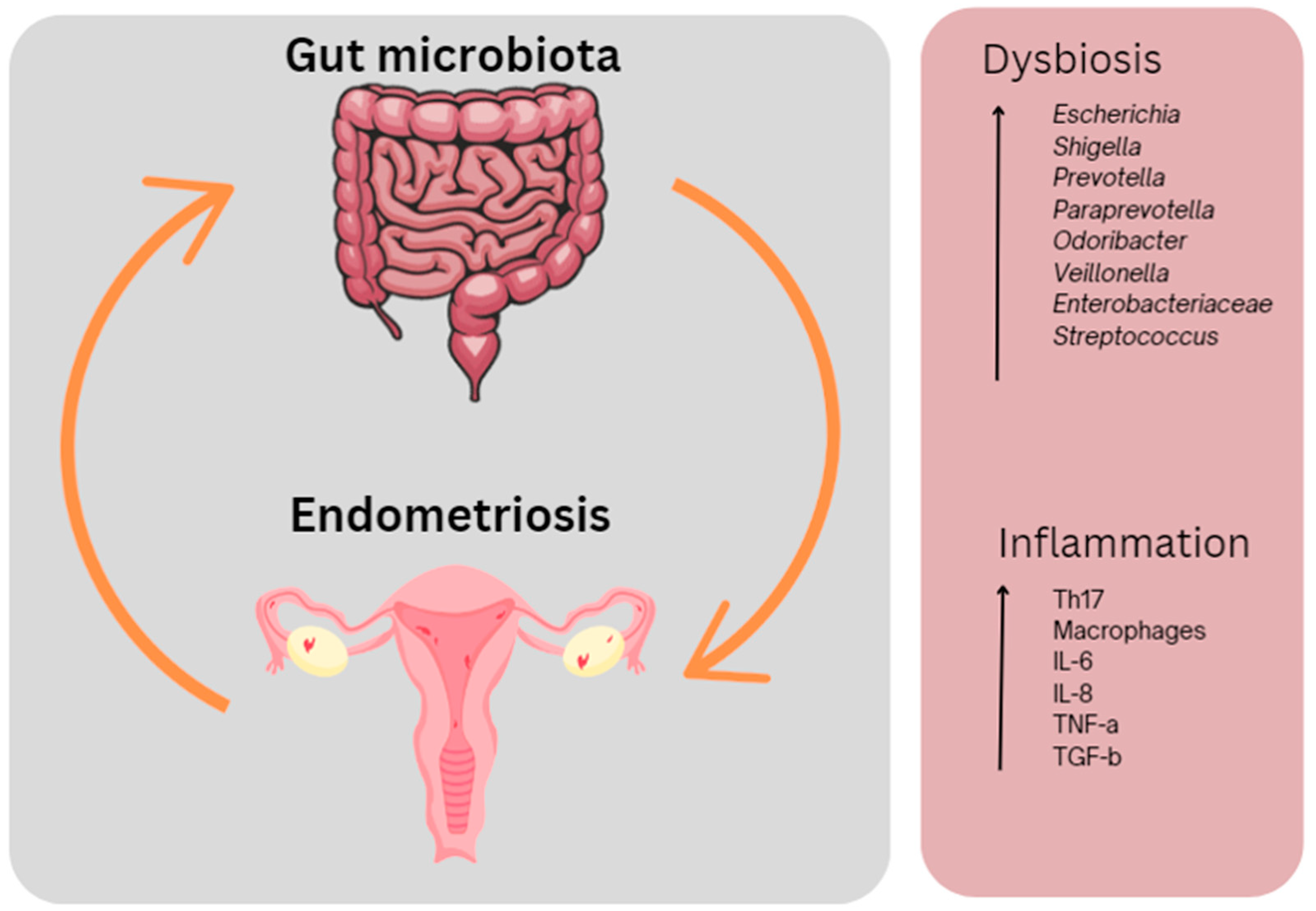
1.3. Endometriosis and the Gut Microbiota
1.3.1. Microbial dysbiosis in endometriosis
1.3.2. Microbial dysbiosis and endometriosis symptoms
| Author | Year | Microbiota | Methodology | Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Svensson, et al. | 2021 |
Prevotella, Bacilli, Bacteriodia, Clostridia, Coriobacteria and Gammaproteobacter |
16s rRNA sequencing |
Prevotella has been associated with common endometriosis gastrointestinal symptoms such as constipation, flatulence, bloating, vomiting and nausea. People with endometriosis were found to have a high abundance of Lactococcus (Bacilli), lower abundance of Odoribacter and higher abundance of Prevotella. |
| Sandstrom, et al. | 2020 | Rumincoccus | 16s rRNA sequencing | Decrease in Ruminococcus correlated with an increase in IL-6 in a murine model of endometriosis, resulting in peritoneal inflammation. |
| Ata, et al. | 2019 | Complete absence of Atopobium, Gardnerella, Streptococcus, Escherichia, Shigella, Ureoplasma |
PCR amplification16s rRNA sequencing | Absence of Atopobium in vaginal and cervical microbiota Increased Gardnerella in cervical microbiota Dominant gut microbiota in endometriosis group – Escherichia and Shigella Predominant population of lower genital tract – Lactobacillus Alloprevotella significantly decreased in the cervix |
| Xu, et al. | 2017 |
Paraprevotella, Odoribacter, Veillonella and Ruminococcus |
16s rRNA sequencing Immunohistochemistry |
The development of chronic stress in people with endometriosis occurs through the activation of β-adrenergic signalling, which occurs as a result of dysbiosis – decrease in specific unknown genus. |
| Khan, et al. | 2010 | E. coli | ELISA of macrophages from peritoneal fluid and epithelial/stromal cells from biopsy specimens of eutopic/ectopic endometria of women with and without endometriosis RT-PCR |
Menstrual blood of people with endometriosis has a higher concentration of E. coli compared to healthy controls. An infiltration of macrophages in eutopic/ectopic endometria of people with endometriosis was noted. |
Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zondervan, K.T., C. M. Becker, and S.A. Missmer, Endometriosis. N Engl J Med 2020, 382, 1244–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulun, S.E. , Endometriosis. N Engl J Med 2009, 360, 268–279. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Parazzini, F. , et al., Epidemiology of endometriosis and its comorbidities. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2017, 209, 3–7. [Google Scholar]
- Rowlands, I.J. , et al., Prevalence and incidence of endometriosis in Australian women: a data linkage cohort study. BJOG 2021, 128, 657–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armour, M. , et al., Endometriosis and chronic pelvic pain have similar impact on women, but time to diagnosis is decreasing: an Australian survey. Sci Rep 2020, 10, 16253. [Google Scholar]
- Armour, M. , et al., Self-management strategies amongst Australian women with endometriosis: a national online survey. BMC Complement Altern Med 2019, 19, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tewhaiti-Smith, J. , et al., An Aotearoa New Zealand survey of the impact and diagnostic delay for endometriosis and chronic pelvic pain. Sci Rep 2022, 12, 4425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagana, A.S. , et al., Anxiety and depression in patients with endometriosis: impact and management challenges. Int J Womens Health 2017, 9, 323–330. [Google Scholar]
