Submitted:
17 October 2023
Posted:
18 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
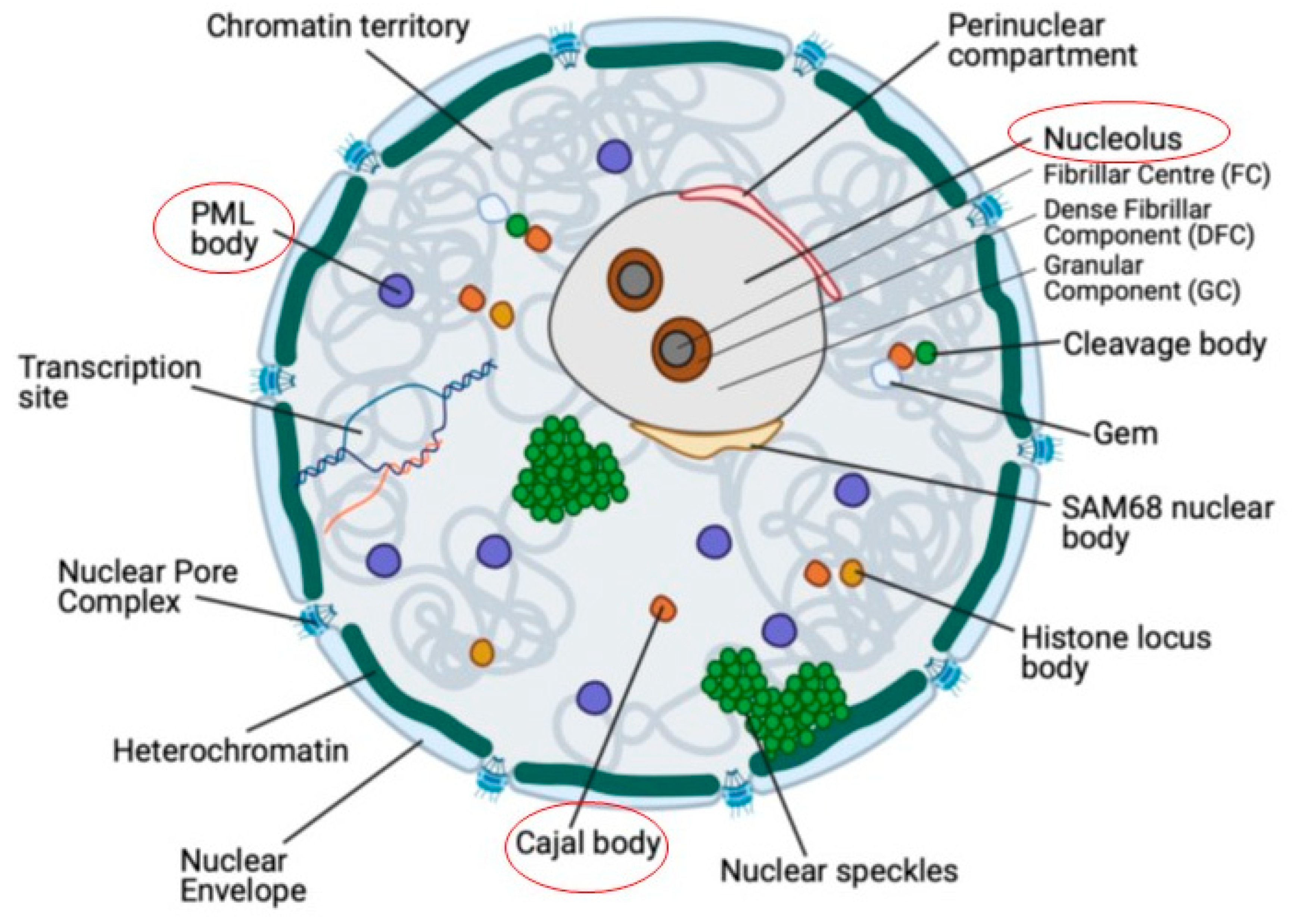
1.1. Cajal Bodies
1.2. The Nucleolus
1.3. Promyelocytic leukaemia (PML) bodies
1.4. Components of Cajal Bodies
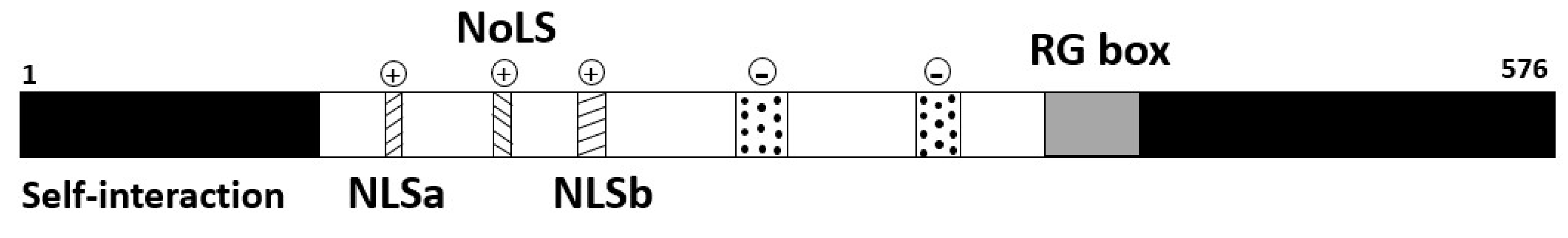
1.4.1. p80-coilin
1.4.2. SMN
1.4.3. TOE1
1.4.4. WRAP53
1.4.5. Nopp140 and fibrillarin
1.4.6. snRNPs, snoRNPs and scaRNPs
2. Viruses that Interact with Nuclear Bodies
2.1. Animal Viruses interacting with Nuclear Bodies
2.2. Animal Viruses that target Cajal Bodies
2.2.1. Minute virus of Mice
2.2.2. African Swine Fever Virus
2.3. Human Viruses interacting with Cajal Body components to induce anti-virus defence
Human Immunodeficiency Virus
2.4. Human viruses interacting with Cajal Body components
2.4.1. Influenza a Virus
2.4.2. Zika Virus
2.4.3. Adenoviruses
2.4.4. Herpesviruses
2.5. Plant Viruses interacting with Nuclear Bodies
2.5.1. Virus interactions with the Cajal Body component, Fibrillarin
Potato Virus A
Citrus Tristeza Virus
Groundnut Rosette Virus
2.5.2. Virus interaction with the Cajal Body protein p80-coilin, resulting in increased pathogenicity
Poa Semilatent Virus
2.5.3. Virus interaction with Cajal Body marker protein p80-coilin, resulting in decreased pathogenicity
Tobacco Rattle Virus
Barley Stripe Mosaic Virus
Rice Stripe Virus
Grapevine red blotch-associated virus
2.5.4. Targeting Argonaute 4
Tomato Yellow Leaf Curl Virus
Cucumber mosaic virus
3. Concluding remarks: common threads and future perspectives
3.1. Nuclear Architecture can be re-modelled in similar ways by diverse viruses
3.2. Involvement of Nuclear Bodies in Anti-virus Defence
References
- Sharp, P.A., Chakraborty, A. K., Henninger, J. E., & Young, R. A, RNA in formation and regulation of transcriptional condensates. Rna 2022, 28, 52–57. [CrossRef]
- Collier, S., et al., A distant coilin homologue is required for the formation of cajal bodies in Arabidopsis. Molecular biology of the cell 2006, 17, 2942–2951. [CrossRef]
- Strzelecka, M., et al., Coilin-dependent snRNP assembly is essential for zebrafish embryogenesis. Nature structural molecular biology of the cell 2010, 17, 403–409. [CrossRef]
- Tucker, K.E., et al., Residual Cajal bodies in coilin knockout mice fail to recruit Sm snRNPs and SMN, the spinal muscular atrophy gene product. The Journal of cell biology 2001, 154, 293–308. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.a.D., G, A novel nuclear structure containing the survival of motor neurons protein. The EMBO journal 1996, 15, 3555–3565. [CrossRef]
- Fong, K.-w., et al., Whole-genome screening identifies proteins localized to distinct nuclear bodies. Journal of Cell Biology 2013, 203, 149–164. [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudi, S., et al., WRAP53 is essential for Cajal body formation and for targeting the survival of motor neuron complex to Cajal bodies. PLoS biology 2010, 8, e1000521.
- Isaac, C., Yang, Y., Thomas M. U, Nopp140 functions as a molecular link between the nucleolus and the coiled bodies. The Journal of cell biology 1998, 142, 319–329. [CrossRef]
- Jones, K., Gorzynski, K., Hales, C., Fischer, U., Badbanchi, F., Terns, R. and Terns, M, Direct Interaction of the Spinal Muscular Atrophy Disease Protein SMN with the Small Nucleolar RNA-associated Protein Fibrillarin. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2001, 276, 38645–38651. [CrossRef]
