Submitted:
18 October 2023
Posted:
18 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Background
1.2. Research Aim and Objectives
- (1)
- To develop a Hyperledger fabric blockchain for privacy protection of personal information and safety among construction workers.
- (2)
- To optimize Amazon Web Services (AWS) as the cloud provider and storage service to deploy the blockchain solution.
- (3)
- To test and evaluate the effectiveness of the blockchain on privacy protection and security of construction workers’ personal information.
- (4)
- To develop a conceptual blockchain model to enhance the privacy and safety of construction workers personal information; and to illustrate the practical implementation of the proposed model to validate its usability and benefits for the construction industry.
1.3. Problem Statement
1.4. Research Motivation and Significance
2. Literature Review
2.1. Traditional Methods of Data Management
2.2. Advanced Privacy Management Practices and the Adoption of Secure and Efficient Digital Solutions
2.3. Evolution of Blockchain Technology: From Bitcoin to Blockchain 3.0
2.4. Blockchain Technology as an Information Management System
2.5. Blockchain Types
2.6. Key Concepts of Blockchain Technology
3. Methodology
4. Experimental Design of Proposed Blockchain
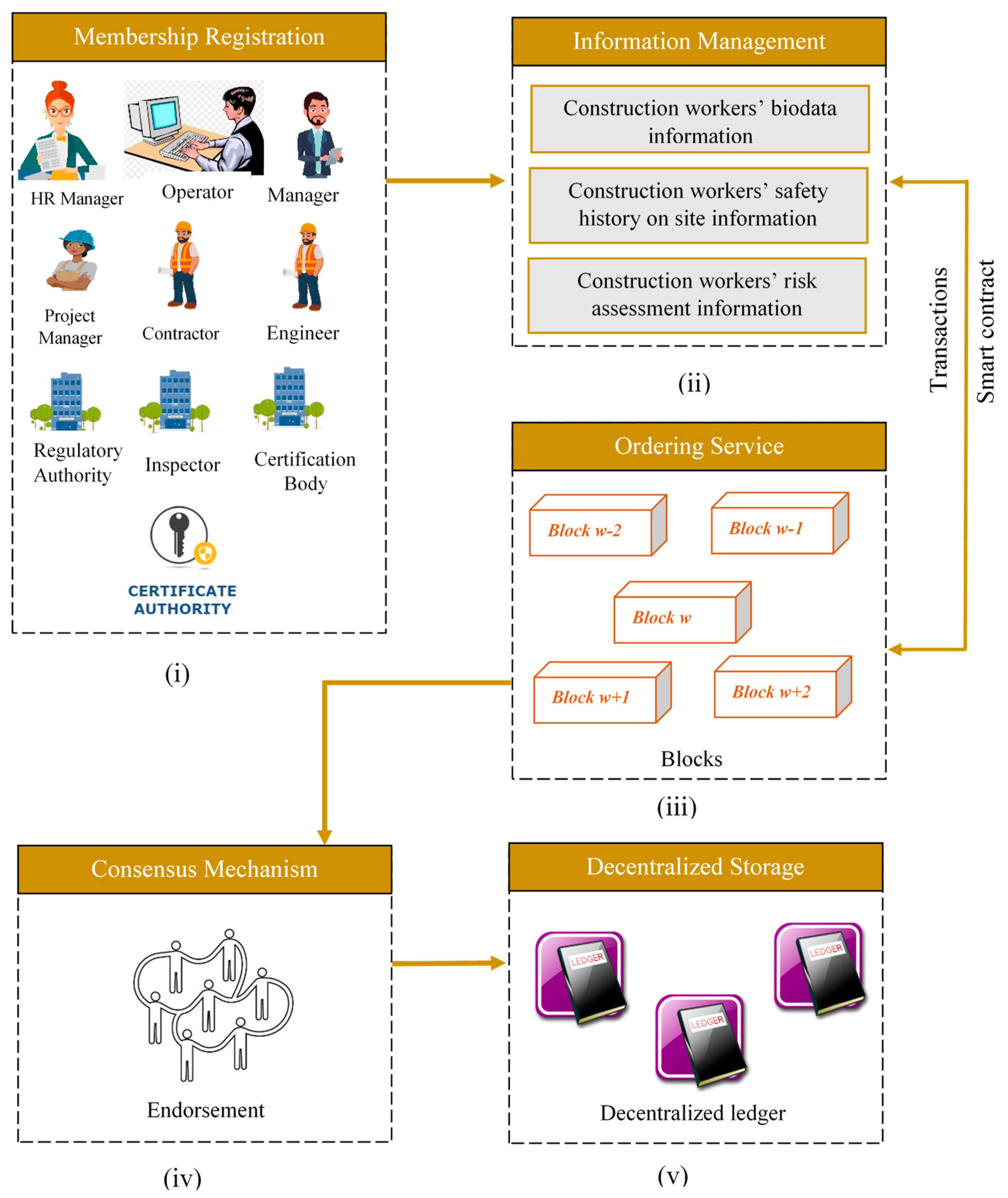
4.1. Blockchain System Architecture of Case Study
4.2. System Structure of Proposed Blockchain
4.3. Deployment of Proposed Blockchain
5. Results and Discussions
5.1. A Conceptual Blockchain-Based Model for Enhancing Privacy and Safety of Construction Workers’ Personal Information
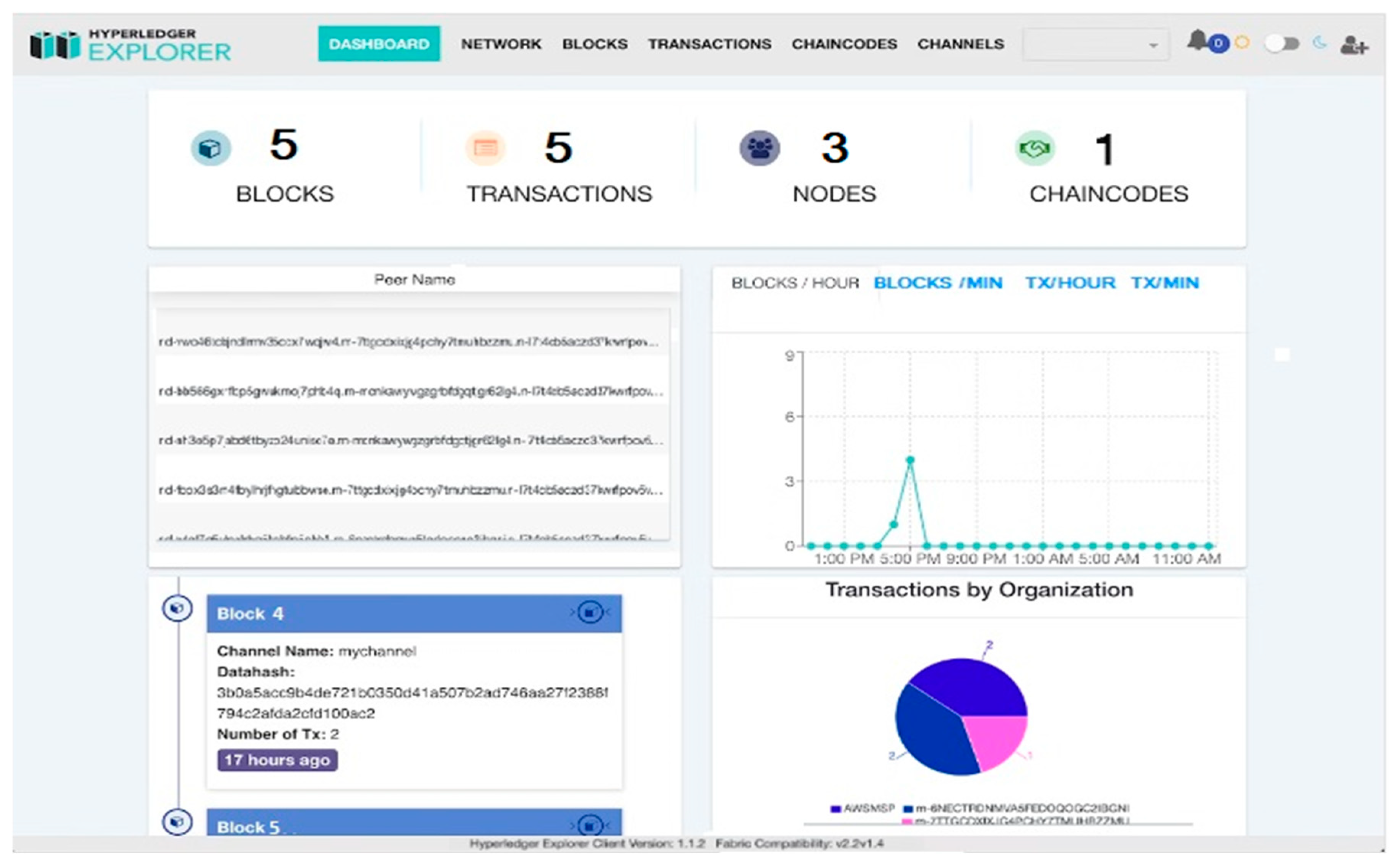
5.2. Testing of Conceptual Blockchain-Based System Using the Transaction Testing Approach
6. Conclusion, Limitations, Recommendations, and Future Work
6.1. Conclusion
- (1)
- Informed decision-making for high-risk activities: By storing safety data, especially work-related musculoskeletal disorders (WMSDs) risk assessments, on the blockchain, construction stakeholders gain access to verified and authenticated information. This empowers them to make informed decisions related to workforce management during high-risk construction tasks. Comprehensive safety data facilitates effective risk assessment, optimal resource allocation, and the assignment of skilled workers to specific high-risk activities. This proactive approach enhances safety measures, reduces accidents, and ensures the well-being of construction personnel.
- (2)
- Enhanced data security and privacy: Storing workers' biographic data on the blockchain enhances security and privacy compared to centralized systems. The blockchain's decentralized architecture distributes data across multiple nodes, making unauthorized manipulation challenging. Cryptographic techniques further safeguard sensitive information, ensuring its confidentiality. This heightened data security fosters trust between construction stakeholders and workers, assuring them that their information is handled with the utmost security.
- (3)
- Promotion of Industry Innovation and Trust: The successful implementation of blockchain within the construction sector sets a precedent for technological innovation. Demonstrating the practical application of blockchain in enhancing data security and privacy inspires confidence among stakeholders. This newfound trust encourages further adoption of advanced technologies to modernize construction practices, driving industry-wide innovation and fostering a culture of continuous improvement.