- Ramin-Wright, A. , et al., Fatigue – a symptom in endometriosis. Human Reproduction 2018, 33, 1459–1465. [Google Scholar]
- Sepulcri Rde, P. and V.F. do Amaral, Depressive symptoms, anxiety, and quality of life in women with pelvic endometriosis. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2009, 142, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armour, M. , et al., Endometriosis and the workplace: Lessons from Australia's response to COVID-19. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol 2022, 62, 164–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armour, M. , et al., The cost of illness and economic burden of endometriosis and chronic pelvic pain in Australia: A national online survey. PLoS One 2019, 14, e0223316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nnoaham, K.E. , et al., Impact of endometriosis on quality of life and work productivity: a multicenter study across ten countries. Fertil Steril 2011, 96, 366–373e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cousins, F.L. , et al., New concepts on the etiology of endometriosis. J Obstet Gynaecol Res 2023, 49, 1090–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forster, R. , et al., Macrophage-derived insulin-like growth factor-1 is a key neurotrophic and nerve-sensitizing factor in pain associated with endometriosis. FASEB J 2019, 33, 11210–11222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnez, J. and M.M. Dolmans, Endometriosis and Medical Therapy: From Progestogens to Progesterone Resistance to GnRH Antagonists: A Review. J Clin Med 2021, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Yilmaz, B.D. and S.E. Bulun, Endometriosis and nuclear receptors. Hum Reprod Update 2019, 25, 473–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnez, J. and M.M. Dolmans, GnRH Antagonists with or without Add-Back Therapy: A New Alternative in the Management of Endometriosis? Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkey, A. , et al., “A day-to-day struggle”: A comparative qualitative study on experiences of women with endometriosis and chronic pelvic pain. Feminism & Psychology, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, S. , et al., Treatment use and satisfaction in Australian women with endometriosis: A mixed-methods study. Intern Med J 2021.
- Sinaii, N. , et al., Treatment utilization for endometriosis symptoms: a cross-sectional survey study of lifetime experience. Fertil Steril 2007, 87, 1277–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- As-Sanie, S. , et al., Healthcare utilization and cost burden among women with endometriosis by opioid prescription status in the first year after diagnosis: a retrospective claims database analysis. J Med Econ 2020, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Chiuve, S.E. , et al., Chronic opioid use and complication risks in women with endometriosis: a cohort study in US administrative claims. Pharmacoepidemiology and Drug Safety 2021.
