Introduction
Health services play an important role in people's lives and are the basic right of every individual. Equal and quality access to health services is crucial for people's welfare (Rokom, 2016). In Indonesia, health service programs such as BPJS, JKN-KIS, and ASKES have been implemented to ensure equal availability of health services for the entire population. However, the current situation shows that the Universal Health Coverage (UHC) system in Semarang City is still not fully accessible to the public (Basuki et al., 2016).
The city of Semarang has a population of 1.65 million people (Kusnandar, 2021). In this significant population scale, it is important for the government and related institutions to provide assurance of adequate health services for the entire population. However, the reality on the ground shows that there are still a number of people in the city of Semarang who have not received benefits from the existing health insurance. Therefore, efforts are needed to increase access to and quality of health services (Agustin et al., 2023).
This study aims to analyze the effectiveness of achieving 100% UHC in Semarang City through public service innovation, with a focus on the inspirational contribution of the figure of PANGERAN DIPONEGORO. This research aims to provide in-depth insights into the implementation of health insurance programs at the local level and the impact of public service innovation on achieving UHC.
The results of this study are expected to contribute to health policy makers and public services in the city of Semarang in order to increase the efficiency of the health insurance program and achieve the UHC target more effectively. In addition, this research is also expected to provide valuable input for the development of similar programs in other cities in Indonesia, which face similar challenges in achieving UHC. The aspect of community participation in strengthening the implementation of programs and strategies to increase citizen involvement in achieving UHC in a sustainable manner will also be a concern in this research.
Literature Review
This research is based on four main theoretical components. First, health services are seen as an integral part of public services that underlie the fulfillment of the basic needs of society. The concept of public service focuses on providing quality, equitable and just services for all citizens. This understanding is the key in appreciating the significance of access to quality health services for all levels of society in the city of Semarang.
Second, health insurance is identified as an important instrument in increasing the coverage and quality of health services. The National Health Insurance Program is the basis for national policy to achieve Universal Health Coverage (UHC) by providing fair and equitable protection and access to health for the entire population. In this study, understanding the concept of health insurance is the basis for evaluating the level of success and challenges faced in achieving the 100% UHC target in Semarang City.