6.2. Limitations
6.3. Recommendations
- (1)
- Continuous Monitoring and Auditing: Ensuring compliance with data protection regulations and preemptively identifying vulnerabilities requires consistent monitoring and auditing of the blockchain system. Regular updates and patches should be swiftly applied to mitigate potential security risks, creating a robust environment for data management.
- (2)
- Real-world Testing and Iterative Enhancement: Real-world testing and pilot implementation of the blockchain platform in construction projects is essential. This approach facilitates the identification of practical challenges and permits iterative refinements. Collecting user feedback and promptly addressing any emerging issues will optimize the system's performance and tailor its functionality to the specific requirements of the construction industry.
6.4. Future Work
References
- Agenda, I. (2016). Shaping the future of construction a breakthrough in mindset and technology. In World Economic Forum.
- Ahmad, S. Green human resource management: Policies and practices. Cogent business & management 2015, 2, 1030817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaloul, W.S. , Liew, M. S., Zawawi, N. A. W. A., & Kennedy, I. B. (2020). Industrial Revolution 4.0 in the construction industry: Challenges and opportunities for stakeholders. Ain shams engineering journal, 11(1), 225-230. [CrossRef]
- Androulaki, E., Barger, A., Bortnikov, V., Cachin, C., Christidis, K., De Caro, A., & Yellick, J. (2018). Hyperledger fabric: a distributed operating system for permissioned blockchains. In Proceedings of the thirteenth EuroSys conference (pp. 1-15). [CrossRef]
- Antwi-Afari, M.F. , Li, H., Edwards, D. J., Pärn, E. A., Seo, J., & Wong, A. Y. L. (2017). Biomechanical analysis of risk factors for work-related musculoskeletal disorders during repetitive lifting task in construction workers. Automation in Construction, 83, 41-47. [CrossRef]
- Antwi-Afari, M. F., Li, H., Yu, Y., & Kong, L. (2018). Wearable insole pressure system for automated detection and classification of awkward working postures in construction workers. Automation in Construction, 96, 433-441. [CrossRef]
- Al-Zaben, N. , Onik, M. M. H., Yang, J., Lee, N. Y., & Kim, C. S. (2018). General data protection regulation complied blockchain architecture for personally identifiable information management. In 2018 International Conference on Computing, Electronics & Communications Engineering (iCCECE) (pp. 77-82). IEEE.
- Baliga, A. , Subhod, I., Kamat, P., & Chatterjee, S. (2018). Performance evaluation of the quorum blockchain platform. arXiv 2008, arXiv:1809.03421. [Google Scholar]
- Bazarevsky, V. , & Grishchenko, I. (2020). On-device, Real-time Body Pose Tracking with MediaPipe BlazePose. Retrieved from https://ai.googleblog.com/2020/08/on-device-real-time-body-pose-tracking.html.
- Belle, I. (2017). The architecture, engineering and construction industry and blockchain technology. Digital Culture, 2017, 279-284.
- Bhanot, R., & Hans, R. (2015). A review and comparative analysis of various encryption algorithms. International Journal of Security and Its Applications, 9(4), 289-306. [CrossRef]
- Bonnici, C.J. , & Coles-Kemp, L. (2010). Principled electronic consent management: A preliminary research framework. In 2010 International Conference on Emerging Security Technologies (pp. 119-123). IEEE.
