Submitted:
01 November 2023
Posted:
01 November 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Numerical Simulation Procedure
2.1. Considered Governing Equations
3. Results and Discussion
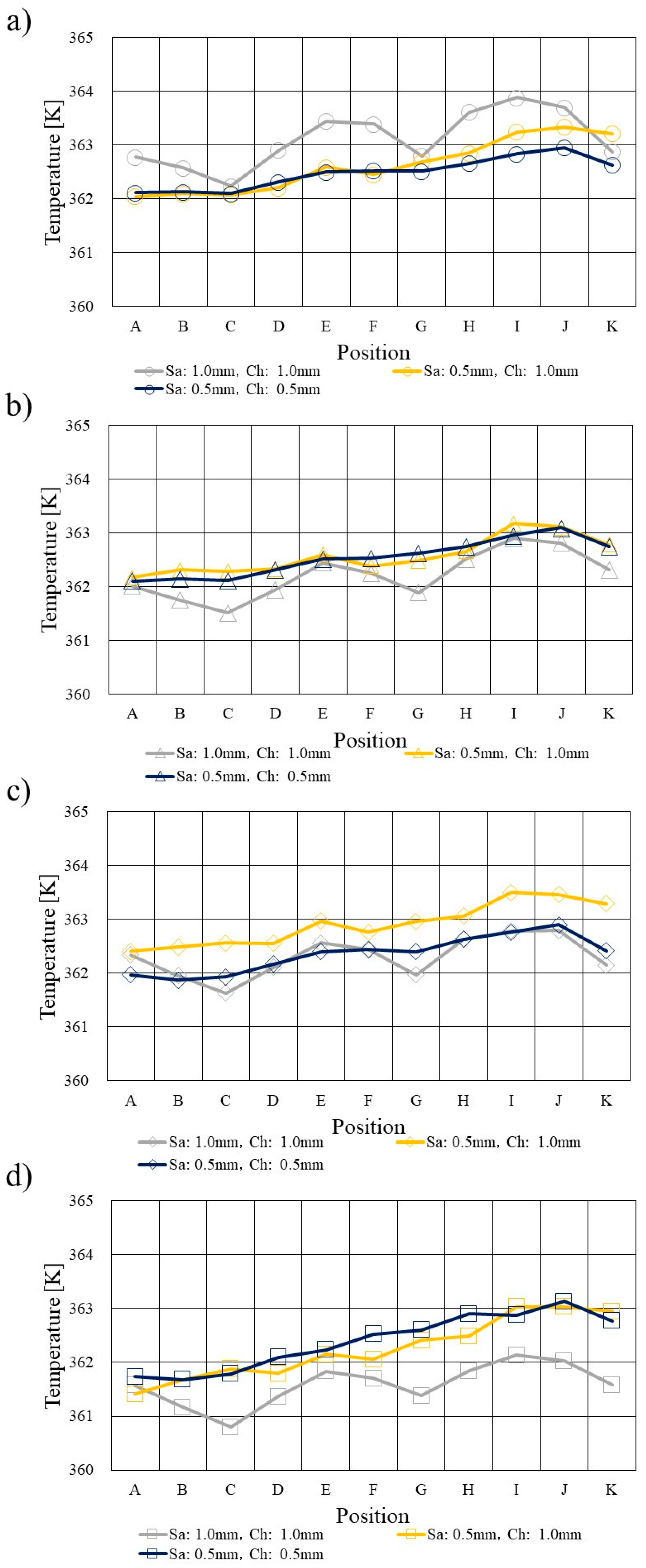
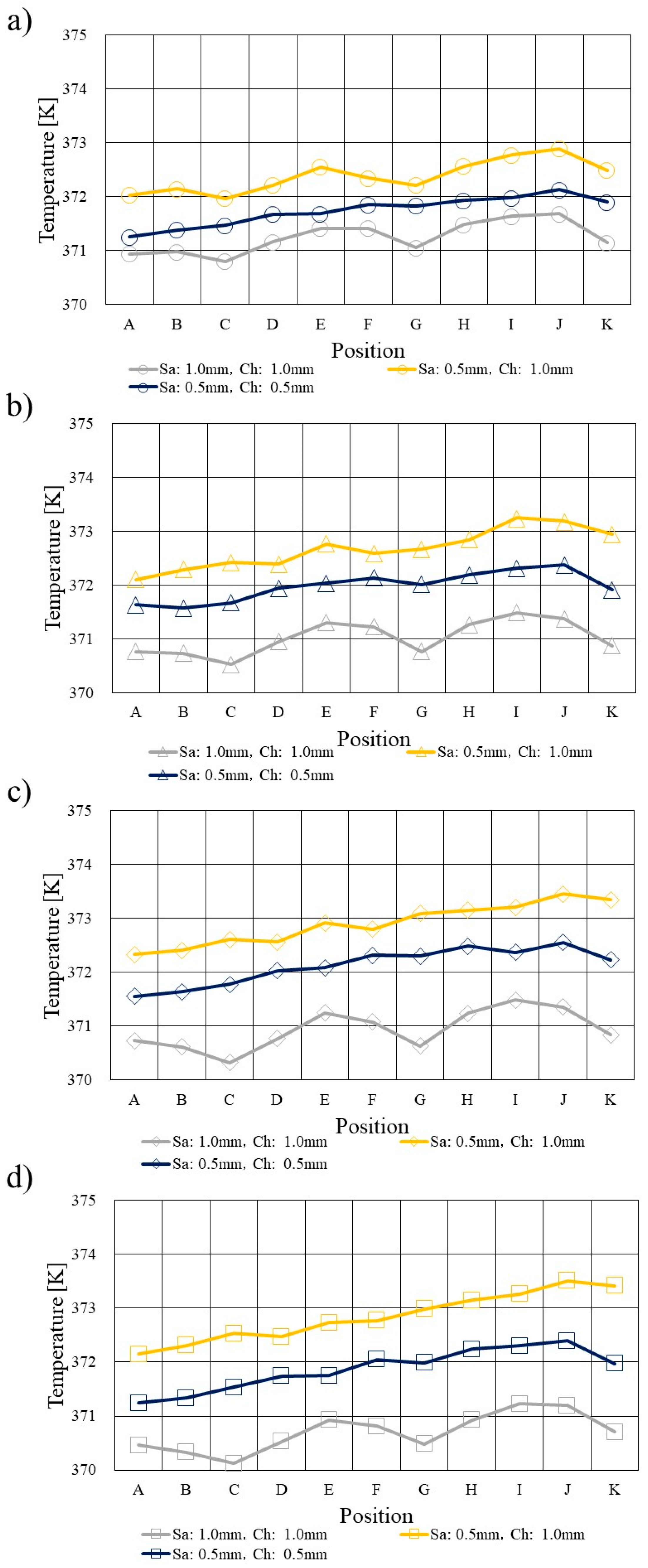
3.1. Comparison of Temperature Profile
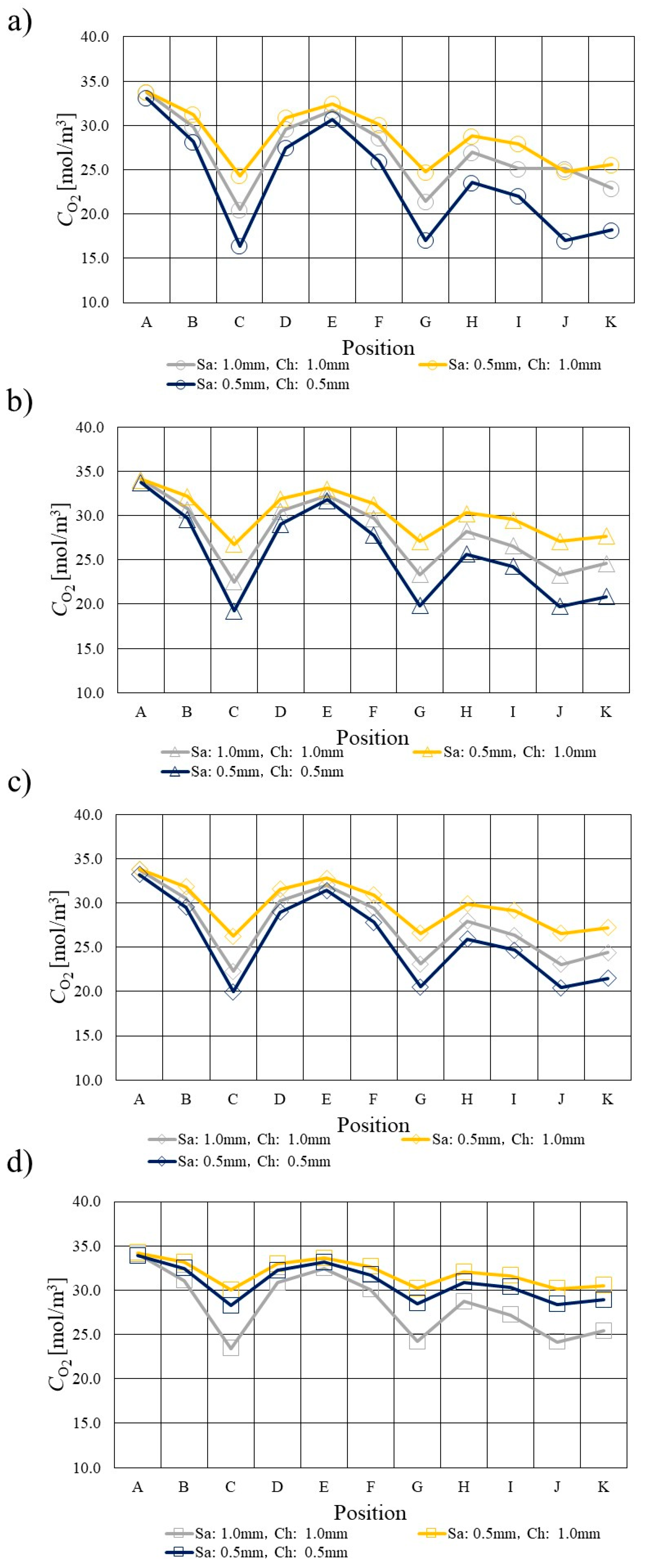
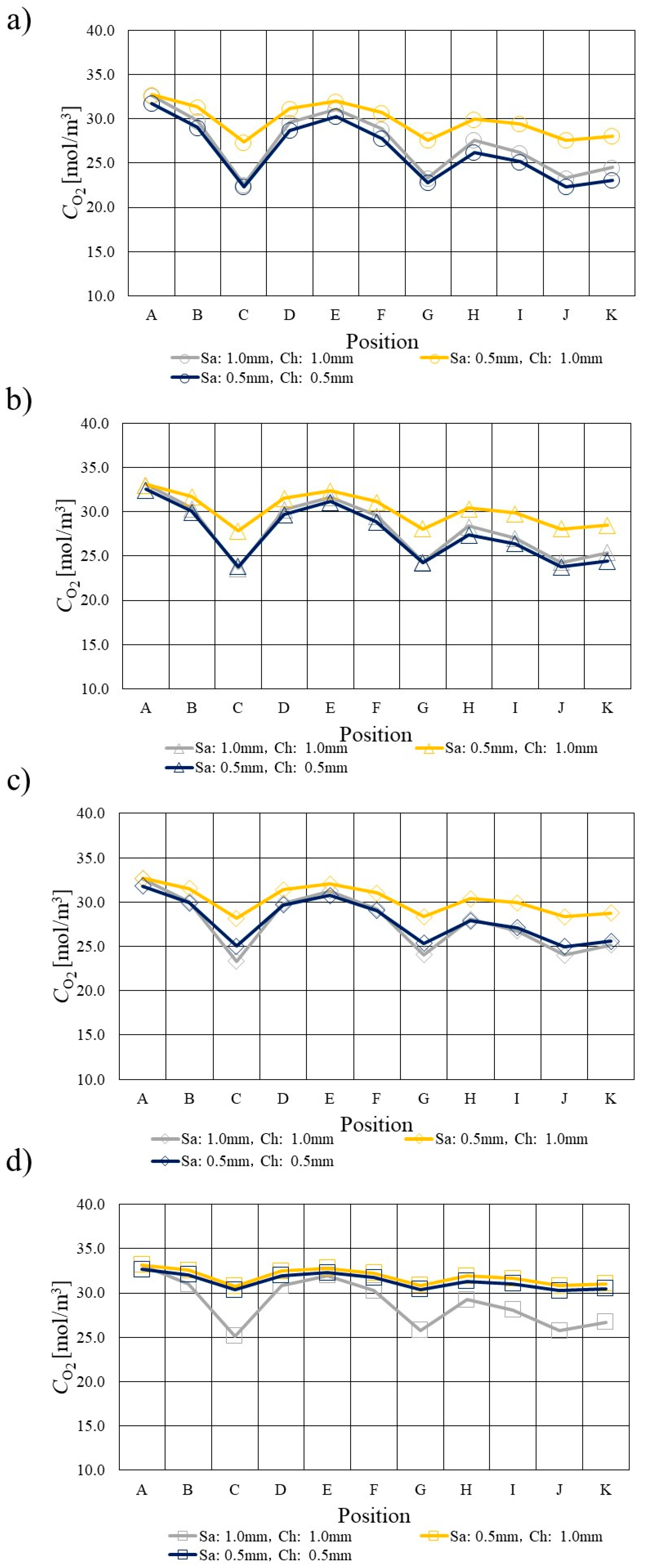