Third, innovation in the context of health services is defined as a new approach or system change aimed at increasing the efficiency and effectiveness of services. The focus on public service innovation allows the identification and analysis of various forms of innovation that have been implemented in an effort to achieve UHC in the city of Semarang. The use of the concept of innovation helps measure the impact of these innovative initiatives in increasing access to and quality of health services at the local level.
Fourth, the partnership strategy is considered an important approach to achieve the goals of inclusive and sustainable health services. Within the framework of the partnership strategy, the participation of various stakeholders, including government, private sector and civil society, is integrated to reach mutual agreements and increase program effectiveness. This research explores the role of the partnership strategy in the implementation of the health insurance program in Semarang City to identify potentials and obstacles in achieving UHC in a comprehensive manner.
Methods
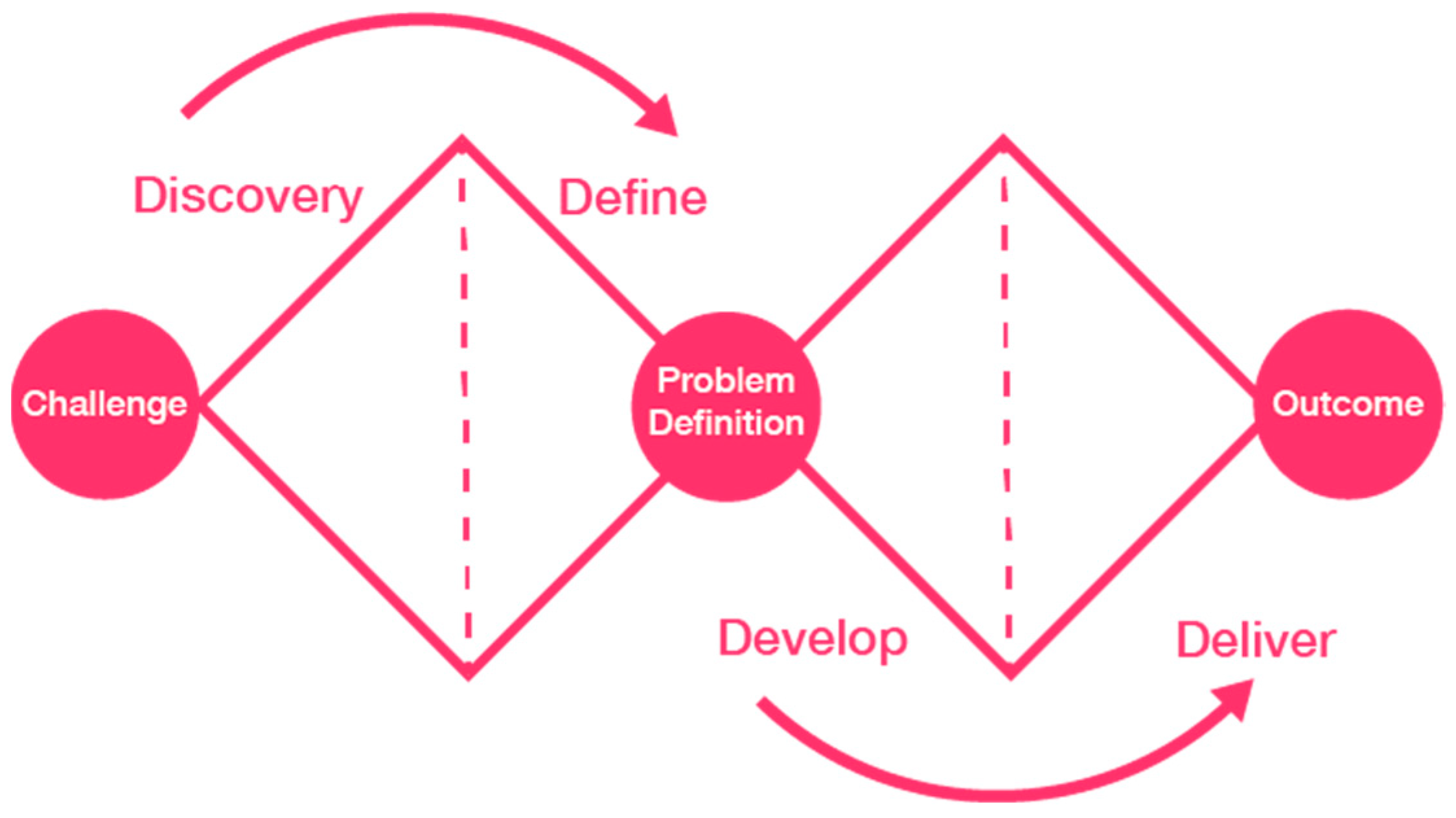
The method used in this research is qualitative with the Double Diamond approach (Ledbury, 2017). This approach has four main stages consisting of Define, Discover, Develop, and Deliver to obtain comprehensive research results (Andriana, 2021; Yapary, 2022). Data was obtained primary, namely through innovation supporting documents from the Semarang City Health Office and secondary data collection was taken through literature studies and Focus Group Discussions (Mayer, 2022) which were carried out for two months, from April to June 2023. Furthermore, data triangulation carried out to obtain valid and reliable data (Pajo, 2022). The conceptual framework is used as a research flow. Furthermore, a qualitative comparative analysis (QCA) was carried out using the IE Matrix, VRIO, and Value Chain to obtain analysis relevant to this study (Barney & Hesterly, 2019; Mello, 2021).
Figure 1.
Conceptual framework. Source: Author's Elaboration, 2023.
Figure 1.
Conceptual framework. Source: Author's Elaboration, 2023.
Results
Innovation Profile 'PRINCIPLE OF DIPONEGORO'
The Universal Health Coverage (UHC) program in Semarang City aims to provide access to health insurance for urban communities who have not been covered by previous health programs. In an effort to achieve this goal, a policy change was made by integrating the City Community Health Insurance (Jamkesmaskot) program into the National Health Insurance program - Healthy Indonesia Cards Social Security Administration Agency (JKN-KIS BPJS Kesehatan). In this policy change, there is a target to register as many as 50,000 poor people in the program.
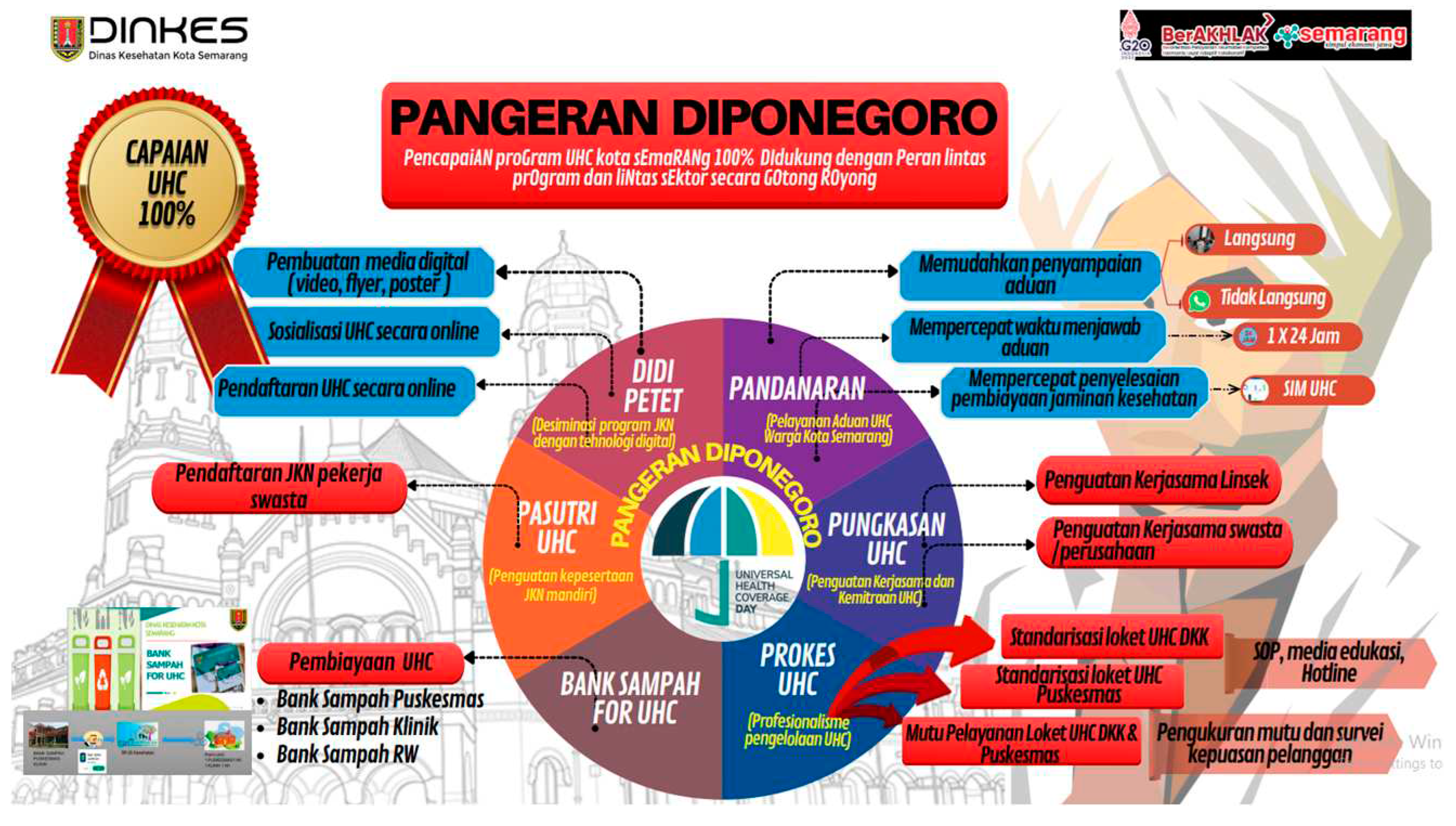
Figure 2.