- Boniface, C. , Fouad, I., Bielova, N., Lauradoux, C., & Santos, C. (2019). Security analysis of subject access request procedures: How to authenticate data subjects safely when they request for their data. In Privacy Technologies and Policy: 7th Annual Privacy Forum, APF 2019, Rome, Italy, June 13–14, 2019, Proceedings 7 (pp. 182-209). Springer International Publishing.
- Cachin, C. , Camenisch, J., Freire-Stögbuchner, E., & Lehmann, A. (2017). Updatable tokenization: Formal definitions and provably secure constructions. In Financial Cryptography and Data Security: 21st International Conference, FC 2017, Sliema, Malta, April 3-7, 2017, Revised Selected Papers (pp. 59-75). Cham: Springer International Publishing.
- Casino, F. , Dasaklis, T. K., and Patsakis, C. (2019). "A systematic literature review of blockchain-based applications: Current status, classification and open issues." Telematics and Informatics, 36 55-81. [CrossRef]
- Chanal, P.M.; Kakkasageri, M.S. Security and privacy in IOT: A survey. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2020, 115, 1667–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J., Lv, Z., & Song, H. (2019). Design of personnel big data management system based on blockchain. Future generation computer systems, 101, 1122-1129. [CrossRef]
- Chen, C. (2017). "Science Mapping: A Systematic review of the literature." Journal of Data and Information Science (Warsaw, Poland), 2(2), 1-40.
- Cheng, M. , Liu, G., Xu, Y., & Chi, M. (2021). "When blockchain meets the AEC industry: Present status, benefits, challenges, and future research opportunities." Buildings (Basel), 11(8), 340. [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S. , Daub, M., Domeyer, A., & Lundqvist, M. (2017). Using blockchain to improve data management in the public sector.
- Cranor, L.F. (2012). Necessary but not sufficient: Standardized mechanisms for privacy notice and choice. J. on Telecomm. & High Tech. L., 10, 273.
- Clough, R.H. , Sears, G. A., Sears, S. K., Segner, R. O., & Rounds, J. L. (2015). Construction contracting: A practical guide to company management. John Wiley & Sons.
- Curzon, J., Almehmadi, A., & El-Khatib, K. (2019). A survey of privacy enhancing technologies for smart cities. Pervasive and Mobile Computing, 55, 76-95. [CrossRef]
- Dalla Palma, S. , Pareschi, R., & Zappone, F. (2021). What is your distributed (hyper) ledger? In 2021 IEEE/ACM 4th International Workshop on Emerging Trends in Software Engineering for Blockchain (WETSEB) (pp. 27-33). IEEE.
- David, A. , Zarli, A., Mirarchi, C., Naville, N., & Perissich, L. (2021). DigiPLACE: Towards a reference architecture framework for digital platforms in the EU construction sector. In ECPPM 2021–eWork and eBusiness in Architecture, Engineering and Construction (pp. 511-518). CRC Press.
- de Ocáriz Borde, H.S. (2022). An Overview of Trees in Blockchain Technology: Merkle Trees and Merkle Patricia Tries.
- Dhillon, V. , Metcalf, D., Hooper, M., Dhillon, V., Metcalf, D., & Hooper, M. (2017). The hyperledger project. Blockchain enabled applications: Understand the Blockchain ecosystem and how to make it work for you.
- Di Pierro, M. (2017). What is the blockchain? Computing in Science & Engineering, 19(5), 92-95. [CrossRef]
- Donet Donet, J.A. , Pérez-Sola, C., & Herrera-Joancomartí, J. (2014). The bitcoin P2P network. In Financial Cryptography and Data Security: FC 2014 Workshops, BITCOIN and WAHC 2014, Christ Church, Barbados, 7 March 2014, Revised Selected Papers 18 (pp. 87-102). Springer Berlin Heidelberg.
- Gamil, Y. , & Alhagar, A. (2020). The impact of pandemic crisis on the survival of construction industry: a case of COVID-19. Mediterranean Journal of Social Sciences, 11(4), 122-122. [CrossRef]
- Giancaspro, M. (2017). "Is a ‘smart contract’ really a smart idea? Insights from a legal perspective." The Computer Law and Security Report, 33(6), 825-835. [CrossRef]
- Grishchenko, I. , Bazarevsky, V., Zanfir, A., Bazavan, E. G., Zanfir, M., Yee, R., & Sminchisescu, C. (2022). BlazePose GHUM Holistic: Real-time 3D Human Landmarks and Pose Estimation. arXiv:2206.11678. [CrossRef]
- Gruschka, N. , Mavroeidis, V., Vishi, K., & Jensen, M. (2018). Privacy issues and data protection in big data: a case study analysis under GDPR. In 2018 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data) (pp. 5027-5033). IEEE.
- Gourévitch, A. , Fæste, L., Baltassis, E., & Marx, J. (2017). Data-Driven Transformation. BCG Perspectives, 5(17), 8.
- Guo, L., Xie, H., & Li, Y. (2020). Data encryption based blockchain and privacy preserving mechanisms towards big data. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, 70, 102741. [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M. (2019). Blockchain for dummies. John Wiley & Sons, Inc., Hoboken, NJ 07030-5774.
- Gupta, S.S. (2017). Blockchain. IBM Online (http://www. IBM. COM).
- Heilig, L. , & Voß, S. (2016). A holistic framework for security and privacy management in cloud-based smart ports. In 15th International Conference on Computer and IT Applications in the Maritime Industries-COMPIT ‘16, Lecce Italy.
- Ho, P.H. (2016). Labour and skill shortages in Hong Kong’s construction industry. Engineering, Construction and Architectural Management, 23(4), 533-550. [CrossRef]
- Jing, N. , Liu, Q., & Sugumaran, V. (2021). A blockchain-based code copyright management system. Information Processing & Management 58, 102518. [CrossRef]
- Johnson, V. R. (2005). Cybersecurity, Identity Theft, and the Limits of Tort Liability. ScL REv., 57, 255.
- Karia, J. , Sundararajan, M., & Raghavan, G. S. (2021). Distributed Ledger Systems to Improve Data Synchronization in Enterprise Processes. In 2021 IEEE International Conference on Distributed Computing, VLSI, Electrical Circuits and Robotics (DISCOVER) (pp. 41-45). IEEE.
- Kerrest, F. (2018) "Commentary: How Blockchain Could Put an End to Identity Theft." Fortune. http://fortune.com/2018/04/20/blockchain-technology-identity-theft-dataprivacy-protection/ (accessed 27 September, 2018).