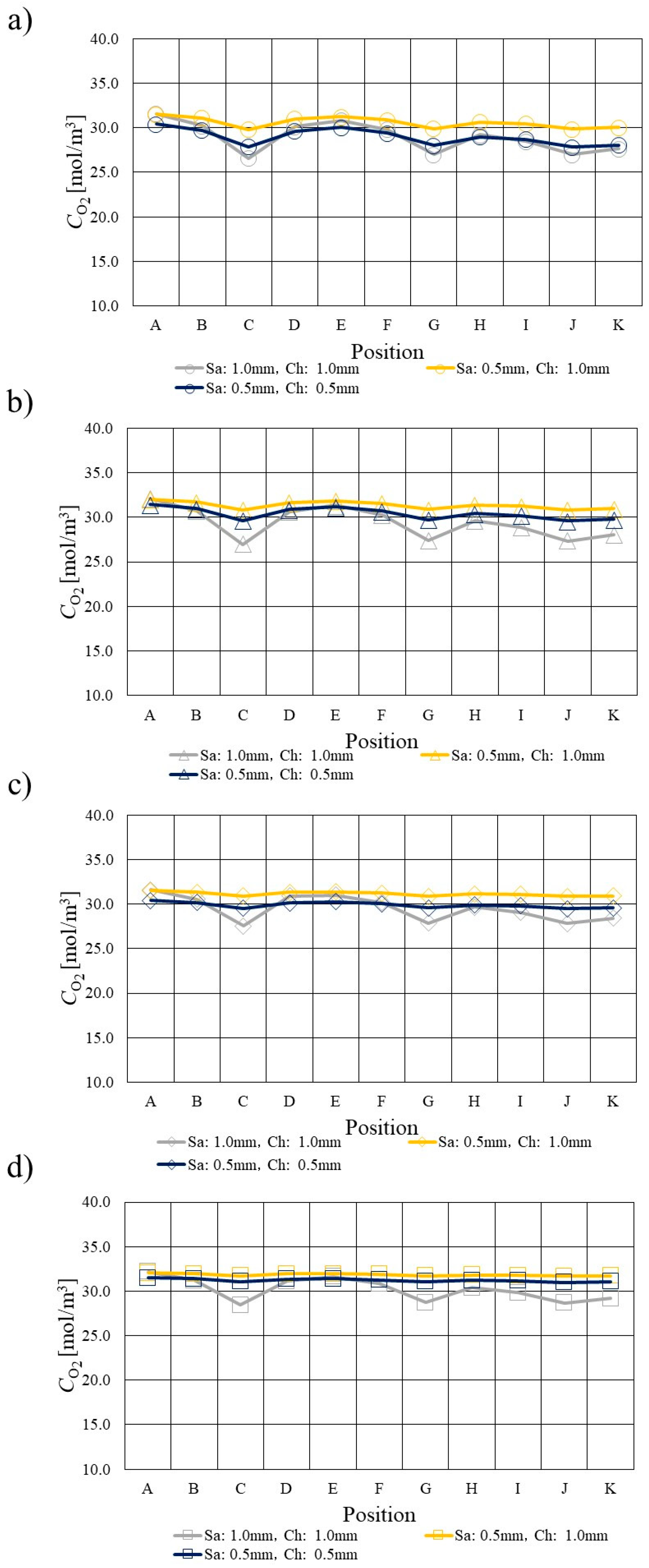
3.2. Comparison of O2 Distribution
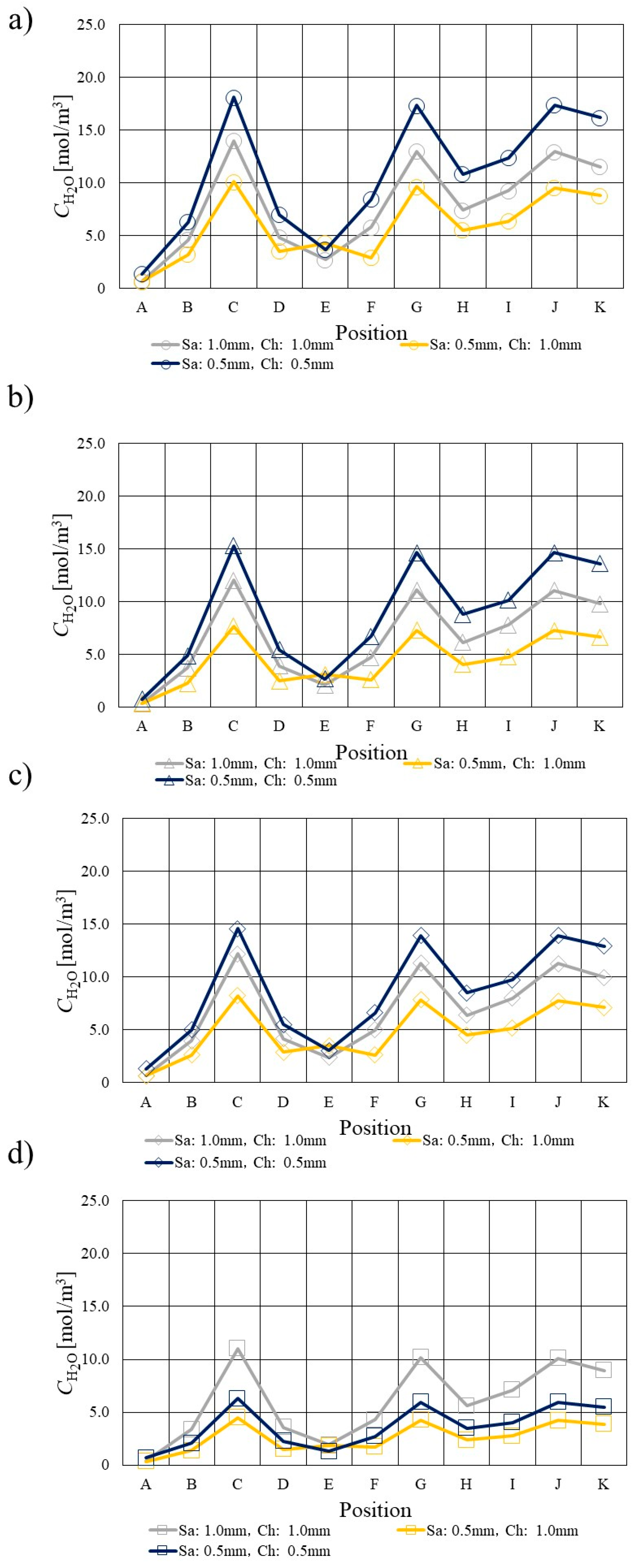
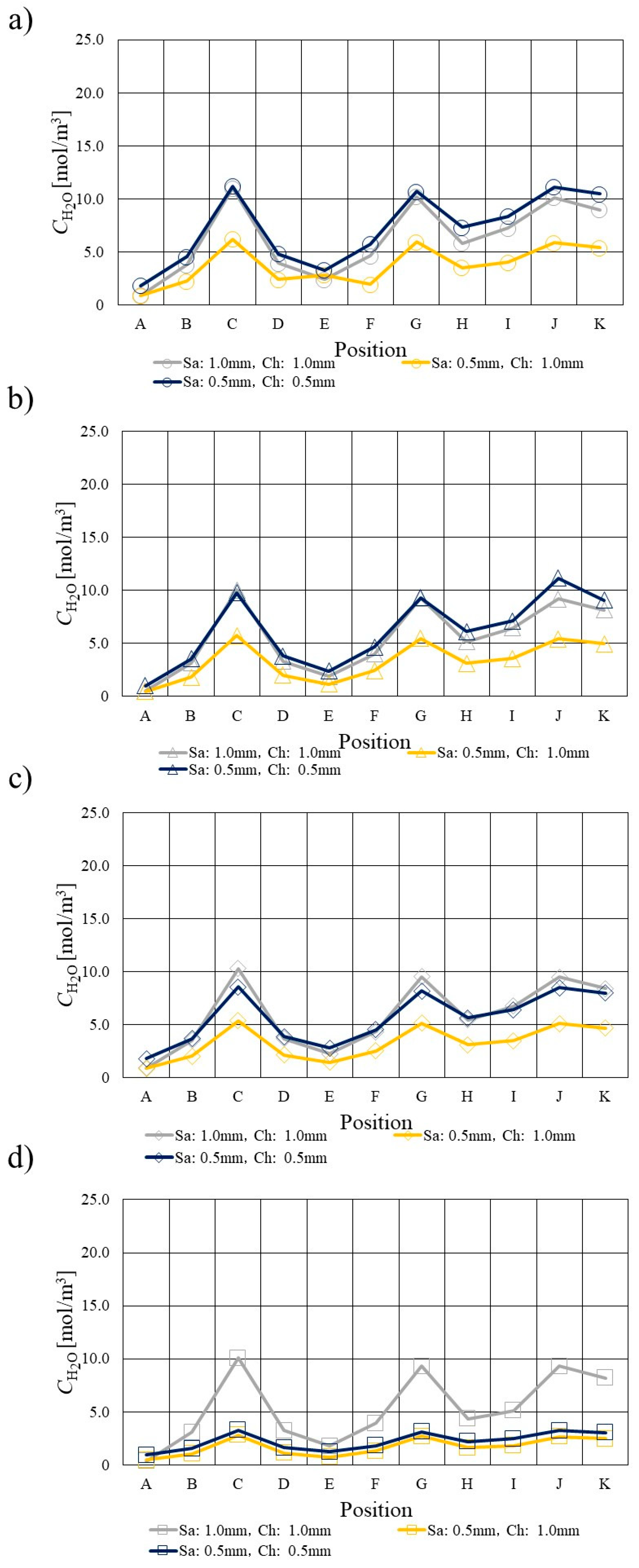
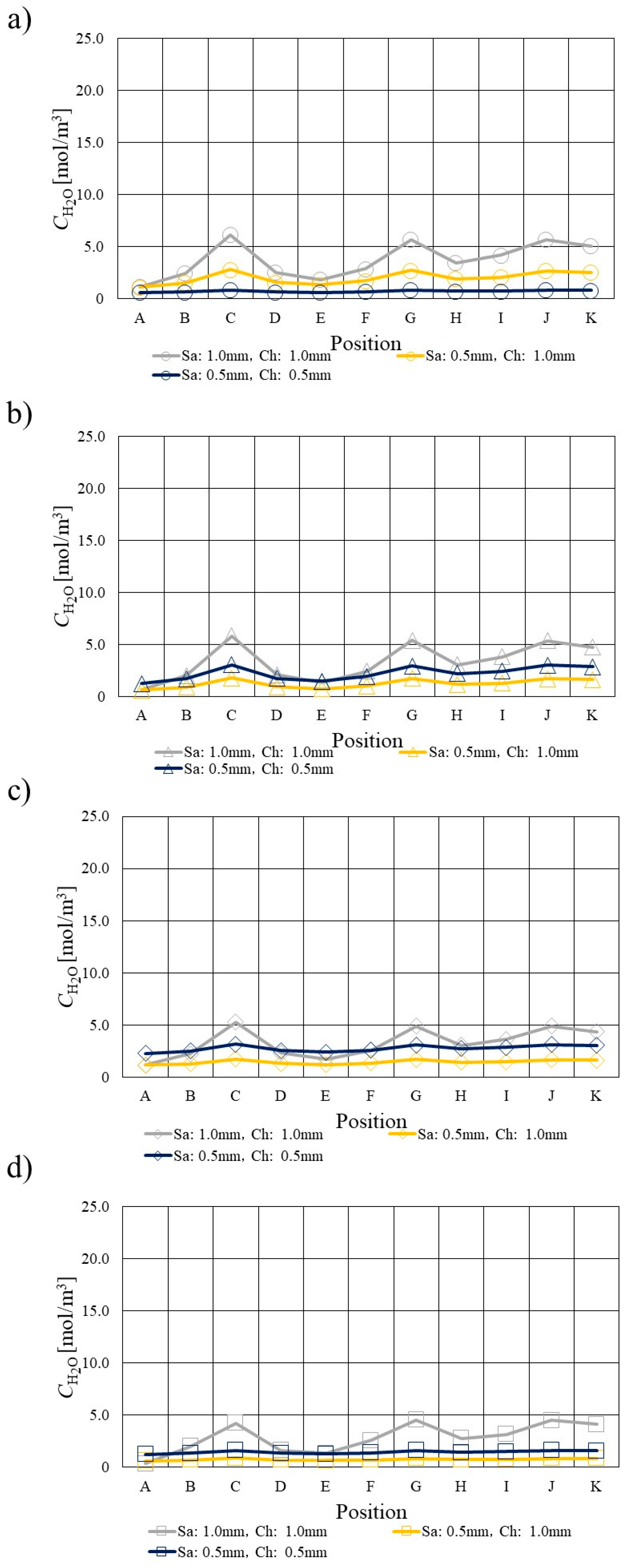