PANGERAN DIPONEGORO Innovation Roadmap. Source: Author's Elaboration, 2023.
Figure 2.
PANGERAN DIPONEGORO Innovation Roadmap. Source: Author's Elaboration, 2023.
The implementation of the Semarang City UHC Program is based on Semarang Mayor Regulation Number 43 of 2017 which stipulates the registration of residents of the City of Semarang as Participants Receiving BPJS Health Contribution Assistance (PBI). Even so, the problem faced is that there are still many people who have not received adequate health insurance.
Therefore, innovation is needed to overcome these challenges. This innovation is expected to increase community participation in the UHC program, especially among urban residents who have not been covered by the previous program. Thus, this effort is expected to improve access and quality of health services for all people in Semarang City who need it.
The PANGERAN DIPONEGORO innovation is an effort to increase speed in achieving Universal Health Coverage (UHC) in Semarang City. The aim of this innovation is that all residents of Semarang City can access health services through participation in the National Health Insurance (JKN). This innovation has had a significant impact on achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (TPB), especially in reducing poverty by increasing the proportion of Health Insurance participants through the National Social Security System (SJSN) in the health sector. After optimizing cooperation in the implementation of PANGERAN DIPONEGORO innovations since 2019, the current UHC achievement has reached 100%, which can be achieved thanks to this innovative intervention. The proportion of Health Insurance participants through the SJSN in the health sector makes an important contribution in achieving the goals, targets and indicators of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) in Semarang City.
Innovation Feasibility Study
- a)
MatrixInternal-External Factors
In this report, the Internal-External Factor Matrix is used to help implement more targeted innovations (Grant, 2010; Sarsby, 2016). This matrix is used to analyze internal and external factors that influence the implementation of innovations in the context of health services. The following table describes the details of the matrix and relevant factors in achieving Universal Health Coverage (UHC) in Semarang City.
Table 1.
Matrix I-E.
| Internal factors |
Weight |
Rating |
Score |
| Achievements of Community Participation |
0.22 |
4 |
0.88 |
| Service quality |
0.24 |
4 |
0.96 |
| Technology Innovation |
0.18 |
4 |
0.72 |
| Implementing Human Resources |
0.21 |
3 |
0.63 |
| Program Management |
0.15 |
4 |
0.60 |
| Total |
3.79 |
| External Factors |
Weight |
Rating |
Score |
| Related Stakeholder Support |
0.24 |
4 |
0.96 |
| Community Compliance |
0.24 |
3 |
0.72 |
| Budget Availability |
0.19 |
4 |
0.76 |
| Potential Collaboration |
0.15 |
4 |
0.60 |
| Policy Support |
0.18 |
3 |
0.54 |
| Total |
3.58 |
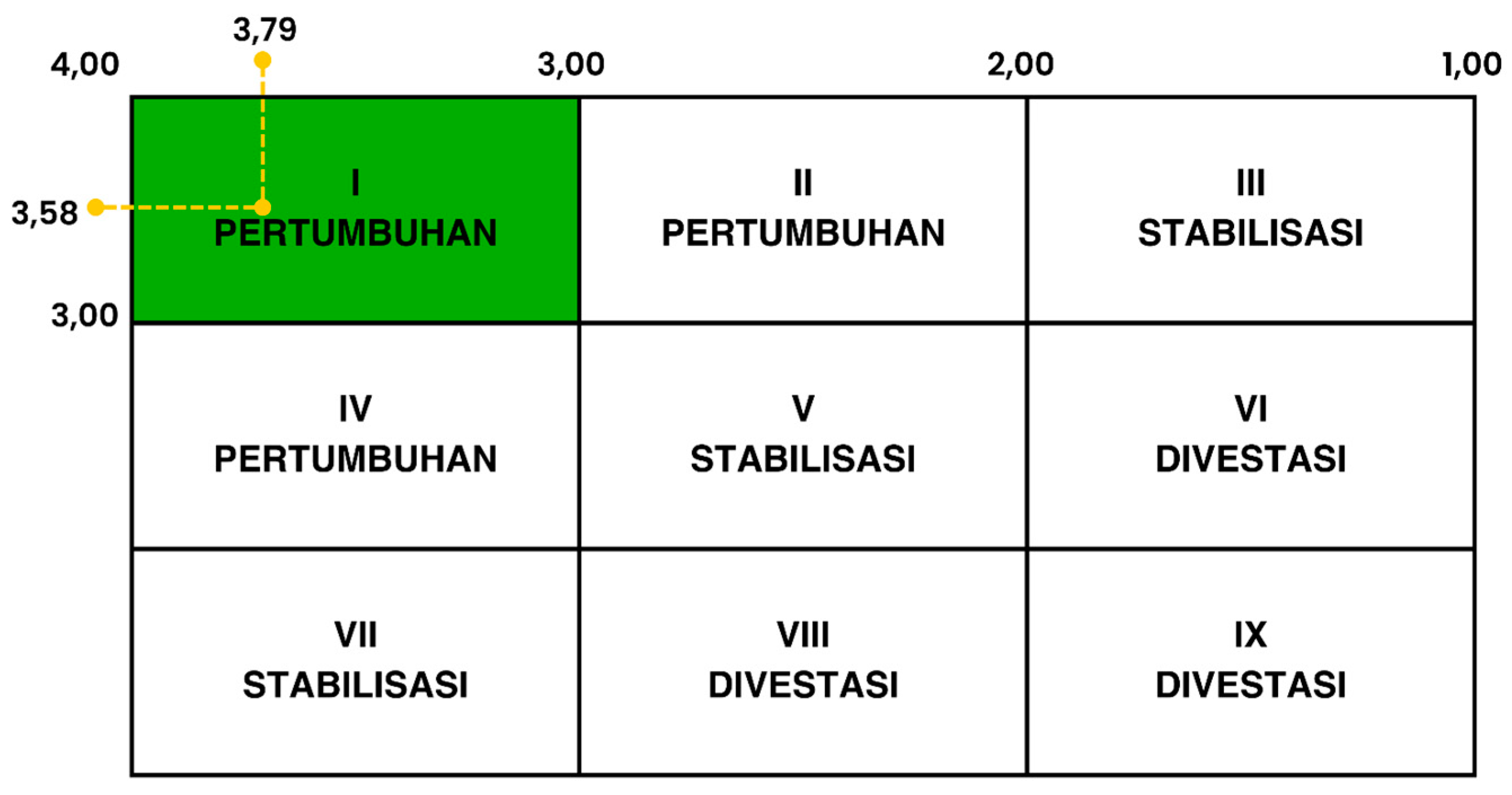
