Submitted:
24 October 2023
Posted:
25 October 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Description of Location and Year
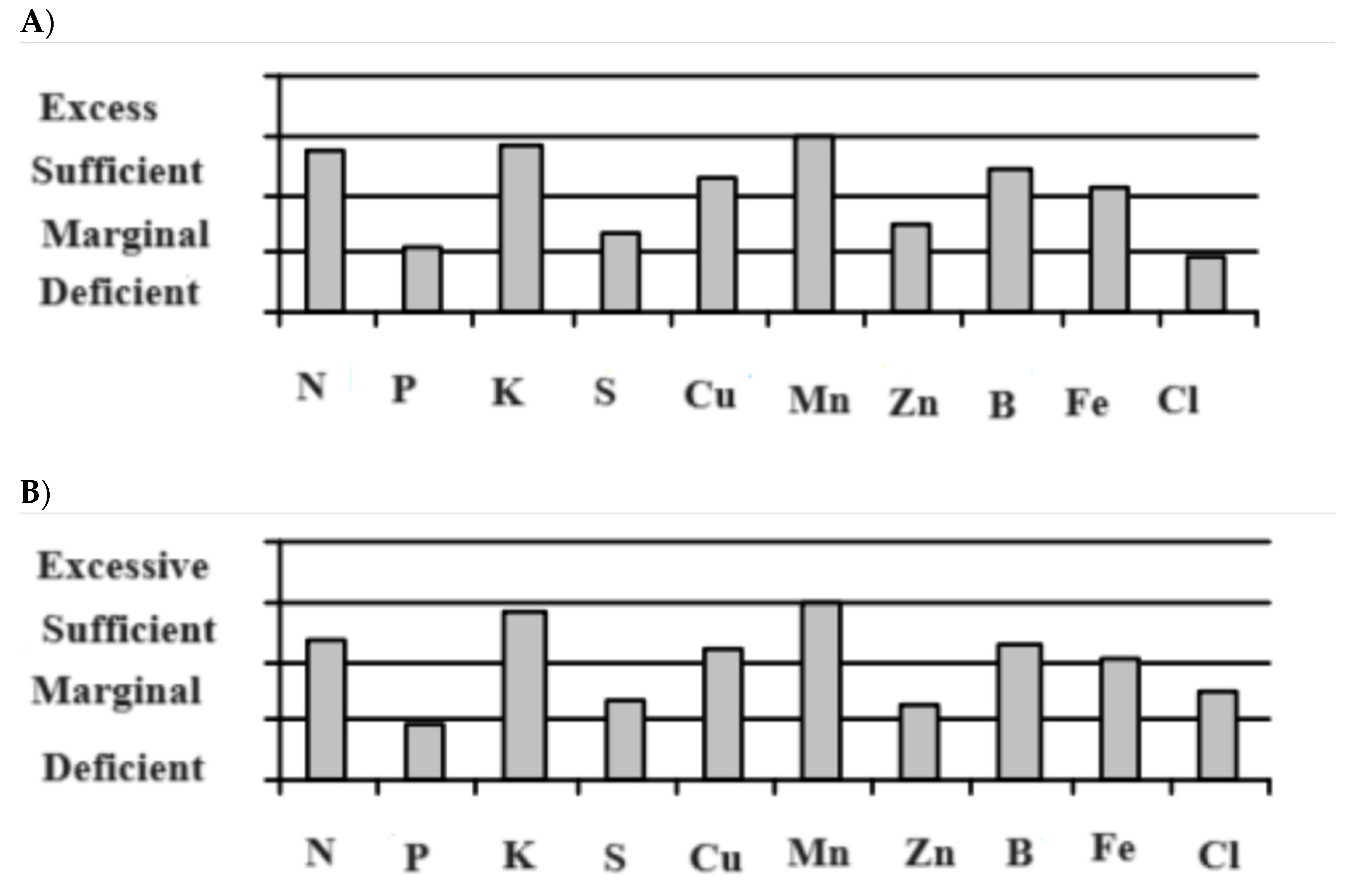
2.2. Soil Sample Analysis
| Before Fertilization | After Fertilization | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Location | Location | |||||||||||||||
| Elrose | Moose Jaw | Elrose | Moose Jaw | Elrose | Moose Jaw | Elrose | Moose Jaw | |||||||||
| 2015 | 2016 | 2015 | 2016 | |||||||||||||
| Depth (inches) | Depth (inches) | Depth (inches) | Depth (inches) | |||||||||||||
| Soil Properties | 0-6 | 6-12 | 0-6 | 6-12 | 0-6 | 6-12 | 0-6 | 6-12 | 0-6 | 6-12 | 0-6 | 6-12 | 0-6 | 6-12 | 0-6 | 6-12 |
| pH | 7.5 | 7.9 | 7.9 | 8.2 | 7.9 | 8.1 | 7.5 | 8.2 | 7.2 | 7.6 | 7.9 | 8.2 | 7.4 | 8.1 | 7.7 | 8.2 |
| N (mg kg-1) | 13.0 | 10.0 | 6.5 | 3.5 | 8.6 | 8.1 | 12.4 | 7.6 | 8.8 | 4.8 | 8.1 | 5.4 | 4.4 | 1.7 | 6.6 | 1.0 |
| P (mg kg-1) | 13.0 | 3.5 | 9.5 | 2.0 | 3.6 | 2.0 | 14.4 | 3.9 | 19.3 | 7.5 | 10.8 | 2.0 | 11.9 | 2.0 | 13.2 | 2.1 |
| K (mg kg-1) | 270 | 255 | 270 | 255 | 699 | 501 | 756 | 614 | 1120 | 856 | 849 | 420 | 932 | 582 | 885 | 507 |
| Fe (mg kg-1) | 20.5 | 11.4 | 13.3 | 9.4 | 19.8 | 19.8 | 18.3 | 17.0 | 22.1 | 23.0 | 16.7 | 13.8 | 20.7 | 21.3 | 22.1 | 19.7 |
2.3. Plant Materials
| Entry | Cultivars | Types | 1000 Seed Weight(g) (Avg. of 2015 and 2016) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | 1173-1 | Kabuli | 349 |
| 2. | 1460-2 | Desi | 203 |
| 3. | AB06-156-2 | Kabuli | 376 |
| 4. | Amit | Kabuli | 252 |
| 5. | CA05-75-45 | Kabuli | 265 |
| 6. | CDC Alma | Kabuli | 293 |
| 7. | CDC Cabri | Desi | 286 |
| 8. | CDC Consul | Desi | 299 |
| 9. | CDC Corinne | Desi | 255 |
| 10. | CDC Cory | Desi | 266 |
| 11. | CDC Frontier | Kabuli | 309 |
| 12. | CDC Leader | Kabuli | 356 |
| 13. | CDC Luna | Kabuli | 297 |
| 14. | CDC Orion | Kabuli | 360 |
| 15. | CDC Palmer | Kabuli | 393 |
| 16. | CDC Vanguard | Desi | 219 |
| 17. | X05TH20-2 | Kabuli | 371 |
| 18. | X05TH47-3 | Kabuli | 351 |
2.4. Fe Fertilizer and Application
| Fe fertilizer | Stability | Fe deficiency |
|---|---|---|
| Fe-EDTA, Fe-DTPA and Fe-HEDTA | Low | Limited/no results |
| Fe-EDDHA | High | Effective |
2.5. Experimental Design
2.6. Data Collection
2.6.1. Agronomic Traits
| Rating | Symptoms |
|---|---|
| 0 | No symptoms |
| 1 | Few, very small (<2mm2) lesions on leaves and/or stems, <2% plant area affected (PAA) |
| 2 | Very small ((<2mm2) lesions, 2-5% PAA |
| 3 | Many small lesions (#2-5mm2), 5-10% PAA |
| 4 | Many small lesions, few large (>5 mm2) lesions, 10-25% PAA |
| 5 | Many large lesions, 25-50% PAA |
| 6 | Lesions coalescing, 50-75% PAA |
| 7 | Lesions coalescing with stem girdling, 75-90% PAA |