3.3. Comparison of H2O Profile
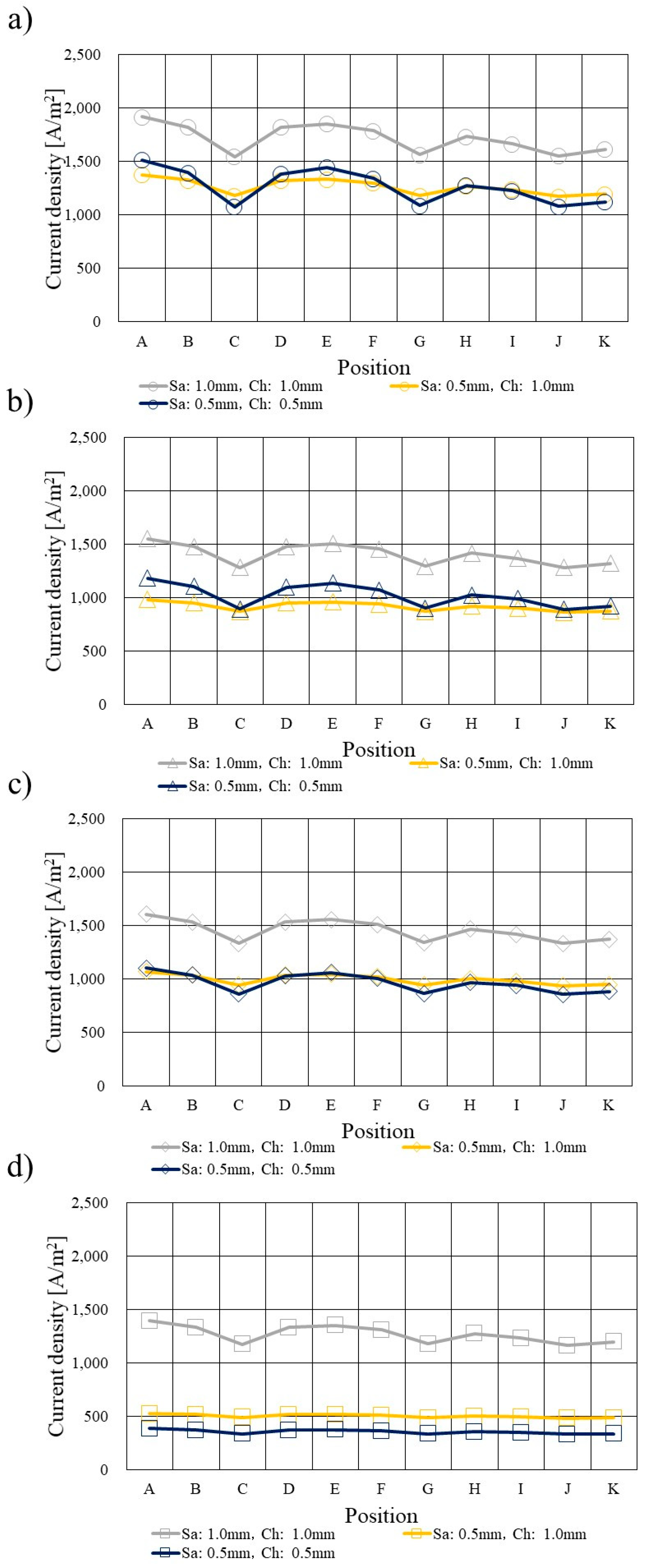
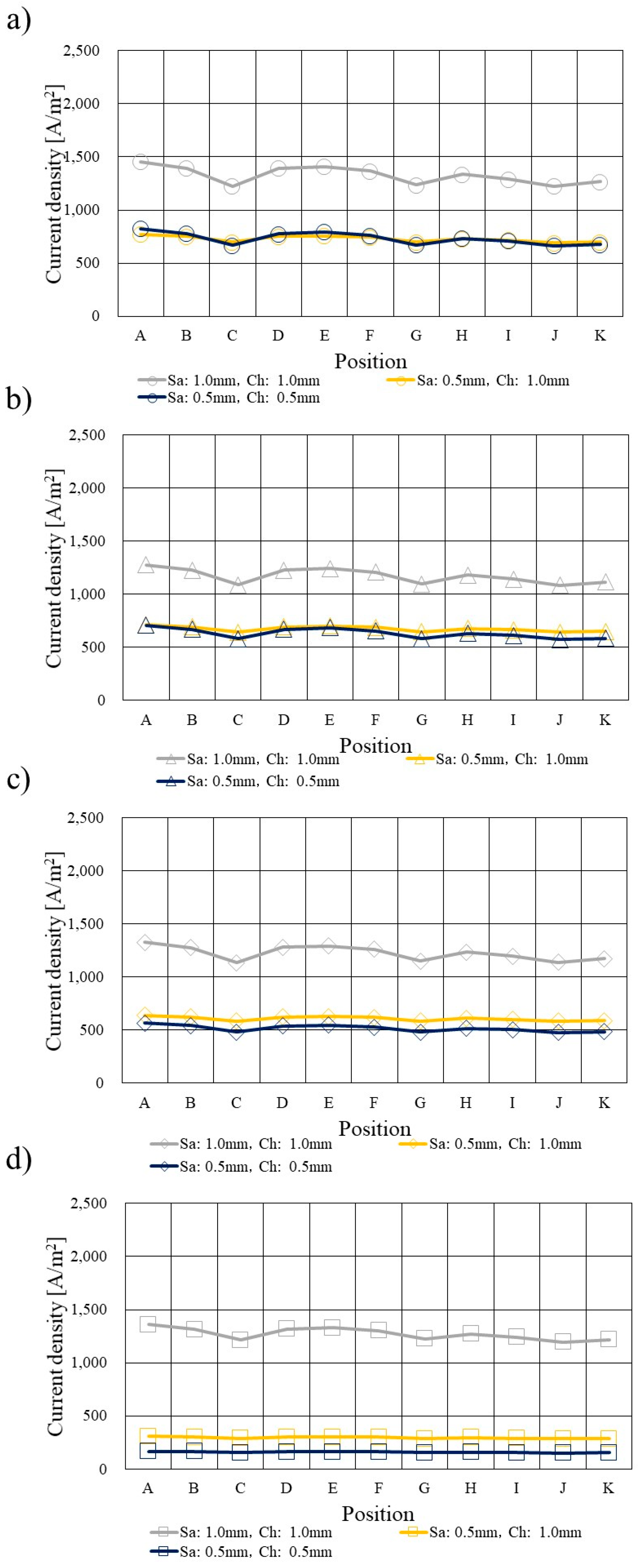
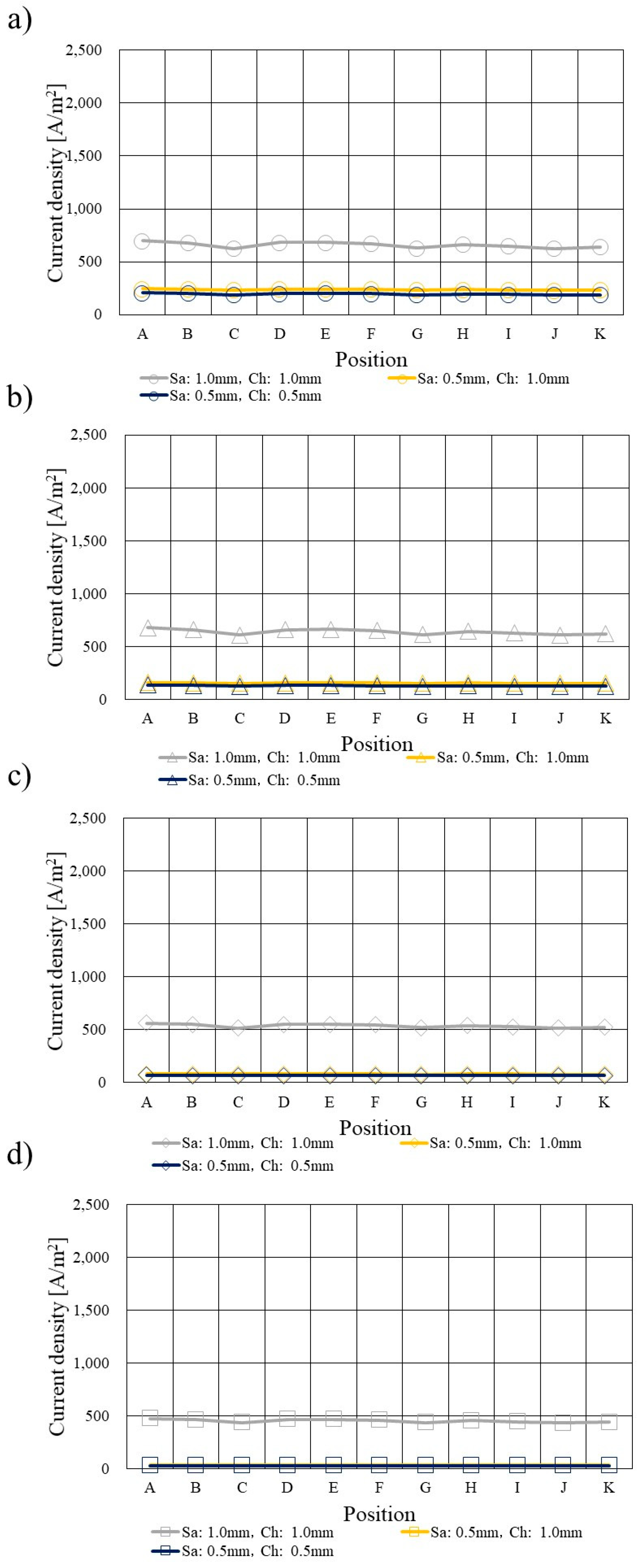
3.4. Comparison of Current Density Profile
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- NEDO (New Energy and Industry Technology Development Organization). Available online: http://www.nedo.go.jp/cotent/100871973 (in Japanese; accessed on 2, October, 2023).