Based on the results of the matrix that has been presented, PANGERAN DIPONEGORO's innovation shows internal strength with a value of 3.79 and external strength with a value of 3.58. These values indicate that internal factors have a more significant influence than external factors on the innovation success of PANG DIPONEGORO. Therefore, it can be concluded (
Figure 3) that this innovation is entering the growth phase, and can continue to grow, and has high potential to achieve goals.
Universal Health Coverage (UHC) in Semarang City.
- b)
BOILINGFramework
Furthermore, the innovation of PANGERAN DIPONEGORO is assessed for competitive advantage through the VRIO Framework (Luenendonk, 2019), namely an assessment based onValue, Rarity, Imitability, dan Organization.
In the value aspect, PANGERAN DIPONEGORO's innovation provides significant benefits in achieving
Universal Health Coverage (UHC) in Semarang City, which reached 99.23% in UHC membership outcomes (see
Table 2)
This significance shows that the implementation of the UHC Program in Semarang City was successful through the innovation of PANGERAN DIPONEGORO as evidenced by the increased public confidence in participating in the UHC program (2018 UHC membership achievement: 93.73% and 2023 achievement: 99.23%). This is equivalent to an increase in the UHC target in the 2020-2024 RPJMN, namely 95-98%. This condition brings very broad benefits in the health sector where participants in the UHC program can easily access health services so that their illnesses are treated more quickly and the recovery rate is higher.
Meanwhile, regarding the aspect of scarcity, the innovation of PANGERAN DIPONEGORO has a high value because not many health services have directly verified JKN membership. The ability of this innovation to overcome obstacles and challenges in achieving UHC in Semarang City provides a competitive advantage that is rarely owned by other agencies. Meanwhile, in the aspect of imitation, PANGERAN DIPONEGORO's innovation has an easy level of difficulty. As a result, this innovation creates adaptability for health care institutions in other regions. This was marked by the replication of the innovation of PANGERAN DIPONEGORO by Demak, Batang and Gresik Regencies through replication statements and a comparative study conducted by DI Yogyakarta Province on UHC achievements in Semarang City.
In the organizational aspect, the implementation of PANGERAN DIPONEGORO's innovation requires good coordination between various related parties, including the government, health institutions, and the community. In this aspect, a managerial strategy has been carried out in order to support the sustainability of innovation. Such as performance quality assurance through innovative SOP and SPP, service quality improvement through regular meetings with the Main Stakeholder Communication Forum regarding the sustainability of the Semarang City UHC Program, and digitalization of services through the JKN Mobile application. In addition, JKN First Level Health Facility (FKTP) support through accreditation and implementation of BLUD management is also carried out to support program sustainability.