| 8 | Stem girdling or breakage, >90% PAA |
| 9 | Plant dead |
2.6.2. Seed Fe Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
| Sources of Variation | df | Germination | Node Number | Days to Flowering | Days to Maturity | Plant Height | Biomass | 1000 Seed Weight | Yield | Seed Fe Conc |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LOC | 1 | 68.3** | 3.6ns | 1232** | 536** | 766** | 101** | 0.6ns | 1254** | 1248** |
| YEAR | 1 | 227** | 93.8** | 131** | 12804** | 5701** | 0.8ns | 1385** | 1367** | 884** |
| REP | 3 | 0.9ns | 3.0* | 3.2* | 1.9ns | 4.7* | 2.4* | 7.8** | 22.0** | 12.4** |
| CUL | 17 | 4.3** | 9.9** | 12.2** | 8.2** | 17.5** | 8.1** | 116** | 35.1** | 19.3** |
| DOS | 2 | 1.3ns | 0.7ns | 1.8ns | 2.7ns | 0.3ns | 61.7** | 1.7ns | 0.0ns | 14.1** |
| LOC*YEAR | 1 | 0.9ns | 19.0** | 395** | 968** | 157** | 1292** | 99.0** | 1866** | 88.9** |
| LOC*CUL | 17 | 1.4ns | 1.4ns | 2.1* | 2.4* | 1.9* | 6.0** | 3.1** | 5.9** | 2.5* |
| LOC*DOS | 2 | 1.6ns | 1.4ns | 4.3* | 15.8** | 2.0ns | 25.5** | 3.4* | 3.6* | 0.9ns |
| CUL*YEAR | 17 | 6.9** | 3.5** | 6.8** | 6.1** | 3.2** | 9.4** | 17.0** | 7.7** | 11.0** |
| CUL*DOS | 34 | 1.2ns | 1.2ns | 0.6ns | 0.7ns | 0.5ns | 1.4ns | 0.7ns | 1.6* | 0.6ns |
| DOS*YEAR | 2 | 2.5ns | 0.2ns | 1.4ns | 1.5ns | 2.6ns | 2.4ns | 2.0ns | 1.3ns | 4.1* |
| LOC*YEAR*CUL | 17 | 1.5ns | 3.1** | 6.0** | 2.4* | 2.6* | 3.2** | 4.2** | 12.6** | 2.0* |
| LOC*YEAR*DOS | 2 | 2.0ns | 0.4ns | 0.5ns | 11.3** | 0.6ns | 32.1** | 1.5ns | 1.3ns | 1.4ns |
| CUL*YEAR*DOS | 34 | 1.1ns | 1.6* | 0.7ns | 0.8ns | 0.7ns | 1.0ns | 0.8ns | 2.4** | 0.7ns |
| CUL*LOC*DOS | 34 | 0.9ns | 0.8ns | 0.6ns | 0.7ns | 0.7ns | 1.1ns | 0.8ns | 1.7* | 0.9ns |
| LOC*YEAR*CUL*DOS | 34 | 1.1ns | 1.3ns | 0.9ns | 0.8ns | 0.5ns | 1.9* | 0.8ns | 1.5* | 1.2ns |
| Sources of Variation | df | Disease score |
|---|---|---|
| LOC | 1 | 62.4** |
| REP | 3 | 37.7** |
| CUL | 17 | 8.9** |
| DOS | 2 | 2.1ns |
| LOC*CUL | 17 | 0.6ns |
| LOC*DOS | 2 | 13.2** |
| CUL*DOS | 34 | 0.5ns |
| LOC*CUL*DOS | 34 | 0.7ns |
3.1. Biomass
|
Cultivars |
Elrose | Moose Jaw | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2015 | 2016 | 2015 | 2016 | ||||||||||
| 0 kg ha-1 | 10 kg ha-1 | 30 kg ha-1 | 0 kg ha-1 | 10 kg ha-1 | 30 kg ha-1 | 0 kg ha-1 | 10 kg ha-1 | 30 kg ha-1 | 0 kg ha-1 | 10 kg ha-1 | 30 kg ha-1 | Cultivars Mean | |
| 1173-1 | 199 | 208 | 255 | 109 | 119 | 127 | 89 | 125 | 99 | 157 | 166 | 182 | 153 |
| 1460-2 | 175 | 232 | 244 | 112 | 116 | 124 | 118 | 89 | 105 | 171 | 257 | 171 | 159 |
| AB06-156-2 | 149 | 280 | 295 | 101 | 117 | 146 | 149 | 127 | 157 | 198 | 201 | 207 | 177 |
| Amit | 195 | 220 | 244 | 126 | 136 | 160 | 118 | 125 | 148 | 216 | 246 | 247 | 182 |