- Zhang, G.; Kandlikar, S. G. A. Critical Review of Cooling Technique in Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell Stacks. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2012, 37, 2412-2429.
- Agbossou, K.; Kolhe, M.; Hamelin, J.; Bose, T. K. Performance of a Stand-Alone Renewable Energy System Based on Energy Storage as Hydrogen. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion 2004, 19, 633-640.
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, C.; Hao D.; Ni M.; Huang S.; Liu D.; Zheng, Y. 3D Non-isothermal Dynamic Simulation of High Temperature Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell in Start-up Process. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 2577-2593.
- Li, Q.; He, R.; Jensen, J. O.; Bjerrum, N. J. Approaches and Recent Development Polymer Electrolyte Membrane for Fuel Cells Operating above 100 ℃. Chemistry of Materials 2003, 15, 4896-4915.
- Lee, C. Y.; Wng, F.; Kuo, Y. W.; Tsai, C. H.; Cheng, Y. T.; Cheng, C. K.; Lin, J. T. In-situ Measurement of High-temperature Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell Stack Using Flexible Five-in-one Micro Sensor. Sensors 2016, 16. [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, A.; Sato, A.; Yoshimura, M.; Kamiya, S.; Hirota, M. Impact of Thickness of Polymer Electrolyte Membrane on Temperature Distribution in Single Cell of Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cell Operated at High Temperature. J. Energy Power Eng. 2018, 12, 80–92.
- Nishimura, A.; Kamiya, S.; Okado, T.; Sato, Y.; Hirota, M.; Kolhe, M.L. Heat and Mass Transfer Analysis in Single Cell of PEFC Using Different PEM and GDL at Higher Temperature. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2019, 44, 29631–29640.
- Nishimura, A.; Okado, T.; Kojima, Y.; Hirota, M.; Hu, E. Impact of MPL on Temperature Distribution in Single Polymer Fuel Cell with Various Thickness of Polymer Electrolyte Membrane. energies 2020, 13, 10, jttps://doi.10.3390/en13102499.
- Nishimura, A.; Yamamoto, K.; Okado, T.; Kojima, Y.; Hirota, M.; Kolhe, M.L. Impact Analysis of MPL and PEM Thickness on Temperature Distribution within PEFC Operating at Relatively Higher Temperature. Energy 2020, 205, 117875. [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, A.; Toyoda, K.; Kojima, Y.; Ito, S.; Hu, E. Numerical Simulation on Impacts of Thickness of Nafion Series Membranes and Relative Humidity on PEMFC Operated at 363 K and 373 K. Energies 2021, 14, 8256. [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, A.; Mishima, D.; Toyoda, K.; Ito, S.; Kolhe, L. M. Numerical Simulation on Effect of Separator Thickness on Coupling Phenomena in Single Cell of PEFC under Higher Temperature Operation Condition at 363 K and 373 K. Energies 2023, 16, 606. [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, A.; Kojima, Y.; Ito, S.; Hu, E. Impacts of Separator Thickness on Temperature Distribution and Power Generation Characteristics of a Single PEMFC Operated at Higher Temperature of 363 and 373 K. Energies 2022, 15, 1558. [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, H.; Thosar, U. A.; Bhat, D. S.; Lele, K. A. Interdigitated Flow Filed Impact on Mass Transport and Electrochemical Reaction in High-temperature Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cell. Journal of Power Sources 2022, 532, 231319. [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, J.; Zeng, T.; Yi, F.; Hu, D.; Zhang, X. Numerical Investigation of Enhanced Mass Transfer Flow Field on Performance Improvement of High-temperature Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell. Fuel Cells 2023, 23, 251-263.
- Hazar, H.; Yilmaz, M.; Sevinc, H. A Comparative Analysis of a Novel Flow Filed Pattern with Different Channel Size Configurations. Fuel 2022, 319, 123867. [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Q.; Li, Q.; Chen, W.; Peng, R.; Zhu, X.; Xie, Y.; Tang, Y.; Shen, Z.; Yang, X. Optimization of Blocked Field Performance of Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell with Auxiliary Channels. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2022, 47, 39943-39960.
- Yan, F.; Pei, X.; Yao, J. Numerical Simulation of Performance Improvement of PEMFC by Four-serpentine Wave Flow Field. Ionics 2023, 29, 695-709.
- Yu, D.; Yu, S. Analysis of Flow Variation in a Straight Channel with Baffled Obstacles on a Bipolar Plate in a Proton-exchange Membrane Fuel Cell. International Journal of Automotive Technology 2023, 24, 3, 759-771.
- Yu, X.; Luo, X.; Tu, Z. Development of a Compact High-power Density Air-cooled Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell Stack with Ultrathin Bipolar Plates. Energy 2023, 270, 126936. [CrossRef]
- Kahraman, H.; Orhan, M. F. Flow Filed Bipolar Plate in a Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell: Analysis & Modeling. Energy Conversion and Management 2017, 133, 363-384.
- Han, Y.; Zhuge, W.; Peng, J.; Qian, Y.; Ming, P.; Zhang, Y. A Novel Heat Pipe Bipolar Plate for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells. Energy Conversion and Management 2023, 284, 116945. [CrossRef]
- Kanchan, B.K.; Randive, P.; Pati, S. Implications of Non-uniform Porosity Distribution in Gas Diffusion Layer on the Performance of a High Temperature PEM Fuel Cell. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2021, 46, 18571–18588.