- Lamvu, G. , et al., Patterns of prescription opioid use in women with endometriosis: evaluating prolonged use, daily dose, and concomitant use with benzodiazepines. Obstetrics and gynecology 2019, 133, 1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Els, C. , et al., Adverse events associated with medium- and long-term use of opioids for chronic non-cancer pain: an overview of Cochrane Reviews. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2017, 10, CD012509. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bachhuber, M.A. , et al., Increasing benzodiazepine prescriptions and overdose mortality in the United States, 1996–2013. American journal of public health 2016, 106, 686–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deering, D.E. , et al., Potential risk for fatal drug overdose perceived by people using opioid drugs. 2018, Wiley Online Library.
- Leonardi, M. , et al., When to Do Surgery and When Not to Do Surgery for Endometriosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J Minim Invasive Gynecol 2020, 27, 390–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armour, M. , et al., Lessons from implementing the Australian National Action Plan for Endometriosis. Reproduction and Fertility, 2022; RAF-22-0003. [Google Scholar]
- Roman, H. , et al., Long-term risk of repeated surgeries in women managed for endometriosis: a 1,092 patient-series. Fertility and Sterility 2023.
- Young, K., J. Fisher, and M. Kirkman, Endometriosis and fertility: women's accounts of healthcare. Hum Reprod 2016, 31, 554–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- As-Sanie, S. , et al., Assessing research gaps and unmet needs in endometriosis. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2019, 221, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Australian Government Department of Health. National Action Plan for Endometriosis. 2018 12/1/19]; Available from: http://www.health.gov.au/internet/main/publishing.nsf/Content/endometriosis.
- Armour, M. et al., Endometriosis research priorities in Australia. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol 2023, n/a(n/a).
- Armour, M. and J. Sinclair, Cannabis for endometriosis-related pain and symptoms: It's high time that we see this as a legitimate treatment. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol 2023, 63, 118–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouaziz, J. , et al., The Clinical Significance of Endocannabinoids in Endometriosis Pain Management. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res 2017, 2, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devane, W.A. , et al., Isolation and structure of a brain constituent that binds to the cannabinoid receptor. Science 1992, 258, 1946–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y. , et al., Endocannabinoid activation of the TRPV1 ion channel is distinct from activation by capsaicin. J Biol Chem 2021, 297, 101022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez de Fonseca, F. , et al., The endocannabinoid system: physiology and pharmacology. Alcohol Alcohol 2005, 40, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lingegowda, H. , et al., Role of the endocannabinoid system in the pathophysiology of endometriosis and therapeutic implications. J Cannabis Res 2022, 4, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dmitrieva, N. , et al., Endocannabinoid involvement in endometriosis. Pain 2010, 151, 703–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuddihey, H., W. K. MacNaughton, and K.A. Sharkey, Role of the Endocannabinoid System in the Regulation of Intestinal Homeostasis. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol 2022, 14, 947–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kienzl, M., J. Kargl, and R. Schicho, The Immune Endocannabinoid System of the Tumor Microenvironment. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, R.S. , et al., Cannabidiol reduces lipopolysaccharide-induced nociception via endocannabinoid system activation. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 2023, 133, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakotoarivelo, V., J. Sihag, and N. Flamand, Role of the Endocannabinoid System in the Adipose Tissue with Focus on Energy Metabolism. Cells 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.J. and D.S. McQueen, Anandamide induces cardiovascular and respiratory reflexes via vasosensory nerves in the anaesthetized rat. Br J Pharmacol 2001, 134, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murillo-Rodriguez, E. , et al., The emerging role of the endocannabinoid system in the sleep-wake cycle modulation. Cent Nerv Syst Agents Med Chem 2011, 11, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodhams, S.G. , et al., The cannabinoid system and pain. Neuropharmacology 2017, 124, 105–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fine, P.G. and M.J. Rosenfeld, The endocannabinoid system, cannabinoids, and pain. Rambam Maimonides Med J 2013, 4, e0022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guindon, J. and A.G. Hohmann, The endocannabinoid system and pain. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 2009, 8, 403–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burston, J.J. and S.G. Woodhams, Endocannabinoid system and pain: an introduction. Proc Nutr Soc 2014, 73, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maldonado, R. E. Banos, and D. Cabanero, The endocannabinoid system and neuropathic pain. Pain, 2016; 157 (Suppl 1), S23–S32. [Google Scholar]
- Curto-Reyes, V. , et al., Antinociceptive effects induced through the stimulation of spinal cannabinoid type 2 receptors in chronically inflamed mice. Eur J Pharmacol 2011, 668, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, T. , et al., Activation of peripheral cannabinoid CB1 and CB2 receptors suppresses the maintenance of inflammatory nociception: a comparative analysis. Br J Pharmacol 2007, 150, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- !!! INVALID CITATION !!! (Abrams et al., 2007).
- !!! INVALID CITATION !!! (Conte et al., 2009).