Thus, the overall results of the analysis show that PANG DIPONEGORO's innovation in achieving Universal Health Coverage (UHC) in Semarang City has had a significant positive impact. The success of this program is evident from the increase in public trust, high levels of participation, and competitive advantages that are rarely possessed by other agencies. In addition, good implementation through good coordination between related parties has also ensured the sustainability of PANG DIPONEGORO's innovations.
- c)
AnalysisValue Chain
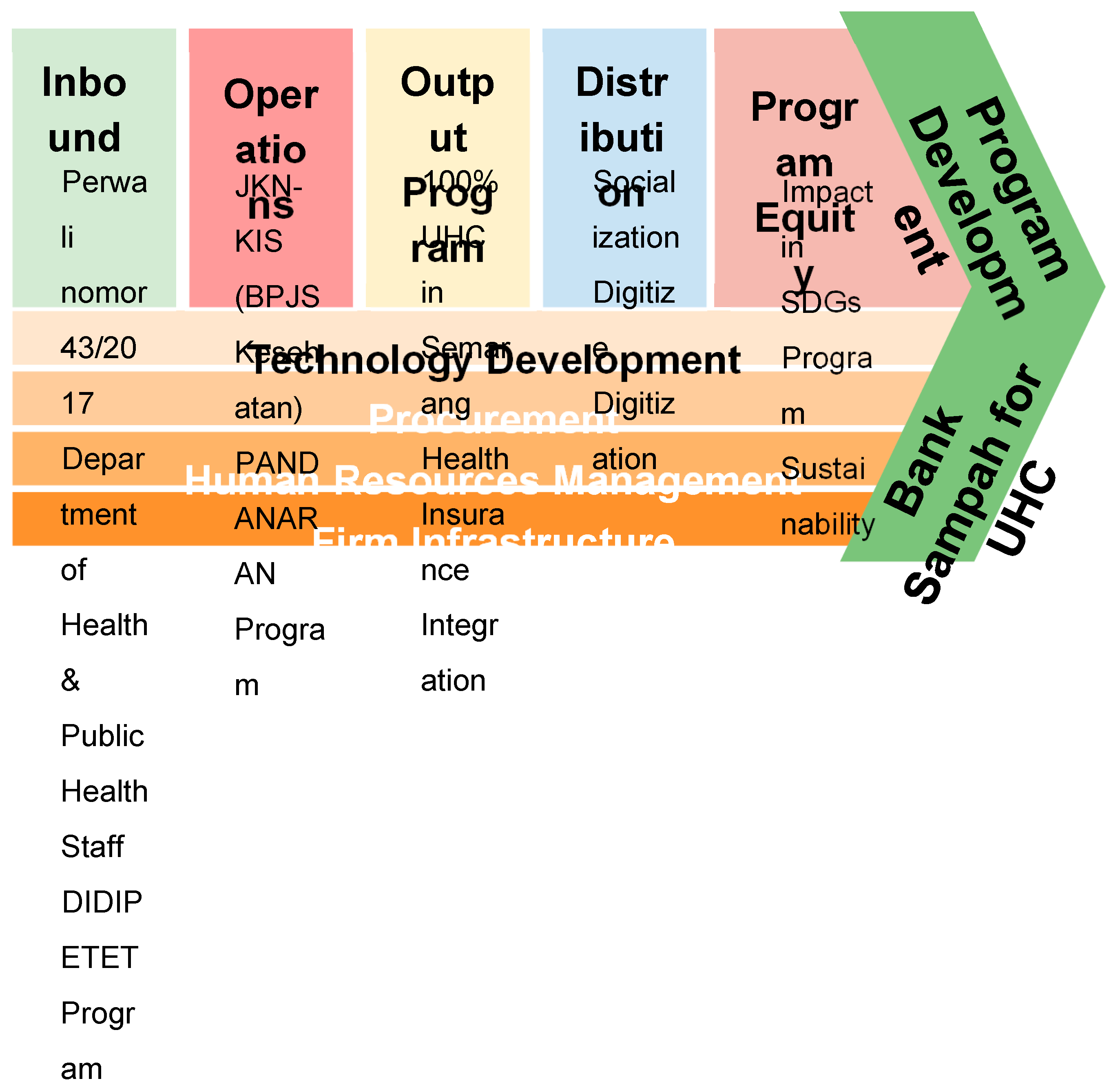
The Universal Health Coverage (UHC) program in Semarang City has added value in creating access to health insurance for people who have not been covered before. In this context, the "PANGERAN DIPONEGORO" innovation plays an important role in optimizing the Value Chain to achieve inclusive and sustainable UHC (Presutti & Mawhinney, 2013; Suwandi, 2019). The following is an analysis of the innovation Value Chain:
-
Inbound Program
Policy and regulation:Semarang Mayor Regulation No. 43 of 2017 stipulates the registration of Semarang City residents as BPJS Health Contribution Beneficiary Participants (PBI), providing a legal basis for the implementation of the UHC program.
Human Resources: A workforce that is trained and skilled in providing health services, including Semarang City Health Office staff who are involved in implementing innovations.
digital technology:The use of social media, mobile applications, and websites as a tool in the "DIDI PETET" program to reach a wider population quickly and efficiently.