- Das, S.K.; Gibson, H.A. These Dimensional Multi-Physics Modeling and Simulation for Assessment of Mass Transport Impact on the Performance of a High Temperature Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cell. J. Power Sources 2021, 499, 161–188.
- Panesi, A.R.Q.; Silva, R.P.; Cunha, E.F.; Korkischko, I.; Santiago, E.I. Three-dimensional CFD Modeling of H2/O2 HT-PEMFC Based on H3PO4-doped PBI Membranes. Ionics 2021, 27, 3461–3475.
- Penga, Z.; Tolj, I.; Barbir, F. Computational Fluid Dynamics Study of PEM Fuel Cell Performance. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2016, 41, 17585–17594.
- Copper, N.J.; Santamaria, A.D.; Becton, M.K.; Park, J.W. Neutron Radiography Measurements of In-situ PEMFC Liquid Water Saturation in 2D & 3D Morphology Gas Diffusion Layers. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2017, 42, 16269–16278.
- The Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers. JSME Heat Transfer Handbook, 1st ed.; The Japan Society of Mechanical Engineers; Maruzen: Tokyo, Japan, 1993; p. 387.
- Freunberger, S.A.; Reum, M.; Evertz, J.; Wokuan, A.; Buchi, F.M. Measuring the Current Distribution in PEFCs with Sub-Millimeter Resolution. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2006, 153, A2158–A2165.
- Nishimura, A.; Shibuya, K.; Morimoto, A.; Tanaka, S.; Hirota, M.; Nakamura, M.; Kojima, Y.; Narita, M.; Hu, E. Dominant Factor and Mechanism of Coupling Phenomena in Single Cell of Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cell. Appl. Energy 2012, 1, 73–79.
- Xia, L.; Ni, M.; He, Q.; Xu, Q.; Cheng, C. Optimization of Gas Diffusion Layer in High Temperature PEMFC with the Focuses on Thickness and Porosity. Appl. Energy 2021, 300, 117357. [CrossRef]
- TORAY. Available online: http://www.cf-composites.toray/ja/resources/data_sheets/ (assessed on 4 October 2023).
- Kang, K.; Ju, H. Numerical Modeling and Analysis of Micro-porous Layer Effects in Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cells. J. Power Sources 2006, 194, 763–773.
- Bit Tech. Product Catalog; Bit Tech.: Gosyogawara, Japan, 2008; p. 1.
- Reid, R.C.; Prausnitz, J.M.; Poling, B.E. The Properties of Gases and Liquids, 1st ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1987; p. 591.
- Merck. Available online: http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/japan/materialscience/alternative/nafion.html (assessed on 4 October 2023).
- Senn, S.M.; Poulikakos, D. Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cells with Porous Materials as Fluid Distributors and Comparisons with Traditional Channeled Systems. Trans. ASME 2004, 126, 410–418.
- Takayama, T. Numerical Simulation of Transient Internal States of PEFC Cell and Stack Considering Control of Anode System. Res. Rep. Mizuho Res. Technol. 2018, 9, 1–14.
- Rostami, L.; Nejad, P.M.G.; Vatani, A. A Numerical Investigation of Serpentine Flow Channel with Different Bend Sizes in Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells. Energy 2016, 97, 400–410.
- Huang, Y.; Xiao, X.; Kang, H.; Lv, J.; Zeng, R.; Shen, J. Thermal Management of Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells: A Critical Review of Heat Transfer Mechanisms, Cooling Approaches, and Advanced Cooling Techniques Analysis. Energy Conversion and Management 2022, 254, 115221. [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Das, P. K.; Song, X.; Mamlouk, M.; Scott, K. Numerical Analysis of the Optimum Membrane/Ionomer Water Content of PEMFCs: The Interface of Nafion Ionomer Content and Cathode Relative Humidity. Applied Energy 2015, 138, 242-257.
- Nishimura, A.; Toyoda, K.; Mishima, D.; Hu, R. Numerical Analysis on Temperature Distribution in a Single Cell of PEFC Operated at Higher Temperature by 1D Heat Transfer Model and 3D Multi-physics Simulation Model. Energy and Power Engineering 2023, 15, 205-227.
- Nishimura, A.; Toyoda, K.; Mishima, D.; Ito, S.; Hu, E. Numerical Analysis on Impact of Thickness of PEM and GDL with and without MPL on Coupling Phenomena in PEFC Operated at Higher Temperature Such as 363 K and 373 K. Energies 2022, 15, 5936. [CrossRef]
- Salomov, U. R.; Chiavazzo, E.; Fasano, M.; Asinari, P. Pore- and Macro-scale Simulations of High Temperature Proton Exchange Fuel Cell Cells – HTPEMFC – and Possible Strategies for Enhancing Durability. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 26730-26743.
- Quan, P.; Lai, M. C. Numerical Study of Water Management in the Air Flow Channel of a PEM Fuel Cell Cathode. J. Power Sources 2007, 164, 222-237.
- Jiao, K.; Park, J.; Li, X. Experimental Investigation on Liquid Water Removal from the Gas Diffusion Layer by Reaction Flow in PEM Fuel Cell. Appl. Energy 2010, 87, 2770-2777.
- Nishimura, A.; Yoshimura, M.; Kamiya, S.; Hirota, M.; Hu, E. Impact of Relative Humidity of Supply Gas on Temperature Distribution in Single Cell of Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cell when Operated at High Temperature. J. Energy Power Eng. 2017, 11, 706-718.