- Di Blasio, A.M., M. Vignali, and D. Gentilini, The endocannabinoid pathway and the female reproductive organs. J Mol Endocrinol 2013, 50, R1–R9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, O.S., A. C. Holloway, and S. Raha, The role of the endocannabinoid system in female reproductive tissues. J Ovarian Res 2019, 12, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemenza, S. , et al., From pathogenesis to clinical practice: Emerging medical treatments for endometriosis. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol 2018, 51, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bifulco, M. , et al., Endocannabinoids as emerging suppressors of angiogenesis and tumor invasion (review). Oncol Rep 2007, 17, 813–816. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bilgic, E. , et al., Endocannabinoids modulate apoptosis in endometriosis and adenomyosis. Acta Histochem 2017, 119, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gentilini, D. , et al., Endocannabinoid system regulates migration of endometrial stromal cells via cannabinoid receptor 1 through the activation of PI3K and ERK1/2 pathways. Fertil Steril 2010, 93, 2588–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leconte, M. , et al., Antiproliferative effects of cannabinoid agonists on deep infiltrating endometriosis. Am J Pathol 2010, 177, 2963–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyd, S.T. , The endocannabinoid system. Pharmacotherapy 2006, 26 12 Pt 2 Pt 2, 218S–221S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermanson, D.J. and L.J. Marnett, Cannabinoids, endocannabinoids, and cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev 2011, 30, 599–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayakannu, T. , et al., The endocannabinoid system and sex steroid hormone-dependent cancers. Int J Endocrinol 2013, 2013, 259676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, K. , et al., The role of the endocannabinoid system in aetiopathogenesis of endometriosis: A potential therapeutic target. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2020, 244, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, A.M. , et al., Elevated Systemic Levels of Endocannabinoids and Related Mediators Across the Menstrual Cycle in Women With Endometriosis. Reprod Sci 2016, 23, 1071–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, A.M. , et al., The molecular connections between the cannabinoid system and endometriosis. Mol Hum Reprod 2012, 18, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, C.M. , et al., Identification of local angiogenic and inflammatory markers in the menstrual blood of women with endometriosis. Biomed Pharmacother 2014, 68, 899–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naseri, S. , et al., A cross-sectional study comparing the inflammatory profile of menstrual effluent vs. peripheral blood. Health Sci Rep 2023, 6, e1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha, M.G. , et al., TRPV1 expression on peritoneal endometriosis foci is associated with chronic pelvic pain. Reprod Sci 2011, 18, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrieu, T. , et al., Association of endocannabinoids with pain in endometriosis. Pain 2022, 163, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allam, S. , et al., Detection of Cannabinoid Receptor Expression by Endometriotic Lesions in Women with Endometriosis as an Alternative to Opioid-Based Pain Medication. J Immunol Res 2022, 2022, 4323259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escudero-Lara, A. , et al., Disease-modifying effects of natural Delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol in endometriosis-associated pain. Elife 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okten, S.B. , et al., Cannabidiol as a potential novel treatment for endometriosis by its anti-inflammatory, antioxidative and antiangiogenic effects in an experimental rat model. Reprod Biomed Online 2023, 46, 865–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genovese, T. , et al., Molecular and Biochemical Mechanism of Cannabidiol in the Management of the Inflammatory and Oxidative Processes Associated with Endometriosis. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinross, J.M., A. W. Darzi, and J.K. Nicholson, Gut microbiome-host interactions in health and disease. Genome Med 2011, 3, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ley, R.E., R. Knight, and J.I. Gordon, The human microbiome: eliminating the biomedical/environmental dichotomy in microbial ecology. Environ Microbiol 2007, 9, 3–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costello, E.K. , et al., Bacterial community variation in human body habitats across space and time. Science 2009, 326, 1694–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartor, R.B. , Therapeutic manipulation of the enteric microflora in inflammatory bowel diseases: antibiotics, probiotics, and prebiotics. Gastroenterology 2004, 126, 1620–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ley, R.E., D. A. Peterson, and J.I. Gordon, Ecological and evolutionary forces shaping microbial diversity in the human intestine. Cell 2006, 124, 837–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, K. , et al., Differential expression of cannabinoid receptors in the human colon: cannabinoids promote epithelial wound healing. Gastroenterology 2005, 129, 437–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grill, M. , et al., Cellular localization and regulation of receptors and enzymes of the endocannabinoid system in intestinal and systemic inflammation. Histochem Cell Biol 2019, 151, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousseaux, C. , et al., Lactobacillus acidophilus modulates intestinal pain and induces opioid and cannabinoid receptors. Nat Med 2007, 13, 35–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, W. and S. Katz, Therapeutic Use of Cannabis in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y) 2016, 12, 668–679. [Google Scholar]
- Alhamoruni, A. , et al., Pharmacological effects of cannabinoids on the Caco-2 cell culture model of intestinal permeability. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2010, 335, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhamoruni, A. , et al., Cannabinoids mediate opposing effects on inflammation-induced intestinal permeability. Br J Pharmacol 2012, 165, 2598–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gioacchini, G., G. Rossi, and O. Carnevali, Host-probiotic interaction: new insight into the role of the endocannabinoid system by in vivo and ex vivo approaches. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Distrutti, E. , et al., Modulation of intestinal microbiota by the probiotic VSL#3 resets brain gene expression and ameliorates the age-related deficit in LTP. PLoS One 2014, 9, e106503. [Google Scholar]
- Everard, A. , et al., Cross-talk between Akkermansia muciniphila and intestinal epithelium controls diet-induced obesity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2013, 110, 9066–9071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaderi, F. , et al., Effects of active, inactive, and derivatives of Akkermansia muciniphila on the expression of the endocannabinoid system and PPARs genes. Sci Rep 2022, 12, 10031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forte, N. , et al., Obesity Affects the Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis and the Regulation Thereof by Endocannabinoids and Related Mediators. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijay, A. , et al., The anti-inflammatory effect of bacterial short chain fatty acids is partially mediated by endocannabinoids. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1997559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohnalova, L. , et al., A microbiome-dependent gut-brain pathway regulates motivation for exercise. Nature 2022, 612, 739–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, D.N. , et al., Molecular-phylogenetic characterization of microbial community imbalances in human inflammatory bowel diseases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2007, 104, 13780–13785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, K. , et al., Construction of a Model Culture System of Human Colonic Microbiota to Detect Decreased Lachnospiraceae Abundance and Butyrogenesis in the Feces of Ulcerative Colitis Patients. Biotechnol J 2019, 14, e1800555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, P.E. , et al., Endocannabinoid signaling and synaptic function. Neuron 2012, 76, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cani, P.D. , et al., Endocannabinoids--at the crossroads between the gut microbiota and host metabolism. Nat Rev Endocrinol 2016, 12, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisogno, T., A. Lauritano, and F. Piscitelli, The Endocannabinoid System: A Bridge between Alzheimer's Disease and Gut Microbiota. Life (Basel) 2021, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Argueta, D.A. and N.V. DiPatrizio, Peripheral endocannabinoid signaling controls hyperphagia in western diet-induced obesity. Physiol Behav 2017, 171, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Actis, G.C. , The gut microbiome. Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets 2014, 13, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lal, S. , et al., Cannabis use amongst patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2011, 23, 891–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravikoff Allegretti, J. , et al., Marijuana use patterns among patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2013, 19, 2809–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Sabatino, A. , et al., The endogenous cannabinoid system in the gut of patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Mucosal Immunol 2011, 4, 574–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strisciuglio, C. , et al., Increased expression of CB2 receptor in the intestinal biopsies of children with inflammatory bowel disease. Pediatr Res 2023, 93, 520–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogale, K. , et al., Cannabis and Cannabis Derivatives for Abdominal Pain Management in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Med Cannabis Cannabinoids 2021, 4, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtman, A.H.N., P. S.; Booker, L.; Boger, D.L.; Cravatt, B.F., Targeting FAAH and COX to treat visceral pain. FASEB J 2008, 22, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakin, Y.S. , et al., The effect of FAAH, MAGL, and Dual FAAH/MAGL inhibition on inflammatory and colorectal distension-induced visceral pain models in Rodents. Neurogastroenterol Motil 2015, 27, 936–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coates, M.D. , et al., Symptoms and Extraintestinal Manifestations in Active Cannabis Users with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res 2022, 7, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.E. , et al., Factors Associated with Severity of Irritable Bowel Syndrome Symptoms in Patients with Endometriosis. J Obstet Gynaecol Can 2018, 40, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.S. , et al., Endometriosis in patients with irritable bowel syndrome: Specific symptomatic and demographic profile, and response to the low FODMAP diet. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol 2017, 57, 201–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabi, M.Y. , et al., Endometriosis and irritable bowel syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analyses. Front Med (Lausanne) 2022, 9, 914356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, M.T. , et al., Microbial imbalance in inflammatory bowel disease patients at different taxonomic levels. Gut Pathog 2020, 12, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buhas, M.C. , et al., Gut Microbiota in Psoriasis. Nutrients 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagniere, J. , et al., Gut microbiota imbalance and colorectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2016, 22, 501–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allaband, C. , et al., Microbiome 101: Studying, Analyzing, and Interpreting Gut Microbiome Data for Clinicians. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2019, 17, 218–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muraoka, A. , et al., Fusobacterium infection facilitates the development of endometriosis through the phenotypic transition of endometrial fibroblasts. Sci Transl Med 2023, 15, eadd1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ata, B. , et al., The Endobiota Study: Comparison of Vaginal, Cervical and Gut Microbiota Between Women with Stage 3/4 Endometriosis and Healthy Controls. Sci Rep 2019, 9, 2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaud, D., P. Tailliez, and J. Anba-Mondoloni, Genetic characterization of the beta-glucuronidase enzyme from a human intestinal bacterium, Ruminococcus gnavus. Microbiology (Reading) 2005, 151 Pt 7, 2323–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwa, M. , et al., The Intestinal Microbiome and Estrogen Receptor-Positive Female Breast Cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 2016, 108. [Google Scholar]
- Possemiers, S. , et al., The intestinal microbiome: a separate organ inside the body with the metabolic potential to influence the bioactivity of botanicals. Fitoterapia 2011, 82, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonardi, M. , et al., Endometriosis and the microbiome: a systematic review. BJOG 2020, 127, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, K.N. , et al., Escherichia coli contamination of menstrual blood and effect of bacterial endotoxin on endometriosis. Fertil Steril 2010, 94, 2860–2863e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, K.N. , et al., Toll-like receptor 4-mediated growth of endometriosis by human heat-shock protein 70. Hum Reprod 2008, 23, 2210–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.L., K.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Q.Y.; Huang, Y.K; Kang, Y.; Xu, C.J. Dysbiosis of gut microbiota contributes to chronic stress in endometriosis patients via activating inflammatory pathway. Reprod Dev Med 2017, 1, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iavarone, I. , et al., Correlations between Gut Microbial Composition, Pathophysiological and Surgical Aspects in Endometriosis: A Review of the Literature. Medicina (Kaunas) 2023, 59. [Google Scholar]