- Kim, K. H. , Kim, K. S., Kim, D. S., Jang, S. J., Hong, K. H., & Yoo, S.-W. (2010). Characteristics of Work-related Musculoskeletal Disorders in Korea and Their Work-relatedness Evaluation. Journal of Korean Medical Science, 25(Suppl), S77. [CrossRef]
- Kobsa, A. Privacy-enhanced personalization. Commun. ACM 2007, 50, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinc, R. , & Turk, Ž. (2019). Construction 4.0–digital transformation of one of the oldest industries. Economic and Business Review, 21(3), 4. [CrossRef]
- Kuperberg, M. (2020). "Blockchain-Based Identity Management: A Survey from the enterprise and ecosystem perspective." Tem, 67(4), 1008-1027. [CrossRef]
- Lee, D. , Lee, S. H., Masoud, N., Krishnan, M. S., and Li, V. C. (2021). "Integrated digital twin and blockchain framework to support accountable information sharing in construction projects." Automation in Construction, 127(103688), 103688. [CrossRef]
- Li, H. , Lu, M., Hsu, S. C., Gray, M., & Huang, T. Proactive behavior-based safety management for construction safety improvement. Saf. Sci. 2015, 75, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H. , Han, S., & Zhu, Z. (2023). Blockchain technology toward smart construction: Review and future directions. Journal of Construction Engineering and Management, 149(3), 03123002. [CrossRef]
- Lu, W. , Wu, L., & Zhao, R. (2023). Rebuilding trust in the construction industry: A blockchain-based deployment framework. International Journal of Construction Management, 23(8), 1405-1416. [CrossRef]
- Maciel, A. (2020). Use of blockchain for enabling Construction 4.0. In Construction 4.0 (pp. 395-418).
- Liu, X. , Farahani, B., & Firouzi, F. (2020). Distributed ledger technology. Intelligent Internet of Things: From Device to Fog and Cloud, 393-431.
- MacKenzie, D. (2019). Pick a nonce and try a hash. London Review of Books, 41(8), 35-38.
- Meunier, S. (2018). Blockchain 101: What is blockchain and how does this revolutionary technology work?. In Transforming climate finance and green investment with Blockchains (pp. 23-34). Academic Press.
- Monahan, T. (2009). Identity theft vulnerability: Neoliberal governance through crime construction. Theoretical criminology, 13(2), 155-176. [CrossRef]
- Manoharan, K. , Dissanayake, P., Pathirana, C., Deegahawature, D., & Silva, R. (2020). Assessment of critical factors influencing the performance of labour in Sri Lankan construction industry. International Journal of Construction Management, 1-35. [CrossRef]
- Murthy, S. , Bakar, A. A., Rahim, F. A., & Ramli, R. (2019). A comparative study of data anonymization techniques. In 2019 IEEE 5th Intl Conference on Big Data Security on Cloud (BigDataSecurity), IEEE Intl Conference on High Performance and Smart Computing,(HPSC) and IEEE Intl Conference on Intelligent Data and Security (IDS) (pp. 306-309). IEEE.
- Nakamoto, S. (2009). Bitcoin v0. 1 released. The Mail Archive, 9. https://www.mail-archive.com/cryptography@metzdowd.com/msg10142.html.
- Nanayakkara, S. , Perera, S., Bandara, D., Weerasuriya, T., & Ayoub, J. (2019). Blockchain technology and its potential for the construction industry. In AUBEA Conference 2019 (pp. 662-72).
- Nunes, I.L. , & Bush, P. M. (2012). Work-related musculoskeletal disorders assessment and prevention. Ergonomics-A Systems Approach, 1, 30. [CrossRef]
- Nikmehr, B. , Hosseini, M. R., Martek, I., Zavadskas, E. K., & Antucheviciene, J. (2021). Digitalization as a strategic means of achieving sustainable efficiencies in construction management: A critical review. Sustainability, 13(9), 5040. [CrossRef]
- Oetzel, M. C. , & Spiekermann, S. (2014). A systematic methodology for privacy impact assessments: A design science approach. European Journal of Information Systems, 23(2), 126-150. [CrossRef]
- Olanrewaju, A., Tan, S. Y., & Kwan, L. F. (2017). Roles of communication on performance of the construction sector. Procedia engineering, 196, 763-770. [CrossRef]
- Olsen, D. , Tatum, M., & Defnall, C. (2012). How industrial contractors are handling skilled labor shortages in the United States. In 48th ASC Annual International Conference Proceedings.
- Panda, S. K. , Daliyet, S. P., Lokre, S. S., and Naman, V. (2022). Distributed Ledger Technology in the Construction Industry Using Corda. The New Advanced Society: Artificial Intelligence and Industrial Internet of Things Paradigm, 15-41. [CrossRef]
- Perera, S. , Nanayakkara, S., Rodrigo, M. N. N., Senaratne, S., and Weinand, R. (2020). "Blockchain technology: Is it hype or real in the construction industry?" Journal of Industrial Information Integration, 17(100125), 1-20. [CrossRef]
- Penzes, B. , KirNup, A., Gage, C., Dravai, T., and Colmer, M. (2018). Blockchain technology in the construction industry: Digital transformation for high productivity. In Institution of civil engineers (ICE).
- Politou, E. , Casino, F., Alepis, E., & Patsakis, C. (2019). Blockchain mutability: Challenges and proposed solutions. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Top. Comput. 1986; 9, 1972–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purnomo, H., & Apsari, A. E. (2016). REBA analysis for construction workers in Indonesia. Journal of built environment, Technology and Engineering, 1(9), 104-110.
- Rahardja, U., Hidayanto, A. N., Lutfiani, N., Febiani, D. A., & Aini, Q. (2021). Immutability of Distributed Hash Model on Blockchain Node Storage. Sci. J. Informatics, 8(1), 137-143. [CrossRef]
- Read, C. L. (2022). The Genesis Block. In The Bitcoin Dilemma: Weighing the Economic and Environmental Costs and Benefits (pp. 29-36). Cham: Springer International Publishing.
- Saah, A. E. N. , & Choi, J. H. (2023). Blockchain technology in the AEC industry: Scientometric analysis of research activities. Journal of Building Engineering, 106609. [CrossRef]
- Safa, N. S., Mitchell, F., Maple, C., Azad, M. A., & Dabbagh, M. (2022). Privacy Enhancing Technologies (PETs) for connected vehicles in smart cities. Transactions on Emerging Telecommunications Technologies, 33(10), e4173. [CrossRef]
- Shah, T. , & Jani, S. (2018). Applications of blockchain technology in banking & finance. Parul CUniversity, Vadodara, India.
- Siegel, K. M. (2006). Protecting the Most Valuable Corporate Asset: Electronic Data, Identity Theft, Personal Information, and the Role of Data Security in the Information Age. Penn St. L. Rev., 111, 779.
- Sheth, H. , & Dattani, J. (2019). Overview of blockchain technology. Asian Journal For Convergence In Technology (AJCT) ISSN-2350-1146.
- Singh, A. K. , Kumbhare, V. A., & Arthi, K. (2021, June). Real-time human pose detection and recognition using mediapipe. In International Conference on Soft Computing and Signal Processing (pp. 145-154). Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore.
- Smallwood, R. F. (2019). Information governance: Concepts, strategies and best practices. John Wiley & Sons.