- Meier, U.T. and G. Blobel, Nopp 140 shuttles on tracks between nucleolus and cytoplasm. Cell 1992, 70, 127–138. [CrossRef]
- Pellizzoni, L., et al., The survival of motor neurons (SMN) protein interacts with the snoRNP proteins fibrillarin and GAR1. Current Biology 2001, 11, 1079–1088. [CrossRef]
- Rampersad, S. and P. Tennant, Replication and expression strategies of viruses. Viruses, 2018: p. 55.
- Wang, P., et al., RING tetramerization is required for nuclear body biogenesis and PML sumoylation. Nature communications 2018, 9, 1277.
- S, R.y.C., A simple method of selective staining of the protoplasmic reticulum and its effects on the various nervous organs of vertebrates and invertebrates. . Trab. Lab. Invest. Biol. (Madrid), 1903(2): 129–221.
- Lafarga, M., Herv's, J., Santa-Cruz, M., Villegas, J. and Crespo, D, The "Accessory Body" of Cajal in the Neuronal Nucleus. Anatomy and Embryology 1983, 166, 19–30. [CrossRef]
- Cioce, M. and A.I. Lamond, Cajal bodies: a long history of discovery. Annual Review of Cell and Developmental Biology 2005, 21, 105–131.
- Young, P., Le, T., Dunckley, M., thi Man, N., Burghes, A. and Morris, G, Nuclear Gems and Cajal (Coiled) Bodies in Fetal Tissues: Nucleolar Distribution of the Spinal Muscular Atrophy Protein, SMN. Experimental Cell Research 2001, 265, 252–261. [CrossRef]
- Young, P., Le, T., thi Man, N., Burghes, A. and Morris, G, The Relationship between SMN, the Spinal Muscular Atrophy Protein, and Nuclear Coiled Bodies in Differentiated Tissues and Cultured Cells. Experimental Cell Research 2000, 256, 365–374. [CrossRef]
- Boudonck, K., Dolan, L. and Shaw, P, The Movement of Coiled Bodies Visualized in Living Plant Cells by the Green Fluorescent Protein. Molecular biology of the cell 1999, 10, 2297–2307. [CrossRef]
- Platani, M., Goldberg, I., Swedlow, J. and Lamond, A, In Vivo Analysis of Cajal Body Movement, Separation, and Joining in Live Human Cells. Journal of Cell Biology 2000, 151, 1561–1574. [CrossRef]
- Andrade, L.T., E.; Chan, E., Immunocytochemical Analysis of the Coiled Body in the Cell Cycle and During Cell Proliferation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 1993, 90, 1947–1951.
- Cantarero, L., Sanz-García, M., Vinograd-Byk, H., Renbaum, P., Levy-Lahad, E. and Lazo, P, VRK1 regulates Cajal body dynamics and protects coilin from proteasomal degradation in cell cycle. Scientific Reports 2015. 5(1). [CrossRef]
- Cioce, M., et al., UV-induced fragmentation of Cajal bodies. The Journal of cell biology 2006, 175, 401–413. [CrossRef]
- Satyanarayana, A., Manns, M. and Rudolph, K, Telomeres, Telomerase and Cancer: An Endless Search to Target the Ends. Cell Cycle 2004, 3, 1136–1148. [CrossRef]
- Love, A., Yu, C., Petukhova, N., Kalinina, N., Chen, J. and Taliansky, M, Cajal bodies and their role in plant stress and disease responses. RNA Biology 2016, 14, 779–790.
- Kroiss, M., Schultz, J., Wiesner, J., Chari, A., Sickmann, A. and Fischer, U, Evolution of an RNP assembly system: A minimal SMN complex facilitates formation of UsnRNPs in Drosophila melanogaster. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2008, 105, 10045–10050. [CrossRef]
- Barneche, F.S., F;. Echeverrı́a, M., Fibrillarin Genes Encode Both a Conserved Nucleolar Protein and a Novel Small Nucleolar RNA Involved in Ribosomal RNA Methylation in Arabidopsis Thaliana. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2000, 275, 27212–27220.