| CA05-75-45 | 179 | 198 | 263 | 125 | 128 | 149 | 87 | 108 | 139 | 173 | 189 | 263 | 167 |
| CDC Alma | 183 | 170 | 208 | 82 | 92 | 100 | 102 | 119 | 85 | 162 | 121 | 113 | 128 |
| CDC Cabri | 166 | 260 | 329 | 129 | 144 | 161 | 81 | 73 | 111 | 127 | 178 | 153 | 159 |
| CDC Consul | 116 | 215 | 223 | 133 | 139 | 143 | 83 | 125 | 85 | 176 | 207 | 261 | 159 |
| CDC Corinne | 167 | 226 | 260 | 147 | 148 | 170 | 129 | 138 | 134 | 196 | 217 | 219 | 179 |
| CDC Cory | 167 | 250 | 262 | 160 | 162 | 174 | 109 | 143 | 123 | 229 | 245 | 301 | 194 |
| CDC Frontier | 238 | 240 | 263 | 136 | 161 | 169 | 136 | 137 | 121 | 243 | 264 | 248 | 196 |
| CDC Leader | 195 | 222 | 235 | 137 | 141 | 145 | 94 | 82 | 86 | 205 | 216 | 259 | 168 |
| CDC Luna | 150 | 248 | 304 | 115 | 134 | 130 | 102 | 90 | 93 | 100 | 164 | 165 | 150 |
| CDC Orion | 207 | 316 | 389 | 130 | 134 | 148 | 105 | 109 | 106 | 191 | 191 | 197 | 185 |
| CDC Palmer | 166 | 170 | 215 | 119 | 132 | 141 | 113 | 112 | 95 | 222 | 229 | 266 | 165 |
| CDC Vanguard | 201 | 259 | 261 | 127 | 129 | 157 | 157 | 127 | 149 | 132 | 238 | 141 | 173 |
| X05TH20-2 | 270 | 302 | 325 | 117 | 124 | 147 | 122 | 122 | 114 | 172 | 172 | 178 | 180 |
| X05TH47-3 | 160 | 166 | 258 | 129 | 156 | 186 | 131 | 134 | 111 | 210 | 214 | 223 | 173 |
| Dose Mean | 182 | 232 | 268 | 124 | 134 | 149 | 112 | 116 | 115 | 182 | 206 | 211 | 169 |
| LSD0.05 | 51.9 | 72.9 | 58.1 | 30.0 | 29.6 | 39.8 | 40.9 | 37.7 | 36.4 | 55.9 | 53.9 | 71.7 | 48.2 |
3.2. Seed Fe
| Elrose | Moose Jaw | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2015 | 2016 | 2015 | 2016 | Cultivar | |||||||||
| Cultivars | 0 kg ha-1 | 10 kg ha-1 | 30 kg ha-1 | 0 kg ha-1 | 10 kg ha-1 | 30 kg ha-1 | 0 kg ha-1 | 10 kg ha-1 | 30 kg ha-1 | 0 kg ha-1 | 10 kg ha-1 | 30 kg ha-1 | Mean |
| 1173-1 | 43 | 48 | 49 | 61 | 63 | 67 | 38 | 37 | 41 | 46 | 46 | 52 | 49 |
| 1460-2 | 47 | 52 | 54 | 56 | 60 | 61 | 39 | 39 | 44 | 45 | 44 | 50 | 49 |
| AB06-156-2 | 51 | 52 | 57 | 67 | 70 | 71 | 41 | 43 | 41 | 47 | 49 | 55 | 54 |
| Amit | 49 | 50 | 48 | 59 | 65 | 72 | 40 | 41 | 43 | 46 | 49 | 51 | 51 |
| CA05-75-45 | 48 | 43 | 49 | 58 | 57 | 59 | 35 | 34 | 34 | 49 | 44 | 51 | 47 |
| CDC Alma | 43 | 50 | 50 | 65 | 72 | 80 | 38 | 39 | 39 | 48 | 50 | 54 | 52 |
| CDC Cabri | 46 | 46 | 54 | 57 | 57 | 60 | 37 | 40 | 40 | 47 | 48 | 51 | 49 |
| CDC Consul | 52 | 52 | 54 | 57 | 63 | 57 | 42 | 47 | 43 | 41 | 44 | 47 | 50 |
| CDC Corinne | 46 | 50 | 50 | 55 | 55 | 60 | 41 | 39 | 41 | 41 | 41 | 43 | 47 |
| CDC Cory | 47 | 48 | 51 | 56 | 60 | 64 | 42 | 44 | 45 | 42 | 45 | 48 | 49 |
| CDC Frontier | 57 | 55 | 55 | 66 | 73 | 76 | 43 | 45 | 46 | 49 | 52 | 57 | 56 |