-
Operational Process
Program integration: Integration into the JKN-KIS BPJS Health program allows the people of Semarang City to obtain wider health insurance benefits through participation in JKN.
Tech innovation: The use of digital technology in the "DIDI PETET" program and the "PANDANARAN" program accelerates communication and provides an effective complaint channel between the community and the Semarang City Health Office.
-
External Program
Society participation: The "PANGERAN DIPONEGORO" innovation succeeded in increasing community participation in the UHC program by achieving 99.23% in achieving UHC.
Improved access and service quality: Through this innovation, access to and quality of health services will increase, especially for city dwellers who have not been covered before.
-
Distribution
Information dissemination: The use of social media, mobile applications, and websites in the "DIDI PETET" program helps in the dissemination of information about UHC in an effective and comprehensive manner.
Health care services: The "PANDANARAN" program supports effective communication channels between the community and the Semarang City Health Office, ensuring quality and affordable health services.
-
Program Equity
Impact on the Sustainable Development Goals: The "PANGERAN DIPONEGORO" innovation contributes to achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (TPB), especially in reducing poverty and increasing the proportion of Health Insurance participants through the National Social Security System (SJSN) in the health sector.
Sustainability Aspect:In order to achieve inclusive and sustainable UHC in Semarang City, supporting programs such as the "Waste Bank for UHC" play an important role in strengthening JKN membership to reduce health insurance coverage costs.
It can be concluded that the "PANGERAN DIPONEGORO" innovation succeeded in increasing efficiency and effectiveness in achieving UHC in Semarang City by involving various supporting programs that work integrated and complementary. Overall, the innovation "PANGERAN DIPONEGORO" managed to have a significant positive impact in achievingUniversal Health Coverage (UHC) in Semarang City. There has been an increase in community participation, accessibility and quality of health services, as well as a competitive advantage that is rarely possessed by other agencies.
Discussion
The development of the Universal Health Coverage (UHC) Program in Semarang City began by involving participants from various segments, including Contribution Assistance Recipients (PBI), PNS Askes, TNI Participants, POLRI, and JPK Jamsostek Participants (Thabrany, 2015). The main objective of this program is to provide access to health insurance for all Semarang City residents who do not yet have health insurance, including those who are sick in hospitals without health insurance and newborns from regional PBI participants (Anita, 2019). Over time, the UHC Program continues to experience developments in increasing participation from other sectors. In March 2017, the Semarang City Government integrated Jamkesmaskot into the National Health Insurance-Indonesian Health Card (JKN-KIS BPJS Health) with a target of registering around 50,000 poor and underprivileged people as JKN-KIS BPJS Kesehatan participants. In line with that, Semarang Mayor Regulation Number 43 of 2017 concerning the Implementation of Semarang City Health Insurance stipulates the Universal Health Coverage (UHC) Program by registering Semarang City residents as Recipients of BPJS Health Contribution Assistance (PBI) (Tavares, 2019). Despite achieving a UHC of 93.73% in 2018, there are 114,453 people who do not have health insurance, including wage workers and residents who are able to pay contributions independently.
To increase the achievements of the UHC Program in Semarang City and provide access to the National Health Insurance (JKN) for the entire population of 114,453 people, the PANGERAN DIPONEGORO innovation was implemented. This innovation has a very significant contribution in achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) to end poverty in all its forms and everywhere. In this context, the indicator for the proportion of health insurance participants through the Health Sector National Social Security System (SJSN) is one of the influential factors in achieving this goal. Since the implementation of the PANGERAN DIPONEGORO innovation in 2023, the UHC achievement has increased to 99.23% (Syaifurahman, 2023), which is largely influenced by this innovative intervention. The success in achieving the proportion of JKN participants through the SJSN Health Sector has made an important contribution in achieving the goals, targets and indicators of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) in Semarang City.
In an effort to maintain and improve the sustainability of PANGERAN DIPONEGORO innovations, these innovations have been evaluated and assessed by various parties, both internally and externally. The internal evaluation was carried out by the Semarang City Government and the Semarang City DPRD with a focus on the extent to which PANGERAN DIPONEGORO's innovation ability increased the achievements of the UHC Program to provide the maximum level of satisfaction to the community. Meanwhile, an external evaluation was carried out by BPJS Health and the Central Government to see the progress of achieving the UHC Program in Semarang City as a real commitment to support the National Health Insurance Program (JKN). The results of the evaluation provide recommendations for continuous improvement and refinement which are immediately responded to by the Semarang City Health Office to improve the performance of the UHC Program.
Semarang City Government continues to be committed to maintaining Universal Health Coverage (UHC) for seven consecutive years. Through the National Health Insurance Program (JKN) organized through the PANGERAN DIPONEGORO innovation, as much as 99.23% or 1,675,108 residents in Semarang City can access health services that include promotive, preventive, rehabilitative and curative aspects. With this universal health insurance, poverty alleviation (health) occurs because people are no longer burdened with medical and nursing expenses when they are sick and need health care facilities.