- Beven, A.F.S., G. G.; Brown, J. W. S.; Shaw, P. J., The Organization of Spliceosomal Components in the Nuclei of Higher Plants. Journal of Cell Science 1995, 108, 509–518. [CrossRef]
- Bassett, C., Cajal Bodies and Plant RNA Metabolism. Critical Reviews in Plant Sciences 2012, 31, 258–270.
- Kim, S., Spensley, M., Choi, S., Calixto, C., Pendle, A., Koroleva, O., Shaw, P. and Brown, J, Plant U13 orthologues and orphan snoRNAs identified by RNomics of RNA from Arabidopsis nucleoli. Nucleic Acids Research 2010, 38, 3054–3067. [CrossRef]
- Li, C.F., et al., An ARGONAUTE4-containing nuclear processing center colocalized with Cajal bodies in Arabidopsis thaliana. Cell 2006, 126, 93–106. [CrossRef]
- Scheer, U. and R. Hock, Structure and function of the nucleolus. Current opinion in cell biology 1999, 11, 385–390. [CrossRef]
- Iarovaia, O.V., et al., Nucleolus: a central hub for nuclear functions. Trends in cell biology 2019, 29, 647–659. [CrossRef]
- Boulon, S., et al., The nucleolus under stress. Molecular cell 2010, 40, 216–227. [CrossRef]
- Guldner, H.-H., et al., Scl 70 autoantibodies from scleroderma patients recognize a 95 kDa protein identified as DNA topoisomerase I. Chromosoma 1986, 94, 132–138. [CrossRef]
- Reimer, G., et al., Autoantibody to RNA polymerase I in scleroderma sera. The Journal of clinical investigation 1987, 79, 65–72. [CrossRef]
- Masson, C., et al., A 116000 M r nucleolar antigen specific for the dense fibrillar component of the nucleoli. Journal of Cell Science 1990, 95, 371–381. [CrossRef]
- Padeken, J. and P. Heun, Nucleolus and nuclear periphery: velcro for heterochromatin. Current opinion in cell biology 2014, 28, 54–60. [CrossRef]
- Guarente, L., Link between aging and the nucleolus. Genes development 1997, 11, 2449–2455. [CrossRef]
- Visintin, R., E.S. Hwang, and A. Amon, Cfi1 prevents premature exit from mitosis by anchoring Cdc14 phosphatase in the nucleolus. Nature 1999, 398, 818–823. [CrossRef]
- Weber, J.D., et al., Nucleolar Arf sequesters Mdm2 and activates p53. Nature cell biology 1999, 1, 20–26. [CrossRef]
- Daniely, Y. and J.A. Borowiec, Formation of a complex between nucleolin and replication protein A after cell stress prevents initiation of DNA replication. The Journal of cell biology 2000, 149, 799–810. [CrossRef]
- Higashiura, M., et al., Immunolocalization of Ku-proteins (p80/p70): localization of p70 to nucleoli and periphery of both interphase nuclei and metaphase chromosomes. Experimental cell research 1992, 201, 444–451.
- Boisvert, F.-M., et al., The multifunctional nucleolus. Nature reviews Molecular cell biology 2007, 8, 574–585.
- Ogawa, L.a.B., S., Crosstalk between the nucleolus and the DNA damage response. Molecular BioSystems 2017, 13, 443–455. [CrossRef]
- Govoni, M., Farabegoli, F., Pession, A. and Novello, F., Inhibition of Topoisomerase II Activity and Its Effect on Nucleolar Structure and Function. Experimental Cell Research 1994, 211, 36–41. [CrossRef]
- Al-Baker, E.B., J.; Harry, R.; Kill, I., A p53-independent pathway regulates nucleolar segregation and antigen translocation in response to DNA damage induced by UV irradiation. Exp Cell Res 2004, 292, 179–186.
- Miller, M., Andringa, A., Dixon, K. and Carty, M., Insights into UV-induced apoptosis: ultrastructure, trichrome stain and spectral imaging. Micron 2002, 33, 157–166. [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Verdun, D., Nucleolus: from structure to dynamics. Histochemistry and Cell Biology 2005, 125, 127–137. [CrossRef]
- Lallemand-Breitenbach, V.a.d.T., H, PML nuclear bodies: from architecture to function. Current Opinion in Cell Biology 2018, 52, 154–161.
- Zhong, S., Müller, S., Ronchetti, S., Freemont, P., Dejean, A. and Pandolfi, P, Role of SUMO-1–modified PML in nuclear body formation. Blood 2000, 95, 2748–2752. [CrossRef]
- Borden, K., Lally, J., Martin, S., O'Reilly, N., Solomon, E. and Freemont, P and pp.1601-1606., In vivo and in vitro characterization of the B1 and B2 zinc-binding domains from the acute promyelocytic leukemia protooncoprotein PML. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 1996, 93(4). [CrossRef]
- Sahin, U., Ferhi, O., Jeanne, M., Benhenda, S., Berthier, C., Jollivet, F., Niwa-Kawakita, M., Faklaris, O., Setterblad, N., de Thé, H. and Lallemand-Breitenbach, V, Oxidative stress–induced assembly of PML nuclear bodies controls sumoylation of partner proteins. Journal of cell biology 2014, 204, 931–945. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z., Ruggero, D., Ronchetti, S., Zhong, S., Gaboli, M., Rivi, R. and Pandolfi, P, Pml is essential for multiple apoptotic pathways. Nature Genetics 1998, 20, 266–272. [CrossRef]
- Regad, T.a.C.-A., M, Role and fate of PML nuclear bodies in response to interferon and viral infections. Oncogene 2001, 20, 7274–7286.
- Raška, I., Andrade, L., Ochs, R., Chan, E., Chang, C., Roos, G. and Tan, E, Immunological and ultrastructural studies of the nuclear coiled body with autoimmune antibodies. Experimental Cell Research 1991, 195, 27–37. [CrossRef]
- Andrade, L.C., E.; Raska, I.; Peebles, C.; Roos, G.; Tan, E., Human autoantibody to a novel protein of the nuclear coiled body: immunological characterization and cDNA cloning of p80-coilin. Journal of Experimental Medicine 1991, 173, 1407–1419.