- Sandstrom, A. , et al., Effect of hysterectomy on pain in women with endometriosis: a population-based registry study. BJOG 2020, 127, 1628–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, A. , et al., Associations Between Endometriosis and Gut Microbiota. Reprod Sci 2021, 28, 2367–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, K.N. , et al., Molecular detection of intrauterine microbial colonization in women with endometriosis. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2016, 199, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.Y. , et al., A More Diverse Cervical Microbiome Associates with Better Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Endometriosis: A Pilot Study. Biomedicines 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salliss, M.E. , et al., The role of gut and genital microbiota and the estrobolome in endometriosis, infertility and chronic pelvic pain. Hum Reprod Update 2021, 28, 92–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
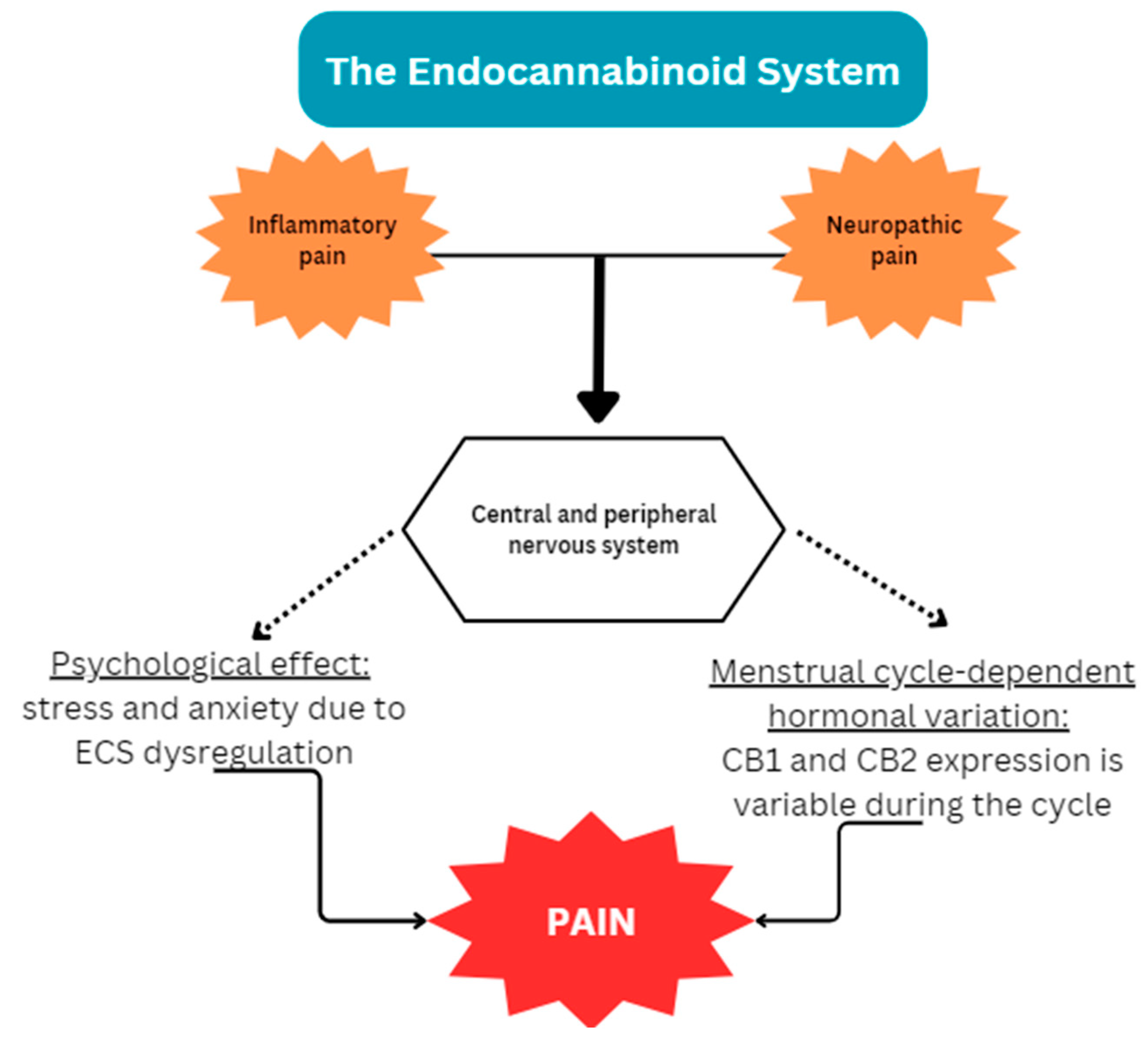

| Endocannabinoid | Abbreviation | Roles |
|---|---|---|
| Cannabinoid receptor 1 | CB1 | G-protein coupled receptor found on cells in the central and peripheral nervous system – involved in processes of mood, appetite, learning, memory and pain. |
| Cannabinoid receptor 2 | CB2 | G-protein coupled receptor found on cells in the central and peripheral nervous system – expressed during active inflammation |
| Anandamide | AEA | Agonist towards CB1 and CB2 receptors |
| Arachidonoyl glycerol | 2-AG | Agonist towards CB1 and CB2 receptors |
| Transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 | TRPV1 | Ion channel involved in endocannabinoid signalling |
| N-oleoylethanolamine | OEA | Fatty acid ethanolamine – involved in food intake, inflammation and pain |
| N-palmitoylethanolamine | PEA | Low affinity for CB1, CB2 and TRPV1 – induces peripheral antinociception upon activating CB1 and CB2 |
| Fatty acid amide hydrolase | FAAH | Metabolises endogenous ligands |
| Monoglyceride lipase | MGL | Metabolises endogenous ligands |
| Author | Year | Type of study | Endocannabinoid/cannabinoid | Methodology | Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Andrieu, et al. | 2022 | Human – endometriosis | 2-AG and AEA | LCMS analysis of endocannabinoids ELISA analysis of cytokines |
An increase in abdominal pain was associated with a high level of 2-AG and a low level of AEA in the peritoneal fluid of people with endometriosis |
| Sanchez, et al. | 2016 | Human - endometriosis | CB1 | PCR analysis of menstrual cups of people with endometriosis | The availability of endocannabinoids in the human endometrium is regulated by the availability of enzymes across the menstrual cycle. The absence of CB1 regulation in endometriosis in the secretory phase might reflect an impaired response to progesterone. |
| Rocha, et al. | 2011 | Human - endometriosis | TRPV1 | Immunohistochemistry analysis of rectouterine peritoneum | There is a correlation between greater expression of TRPV1 in the peritoneum of people with endometriosis who experience chronic pelvic pain compared to those with endometriosis who do not. |
| Bilgic, et al. | 2017 | Human endometrial archive samples | Cannabinoid agonists | Immunohistochemistry analysis | Cannabinoid agonists inhibit endometriotic cell proliferation, modulating apoptosis of endometriotic cells. |
| Okten, et al. | 2023 | Female Wistar albino female rats | CBD | Immunohistochemical staining | CBD reduced endometriotic implant surface area and proinflammatory cytokine levels. |
| Escudero-Lara, et al. | 2020 | Female C57Bl/6J mice | THC | Immunostaining | Repetitive administration of THC hindered ectopic endometriotic growths, alleviating hypersensitivity. |
| Genovese, et al. | 2022 | Sprague-Dawley rats | CBD | Histological analysisELISA | CBD reduced endometriotic lesion diameter and demonstrated antioxidant effects, as viewed by downregulated expression of MMP-9, iNOS and TGFβ). |
| Author | Year | Type of study | Endocannabinoid/cannabinoid + microbiota | Methodology | Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strisciuglio, et al. | 2023 | Human- Crohn's disease | CB2 receptors | Western blot immunofluorescence |