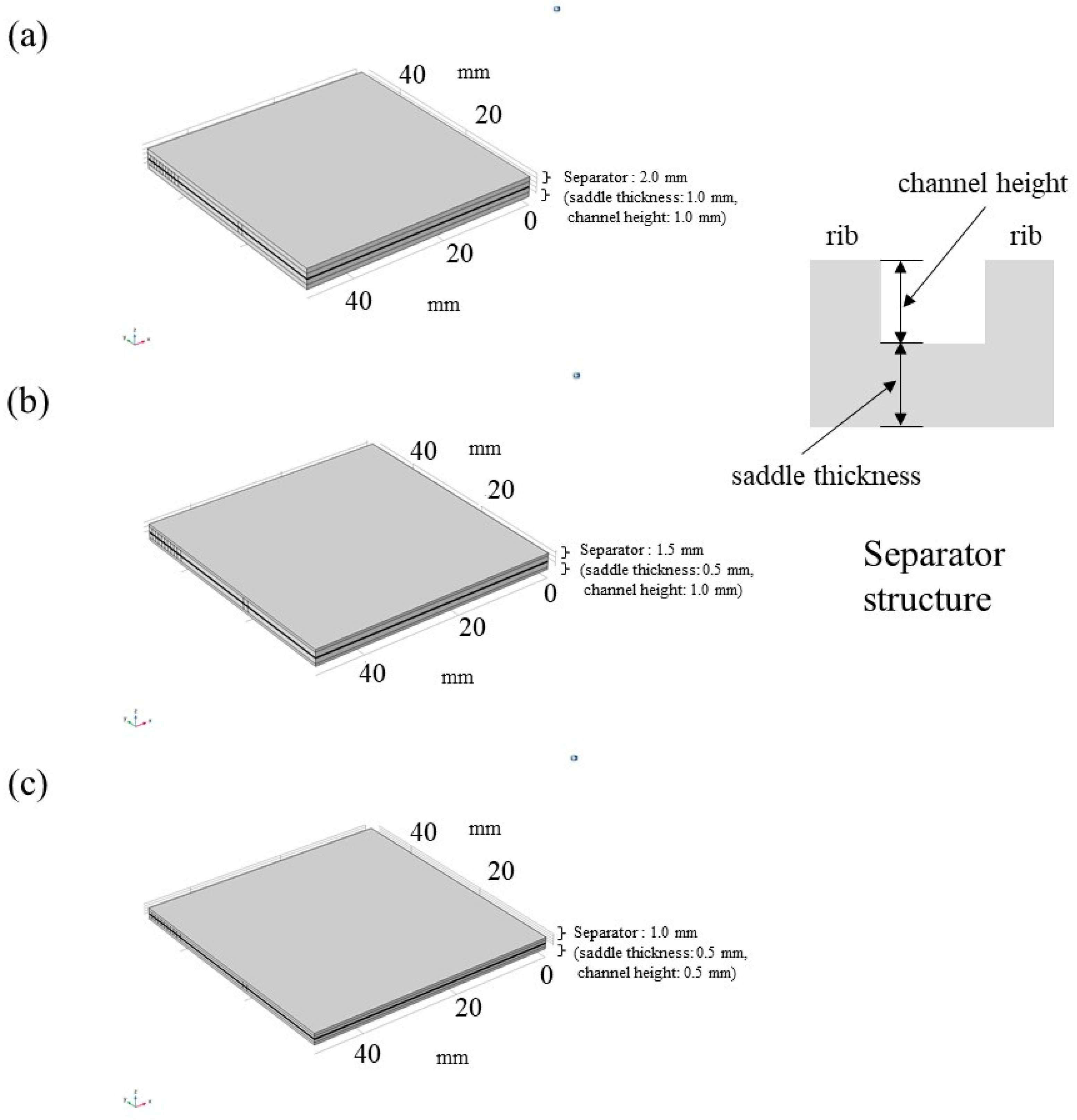

| Components of single cell | Each size [mm] | Specification |
| PEM | Width: 50.0, Length: 50.0, Depth: 0.025 |
Nafion NRE-211 (manufactured by Du Pont Corp.) |
| Catalyst layer | Width: 50.0, Length: 50.0, Depth: 0.01 |
Pt/C (Weight percentage of Pt: 20) |
| MPL | Width: 50.0, Length: 50.0, Depth: 0.003 |
PTFE + carbon black |
| GDL | Width: 50.0, Length: 50.0, Depth: 0.11 |
TGP-H-030 (produced by Toray Corp.) |
| Separator | Width: 75.4, Length: 75.4, Depth: 2.0 (saddle thickness: 1.0, channel height: 1.0), 1.5 (saddle thickness: 0.5, channel height: 1.0), 1.0 (saddle thickness: 0.5, channel height: 0.5); Width: 50.0, Length: 50.0 (as to gas supply area) |
Carbon graphite, serpentine flow |
| Physical parameters | Values |
| Gas density (H2) [kg/m3] | 7.10×10-2 (@ 353 K), 6.89×10-2 (@ 363 K), 6.69×10-2 (@ 373 K) [27] |
| Gas density (O2) [kg/m3] | 1.11 (@ 353 K), 1.08 (@ 363 K), 1.05 (@ 373 K) [27] |
| Gas density (H2O) [kg/m3] | 2.95×10-1 (@ 353 K), 4.26×10-1 (@ 363 K), 6.01×10-1 (@ 373 K) [27] |
| Pressure of supply gas at inlet of cell (absolute based) (MPa) | 0.4 [13] |
| Gas viscosity (H2) [Pa·s] | 9.96×10-6 (@ 353 K), 1.02×10-5 (@ 363 K), 1.03×10-5 (@ 373 K) [27] |
| Gas viscosity (O2) [Pa·s] | 2.35×10-5 (@ 353 K), 2.40×10-5 (@ 363 K), 2.45×10-5 (@ 373 K) [27] |
| Gas viscosity (H2O) [Pa·s] | 1.16×10-5 (@ 353 K), 1.19×10-5 (@ 363 K), 1.23×10-5 (@ 373 K) [27] |
| Binary diffusion constant (H2 - H2O) [m2/s] | 9.27×10-5 [28] |
| Binary diffusion constant (O2 - H2O) [m2/s] | 3.57×10-5 [28] |
| Porosity (catalyst layer) [-] | 0.78 [7,10,29,30,31] |
| Permeability (catalyst layer) [m2] | 8.69×10-12 [7,10,29,30,31] |
| Thermal conductivity (catalyst layer) [(W/(m·K))] |
1.70 [32] |
| Porosity (MPL) [-] | 0.60 [7,10,29,30,31] |
| Permeability (MPL) [m2] | 1.00×10-13 [7,10,29,30,31] |
| Thermal conductivity (MPL) [(W/(m·K))] |
1.00 [33] |
| Porosity (GDL) [-] | 0.78 [7,10,29,30,31] |
| Permeability (GDL) [m2] | 8.69×10-12 [7,10,29,30,31] |
| Thermal conductivity (GDL) [(W/(m·K))] |
1.70 [32] |
| Porosity (separator) [-] | 0.15 [34] |
| Permeability (separator) [m2] | 1.50×10-5 [34] |
| Thermal conductivity (separator) [(W/(m·K))] |
0.151 [34] |
| Conductivity (PEM) [S/m] | 10 [35] |
| Conductivity (catalyst layer) [S/m] | 53 [36] |
| Conductivity (MPL) [S/m] | 1000 [37] |
| Conductivity (GDL) [S/m] | 1250 [33] |
| Conductivity (separator) [S/m] | 83000 [34] |
| Reference equilibrium voltage (Anode) [V] | 0 |
| Reference equilibrium voltage (Cathode) [V] | 1.229 |
| Reference exchange current density (Anode) [A/m2] | 1000 [32] |
| Reference exchange current density (Cathode) [A/m2] | 1 [32] |
| Charge transfer constant (Anode) [-] | 0.5 [38] |
| Charge transfer constant (Cathode) [-] | 0.5 [39] |
| Operation parameters | Conditions | |
| The initial temperature of cell (Tini) (K) | 353, 363, 373 | |
| Total cell voltage (V) | Experimental data are used [8,9,13] | |
| Supply gas condition | Anode | Cathode |
| Gas type | H2 | O2 |
| Temperature of supply gas at inlet of cell (K) | 353, 363, 373 | 353, 363, 373 |
| RH of supply gas (%RH) | 40, 80 | 40, 80 |
| Pressure of supply gas at inlet of cell (absolute based) (MPa) | 0.4 | 0.4 |
| Flow rate of supply gas at inlet of cell (NL/min) (Stoichiometric ratio (-)) | 0.210 (1.5) | 0.105 (1.5) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