| CDC Leader | 48 | 47 | 45 | 60 | 60 | 62 | 38 | 37 | 39 | 43 | 46 | 53 | 48 |
| CDC Luna | 48 | 47 | 48 | 78 | 73 | 80 | 38 | 39 | 37 | 49 | 56 | 56 | 54 |
| CDC Orion | 46 | 53 | 52 | 70 | 68 | 71 | 39 | 37 | 40 | 47 | 52 | 54 | 52 |
| CDC Palmer | 48 | 48 | 48 | 64 | 63 | 69 | 37 | 40 | 39 | 46 | 44 | 48 | 50 |
| CDC Vanguard | 44 | 47 | 48 | 53 | 49 | 57 | 40 | 39 | 47 | 41 | 44 | 48 | 46 |
| X05TH20-2 | 55 | 57 | 58 | 75 | 72 | 76 | 49 | 50 | 46 | 50 | 51 | 54 | 58 |
| X05TH47-3 | 53 | 50 | 56 | 72 | 67 | 70 | 46 | 49 | 48 | 49 | 52 | 51 | 55 |
| Dose Mean | 48 | 50 | 51 | 63 | 64 | 67 | 40 | 41 | 42 | 46 | 48 | 51 | 51 |
| LSD0.05 | 7.0 | 11.4 | 7.6 | 9.6 | 11.6 | 9.3 | 4.9 | 4.8 | 5.5 | 7.1 | 5.5 | 6.8 | 7.6 |
3.3. Fe Yield
| Cultivars | Elrose | Moose Jaw | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2015 | 2016 | 2015 | 2016 | ||||||||||
| 0 kg ha-1 | 10 kg ha-1 | 30 kg ha-1 | 0 kg ha-1 | 10 kg ha-1 | 30 kg ha-1 | 0 kg ha-1 | 10 kg ha-1 | 30 kg ha-1 | 0 kg ha-1 | 10 kg ha-1 | 30 kg ha-1 | Cultivar Mean |
|
| 1173-1 | 311 | 347 | 316 | 129 | 116 | 31 | 86 | 83 | 111 | 141 | 131 | 170 | 164 |
| 1460-2 | 340 | 337 | 369 | 137 | 125 | 126 | 113 | 91 | 113 | 171 | 132 | 184 | 187 |
| AB06-156-2 | 396 | 410 | 447 | 137 | 170 | 125 | 93 | 104 | 104 | 145 | 98 | 199 | 202 |
| Amit | 306 | 337 | 335 | 132 | 113 | 174 | 93 | 86 | 89 | 132 | 150 | 150 | 175 |
| CA05-75-45 | 305 | 250 | 311 | 160 | 132 | 138 | 74 | 59 | 61 | 112 | 171 | 126 | 158 |
| CDC Alma | 234 | 250 | 247 | 62 | 65 | 63 | 89 | 79 | 109 | . | . | . | 133 |
| CDC Cabri | 291 | 326 | 319 | 284 | 172 | 187 | 74 | 99 | 90 | 152 | 72 | 107 | 181 |
| CDC Consul | 430 | 405 | 419 | 172 | 171 | 135 | 132 | 127 | 129 | 196 | 253 | 291 | 238 |
| CDC Corinne | 405 | 438 | 434 | 174 | 248 | 211 | 122 | 110 | 100 | 149 | 182 | 189 | 230 |
| CDC Cory | 376 | 351 | 374 | 262 | 264 | 155 | 122 | 144 | 159 | 127 | 203 | 141 | 223 |
| CDC Frontier | 443 | 433 | 427 | 130 | 150 | 314 | 140 | 131 | 131 | 78 | 62 | 75 | 209 |
| CDC Leader | 359 | 420 | 367 | 152 | 135 | 69 | 98 | 104 | 104 | 190 | 156 | 165 | 193 |
| CDC Luna | 282 | 294 | 291 | 149 | 112 | 141 | 100 | 107 | 110 | . | . | . | 136 |
| CDC Orion | 267 | 379 | 315 | 139 | 96 | 185 | 106 | 96 | 104 | 106 | 89 | 81 | 164 |
| CDC Palmer | 416 | 342 | 422 | 190 | 206 | 204 | 97 | 95 | 98 | 173 | 170 | 300 | 226 |
| CDC Vanguard | 272 | 372 | 288 | 168 | 151 | 156 | 105 | 95 | 94 | 108 | 97 | 104 | 167 |
| X05TH20-2 | 263 | 334 | 306 | 109 | 97 | 147 | 85 | 92 | 83 | 104 | 98 | 109 | 152 |
| X05TH47-3 | 346 | 367 | 387 | 133 | 182 | 113 | 103 | 141 | 123 | 198 | 153 | 209 | 205 |
| Dose Mean | 335 | 355 | 354 | 157 | 150 | 148 | 102 | 102 | 106 | 135 | 131 | 155 | 186 |