In addition, the Municipal Government of Semarang shows high concern for the health needs of its citizens by participating in improving welfare through health programs. This step is in line with the government's goal to improve the quality of life of Indonesian citizens, especially from the health aspect. The success of the UHC Program can be achieved thanks to collaboration and synergy between the government, partners, participants and the community, which is one of the keys to success in implementing the UHC Program. Through UHC coverage, the Municipal Government of Semarang does not only focus on the level of participation, but also on aspects of the quality of health services in the City of Semarang. By providing access to 245 First Level Health Facilities (FKTP), 28 Advanced Referral Health Facilities (FKRTL), 7 laboratories, and 18 Optics for JKN-registered participants, Semarang City Government and related agencies continue to oversee fast but optimal health services . UHC Program participants also get convenience in accessing health services through the use of digital technology, such as the Mobile JKN application which provides the main services of the JKN Program in one hand. For example, telephone consultations, online queues, and digital JKN cards. People don't need to worry if they don't carry their JKN card because digital cards can be accessed by using the National Identity Number (NIK) on the National Identity Card (KTP).
PANGERAN DIPONEGORO's innovations have proven to be very relevant to answering problems and become a solution in accelerating the achievement of UHC Program targets. Evidently, this innovation has been successfully replicated by Demak Regency, and has become an inspiration for the City of Tangerang, Batang Regency, Gresik Regency, and Yogyakarta Special Region in conducting a Comparative Study regarding the success of the UHC Program in Semarang City. PANGERAN DIPONEGORO's innovations are easy to implement and adapt to other Regencies/Cities. This is due to the obligation of districts/cities to ensure that all people have health insurance based on Law Number 40 of 2004 concerning the national social security system. Support from regional heads and community independence are key factors in the successful implementation of innovations. PANGERAN DIPONEGORO's innovation also involves cross-program and cross-sectoral roles through collaboration with various stakeholders related to the UHC Program in Semarang City, which makes it easy to replicate by other regions. In its implementation, the community gets benefits and convenience, because JKN participants who need treatment at a health facility only need to show their Resident Identity Number (NIK) on the participant's Identity Card (KTP). In addition, digitizing the UHC Program makes it easier for administrators to register, verify, socialize, and disseminate information to the public.
PANGERAN DIPONEGORO's innovation is supported by various resources that influence its successful implementation (Du Toit, 2002; Deschamps & Nelson, 2014). Financial resources from the Semarang City APBD from 2018 to 2023 are an important factor in supporting the implementation of innovations to achieve Universal Health Coverage (UHC) in Semarang City. In addition, the human resources involved in this innovation, such as stakeholders from various agencies, play a key role in implementing the innovation. Implementation methods, such as collaboration with Semarang City Health Office partners, universities, companies and business entities, facilitate the replication of this innovation by other regions. Physical equipment and materials, such as JKN counters at the BPJS office, UHC counters at the Public Service Mall, and DTKS service counters at the Social Service, are important facilitators in public access to health services. Utilization of digital technology, such as the JKN Mobile Application, also supports the implementation of the UHC Program by providing integrated and easily accessible services.
To maintain and increase the sustainability of PANGERAN DIPONEGORO's innovation in the city of Semarang, strategies are implemented in three dimensions (Shi & Hoskisson, 2021; Joyce, 2022), namely institutional, managerial and social strategies. The institutional strategy is supported by various regulations, rules and decrees governing the National Health Insurance Program (JKN) and Universal Health Coverage (UHC) at the national and local levels. In addition, there is a memorandum of understanding between BPJS Health and the Semarang City Government, as well as a decree from the head of the Semarang City Health Service which officially forms the PANGERAN DIPONEGORO Innovation. The managerial strategy involves standardizing the quality of performance by using the Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) and Standard Performance Procedure (SPP) for innovation, as well as improving service quality through regular meetings of the Main Stakeholder Communication Forum related to the UHC Program in Semarang City. The social strategy focuses on collaboration with various parties, such as BPJS Health, Dispendukcapil, Social Service, Labor Office, and the private sector, and involves the sub-district, RW, and RT levels, as well as the Kelurahan Health Forum, Community Health Cadres, and UHC Cadres to socialize JKN program for the community. By implementing institutional, managerial and social strategies synergistically, it is hoped that PANGERAN DIPONEGORO's innovations can continue and have a positive impact in achieving inclusive and sustainable Universal Health Coverage in the City of Semarang.
Conclusion
The 'PANGERAN DIPONEGORO' innovation has succeeded in becoming a Universal Health Coverage (UHC) program in Semarang City with the main objective of providing access to health insurance for all people who were previously not covered by health programs. The integration of Jamkesmaskot into the National Health Insurance-Indonesian Health Card (JKN-KIS BPJS Health) and the target of registering 50,000 poor people as JKN-KIS participants have pushed UHC achievements to increase to 100% in 2023. This innovation shows high potential to achieve the goal UHC is inclusive and sustainable, and relevant to the Sustainable Development Goals to end poverty in all its forms everywhere. By involving various segments of participants and support from various related parties, this program succeeded in increasing community participation, access, and quality of health services. Through optimizing the Value Chain, this innovation has succeeded in optimizing the implementation process and having a significant positive impact in achieving UHC in Semarang City. The UHC program continues to be committed to maintaining its achievements and providing optimal health services with the full support of the government and the community.
References
- Andriana, M. (2021, October 8). Double Diamond Design Thinking – School of Information Systems. School of Information Systems. Retrieved July 12, 2023, from https://sis.binus.ac.id/2021/10/08/double-diamond-design-thinking/.