Increased expression of CB2 receptors in ileum of people with Crohn’s disease. |
| Vijay, et al. | 2021 |
People with knee osteoarthritis | 2-AG, OEA, AEA, PEA Bifidobacterium, Coprococcus , Faecalibacterium, Colinsella |
Metabolomic analysis Gut microbiome analysis Gene expression assay |
An association between increased levels of SCFAs with circulating levels of endocannabinoids, higher microbiome diversity and low levels of proinflammatory Colinsella. |
| Pagano, et al. | 2019 | Pedriatic patients with ulcerative colitis and male adult CD1 mice | Cannabidivarin TRPA1 |
RT-PCR | In a TRPA1 antagonist manner, cannabidivarin regulates systemic inflammation and intestinal permeability. |
| Di Sabatino, et al. | 2011 | Human- Crohn’s diseaseMucosal samples | AEA | HPLC-MS Wound healing scratch assay Immunohistochemistry |
Significantly low levels of AEA in inflamed gut mucosa. |
| Grill, et al. | 2019 |
C57BL/6 mice | CB1 receptors |
In situ hybridisation Immunohistochemistry |
Changes in gene expression of CB1 and CB2 receptors, GPR-55 and monoglycerol lipase in the gut after LPS treatment, demonstrating involvement in intestinal and systemic inflammation. These were observed in comparison to CB1 and MGL knockout mice.High expression of CB1 receptors in the submucosal and myenteric plexus. Reduced MGL expression in the ileum following LPS treatment. GPR-55 mRNA present alongside T-cell and macrophage markers in the ileum of healthy and treated mice. |
| Argueta & DiPatrizio | 2017 | Male C57BL/6Tac mice | CB 1 receptor, 2-AG and AEA |
LCMS Gene expression analysis |
In diet-induced obesity, the increase of CB1 receptor activity inhibits CCK-8, resulting in delayed satiation and overeating. |
| Mehrpouya-Bahrami, et al. | 2017 | Male C57BL/6J mice | CB1 receptor Akkermansia muciniphila, Lachnospiraceae, Erysipelotrichaceae, |
16s RNA metagenomics | Blocking CB1 receptor activity resulted in decreased LPS activity, enhancing anti-inflammatory effects by increasing the abundance of A. muciniphia, Lachnospiraceae and Erysipelotrichaceae. |
| Cluny, et al. | 2015 | Male C57BL/6N mice |
Firmicutes, Bacteriodetes A. muciniphila THC |
qPCR | Chronic administration of THC in obesogenic mice increased the Firmicutes:Bacteriodetes ratio and the abundance of A. muciniphila. |
| Sakin, et al. | 2015 | Adult male Balb-C mice and Sprague-Dawley rats | CB1 and CB2 receptors | Colorectal distension test Nociceptive testing |
Availability of CB1 and CB2 receptors diminishes visceral pain. |
| Kiran, Rakib, Moore & Singh | 2022 | Female C57BL/6 mice | CB2 inverse agonist SMM-189 |
Flow cytometry analysis Western blot analysis Histology |
CB 2 inverse agonist SMM-189 suppressed colitis, while ameliorating the loss of body weight, reducing the inflammatory disease score and disease severity. |
| Dohnalova, et al. | 2022 | C57BL/6J mice | CB1 | Fibre photometry analysis DRG extraction, culture and calcium imaging Amplex flurometry analysis PCR, qPCR, RNA-seq Transcriptional profiling |
Fatty acid amide metabolites trigger CB1-expressing TRPV1 sensory neurons, thus elevating dopamine levels during exercise. |
| Jamontt, Molleman, Pertwee & Parsons | 2010 | Male Charles River Wister rats Distal colon tissue |
CBD + THC |
In vitro evaluationMPO assay BCA protein assay |
CBD and THC reduced inflammation and functional disturbances by reducing the release of TNFa, IFNγ and nitric oxide in vitro and in vivo. |
| Borelli, et al. | 2009 | Male ICR mice | CBD | Western blot ELISA LCMS |
CBD reduced colon injury, decreased expression of inflammatory markers, including nitric oxide synthase and reactive oxygen species. |
| Alhamoruni, et al. | 2012 | Caco-2 cells | CB1 and CB 2 receptors, TRPV1, PPARγ and PPARα THC and CBD |
Measurements of transepithelial electrical resistance | THC and CBD accelerated recovery of cytokine-induced intestinal permeability. |
| Distrutti, et al. | 2014 | Zebrafish |
Bifidobacteria, Lactobacilli spp. and Streptococcus thermophilus |
TUNEL assay | Administration of a probiotic mixture containing Bifidobacteria, Lactobacilli spp. and Streptococcus thermophilus in zebrafish led to an increase in CB1 and CB 2 expression. |
| Gioacchini, et al. | 2017 | Adult male zebrafish |
Bifidobacteria, Lactobacilli spp. and S. thermophilus Bacteriodetes and Actinobacteria |
RT-PCR Immunohistochemistry |
Administration of a probiotic mixture containing Bifidobacteria, Lactobacilli spp. and S. thermophilus in aged zebrafish resulted in an increased abundance of Bacteriodetes and Actinobacteria, alongside increases in CB1, demonstrating anti-inflammatory effects. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