- Walker, M., Tian, L. and Matera, A, Reduced Viability, Fertility and Fecundity in Mice Lacking the Cajal Body Marker Protein, Coilin. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, 6171. [CrossRef]
- Carmo-Fonseca, M., Ferreira, J. and Lamond, A, Assembly of snRNP-containing coiled bodies is regulated in interphase and mitosis--evidence that the coiled body is a kinetic nuclear structure. Journal of Cell Biology 1993, 120, 841–852.
- Bohmann, K., Ferreira, J. and Lamond, A and pp.. Mutational analysis of p80 coilin indicates a functional interaction between coiled bodies and the nucleolus. Journal of Cell Biology 1995, 131, 817–831. [CrossRef]
- Hebert, M.a.M., A, Self-association of Coilin Reveals a Common Theme in Nuclear Body Localization. Molecular Biology of the Cell 2000, 11, 4159–4171.
- Hebert, M., Szymczyk, P., Shpargel, K. and Matera, A, Coilin forms the bridge between Cajal bodies and SMN, the Spinal Muscular Atrophy protein. Genes & Development 2001, 15, 2720–2729. [CrossRef]
- Meister, G., Characterization of a nuclear 20S complex containing the survival of motor neurons (SMN) protein and a specific subset of spliceosomal Sm proteins. Human Molecular Genetics 2000, 9, 1977–1986. [CrossRef]
- Gubitz, A., Feng, W. and Dreyfuss, G, The SMN complex. Experimental Cell Research 2004, 296, 51–56.
- Pellizzoni, L., Kataoka, N., Charroux, B. and Dreyfuss, G, A Novel Function for SMN, the Spinal Muscular Atrophy Disease Gene Product, in Pre-mRNA Splicing. Cell 1998, 95, 615–624. [CrossRef]
- Sleeman, J., Cajal body proteins SMN and Coilin show differential dynamic behaviour in vivo. Journal of Cell Science 2003, 116, 2039–2050. [CrossRef]
- Lanfranco, M., Vassallo, N. and Cauchi, R, Spinal Muscular Atrophy: From Defective Chaperoning of snRNP Assembly to Neuromuscular Dysfunction. Frontiers in MolecularBiosciences 2017. 4. [CrossRef]
- Young, P.J., et al., A direct interaction between the survival motor neuron protein and p53 and its relationship to spinal muscular atrophy. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2002, 277, 2852–2859. [CrossRef]
- de Belle, I., Wu, J., Sperandio, S., Mercola, D. and Adamson, E, In Vivo Cloning and Characterization of a New Growth Suppressor Protein TOE1 as a Direct Target Gene of Egr1. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2003, 278, 14306–14312. [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudi, S., Henriksson, S., Corcoran, M., Méndez-Vidal, C., Wiman, K. and Farnebo, M, Wrap53, a Natural p53 Antisense Transcript Required for p53 Induction upon DNA Damage. Molecular cell 2009, 33, 462–471. [CrossRef]
- Henriksson, S.a.F., M, On the road with WRAP53β: guardian of Cajal bodies and genome integrity. Frontiers in Genetics 2015, 6.
- Venteicher, A., Abreu, E., Meng, Z., McCann, K., Terns, R., Veenstra, T., Terns, M. and Artandi, S, A Human Telomerase Holoenzyme Protein Required for Cajal Body Localization and Telomere Synthesis. Science 2009, 323, 644–648. [CrossRef]
- Machyna, M., Kehr, S., Straube, K., Kappei, D., Buchholz, F., Butter, F., Ule, J., Hertel, J., Stadler, P. and Neugebauer, K, The Coilin Interactome Identifies Hundreds of Small Noncoding RNAs that Traffic through Cajal Bodies. Molecular Cell 2014, 56, 389–399. [CrossRef]
- Staněk, D., Cajal bodies and snRNPs - friends with benefits. RNA Biology 2017, 14, 671–679. [CrossRef]
- Carmo-Fonseca, M., Pepperkok, R., Sproat, B., Ansorge, W., Swanson, M. and Lamond, A, In vivo detection of snRNP-rich organelles in the nuclei of mammalian cells. The EMBO Journal 1991, 10, 1863–1873.
- Matera, A.a.W., D, Nucleoplasmic organization of small nuclear ribonucleoproteins in cultured human cells. Journal of Cell Biology 1993, 121, 715–727. [CrossRef]
- Burke, M., Logan, M. and Hebert, M, Identification of additional regulatory RNPs that impact rRNA and U6 snRNA methylation. Biology Open 2018, 7, bio036095. [CrossRef]
- Darzacq, X., et al., Cajal body-specific small nuclear RNAs: a novel class of 2′-O-methylation and pseudouridylation guide RNAs. The EMBO journal 2002, 21, 2746–2756. [CrossRef]
- Jády, B.E. and T. Kiss, A small nucleolar guide RNA functions both in 2′-O-ribose methylation and pseudouridylation of the U5 spliceosomal RNA. The EMBO journal 2001, 20, 541–551. [CrossRef]
- Kiss, A.M., et al., A Cajal body-specific pseudouridylation guide RNA is composed of two box H/ACA snoRNA-like domains. Nucleic acids research 2002, 30, 4643–4649.
- Tycowski, K., You, Z., Graham, P. and Steitz, J, Modification of U6 Spliceosomal RNA Is Guided by Other Small RNAs. Molecular Cell. 1998, 2, 629–638. [CrossRef]
- Ganot, P., Jády, B., Bortolin, M., Darzacq, X. and Kiss, T, Nucleolar Factors Direct the 2′-O-Ribose Methylation and Pseudouridylation of U6 Spliceosomal RNA. Molecular and Cellular Biology 1999, 19, 6906–6917. [CrossRef]
- Richard, P., Darzacq, X., Bertrand, E., Jady, B., Verheggen, C. and Kiss, T, A common sequence motif determines the Cajal body-specific localization of box H/ACA scaRNAs. The EMBO Journal 2003, 22, 4283–4293. [CrossRef]
- Tycowski, K., Shu, M., Kukoyi, A. and Steitz, J, A Conserved WD40 Protein Binds the Cajal Body Localization Signal of scaRNP Particles. Molecular Cell 2009, 34, 47–57.