- Smith, A. D. , & Lias, A. R. (2005). Identity theft and e-fraud as critical CRM concerns. International Journal of Enterprise Information Systems (IJEIS), 1(2), 17-36. [CrossRef]
- Supanich, W. , Kulkarineetham, S., Sukphokha, P., & Wisarnsart, P. (2023, March). Machine Learning-Based Exercise Posture Recognition System Using MediaPipe Pose Estimation Framework. In 2023 9th International Conference on Advanced Computing and Communication Systems (ICACCS) (Vol. 1, pp. 2003-2007). IEEE.
- Swan, M. (2015). Blockchain: Blueprint for a new economy. " O'Reilly Media, Inc.".
- Tam, C. M., Zeng, S. X., & Deng, Z. M. (2004). Identifying elements of poor construction safety management in China. Safety science, 42(7), 569-586. [CrossRef]
- Tikkinen-Piri, C. , Rohunen, A., & Markkula, J. (2018). EU General Data Protection Regulation: Changes and implications for personal data collecting companies. Computer Law & Security Review, 34(1), 134-153. [CrossRef]
- Toumia, S.B. , Berger, C.; Reiser, H.P. Evaluating blockchain application requirements and their satisfaction in Hyperledger Fabric. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2111.15399. [Google Scholar]
- vom Brocke, J., Hevner, A., & Maedche, A. (2020). Introduction to design science research. Design science research. Cases, 1-13.