| LSD0.05 | 73.4 | 90.8 | 69.6 | 73.0 | 98.8 | 136.2 | 24.8 | 24.5 | 34.4 | 57.3 | 59.6 | 65.7 | 67.3 |
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author’s contributions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of interest
References
- Grillet, L.; Mari, S.; Schmidt, W. Fe in seeds – loading pathways and subcellular localization. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 4, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, G. Z. H.; Das Bhowmik, S. S.; Hoang, T. M. L.; Karbaschi, M. R.; Johnson, A. A. T.; Williams, B.; Mundree, S. G. Finger on the pulse: Pumping Fe into chickpea. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, Y.; Zhang, F. Soil and crop management strategies to prevent Fe deficiency in crops. Plant Soil. 2011, 339, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, C.; Palumbo, G.; He, J. Z.; Pinton, R.; Cesco, S. Review on Fe availability in soil: Interaction of Fe minerals, plants, and microbes. J. Soils Sediments. 2014, 14, 538–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukhalfa, H.; Crumbliss, A. L. Chemical aspects of siderophore mediated Fe transport. Biometals. 2002, 15, 325–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Römheld, V.; Marschner, H. Evidence for a specific uptake system for Fe phytosiderophores in roots of grasses. Plant Physiol. 1986, 80, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, N. J.; Procter, C. M.; Connolly, E. L.; Guerinot, M. L. A ferric-chelate reductase for Fe uptake from soils. Nature. 1999, 397, 694–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrissey, J.; Guerinot, M. Fe uptake and transport in plants: The good, the bad, and the ionome. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 4553–4567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.; Connolly, E. L. Fe uptake mechanisms in plants: Functions of the FRO family of ferric reductases. Plant Sci. 2009, 176, 709–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chugh, V.; Dhaliwal, H. Biofortification of Staple Crops. In Agricultural Sustainability, Elsevier, 2013, 177-196. [CrossRef]
- Mayer, J.; Pfeiffer, W.; Beyer, P. Biofortified crops to alleviate micronutrient malnutrition. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2008, 11, 166–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briat, J.F. Fe Nutrition and Implications for Biomass Production and the Nutritional Quality of Plant Products. In Molecular and physiological basis of nutrient use efficiency in crops, Hawkesford, M. J.; Barraclough, P., Ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 2011; pp. 309–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cakmak, I. Enrichment of cereal