- Fischer, U., Englbrecht, C. and Chari, A, Biogenesis of spliceosomal small nuclear ribonucleoproteins. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: RNA 2011, 2, 718–731. [CrossRef]
- Skaar, J., Ferris, A., Wu, X., Saraf, A., Khanna, K., Florens, L., Washburn, M., Hughes, S. and Pagano, M, The Integrator complex controls the termination of transcription at diverse classes of gene targets. Cell Research 2015, 25, 288–305. [CrossRef]
- Takata, H., Nishijima, H., Maeshima, K. and Shibahara, K, The integrator complex is required for integrity of Cajal bodies. Journal of Cell Science 2012, 125, 166–175. [CrossRef]
- Matera, A.a.W., Z, A day in the life of the spliceosome. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology 2014, 15, 108–121.
- Jady, B., Darzacq, X., Tucker, K., Matera, A., Bertrand, E. and Kiss, T, Modification of Sm small nuclear RNAs occurs in the nucleoplasmic Cajal body following import from the cytoplasm. The EMBO Journal 2003, 22, 1878–1888. [CrossRef]
- Tsukaya, H., et al., How do ‘housekeeping’genes control organogenesis?—Unexpected new findings on the role of housekeeping genes in cell and organ differentiation. Journal of plant research 2013, 126, 3–15.
- Cotmore, S., Sturzenbecker, L. and Tattersall, P, The autonomous parvovirus MVM encodes two nonstructural proteins in addition to its capsid polypeptides. Virology 1983, 129, 333–343. [CrossRef]
- Cotmore, S.a.T., P, Organization of nonstructural genes of the autonomous parvovirus minute virus of mice. Journal of Virology 1986, 58, 724–732. [CrossRef]
- Cziepluch, C., Lampel, S., Grewenig, A., Grund, C., Lichter, P. and Rommelaere, J, H-1 Parvovirus-Associated Replication Bodies: a Distinct Virus-Induced Nuclear Structure. Journal of Virology 2000, 74, 4807–4815. [CrossRef]
- Bashir, T.R., J.; Cziepluch, C., In Vivo Accumulation of Cyclin A and Cellular Replication Factors in Autonomous Parvovirus Minute Virus of Mice-Associated Replication Bodies. Journal of Virology 2001, 75, 4394–4398.
- Young, P., Jensen, K., Burger, L., Pintel, D. and Lorson, C, Minute Virus of Mice NS1 Interacts with the SMN Protein, and They Colocalize in Novel Nuclear Bodies Induced by Parvovirus Infection. Journal of Virology 2002, 76, 3892–3904. [CrossRef]
- Simões, M., Rino, J., Pinheiro, I., Martins, C. and Ferreira, F, Alterations of Nuclear Architecture and Epigenetic Signatures during African Swine Fever Virus Infection. Viruses 2015, 7, 4978–4996. [CrossRef]
- Dixon, L., Chapman, D., Netherton, C. and Upton, C, African swine fever virus replication and genomics. Virus Research 2013, 173, 3–14. [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, E., Quintas, A., Nogal, M., Castelló, A. and Revilla, Y, African swine fever virus controls the host transcription and cellular machinery of protein synthesis. Virus Research 2013, 173, 58–75.
- Fanales-Belasio, E., Raimondo, M., Suligoi, B. and Buttò, S, HIV virology and pathogenetic mechanisms of infection: a brief overview. Annali dell’Istituto Superiore di Sanità 2010, 46(1). [CrossRef]
- Sperandio, S., Barat, C., Cabrita, M., Gargaun, A., Berezovski, M., Tremblay, M. and de Belle, I, TOE1 is an inhibitor of HIV-1 replication with cell-penetrating capability. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2015, 112, E3392–E3401. [CrossRef]
- Webster, R.G., Bean, W. J., Gorman, O. T., Chambers, T. M., & Kawaoka, Y Evolution and ecology of Influenza A viruses. Microbiological Reviews 1992, 56, 152– 179.
- Höfer, C., Jolmes, F., Haralampiev, I., Veit, M. and Herrmann, A Influenza A virus nucleoprotein targets subnuclear structures. Cellular Microbiology 2016, 19, p. p.e12679. [CrossRef]
- Josset, L., Frobert, E. and Rosa-Calatrava, M, Influenza A replication and host nuclear compartments: Many changes and many questions. Journal of Clinical Virology 2008, 43, 381–390. [CrossRef]
- Engelhardt, O.a.F., E, Functional association between viral and cellular transcription during influenza virus infection. Reviews in Medical Virology 2006, 16, 329–345.
- Sato, Y., Yoshioka, K., Suzuki, C., Awashima, S., Hosaka, Y., Yewdell, J. and Kuroda, K, Localization of influenza virus proteins to nuclear dot 10 structures in influenza virusinfected cells. Virology 2003, 310, 29–40. [CrossRef]
- Chelbi-Alix, M., Quignon, F., Pelicano, L., Koken, M. and de Thé, H, Resistance to Virus Infection Conferred by the Interferon-Induced Promyelocytic Leukemia Protein. Journal of Virology 1998, 72, 1043–1051. [CrossRef]
- Compans, R.a.D., N, An electron microscopic study of single-cycle infection of chick embryo fibroblasts by influenza virus. Virology 1969, 39, 499–515.
- Shaw, M.a.C., R, Isolation and characterization of cytoplasmic inclusions from influenza A virus-infected cells. Journal of Virology 1978, 25, 608–615. [CrossRef]
- Terrier, O., Moules, V., Carron, C., Cartet, G., Frobert, E., Yver, M., Traversier, A., Wolff, T., Riteau, B., Naffakh, N., Lina, B., Diaz, J. and Rosa-Calatrava, M, The influenza fingerprints: NS1 and M1 proteins contribute to specific host cell ultrastructure signatures upon infection by different influenza A viruses. Virology 2012, 432, 204–218. [CrossRef]
- Davey, J., Colman, A. and Dimmock, N, Location of Influenza Virus M, NP and NS1 Proteins in Microinjected Cells. Journal of General Virology 1985, 66, 2319–2334. [CrossRef]
- Murayama, R., Harada, Y., Shibata, T., Kuroda, K., Hayakawa, S., Shimizu, K. and Tanaka, T, Influenza A virus non-structural protein 1 (NS1) interacts with cellular multifunctional protein nucleolin during infection. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 2007, 362, 880–885. [CrossRef]
- Ozawa, M., Fujii, K., Muramoto, Y., Yamada, S., Yamayoshi, S., Takada, A., Goto, H., Horimoto, T. and Kawaoka, Y, Contributions of Two Nuclear Localization Signals of Influenza A Virus Nucleoprotein to Viral Replication. Journal of Virology 2007, 81, 30–41. [CrossRef]
- Fortes, P., Lamond, A. and Ortin, J, Influenza virus NS1 protein alters the subnuclear localization of cellular splicing components. Journal of General Virology 1995, 76, 1001–1007. [CrossRef]
- Coyaud, E., Ranadheera, C., Cheng, D., Gonçalves, J., Dyakov, B., Laurent, E., St-Germain, J., Pelletier, L., Gingras, A., Brumell, J., Kim, P., Safronetz, D. and Raught, B, Global Interactomics Uncovers Extensive Organellar Targeting by Zika Virus. Molecular & Cellular Proteomics 2018, 17, 2242–2255. [CrossRef]
- Shankar, A., Patil, A. and Skariyachan, S, Recent Perspectives on Genome, Transmission, Clinical Manifestation, Diagnosis, Therapeutic Strategies, Vaccine Developments, and Challenges of Zika Virus Research. Frontiers in Microbiology 2017, 8. [CrossRef]
- Hearing, P., Adenoviridae: The Viruses and Their Replication. 7th ed. In Fields Virology: DNA Viruses., ed. P.M. Howley, Knipe, D. M. Vol. 2. 2021, Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Health.