- Voss, W. G. (2019). Cross-border data flows, the GDPR, and data governance. Wash. Int'l LJ, 29, 485. [CrossRef]
- Wang, W. , Yuan, Y., & Archer, N. (2006). A contextual framework for combating identity theft. IEEE Security & Privacy, 4(2), 30-38. [CrossRef]
- Wang, S. , Yuan, Y., Wang, X., Li, J., Qin, R., & Wang, F. Y. (2018). An overview of smart contract: architecture, applications, and future trends. In 2018 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV) (pp. 108-113). IEEE.
- Weise, J. (2001). Public key infrastructure overview. Sun BluePrints OnLine, August, 1-27.
- Wiatt, R. G. (2019). From the mainframe to the blockchain. Strategic Finance, 100(7), 26-35.
- Wu, L., Lu, W., Zhao, R., Xu, J., Li, X., & Xue, F. (2022). Using blockchain to improve information sharing accuracy in the onsite assembly of modular construction. Journal of Management in Engineering, 38(3), 04022014. [CrossRef]
- Wu, H. , Zhang, P., Li, H., Zhong, B., Fung, I. W., & Lee, Y. Y. R. (2022). Blockchain Technology in the Construction Industry: Current Status, Challenges, and Future Directions. Journal of Construction Engineering and Management 2022, 148, 03122007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X. , Weber, I., & Staples, M. (2019). Architecture for blockchain applications (pp. 1-307). Cham: Springer.