- Anita, B. (2019). Puskesmas Dan Jaminan Kesehatan Nasional. Deepublish.
- Barney, J. B., & Hesterly, W. S. (2019). Strategic Management and Competitive Advantage: Concepts and Cases. Pearson. https://www.amazon.com/Strategic-Management-Competitive-Advantage-Concepts/dp/0134741145/ref=d_pd_sbs_sccl_1_2/144-4074874-7800860?pd_rd_w=f4vSC&content-id=amzn1.sym.3676f086-9496-4fd7-8490-77cf7f43f846&pf_rd_p=3676f086-9496-4fd7-8490-77cf7f43f846&pf_rd_r=.
- Basuki, E. W., Sulistyowati, & Herawati, N. R. (2016). Implementasi Kebijakan Jaminan Kesehatan Nasional oleh BPJS Kesehatan di Kota Semarang. Journal of Politic and Government Studies, 5(4). https://ejournal3.undip.ac.id/index.php/jpgs/article/view/13543.
- Deschamps, J.-P., & Nelson, B. (2014). Innovation Governance: How Top Management Organizes and Mobilizes for Innovation. Wiley.
- Du Toit, D. (2002). Service Excellence in Governance. Heinemann.
- Grant, R. M. (2010). Contemporary Strategy Analysis: Text Only. Wiley. https://sma1halim.sekolah-angkasa.sch.id/x7//content/publication?ID=G78057f&readPDF=apple-internal-matrix-analysis-pdf.pdf.
- Istanti, N. D. (2023). Evaluasi Pelaksanaan Program Jaminan Kesehatan Nasional (JKN) dalam Upaya Meningkatkan Akses Kesehatan Masyarakat di Indonesia. Jurnal Anestesi: Jurnal Ilmu Kesehatan dan Kedokteran, 1(3). [CrossRef]
- Joyce, P. (2022). Strategic Management and Governance: Strategy Execution Around the World. Routledge.
- Kusnandar. (2021, October 6). Jumlah Penduduk Kota Semarang 1,65 Juta Jiwa pada 2020. Databoks. Retrieved July 23, 2023, from https://databoks.katadata.co.id/datapublish/2021/10/06/jumlah-penduduk-kota-semarang-165-juta-jiwa-pada-2020.
- Ledbury, J. (2017). Design and product development in high-performance apparel. In J. McLoughlin & T. Sabir (Eds.), High-Performance Apparel: Materials, Development, and Applications (pp. 175-189). Elsevier Science. [CrossRef]
- Luenendonk, M. (2019, September 25). VRIO Framework Guide on Creating Sustainable Competitive Advantages. Cleverism. Retrieved July 2, 2023, from https://www.cleverism.com/vrio-framework-guide-on-creating-sustainable-competitive-advantages/.
- Mayer, L. (2022). Design Thinking Research: Achieving Real Innovation (C. Meinel & L. Leifer, Eds.). Springer International Publishing. https://www.amazon.com/Design-Thinking-Research-Innovation-Understanding/dp/3031092961.
- Mello, P. A. (2021). Qualitative Comparative Analysis: An Introduction to Research Design and Application. Georgetown University Press. amazon.com/Qualitative-Comparative-Analysis-Introduction-Application/dp/1647121450.
- Pajo, B. (2022). Introduction to Research Methods: A Hands-on Approach. SAGE Publications, Incorporated. https://us.sagepub.com/en-us/nam/introduction-to-research-methods/book270534.
- Presutti, W. D., & Mawhinney, J. R. (2013). Understanding the Dynamics of the Value Chain. Business Expert Press. https://www.oreilly.com/library/view/understanding-the-dynamics/9781606494509/.
- Rokom. (2016, November 4). Kuatkan Layanan Kesehatan, Pemerintah Lakukan Lima Upaya Secara Simultan. Sehat Negeriku. Retrieved August 2, 2023, from https://sehatnegeriku.kemkes.go.id/baca/umum/20161104/2918732/kuatkan-layanan-kesehatan-pemerintah-lakukan-lima-upaya-secara-simultan/.
- Sarsby, A. (2016). SWOT Analysis. Spectaris Limited. https://books.google.co.id/books?id=Yrp3DQAAQBAJ&printsec=frontcover&hl=id#v=onepage&q&f=false.
- Shi, W., & Hoskisson, R. E. (2021). Understanding and Managing Strategic Governance. Wiley.
- Suwandi, I. (2019). Value Chains: The New Economic Imperialism. Monthly Review Press. https://www.amazon.com/Value-Chains-New-Economic-Imperialism/dp/1583677828.
- Syaifurahman, B. (2023, March 14). Tembus 99,23%, Semarang Jadi Kota Tertinggi dalam Capaian Program UHC. detikNews. Retrieved May 3, 2023, from https://news.detik.com/berita/d-6619225/tembus-9923-semarang-jadi-kota-tertinggi-dalam-capaian-program-uhc.
- Tavares, A. I. (Ed.). (2019). Universal Health Coverage. IntechOpen.
- Thabrany, H. (2015). Jaminan Kesehatan Nasional Edisi Kedua. Rajawali Pres.
- Yapary, V. (2022, August 24). Proses Design Thinking Menggunakan Double Diamond? Filemagz. Retrieved July 2, 2023, from https://www.filemagz.com/proses-design-thinking-menggunakan-double-diamond/.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).