- Rodrigues S. H., S.N.P., Delício L. R., Granato C., Andrade L. E, The behaviour of the coiled body in cells infected with adenovirus in vitro. Molecular Biolology Rep 1996. 23(3-4): 183–189.
- James, N., Howell, G., Walker, J. and Blair, G, The role of Cajal bodies in the expression of late phase adenovirus proteins. Virology 2010, 399, 299–311. [CrossRef]
- White, L.E., B.; Blair, G.E., The Cajal Body Protein p80-coilin Forms a Complex with the Adenovirus L4-22K Protein and Facilitates the Nuclear Export of Adenovirus mRNA. mBio 2023, 0, 01459–23.
- Gedge, L., Morrison, E., Blair, G. and Walker, J, Nuclear actin is partially associated with Cajal bodies in human cells in culture and relocates to the nuclear periphery after infection of cells by adenovirus 5. Experimental Cell Research 2005, 303, 229–239. [CrossRef]
- Guimet, D., & Hearing, P., The adenovirus L4-22K protein has distinct functions in the posttranscriptional regulation of gene expression and encapsidation of the viral genome. Journal of virology 2013, 87, 7688–7699. [CrossRef]
- Biasiotto, R., & Akusjärvi, G., Regulation of human adenovirus alternative RNA splicing by the adenoviral L4-33K and L4-22K proteins. International journal of molecular sciences 2015, 16, 2893–2912.
- Carvalho, T., Seeler, J., Ohman, K., Jordan, P., Pettersson, U., Akusjärvi, G., Carmo-Fonseca, M. and Dejean, A, Targeting of adenovirus E1A and E4-ORF3 proteins to nuclear matrix-associated PML bodies. Journal of Cell Biology 1995, 131, 45–56. [CrossRef]
- Ullman, A.a.H., P, Cellular Proteins PML and Daxx Mediate an Innate Antiviral Defense Antagonized by the Adenovirus E4 ORF3 Protein. Journal of Virology 2008, 82, 7325–7335.
- Salsman, J., Zimmerman, N., Chen, T., Domagala, M. and Frappier, L, Genome-Wide Screen of Three Herpesviruses for Protein Subcellular Localization and Alteration of PML Nuclear Bodies. PLoS Pathogens 2008, 4, p. p.e1000100. [CrossRef]
- Anobile, J.A., V.; Downs, D.; Czymmek, K.; Parcells, M.; Schmidt, C., Nuclear Localization and Dynamic Properties of the Marek's Disease Virus Oncogene Products Meq and Meq/vIL8. Journal of Virology 2006, 80, 1160–1166.
- Liu, J., Lee, L., Ye, Y., Qian, Z. and Kung, H, Nucleolar and nuclear localization properties of a herpesvirus bZIP oncoprotein MEQ. Journal of virology 1997, 71, 3188–3196. [CrossRef]
- Rajamäki, M.a.V., J, Control of Nuclear and Nucleolar Localization of Nuclear Inclusion Protein a of Picorna-Like Potato virus A in Nicotiana Species. The Plant Cell 2009, 21, 2485–2502.
- Schaad, M., Haldeman-Cahill, R., Cronin, S. and Carrington, J, Analysis of the VPgproteinase (NIa) encoded by tobacco etch potyvirus: effects of mutations on subcellular transport, proteolytic processing, and genome amplification. Journal of virology 1996, 70, 7039–7048.
- Ruiz-Ruiz, S., Soler, N., Sánchez-Navarro, J., Fagoaga, C., Lopez, C., Navarro, L., ... & Flores, R, Citrus tristeza virus p23: determinants for nucleolar localization and their influence on suppression of RNA silencing and pathogenesis. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions 2013, 26, 306–318. [CrossRef]
- Taliansky, M.a.R., D, Molecular biology of umbraviruses: phantom warriors. Journal of General Virology 2003, 84, 1951–1960.
- Ryabov, E., Oparka, K., Santa Cruz, S., Robinson, D. and Taliansky, M, Intracellular Location of Two Groundnut Rosette Umbravirus Proteins Delivered by PVX and TMV Vectors. Virology 1998, 242, 303–313. [CrossRef]
- Ryabov, E., Robinson, D. and Taliansky, M, A plant virus-encoded protein facilitates long-distance movement of heterologous viral RNA. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 1999, 96, 1212–1217. [CrossRef]
- Kim, S., Ryabov, E., Kalinina, N., Rakitina, D., Gillespie, T., MacFarlane, S., Haupt, S., Brown, J. and Taliansky, M, Cajal bodies and the nucleolus are required for a plant virus systemic infection. The EMBO Journal 2007, 26, 2169–2179. [CrossRef]
- Kim, S., MacFarlane, S., Kalinina, N., Rakitina, D., Ryabov, E., Gillespie, T., Haupt, S., Brown, J. and Taliansky, M, Interaction of a plant virus-encoded protein with the major nucleolar protein fibrillarin is required for systemic virus infection. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2007, 104, 11115–11120. [CrossRef]
- Taliansky, M., Roberts, I., Kalinina, N., Ryabov, E., Raj, S., Robinson, D. and Oparka, K, An Umbraviral Protein, Involved in Long-Distance RNA Movement, Binds Viral RNA and Forms Unique, Protective Ribonucleoprotein Complexes. Journal of Virology 2003, 77, 3031–3040. [CrossRef]
- Solovyev, A., Savenkov, E., Agranovsky, A. and Morozov, S, Comparisons of the Genomiccis-Elements and Coding Regions in RNAβ Components of the Hordeiviruses Barley Stripe Mosaic Virus, Lychnis Ringspot Virus, and Poa Semilatent Virus. Virology 1996, 219, 9–18.