- Yaqoob, I. , Salah, K., Jayaraman, R., & Al-Hammadi, Y. Blockchain for healthcare data management: opportunities, challenges, and future recommendations. Neural Computing and Applications 2021, 34, 11475–11490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X. , & Wu, J. Research on safety management of construction engineering personnel under “big data+ artificial intelligence”. Open Journal of Business and Management 2020, 8, 1059–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, B. , Wu, H., Ding, L., Luo, H., Luo, Y., & Pan, X. (2020). Hyperledger fabric-based consortium blockchain for construction quality information management. Frontiers of engineering management 2020, 7, 512–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
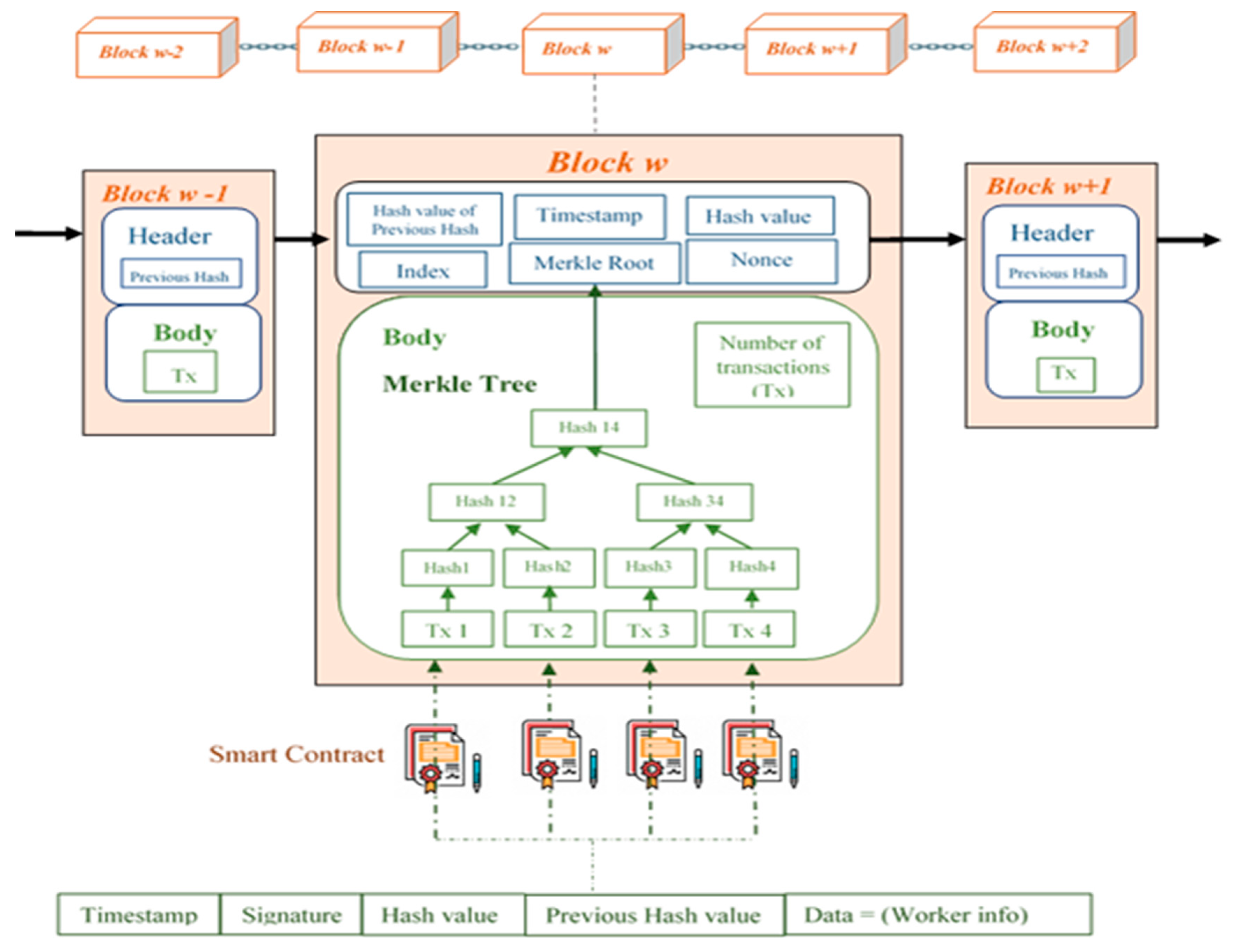
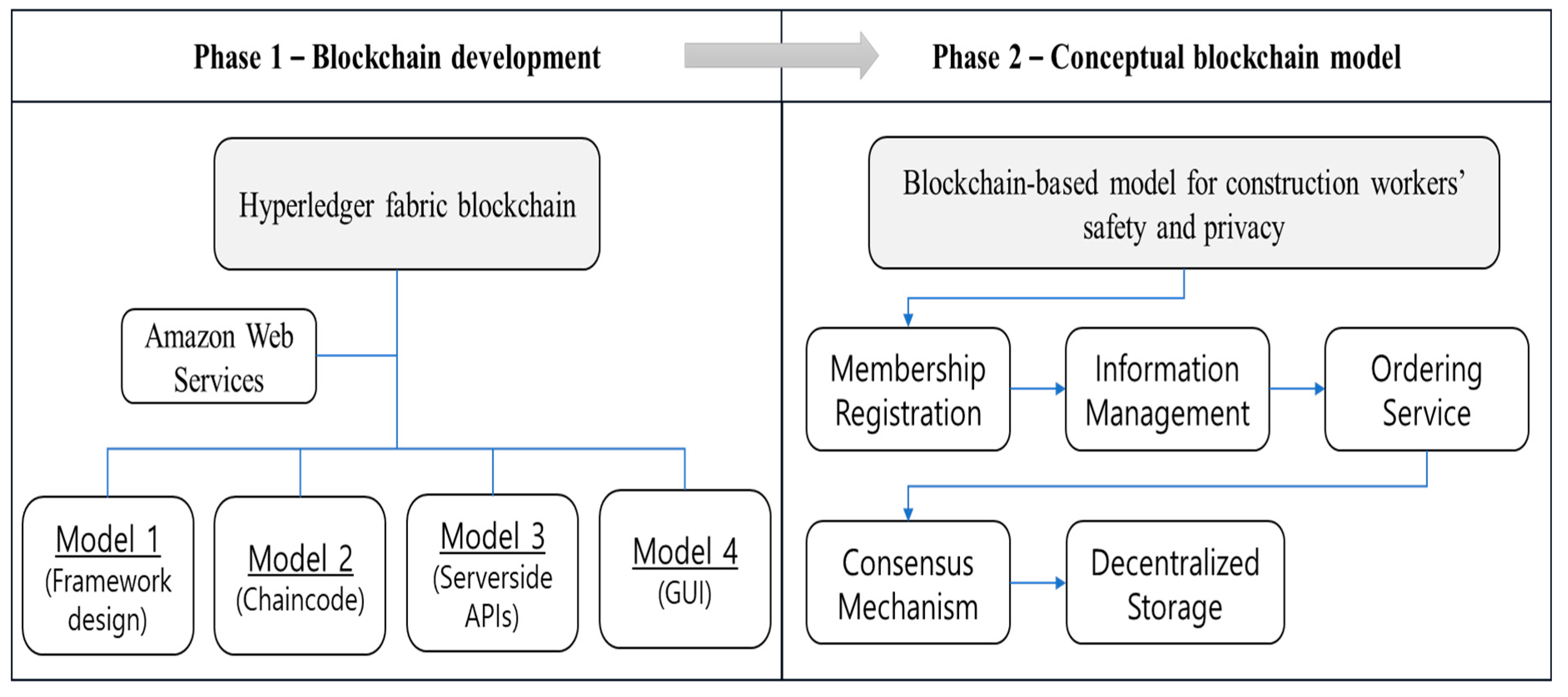
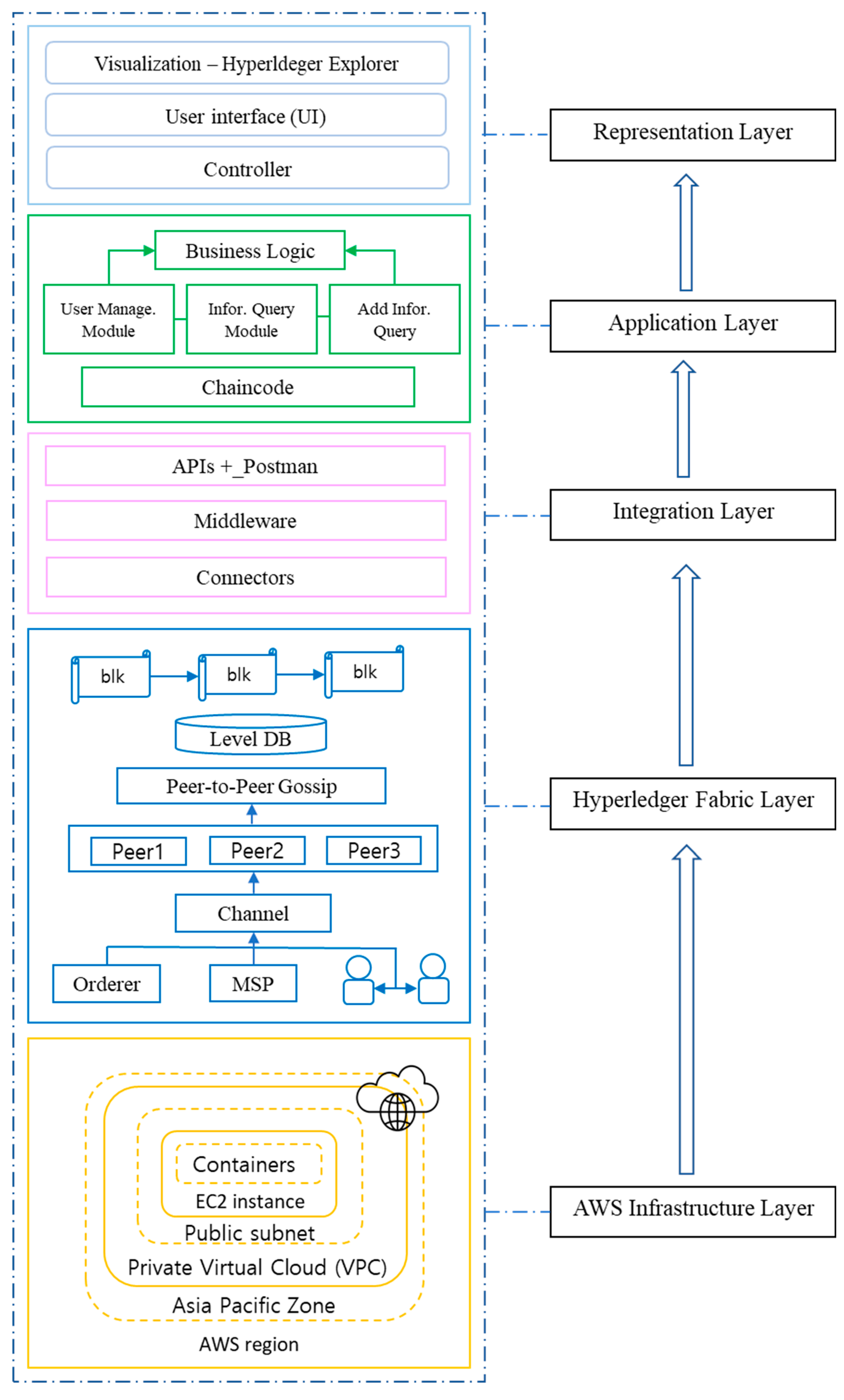
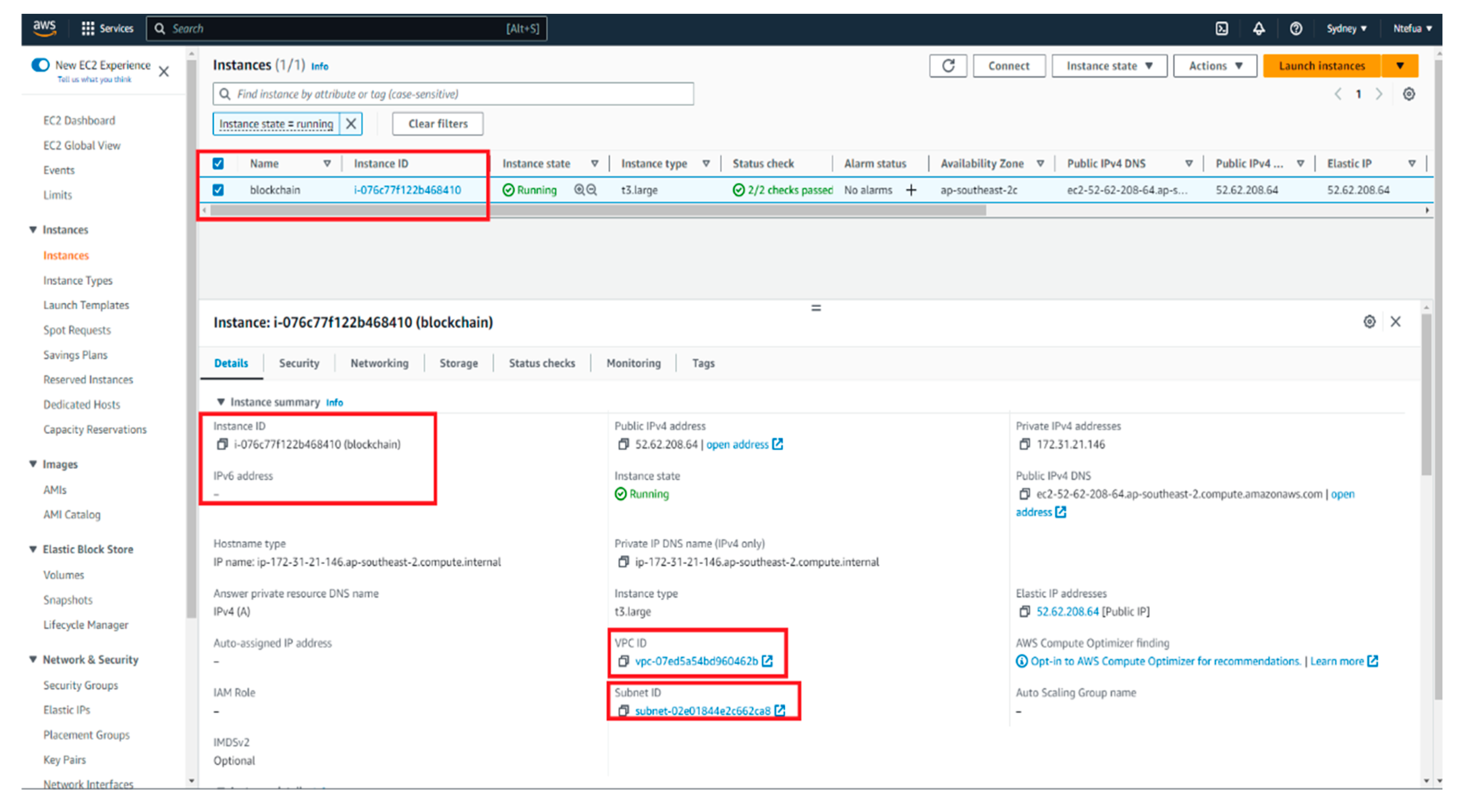
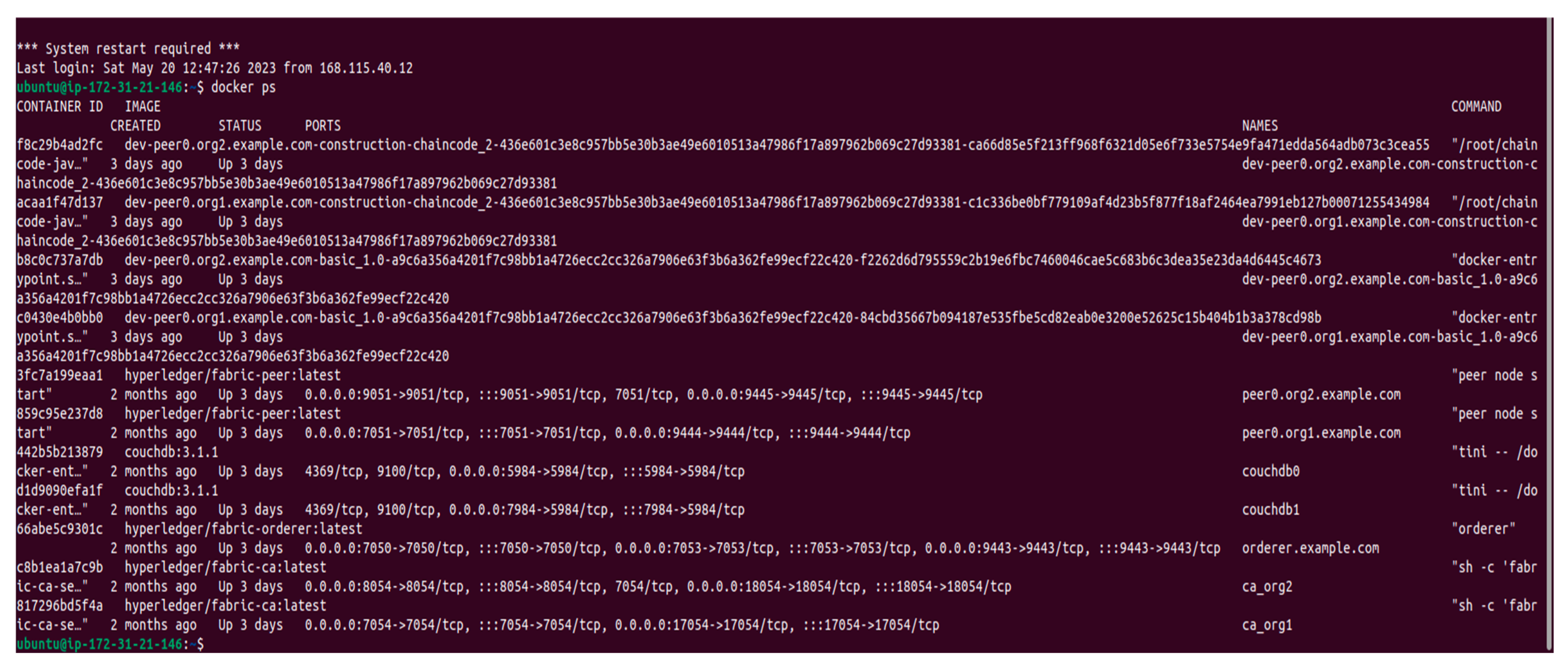
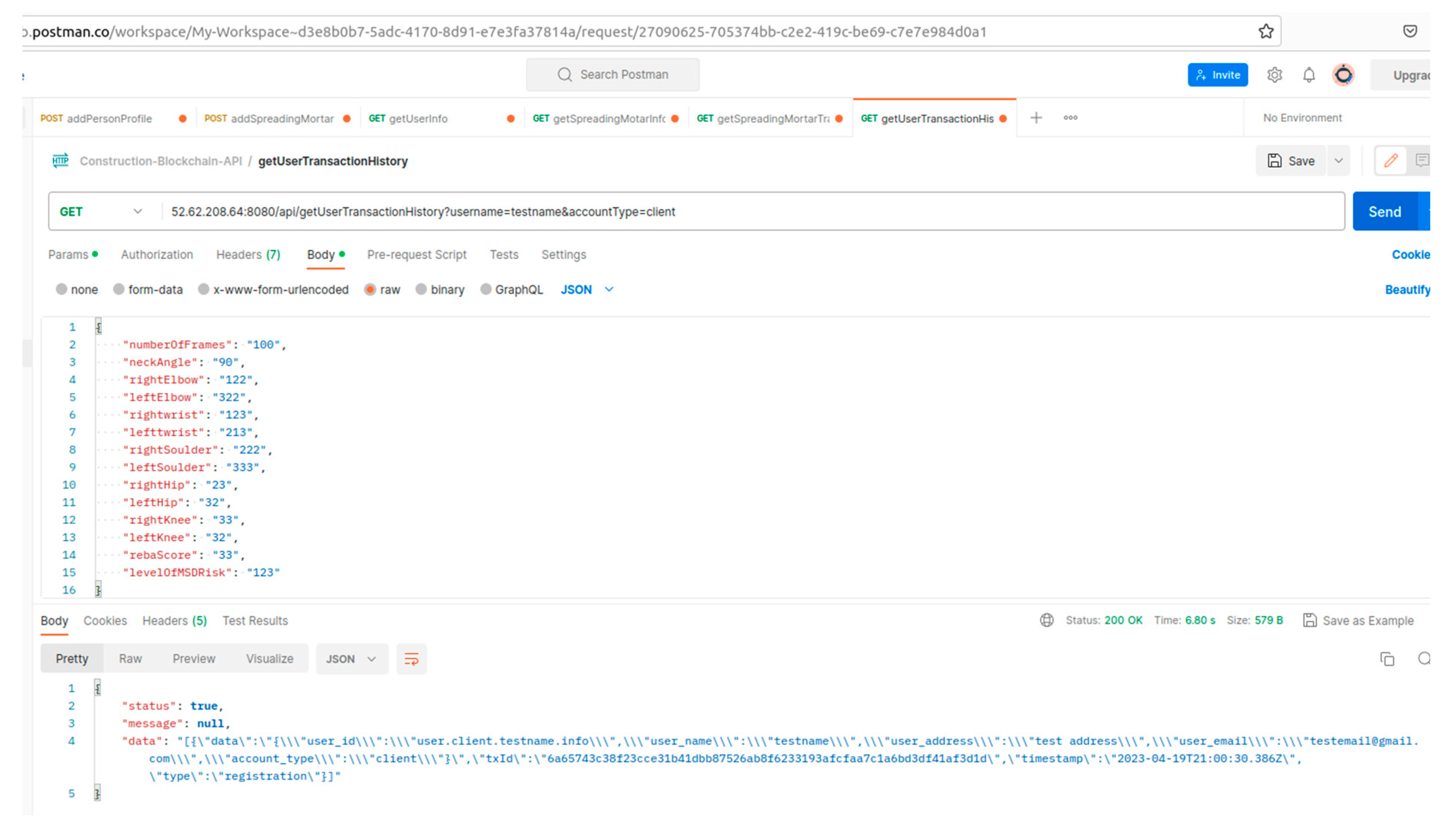
| Container ID | Names |
|---|---|
| 76f609623b6e | dev-peer0.org2.example.com-construction-chaincode |
| 5fcc2dcfae2c | dev-peer0.org1.example.com-construction-chaincode |
| 2b0446d09f92 | dev-peer0.org2.example.com-basic |
| 89cadb858e55 | dev-peer0.org1.example.com-basic |
| e7a5f020a84f | cli |
| 3fc7a199eaa1 | Peer0.org2.example.com |
| 859c95e237d8 | Peer0.org.example.com |
| 442b5b213879 | couchdb0 |
| d1d9090efa1f | couchdb1 |