grains with zinc: Agronomic or genetic biofortification? Plant Soil, 2008, 302, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Valença, A.; Bake, A.; Brouwer, I.; Giller, K. Agronomic biofortification of crops to fight hidden hunger in sub-Saharan Africa. Global Food Security, 2017, 12, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, R. Ferti-fortifcation of grains an easy option to alleviate malnutrition of some micronutrients in human beings. Indian J. Fertilisers. 2009, 5, 129–133. [Google Scholar]
- Manzeke, G.; Mapfumo, M.; Mtambanengwe, P.; Chikowo, F.; Tendayi, R.; Cakmak, T. Soil fertility management effects on maize productivity and grain zinc content in smallholder farming systems of Zimbabwe. Plant Soil, 2012, 361(1-2), 57-69. [CrossRef]
- Vanlauwe, B.; Descheemaeker, K.; Giller, K.; Huising, J.; Merckx, R.; Nziguheba, G.; Zingore. S. Integrated soil fertility management in sub-Saharan Africa: Unravelling local adaptation. Soil, 2015, 1, 491–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voortman, R.L.; Bindraban, P.S. Beyond N and P: Towards a land resource ecology perspective and impactful fertilizer interventions in Sub-Sahara Africa. In VFRC Report 2015/1; Virtual Fertilizer Research Center: Washington, D.C. USA,, 2015; 49. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, M.; Prasad, K. Agronomic Aspects of Zinc Biofortification in Rice (Oryza sativa L.). Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, India Section B: Biol. Sci. 2014, 84, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rietra, R.P.J.J.; Heinen, M.; Dimpla, C.; Bindraban, P.S. Effects of nutrients antagonism and synergism on fertilizer use efficiency. VFRC Report 2015/5. Virtual Fertilizer Research Centre. Available online: http://www.vfrc.org/getdoc/e738b7d3-8f70-4b18-b3d9-980694b5f26c/vfrc_2015-5_effects_of_nutrient_antagonism_and_syn.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2018).
- Walworth, D. J. Recognizing and Treating Fe Deficiency in the Home Yard. Available online: https://extension.arizona.edu/sites/extension.arizona.edu/files/pubs/az1415.pdf (accessed on 10 May 2019).
- Millán, T.; Madrid, E.; Cubero, J. I.; Amri, M.; Patricia, C.; Rubio, J. Chickpea. In Handbook of Plant Breeding; De Ron. A. M., D., Ed.; Springer: Pontevedra, Spain, 2015; pp. 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Choi, H.; Cook, D. R.; Shoemaker, R. C. Bridging model and crop legumes through comparative genomics. Plant Physiol. 2005, 137, 1189–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FAOSTAT. FAO Statistical Database. Available online: http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QC (accessed on 15 May 2018).