- Jackson, A., Lim, H., Bragg, J., Ganesan, U. and Lee, M, Hordeivirus Replication, Movement, and Pathogenesis. Annual Review of Phytopathology 2009, 47, 385–422.
- Lim, H., Bragg, J., Ganesan, U., Lawrence, D., Yu, J., Isogai, M., Hammond, J. and Jackson, A, Triple Gene Block Protein Interactions Involved in Movement of Barley Stripe Mosaic Virus. Journal of Virology 2008, 82, 4991–5006. [CrossRef]
- Semashko, M., Rakitina, D., González, I., Canto, T., Kalinina, N. and Taliansky, M, Movement protein of hordeivirus interacts in vitro and in vivo with coilin, a major structural protein of Cajal bodies. Doklady Biochemistry and Biophysics 2012, 442, 57–60. [CrossRef]
- MacFarlane, S., Tobraviruses-plant pathogens and tools for biotechnology. Molecular Plant Pathology 2010, 11, 577–583. [CrossRef]
- Shaw, J., Love, A., Makarova, S., Kalinina, N., Harrison, B. and Taliansky, M, Coilin, the signature protein of Cajal bodies, differentially modulates the interactions of plants with viruses in widely different taxa. Nucleus 2014, 5, 85–94. [CrossRef]
- Shaw, J., Yu, C., Makhotenko, A., Makarova, S., Love, A., Kalinina, N., MacFarlane, S., Chen, J. and Taliansky, M, Interaction of a plant virus protein with the signature Cajal body protein coilin facilitates salicylic acid-mediated plant defence responses. New Phytologist 2019, 224, 439–453. [CrossRef]
- Spechenkova, N., Samarskaya, V. O., Kalinina, N. O., Zavriev, S. K., MacFarlane, S., Love, A. J., & Taliansky, M, Plant Poly (ADP-ribose) Polymerase 1 Is a Potential Mediator of Cross-Talk between the Cajal Body Protein Coilin and Salicylic Acid-Mediated Antiviral Defence. Viruses 2023, 15, 1282. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.a.J., A, Expression of the Barley Stripe Mosaic Virus RNAβ “Triple Gene Block”. Virology 1996, 216, 367–379.
- Li, Z., Zhang, Y., Jiang, Z., Jin, X., Zhang, K., Wang, X., Han, C., Yu, J. and Li, D, Hijacking of the nucleolar protein fibrillarin by TGB1 is required for cell-to-cell movement of Barley stripe mosaic virus. Molecular Plant Pathology 2017, 19, 1222–1237. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L., Du, Z., Lin, C., Mao, Q., Wu, K., Wu, J., Wei, T., Wu, Z. and Xie, L, Rice stripe tenuivirus p2 may recruit or manipulate nucleolar functions through an interaction with fibrillarin to promote virus systemic movement. Molecular Plant Pathology 2015, 16, 921–930. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L., He, J., Ding, Z., Zhang, C. and Meng, R, Identification of Functional Domain(s) of Fibrillarin Interacted with p2 of Rice stripe virus. Canadian Journal of Infectious Diseases and Medical Microbiology 2018, 2018, 1–6. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L., Hong, P., Guo, X., Li, Y. and Xie, L, Rice stripe virus p2 Colocalizes and Interacts with Arabidopsis Cajal Bodies and Its Domains in Plant Cells. BioMed Research International 2020, 2020, 1–7. [CrossRef]
- Guo, T., Vimalesvaran, D., Thompson, J., Perry, K. and Krenz, B, Subcellular localization of grapevine red blotch-associated virus ORFs V2 and V3. Virus Genes 2015, 51, 156–158. [CrossRef]
- Wang, L., Ding, Y., He, L., Zhang, G., Zhu, J. and Lozano-Duran, R, A virus-encoded protein suppresses methylation of the viral genome through its interaction with AGO4 in the Cajal body. eLife 2020. 9.
- Czosnek, H., Eybishtz, A., Sade, D., Gorovits, R., Sobol, I., Bejarano, E., ... & Lozano-Durán, R, Discovering host genes involved in the infection by the Tomato Yellow Leaf Curl Virus complex and in the establishment of resistance to the virus using Tobacco Rattle Virus-based post transcriptional gene silencing. Viruses 2013, 5, 998–1022. [CrossRef]
- Ceniceros-Ojeda, E., Rodríguez-Negrete, E. and Rivera-Bustamante, R, Two Populations of Viral Minichromosomes Are Present in a Geminivirus-Infected Plant Showing Symptom Remission (Recovery). Journal of Virology 2016, 90, 3828–3838. [CrossRef]
- Deuschle, K., Kepp, G. and Jeske, H, Differential methylation of the circular DNA in geminiviral minichromosomes. Virology 2016, 499, 243–258. [CrossRef]
- Raja, P., Sanville, B., Buchmann, R. and Bisaro, D, Viral Genome Methylation as an Epigenetic Defense against Geminiviruses. Journal of Virology 2008, 82, 8997–9007. [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Negrete, E., Carrillo-Tripp, J. and Rivera-Bustamante, R, RNA Silencing against Geminivirus: Complementary Action of Posttranscriptional Gene Silencing and Transcriptional Gene Silencing in Host Recovery. Journal of Virology 2008, 83, 1332–1340. [CrossRef]
- Wang, B., Li, F., Huang, C., Yang, X., Qian, Y., Xie, Y. and Zhou, X, V2 of tomato yellow leaf curl virus can suppress methylation-mediated transcriptional gene silencing in plants. Journal of General Virology 2014, 95, 225–230. [CrossRef]
- Zrachya, A., Glick, E., Levy, Y., Arazi, T., Citovsky, V. and Gafni, Y, Suppressor of RNA silencing encoded by Tomato yellow leaf curl virus-Israel. Virology 2007, 358, 159–165. [CrossRef]
- Wang, B., Yang, X., Wang, Y., Xie, Y. and Zhou, X, Tomato Yellow Leaf Curl Virus V2 Interacts with Host Histone Deacetylase 6 To Suppress Methylation-Mediated Transcriptional Gene Silencing in Plants. Journal of Virology 2018. 92(18). [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y., Wu, Y., Gong, Q., Ismayil, A., Yuan, Y., Lian, B., Jia, Q., Han, M., Deng, H., Hong, Y., Hanley-Bowdoin, L., Qi, Y. and Liu, Y, Geminiviral V2 Protein Suppresses Transcriptional Gene Silencing through Interaction with AGO4. Journal of Virology 2019. 93(6). [CrossRef]
- Hamera, S., Song, X., Su, L., Chen, X., & Fang, R, Cucumber mosaic virus suppressor 2b binds to AGO4-related small RNAs and impairs AGO4 activities. The Plant Journal 2012, 69, 104–115. [CrossRef]
- Duan, C.G., Fang, Y. Y., Zhou, B. J., Zhao, J. H., Hou, W. N., Zhu, H., ... & Guo, H. S, Suppression of Arabidopsis ARGONAUTE1-mediated slicing, transgene-induced RNA silencing, and DNA methylation by distinct domains of the Cucumber mosaic virus 2b protein. The Plant Cell 2012, 24, 259–274.