| 66abe5c9301c | orderer.example.com |
| d453f4b69751 | ca_orderer |
| c8b1ea1a7c9b | ca_org2 |
| 817296bd5f4a | ca_org1 |
| Algorithm 1 Biodata of construction workers in Case study |
|---|
| // Define a User class |
| class User { |
| // Define private member variables |
| String user_id |
| String user_name |
| String user_address |
| String user_email |
| String account_type |
| // Define getters and setters for the member variables |
| method getUser_id() : String |
| method setUser_id(user_id : String) : void |
| method getUser_name() : String |
| Algorithm 2 Safety data of construction workers |
|---|
| // Define a SpreadingMortar class |
| class SpreadingMortar { |
| // Declare private member variables |
| String id |
| String numberOfFrames |
| String neckAngle |
| String rightElbow |
| String leftElbow |
| String rightwrist |
| String lefttwrist |
| String rightSoulder |
| String leftSoulder |
| String rightHip |
| String leftHip |
| String rightKnee |
| String leftKnee |
| String rebaScore |
| String levelOfMSDRisk |
| // Define a parameterized constructor |
| method SpreadingMotor(id : String, numberOfFrames : String, neckAngle : String, rightElbow : String, leftElbow : String, rightwrist : String, lefttwrist : String, rightSoulder : String, leftSoulder : String, |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