- Akibode, C. S.; Maredia, M. K. Global and regional trends in production, trade and consumption of food legume crops. Michigan State University, Michigan, USA. 2012. [CrossRef]
- Wells, H. F.; Bond, J.K. Vegetables and Pulses Yearbook Data. Economic Research Service, USDA. 2016. 2016. Available online: https://downloads.usda.library.cornell.edu/usda-esmis/files/1n79h429p/z890rw81t/rj430695g/VGS-08-30-2016.pdf (accessed on 15 March 2019).
- Ibrikci, H.; Knewtson, S.; Grusak, M. Chickpea leaves as a vegetable green for humans: Evaluation of mineral composition. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 2003, 83, 945–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S. S.; Longnecker, N.; Dusunceli, F.; Bejiga, G.; Yadav, M.; Rizvi, A. H.; … Chen, W. Uses, consumption and utilization. In Chickpea Breeding and Management, Yadav, S.S.; Redden, R.J., Chen, W., Eds.; Sharma, B. Eds. CABI: Cambridge, MA , USA, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diapari, M.; Sindhu, A.; Bett, K.; Deokar, A.; Warkentin, T.; Tar'an, B. Genetic diversity and association mapping of Fe and zinc concentrations in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). Genome, 2014, 57, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USDA. National Nutrient Database for Standard Reference. Available online: http://www.ars.usda.gov/Services?docs.htm?docid=8964 (accessed on 25 March 2018).
- Chilimba, A.; Young, S.; Black, C.; Meacham, M.; Lammel, J.; Broadley, M. Agronomic biofortification of maize with selenium (Se) in Malawi. Field Crops Res. 2012, 125, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, A.; Ekiz, H.; Torun, B.; Gultekin, I.; Karanlik, S.; Bagci, S.A.; Cakmak, I. Effect of different zinc application methods on grain yield and zinc concentration in wheat cultivars grown on zinc-deficient calcareous soils. J. Plant. Nutr. 1997, 20(4-5), 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidoto, L.; Worku, W.; Mohammed, H.; Bunyamin, T. Effects of zinc application strategy on zinc content and productivity of chickpea grown under zinc deficient soils. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2017, 17(1), 0. [CrossRef]
- Ali, B.; Ali, A.; Tahir, M.; Ali, S. Growth, Seed yield and quality of mungbean as influenced by foliar application of Fe sulfate. Pak J Life Soc Sci. 2014, 12, 20–25. [Google Scholar]
- Smrkolj, P.; Germ, M.; Kreft, I.; Stibilj, V. Respiratory potential and Se compounds in pea (Pisum sativum L.) plants grown from Se-enriched seeds. J Exp Bot. 2006, 57, 3595–3600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smrkolj, P.; Osvald, M.; Osvald, J.; Stibilj, V. Selenium uptake and species distribution in selenium-enriched bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) seeds obtained by two different cultivations. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2007, 225, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, M. G.; Quiroz, C. M.; de la Cruz, L. E.; Martinez, J. R.V.; Parra, J. M. S; Carrillo, M. G.; Vidal, J.A.O. Biofortification of cowpea beans (Vigna unguiculata L. Walp) with Fe and zinc. Mexican Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 17, 3427–3438. [Google Scholar]
- Sida-Arreola, J.; Sánchez, E.; Ojeda-Barrios, D.; Ávila-uezada, G.; Flores-Córdova, M.; Márquez-Quiroz, C.; Preciado-Rangel, P. Can biofortification of zinc improve the antioxidant capacity and nutritional quality of beans? Emir J Food Agric. 2017, 29, 237–241. [Google Scholar]
- Márquez-Quiroz, C.; De-La-Cruz-Lázaro, E.; Osorio-Osorio, R.; Sánchez-Chávez., E. Biofortification of cowpea beans with Fe: Fe´s influence on mineral content and yield. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. ahead of print. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Rengel, Z.; Aziz, T.; Abid, M. Estimated Zinc Bioavailability in Milling Fractions of Biofortified Wheat Grains and in Flours of Different Extraction Rates. Int J Agric Biol. 2013, 15, 921–926. [Google Scholar]