- Lin, J., Chen, J., Elenbaas, B. and Levine, A, Several hydrophobic amino acids in the p53 amino-terminal domain are required for transcriptional activation, binding to mdm-2 and the adenovirus 5 E1B 55-kD protein. Genes & Development 1994, 8, 1235–1246. [CrossRef]
- Schreiner, S., Wimmer, P., Sirma, H., Everett, R., Blanchette, P., Groitl, P. and Dobner, T, Proteasome-Dependent Degradation of Daxx by the Viral E1B-55K Protein in Human Adenovirus-Infected Cells. Journal of Virology 2010, 84, 7029–7038. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L., Colosimo, A., Liu, Y., Wan, Y. and Liao, D, Adenovirus E1B 55-Kilodalton Oncoprotein Binds to Daxxand Eliminates Enhancement of p53-Dependent Transcription byDaxx. Journal of Virology 2003, 77, 11809–11821. [CrossRef]
| Species infected by virus | Name of Virus | Virus protein that interacts with Cajal bodies | Cajal body protein that Interacts with virus | Function of interaction | Other Nuclear Bodies that interact with virus (along with CBs) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aves (Birds),principally Gallus gallus domesticus (Chicken) | Marek's Disease Virus (MDV) (Avian alphaherpesvirus) | Meq/ Meq/vIL8 | p80-Coilin | Unknown | Nucleoplasm, nucleolus | [91,92] |
| Several mammalian species, including Homo sapiens (Human) | Adenovirus Type 5 (Ad5) | L4-22K | p80-coilin | Ad5 infection disrupts CBs, redistributed into CB microfoci; L4-22K forms complex with p80-coilin. Depletion of p80-coilin reduces export of virus mRNAs from nucleus in infected cells. | PML bodies (E4-ORF3 11kDa), PML bodies (E1A) | [93,94,95,96] |
| Several animal species, including Homo sapiens (Human) | Zika Virus (ZIKV) | NS5 | p80-coilin | Unknown, disrupt CBs, resulting in an increased number of smaller CBs | Unknown | [98] |
| Murinae (Murine), principally Mus musculus (Mouse) | Minute Virus of Mice (MVM) | NS1 | SMN | Disrupt components of CBs, recombined into SAABs (sites of virus replication) | Unknown | [99] |
| Homo sapiens (Human) | Human Cytomegalovirus (HCMV) | UL3 and UL30 | Unknown | Unknown, expression of UL3 and UL30 decreased number of CBs in cell | PML bodies | [100,101,102,103] |
| Several animal species, including Homo sapiens (Human) | Influenza A virus | NP | Unknown | Unknown, expression of NP results in an increased number of smaller CBs | PML bodies, nucleolus (virus NS1) | [97,104,105,106,107,108,109] |
| Sus scrofa domesticus (Swine) | African Swine Fever Virus (AFSV) | Unknown | Unknown | Unknown, disrupt CBs, results in an increased number of smaller CBs | Nuclear speckles, PML bodies | [110] |
| Homo sapiens (Human) | Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) | TAR | TOE1 | Host anti-virus defence | Unknown | [111] |
| Species infected by virus |
Name of Virus | Virus protein that interacts with Cajal bodies |
Cajal body protein that Interacts with virus |
Function of interaction | Other Nuclear Bodies that interact with virus (along with CBs) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nicotiana benthamiana | Citrus tristeza virus (CTV) | P23 | Fibrillarin | Suppression of RNA silencing, enhancing systemic infection and virus accumulation | Nucleolus | [131] |
| Solanum tuberosum (Potato) | Potato Virus A (PVA) | NIa | Fibrillarin | Unknown, reduced fibrillarin resulted in reduced accumulation of PVA | Nucleolus | [132] |
|
Arachis hypogaea (Groundnut) |
Groundnut Rosette Virus (GRV) |
ORF3 | Fibrillarin | Long-distance movement, establishing systemic infection, stabilisation of virus RNA | Nucleolus | [133,134] |
| Vitis (Grapevine) | Grapevine Red Blotch-associated Virus (GRBaV) |
V2 | Fibrillarin | Unknown | Nucleolus, inclusions in the nucleoplasm | [135] |
| Oryza sativa (Rice) | Rice Stripe Virus (RSV) |
P2 | Coilin | Unknown | Nucleolus (via fibrillarin to establish systemic infection) |
[136,137,138] |
| Poaceae (Grass) | Poa Semilatent Virus (PSLV) |
TGBp1 | Coilin | Cell-to-cell movement, long distance transport, establishing a systemic infection | Nucleolus | [139,140] |
| A wide variety of species |
Tobacco Rattle Virus (TRV) |
16K | Coilin | Host anti-virus defence (RNA and SA silencing pathways) |
Nucleolus | [141,142] |
|
Hordeum vulgare (Barley) |
Barley Stripe Mosaic Virus (BSMV) | Unknown | Coilin | Host anti-virus defence | Unknown | [141] |
| Solanum ycopersicum (Tomato) | Tomato Yellow Leaf Curl Virus (TYLCV) |
V2 | AGO4 | Suppression of host anti-virus defence (Inhibit TGS and PTGS pathways) |
Nucleoplasm | [143] |
| A wide variety of species | Cucumber mosaic virus (CMV) | 2b | AGO4 | RNA-directed DNA methylation | Nucleolus | [144,145] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