- White, P. J.; Broadley, M. R. Biofortification of crops with seven mineral elements often lacking in human diets. The New Phytologist, 2009, 182, 49–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfthan, G.; Eurola, M.; Ekholm, P.; Venäläinen, E.; Root, T.; Korkalainen, K.; Aero, A. Effects of nationwide addition of selenium to fertilizers on foods, and animal and human health in Finland: From deficiency to optimal selenium status of the population. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2015, 31, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucena, J. Synthetic Iron Chelates to Correct Iron Deficiency in Plants. In Iron Nutrition in Plants and Rhizospheric Microorganisms; Barton, L.L., Abadia, J., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, Netherland, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chongo, G.; Gossen, B. D.; Buchwaldt, L.; Adhikari, T.; Rimmer, S. R. Genetic diversity of Ascochyta rabiei in Canada. Plant Dis. 2004, 88(1), 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DellaValle, D. M.; Thavarajah, D.; Thavarajah, P.; Vandenberg, A.; Glahn, R. P. Lentil (Lens culinaris L.) as a candidate crop for Fe biofortification: Is there genetic potential for Fe bioavailability? Field Crops Res. 2013, 144, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraghan, J.; Padilla, T.; Etchevers, J.; Grafton, K.; Acosta-Gallegos, J. Fe accumulation in seed of common bean. Plant Soil. 2002, 246, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Dwivedi, V. N.; Tiwari, D. D. Effect of phosphorous and Fe on yield and mineral nutrition in chickpea. Ann. Plant soil res. 2009, 11, 16–18. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, S.; Sharma, M.; Ramesh, A. Biofortification of crops with micronutrients through agricultural approaches. Indian Farming. 2010, 60, 7–12. [Google Scholar]
- Kumawat, R. N.; Rathore, P. S.; Pareek, N. Response of mung bean to sulphur and Fe nutrition grown on calcareous soil of Western Rajasthan. Indian J Pulses Res. 2006, 19, 228–230. [Google Scholar]
- Sahu, S.; Lidder, R. S.; Singh. P., K. Effect of micronutrients and biofertilizers on growth, yield and nutrient uptake by chickpea (Cicer aeritinum L.) in Vertisols of Madhya Pradesh. Adv Plant Sci. 2008, 21, 501–503. [Google Scholar]
- Mahriya, A. K.; Meena, N. Response of phosphorous and Fe on growth and quality of cowpea (Vigna unguiculata L.). Ann. Agric. Biologic. Res. 1999, 4, 203–205. [Google Scholar]
- Bansal, R. L.; Chahal, D. S. Interaction effect of Fe and Mn on growth and nutrient content of moong (Phaseolus aureus L.). Acta Agronomica Hungarica 1990, 39, 59–63. [Google Scholar]
- Ghasemi-Fasaei, R.; Ronaghi, A.; Maftoun, M.; Karimian, N.; Soltanpour, P. Fe-Manganese Interaction in Chickpea as Affected by Foliar and Soil Application of Fe in a Calcareous Soil. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2005, 36(13-14), 1717–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moosavi, A. A.; Ronaghi, A. Influence of foliar and soil applications of Fe and manganese on soybean dry matter yield and Fe-manganese relationship in a calcareous soil. Aust J Crop Sci. 2011, 5, 1550–1556. [Google Scholar]
- Ronaghi, A.; Ghasemi-Fasaei, R. Field Evaluations of Yield, Fe-Manganese Relationship, and Chlorophyll Meter Readings in Soybean Genotypes as Affected by Fe-Ethylenediamine Di-o-hydroxyphenylacetic Acid in a Calcareous Soil. J. Plant Nutr. 2007, 31, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mevada, K. D.; Patel, J. J.; Petel, K.P. Effect of micronutrients on yield of urdbean. Indian J Pulses Res. 2005, 18, 214–216. [Google Scholar]
- Ariza-Nieto, M.; Blair, M.; Welch, R; Glahn, R. Screening of Fe bioavailability patterns in eight bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) genotypes using the Caco-2 cell in vitro model. J Agric Food Chem. 2007, 55, 7950–7956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janmohammadi, M.; Abdoli, H.; Sabaghnia, N.; Esmailpour, M.; Aghaei, A. The Effect Of Fe, Zinc and Organic Fertilizer on Yield of Chickpea (Cicer Artietinum L.) in Mediterranean Climate. Acta Universitatis Agriculturae et Silviculturae Mendelianae Brunensis, 2018, 66, 0049–0060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, V. S. I. Effect of Fe, Mo, Zn and P on symbiotic nitrogen fixation of chickpea. Indian J Agric. Chemis. 1994, 32, 118–123. [Google Scholar]
- Balachandar, D.; Nagarajan, P.; Gunasekaran, S. Effect of organic amendments and micronutrients on nodulation of black gram in acid soil. Legumes Res, 2003, 26, 192–195. [Google Scholar]
- Mahriya, A. K.; Meena, N. Response of phosphorous and Fe on growth and quality of cowpea (Vigna unguiculata L.). Ann Agric Biologic Res. 1999, 4, 203–205. [Google Scholar]
- Thapu, U.; Rai, P.; Suresh, C. P.; Pal., P. Effect of micronutrients on the growth and yield of pea in gangetic alluvial of West Bengal. Environment and Ecology, 2003, 21, 179–182. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





